 ), 衷敬红
), 衷敬红 武汉大学哲学学院心理学系, 武汉 430072
收稿日期:2018-03-02出版日期:2018-12-15发布日期:2018-10-30通讯作者:严瑜E-mail:yanyu@whu.edu.cn基金资助:*国家社科基金一般项目(18BGL119);教育部人文社科一般规划项目资助(17YJA190013)Workplace cyber incivility: The spillover and anti-spillover mechanisms between the reality and the virtual world
YAN Yu( ), ZHONG Jinghong
), ZHONG Jinghong Department of Psychology, School of Philosophy, Wuhan University, Wuhan 430072, China
Received:2018-03-02Online:2018-12-15Published:2018-10-30Contact:YAN Yu E-mail:yanyu@whu.edu.cn摘要/Abstract
摘要: 以往研究主要关注职场不文明行为的面对面形式, 发现了其在工作领域和家庭领域间的溢出和交叉效应。但近来研究指出, 职场不文明行为的虚拟形式有其特殊之处, 并具有更加恶劣的影响后果。在综述已有的网络不文明行为研究基础之上, 引入社会临场感的概念, 总结了职场不文明行为在现实工作领域和虚拟工作领域之间的溢出与反溢出机制; 并基于此提出多个研究展望, 建议未来研究以此为出发点, 考察职场网络不文明行为的不同演变模式。
图/表 2
表1网络不文明行为相关研究摘要
| 研究 | 前因变量 | 结果变量 | 中介/调节变量 | 主要发现 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lim & Chin, 2006 | 网络不文明行为 | 领导满意度、离职意图、组织承诺 | 调节: 领导性别 | 男性领导的网络不文明行为明显、直接; 女性领导则隐蔽、间接; 网络不文明行为与领导满意度负相关, 与离职意图正相关, 与组织承诺负相关 |
| 网络不文明行为 | 愤怒、挫折 | 中介: 互动不 公正 调节: 领导性别 | 明显的和隐蔽的网络不文明行为均会导致员工的愤怒和挫折情绪, 互动不公正中介这一过程, 领导性别调节受害者对网络不文明行为的应对方式 | |
| Lim & Teo, 2008 | 网络不文明行为 | 工作满意度 | 调节: 领导性别 | 网络不文明行为会降低员工对领导的满意度, 领导性别调节这一过程 |
| 发送者性别、相对地位、联系时间; 接收者年龄、消极情绪 | 对邮件的情绪 误判 | 调节: 社会背 景、消息内容 (情绪线索) | 工作邮件接收者更易将邮件内容中的情绪性信息误解为消极的, 以此造成不必要的冲突 | |
Teo, 2009 | 网络不文明行为 | 工作满意度、组织承诺、离职意图、职场偏离行为 | 网络不文明行为与员工的工作满意度和组织承诺负相关; 与离职意图和职场偏离行为正相关 | |
et al., 2012 | 网络不文明行为 | 倦怠、旷工、 离职意图 | 调节: 神经质 | 领导网络不文明行为与员工的倦怠、旷工和离职意图正相关, 神经质调节这一过程 |
et al., 2013 | 领导网络行为 (不文明/支持) | 情绪、工作投入度、工作绩效 | 中介: 精力水平 | 领导网络不文明行为与工作投入度、工作绩效负相关; 精力水平中介领导网络不文明行为与消极情绪之间的正相关关系 |
| - | - | - | 探讨了职场网络不文明行为的煽动者、消极后果、干预措施 | |
et al., 2015 | 网络不文明行为 | 工作绩效、工作环境氛围 | 对比了网络不文明行为、网络欺凌、网络骚扰三者之间的区别和概念重叠; 网络不文明行为会降低工作绩效, 污染工作环境 | |
et al., 2015 | 网络行为的文明度 | 规则违反行为 | 调节: 工作负荷 | 高工作负荷的员工更易被网络不文明行为激惹, 进而表现出不文明行为 |
et al., 2015 | 网络不文明行为 | 情绪痛苦、身体 痛苦 | 调节: 工作控制感、与工作的心理分离 | 网络不文明行为造成的情绪和身体痛苦具有延续效应, 工作控制感和与工作的心理分离可以缓冲网络不文明行为的消极效应 |
2016 | 外向性、情绪稳定性 | 网络不文明行为 | 调节: 责任心 | 网络不文明行为与外向性正相关, 与情绪稳定性负相关; 责任心负向调节外向性和情绪稳定性与网络不文明行为的关系 |
et al., 2016 | 网络不文明行为 | 工作绩效 | 中介: 工作满意 度 调节: 积极情绪 | 工作满意度中介网络不文明行为与工作绩效之间的负相关关系; 积极情绪调节网络不文明行为与工作绩效之间的负相关关系 |
| Kim & Carthy, 2016 | 感知的不文明行为的普遍性 | 职场人际关系、工作绩效 | 面对面不文明行为和网络不文明行为之间的潜在差异; 不文明行为对职场人际关系具有消极影响 | |
et al., 2017 | Study1: 网络欺凌、传统欺凌 Study2: 面对面欺凌、面对面不文明行为、网络欺凌、网络不文明行为 | Study1: 抑郁、社会焦虑、自尊 Study2: 旷工、离职、工作满意度、CWB | 调节: 行为的 来源 | 四种类型的职场不当行为均会产生与心理和工作相关的消极后果; 职场网络不文明行为具有更高的发生率, 但其消极效应小于网络欺凌。 |
表1网络不文明行为相关研究摘要
| 研究 | 前因变量 | 结果变量 | 中介/调节变量 | 主要发现 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lim & Chin, 2006 | 网络不文明行为 | 领导满意度、离职意图、组织承诺 | 调节: 领导性别 | 男性领导的网络不文明行为明显、直接; 女性领导则隐蔽、间接; 网络不文明行为与领导满意度负相关, 与离职意图正相关, 与组织承诺负相关 |
| 网络不文明行为 | 愤怒、挫折 | 中介: 互动不 公正 调节: 领导性别 | 明显的和隐蔽的网络不文明行为均会导致员工的愤怒和挫折情绪, 互动不公正中介这一过程, 领导性别调节受害者对网络不文明行为的应对方式 | |
