 ,1, 张武汉1, 张莉2, 舒服1, 何强1, 彭志荣1, 邓华凤
,1, 张武汉1, 张莉2, 舒服1, 何强1, 彭志荣1, 邓华凤 ,1,3,*
,1,3,*Development and application of functional marker for high nitrogen use efficiency and chilling tolerance gene OsGRF4 in rice
SUN Ping-Yong ,1, ZHANG Wu-Han1, ZHANG Li2, SHU Fu1, HE Qiang1, PENG Zhi-Rong1, DENG Hua-Feng
,1, ZHANG Wu-Han1, ZHANG Li2, SHU Fu1, HE Qiang1, PENG Zhi-Rong1, DENG Hua-Feng ,1,3,*
,1,3,*通讯作者:
收稿日期:2020-05-22接受日期:2020-08-19网络出版日期:2021-04-12
| 基金资助: |
Received:2020-05-22Accepted:2020-08-19Online:2021-04-12
| Fund supported: |
作者简介 About authors
E-mail:

摘要
关键词:
Abstract
Keywords:
PDF (582KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
本文引用格式
孙平勇, 张武汉, 张莉, 舒服, 何强, 彭志荣, 邓华凤. 水稻氮高效、耐冷基因OsGRF4功能标记的开发及其利用[J]. 作物学报, 2021, 47(4): 684-690. doi:10.3724/SP.J.1006.2021.02035
SUN Ping-Yong, ZHANG Wu-Han, ZHANG Li, SHU Fu, HE Qiang, PENG Zhi-Rong, DENG Hua-Feng.
2020年5月, 世界实时统计数据显示全球人口已达77.85亿。按照每年1亿的增长速度, 到2050年, 全球人口总数将接近100亿。据预测, 到本世纪中叶全世界的农业水平要比2005年提高60%~120%才能养活100亿人口。水稻是最重要的粮食作物之一, 稻谷的增产与稳产对我国乃至世界的粮食安全至关重要。适量的氮肥使用对于提高水稻产量和改善稻米品质起着重要作用。然而, 近年来我国在追求水稻高产过程中, 过量施用氮肥及氮肥利用率低已成为普遍现象[1,2]。这不仅增加水稻生产成本, 影响稻米品质, 而且对生态环境造成严重的影响。因此, 提高水稻的氮利用率刻不容缓。研究表明, 不同施氮水平下, 氮高效水稻“库”大、“源”足、“流”畅, 其库容量和产量均明显高于氮低效水稻[3]。因此, 挖掘水稻氮高效基因并通过分子标记辅助选择(molecular marker- assisted selection, MAS)培育氮高效水稻品种是发展绿色、高效和可持续发展农业的一个重要途经[4]。
近年来, 随着测序技术、基因编辑和功能基因组学的飞快发展, 加速了水稻氮吸收与调控基因的克隆及其分子机理的解析。目前, OsNRT1[5]、DEP1[6]、TOND1[7]、OsPTR6[8]、OsNAR2.1[9]、NRT1.1B[10,11]、OsNRT2.3[12]、OsGRF4[13]、OsNR2[14]、OsNPF6.1[15]、OsNAC42[15]等参与氮吸收和转运的基因被成功克隆。其中, OsGRF4是氮高效利用的一个关键基因, 通过平衡生长调节因子OsGRF4与生长抑制因子DELLA之间的关系, 可以同时增加“绿色革命”水稻品种的氮利用效率和产量[13]。OsGRF4是一个多效基因, 本团队最先将粒形基因GS2/OsGRF4精细定位在水稻第2染色体33 kb的区间[16]。后来发现水稻OsGRF4基因编码区序列全长1185 bp, 有5个外显子。第3外显子的SNP3位点由TC突变为AA, 导致丝氨酸变异为赖氨酸, 使得水稻籽粒落粒性降低、产量增加、氮利用率提高和苗期耐冷性增强。此突变正好位于miR396的调控结合部位, 为功能位点[13,17-22]。
为了通过MAS方法培育氮高效、耐冷和高产水稻新品种, 加快育种进程, 本研究根据OsGRF4基因功能位点的碱基差异, 设计了2组功能标记。进一步利用该标记对水稻种质资源和川大粒/巨穗稻F2群体的OsGRF4基因进行了鉴定, 结合测序数据证明了该功能标记只需通过PCR (polymerase chain reaction)扩增和琼脂糖电泳即可快速准确鉴定出OsGRF4纯合型、杂合型和Osgrf4纯合型3种基因型。本研究开发的功能标记为OsGRF4基因的分子育种奠定了基础。
1 材料与方法
1.1 供试材料
供试水稻材料包括携带OsGRF4功能基因的对照品种川大粒与近等基因系NIL-OsGRF4, 不携带功能基因的对照品种巨穗稻与NIL-Osgrf4, 不同来源的20个品种资源, 以及川大粒/巨穗稻的F2群体22个单株。所有材料均于2019年正季种植于湖南杂交水稻研究中心试验田。供试引物: 与OsGRF4共分离的分子标记GL2-11-F: 5′-GAGAAAGCCATTAGTG CA-3′, GL2-11-R: 5′-TCTACCAAACCAAAACAA-3′ [16]。1.2 OsGRF4基因功能标记的设计与合成
根据OsGRF4基因序列和功能位点的差异, 通过Primer Premier 5软件设计了6条引物。引物序列为PF: 5′-CTGTGAACCAACACCCTG-3′, PR: 5′-CGGC AATAGCAGGGTAAA-3′, DR: 5′-CGTTTCCACAG GCTTTCTTTT-3′, XR: 5′-CGTTTCCACAGGCTTT CTTGA-3′, DMR: 5′-CGTTTCCACAGGCTTTCCTT T-3′, XMR: 5′-CGTTTCCACAGGCTTTCCTGA-3′, 其中下划线的碱基C是人为引入的错配碱基。引物由北京擎科新业生物技术有限公司合成。1.3 DNA提取、PCR扩增和电泳检测
取水稻幼苗期叶片, CTAB法提取基因组DNA。利用T3 Super Mix体系(北京擎科新业生物技术有限公司)进行PCR扩增: 98℃预变性2 min; 98℃变性10 s、57℃复性10 s、72℃延伸10 s, 35个循环; 72℃延伸2 min; 4℃冷却, 反应产物在1.5%的琼脂糖凝胶上100 V电泳40 min; 染色后于凝胶成像系统下观察分析。2 结果与分析
2.1 OsGRF4基因功能标记的开发策略
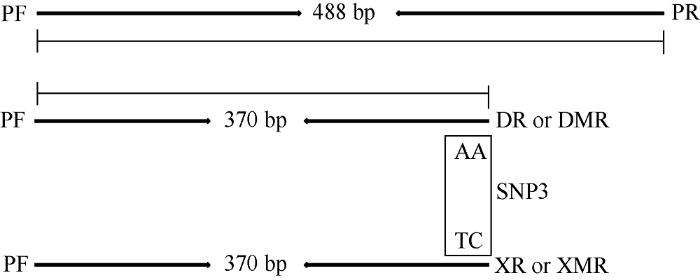
根据OsGRF4基因功能位点SNP3 (TC-AA)的突变设计功能标记, 总共开发了6条引物。首先, 设计一对外引物PF和PR用作参考对照, 无论是哪种基因型都能扩增出488 bp的条带, 其扩增产物包含SNP3位点; 再根据SNP3的多态性设计2条反向内引物DR和XR, 其3′端分别对应碱基AA和TC, DR与OsGRF4基因完全匹配, XR与Osgrf4完全匹配; 此外, 为了增强PCR扩增的特异性, 分别在引物DR和XR的3′端第4位人为引入错配碱基C, 设计了引物DMR和XMR。根据设计引物的原理进行预测: 如果含有OsGRF4基因, 引物组合PF、DR (或DMR)和PR则能扩增出488 bp和370 bp两条目的带, 而PF、XR (或XMR)和PR组合则只能扩增出488 bp的目的带; 如果含有等位基因Osgrf4, 引物组合PF、DR (或DMR)和PR只能扩增出488 bp的目的带, PF、XR (或XMR)和PR组合能扩增出488 bp和370 bp两条目的带; 假如是杂合型, PF、DR (或DMR)和PR组合以及PF、XR (或XMR)和PR组合均能扩出370 bp和488 bp两条目标带(图1)。因此, 利用2种引物组合通过2次PCR扩增就可以区分2种纯合和1种杂合基因型。图1
