 )
) 江西师范大学心理学院, 南昌 330022
收稿日期:2017-11-27出版日期:2018-10-15发布日期:2018-08-27通讯作者:胡竹菁E-mail:huzjing@jxnu.edu.cn基金资助:*国家自然科学基金项目(31460252)The cooperation and transformation mechanism of dual processing in reasoning and judgment
AI Yan, HU Zhujing( )
) School of Psychology, Jiangxi Normal University, Nanchang 330022, China
Received:2017-11-27Online:2018-10-15Published:2018-08-27Contact:HU Zhujing E-mail:huzjing@jxnu.edu.cn摘要/Abstract
摘要: 推理判断中双重加工理论的发展经历了不同发展阶段, 早期主要对两个加工过程的定义及特征的关注, 当前转向对两者间的协作及转换机制的研究。本研究梳理了双重加工过程协作及转换机制的代表性模型及其相关实验支持证据, 综合归纳为以下三类模型:序列加工模型(Serial processing model)、平行竞争模型(Parallel competitive model)以及混合模型(Hybrid model), 并比较和论述了三类模型在两个加工过程的转换和协作机制、冲突探查的加工机制、偏差反应的解释机制上的异同, 以及三类模型各自面临的问题。
图/表 8
表1不同双重加工理论者的双重加工过程命名及特征
| 双重加工理论提出者 | T1 | T2 |
|---|---|---|
| Posner & | 自动激活系统(automatic activation system) | 意识加工系统(conscious processing system) |
| Shiffrin & | 自动加工过程(automatic processing) | 控制加工过程(controlled processing) |
| Johnson-Laird (1983) | 内隐推理(implicit inferences) | 外显推理(explicit inferences) |
| Evans (1984, 1989) | 启发式过程(heuristic processing) | 分析式过程(analytic processing) |
| Pollock (1991) | 快速和灵活模块(quick and inflexible modules) | 智力(intellection) |
| Reber (1993) | 内隐认知 (implicit cognition) | 外显学习(explicit learning) |
| Epstein (1973, 1994) | 经验系统(experiential system) | 理性系统(rational system) |
| Levinson (1995) | 交互智力(interactional intelligence) | 分析智力(analytic intelligence) |
| Sloman (1996) | 联想系统(associative system) | 规则系统(rule-based system) |
| Evans & Over (1996) | 内隐思维过程(tacit thought processes) | 外显思维过程(explicit thought processes) |
| Hammond (1996) | 直觉认知(intuitive cognition) | 分析认知(analytical cognition) |
| Klein (1998) | 预先认知决策(recognition-primed decisions) | 理性选择策略(rational choice strategy) |
| Stanovich & West (2000) | 系统1 (System 1) | 系统2 (System 2) |
| 自动启发式加工(Automatic-heuristic processing) | 执行分析式加工(executive-analytic processing) | |
| Evans (2011) | 直觉加工(Intuitive processing) | 反思性加工(Reflective processing) |
| 特征 | 联想的(associative) | 以规则为基础的(rule-based) |
| 整体性(holistic) | 分析性(analytic) | |
| 自动的(automatic) | 控制性的(controlled) | |
| 不需要认知能力(relatively undemanding of cognitive capacity) | 需要认知能力(demanding of cognitive capacity) | |
| 快速的(relatively fast) | 缓慢的(relatively slow) | |
| 通过生理、暴露和个体经验获得(acquisition by biology, exposure, and personal experience) | 通过文化和形式指导获得(acquisition by cultural and formal tuition) |
表1不同双重加工理论者的双重加工过程命名及特征
| 双重加工理论提出者 | T1 | T2 |
|---|---|---|
| Posner & | 自动激活系统(automatic activation system) | 意识加工系统(conscious processing system) |
| Shiffrin & | 自动加工过程(automatic processing) | 控制加工过程(controlled processing) |
| Johnson-Laird (1983) | 内隐推理(implicit inferences) | 外显推理(explicit inferences) |
| Evans (1984, 1989) | 启发式过程(heuristic processing) | 分析式过程(analytic processing) |
| Pollock (1991) | 快速和灵活模块(quick and inflexible modules) | 智力(intellection) |
| Reber (1993) | 内隐认知 (implicit cognition) | 外显学习(explicit learning) |
