 ,1,2
,1,2MEK inhibitor PD0325901 significantly boosts ssODN-mediated HDR efficiency in porcine fetal fibroblasts
Hao Ou1, Guoling Li1, Haoqiang Wang1, Guangyan Huang1, Gengyuan Cai1,2, Zicong Li1, Zhenfang Wu1,2, Xianwei Zhang ,1,2
,1,2通讯作者:
第一联系人:
编委: 任军
收稿日期:2018-10-29修回日期:2019-03-2网络出版日期:2019-04-20
| 基金资助: |
Received:2018-10-29Revised:2019-03-2Online:2019-04-20
| Fund supported: |
作者简介 About authors
欧浩,硕士,专业方向:动物遗传育种E-mail:
李国玲,博士,研究方向:基因编辑与遗传育种E-mail:

摘要
关键词:
Abstract
Keywords:
PDF (852KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
本文引用格式
欧浩, 李国玲, 王豪强, 黄广燕, 蔡更元, 李紫聪, 吴珍芳, 张献伟. MEK抑制剂PD0325901显著提高猪胎儿成纤维细胞ssODN介导的HDR效率[J]. 遗传, 2019, 41(4): 327-336 doi:10.16288/j.yczz.18-294
Hao Ou, Guoling Li, Haoqiang Wang, Guangyan Huang, Gengyuan Cai, Zicong Li, Zhenfang Wu, Xianwei Zhang.
传统转基因技术是将目的基因随机整合到基因组中并使之表达,无法控制转基因的整合位点,且伴随着效率低、表达稳定性差等问题,为转基因动物品系和育种品系的建立带来诸多不便。随着锌指核酸内切酶(zinc-finger endonuclease, ZFN)[1]、类转录激活因子效应物核酸酶(transcription activator-like effector nuclease, TALEN)[2]、规律成簇的间隔短回文重复(clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats, CRISPR)[3],以及结构引导的核酸酶(structure- guided nuclease, SGN)[4]等新型基因编辑技术的出现,使动物基因组DNA突变的效率和准确性大大提高,推动了基因定向修饰动物的研究[5]。新型基因编辑技术可在基因组内高效产生双链断裂(double strand break, DSB),激活细胞中两种DNA修复路径——同源重组定向修复(homologous-directed repair, HDR)和非同源末端连接(nonhomologous end joining, NHEJ)。NHEJ无需同源修复模板,由NHEJ修复因子将DNA双链断裂的两端强行拼接起来,容易造成基因片段的缺失、突变或外源基因的插入等,是基因敲除的有效途径;HDR路径需要同源DNA模板,修复过程产生错误的概率较低,是定向突变和定点敲入(knock-in, KI)最为依赖的修复路径[6]。尽管运用新型基因编辑工具能够使细胞DNA发生DSB的效率和准确性极大的提高,但双链DNA模板修复效率相对较低,只有0.5%~20%左右,利用HDR进行高效的定点敲入具有较大的难度[3,7]。相比双链DNA模板,单链寡聚核苷酸(single-stranded oligodeoxyribonucleotide, ssODN)作为同源修复模板具有更高的定向修复效率[8,9,10]。目前,ssODN介导的DNA修复的具体通路仍然不是很清楚,但该途径也需要在DSB的断裂末端进行DNA末端剪切(DNA resection),因此与其他HDR通路具有相同的起始途径[11]。一般认为ssODN介导的同源定向修复途径也属于HDR的一种,有研究表明通过小分子化合物调控HDR通路,可以促进ssODN介导的定向修复效率。Maruyama等[12]使用小分子化合物Scr7(DNA连接酶Ⅳ抑制剂)将ssODN介导的定点整合效率提高了19倍;将Scr7直接注射至小鼠受精卵,使定点整合效率提高2倍。Ma等[13]使用VE-822 (Rad3相关激酶抑制剂)和AZD-7762 (检查点激酶CHEK1的特异性抑制剂)将ssODN介导的定点整合效率提高3倍。虽然这些小分子化合物可显著提高HDR效率[14],但都主要集中在对人和小鼠的研究,对猪的研究鲜有报道[15,16]。由于大部分小分子化合物对细胞和胚胎存在一定的毒害作用,剂量过大会损伤细胞或基因编辑胚[17],因此小分子化合物的使用剂量和新化合物的开发还需要继续优化。
RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK信号通路是调节细胞增殖、分化、代谢、凋亡和细胞周期等众多细胞生理过程的主干信号通路,丝裂原活化的细胞外信号调节激酶(mitogen-activated extracellular signal-regulated kinase, MEK)是该信号通路的重要组成部分[18]。PD0325901是一种选择性的非ATP竞争性MEK抑制剂,其与MEK结合会使MEK与ATP结合位点的构象发生变化,从而抑制MEK的激活[19,20]。Lin等[21]研究显示,使用PD0325901和CHIR99021 (GSK3β抑制剂)能消除ESC (embryonic stem cell)细胞系之间同源重组效率的差异,表明MEK信号通路可能参与细胞DNA的同源重组修复,但该信号通路是否参与体细胞同源重组目前还没有研究报道。
猪的生理学、解剖学和遗传学特征与人类非常相似,是研究人类疾病的重要动物模型。杜氏肌营养不良症(Duchenne muscular dystrophy, DMD)是一种X连锁隐性遗传病,由DMD基因突变导致的人类肌肉萎缩无力,丧失独立行走能力为特点的疾病,提高猪该位点的定点编辑效率对制备人类DMD疾病猪模型具有重要意义[22]。此外,ROSA26基因位点是猪基因组上最常用的安全港位点,外源性的基因定点插入该位点能高效稳定表达,同时不会影响其他内源基因的表达,因此常用该位点来构建基因编辑猪模型[23]。本研究以猪胎儿成纤维细胞(porcine fetal fibroblasts, PFFs)为研究对象,以DMD和ROSA26位点为靶点,利用MEK抑制剂PD0325901提高PFFs细胞中ssODN介导定向修复效率,为高效制备基因定向编辑猪模型提供重要参考信息。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料