| Lim & Teo, 2008 | 网络不文明行为 | 工作满意度 | 调节: 领导性别 | 网络不文明行为会降低员工对领导的满意度, 领导性别调节这一过程 |
| 发送者性别、相对地位、联系时间; 接收者年龄、消极情绪 | 对邮件的情绪 误判 | 调节: 社会背 景、消息内容 (情绪线索) | 工作邮件接收者更易将邮件内容中的情绪性信息误解为消极的, 以此造成不必要的冲突 | |
Teo, 2009 | 网络不文明行为 | 工作满意度、组织承诺、离职意图、职场偏离行为 | 网络不文明行为与员工的工作满意度和组织承诺负相关; 与离职意图和职场偏离行为正相关 | |
et al., 2012 | 网络不文明行为 | 倦怠、旷工、 离职意图 | 调节: 神经质 | 领导网络不文明行为与员工的倦怠、旷工和离职意图正相关, 神经质调节这一过程 |
et al., 2013 | 领导网络行为 (不文明/支持) | 情绪、工作投入度、工作绩效 | 中介: 精力水平 | 领导网络不文明行为与工作投入度、工作绩效负相关; 精力水平中介领导网络不文明行为与消极情绪之间的正相关关系 |
| - | - | - | 探讨了职场网络不文明行为的煽动者、消极后果、干预措施 | |
et al., 2015 | 网络不文明行为 | 工作绩效、工作环境氛围 | 对比了网络不文明行为、网络欺凌、网络骚扰三者之间的区别和概念重叠; 网络不文明行为会降低工作绩效, 污染工作环境 | |
et al., 2015 | 网络行为的文明度 | 规则违反行为 | 调节: 工作负荷 | 高工作负荷的员工更易被网络不文明行为激惹, 进而表现出不文明行为 |
et al., 2015 | 网络不文明行为 | 情绪痛苦、身体 痛苦 | 调节: 工作控制感、与工作的心理分离 | 网络不文明行为造成的情绪和身体痛苦具有延续效应, 工作控制感和与工作的心理分离可以缓冲网络不文明行为的消极效应 |
2016 | 外向性、情绪稳定性 | 网络不文明行为 | 调节: 责任心 | 网络不文明行为与外向性正相关, 与情绪稳定性负相关; 责任心负向调节外向性和情绪稳定性与网络不文明行为的关系 |
et al., 2016 | 网络不文明行为 | 工作绩效 | 中介: 工作满意 度 调节: 积极情绪 | 工作满意度中介网络不文明行为与工作绩效之间的负相关关系; 积极情绪调节网络不文明行为与工作绩效之间的负相关关系 |
| Kim & Carthy, 2016 | 感知的不文明行为的普遍性 | 职场人际关系、工作绩效 | 面对面不文明行为和网络不文明行为之间的潜在差异; 不文明行为对职场人际关系具有消极影响 | |
et al., 2017 | Study1: 网络欺凌、传统欺凌 Study2: 面对面欺凌、面对面不文明行为、网络欺凌、网络不文明行为 | Study1: 抑郁、社会焦虑、自尊 Study2: 旷工、离职、工作满意度、CWB | 调节: 行为的 来源 | 四种类型的职场不当行为均会产生与心理和工作相关的消极后果; 职场网络不文明行为具有更高的发生率, 但其消极效应小于网络欺凌。 |
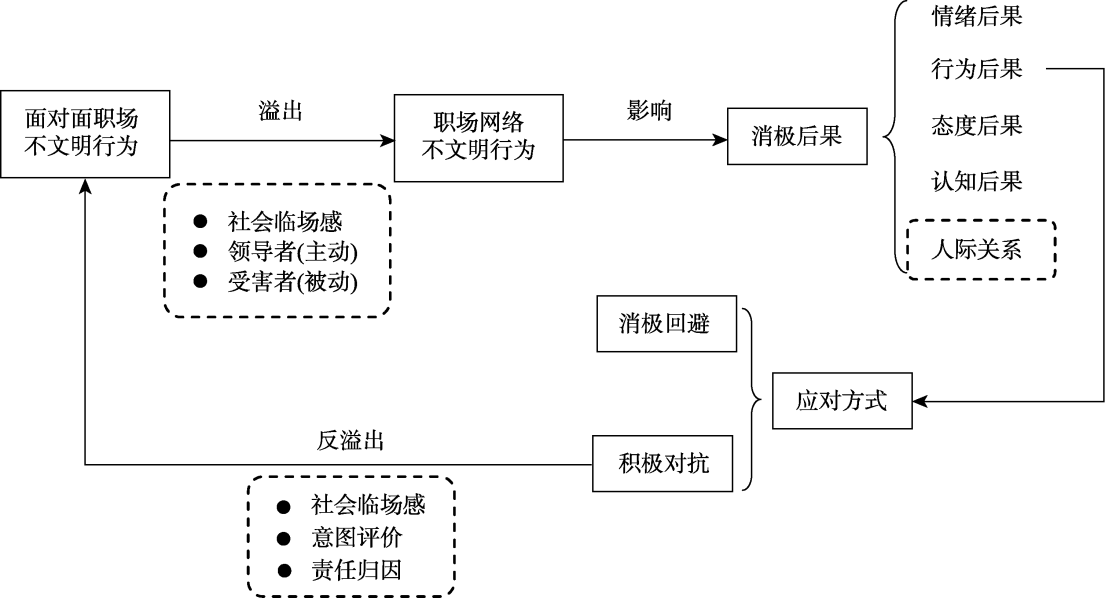
图1不文明行为在现实工作情境和虚拟工作情境之间的溢出与反溢出假设模型
 图1不文明行为在现实工作情境和虚拟工作情境之间的溢出与反溢出假设模型
图1不文明行为在现实工作情境和虚拟工作情境之间的溢出与反溢出假设模型参考文献 62
| 1 | 刘嫦娥 . ( 2012). 工作场所无礼行为研究. 北京: 中国物资出版社. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-884X.2012.07.024URL |
| 2 | 严瑜, 王轶鸣 . ( 2016). 工作场所无礼行为的溢出和交叉效应: 超越职场范围的负性作用机制. 心理科学进展,24( 12), 1934-1945. |
| 3 | 严瑜, 李佳丽 . ( 2017). 超越不文明: 从消极无礼的恶化升级到积极的文明干预. 心理科学进展, 25( 2), 319-330. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2017.00319URL |
| 4 | Anderson, L.M., &Pearson, C.M . ( 1999). Tit for tat? the spiraling effect of incivility in the workplace. Academy of Management Review, 24( 3), 452-471. doi: 10.2307/259136URL |
| 5 | Barber L. K., Taylor S. G., Burton J. P., & Bailey S. F . ( 2017). A self-regulatory perspective of work-to-home undermining spillover/crossover: Examining the roles of sleep and exercise. Journal of Applied Psychology, 102( 5), 753-763. doi: 10.1037/apl0000196URL |
| 6 | Byron, K. ( 2008). Carrying too heavy a load? The communication and miscommunication of emotion by email. The Academy of Management Review, 33( 2), 309-327. doi: 10.2307/20159399URL |
| 7 | Cortina L. M., & Magley V. J . ( 2009) Patterns and profiles of response to incivility in the workplace. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 14( 3), 272-288. doi: 10.1037/a0014934. doi: 10.1037/a0014934URLpmid: 19586222 |
