 ,**, 赵冰冰
,**, 赵冰冰 ,**, 于国玲, 李凤菲, 朱小燕, 马福盈, 李云峰, 何光华, 赵芳明
,**, 于国玲, 李凤菲, 朱小燕, 马福盈, 李云峰, 何光华, 赵芳明 ,*西南大学水稻研究所 / 西南大学农业科学研究院 / 转基因植物与安全控制重庆市重点实验室, 重庆 400715
,*西南大学水稻研究所 / 西南大学农业科学研究院 / 转基因植物与安全控制重庆市重点实验室, 重庆 400715Identification of an excellent rice chromosome segment substitution line Z746 and QTL mapping and verification of important agronomic traits
SHEN Wen-Qiang ,**, ZHAO Bing-Bing
,**, ZHAO Bing-Bing ,**, YU Guo-Ling, LI Feng-Fei, ZHU Xiao-Yan, MA Fu-Ying, LI Yun-Feng, HE Guang-Hua, ZHAO Fang-Ming
,**, YU Guo-Ling, LI Feng-Fei, ZHU Xiao-Yan, MA Fu-Ying, LI Yun-Feng, HE Guang-Hua, ZHAO Fang-Ming ,*Rice Research Institute, Southwest University / Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Southwest University / Transgenic Plants and Safety Control, Chongqing Key Laboratory, Chongqing 400715, China
,*Rice Research Institute, Southwest University / Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Southwest University / Transgenic Plants and Safety Control, Chongqing Key Laboratory, Chongqing 400715, China通讯作者:
收稿日期:2019-01-9接受日期:2020-10-14网络出版日期:2021-03-12
| 基金资助: |
Received:2019-01-9Accepted:2020-10-14Online:2021-03-12
| Fund supported: |
作者简介 About authors
沈文强, E-mail:
赵冰冰, E-mail:

摘要
关键词:
Abstract
Keywords:
PDF (1246KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
本文引用格式
沈文强, 赵冰冰, 于国玲, 李凤菲, 朱小燕, 马福盈, 李云峰, 何光华, 赵芳明. 优良水稻染色体片段代换系Z746的鉴定及重要农艺性状QTL定位及其验证[J]. 作物学报, 2021, 47(3): 451-461. doi:10.3724/SP.J.1006.2021.92002
SHEN Wen-Qiang, ZHAO Bing-Bing, YU Guo-Ling, LI Feng-Fei, ZHU Xiao-Yan, MA Fu-Ying, LI Yun-Feng, HE Guang-Hua, ZHAO Fang-Ming.
粒型、株高和穗部组成与水稻产量形成紧密相关, 是水稻重要的农艺性状。水稻粒型不仅影响千粒重, 还影响稻米的外观品质和商品价值[1]。株高和穗部组成性状决定每穗粒数的多少, 是产量形成的重要因素[2]。
粒型一直是研究的热点。目前, 已克隆了一些和粒型相关的基因并对其部分遗传机制进行了解析。GS3是调控水稻谷粒大小的主要基因, 编码跨膜蛋白, 该蛋白存在相互对抗的前后两部分, N端是控制水稻粒型的关键区, 即OSR, 而C端对OSR功能有抑制作用, 这两部分的“博弈”决定水稻粒型。没有GS3蛋白的水稻品种为长粒型, 含有完整GS3蛋白的水稻品种为中间型, 只有OSR的水稻品种为短粒[3]。此外, SLG编码类BAHD酰基转移酶, 参与油菜素内酯稳态的调控, 其突变引起籽粒变长[4]。GAD1编码一个表皮模式因子类蛋白EPFL1, 通过激活OsCKX2和DST的表达降低植株内源细胞分裂素的含量, 从而控制粒长和穗粒数发育[5]。GW6a编码类GNAT 蛋白, 具有组蛋白乙酰转移酶(OsglHAT1)活性, 其高表达会导致转基因植株中组蛋白H4的乙酰化水平提高, 增加籽粒颖壳细胞数目并加速籽粒灌浆, 从而增加粒重和产量[6]。GL3.1 编码蛋白磷酸酶PPKL家族的丝氨酸/苏氨酸磷酸酶, 通过调控细胞周期蛋白T1;3控制水稻籽粒大小和产量[7]。GL3.2与CYP78A13同源, 含有CYP78A13或GL3.2的转基因植株都能促进水稻的籽粒伸长[8]。
水稻株高与抗倒伏及产量密切相关。目前, 已经鉴定出许多矮秆及半矮秆基因。例如多个调控GA合成途径的基因SD1、D18、D35等突变, 导致不同程度的水稻矮化[9,10,11]; 水稻BR生物合成的关键酶OsBR6ox基因突变引起水稻植株矮化[12]; SLs的生物合成途径基因突变也会使水稻植株矮化, 如矮秆突变体d10 [13]。
水稻穗部组成是体现产量的最终部位, 因此, 穗部性状在产量构成中起至关重要的作用[11]。迄今为止, 已初步定位并鉴定了较多的穗部QTL, 同时也克隆了一些相关基因。SPL14受miR156负调控, 当miR156识别位点突变后, 转基因植株的枝梗数和每穗粒数增加[14]; Gnla 编码一种细胞分裂素氧化酶OsCKX2, 通过降低该基因的表达使细胞分裂素在顶端分生组织中积累, 从而使一次枝梗和二次枝梗数目增加, 最终导致穗粒数增加[15]; 水稻密穗多粒的DEP1编码一个类磷脂酰乙醇胺结合蛋白, 通过促进细胞分裂, 降低穗颈节长度和增加枝梗数使稻穗变密来增加每穗粒数[16]; FZP编码一个ERF转录因子, 该基因突变导致穗轴过度分枝[17]; 此外, 还有一些未知功能的蛋白也参与水稻穗部发育, 如密穗多粒基因DEP2 [18]。