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图1OsGRF4基因功能标记设计策略
SNP3为功能性多态位点, PF和PR为外引物, DR和XR为反向内引物, 分别与碱基AA和TC匹配。分别在DR和XR的3′端引入错配碱基C开发了DMR和XMR。箭头表示扩增方向。
Fig. 1Strategy of functional markers design for OsGRF4
SNP3 indicates functional polymorphic sites; PF and PR are outer primers; DR and XR are reverse inner primers, which matching the bases AA and TC, respectively. A mismatch base C was introduced in the 3′ end of DR and XR to develop DMR and XMR. The arrows indicate amplification direction of the primers.
2.2 OsGRF4基因功能标记的筛选和验证
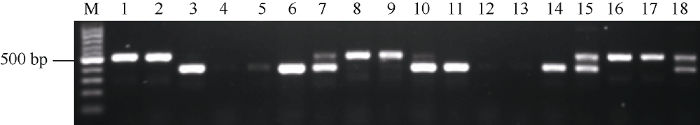
为了筛选最优的功能标记, 以川大粒(携带功能基因OsGRF4)和巨穗稻(携带Osgrf4)的DNA为模板, 通过不同引物组合进行PCR扩增。图2所示, PF+PR引物在川大粒和巨穗稻中均能扩出488 bp的目标带(泳道1和泳道2); PF+DR或PF+DMR在川大粒中能扩出370 bp的目标带(泳道3和泳道11), 而在巨穗稻中扩不出(泳道4和泳道12); PF+XR或PF+XMR在巨穗稻中能扩出370的目标带(泳道6和泳道14), PF+XR在川大粒中能扩出淡淡的目的带(泳道5, 理论上应该扩不出), 而PF+XMR在川大粒中扩不出(泳道13), 因此PF+XMR优于PF+XR组合; PF+DR+PR或PF+DMR+PR组合在川大粒中能扩出370 bp和488 bp的两条目标带(泳道7和泳道15), 而在巨穗稻中只能扩出一条488 bp的带(泳道8和泳道16); PF+XR+PR或PF+XMR+PR在巨穗稻中能扩出370 bp和488 bp的两条目标带(泳道10和泳道18), 但是PF+XMR+PR的扩增效果要优于PF+XR+PR, 2种组合在川大粒中均只能扩出一条488 bp的带(泳道9和泳道17)。因此, 确定PF+DMR+PR和PF+XMR+PR为最优的功能标记组合。图2
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图2不同引物组合对川大粒和巨穗稻的PCR 扩增效果
单数泳道为川大粒; 双数泳道为巨穗稻; M: 100 bp marker; 1, 2: PF+PR; 3, 4: PF+DR; 5, 6: PF+XR; 7, 8: PF+DR+PR; 9, 10: PF+XR+PR; 11, 12: PF+DMR; 13, 14: PF+XMR; 15, 16: PF+DMR+PR; 17, 18: PF+XMR+PR.
Fig. 2PCR amplification of Chuandali and Jusuidao using different primer pairs
The singular lane is ‘Chuandali’, the dual lane is ‘Jusuidao’. M: 100 bp marker; 1, 2: PF+PR; 3, 4: PF+DR; 5, 6: PF+XR; 7, 8: PF+DR+PR; 9, 10: PF+XR+PR; 11, 12: PF+DMR; 13, 14: PF+XMR; 15, 16: PF+DMR+PR; 17, 18: PF+XMR+PR.
2.3 功能标记对不同品种OsGRF4基因型的鉴定
以川大粒、巨穗稻以及近等基因系NIL-OsGRF4和NIL-Osgrf4为对照, 利用设计的功能标记对20份不同来源的种质资源进行检测。结果显示: 川大粒与NIL-OsGRF4的扩增结果一致, 巨穗稻与NIL-Osgrf4的结果一致。当以PF+DMR+PR组合进行扩增时, 20份资源均只能得到1条488 bp的目标带(图3-A); 当以PF+XMR+PR组合进行扩增时, 20份资源均能扩出370 bp和488 bp两条目标带(图3-B)。说明这些品种均不含有OsGRF4功能基因, 这与文献报道的OsGRF4突变位点为稀有变异一致[19,21]。此外, 功能标记PF+DMR+PR和PF+XMR+PR的检测结果与测序结果[21]完全一致, 因此, 利用此功能标记可以准确快速鉴定出水稻资源中是否含有氮高效、耐冷基因OsGRF4。图3
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图3功能标记对不同水稻品种OsGRF4基因型的检测
A: PF+DMR+PR引物组合; B: PF+XMR+PR引物组合; M: 100 bp marker; 1: 川大粒; 2: 巨穗稻; 3: NIL-OsGRF4; 4: NIL-Osgrf4; 5~24: 农香99, 玉针香, 湘晚籼17, 冈46B, BL122, 佳辐占, 农香18, 明恢86, 新银占, 玉柱香, R700, 丰源 B, 农香29, 南洋占, R299, 02428, C418, P7144, 农香16, CY016。
Fig. 3Molecular detection of OsGRF4 genotypes by functional markers in different rice varieties
A: PF+DMR+PR; B: PF+XMR+PR; M: 100 bp marker; 1: Chuandali; 2: Jusuidao; 3: NIL-OsGRF4; 4: NIL-Osgrf4; 5-24: Nongxiang 99, Yuzhenxiang, Xiangwanxian 17, Gang 46B, BL122, Jiafuzhan, Nongxiang 18, Minghui 86, Xinyinzhan, Yuzhuxiang, R700, Fengyuan B, Nongxiang 29, Nanyangzhan, R299, 02428, C418, P7144, Nongxiang 16, CY016.
2.4 功能标记对F2分离群体OsGRF4基因型的鉴定
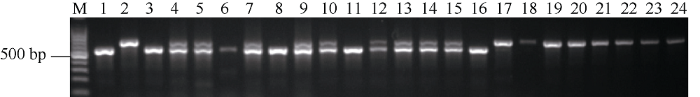
为了进一步验证功能标记对杂合基因型的鉴定效果, 对川大粒/巨穗稻F2群体的22个单株进行检测。首先, 利用与OsGRF4共分离标记GL2-11对F2的22个单株进行基因型分析, 结果显示有5个单株(泳道3、泳道6、泳道8、泳道11和泳道16)为OsGRF4纯合型, 8个单株为Osgrf4纯合型(泳道17~24), 9个单株能扩出2种亲本条带为杂合型(图4)。然后, 利用功能标记对这22个单株进行PCR扩增, 为了便于观察分析, 根据GL2-11的结果将样品以OsGRF4纯合型、杂合型和Osgrf4纯合型的顺序排列。结果显示, 如果是OsGRF4纯合型(泳道3~7), 当以PF+DMR+PR组合进行扩增时, 能扩出370 bp和488 bp的2条目标带, 而PF+XMR+PR组合则只能得到1条488 bp的目标带; Osgrf4纯合型(泳道17~24)的结果与OsGRF4纯合型恰好相反; 而杂合型(泳道8~16), PF+DMR+PR组合和PF+XMR+PR组合均能扩出370 bp和488 bp两条目标带(图5), 检测结果与预期的结果完全一致。因此, 本文设计的功能标记可以有效对OsGRF4纯合、杂合型和Osgrf4纯合3种基因型进行准确鉴定, 适合用于OsGRF4基因的MAS育种。图4
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图4与OsGRF4共分离标记GL2-11对川大粒/巨穗稻部分F2群体基因型的检测