| 8 | Cortina L. M., Magley V. J., Williams J. H., & Langhout R. D . ( 2001). Incivility in the workplace: Incidence and impact. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 6(1), 64-80. doi: 10.1037/1076-8998.6.1.64URLpmid: 11199258 |
| 9 | Cortina L. M., Kabat-Farr D., Magley V. J., & Nelson K . ( 2017). Researching rudeness: The past, present, and future of the science of incivility. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 22( 3), 299-313. |
| 10 | Dionisi, A.M., &Barling, J . ( 2015). Spillover and crossover of sex-based harassment from work to home: Supervisor gender harassment affects romantic relationship functioning via targets' anger. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 36( 2), 196-215. doi: 10.1002/job.1969URL |
| 11 | Dyer R., Green R., Pitts M. , & Millward, G.(1995). What's the flaming problem? or Computer Mediated Communication — deindividuating or disinhibiting? In M. A. R. Kirby, A. J. Dix, and J. E. Finlay (Eds.), Proceedings of the HCI'95 conference on People and computers X (HCI '95) (pp. 289-302). Cambridge University Press, New York, NY, USA. |
| 12 | Ferguson, M. ( 2012). You cannot leave it at the office: Spillover and crossover of coworker incivility. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 33( 4), 571-588. doi: 10.1002/job.774 |
| 13 | Flanagin, A., Pearce, K. E. & Bondad-Brown, B.A . ( 2008, May). The Destructive Potential of Electronic Communication Technologies in Organizations. Paper presented at the annual meeting of the International Communication Association, TBA, Montreal, Quebec, Canada Online. |
| 14 | Francis L., Holmvall C. M., & O’Brien L. E . ( 2015). The influence of workload and civility of treatment on the perpetration of email incivility. Computers in Human Behavior, 46, 191-201. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2014.12.044URL |
| 15 | Gallus J. A., Bunk J. A., Matthews R. A., Barnes-Farrell J. L., & Magley V. J . ( 2014). An eye for an eye? Exploring the relationship between workplace incivility experiences and perpetration. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology,19( 2), 143-154. doi: 10.1037/a0035931URLpmid: 24635736 |
| 16 | Giumetti G. W., Hatfield A. L., Scisco J. L., Schroeder A. N., Muth E. R., & Kowalski R. M . ( 2013). What a rude e-mail! examining the differential effects of incivility versus support on mood, energy, engagement, and performance in an online context. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 18( 3), 297-309. doi: 10.1037/a0032851URLpmid: 23834445 |