可见, 这些性状的遗传机理异常复杂, 目前克隆的基因还不足以揭示这些性状的遗传多样性和分子机理。水稻染色体片段代换系可创造丰富的自然变异, 且仅存在少量代换片段的差异, 因而是复杂性状研究的理想材料。本研究以日本晴为受体亲本、西恢18为供体亲本鉴定了一个7代换片段的水稻优良染色体片段代换系Z746。利用日本晴/Z746构建的次级F2群体进行株高、粒长和穗部性状的QTL定位, 进一步进行单片段代换系培育和相关QTL验证, 研究结果对目标QTL的进一步分子机制研究及分子育种有重要意义。
1 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
水稻染色体片段代换系Z746, 是以日本晴为受体亲本、西恢18为供体亲本, 经多代回交和自交, 结合SSR分子标记辅助选择选育而成的7片段优良代换系。QTL定位群体材料为受体亲本日本晴和Z746杂交构建的次级F2群体, 鉴于Z746与日本晴仅存在7个代换片段的差异, 其余基因组与受体亲本日本晴基因组完全一致, 因而理论上, 次级F2群体遗传交换仅发生在代换片段区域。
次级单片段代换系(single segment substitution lines, SSSL)选育材料: 在2018年QTL定位结果的基础上, 据基因型和表型从F2代选择8个单株, 2019年种成株系, 每个株系取20株, 利用分子标记辅助选择(molecular marker-assisted method selection, MAS)进一步对其中的杂合标记进行跟踪筛选, 最后选出8个SSSL, 然后2020年用这些SSSL进一步进行QTL验证。
1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 Z746代换片段系培育 采用均匀分布于水稻12条染色体的429个标记, 对日本晴和西恢18进行多态性分析, 选出263个多态性标记[19], 然后用这些多态性标记从BC2F1进行分子标记辅助选择, 在BC2F4鉴定到一个18代换片段的良好株系, 然后以日本晴与这一株系杂交, 产生的F1再与日本晴回交、自交, 直至其F5代初步选育出7代换片段的Z746。参照周可等[20]描述的方法分析代换片段。按Paterson等[21]方法估计代换片段长度。1.2.2 材料种植 2017年以日本晴与Z746杂交, 收获杂交种并于同年秋季种植于海南基地, 分单株收获F1代种子。2018年3月10日, 将亲本(日本晴和Z746)及F2代群体于重庆西南大学水稻研究所实验基地育苗。4月18日, 以株、行距分别为16.65 cm和26.65 cm移栽日本晴和Z746各40株及164个F2单株于同一试验田, 常规管理。2019年3月和2020年3月, 以同样规格和管理种植F2代所选的用于次级代换片段系选育的8个株系、F3代选出的8个纯合SSSL和其受体亲本日本晴于西南大学水稻研究所实验基地。
1.2.3 农艺性状调查 在成熟期, 平地面随机收取日本晴和Z746各10株以及F2群体164株作为样本, 考察株高、有效穗数、每穗穗长、一次枝梗数、二次枝梗数、粒长、粒宽、每穗总粒数、每穗实粒数、千粒重和单株产量, 各农艺性状的测定参照崔国庆等[22]描述的方法进行。分别利用Microsoft Excel 2016统计10株日本晴和10株Z746各性状的平均值、标准差及进行t检验, 统计F2代群体各参数如平均数、最小值、最大值、偏度和峰度。
1.2.4 QTL定位 采用CTAB法提取亲本和用于QTL定位的164个F2代单株的基因组DNA[23]。参照周可等[21]描述的方法进行PCR扩增和非变性聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳和快速银染。将日本晴带型标以“-1”, Z746带型标以“1”, 杂合带型标以“0”, 缺失带型标以“.”。将F2的164个单株的各性状平均值及标记赋予值一同用于QTL定位。在SAS统计软件上, 利用加州大学河滨分校徐世忠教授编写的HPMIXED 程序限制性最大似然(REML)法(加以修改)定位QTL[24], 以P < 0.05为阈值决定一个QTL与代换片段上的某标记连锁。
1.2.5 基于8个SSSL的QTL验证 2020年7月下旬, 在日本晴和8个SSSL (S1~S8)的小区中间各收获10株, 并按1.2.3描述的方法测量株高、有效穗数、穗长等性状。因每个SSSL与受体亲本相比, 仅存在唯一代换片段的差异, 因此本研究使用t测验进行每个SSSL携带QTL的鉴定。对10株SSSL和10株日本晴的2018年鉴定出QTL的性状进行统计分析, 当P值小于0.05时, 认为该SSSL存在某一性状的QTL。QTL的加性效应以每个SSSL和日本晴表型值之间差异的一半计算[25]。所有计算均在Microsoft Excel 2016中完成。
2 结果与分析
2.1 Z746的代换片段鉴定
用Z746代换片段上的所有SSR标记及代换片段外的36个SSR标记对5株Z746进行进一步代换片段鉴定和遗传背景纯度检测, 发现5个单株的代换片段一致, 且没有检测出除代换片段外的西恢18其他残留片段, 表明Z746已经纯合。Z746的7个来自西恢18的代换片段, 分布于水稻2号、3号、4号、6号和11号染色体(图1)。总代换长度为27.96 Mb, 最长代换长度为7.34 Mb, 最短代换长度为1.43 Mb, 平均代换长度为3.99 Mb。图1
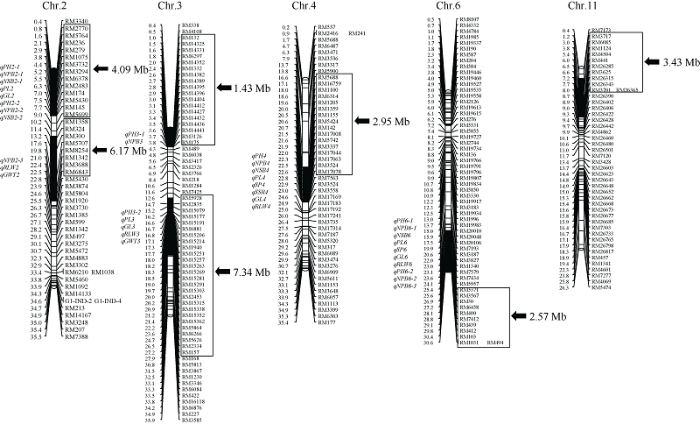 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图1水稻染色体片段代换系Z746的代换片段及所携带的QTL
每条染色体左侧为物理距离(Mb)和定位的QTL; 右侧为标记名称、代换区间(框内标记)和代换长度(黑箭头指向)。