| Epstein (1973, 1994) | 经验系统(experiential system) | 理性系统(rational system) |
| Levinson (1995) | 交互智力(interactional intelligence) | 分析智力(analytic intelligence) |
| Sloman (1996) | 联想系统(associative system) | 规则系统(rule-based system) |
| Evans & Over (1996) | 内隐思维过程(tacit thought processes) | 外显思维过程(explicit thought processes) |
| Hammond (1996) | 直觉认知(intuitive cognition) | 分析认知(analytical cognition) |
| Klein (1998) | 预先认知决策(recognition-primed decisions) | 理性选择策略(rational choice strategy) |
| Stanovich & West (2000) | 系统1 (System 1) | 系统2 (System 2) |
| 自动启发式加工(Automatic-heuristic processing) | 执行分析式加工(executive-analytic processing) | |
| Evans (2011) | 直觉加工(Intuitive processing) | 反思性加工(Reflective processing) |
| 特征 | 联想的(associative) | 以规则为基础的(rule-based) |
| 整体性(holistic) | 分析性(analytic) | |
| 自动的(automatic) | 控制性的(controlled) | |
| 不需要认知能力(relatively undemanding of cognitive capacity) | 需要认知能力(demanding of cognitive capacity) | |
| 快速的(relatively fast) | 缓慢的(relatively slow) | |
| 通过生理、暴露和个体经验获得(acquisition by biology, exposure, and personal experience) | 通过文化和形式指导获得(acquisition by cultural and formal tuition) |

图1默认干预模型注:A1为直觉加工的初始反应, A2为反思性加工的替代性反应。资料来源:Evans (2011)
 图1默认干预模型注:A1为直觉加工的初始反应, A2为反思性加工的替代性反应。资料来源:Evans (2011)
图1默认干预模型注:A1为直觉加工的初始反应, A2为反思性加工的替代性反应。资料来源:Evans (2011)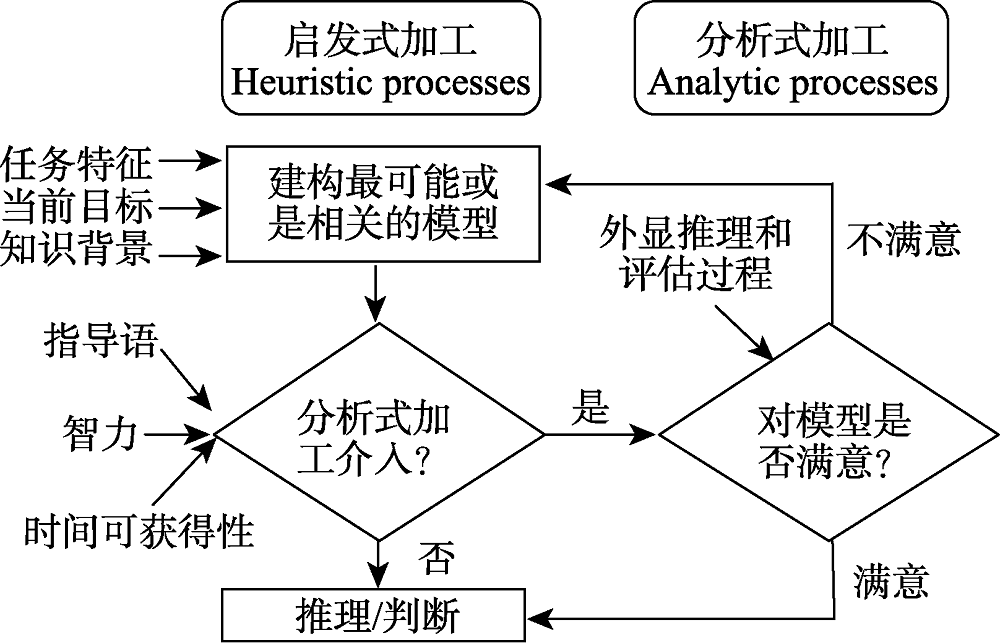
图2启发式与分析式理论的扩展与校正资料来源:Evans (2006)
 图2启发式与分析式理论的扩展与校正资料来源:Evans (2006)
图2启发式与分析式理论的扩展与校正资料来源:Evans (2006)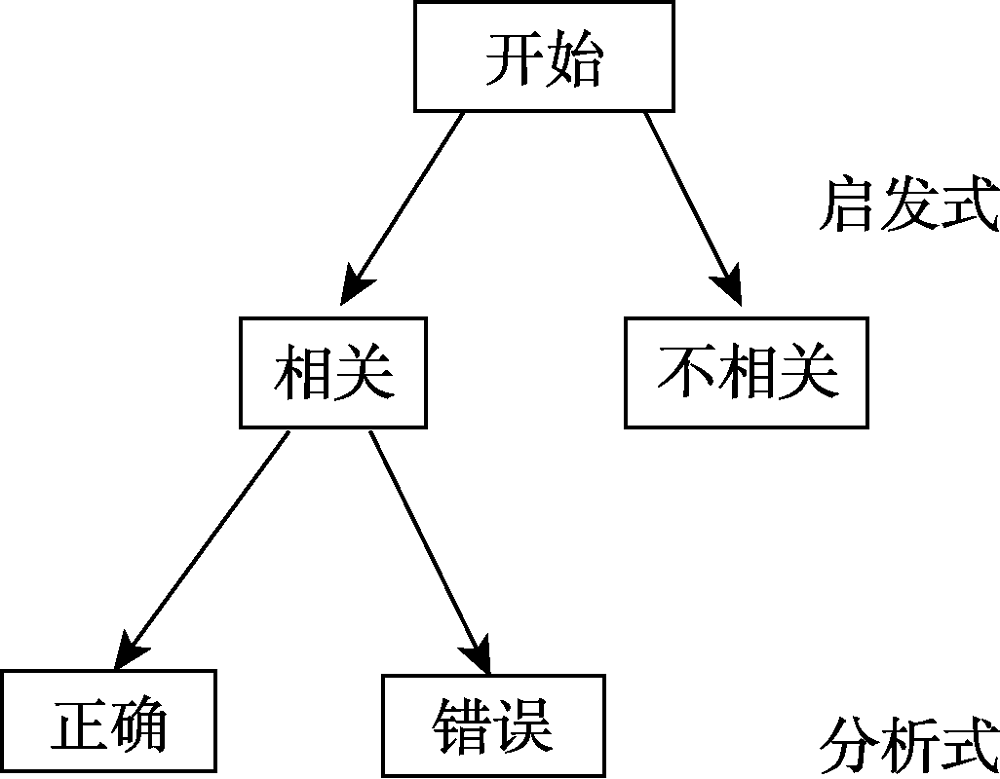
图3认知加工的两阶段模型资料来源:Evans (1984)
 图3认知加工的两阶段模型资料来源:Evans (1984)
图3认知加工的两阶段模型资料来源:Evans (1984)
图4平行竞争模型资料来源:Handley和Trippas (2015)
 图4平行竞争模型资料来源:Handley和Trippas (2015)
图4平行竞争模型资料来源:Handley和Trippas (2015)
图5逻辑直觉模型资料来源:De Neys (2012)
 图5逻辑直觉模型资料来源:De Neys (2012)
图5逻辑直觉模型资料来源:De Neys (2012)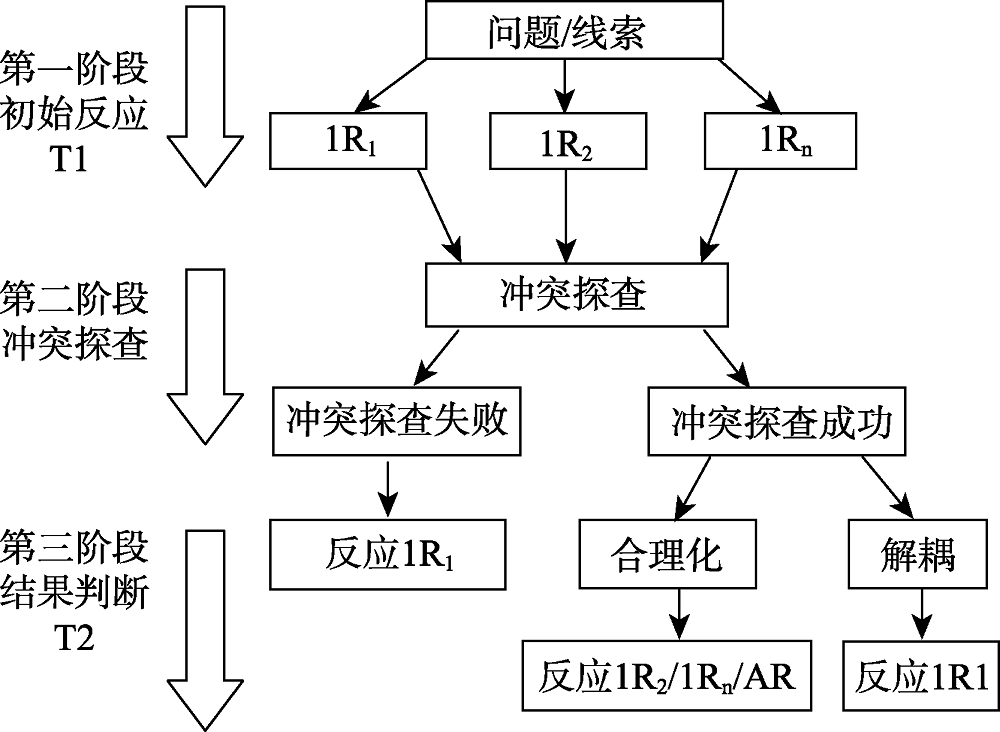
图6分析式参与的三阶段双重加工模型注:1R, T1 的初始反应; 1R1最突出和流畅的直觉反应, 例如信念偏差反应; 1Rn初始阶段可能的、潜在的竞争反应; AR替代性反应。资料来源:Pennycook et al. (2015)
 图6分析式参与的三阶段双重加工模型注:1R, T1 的初始反应; 1R1最突出和流畅的直觉反应, 例如信念偏差反应; 1Rn初始阶段可能的、潜在的竞争反应; AR替代性反应。资料来源:Pennycook et al. (2015)
图6分析式参与的三阶段双重加工模型注:1R, T1 的初始反应; 1R1最突出和流畅的直觉反应, 例如信念偏差反应; 1Rn初始阶段可能的、潜在的竞争反应; AR替代性反应。资料来源:Pennycook et al. (2015)
图7序列加工、平行竞争以及混合模型的时间进程注:序列加工模型与平行竞争模型的时间进程参考资料为De Neys (2012)
 图7序列加工、平行竞争以及混合模型的时间进程注:序列加工模型与平行竞争模型的时间进程参考资料为De Neys (2012)
图7序列加工、平行竞争以及混合模型的时间进程注:序列加工模型与平行竞争模型的时间进程参考资料为De Neys (2012)参考文献 85
| 1 | 胡竹菁, 胡笑羽 . ( 2012). Evans双重加工理论的发展过程简要述评. 心理学探新, 32( 4), 310-316. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5184.2012.04.004URL |
| 2 | 姚志强, 李亚非 . ( 2016). 逻辑-信念冲突与推理难度对逻辑和信念判断的影响. 心理科学, 39( 1), 36-42. |
| 3 | Banks A. P., & Hope, C. ( 2014). Heuristic and analytic processes in reasoning: An event-related potential study of belief bias. Psychophysiology, 51( 3), 290-297. doi: 10.1111/psyp.12169URLpmid: 25003167 |
| 4 | Barbey A. K., & Sloman, S. A . ( 2007). Base-rate respect: From ecological rationality to dual processes. Behavioural and Brain Sciences, 30( 3), 241-254. |