M: 100 bp marker; 1: 川大粒; 2: 巨穗稻; 3~24: F2分离单株。
Fig. 4Molecular detection of genotypes by co-separation marker GL2-11 in F2 population derived from Chuandali/Jusuidao
M: 100 bp marker; 1: Chuandali; 2: Jusuidao; 3-24: individual plants isolated from F2 population.
图5
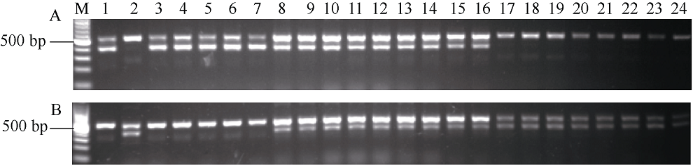 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图5功能标记对川大粒/巨穗稻部分F2群体OsGRF4基因型的检测
M: 100 bp marker; A: PF+DMR+PR; B: PF+XMR+PR; 1: 川大粒; 2: 巨穗稻; 3~24: F2分离单株。
Fig. 5Molecular detection of OsGRF4 genotypes by functional markers in F2 population derived from Chuandali/Jusuidao
M: 100 bp marker; A: PF+DMR+PR; B: PF+XMR+PR; 1: Chuandali; 2: Jusuidao; 3-24: individual plants isolated from F2 population.
3 讨论
MAS育种是利用与目标基因紧密连锁或者来自目标基因内部的分子标记, 对杂交后代的基因型进行快速准确鉴定, 达到选择目标性状的目的。它不受外界环境的干扰, 因此能显著提高育种的效率, 已成为作物遗传改良的重要辅助工具。根据基因组测序数据库预测, 水稻大约有4~5万个功能基因, 目前有1000多个控制产量、品质、株型以及抗生物逆境与非生物逆境的基因被克隆[23]。虽然已克隆的基因较多, 但是通过MAS手段在水稻育种中得以利用的却是少数, 主要是缺乏简单实用的分子标记[24]。开发简便、经济和实用的分子标记是高效开展作物MAS育种的基础。早期开发的大多是与目标基因紧密连锁或共分离的分子标记, 这种标记与目标基因之间会发生重组交换, 容易导致假阳性和选择效率低。如程保山等[25]利用连锁SSR标记对育性恢复基因Rf-1进行选择, 结果表明3726R系列的育性恢复力只有94.1%。梁毅等[26]利用共显性InDel标记对广谱抗稻瘟基因Pigm进行选择, R640×谷梅4号组合的稻瘟病抗性选择率只有95%。后来Andersen等[27]提出功能标记的概念, 它是根据等位基因功能位点的DNA序列差异设计的标记。由于来自基因本身, 功能标记不会发生重组交换而导致假阳性, 对目标基因的选择效率可以达到100%, 因此功能标记在水稻MAS中被广泛应用[28,29]。胡雪娇等[30]根据水稻耐高温基因TT1功能SNP (single nucleotide polymorphisms)的差异设计了dCAPS标记, 可以对F2群体的不同基因型进行准确鉴定。陈涛等[31]根据除草剂抗性基因ALS编码区碱基差异开发的功能标记, 可以准确区分3种不同的基因型, 并且选择的结果与苗期除草剂的抗性完全一致。
水稻很多基因的功能是由于SNP的变异造成的, 比如水稻香味基因OsBADH2[32]、稻瘟病抗性基因Bsr-d1[33]、粒重主效基因GS3[34]、抗除草剂基因bel[35]、氮高效基因NRT1.1B[36]、耐冷基因COLD1[37], 以及本研究的氮高效、耐冷基因OsGRF4[17,18,19,20,21,22]。SNP检测的主要方法是通过PCR扩增, 然后对扩增产物进行回收测序。另一种方法是根据SNP信息开发CAPS或者dCAPS标记, 它受酶切位点的限制, 同时需要增加酶切的步骤。测序和酶切的方法增加了检测成本和劳动强度, 不适合检测大量的遗传材料。扩增阻滞突变系统PCR (amplification refractory mutation system PCR, ARMS-PCR)又称等位基因特异性PCR (allele-specific PCR, AS-PCR), 其原理是根据目的基因SNP的差异分别设计特异引物, 只在匹配的基因型中有扩增产物, 可以鉴定出包括杂合型的3种基因型。AS-PCR省去了测序和酶切的步骤, 具有快速和费用低的特点, 已广泛用于水稻MAS育种。王军等根据水稻稻瘟病抗性基因Bsr-d1功能区域的核苷酸差异开发了AS-PCR功能标记, 可以准确鉴定出Bsr-d1的不同基因型[38]。后来在ARMS-PCR的基础之上开发了四引物扩增受阻突变PCR (tetra-primer ARMS-PCR), 通过1次PCR扩增就可以区分3种基因型[39]。然而Tetra-Primer ARMS-PCR的4条引物在同一PCR体系中, 引物的浓度比、酶的浓度以及退火温度都会影响扩增效率和特异性, 因此很难避免扩增效率低和非特异延伸的问题, 最终导致检测准确性降低, 限制了其在MAS中的应用[39,40]。
氮素是水稻生长发育所必需的营养元素, 水稻产量与氮肥的施用量密切相关。研究表明粳稻比籼稻的氮肥利用率要低[41]。过量施用氮肥会造成严重的生态环境问题, 解决此问题的关键是通过MAS培育氮高效利用的水稻品种。OsGRF4是氮高效利用的一个重要基因, 利用OsGRF4可以实现产量和氮肥利用率的双增长[13]。此外, OsGRF4的突变类型属于稀有变异[19,21], 是一种新的遗传资源, 因此它在水稻遗传育种中具有较大的应用前景。Makoto Matsuoka在Nature上评论说, OsGRF4将在可持续农业中发挥巨大的作用[42]。开发OsGRF4基因的功能标记是开展该基因MAS育种的前提。本研究对AS-PCR进行了改进, 增加了1对外引物用作参考对照, 无论是哪种基因型都能扩增出488 bp的条带; 此外, 根据OsGRF4功能位点SNP3 (TC-AA)的突变开发了相应的内引物。通过优化筛选证明, 在3′端第4位引入错配碱基的引物组合比没有引入错配的组合的扩增效果要好, 最终确定PF+DMR+PR和PF+XMR+PR为OsGRF4基因最优的功能标记组合。通过2次PCR扩增, 对水稻不同品种资源以及F2群体的OsGRF4进行鉴定, 结合测序的结果, 证明本研究开发的功能标记可以同时对OsGRF4纯合、杂合型和Osgrf4纯合3种基因型进行精准快速鉴定。在利用OsGRF4基因进行回交选育的过程中, 大多情况只需把目标基因型AA纯合和AA/TC杂合型筛选出来就可以, 利用本研究的PF+DMR+PR引物组合进行1次PCR反应就可以准确快速筛选出2种目标基因型。因此本研究开发的功能标记组合可以很好的应用于相关资源OsGRF4基因鉴定与MAS育种。
4 结论
根据氮高效、耐冷基因OsGRF4功能区域存在的单核苷酸差异(TC-AA), 并在3′端第4位引入1个错配碱基, 开发了AS-PCR功能标记组合PF+DMR+PR和PF+XMR+PR。PF+DMR+PR能特异扩增OsGRF4纯合基因型; PF+XMR+PR能特异扩增Osgrf4纯合基因型; PF+DMR+PR与PF+XMR+PR均能扩增出2条带的为杂合型。该标记可以对水稻品种资源以及F2群体的OsGRF4进行精准快速鉴定, 因此能用于分子育种培育氮高效、高产和耐冷水稻新品种。参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
DOI:10.1016/j.fcr.2015.02.007URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
.
URLPMID:10677431 [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1038/ng.2958URLPMID:24777451 [本文引用: 1]