Fig. 1Substitution segments and detected QTL of chromosome segment substition line Z746
Physical distances (Mb) and mapped QTL are marked at the left of each chromosome; markers substitution interval squared by frame, and substitution length (black arrow direction) are displayed at the right of each chromosome.
2.2 Z746的农艺性状分析
Z746的株型与受体日本晴相近(图2-A)。粒长与日本晴相比极显著增加, 每粒平均增加0.15 mm, 而粒宽显著减少(图2-B~F和表1)。此外, Z746的株高、籽粒长宽比、一次枝梗数、二次枝梗数、每穗总粒数、每穗实粒数均显著增加; 而结实率显著减少, 但是Z746的结实率仍达89.01%; Z746的有效穗数、穗长、千粒重和单株产量与日本晴无显著差异(表1)。图2
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图2成熟期日本晴和Z746的株型、穗型和籽粒
A: 日本晴和Z746的株型, 标尺为10 cm; B: 日本晴和Z746的穗型, 标尺为5 cm; C, D: 日本晴和Z746的籽粒, 标尺为5 mm; E, F: 日本晴和Z746的糙米, 标尺为5 mm。
Fig. 2Plant type, panicle type, and grain of Nipponbare and Z746 at maturity stage
A: plant type of Nipponbare (left) and Z746 (right). Scale bar, 10 cm; B: main panicle of Nipponbare (left) and Z746 (right). Scale bar, 5 cm; C, D: grains of Nipponbare (C) and Z746 (D). Scale bar, 5 mm; E, F: brown grains of Nipponbare (E) and Z746 (F). Scale bar, 5 mm.
Table 1
表1
表1日本晴和Z746 及F2 群体各性状统计参数
Table 1
| 性状 Trait | 平均值±标准差(亲本) Mean±SD (parents) | F2群体 F2 population | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 日本晴 Nipponbare | Z746 | 平均值±标准差 Mean±SD | 范围 Range | 偏度 Skewness | 峰度 Kurtosis | |
| 株高Plant height (cm) | 87.93±5.32 | 96.70±2.11** | 89.61±8.43 | 78.00-124.00 | 2.16 | 5.33 |
| 有效穗数Panicle number per panicle | 18.40±5.55 | 17.70±5.42 | 14.41±4.56 | 6.00-28.00 | 0.67 | 0.23 |
| 穗长Panicle length (cm) | 19.68±0.88 | 20.64±0.62 | 19.38±1.70 | 15.86-29.25 | 1.93 | 6.44 |
| 一次枝梗数Number of primary branch | 7.42±0.43 | 8.05±0.67* | 8.36±1.49 | 6.67-14.47 | 2.75 | 7.62 |
| 二次枝梗数Number of secondary branch | 14.62±1.67 | 22.99±2.42** | 14.59±4.38 | 7.17-34.73 | 2.20 | 6.71 |
| 粒长Grain length (mm) | 7.40±0.08 | 8.93±0.19** | 7.71±0.57 | 7.03-9.42 | 1.16 | 0.19 |
| 粒宽Grain width (mm) | 3.44±0.06 | 2.85±0.11** | 3.26±0.56 | 2.63-3.48 | 10.85 | 132.05 |
| 长宽比Ratio of length to width | 2.15±0.03 | 3.13±0.15** | 2.40±0.34 | 2.11-3.53 | 0.56 | 4.21 |
| 结实率Seed-setting rate (%) | 91.79±2.02 | 89.01±2.34* | 87.00±11.02 | 30.00-96.05 | -3.25 | 11.54 |
| 每穗总粒数Spikelets per panicle | 97.70±23.84 | 122.66±10.99* | 91.75±18.10 | 62.56-182.67 | 2.24 | 7.62 |
| 每穗实粒数Grains per panicle | 89.68±22.56 | 109.23±10.58* | 78.77±15.17 | 26.11-166.73 | 0.90 | 7.86 |
| 千粒重1000-grain weight (g) | 25.41±0.91 | 26.09±0.71 | 25.34±1.58 | 18.33-30.10 | 0.04 | 2.15 |
| 单株产量Yield per plant (g) | 38.44±10.23 | 44.42±15.42 | 28.87±11.46 | 9.91-64.25 | 0.89 | 0.36 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
2.3 重要农艺性状QTL定位