| 5 | Barr N., Pennycook G., Stolz J. A., & Fugelsang J. A . ( 2015). Reasoned connections: A dual-process perspective on creative thought. Thinking & Reasoning, 21( 1), 61-75. doi: 10.1080/13546783.2014.895915URL |
| 6 | Barrouillet P., ( 2011). Dual-process theories and cognitive development: Advances and challenges. Developmental Review, 31( 2-3), 79-85. doi: 10.1016/j.dr.2011.07.002URL |
| 7 | Beevers, C. G . ( 2005). Cognitive vulnerability to depression: A dual process model. Clinical Psychology Review, 25( 7), 975-1002. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2005.03.003URL |
| 8 | Bhatia S., ( 2017). Conflict and bias in heuristic judgment. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 43( 2), 319-325. doi: 10.1037/xlm0000307URLpmid: 27685023 |
| 9 | Chaiken S. , & Trope, Y.( 1999) . Dual-process theories in social psychology. New York: Guilford Press. |
| 10 | De Neys W. , ( 2006). Automatic-heuristic and executive- analytic processing during reasoning: Chronometric and dual-task considerations. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 59( 6), 1070-1100. doi: 10.1080/02724980543000123URL |
| 11 | De Neys W. , ( 2012). Bias and conflict: A case for logical intuitions. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 7( 1), 28-38. doi: 10.1177/1745691611429354URL |
| 12 | De Neys W. , ( 2014). Conflict detection, dual processes, and logical intuitions: Some clarifications. Thinking & Reasoning, 20( 2), 169-187. |
| 13 | De Neys W., Cromheeke S., & Osman M . ( 2011). Biased but in doubt: Conflict and decision confidence. PLoS One, 6( 1), e15954. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015954URLpmid: 21283574 |
| 14 | De Neys W., , & Glumicic, T. ( 2008). Conflict monitoring in dual process theories of thinking. Cognition, 106( 3), 1248-1299. doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2007.06.002URLpmid: 17631876 |
| 15 | De Neys W., Rossi S., & Houdé O . ( 2013). Bats, balls, and substitution sensitivity: Cognitive misers are no happy fools. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 20( 2), 269-273. doi: 10.3758/s13423-013-0384-5URLpmid: 23417270 |
| 16 | De Neys W., Vartanian O., & Goel V . ( 2008). Smarter than we think: When our brains detect that we are biased. Psychological Science, 19( 5), 483-489. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9280.2008.02113.xURL |
| 17 | Epstein S., ( 1973). The self-concept revisited or a theory of a theory . American Psychologist 28( 5), 404-416. doi: 10.1037/h0034679URLpmid: 4703058 |
| 18 | Epstein S., ( 1994). Integration of the cognitive and the psychodynamic unconscious. American Psychologist, 49( 8), 709-724. doi: 10.1037/0003-066X.49.8.709URL |
| 19 | Evans, J. St. B. T . ( 1984). Heuristic and analytic processes in reasoning. British Journal of Psychology, 75( 4), 451-468. doi: 10.1111/j.2044-8295.1984.tb01915.xURL |
| 20 | Evans, J. St. B. T . ( 1989). Bias in human reasoning: Causes and consequences. Lawrence Erlbaum. |