报告载体ssODN-mediated HDR reporter由本实验室前期构建[24]。该报告载体中EGFP (enhanced green fluorescent protein)序列中间插入一个终止密码子和一个BamHⅠ限制性内切酶位点,BamHⅠ用于线性化报告载体;该报告载体能与EGFP基因相应的同源模板重组,使EGFP表达绿色荧光信号,而没有发生同源定向修复的则被提前终止翻译。Cas9/sgRNA共表达质粒pX330 (Plasmid #42230)购自美国Addgene公司;PFFs细胞由温氏食品集团股份有限公司提供;MEK抑制剂PD0325901购自美国Selleck公司;引物和ssODN由深圳华大基因科技有限公司合成。1.2 Cas9/sgRNA共表达质粒的构建
在CCtop CRISPR/Cas9网站(https://crispr.cos. uni-heidelberg.de/index.html)设计DMD和ROSA26基因的sgRNA[25,26],序列见表1。sgRNA引物混匀后置于95℃水中自然冷却至室温,使其形成双链DNA,克隆到pX330-U6-hSpCas9质粒的BpiⅠ位点上。Table 1
表1
表1 sgRNA序列信息
Table 1
| 基因 | sgRNA序列(5°→3°) |
|---|---|
| DMD | F:GTTGGAGACTGAAGTAAACC |
| R:GGTTTACTTCAGTCTCCAAC | |
| ROSA26 | F:GTGAGAGTTATCTGACCGTA |
| R:TACGGTCAGATAACTCTCAC |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
1.3 PD0325901配制及细胞培养
取适量PD0325901溶解于DMSO溶剂,添加至完全培养基(DMEM细胞培养基+10%胎牛血清)分别配置成25 nmol/L、50 nmol/L、100 nmol/L和250 nmol/L的溶液备用,复苏后的PFF细胞培养至汇合度90% (10 cm板),进行后续实验。1.4 MTT法检测细胞活性
复苏后的PFF细胞培养至汇合度90% (10 cm板),用0.25%胰酶消化,调整细胞密度为103~105个/孔至96孔板,加入100 μL/孔不同浓度梯度的培养基溶液,每个梯度设置8个重复,培养48 h。加20 μL/孔MTT溶液(5 mg/mL,即0.5%MTT),培养4 h后去掉孔内培养液,加150 μL/孔二甲基亚砜,置摇床上低速振荡10 min,使结晶物充分溶解。在酶联免疫检测仪OD490 nm处测量各孔的吸光值,对结果进行统计分析。1.5 流式细胞术检测细胞周期
复苏后的PFF细胞培养至汇合度90% (10 cm板),用0.25%胰酶消化,铺至6孔板,加入2 mL/孔不同浓度梯度的培养基溶液,每个梯度设置3个重复,继续培养48 h。消化细胞至1.5 mL离心管并去掉培养基,每管加500 μL预冷的70%乙醇(-20℃),重悬,置于4℃固定过夜。隔天每管加500 μL碘化丙啶(propidium iodide, PI)染色液,充分振荡,4℃避光孵育30 min,使用流式细胞仪进行检测,利用软件Modifit 5.0进行统计分析。1.6 HDR和NHEJ相关基因表达水平的检测
复苏后的PFF细胞培养至汇合度90% (10 cm板),用0.25%胰酶消化,铺至6孔板,加入2 mL/孔不同浓度梯度的培养基溶液,每个梯度设置3个重复,继续培养48 h。使用RNA抽提试剂盒抽提总RNA,反转录后对cDNA进行实时荧光定量PCR检测,分析NHEJ相关基因XRCC5、XRCC6、LIG4、PNKP和HDR相关基因Rad50、Rad51、Rad52、BRCA1的表达水平。qRT-PCR反应条件:95℃预变性5 min;95℃变性15 s,60℃复性15 s,72℃延伸15 s,40个循环;溶解曲线95℃ 30 s;60℃ 30 s;95℃ 30 s。qRT-PCR引物见表2。Table 2
表2
表2 qRT-PCR引物序列信息
Table 2
| 基因 | 序列(5°→3°) | 产物大小 (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| LIG4 | F:GCCGCTATCGCAGACATTG | 251 |
| R:GCCATCATCTCACCATCAAGG | ||
| PNKP | F:GGACCGTGGCAGTGAAACAG | 221 |
| R:CTCTTCCTCCTCCTCGTGTGG | ||
| XRCC5 | F:GAGGAAGGCACCGTTGAAG | 188 |
| R:GAGAGAGGAATCTGACACTTAGC | ||
| XRCC6 | F:GCGATGAAGAAGAAGAAGAGGAG | 225 |
| R:CATAGAACACCACTGCCAAGAG | ||
| BRCA1 | F:ACGCCACTCTCAACTTCTG | 195 |
| R:CAAGCCTGATGCCACAATAG | ||
| Rad52 | F:CTACTGGTGGCAACTCTGTATTATG | 163 |
| R:ACCCTGTGACCCTCAATGTAAC | ||
| Rad50 | F:GTGGTGATGCTAAAGGGAGAC | 232 |
| R:GGAAGTTACGCTGCTGTGAG | ||
| Rad51 | F:CGTTCAACACAGACCACCAG | 187 |
| R:GCAAGTCGCAGAAGCATCC |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
1.7 ssODN介导的HDR效率检测
复苏后的PFF细胞培养至汇合度90% (10 cm板),用0.25%胰酶消化。参考美国Thermo fisher公司的Lipofectamine? LTX & Plus Reagent protocol说明书,共转染8 μg/孔线性化的ssODN-mediate HDR reporter (BamHⅠ酶切)和1 μg/孔ssODN (序列见表3),每个处理设置3个重复。铺至6孔板培养24 h,加入2 mL/孔不同浓度梯度的培养基溶液,继续培养48 h,使用流式细胞术检测细胞荧光数的百分比。Table 3
表3
表3 ssODN序列信息
Table 3
| 基因 | 序列(5°→3°) | 长度(nt) |
|---|---|---|
| EGFP | CTTCAGCCGCTACCCCGACCACATGAAGCAGCACGACTTCTTCAAGTCCGCCATGCCCGAAGGCTACGTCCAGGAGCGCACCATCTTCTTCAAGGACGACGGCAACTACAAGACCCGCGCCGAGGTGAAGTTCGAGGGCG | 140 |