利用日本晴与Z746构建的次级F2群体共鉴定出36个粒长等重要农艺性状QTL (表2), 分布于2号、3号、4号和6号染色体。Table 2
表2
表2水稻重要农艺性状QTL
Table 2
| 性状 Trait | QTL | 染色体 Chr. | 连锁标记 Linked marker | 估计效应 Additive | 贡献率 Var. (%) | P值 P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株高 Plant height (cm) | qPH2-1 | 2 | RM1075 | -5.06 | 15.06 | < 0.0001 |
| qPH2-2 | 2 | RM6378 | 4.11 | 13.70 | 0.0037 | |
| qPH3-1 | 3 | RM14389 | 3.17 | 2.71 | 0.0108 | |
| qPH3-2 | 3 | RM6266 | 1.92 | 5.06 | 0.0258 | |
| qPH4 | 4 | RM1155 | 4.71 | 16.67 | < 0.0001 | |
| qPH6-1 | 6 | RM7412 | 3.01 | 13.59 | 0.0009 | |
| qPH6-2 | 6 | RM103 | -4.13 | 26.98 | 0.0075 | |
| 穗长 Panicle length (cm) | qPL2 | 2 | RM1075 | -0.99 | 13.12 | < 0.0001 |
| qPL3 | 3 | RM6266 | 0.39 | 4.85 | 0.0346 | |
| qPL4 | 4 | RM1155 | 0.49 | 4.16 | 0.0276 | |
| qPL6 | 6 | RM7412 | 0.64 | 13.81 | 0.0011 | |
| 一次枝梗数 Number of primary branch | qNPB2-1 | 2 | RM1075 | -0.49 | 4.19 | 0.0198 |
| qNPB2-2 | 2 | RM6378 | 0.70 | 11.59 | 0.0074 | |
| qNPB2-3 | 2 | RM13262 | -0.47 | 5.43 | 0.0449 | |
| qNPB3 | 3 | RM14389 | 0.46 | 5.92 | 0.0424 | |
| qNPB4 | 4 | RM1155 | 1.10 | 27.43 | < 0.0001 | |
| qNPB6-1 | 6 | RM7412 | 0.57 | 14.32 | 0.0007 | |
| qNPB6-2 | 6 | RM103 | -0.87 | 35.15 | 0.0023 | |
| qNPB6-3 | 6 | RM494 | 0.63 | 18.95 | 0.0165 | |
| 二次枝梗数 Number of secondary branch | qNSB2-1 | 2 | RM1075 | -1.42 | 3.35 | 0.0366 |
| qNSB2-2 | 2 | RM6378 | 1.76 | 7.10 | 0.0284 | |
| qNSB4 | 4 | RM1155 | 2.01 | 8.73 | 0.0015 | |
| qNSB6 | 6 | RM7412 | 1.80 | 13.81 | 0.0011 | |
| 粒长 Grain length (mm) | qGL2 | 2 | RM1075 | -0.11 | 3.63 | 0.0302 |
| qGL3 | 3 | RM6266 | 0.34 | 60.28 | < 0.0001 | |
| qGL4 | 4 | RM1155 | 0.26 | 27.47 | < 0.0001 | |
| qGL6 | 6 | RM7412 | 0.08 | 4.77 | 0.0467 | |
| 长宽比 Ratio of length to width | qRLW2 | 2 | RM13262 | 0.16 | 12.97 | 0.0017 |
| qRLW3 | 3 | RM6266 | 0.13 | 14.23 | 0.0004 | |
| qRLW4 | 4 | RM1155 | 0.15 | 10.41 | 0.0005 | |
| qRLW6 | 6 | RM7412 | 0.08 | 5.30 | 0.0414 | |
| 结实率 Seed-setting rate (%) | qSSR4 | 4 | RM1155 | -0.07 | 17.33 | < 0.0001 |
| 每穗粒数 Spikelets per panicle | qSP4 | 4 | RM1155 | 6.24 | 4.73 | 0.0122 |
| qSP6 | 6 | RM7412 | 4.33 | 4.51 | 0.0481 | |
| 千粒重 1000-grain weight (g) | qGWT2 | 2 | RM13262 | -0.88 | 14.82 | 0.0009 |
| qGWT3 | 3 | RM6266 | 1.13 | 40.50 | < 0.0001 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
影响Z746籽粒长度的QTL共有4个, 其中qGL3、qGL4和qGL6的加性效应分别增加粒长0.36、0.26和0.08 mm, 对长度变异的贡献率分别为80.23%、27.47%和4.77%, qGL2减少粒长0.11 mm, 对长度变异的贡献率为3.63%。籽粒长宽比QTL共鉴定出4个, qRLW2、qRLW3、qRLW4和qRLW6的加性效应分别增加长宽比0.16、0.13、0.15和0.08, 对粒型变异的贡献率分别为12.97%、14.23%、10.41%和5.30%。
Z746的株高由7个QTL共同控制, 其中qPH2-2、qPH3-1、qPH3-2、qPH4和qPH6-1的加性效应分别增加株高4.11、3.17、1.92、4.71和3.01 cm, 对株高变异的贡献率分别为13.7%、2.71%、5.06%、16.67%和13.59%; qPH2-1和qPH6-2分别减少株高5.06 cm和4.13 cm, 对株高变异的贡献率为15.06%和26.98%。