| 17 | Giumetti G. W., Mckibben E. S., Hatfield A. L., Schroeder A. N., & Kowalski R. M . ( 2012). Cyber incivility @work: The new age of interpersonal deviance. Cyberpsychology Behavior & Social Networking, 15( 3), 148-154. doi: 10.1089/cyber.2011.0336URLpmid: 22304404 |
| 18 | Giumetti G. W., Saunders L. A., Brunette J. P., Difrancesco F. M., & Graham P. G . ( 2016), Linking cyber incivility with job performance through job satisfaction: The buffering role of positive affect. Journal of Psychological Research, 21( 4), 230-240. |
| 19 | Heldal I., Roberts D., Bråthe L., & Wolff R . (E) ( 2007). Presence, Creativity and Collaborative Work in Virtual Environments. In Julie A. Jacko (Eds.), Proceedings of the 12th international conference on Human-computer interaction: Interaction design and usability (HCI'07)( PP 802-811). Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-73105-4_88URL |
| 20 | Hobfoll, S.E. ( 2001). Social support and stress. International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences, ( 5), 14461-14465. |
| 21 | Hershcovis M. S., Cameron A. F., Gervais L., & Bozeman J. ( 2018). The effects of confrontation and avoidance coping in response to workplace incivility. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 23(2), 163-174. |
| 22 | Hershcovis M. S., Ogunfowora B., Reich T. C., & Christie A. M . ( 2017). Targeted workplace incivility: The roles of belongingness, embarrassment, and power. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 38( 7), 1057-1075. doi: 10.1002/job.2183URL |
| 23 | Judge, T.A., &Ilies, R . ( 2004). Affect and job satisfaction: A study of their relationship at work and at home. Journal of Applied Psychology, 89( 4), 661-673. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.89.4.661URLpmid: 15327352 |
| 24 | Kato Y., Kato S., & Akahori K . ( 2007). Effects of emotional cues transmitted in e-mail communication on the emotions experienced by senders and receivers. Computers in Human Behavior,23( 4), 1894-1905. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2005.11.005URL |
| 25 | Keskin H., AkgÜn A. E., Ayar H., & Kayman Ş. S . ( 2016). Cyberbullying victimization, counterproductive work behaviours and emotional intelligence at workplace. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 235, 281-287. doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2016.11.031URL |
| 26 | Kowalski, R.M., &Limber, S.P . ( 2007). Electronic bullying among middle school students. Journal of Adolescent Health Official Publication of the Society for Adolescent Medicine, 41( 6), 22-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2007.08.017URLpmid: 18047942 |
| 27 | Kowalski R. M., Toth A., & Morgan M . ( 2017). Bullying and cyberbullying in adulthood and the workplace. Journal of Social Psychology, 158( 1), 64-81. doi: 10.1080/00224545.2017.1302402URLpmid: 28402201 |