| 21 | Evans, J. St. B. T . ( 2003). In two minds: Dual-process accounts of reasoning. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 7( 10), 454-459. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2003.08.012URLpmid: 14550493 |
| 22 | Evans, J. St. B. T . ( 2006). The heuristic-analytic theory of reasoning: Extension and evaluation. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 13( 3), 378-395. doi: 10.3758/BF03193858URLpmid: 17048720 |
| 23 | Evans, J. St. B. T . ( 2007). On the resolution of conflict in dual process theories of reasoning. Thinking & Reasoning, 13( 4), 321-339. doi: 10.1080/13546780601008825URL |
| 24 | Evans, J. St. B. T . ( 2008). Dual-processing accounts of reasoning, judgment, and social cognition. Annual Review of Psychology, 59, 255-278. doi: 10.1146/annurev.psych.59.103006.093629URLpmid: 18154502 |
| 25 | Evans, J. St B. T.. ( 2009) . How many dual-process theories do we need? One, two, or many? In J. St. B. T. Evans & K. Frankish (Eds.), In two minds: Dual processes and beyond (pp. 33-54). Oxford: Oxford University Press. doi: 10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199230167.003.0002URL |
| 26 | Evans, J. St. B. T . ( 2010). Intuition and reasoning: A dual- process perspective. Psychological Inquiry, 21( 4), 313-326. doi: 10.1080/1047840X.2010.521057URL |
| 27 | Evans, J. St. B. T . ( 2011). Dual-process theories of reasoning: Contemporary issues and developmental applications. Developmental Review, 31( 2-3), 86-102. doi: 10.1016/j.dr.2011.07.007URL |
| 28 | Evans J. St. B. T., & Curtis-Holmes, J. ( 2005). Rapid responding increases belief bias: Evidence for the dual- process theory of reasoning. Thinking & Reasoning, 11( 4), 382-389. doi: 10.1080/13546780542000005URL |
| 29 | Evans, J. St. B. T ., & Over, D. E.( 1996). Rationality and reasoning. Hove, England: Psychology Press. |
| 30 | Evans J. St. B. T., Venn S., & Feeney A . ( 2002). Implicit and explicit processes in a hypothesis testing task. British Journal of Psychology, 93, 31-46. doi: 10.1348/000712602162436URLpmid: 11839100 |
| 31 | Evans J. St. B. T., & Stanovich, K. E . ( 2013 a). Dual-process theories of higher cognition. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 8( 3), 223-241. doi: 10.1177/1745691612460685URL |
| 32 | Evans J. St. B. T., & Stanovich, K. E . ( 2013 b). Theory and metatheory in the study of dual processing: Reply to comments. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 8( 3), 263-271. doi: 10.1177/1745691613483774URL |
| 33 | Franssens S., & De Neys, W. (2009). The effortless nature of conflict detection during thinking. Thinking & Reasoning, 15( 2), 105-128. doi: 10.1080/13546780802711185URL |
| 34 | Frey D., Johnson E. D., & De Neys W . ( 2018). Individual differences in conflict detection during reasoning. The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 71( 5), 1188-1208. doi: 10.1080/17470218.2017.1313283URL |