影响Z746穗长的QTL共有4个, 其中qPL3、qPL4和qPL6的加性效应分别增加穗长0.39、0.49和0.64 cm, 对穗长变异的贡献率分别为4.85%、4.16%和13.81%; 而qPL2减少穗长0.99 cm, 对穗长变异的贡献率为13.12%。影响一次枝梗数的QTL共有8个, 其中qNPB2-2、qNPB3、qNPB4、qNPB6-1和qNPB6-3的加性效应分别为增加一次枝梗数0.7个、0.46个、1.10个、0.57个和0.63个, 对一次枝梗数变异的贡献率分别为11.59%、5.92%、27.43%、14.32%和18.95%; 而qNPB2-1、qNPB2-3和qNPB6-2减少一次枝梗数0.49个、0.47个和0.87个, 对一次枝梗数变异的贡献率分别为4.19%、5.43%和35.15%。影响二次枝梗数的QTL共有4个, 其中qNSB2-2、qNSB4和qNSB6的加性效应为1.76个、2.01个和1.8个, 对二次枝梗数变异的贡献率分别为7.10%、8.73%和13.81%, qNSB2-1减少二次枝梗数1.42个, 对二次枝梗数变异的贡献率为3.35%。表明Z746的二次枝梗数由3个增效QTL和1个减效QTL共同控制。结实率QTL-qSSR4使Z746的结实率减少7个百分点, 对结实变异的贡献率为17.33%。影响Z746每穗粒数的QTL共有2个, 每穗分别增加6.24粒和4.33粒, 对穗粒数变异的贡献率分别为4.73%和4.51%。千粒重QTL共鉴定出2个, 其中qGWT3的加性效应为增加千粒重1.13 g, 对粒重变异的贡献率为40.50%; 而qGWT2减少千粒重0.88 g, 对粒重变异的贡献率为14.82%。
比较有趣的是, 有些性状的QTL连锁于同一标记, 如控制株高的主效QTL-qPH6-2和控制一次枝梗数的主效QTL-qNPB6-2均连锁于标记RM103; 控制粒长的主效QTL-qGL3和控制千粒重的主效QTL-qGWT3均连锁于标记RM6266; 控制一次枝梗数的主效QTL-qNPB4和控制粒长的主效QTL-qGL4均连锁于标记RM1155, 暗示这些QTL可能具有一因多效或成簇状分布。
2.4 次级单片段代换系选育及目标QTL验证
在QTL的初定位基础上, 利用MAS在F3选育出8个单片段代换系(S1~S8), 小区种植进一步验证了24个QTL (如qPH2-1、qPL3、qGL3、qGL6、qGWT6等)的遗传稳定性(表3)。而有9个QTL (qNPB2-2、qNPB3、qNPB4、qNPB6-2、qNPB6-3、qNSB4、qNSB6、qGL2、qGL4)未能被相应的SSSL检测到, 表明这些微效QTL的表达可能易受环境影响。另外3个QTL (qNPB2-3、qRLW2、qGWT2)因未选到相应的SSSL而无法被验证。Table 3
表3
表3SSSL中QTL的加性效应分析
Table 3
| SSSL代码 SSSL code | 代换片段 b Substitution segment b | 长度 Length (Mb) | 染色体 Chr. | 性状 Trait | QTL | 均值±标准差 Mean±SD | 加性效应 Additive | P值 P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N a | — | 株高 Plant height (cm) | 90.60±4.50 | |||||
| S1 | RM2770--RM6378--RM1075 | 1.04 | 2 | qPH2-1 | 101.06±1.65 | 5.23 | 2.86E-06 | |
| S2 | RM6378--RM1075--RM5699 | 2.58 | 2 | qPH2-2 | 128.12±3.46 | 18.76 | 2.58E-13 | |
| S3 | RM132--RM14389--RM175 | 7.34 | 3 | qPH3-1 | 101.15±1.54 | 5.28 | 2.31E-06 | |
| S4 | RM5928--RM6266--RM157 | 1.43 | 3 | qPH3-2 | 110.65±3.48 | 10.02 | 4.55E-08 | |
| S5 | RM5688--RM1155--RM17078 | 2.95 | 4 | qPH4 | 108.66±3.19 | 9.03 | 1.40E-08 | |
| S6 | RM7412--RM103--RM494 | 0.90 | 6 | qPH6-1 | 109.31±2.00 | 9.36 | 1.35E-09 | |
| S7 | RM103--RM494--long arm end | 0.20 | 6 | qPH6-2 | 104.95±1.73 | 9.36 | 4.67E-08 | |
| S8 | RM5371--RM7412-RM103-RM494--long arm end | 2.57 | 6 | qPH6 | 106.20±2.29 | 7.80 | 2.93E-08 | |
| N a | — | 穗长 Panicle length (cm) | 19.02±1.11 | |||||
| S1 | RM2770--RM6378--RM1075 | 1.04 | 2 | qPL2 | 22.70±1.29 | 1.84 | 8.53E-07 | |
| S4 | RM5928--RM6266--RM157 | 1.43 | 3 | qPL3 | 24.60±2.19 | 2.79 | 1.69E-05 | |
| S5 | RM5688--RM1155--RM17078 | 2.95 | 4 | qPL4 | 21.64±1.62 | 1.31 | 0.001 | |
| S7 | RM103--RM494--long arm end | 0.20 | 6 | qPL6 | 26.02±1.92 | 3.50 | 4.63E-08 | |