| DMD | TTTATTGTTCAGCGTTTGGAATCTCCTGAAGACAAGTCATTTGGCAGTTCATTGTTGGAGACTGAAGTAAAAGCTTACCTGGACAGTTACCAAACAGCTTTAGAAGAAGTACTCTCATGGCTTCTTTCAGCTGAGGACACACTGCA | 146 |
| ROSA26 | ATGTCTGGGACTGGATGAGCAAGTACAACAAACAAAATGGGCTTAAAGTATGAGTGAGAGTTATCTGACCAAGCTTGTAAGGATGCAAGTGAGGGGGCCTAAGGTTTGGAGATTAATATTTAATCTCAGATGCTATACTTTGGTGG | 146 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
复苏后的PFF细胞培养至汇合度90% (10 cm板),用0.25%胰酶消化,分别共转染8 μg/孔pX330-DMD-Cas9质粒和1 μg/孔ssODN、8 μg/孔pX330-ROSA26-Cas9质粒和1 μg/孔ssODN(序列见表3),每个处理设置3个重复。铺至6孔板培养24 h,加入2 mL/孔不同浓度梯度的培养基溶液,继续培养48 h。抽提细胞总DNA,PCR扩增目的基因序列(引物序列见表4)。回收纯化后分别使用T7 EndoⅠ和HindⅢ酶切,进行琼脂糖凝胶电泳分离,灰度扫描电泳条带,根据公式:同源定向修复效率=HindⅢ条带灰度值/T7 EndoⅠ条带灰度值,计算同源定向修复效率。同时按照中美泰和生物技术有限公司clone smarter TA克隆试剂盒(产品编号C5853)说明书,对纯化的DNA进行TA克隆测序,计算同源定向修复效率。
Table 4
表4
表4 PCR引物序列
Table 4
| 基因 | 序列(5°→3°) | 产物大小(bp) |
|---|---|---|
| DMD | F:CTACTGTTCATGTCTCTGATAATGCAAGTGG | 554 |
| R:CACATTCCTGTATGAACCACTGGC | ||
| ROSA26 | F:AGATCTTTGTGTCGCAATTTCC | 633 |
| R:CCAGCAACACCTAAGATTTATCAGA |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
1.8 数据分析
采用 SPSS21 软件进行独立样品T-test分析,分析每个处理组与对照组的差异,数据以 Mean ± SEM表示。*P<0.05表示差异显著,**P<0.01表示差异极显著。2 结果与分析
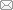
2.1 PD0325901对PFFs细胞活性和细胞周期分布的影响
PFF细胞经25 nmol/L、50 nmol/L、100 nmol/L和250 nmol/L浓度的PD0325901处理,使用MTT方法检测细胞增殖活性。结果显示,25 nmol/L、50 nmol/L、100 nmol/L浓度下细胞活性比对照组分别提高了17.2%、5%、10.12%,经250 nmol/L PD0325901处理后,细胞活性比对照组下降了6.35%。低浓度(25 nmol/L)对细胞活性有促进作用,而高浓度(250 nmol/L)对细胞活性具有一定的抑制作用,但差异不显著(P>0.05),表明这4个浓度梯度的PD0325901对细胞活性没有影响(图1A)。流式细胞术检测细胞结果显示,随着PD0325901浓度增加,处于G2期和S期的PFFs细胞群显著增加(P<0.05),处于G1期细胞群显著减少(P<0.05) (图1B),细胞表现一定程度的同步化。图1
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图1PD0325901对细胞活性和细胞周期的影响
A:不同浓度的PD0325901对细胞活性的影响;B:不同浓度的PD0325901对细胞周期的影响。* P<0.05,表示差异显著。
Fig. 1The cell activity and cell cycle distribution after treatment with PD0325901
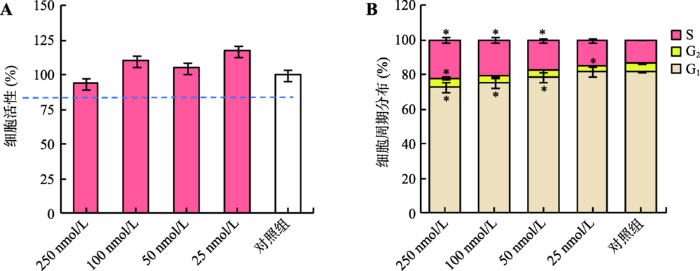
2.2 PD0325901对DNA修复因子表达水平的影响
PFFs细胞经不同浓度的PD0325901处理后,进行qRT-PCR检测。结果显示,NHEJ相关修复基因(XRCC5、XRCC6、LIG4和PNKP)和HDR相关修复基因(Rad50、Rad51、Rad52和BRCA1)表达量随PD0325901添加剂量的升高呈现不规律变化(图2)。在NHEJ通路中,25 nmol/L和250 nmol/L PD0325901对XRCC5、XRCC6和PNKP表达具有上调作用;但对于LIG4基因表达,仅250 nmol/L剂量对其具有上调作用。在HDR通路中,不同浓度PD0325901对Rad50和Rad52表达都有上调作用,在250 nmol/L剂量下,Rad50和Rad52基因表达量提高近3倍(P<0.05),但二者表达量与PD0325901添加量不存在剂量依赖效应;然而对于BRCA1和Rad51基因,100 nmol/L PD0325901对二者的表达呈现下调作用(P<0.05),而经其他剂量处理后,BRCA1和Rad51基因的表达量均表现不同程度的上调作用。图2
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图2PD0325901对DNA修复因子表达水平的影响
XRCC5、XRCC6、LIG4和PNKP为NHEJ相关修复基因;Rad50、Rad51、Rad52和BRCA1为HDR相关修复基因。
* P<0.05,表示差异显著,** P<0.01表示差异极显著。
Fig. 2The mRNA expression levels of DNA repair factors after treatment with PD0325901
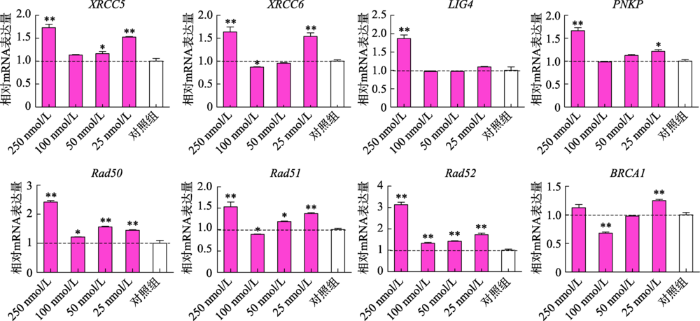
2.3 PD0325901对ssODN介导的HDR效率的影响