The drive toward more sustainable agriculture has raised the profile of crop plant nutrient-use efficiency. Here we show that a major rice nitrogen-use efficiency quantitative trait locus (qNGR9) is synonymous with the previously identified gene DEP1 (DENSE AND ERECT PANICLES 1). The different DEP1 alleles confer different nitrogen responses, and genetic diversity analysis suggests that DEP1 has been subjected to artificial selection during Oryza sativa spp. japonica rice domestication. The plants carrying the dominant dep1-1 allele exhibit nitrogen-insensitive vegetative growth coupled with increased nitrogen uptake and assimilation, resulting in improved harvest index and grain yield at moderate levels of nitrogen fertilization. The DEP1 protein interacts in vivo with both the Galpha (RGA1) and Gbeta (RGB1) subunits, and reduced RGA1 or enhanced RGB1 activity inhibits nitrogen responses. We conclude that the plant G protein complex regulates nitrogen signaling and modulation of heterotrimeric G protein activity provides a strategy for environmentally sustainable increases in rice grain yield.
DOI:10.1111/tpj.12736URLPMID:25439309 [本文引用: 1]

Nitrogen (N), the most important mineral nutrient for plants, is critical to agricultural production systems. N deficiency severely affects rice growth and decreases rice yields. However, excessive use of N fertilizer has caused severe pollution to agricultural and ecological environments. The necessity of breeding of crops that require lower input of N fertilizer has been recognized. Here we identified a major quantitative trait locus on chromosome 12, Tolerance Of Nitrogen Deficiency 1 (TOND1), that confers tolerance to N deficiency in the indica cultivar Teqing. Sequence verification of 75 indica and 75 japonica cultivars from 18 countries and regions demonstrated that only 27.3% of cultivars (41 indica cultivars) contain TOND1, whereas 72.7% of cultivars, including the remaining 34 indica cultivars and all 75 japonica cultivars, do not harbor the TOND1 allele. Over-expression of TOND1 increased the tolerance to N deficiency in the TOND1-deficient rice cultivars. The identification of TOND1 provides a molecular basis for breeding rice varieties with improved grain yield despite decreased input of N fertilizers.
DOI:10.1016/j.plantsci.2014.05.013URLPMID:25219300 [本文引用: 1]