| N a | — | 一次枝梗数 Number of primary branch | 9.47±0.55 | |||||
| S2 | RM6378--RM1075--RM5699 | 2.58 | 2 | qNPB2 | 12.80±1.60 | 1.67 | 1.57E-05 | |
| S8 | RM5371--RM7412-RM103-RM494--long arm end | 2.57 | 6 | qNPB6 | 10.27±0.96 | 0.40 | 0.02 | |
| N a | — | 二次枝梗数 Number of secondary branch | 16.03±2.54 | |||||
| S1 | RM2770--RM6378--RM1075 | 1.04 | 2 | qNSB2-1 | 18.82±2.75 | 1.40 | 0.03 | |
| S2 | RM6378--RM1075--RM5699 | 2.58 | 2 | qNSB2-2 | 25.78±2.97 | 4.88 | 1.38E-06 | |
| N a | — | 粒长 Grain length (mm) | 7.25±0.13 | |||||
| S4 | RM5928--RM6266--RM157 | 1.43 | 3 | qGL3 | 7.71±0.23 | 0.23 | 0.0002 | |
| S7 | RM103--RM494--long arm end | 0.20 | 6 | qGL 6 | 7.55±0.21 | 0.15 | 0.002 | |
| N a | — | 长宽比 Ratio of length to width | 2.17±0.04 | |||||
| S4 | RM5928--RM6266--RM157 | 1.43 | 3 | qRLW3 | 2.31±0.07 | 0.07 | 0.0003 | |
| S5 | RM5688--RM1155--RM17078 | 2.95 | 4 | qRLW4 | 2.33±0.11 | 0.08 | 0.0007 | |
| S7 | RM103--RM494--long arm end | 0.20 | 6 | qRLW6 | 2.50±0.12 | 0.16 | 9.94E-07 | |
| N a | — | 结实率 Seed-setting rate (%) | 92.73±3.59 | |||||
| S5 | RM5688--RM1155--RM119 | 2.95 | 4 | qSSR4 | 81.24±4.32 | -5.75 | 0.0002 | |
| N a | — | 每穗总粒数 Spikelets per panicle | 91.76±8.36 | |||||
| S5 | RM5688--RM1155--RM17078 | 2.95 | 4 | qSP4 | 104.00±9.37 | 6.12 | 0.006 | |
| S7 | RM103--RM494--long arm end | 0.20 | 6 | qSP6 | 117.6±10.12 | 12.92 | 1.30E-05 | |
| N a | — | 千粒重 1000-grain weight (g) | 24.07±0.53 | |||||
| S4 | RM5928--RM6266--RM157 | 1.43 | 3 | qGWT3 | 27.56±0.47 | 1.75 | 7.11E-10 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
3 讨论
产量始终是水稻育种的主要目标之一, 然而它是一个复杂性状, 受多个性状影响。粒型、株高、穗部性状与水稻产量密切相关。这些性状遗传基础复杂, 由多基因控制。水稻染色体片段代换系是利用基因重组交换原理, 通过与受体亲本连续回交和自交的手段, 结合分子标记辅助选择选育而成, 因而是创造自然变异和分解复杂性状的有效途径。而且, 每个代换系与受体亲本仅存在少量代换片段的差异, 减少了个体间遗传背景的干扰, 可使QTL鉴定更加准确[26]。鉴定的QTL准确、分析出优良的等位基因以及将这些分散的优良等位基因聚合在一起是分子设计育种的3个重要环节[27]。日本晴是一个具有完整基因组数据的公认粳稻品种, 西恢18是西南大学水稻研究所培育的优良籼稻恢复系。为了更好地利用和定向改良西恢18, 创造在日本晴背景下西恢18的基因自然变异对明确其重要性状的基因座位有重要意义。我们以日本晴为受体亲本、西恢18为供体亲本鉴定了一个水稻优良染色体片段代换系Z746。Z746含有多个育种有利性状, 如株高、粒长、长宽比、一次枝梗数、二次枝梗数、穗长、每穗粒数、每穗实粒数比受体亲本显著增加, 因而是用于引起这些性状变异的QTL鉴定的良好材料。通过QTL定位, 我们将36个水稻重要农艺性状的QTL分解到了Z746的2号、3号、4号和6号染色体的6个代换片段上, 其中包括10个负效应和26个正效应的QTL。这对于我们进一步利用MAS法进行这些QTL的单片段代换系选育有重要意义。我们鉴定的粒长qGL3、千粒重qGWT3以及株高qPH3-2均连锁于RM6266 (物理距离为23.62 Mb), 而且qGL3、qGWT3和qPH3-2均具有增加对应性状的加性效应。其中qGL3和qGWT3可能具有一因多效性, 粒重的增加应由粒长增加所致。经与已克隆和定位的QTL比较, 在与其连锁标记RM6266 (23.62 Mb) 2 Mb的区域内包含GL3.1和qGL3-1[7,28], 这2个粒长基因均编码OsPPKL1, 属OsPPKL1的不同等位变异。GL3.1通过调控细胞周期蛋白T1;3控制水稻籽粒大小和产量。因而我们定位的qGL3和qGWT3可能也是OsPPKL1的等位变异, 也正是由于这些等位变异的丰富性造就了水稻籽粒长度的多样性和遗传的复杂性。此外, 这2个QTL还与王大川等[29]鉴定的qGL3、qGWT3, Wang等[30]鉴定的qKL3、qKWT3相同, 表明这2个QTL遗传稳定。qPH3-2可能与株高OsHox32基因(物理距离为24.651 Mb~24.657 Mb)等位, 过表达OsHox32导致水稻株高变矮[31]。同时, 该QTL也可被王大川等[29]和Wang等[30]鉴定出, 同样表明qPH3-2是一个遗传稳定的主效QTL。同样地, qGL6和qRLW6也可被Zhang 等[32]鉴定出, 并经DNA测序表明qGL6是生长素响应因子OsARF19的等位基因。