ssODN介导的HDR报告载体和相应ssODN共转染至PFF细胞,流式细胞术结果显示,25 nmol/L、50 nmol/L、100 nmol/L和250 nmol/L浓度PD0325901均能提高HDR效率,提高了32.3%~58.8% (P<0.05) (图3,A~C)。X330-DMD-Cas9质粒和相应的ssODN共转染至PFF细胞后,用HindⅢ酶切方法评估DMD基因位点编辑效率。结果显示,25 nmol/L、50 nmol/L、100 nmol/L和250 nmol/L浓度PD0325901均能提高HDR效率,达2.6%~37.1% (图3,E和F),并表现明显的剂量依赖效应。共转染pX330-ROSA26-Cas9质粒和相应的ssODN,用HindⅢ酶切方法评估ROSA26基因编辑效率。结果显示,25 nmol/L、50 nmol/L和250 nmol/L PD0325901促进ROSA26位点HDR效率,分别提高了4.8%、0.8%和9.6% (图3,H和I),但100 nmol/L剂量时,ROSA26位点HDR效率略微下降。进一步利用TA克隆和测序验证,结果显示,在250 nmol/L PD0325901剂量下DMD和ROSA26基因位点的HDR效率分别提高了48.16%和17.64% (表5;图3,J和K),与HindⅢ酶切结果基本一致。图3
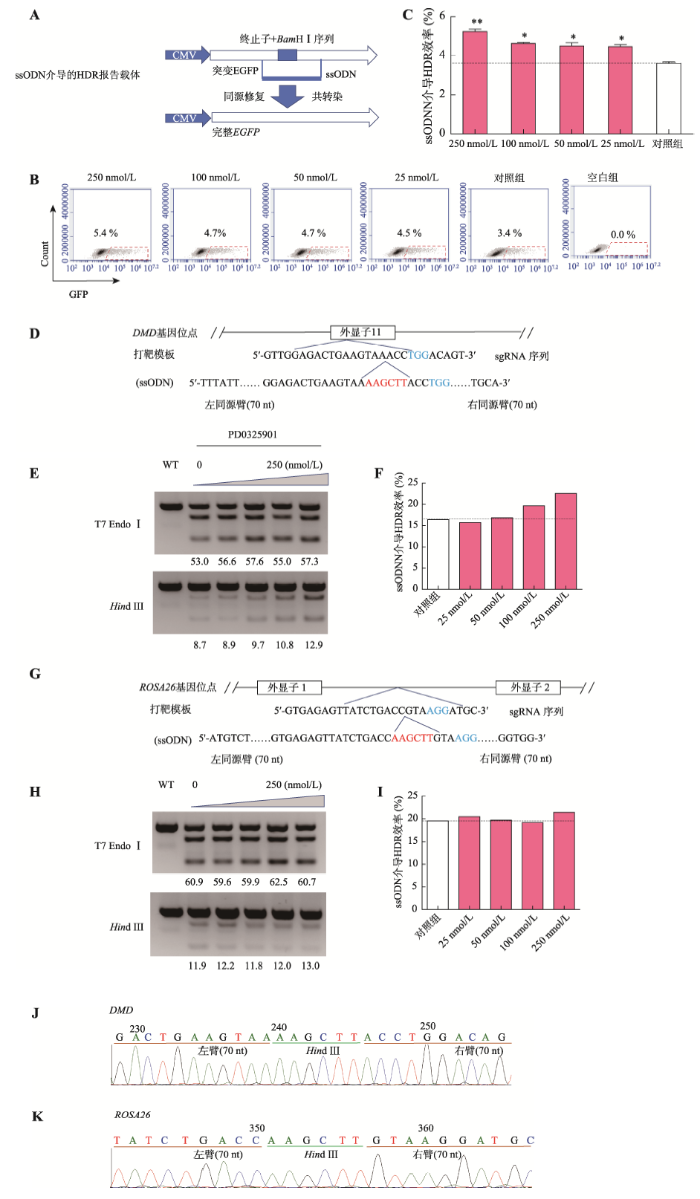 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图3PD0325901对ssODN介导的HDR效率的影响
A:ssODN介导的HDR报告载体修复模式图;B:报告载体HDR修复效率的流式细胞术检测结果(用EGFP荧光细胞百分比表示HDR效率);C:PD032590处理组间ssODN介导报告载体HDR修复的效率比较(n=3)。* P<0.05,表示差异显著,** P<0.01表示差异极显著;D和G:ssODN介导HindⅢ识别序列定点整合至猪基因组模式图。D图为DMD基因位点,G图为ROSA26基因位点;E和H:核酸内切酶酶切法检测DMD位点(图E)和ROSA26位点(图H)编辑效率电泳结果。T7 EndoⅠ为T7核酸内切酶Ⅰ酶切电泳图,图上的数字表示灰度扫描数值,代表目标位点发生DSB的效率;HindⅢ为HindⅢ限制性核酸内切酶酶切电泳图,图上数字表示灰度扫描数值,代表目标位点HindⅢ定点整合效率;F和I:分别为图E和图H灰度扫描值的柱状图展示结果(HDR效率= HindⅢ灰度扫描值/T7 EndoⅠ灰度扫描值,n=3);J和K:分别为定点整合HindⅢ识别序列至DMD(图J)和ROSA26(图K)基因位点的测序峰图。
Fig.3The ssODN-mediated gene editing efficiency after treatment with PD0325901
Table 5
表5
表5 TA克隆数据统计
Table 5
| 基因 | 浓度 | KI效率(阳性/总数) |
|---|---|---|
| DMD | 对照组 | 18.75% (3/16) |
| 250 nmol/L | 27.78% (5/18) | |
| ROSA26 | 对照组 | 25.00% (4/16) |
| 250 nmol/L | 29.41% (5/17) |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
3 讨论
细胞所在的分裂期会显著影响DNA修复双链断裂途径的选择,在修复过程中,NHEJ可以发生在细胞分裂的任一时期,而HDR主要发生在S和G2期,李国玲等[17]通过同步化细胞周期至S和G2期,成功提高了基因组定点修饰的效率。Yang等[27]在人多能干细胞中添加ABT-751化合物,使细胞停滞在G2期,将2~5 kb片段整合至人基因组5个不同区域的效率提高了3~6倍;Lin等[28]添加aphidicolin和nocodazole,使人胚胎干细胞、成纤维细胞和293T细胞停滞在G2期,显著提高ssODN介导的定向修复效率。本研究结果显示,随着PD0325901浓度增加,处于G2期和S期的PFFs细胞群显著增加,处于G1期细胞群显著减少,细胞表现一定程度的同步化,与前人的报道结果不一致[29,30,31]。Wang等[30]研究表明,RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK信号转导通路通过激活MEK-ERK,促进细胞周期素D1 (cyclin D1)的表达及其与细胞周期依赖性激酶4 (cyclin-dependent kinase 4, Cdk4)的结合来调控细胞周期,促进细胞进入S期。Ayunadirah等[31]研究发现添加PD0325901显著降低了MDA-MB-231乳腺癌细胞的增殖,同时发现细胞周期停滞在G1期。本研究用MEK抑制剂PD0325901处理PFFs后,检测到S期细胞数量反而显著增加,推测可能是由于MEK通路受到抑制后影响其他平行信号通路调控细胞周期,或细胞种类差异导致结果不一致,但具体机理尚不明确。已有的研究表明,添加小分子化合物PD0325901使细胞同步至S期和G2期,其可能有利于提高定点整合效率[17,32~34]。本研究结果也显示,250 nmol/L浓度PD0325901能显著提高报告载体、DMD和ROSA26位点上ssODN介导的同源修复效率,表明将细胞周期同步化在S和G2期可以提高细胞定向修复效率。NHEJ和HDR通路的激活需要许多关键因子的参与,它们能调节修复途径的选择,并在修复过程中发挥不可替代的重要作用[17,35,36]。本研究结果显示,不同浓度的PD0325901抑制剂均能提高报告载体、DMD和ROSA26位点上ssODN介导的同源修复效率,并表现明显剂量依赖性。本研究结果推测,PD0325901上调Rad50、Rad51和Rad52的表达可能是提高同源重组效率的关键,但PD0325901添加剂量与上述因子表达并没有剂量依赖性关系,因而,二者间的相关性但仍需进一步研究。另外,PD0325901对NHEJ关键因子的表达也有不同程度的上调作用,尤其是25 nmol/L和250 nmol/L浓度影响较大,呈“U型效应”。在前人研究中也发现类似的现象,如Li等[17]在猪胎儿成纤维细胞中分别添加L755507、Resveratrol和Scr7 3种小分子抑制剂,NHEJ和HDR关键因子的表达水平出现了类似的“U型效应”。Kachhap等[37]在DU-145和LNCaP细胞中添加不同浓度梯度的丙戊酸(valproic acid, VPA),BRCA1基因的表达水平也同样出现类似的“U型效应”。产生“U型效应”的原因可能是小分子浓度过高时,出现负反馈调节,其具体调控机理还有待进一步研究。同时,本研究利用PD0325901提高ssODN介导的同源修复效率,证实了MEK抑制剂PD0325901对猪体细胞HDR效率具有促进作用,与前人报道PD0325901可提高ESC定点整合效率结果一致[15]。本研究通过向猪成纤维细胞培养基中添加MEK抑制剂使EGFP报告载体的同源修复效率显著提高了58.8%,使DMD和ROSA26位点的同源重组效率分别提高了48.16%和17.64%,并表现较低的细胞毒性,这对提高PFFs细胞定向编辑效率及基因定向编辑猪的研究具有重要价值和意义。
参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
URLPMID:8577732 [本文引用: 1]