Nitrogen (N) plays a critical role in plant growth and productivity and PTR/NRT1 transporters are critical for rice growth. In this study, OsPTR6, a PTR/NRT1 transporter, was over-expressed in the Nipponbare rice cultivar by Agrobacterium tumefaciens transformation using the ubiquitin (Ubi) promoter. Three single-copy T2 generation transgenic lines, named OE1, OE5 and OE6, were produced and subjected to hydroponic growth experiments in different nitrogen treatments. The results showed the plant height and biomass of the over-expression lines were increased, and plant N accumulation and glutamine synthetase (GS) activities were enhanced at 5.0mmol/L NH4(+) and 2.5mmol/L NH4NO3. The expression of OsATM1 genes in over-expression lines showed that the OsPTR6 over expression increased OsAMT1.1, OsATM1.2 and OsAMT1.3 expression at 0.2 and 5.0mmol/L NH4(+) and 2.5mmol/L NH4NO3. However, nitrogen utilisation efficiency (NUE) was decreased at 5.0mmol/LNH4(+). These data suggest that over-expression of the OsPTR6 gene could increase rice growth through increasing ammonium transporter expression and glutamine synthetase activity (GSA), but decreases nitrogen use efficiency under conditions of high ammonium supply.
DOI:10.1111/nph.12986URL [本文引用: 1]

In this study, OsNAR2.1 mutations with different carbon (C)-terminal deletions and nine different point mutations in the conserved regions of NAR2 homologs in plants were generated to explore the essential motifs involved in the interaction with OsNRT2.3a.Screening using the membrane yeast two-hybrid system and Xenopus oocytes for nitrogen-15 (N-15) uptake demonstrated that either R100G or D109N point mutations impaired the OsNAR2.1 interaction with OsNRT2.3a. Western blotting and visualization using green fluorescent protein fused to either the N- or C-terminus of OsNAR2.1 indicated that OsNAR2.1 is expressed in both the PM and cytoplasm. The split-yellow fluorescent protein (YFP)/BiFC analyses indicated that OsNRT2.3a was targeted to the PM in the presence of OsNAR2.1, while either R100G or D109N mutation resulted in the loss of OsNRT2.3a-YFP signal in the PM.Based on these results, arginine 100 and aspartic acid 109 of the OsNAR2.1 protein are key amino acids in the interaction with OsNRT2.3a, and their interaction occurs in the PM but not cytoplasm.]]>
DOI:10.1038/ng.3337URLPMID:26053497 [本文引用: 1]

Asian cultivated rice (Oryza sativa L.) consists of two main subspecies, indica and japonica. Indica has higher nitrate-absorption activity than japonica, but the molecular mechanisms underlying that activity remain elusive. Here we show that variation in a nitrate-transporter gene, NRT1.1B (OsNPF6.5), may contribute to this divergence in nitrate use. Phylogenetic analysis revealed that NRT1.1B diverges between indica and japonica. NRT1.1B-indica variation was associated with enhanced nitrate uptake and root-to-shoot transport and upregulated expression of nitrate-responsive genes. The selection signature of NRT1.1B-indica suggests that nitrate-use divergence occurred during rice domestication. Notably, field tests with near-isogenic and transgenic lines confirmed that the japonica variety carrying the NRT1.1B-indica allele had significantly improved grain yield and nitrogen-use efficiency (NUE) compared to the variety without that allele. Our results show that variation in NRT1.1B largely explains nitrate-use divergence between indica and japonica and that NRT1.1B-indica can potentially improve the NUE of japonica.
DOI:10.1038/s41587-019-0104-4URLPMID:31036930 [本文引用: 1]

Nitrogen-use efficiency of indica varieties of rice is superior to that of japonica varieties. We apply 16S ribosomal RNA gene profiling to characterize root microbiota of 68 indica and 27 japonica varieties grown in the field. We find that indica and japonica recruit distinct root microbiota. Notably, indica-enriched bacterial taxa are more diverse, and contain more genera with nitrogen metabolism functions, than japonica-enriched taxa. Using genetic approaches, we provide evidence that NRT1.1B, a rice nitrate transporter and sensor, is associated with the recruitment of a large proportion of indica-enriched bacteria. Metagenomic sequencing reveals that the ammonification process is less abundant in the root microbiome of the nrt1.1b mutant. We isolated 1,079 pure bacterial isolates from indica and japonica roots and derived synthetic communities (SynComs). Inoculation of IR24, an indica variety, with an indica-enriched SynCom improved rice growth in organic nitrogen conditions compared with a japonica-enriched SynCom. The links between plant genotype and root microbiota membership established in this study will inform breeding strategies to improve nitrogen use in crops.
DOI:10.1073/pnas.1525184113URLPMID:27274069 [本文引用: 1]

Cellular pH homeostasis is fundamental for life, and all cells adapt to maintain this balance. In plants, the chemical form of nitrogen supply, nitrate and ammonium, is one of the cellular pH dominators. We report that the rice nitrate transporter OsNRT2.3 is transcribed into two spliced isoforms with a natural variation in expression ratio. One splice form, OsNRT2.3b is located on the plasma membrane, is expressed mainly in the phloem, and has a regulatory motif on the cytosolic side that acts to switch nitrate transport activity on or off by a pH-sensing mechanism. High OsNRT2.3b expression in rice enhances the pH-buffering capacity of the plant, increasing N, Fe, and P uptake. In field trials, increased expression of OsNRT2.3b improved grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) by 40%. These results indicate that pH sensing by the rice nitrate transporter OsNRT2.3b is important for plant adaption to varied N supply forms and can provide a target for improving NUE.
DOI:10.1038/s41586-018-0415-5URLPMID:30111841 [本文引用: 4]

Enhancing global food security by increasing the productivity of green revolution varieties of cereals risks increasing the collateral environmental damage produced by inorganic nitrogen fertilizers. Improvements in the efficiency of nitrogen use of crops are therefore essential; however, they require an in-depth understanding of the co-regulatory mechanisms that integrate growth, nitrogen assimilation and carbon fixation. Here we show that the balanced opposing activities and physical interactions of the rice GROWTH-REGULATING FACTOR 4 (GRF4) transcription factor and the growth inhibitor DELLA confer homeostatic co-regulation of growth and the metabolism of carbon and nitrogen. GRF4 promotes and integrates nitrogen assimilation, carbon fixation and growth, whereas DELLA inhibits these processes. As a consequence, the accumulation of DELLA that is characteristic of green revolution varieties confers not only yield-enhancing dwarfism, but also reduces the efficiency of nitrogen use. However, the nitrogen-use efficiency of green revolution varieties and grain yield are increased by tipping the GRF4-DELLA balance towards increased GRF4 abundance. Modulation of plant growth and metabolic co-regulation thus enables novel breeding strategies for future sustainable food security and a new green revolution.
DOI:10.1038/s41467-019-13110-8URLPMID:31729387 [本文引用: 1]