qPL2与ZFP185 (物理距离为5.345 Mb~5.347 Mb)可能等位, ZFP185编码一个锌指蛋白, 过表达ZFP185表现稻穗变短[33]。qPL2也具有减少穗长的加性效应, 其连锁标记与ZFP185相距1.52 Mb, 可作为qPL2的候选基因。株高qPH3-1与RM14389 (2.70 Mb)连锁, 与PAD和SD37分别相距0.36 Mb和0.48 Mb。PAD 和SD37分别编码OsMCA1和CYP96B4, 这2个基因突变均引起水稻株高矮化[34,35]。因而, PAD和SD37可作为qPH3-1的候选基因。qPH6-1与RM7412 (28.77 Mb)连锁, 可能与OsPIN2 (物理距离为27.200 Mb~27.204 Mb)等位, 过表达OsPIN2引起水稻植株矮化[36]。至于是否等位, 均有待于对这些基因进行日本晴和Z746进一步DNA测序和功能互补验证。此外, qNSB2-1、qNPB2-2、qPH3-2、qPL3也可被崔国庆等[22]、王大川等[29]和Wang等[30]检测到。其中36个QTL中, 24个也被我们选出的8个SSSL验证。表明这些遗传稳定的主效QTL由于受环境影响较小, 对分子设计育种至关重要。
本研究中的其他QTL均未见报道, 可能是新的位点。对于未报道的QTL, 我们进一步精细定位和克隆, 为其生物学功能研究奠定基础。
4 结论
鉴定了一个以日本晴为受体、西恢18为供体亲本的含有7个代换片段的优良水稻染色体片段代换系Z746, 其平均代换长度为3.99 Mb。Z746携带多个育种有利性状。进一步利用日本晴/Z746构建的次级F2群体共鉴定出36个重要性状的QTL。其中24个可被我们选出的8个SSSL所验证, 5个可能与已克隆的基因等位, 8个可被前人多次检出, 表明这些是遗传较稳定的主效QTL。Z746的粒长主要由4个粒长QTL (qGL3、qGL4、qGL2、qGL6)控制; 株高主要由7个QTL控制; 穗长由4个QTL控制; 每穗粒数由2个QTL控制; 千粒重由2个QTL控制。这些结果为目标QTL的遗传机制解析和育种应用奠定了良好基础。参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
URLPMID:27634315 [本文引用: 1]
URLPMID:25535376 [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 2]
DOI:10.1111/pce.12452URLPMID:25255828 [本文引用: 1]

Grain size is one of the most important determinants of crop yield in cereals. Here, we identified a dominant mutant, big grain2 (bg2-D) from our enhancer-trapping population. Genetic analysis and SiteFinding PCR (polymerase chain reaction) revealed that BG2 encodes a cytochrome P450, OsCYP78A13. Sequence search revealed that CYP78A13 has a paralogue Grain Length 3.2 (GL3.2, LOC_Os03g30420) in rice with distinct expression patterns, analysis of transgenic plants harbouring either CYP78A13 or GL3.2 showed that both can promote grain growth. Sequence polymorphism analysis with 1529 rice varieties showed that the nucleotide diversity at CYP78A13 gene body and the 20 kb flanking region in the indica varieties were markedly higher than those in japonica varieties. Further, comparison of the genomic sequence of CYP78A13 in the japonica cultivar Nipponbare and the indica cultivar 9311 showed that there were three InDels in the promoter region and eight SNPs (single nucleotide polymorphism) in its coding sequence. Detailed examination of the transgenic plants with chimaeric constructs suggested that variation in CYP78A13 coding region is responsible for the variation of grain yield. Taken together, our results suggest that the variations in CYP78A13 in the indica varieties hold potential in rice breeding for application of grain yield improvement.