A long-term goal in the field of restriction-modification enzymes has been to generate restriction endonucleases with novel sequence specificities by mutating or engineering existing enzymes. This will avoid the increasingly arduous task of extensive screening of bacteria and other microorganisms for new enzymes. Here, we report the deliberate creation of novel site-specific endonucleases by linking two different zinc finger proteins to the cleavage domain of Fok I endonuclease. Both fusion proteins are active and under optimal conditions cleave DNA in a sequence-specific manner. Thus, the modular structure of Fok I endonuclease and the zinc finger motifs makes it possible to create ``artificial'' nucleases that will cut DNA near a predetermined site. This opens the way to generate many new enzymes with tailor-made sequence specificities desirable for various applications.
URL [本文引用: 1]
URLPMID:24906146 [本文引用: 2]

Derived from a microbial defense system, Cas9 can be guided to specific locations within complex genomes by a short RNA. The development, applications, and future directions of the CRISPR-Cas9 system for genome engineering are discussed here.
URLPMID:5025552 [本文引用: 1]

Engineered endonucleases are a powerful tool for editing DNA. However, sequence preferences may limit their application. We engineer a structure-guided endonuclease (SGN) composed of flap endonuclease-1 (FEN-1), which recognizes the 3′ flap structure, and the cleavage domain of Fok I (Fn1), which cleaves DNA strands. The SGN recognizes the target DNA on the basis of the 3′ flap structure formed between the target and the guide DNA (gDNA) and cut the target through its Fn1 dimerization. Our results show that the SGN, guided by a pair of gDNAs, cleaves transgenic reporter gene and endogenous genes in zebrafish embryonic genome. The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s13059-016-1038-5) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
URL [本文引用: 1]