| 28 | Krishnan, S. ( 2016). Electronic warfare: A personality model of cyber incivility. Computers in Human Behavior, 64, 537-546. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2016.07.031URL |
| 29 | Lai, C.Y., &Tsai, C.H . ( 2016). Cyberbullying in the social networking sites: An online disinhibition effect perspective. In Proceedings of the 3rd Multidisciplinary International Social Networks Conference on Social Informatics 2016, Data Science. |
| 30 | Lazarus, R.S., &Folkman, S . ( 1984). Stress, Appraisal and Coping . New York, NY: Springer. |
| 31 | Lim S., Cortina L. M., & Magley V. J . ( 2008). Personal and workgroup incivility: Impact on work and health outcomes. Journal of Applied Psychology,93( 1), 95-107. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.93.1.95URLpmid: 18211138 |
| 32 | Lim, V. K.G., &Chin, J.Y . ( 2006). Cyber incivility at the workplace: What has supervisor's sex got to do with it?. PACIS 2006-10th Pacific Asia Conference on Information Systems: ICT and Innovation Economy: 1247-1258. |
| 33 | Lim, S., &Lee, A . ( 2011). Work and nonwork outcomes of workplace incivility: Does family support help?. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 16( 1), 95-111. doi: 10.1037/a0021726URLpmid: 21280947 |
| 34 | Lim, V. K.G., &Teo, T. S.H . ( 2009). Mind your E-manners: Impact of cyber incivility on employees' work attitude and behavior. Information and Management, 46( 8), 419-425. doi: 10.1016/j.im.2009.06.006URL |
| 35 | Lim, Y.S., &Lee-Won, R.J . ( 2016). When retweets persuade: The persuasive effects of dialogic retweeting and the role of social presence in organizations’ twitter-based communication. Telematics and Informatics, 34( 5), 422-433. doi: 10.1016/j.tele.2016.09.003URL |
| 36 | McCarthy, K. ( 2014). e-Rudeness at Work: The Impact of Rude Email on Employee Performance (Unpublished master’s thesis). University of California, Irvine, Ann Arbor. |
| 37 | McCarthy, K.A. ( 2016). Is rudeness really that common? An exploratory study of incivility at work. Journal of Organizational Computing and Electronic Commerce, 26( 4), 364-374. DOI: 10.1080/10919392.2016.1228362 doi: 10.1080/10919392.2016.1228362URL |
| 38 | Meijman T. F. , & Mulder, G.(1998) . Psychological aspects of workload. In P. J. D. Drenth, H. Thierry, & C. J. de Wolff (Eds.), Handbook of work and organizational psychology (2nd ed.) (pp. 5-34). Hove, England: Psychology Press/Erlbaum (UK) Taylor & Francis. |
| 39 | Meier, L.L., &Gross, S . ( 2015). Episodes of incivility between subordinates and supervisors: Examining the role of self-control and time with an interaction-record diary study. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 36( 8), 1096-1113. doi: 10.1002/job.2013URL |