[本文引用: 1]
URLPMID:25371548 [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1111/tpj.12714URLPMID:25353370 [本文引用: 2]

Seed germination is a key developmental process in the plant life cycle that is influenced by various environmental cues and phytohormones through gene expression and a series of metabolism pathways. In the present study, we investigated a C2C2-type finger protein, OsLOL1, which promotes gibberellin (GA) biosynthesis and affects seed germination in Oryza sativa (rice). We used OsLOL1 antisense and sense transgenic lines to explore OsLOL1 functions. Seed germination timing in antisense plants was restored to wild type when exogenous GA3 was applied. The reduced expression of the GA biosynthesis gene OsKO2 and the accumulation of ent-kaurene were observed during germination in antisense plants. Based on yeast two-hybrid and firefly luciferase complementation analyses, OsLOL1 interacted with the basic leucine zipper protein OsbZIP58. The results from electrophoretic mobility shift and dual-luciferase reporter assays showed that OsbZIP58 binds the G-box cis-element of the OsKO2 promoter and activates LUC reporter gene expression, and that interaction between OsLOL1 and OsbZIP58 activates OsKO2 gene expression. In addition, OsLOL1 decreased SOD1 gene expression and accelerated programmed cell death (PCD) in the aleurone layer of rice grains. These findings demonstrate that the interaction between OsLOL1 and OsbZIP58 influences GA biosynthesis through the activation of OsKO2 via OsbZIP58, thereby stimulating aleurone PCD and seed germination.
URLPMID:12445121 [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1093/pcp/pcq077URLPMID:20522488 [本文引用: 1]

Several triazole-containing chemicals have previously been shown to act as efficient inhibitors of cytochrome P450 monooxygenases. To discover a strigolactone biosynthesis inhibitor, we screened a chemical library of triazole derivatives to find chemicals that induce tiller bud outgrowth of rice seedlings. We discovered a triazole-type chemical, TIS13 [2,2-dimethyl-7-phenoxy-4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)heptan-3-ol], which induced outgrowth of second tiller buds of wild-type seedlings, as observed for non-treated strigolactone-deficient d10 mutant seedlings. TIS13 treatment reduced strigolactone levels in both roots and root exudates in a concentration-dependent manner. Co-application of GR24, a synthetic strigolactone, with TIS13 canceled the TIS13-induced tiller bud outgrowth. Taken together, these results indicate that TIS13 inhibits strigolactone biosynthesis in rice seedlings. We propose that TIS13 is a new lead compound for the development of specific strigolactone biosynthesis inhibitors.
URLPMID:20495564 [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1242/dev.00564URLPMID:12835399 [本文引用: 1]

Inflorescences of grass species have a distinct morphology in which florets are grouped in compact branches called spikelets. Although many studies have shown that the molecular and genetic mechanisms that control floret organ formation are conserved between monocots and dicots, little is known about the genetic pathway leading to spikelet formation. In the frizzy panicle (fzp) mutant of rice, the formation of florets is replaced by sequential rounds of branching. Detailed analyses revealed that several rudimentary glumes are formed in each ectopic branch, indicating that meristems acquire spikelet identity. However, instead of proceeding to floret formation, axillary meristems are formed in the axils of rudimentary glumes and they either arrest or develop into branches of higher order. The fzp mutant phenotype suggests that FZP is required to prevent the formation of axillary meristems within the spikelet meristem and permit the subsequent establishment of floral meristem identity. The FZP gene was isolated by transposon tagging. FZP encodes an ERF transcription factor and is the rice ortholog of the maize BD1 gene. Consistent with observations from phenotypic analyses, FZP expression was found to be restricted to the time of rudimentary glumes differentiation in a half-ring domain at the base of which the rudimentary glume primordium emerged.
URLPMID:20502443 [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
URLPMID:1673106 [本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
URLPMID:7433111 [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 3]
[本文引用: 3]
[本文引用: 3]
URLPMID:26743769 [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1093/jxb/erv464URLPMID:26512055 [本文引用: 1]

The plant hormones gibberellins (GA) and abscisic acid (ABA) play important roles in plant development and stress responses. Here we report a novel A20/AN1-type zinc finger protein ZFP185 involved in GA and ABA signaling in the regulation of growth and stress response. ZFP185 was constitutively expressed in various rice tissues. Overexpression of ZFP185 in rice results in a semi-dwarfism phenotype, reduced cell size, and the decrease of endogenous GA3 content. By contrast, higher GA3 content was observed in RNAi plants. The application of exogenous GA3 can fully rescue the semi-dwarfism phenotype of ZFP185 overexpressing plants, suggesting the negative role of ZFP185 in GA biosynthesis. Besides GA, overexpression of ZFP185 decreased ABA content and expression of several ABA biosynthesis-related genes. Moreover, it was found that ZFP185, unlike previously known A20/AN1-type zinc finger genes, increases sensitivity to drought, cold, and salt stresses, implying the negative role of ZFP185 in stress tolerance. ZFP185 was localized in the cytoplasm and lacked transcriptional activation potential. Our study suggests that ZFP185 regulates plant growth and stress responses by affecting GA and ABA biosynthesis in rice.
URLPMID:26283354 [本文引用: 1]
URLPMID:24498428 [本文引用: 1]
URLPMID:21777365 [本文引用: 1]