基因组编辑技术能够精确靶向修饰生物体基因组特定位点、人为改造生物遗传信息.自21世纪初,基因组编辑技术得到迅猛发展,锌指核酸酶(zinc finger nucleases,ZFN)、转录激活样受体因子(transcription-activating-like receptor factor,TALEN)和成簇的规律间隔短回文重复序列及其相关系统(clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats/Cas endonucleases,CRISPR/Cas)3种新型基因组编辑系统先后诞生.基因组编辑技术能对生物体内源基因进行精确靶向修饰,被广泛应用于生物医学研究领域.猪与人类亲缘关系接近,在生理特征与病理病程等诸多方面与人类具有相似性,是人类疾病动物模型与异种器官移植研究的重要对象.本文主要介绍了ZFN、TALEN和CRISPR/Cas93种基因组编辑技术的发展概况与作用机理,综述了基因编辑猪在人类疾病模型、器官移植与人源化器官培育等生物医学领域里的最新研究进展,并对基因编辑猪的应用前景进行了展望.
URL [本文引用: 1]

基因组编辑技术能够精确靶向修饰生物体基因组特定位点、人为改造生物遗传信息.自21世纪初,基因组编辑技术得到迅猛发展,锌指核酸酶(zinc finger nucleases,ZFN)、转录激活样受体因子(transcription-activating-like receptor factor,TALEN)和成簇的规律间隔短回文重复序列及其相关系统(clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats/Cas endonucleases,CRISPR/Cas)3种新型基因组编辑系统先后诞生.基因组编辑技术能对生物体内源基因进行精确靶向修饰,被广泛应用于生物医学研究领域.猪与人类亲缘关系接近,在生理特征与病理病程等诸多方面与人类具有相似性,是人类疾病动物模型与异种器官移植研究的重要对象.本文主要介绍了ZFN、TALEN和CRISPR/Cas93种基因组编辑技术的发展概况与作用机理,综述了基因编辑猪在人类疾病模型、器官移植与人源化器官培育等生物医学领域里的最新研究进展,并对基因编辑猪的应用前景进行了展望.
URLPMID:4721590 [本文引用: 1]

Cancer susceptibility genes have been classified into two groups: gatekeepers and caretakers. Gatekeepers are genes that control cell proliferation and death, whereas caretakers are DNA repair genes whose inactivation leads to genetic instability. Abrogation of both caretaker and gatekeeper function markedly increases cancer susceptibility. Although the importance of Ku80 in DNA double-strand break repair is well established, neither Ku80 nor other components of the non-homologous end-joining pathway are known to have a caretaker role in maintaining genomic stability. Here we show that mouse cells deficient for Ku80 display a marked increase in chromosomal aberrations, including breakage, translocations and aneuploidy. Despite the observed chromosome instabilities, Ku80-/- mice have only a slightly earlier onset of cancer. Loss of p53 synergizes with Ku80 to promote tumorigenesis such that all Ku80-/- p53-/- mice succumb to disseminated pro-B-cell lymphoma before three months of age. Tumours result from a specific set of chromosomal translocations and gene amplifications involving IgH and c-Myc, reminiscent of Burkitt's lymphoma. We conclude that Ku80 is a caretaker gene that maintains the integrity of the genome by a mechanism involving the suppression of chromosomal rearrangements.
URL [本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
URLPMID:3805579 [本文引用: 1]