| 35 | Gigerenzer G., & Regier, T. ( 1996). How do we tell an association from a rule? Comment on Sloman (1996). Psychological Bulletin, 119( 1), 23-26. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.119.1.23URL |
| 36 | Goel V., ( 2007). Anatomy of deductive reasoning. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 11( 10), 435-441. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2007.09.003URL |
| 37 | Goel V., & Dolan, R. J . ( 2003). Explaining modulation of reasoning by belief. Cognition, 87( 1), B11-B22. doi: 10.1016/S0010-0277(02)00185-3URLpmid: 12499108 |
| 38 | Gubbins E., & Byrne, R. M. J . ( 2014). Dual processes of emotion and reason in judgments about moral dilemmas. Thinking & Reasoning, 20( 2), 245-268. doi: 10.1080/13546783.2013.877400URL |
| 39 | Hammond K. R. (1996). Human judgment and social policy. Oxford University Press.. |
| 40 | Handley S. J., Newstead S. E., & Trippas D . ( 2011). Logic, beliefs, and instruction: A test of the default interventionist account of belief bias. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 37( 1), 28-43. doi: 10.1037/a0021098URLpmid: 21058879 |
| 41 | Handley S. J., & Trippas, D. ( 2015). Dual processes and the interplay between knowledge and structure: A new parallel processing model. Psychology of Learning and Motivation, 62, 33-58. doi: 10.1016/bs.plm.2014.09.002URL |
| 42 | Johnson E. D., Tubau E., & De Neys W . (2016). The doubting system 1: Evidence for automatic substitution sensitivity. Acta Psychogica, 164, 56-64. doi: 10.1016/j.actpsy.2015.12.008URLpmid: 26722837 |
| 43 | Johnson-Laird, P. N.( 1983). Mental models: Towards a cognitive science of language, inference and consciousness. Harvard University Press. |
| 44 | Kahneman D., ( 2011). Thinking, fast and slow. New York: Farrar, Straus and Giroux. |
| 45 | Kahneman D. , & Frederick, S.( 2005) . A model of heuristic judgment. In K. J. Holyoak & R. G. Morrison (Eds.), The Cambridge handbook of thinking and reasoning (pp. 267-293). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. |
| 46 | Keren G., ( 2013). A tale of two systems: A scientific advance or a theoretical stone soup? Commentary on evans stanovich. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 8( 3), 257-262. doi: 10.1177/1745691613483474URL |
| 47 | Keren G., & Schul, Y. ( 2009). Two is not always better than one: A critical evaluation of two-system theories. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 4( 6), 533-550. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-6924.2009.01164.xURL |
| 48 | Klein G., ( 1998). Sources of power: How people make decisions. MIT Press. |
| 49 | Klein G., ( 2015). A naturalistic decision making perspective on studying intuitive decision making. Journal of Applied Research in Memory and Cognition, 4( 3), 164-168. doi: 10.1016/j.jarmac.2015.07.001URL |