| 40 | Miner K. N., Diaz I., Wooderson R. L., Mcdonald J. N., Smittick A. L., & Lomeli L. C. ( 2017). A workplace incivility roadmap: Identifying theoretical speedbumps and alternative routes for future research. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 23(3), 320-337. |
| 41 | Ophoff J., Machaka T ., & Stander. A. (2015). Exploring the impact of cyber incivility in the workplace. Paper presented at Proceedings of Informing Science & IT Education Conference (InSITE) 2015, 493-504. |
| 42 | Park Y., Fritz C., & Jex S. M . ( 2015). Daily cyber incivility and distress: The moderating roles of resources at work and home. Journal of Management, 5, 2-46. |
| 43 | Patchin, J.W., &Hinduja, S . ( 2006). Bullies move beyond the schoolyard A preliminary look at cyberbullying. Youth Violence & Juvenile Justice,4( 2), 148-169. doi: 10.1177/1541204006286288URL |
| 44 | Pearson, C.M., &Porath, C.L . ( 2005). On the nature, consequences and remedies of workplace incivility: No time for "nice"? Think again. The Academy of Management Executive, 19( 1), 7-18. doi: 10.5465/AME.2005.15841946URL |
| 45 | Porath, C.L., &Pearson, C.M . ( 2010). The cost of bad behavior. Organizational Dynamics, 39( 1), 64-71. doi: 10.1016/j.orgdyn.2009.10.006URL |
| 46 | Porath, C.L., &Pearson, C.M . ( 2012). Emotional and behavioral responses to workplace incivility and the impact of hierarchical status. Journal of Applied Social Psychology, 42( 1), 326-357. doi: 10.1111/j.1559-1816.2012.01020.xURL |
| 47 | Reich, T.C., &Hershcovis, M.S . ( 2015). Observing workplace incivility. Journal of Applied Psychology, 100( 1), 203-215. doi: 10.1037/a0036464URLpmid: 24731181 |
| 48 | Rosen C. C., Koopman J., Gabriel A. S., & Johnson R. E . ( 2016). Who strikes back? A daily investigation of when and why incivility begets incivility. Journal of Applied Psychology, 101( 11), 1620-1634. doi: 10.1037/apl0000140URLpmid: 27504658 |
| 49 | Short J., Williams E., & Christie B . ( 1976). The social psychology of telecommunications. Contemporary Sociology, 7( 1), 175-188. |
| 50 | Shen, K.N., &Khalifa, M . ( 2008). Design for social presence in online communities: A multi-dimensional approach. Transactions on Human-Computer Interaction, 1( 2), 33-54. |
| 51 | Sipior, J,C., &Ward, BT. , (1999). The dark side of employee email. Communications of the ACM, 42( 7), 88-95. doi: 10.1145/306549.306591URL |
| 52 | Song, N. ( 2013). Cyber incivility in the workplace. HR Professional, 30( 2), 48-50. |
| 53 | Suler, J. ( 2010). The online disinhibition effect. International Journal of Applied Psychoanalytic Studies,2( 2), 184-188. |