The indica and japonica rice (Oryza sativa) subspecies differ in nitrate (NO3(-)) assimilation capacity and nitrogen (N) use efficiency (NUE). Here, we show that a major component of this difference is conferred by allelic variation at OsNR2, a gene encoding a NADH/NADPH-dependent NO3(-) reductase (NR). Selection-driven allelic divergence has resulted in variant indica and japonica OsNR2 alleles encoding structurally distinct OsNR2 proteins, with indica OsNR2 exhibiting greater NR activity. Indica OsNR2 also promotes NO3(-) uptake via feed-forward interaction with OsNRT1.1B, a gene encoding a NO3(-) uptake transporter. These properties enable indica OsNR2 to confer increased effective tiller number, grain yield and NUE on japonica rice, effects enhanced by interaction with an additionally introgressed indica OsNRT1.1B allele. In consequence, indica OsNR2 provides an important breeding resource for the sustainable increases in japonica rice yields necessary for future global food security.
DOI:10.1038/s41467-019-13187-1URLPMID:31754193 [本文引用: 2]

Over-application of nitrogen fertilizer in fields has had a negative impact on both environment and human health. Domesticated rice varieties with high nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) reduce fertilizer for sustainable agriculture. Here, we perform genome-wide association analysis of a diverse rice population displaying extreme nitrogen-related phenotypes over three successive years in the field, and identify an elite haplotype of nitrate transporter OsNPF6.1(HapB) that enhances nitrate uptake and confers high NUE by increasing yield under low nitrogen supply. OsNPF6.1(HapB) differs in both the protein and promoter element with natural variations, which are differentially trans-activated by OsNAC42, a NUE-related transcription factor. The rare natural allele OsNPF6.1(HapB), derived from variation in wild rice and selected for enhancing both NUE and yield, has been lost in 90.3% of rice varieties due to the increased application of fertilizer. Our discovery highlights this NAC42-NPF6.1 signaling cascade as a strategy for high NUE and yield breeding in rice.
DOI:10.1016/j.cj.2013.10.003URL [本文引用: 2]
DOI:10.1038/nplants.2015.195URLPMID:27250747 [本文引用: 2]

Given the continuously growing population and decreasing arable land, food shortage is becoming one of the most serious global problems in this century(1). Grain size is one of the determining factors for grain yield and thus is a prime target for genetic breeding(2,3). Although a number of quantitative trait loci (QTLs) associated with rice grain size have been identified in the past decade, mechanisms underlying their functions remain largely unknown(4,5). Here we show that a grain-length-associated QTL, GL2, has the potential to improve grain weight and grain yield up to 27.1% and 16.6%, respectively. We also show that GL2 is allelic to OsGRF4 and that it contains mutations in the miR396 targeting sequence. Because of the mutation, GL2 has a moderately increased expression level, which consequently activates brassinosteroid responses by upregulating a large number of brassinosteroid-induced genes to promote grain development. Furthermore, we found that GSK2, the central negative regulator of rice brassinosteroid signalling, directly interacts with OsGRF4 and inhibits its transcription activation activity to mediate the specific regulation of grain length by the hormone. Thus, this work demonstrates the feasibility of modulating specific brassinosteroid responses to improve plant productivity.
DOI:10.1038/nplants.2015.203URLPMID:27250749 [本文引用: 1]

An increase in grain yield is crucial for modern agriculture(1). Grain size is one of the key components of grain yield in rice and is regulated by quantitative trait loci (QTLs)(2,3). Exploring new QTLs for grain size will help breeders develop elite rice varieties with higher yields(3,4). Here, we report a new semi-dominant QTL for grain size and weight (GS2) in rice, which encodes the transcription factor OsGRF4 (GROWTH-REGULATING FACTOR 4) and is regulated by OsmiR396. We demonstrate that a 2 bp substitution mutation in GS2 perturbs OsmiR396-directed regulation of GS2, resulting in large and heavy grains and increased grain yield. Further results reveal that GS2 interacts with the transcription coactivitors OsGIF1/2/3, and overexpression of OsGIF1 increases grain size and weight. Thus, our findings define the regulatory mechanism of GS2, OsGIFs and OsmiR396 in grain size and weight control, suggesting this pathway could be used to increase yields in crops.
DOI:10.1016/j.molp.2015.07.002URLPMID:26187814 [本文引用: 3]

Grain size determines grain weight and affects grain quality. Several major quantitative trait loci (QTLs) regulating grain size have been cloned; however, our understanding of the underlying mechanism that regulates the size of rice grains remains fragmentary. Here, we report the cloning and characterization of a dominant QTL, grain size on chromosome 2 (GS2), which encodes Growth-Regulating Factor 4 (OsGRF4), a transcriptional regulator. GS2 localizes to the nucleus and may act as a transcription activator. A rare mutation of GS2 affecting the binding site of a microRNA, OsmiR396c, causes elevated expression of GS2/OsGRF4. The increase in GS2 expression leads to larger cells and increased numbers of cells, which thus enhances grain weight and yield. The introduction of this rare allele of GS2/OsGRF4 into rice cultivars could significantly enhance grain weight and increase grain yield, with possible applications in breeding high-yield rice varieties.
DOI:10.1111/pbi.12569URLPMID:27107174 [本文引用: 1]

Grain weight is the most important component of rice yield and is mainly determined by grain size, which is generally controlled by quantitative trait loci (QTLs). Although numerous QTLs that regulate grain weight have been identified, the genetic network that controls grain size remains unclear. Herein, we report the cloning and functional analysis of a dominant QTL, grain length and width 2 (GLW2), which positively regulates grain weight by simultaneously increasing grain length and width. The GLW2 locus encodes OsGRF4 (growth-regulating factor 4) and is regulated by the microRNA miR396c in vivo. The mutation in OsGRF4 perturbs the OsmiR396 target regulation of OsGRF4, generating a larger grain size and enhanced grain yield. We also demonstrate that OsGIF1 (GRF-interacting factors 1) directly interacts with OsGRF4, and increasing its expression improves grain size. Our results suggest that the miR396c-OsGRF4-OsGIF1 regulatory module plays an important role in grain size determination and holds implications for rice yield improvement.
URLPMID:26936408 [本文引用: 4]
DOI:10.1093/jxb/erz192URLPMID:31020332 [本文引用: 2]