| 50 | Kokis J. V., Macpherson R., Toplak M. E., West R. F., & Stanovich K. E . ( 2002). Heuristic and analytic processing: Age trends and associations with cognitive ability and cognitive styles. Joural of Experimental Child Psychology, 83( 1), 26-52. doi: 10.1016/S0022-0965(02)00121-2URL |
| 51 | Kruglanski, A. W . ( 2013). Only one? The default interventionist perspective as a unimodel—Commentary on Evans & Stanovich (2013). Perspectives on Psychological Science, 8( 3), 242-247. doi: 10.1177/1745691613483477URL |
| 52 | Kruglanski A. W., & Gigerenzer, G. ( 2011). Intuitive and deliberate judgments are based on common principles. Psychological Review, 118( 1), 97-109. doi: 10.1037/a0020762URL |
| 53 | Levinson S. C. ( 1995). Interactional biases in human thinking. In E. Goody (Ed. ), Social intelligence and interaction (pp. 221-260). Cambridge University Press. doi: 10.1017/CBO9780511621710.014URL |
| 54 | Liang P. P., Goel V., Jia X. Q., & Li K. C . ( 2014). Different neural systems contribute to semantic bias and conflict detection in the inclusion fallacy task. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 8, 797. |
| 55 | Lieberman, M. D . ( 2007). Social cognitive neuroscience: A review of core processes. Annual Review of Psychology, 58, 259-289. doi: 10.1146/annurev.psych.58.110405.085654URL |
| 56 | Markovits H., Brisson J ., & de Chantal, P. L.( 2015). Additional evidence for a dual-strategy model of reasoning: Probabilistic reasoning is more invariant than reasoning about logical validity. Memory & Cognition, 43( 8), 1208-1215. |
| 57 | Markovits H., Brisson J., de Chantal P. L., & Thompson V. A . ( 2017). Interactions between inferential strategies and belief bias. Memory & Cognition, 45( 7), 1182-1192. doi: 10.3758/s13421-017-0723-2URLpmid: 28608194 |
| 58 | Markovits H., Brunet M.-L., Thompson V., & Brisson J . ( 2013). Direct evidence for a dual process model of deductive inference. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 39( 4), 1213-1222. doi: 10.1037/a0030906URLpmid: 23206167 |
| 59 | Markovits H., Forgues H. L., & Brunet M. L . ( 2012). More evidence for a dual-process model of conditional reasoning. Memory & Cognition, 40( 5), 736-747. doi: 10.3758/s13421-012-0186-4URLpmid: 22287219 |
| 60 | Osman M., ( 2004). An evaluation of dual-process theories of reasoning. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 11( 6), 988-1010. doi: 10.3758/BF03196730URLpmid: 15875969 |
| 61 | Osman M., ( 2013). A case study: Dual-process theories of higher cognition—Commentary on Evans & Stanovich (2013). Perspectives on Psychological Science, 8( 3), 248-252. doi: 10.1177/1745691613483475URL |
| 62 | Pennycook G., ( 2017). A perspective on the theoretical foundation of dual-process models. In W. De Neys (Ed.), Dual process theory 2.0 . New York, NY: Psychology Press. |
| 63 | Pennycook G., Cheyne J. A., Barr N., Koehler D. J., & Fugelsang J. A . ( 2014). Cognitive style and religiosity: The role of conflict detection. Memory and Cognition, 42( 1), 1-10. doi: 10.3758/s13421-013-0340-7URLpmid: 23784742 |