The generation of specific mutant animal models is critical for functional analysis of human genes. The conventional gene targeting approach in embryonic stem cells (ESCs) by homologous recombination is however laborious, slow, expensive, and limited to species with functional ESCs. It is therefore a long-sought goal to develop an efficient and simple alternative gene targeting strategy. Here we demonstrate that, by combining an efficient ZFN pair and ssODN, a restriction site and a loxP site were successfully introduced into a specific genomic locus. A targeting efficiency up to 22.22% was achieved by coinciding the insertion site and the ZFN cleavage site isogenic and keeping the length of the homology arms equal and isogenic to the endogenous target locus. Furthermore, we determine that ZFN and ssODN-assisted HR is ssODN homology arm length dependent. We further show that mutant alleles generated by ZFN and ssODN-assisted HR can be transmitted through the germline successfully. This study establishes an efficient gene targeting strategy by ZFN and ssODN-assisted HR in mouse zygotes, and provides a potential avenue for genome engineering in animal species without functional ES cell lines.
URL [本文引用: 1]

The CRISPR-Cas9 system has been employed to generate mutant alleles in a range of different organisms. However, so far there have not been reports of use of this system for efficient correction of a genetic disease. Here we show that mice with a dominant mutation in Crygc gene that causes cataracts could be rescued by coinjection into zygotes of Cas9 mRNA and a single-guide RNA (sgRNA)... [Show full abstract]
[本文引用: 1]
URLPMID:25798939 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract Methods to introduce targeted double-strand breaks (DSBs) into DNA enable precise genome editing by increasing the rate at which externally supplied DNA fragments are incorporated into the genome through homologous recombination. The efficiency of these methods is limited by nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ), an alternative DNA repair pathway that competes with homology-directed repair (HDR). To promote HDR at the expense of NHEJ, we targeted DNA ligase IV, a key enzyme in the NHEJ pathway, using the inhibitor Scr7. Scr7 treatment increased the efficiency of HDR-mediated genome editing, using Cas9 in mammalian cell lines and in mice for all four genes examined, up to 19-fold. This approach should be applicable to other customizable endonucleases, such as zinc finger nucleases and transcription activator-like effector nucleases, and to nonmammalian cells with sufficiently conserved mechanisms of NHEJ and HDR.
URLPMID:29610531 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract Human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) have potential applications in biological studies and regenerative medicine. However, precise genome editing in hPSCs remains time-consuming and labor-intensive. Here we demonstrate that the recently identified CRISPR-Cpf1 can be used to efficiently generate knockout and knockin hPSC lines. The unique properties of CRISPR-Cpf1, including shorter crRNA length and low off-target activity, are very attractive for many applications. In particular, we develop an unbiased drug-selection-based platform feasible for high-throughput screening in hPSCs and this screening system enables us to identify small molecules VE-822 and AZD-7762 that can promote CRISPR-Cpf1-mediated precise genome editing. Significantly, the combination of CRISPR-Cpf1 and small molecules provides a simple and efficient strategy for precise genome engineering.
URLPMID:25803306 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract The insertion of precise genetic modifications by genome editing tools such as CRISPR-Cas9 is limited by the relatively low efficiency of homology-directed repair (HDR) compared with the higher efficiency of the nonhomologous end-joining (NHEJ) pathway. To enhance HDR, enabling the insertion of precise genetic modifications, we suppressed the NHEJ key molecules KU70, KU80 or DNA ligase IV by gene silencing, the ligase IV inhibitor SCR7 or the coexpression of adenovirus 4 E1B55K and E4orf6 proteins in a 'traffic light' and other reporter systems. Suppression of KU70 and DNA ligase IV promotes the efficiency of HDR 4-5-fold. When co-expressed with the Cas9 system, E1B55K and E4orf6 improved the efficiency of HDR up to eightfold and essentially abolished NHEJ activity in both human and mouse cell lines. Our findings provide useful tools to improve the frequency of precise gene modifications in mammalian cells.
URLPMID:5566437 [本文引用: 2]

CRISPR/Cas9 is an efficient customizable nuclease to generate double-strand breaks (DSBs) in the genome. This process results in knockout of the targeted gene or knock-in of a specific DNA fragment at the targeted locus in the genome of various species. However, efficiency of knock-in mediated by homology-directed repair (HDR) pathway is substantially lower compared with the efficiency of knockout mediated by the nonhomologous end-joining (NHEJ) pathway. Suppressing NHEJ pathway or enhancing HDR pathway has been proven to enhance the nuclease-mediated knock-in efficiency in cultured cells and model organisms. We here investigated the effect of small molecules, Scr7, L755507 and resveratrol, on promoting HDR efficiency in porcine fetal fibroblasts. Results from eGFP reporter assay showed that these small molecules could increase the HDR efficiency by 2 3-fold in porcine fetal fibroblasts. When transfecting with the homologous template DNA and CRISPR/Cas9 plasmid and treating with small molecules, the rate of knock-in porcine fetal fibroblast cell lines with large DNA fragment integration could reach more than 50% of the screened cell colonies, compared with 26.1% knock-in cell lines in the DMSO-treated group. The application of small molecules offers a beneficial approach to improve the frequency of precise genetic modifications in primary somatic cells.
URLPMID:29899280 [本文引用: 1]