| 54 | Schilpzand P., De Pater I. E., & Erez A . ( 2016). Workplace incivility: A review of the literature and agenda for future research. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 37( 1), 57-88. doi: 10.1002/job.1976URL |
| 55 | Shin Y., Lee B., & Kim J . ( 2015). Prosocial activists in sns: The impact of isomorphism and social presence on prosocial behaviors. International Journal of Human computer Interaction, 31( 12), 939-958. doi: 10.1080/10447318.2015.1085699URL |
| 56 | Toubiana, M., &Zietsma, C . ( 2017). The message is on the wall? Emotions, social media and the dynamics of institutional complexity. Academy of Management Journal, 60(3). |
| 57 | Vranjes I., Baillien E., Vandebosch H., Erreygers S., & Witte H. D . ( 2017). The dark side of working online: Towards a definition and an emotion reaction model of workplace cyberbullying. Computers in Human Behavior, 69, 324-334. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2016.12.055URL |
| 58 | Williams, K.J., &Alliger, G.M . ( 1994). Role stressors, mood spillover, and perceptions of work-family conflict in employed parents. Academy of Management Journal,37( 4), 837-868. doi: 10.2307/256602URL |
| 59 | Wright K. B., Abendschein B., Wombacher K., O'Connor M., Hoffman M., Dempsey M., … Shelton A .(2014). Work-related communication technology use outside of regular work hours and work life conflict. Management Communication Quarterly, 28( 4), 507-530. |
| 60 | Williams, K.S., & Loughlin C., (2015). Cyber incivility operationalized in the non-profit sector in Canada. Unpublished manuscript, Sobey School of Business, Saint Mary’s University, Halifax, NS. |
| 61 | Wu L. Z., Zhang H. N., Chiu R. K., Kwan H. K., & He X. G . ( 2014). Hostile attribution bias and negative reciprocity beliefs exacerbate incivility’s effects on interpersonal deviance. Journal of Business Ethics, 120( 2), 189-199. doi: 10.1007/s10551-013-1658-6URL |
| 62 | Yuin, C.J. ( 2006). Mind your e-manners: Impact of cyber incivility on justice, emotions and individual responses (Unpublished master’s thesis). National University of Singapore. |
相关文章 4
| [1] | 晋向东, 范秀成, 朱华伟, 袁靖波. 传统媒体上强势品牌广告竞争溢出效应的作用机制及分布规律[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(12): 1989-1999. |
| [2] | 谢莹, 李纯青, 高鹏, 刘艺. 直播营销中社会临场感对线上从众消费的影响及作用机理研究——行为与神经生理视角[J]. 心理科学进展, 2019, 27(6): 990-1004. |
| [3] | 严瑜;王轶鸣. 工作场所无礼行为的溢出和交叉效应:超越职场范围的负性作用机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2016, 24(12): 1934-1945. |
| [4] | 李爱梅;华涛;高文. 辱虐管理研究的“特征-过程-结果”理论框架[J]. 心理科学进展, 2013, 21(11): 1901-1912. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlkxjz/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=4524