| 64 | Pennycook G., Cheyne J. A., Seli P., Koehler D. J., & Fugelsang J. A . ( 2012). Analytic cognitive style predicts religious and paranormal belief. Cognition, 123( 3), 335-346. doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2012.03.003URLpmid: 22481051 |
| 65 | Pennycook G., Fugelsang J. A., & Koehler D. J . ( 2012). Are we good at detecting conflict during reasoning? Cognition, 124( 1), 101-106. doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2012.04.004URLpmid: 22575046 |
| 66 | Pennycook G., Fugelsang J. A., & Koehler D. J . ( 2015). What makes us think? A three-stage dual-process model of analytic engagement. Cognitive Psychology, 80, 34-72. doi: 10.1016/j.cogpsych.2015.05.001URLpmid: 26091582 |
| 67 | Pennycook G., & Thompson, V. A . ( 2012). Reasoning with base rates is routine, relatively effortless, and context dependent. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 19( 3), 528-534. doi: 10.3758/s13423-012-0249-3URLpmid: 22427266 |
| 68 | Pennycook G., Trippas D., Handley S. J., & Thompson V. A . ( 2014). Base rates: Both neglected and intuitive. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 40( 2), 544-554. doi: 10.1037/a0034887URLpmid: 24219086 |
| 69 | Pollock J. L. ( 1991). OSCAR: A general theory of rationality. In R. Cummins & J. L. Pollock (Eds.), Philosophy and AI: Essays at the interface (pp. 189-213). Cambridge, MA, US: The MIT Press. doi: 10.1080/09528138908953702URL |
| 70 | Posner, M. I. & Snyder, C. R. R . ( 1975). Attention and cognitive control. In Robert L. Solso (Ed.),Information Processing and Cognition: The Loyola Symposium. Lawrence Erlbaum. |
| 71 | Prado J., Kaliuzhna M., Cheylus A., & Noveck I. A . ( 2008). Overcoming perceptual features in logical reasoning: An event-related potentials study. Neuropsychologia, 46( 11), 2629-2637. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2008.04.017URLpmid: 18541277 |
| 72 | Pyszczynski T., Greenberg J., & Solomon S . ( 1999). A dual-process model of defense against conscious and unconscious death-related thoughts: An extension of terror management theory. Psychological Review, 106( 4), 835-845. doi: 10.1037/0033-295X.106.4.835URL |
| 73 | Scherer L. D., Yates J. F., Baker S. G., & Valentine K. D . ( 2017). The influence of effortful thought and cognitive proficiencies on the conjunction fallacy: Implications for dual-process theories of reasoning and judgment. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 43( 6), 874-887. doi: 10.1177/0146167217700607URL |
| 74 | Shiffrin, R. M. & Schneider W. , (1977). Controlled and automatic human information processing: II. Perceptual learning, automatic attending, and a general theory. Psychological Review 84( 2), 127-90. |
| 75 | Sloman, S. A . ( 1996). The empirical case for two systems of reasoning. Psychological Bulletin, 119( 1), 3-22. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.119.1.3URL |