Grain shape is controlled by quantitative trait loci (QTLs) in rice (Oryza sativa L.). A rice mutant (JF178) with long and large grains has been used in a breeding program for over a decade, but its genetic basis has been unclear. Here, a semi-dominant QTL, designated Large Grain Size 1 (LGS1), was cloned and the potential molecular mechanism of LGS1 function was studied. Near-isogenic lines (NILs) and a map-based approach were employed to clone the LGS1 locus. LGS1 encodes the OsGRF4 transcription factor and contains a 2 bp missense mutation in the coding region that coincides with the putative pairing site of miRNA396. The LGS1 transcript levels in the mutant line were found to be higher than the lgs1 transcript levels in the control plants, suggesting that the mutation might disrupt the pairing of the LGS1 mRNA with miR396. In addition to producing larger grains, LGS1 also enhanced cold tolerance at the seedling stage and increased the survival rate of seedlings after cold stress treatment. These findings indicate that the mutation in LGS1 appears to disturb the GRF4-miR396 stress response network and results in the development of enlarged grains and enhancement of cold tolerance in rice.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1006.2010.01425URL [本文引用: 1]

近年来,随着基因组测序等多种技术实现突破,基因组学、表型组学等多门“组学”及生物信息学得到迅猛发展,作物育种理论和技术也发生了重大变革。以分子标记育种、转基因育种、分子设计育种为代表的现代作物分子育种技术逐渐成为了全世界作物育种的主流,在我国也正在成为作物遗传改良的重要手段。本文在界定分子育种的基础上,简要分析了中国作物分子育种研究现状和面临的问题,探讨了未来我国作物分子育种的发展策略。
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.tplants.2003.09.010URLPMID:14607101 [本文引用: 1]

Different approaches (including association studies) have recently been adopted for the functional characterization of allelic variation in plants and to identify sequence motifs affecting phenotypic variation. We propose the term 'functional markers' for DNA markers derived from such functionally characterized sequence motifs. Functional markers are superior to random DNA markers such as RFLPs, SSRs and AFLPs owing to complete linkage with trait locus alleles. We outline the definition, development, application and prospects of functional markers.
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1006.2017.01622URL [本文引用: 1]

近年来,优良食味粳稻品种南粳46、南粳5055和南粳9108在江苏等地大面积推广,促进了优质稻米产业的发展。但这些品种均不抗稻瘟病,且缺乏适合在淮北地区种植的中熟中粳型优良食味粳稻品种。本研究以同时携带稻瘟病抗性基因Pi-ta和Pi-b的江苏抗病、高产粳稻品种武粳15为母本,携带低直链淀粉含量基因Wx-mq的优良食味粳稻品种南粳5055为父本配置杂交组合进行聚合育种。利用Pi-ta和Pi-b基因的分子标记多重PCR体系以及Wx-mq基因的四引物扩增受阻突变体系PCR检测技术,分别在不同的分离世代对目标基因位点进行检测,结合田间多代选育、抗性鉴定和籽粒胚乳外观鉴定,成功地将Pi-ta、Pi-b和Wx-mq基因聚合于一体,选育出稻瘟病抗性好、食味品质优、产量高的水稻新品系“南粳0051”,适合在江苏省淮北地区种植。本研究将三套自主研发的PCR检测体系成功应用于分子标记辅助选择,不仅为水稻多基因聚合育种提供了快捷、高效的选择方法,也为水稻抗病、优质育种创制了新的种质资源。
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1006.2015.01779URL [本文引用: 1]

稻瘟病是水稻生产上的严重病害,利用抗病基因培育抗病品种是控制稻瘟病最经济而有效的措施。在日本,稻瘟病部分抗性基因Pi35作为广谱持久抗性基因已广泛应用于水稻育种和稻瘟病防治实践。但是,Pi35基因在我国的资源和品种中的分布情况不清,制约了这一重要基因在我国育种实践中的应用,急需开发实用的分子标记,并系统研究该基因在我国的品种及其亲本中的分布情况,为稻瘟病抗性育种服务。本研究通过比对抗、感品种中Pi35等位基因序列,发现一个能检测抗、感病性差异的特异SNP(3780 T),并据此开发了Pi35基因的功能性分子标记Pi35-dCAPS。利用该标记检测了抗源藤系138的衍生品种10份、微核心种质204份和主栽品种67份,结合测序鉴定,确认5份藤系138衍生品种(垦鉴稻3号、垦鉴稻6号、垦稻8号、绥粳3号和龙粳34)及2份微核心种质(粳稻品种抚宁紫皮粳子和籼稻品种细麻线)携带Pi35基因。本研究结果为通过分子育种手段高效利用Pi35基因改良我国水稻(特别是籼稻)品种的稻瘟病抗性提供了手段。]]>
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1105/tpc.108.058917URLPMID:18599581 [本文引用: 1]

In rice (Oryza sativa), the presence of a dominant Badh2 allele encoding betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase (BADH2) inhibits the synthesis of 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline (2AP), a potent flavor component in rice fragrance. By contrast, its two recessive alleles, badh2-E2 and badh2-E7, induce 2AP formation. Badh2 was found to be transcribed in all tissues tested except for roots, and the transcript was detected at higher abundance in young, healthy leaves than in other tissues. Multiple Badh2 transcript lengths were detected, and the complete, full-length Badh2 transcript was much less abundant than partial Badh2 transcripts. 2AP levels were significantly reduced in cauliflower mosaic virus 35S-driven transgenic lines expressing the complete, but not the partial, Badh2 coding sequences. In accordance, the intact, full-length BADH2 protein (503 residues) appeared exclusively in nonfragrant transgenic lines and rice varieties. These results indicate that the full-length BADH2 protein encoded by Badh2 renders rice nonfragrant by inhibiting 2AP biosynthesis. The BADH2 enzyme was predicted to contain three domains: NAD binding, substrate binding, and oligomerization domains. BADH2 was distributed throughout the cytoplasm, where it is predicted to catalyze the oxidization of betaine aldehyde, 4-aminobutyraldehyde (AB-ald), and 3-aminopropionaldehyde. The presence of null badh2 alleles resulted in AB-ald accumulation and enhanced 2AP biosynthesis. In summary, these data support the hypothesis that BADH2 inhibits 2AP biosynthesis by exhausting AB-ald, a presumed 2AP precursor.
DOI:10.1016/j.cell.2017.06.008URLPMID:28666113 [本文引用: 1]

Rice feeds half the world's population, and rice blast is often a destructive disease that results in significant crop loss. Non-race-specific resistance has been more effective in controlling crop diseases than race-specific resistance because of its broad spectrum and durability. Through a genome-wide association study, we report the identification of a natural allele of a C2H2-type transcription factor in rice that confers non-race-specific resistance to blast. A survey of 3,000 sequenced rice genomes reveals that this allele exists in 10% of rice, suggesting that this favorable trait has been selected through breeding. This allele causes a single nucleotide change in the promoter of the bsr-d1 gene, which results in reduced expression of the gene through the binding of the repressive MYB transcription factor and, consequently, an inhibition of H2O2 degradation and enhanced disease resistance. Our discovery highlights this novel allele as a strategy for breeding durable resistance in rice.
DOI:10.1007/s00122-008-0913-1URLPMID:19020856 [本文引用: 1]