| 76 | Sloman, S. A . ( 2014). Two systems of reasoning: An update. In J. W. Sherman, B. Gawronski, & Y. Trope (Eds.),Dual-process theories of the social mind (pp. 69-79). New York: Guilford Press |
| 77 | Stanovich K. E., & West, R. F . ( 2000). Individual differences in reasoning: Implications for the rationality debate?. Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 23( 5), 645-665. doi: 10.1017/S0140525X00003435URL |
| 78 | Stollstorff M., Vartanian O., & Goel V . ( 2012). Levels of conflict in reasoning modulate right lateral prefrontal cortex. Brain Research, 1428, 24-32. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2011.05.045URLpmid: 21684531 |
| 79 | Stupple E. J. N., & Ball, L. J . ( 2008). Belief-logic conflict resolution in syllogistic reasoning: Inspection-time evidence for a parallel-process model. Thinking & Reasoning, 14( 2), 168-181. |
| 80 | Toplak M. E., West R. F., & Stanovich K. E . ( 2014). Assessing miserly information processing: An expansion of the Cognitive Reflection Test. Thinking & Reasoning, 20( 2), 147-168. doi: 10.1080/13546783.2013.844729URL |
| 81 | Trippas D., Handley S. J., Verde M. F., & Morsanyi K . ( 2016). Logic brightens my day: Evidence for implicit sensitivity to logical validity. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 42( 9), 1448-1457. doi: 10.1037/xlm0000248URLpmid: 26889685 |
| 82 | Trippas D., Thompson V. A., & Handley S. J . ( 2017). When fast logic meets slow belief: Evidence for a parallel- processing model of belief bias. Memory & Cognition, 45( 4), 539-552. doi: 10.3758/s13421-016-0680-1URLpmid: 28028779 |
| 83 | Thompson V. A., & Johnson, S. C . ( 2014). Conflict, metacognition, and analytic thinking. Thinking & Reasoning, 20( 2), 215-244. doi: 10.1080/13546783.2013.869763URL |
| 84 | Thompson V. A., & Morsany, K. ( 2012). Analytic thinking: Do you feel like it? Mind & Society, 11( 1), 93-105. doi: 10.1007/s11299-012-0100-6URL |
| 85 | Thompson V. A., Turner J. A. P., Pennycook G., Ball L. J., Brack H., Ophir Y., & Ackerman R . ( 2013). The role of answer fluency and perceptual fluency as metacognitive cues for initiating analytic thinking. Cognition, 128( 2), 237-251. doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2012.09.012URL |
相关文章 7
| [1] | 林文毅, 张静, 李广政. 文本−信念一致效应及其消除[J]. 心理科学进展, 2018, 26(5): 789-795. |
| [2] | 闫丁;汪婷;王程瑶;焦璨. 饮酒对反应抑制的影响及其神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2017, 25(4): 586-598. |
| [3] | 雷鸣;戴艳;肖宵;曾灿;张庆林. 心理复原的机制:来自特质性复原力个体的证据[J]. 心理科学进展, 2011, 19(6): 874-882. |
| [4] | 胥遥山;李永娟. 酒精影响个体社会行为的机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2011, 19(4): 565-572. |
| [5] | 高华;彭新波. 抑郁认知易感性的新解释——双重加工模型 [J]. 心理科学进展, 2009, 17(1): 132-137. |
| [6] | 张阳阳;佐斌. 自尊的恐惧管理理论研究述评[J]. 心理科学进展, 2006, 14(2): 273-. |
| [7] | 杨家忠;黄希庭. 印象形成的理论模型述评[J]. 心理科学进展, 1998, 6(1): 9-14. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlkxjz/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=4477