Comparative sequencing of GS3, the most important grain length (GL) QTL, has shown that differentiation of rice GL might be principally due to a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) between C and A in the second exon. A total of 180 varieties representing a wide range of rice germplasm were used for association analysis between C-A mutation and GL in order to confirm the potential causal mutation. A cleaved amplified polymorphic sequence (CAPS) marker, SF28, was developed based on the C-A polymorphism in the GS3 gene. A total of 142 varieties carried allele C with GL from 6.4 to 8.8 mm, while the remaining 38 varieties carried allele A with GL from 8.8 to 10.7 mm. Twenty-four unlinked SSR markers were selected to genotype 180 varieties for population structure analysis. Population structure was observed when the population was classified to three subpopulations. Average GL of either genotype A or genotype C within japonica among the three subpopulations had no significant difference from that in indica, respectively, although indica rice had longer grains on average than japonica in the 180 varieties. However, genotype C always had longer grain length on average than genotype A among three subpopulations. The mutation could explain 79.1, 66.4 and 34.7% of GL variation in the three subpopulations, respectively. These results clearly confirmed the mutation between C and A was highly associated with GL. The SF28 could be a functional marker for improvement of rice grain length.
DOI:10.1007/s11103-006-0058-zURL [本文引用: 1]

Development of hybrid rice has greatly contributed to increased yields during the past three decades. Two bentazon-lethal mutants 8077S and Norin8m are being utilized in developing new hybrid rice systems. When the male sterile lines are developed in such a mutant background, the problem of F1 seed contamination by self-seeds from the sterile lines can be solved by spraying bentazon at seedling stage. We first determined the sensitivity of the mutant plants to bentazon. Both mutants showed symptoms to bentazon starting from 100mg/l, which was about 60-fold, lower than the sensitivity threshold of their wild-type controls. In addition, both mutants were sensitive to sulfonylurea-type herbicides. The locus for the mutant phenotype is bel for 8077S and bsl for Norin8m. Tests showed that the two loci are allelic to each other. The two genes were cloned by map-based cloning. Interestingly, both mutant alleles had a single-base deletion, which was confirmed by PCR-RFLP. The two loci are renamed bel a (for bel) and bel b (for bsl). The wild-type Bel gene encodes a novel cytochrome P450 monooxgenase, named CYP81A6. Analysis of the mutant protein sequence also revealed the reason for bel a being slightly tolerant than bel b . Introduction of the wild-type Bel gene rescued the bentazon- and sulfonylurea-sensitive phenotype of bel a mutant. On the other hand, expression of antisense Bel in W6154S induced a mutant phenotype. Based on these results we conclude that the novel cytochrome P450 monooxygenase CYP81A6 encoded by Bel confers resistance to two different classes of herbicides.]]>
URLPMID:26053497 [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.cell.2015.01.046URLPMID:25728666 [本文引用: 1]

Rice is sensitive to cold and can be grown only in certain climate zones. Human selection of japonica rice has extended its growth zone to regions with lower temperature, while the molecular basis of this adaptation remains unknown. Here, we identify the quantitative trait locus COLD1 that confers chilling tolerance in japonica rice. Overexpression of COLD1(jap) significantly enhances chilling tolerance, whereas rice lines with deficiency or downregulation of COLD1(jap) are sensitive to cold. COLD1 encodes a regulator of G-protein signaling that localizes on plasma membrane and endoplasmic reticulum (ER). It interacts with the G-protein alpha subunit to activate the Ca(2+) channel for sensing low temperature and to accelerate G-protein GTPase activity. We further identify that a SNP in COLD1, SNP2, originated from Chinese Oryza rufipogon, is responsible for the ability of COLD(jap/ind) to confer chilling tolerance, supporting the importance of COLD1 in plant adaptation.
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1006.2018.01612URL [本文引用: 1]

Bsr-d1是对稻瘟病菌具有广谱抗性的一个重要基因。为提高Bsr-d1基因在育种中的选择效率, 根据Bsr-d1与其感病等位基因bsr-d1在功能区域存在的单核苷酸差异, 设计和筛选出Bsr-d1基因不同类型的基因功能标记CAPs5-1和3Bsr-d1/3bsr-d1, 结合测序分析验证, 可准确鉴定出Bsr-d1的不同基因型。利用3Bsr-d1/3bsr-d1对34份籼稻品种、江苏历年来主要推广的110份粳稻品种、其他省份的13份粳稻品种、148份太湖流域地方粳稻资源和19份太湖流域地方籼稻资源进行了Bsr-d1基因型检测, 筛选到携带Bsr-d1基因的籼型资源11份, 271份粳型资源中均不携带Bsr-d1基因, 这也说明Bsr-d1主要分布在籼型水稻资源中, 在粳型资源中几乎不存在。本研究为Bsr-d1基因的育种利用和分子标记辅助选择奠定了基础。]]>
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1093/nar/29.17.e88URLPMID:11522844 [本文引用: 2]

Analysis of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) has been and will be increasingly utilized in various genetic disciplines, particularly in studying genetic determinants of complex diseases. Such studies will be facilitated by rapid, simple, low cost and high throughput methodologies for SNP genotyping. One such method is reported here, named tetra-primer ARMS-PCR, which employs two primer pairs to amplify, respectively, the two different alleles of a SNP in a single PCR reaction. A computer program for designing primers was developed. Tetra-primer ARMS-PCR was combined with microplate array diagonal gel electrophoresis, gaining the advantage of high throughput for gel-based resolution of tetra-primer ARMS-PCR products. The technique was applied to analyse a number of SNPs and the results were completely consistent with those from an independent method, restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis.
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.10017216.2013.05.010URL [本文引用: 1]

根据Wxmq基因存在的单核苷酸变异,利用四引物扩增受阻突变体系PCR(Tetraprimer ARMSPCR)的方法设计特异引物,对12个水稻品种(或品系)以及武育粳3号(不含Wxmq基因)/关东194(含Wxmq基因)的F2分离群体进行扩增,依据其PCR产物的带型,可以准确区分出Wxmq基因纯合、非Wxmq基因纯合以及杂合基因型三种类型,其电泳结果与成熟后对胚乳外观特性鉴定完全一致。因此,作为一种简单、低成本的实用技术,四引物ARMSPCR可以广泛用于Wxmq基因水稻的资源鉴定和分子标记辅助育种。
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/S0378-4290(03)00067-4URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1038/d41586-018-05928-xURLPMID:30143754 [本文引用: 1]