During CRISPR/Cas9 mediated genome editing, site-specific double strand breaks are introduced and repaired either unspecific by non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) or sequence dependent by homology directed repair (HDR). Whereas NHEJ-based generation of gene knock-out is widely performed, the HDR-based knock-in of specific mutations remains a bottleneck. Especially in primary cell lines that are essential for the generation of cell culture and animal models of inherited human diseases, knock-in efficacy is insufficient and needs significant improvement. Here, we tested two different approaches to increase the knock-in frequency of a specific point mutation into theMYH7-gene in porcine fetal fibroblasts. We added a small molecule inhibitor of NHEJ, SCR7 (5,6-bis((E)-benzylideneamino)-2-mercaptopyrimidin-4-ol), during genome editing and screened cell cultures for the point mutation. However, this approach did not yield increased knock-in rates. In an alternative approach, we fused humanized Cas9 (hCas9) to the N-terminal peptide of the Geminin gene (GMNN). The fusion protein is degraded in NHEJ-dominated cell cycle phases, which should increase HDR-rates. Using hCas9-GMNNand point mutation-specific real time PCR screening, we found a two-fold increase in genome edited cell cultures. This increase of HDR by hCas9-GMNNprovides a promising way to enrich specific knock-in in porcine fibroblast cultures for somatic cloning approaches.
URL [本文引用: 5]

传统转基因技术,如显微注射、转座子、慢病毒转染等将目的基因插入基因组内的整合方式是随机的,这些随机整合对后期转基因动物品系组建和育种带来诸多不利,因此有研究人员提出了定点整合转基因技术。目前该技术的定点整合效率非常低,主要取决于两个方面:一是靶位点产生DNA双链断裂(double-strand break,DSB)的效率;二是断裂后的靶位点与携带同源臂及外源基因的供体质粒发生同源重组的效率,其中同源重组修复(homologous recombination repair, HDR)是基因组定点整合最为依赖的修复机制。靶位点产生DSB后,机体的DNA修复既可能发生HDR,也可能发生非同源末端连接(nonhomologous end joining, NHEJ),并且两者之间存在竞争关系,因此激活HDR或抑制NEHJ都可提高定点整合转基因的效率。本文结合影响定点整合的因素,对提高定点整合效率最新探索方面进行了综述。
URL [本文引用: 5]

传统转基因技术,如显微注射、转座子、慢病毒转染等将目的基因插入基因组内的整合方式是随机的,这些随机整合对后期转基因动物品系组建和育种带来诸多不利,因此有研究人员提出了定点整合转基因技术。目前该技术的定点整合效率非常低,主要取决于两个方面:一是靶位点产生DNA双链断裂(double-strand break,DSB)的效率;二是断裂后的靶位点与携带同源臂及外源基因的供体质粒发生同源重组的效率,其中同源重组修复(homologous recombination repair, HDR)是基因组定点整合最为依赖的修复机制。靶位点产生DSB后,机体的DNA修复既可能发生HDR,也可能发生非同源末端连接(nonhomologous end joining, NHEJ),并且两者之间存在竞争关系,因此激活HDR或抑制NEHJ都可提高定点整合转基因的效率。本文结合影响定点整合的因素,对提高定点整合效率最新探索方面进行了综述。
URL [本文引用: 1]

丝裂原活化的细胞外信号调节激酶(mitogen-activated extracellular signal-regulated kinase,MEK)是一种可磷酸化靶蛋白上丝氨酸/苏氨酸和酪氨酸残基的双特异性激酶,也是RASRAF-MEK-ERK信号转导通路的主要组分。该信号通路参与了细胞凋亡,细胞周期进行,细胞迁移、分化、代谢和细胞增殖等众多过程的调节。大量研究表明,MEK结构及其表达水平的改变与肿瘤等多种疾病的发生密切相关。因此,对MEK特异性抑制剂的筛选成了当前国际上关于肿瘤治疗研究的热点。目前,已有多种MEK抑制剂被发现,部分已用于肿瘤等疾病的治疗,并显示出较好的临床疗效。该文将对MEK的结构、功能及MEK抑制剂的临床应用等方面的研究进展作一综述。
URL [本文引用: 1]

丝裂原活化的细胞外信号调节激酶(mitogen-activated extracellular signal-regulated kinase,MEK)是一种可磷酸化靶蛋白上丝氨酸/苏氨酸和酪氨酸残基的双特异性激酶,也是RASRAF-MEK-ERK信号转导通路的主要组分。该信号通路参与了细胞凋亡,细胞周期进行,细胞迁移、分化、代谢和细胞增殖等众多过程的调节。大量研究表明,MEK结构及其表达水平的改变与肿瘤等多种疾病的发生密切相关。因此,对MEK特异性抑制剂的筛选成了当前国际上关于肿瘤治疗研究的热点。目前,已有多种MEK抑制剂被发现,部分已用于肿瘤等疾病的治疗,并显示出较好的临床疗效。该文将对MEK的结构、功能及MEK抑制剂的临床应用等方面的研究进展作一综述。
URL [本文引用: 1]
URLPMID:24840079 [本文引用: 1]

Aberrant activation of the RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK1/2 pathway occurs in more than 30% of human cancers. As part of this pathway, MEK1 and MEK2 have crucial roles in tumorigenesis, cell proliferation and inhibition of apoptosis and, therefore, MEK1/2 inhibition is an attractive therapeutic strategy in a number of cancers. Highly selective and potent non-ATP-competitive allosteric MEK1/2 inhibitors have been developed and assessed in numerous clinical studies over the past decade. These agents are not efficacious in a broad range of unselected cancers, although single-agent antitumour activity has been detected mainly in tumours that harbour mutations in genes encoding the members of the RAS and RAF protein families, such as certain melanomas. Combinations of MEK1/2 inhibitors and cytotoxic chemotherapy, and/or other targeted agents are being studied to expand the efficacy of this class of agents. Identifying predictive biomarkers, and delineating de novo and acquired resistance mechanisms are essential for the future clinical development of MEK inhibitors. We discuss the clinical experience with MEK inhibitors to date, and consider the novel approaches to MEK-inhibitor therapy that might improve outcomes and lead to the wider use of such treatments.
URLPMID:25196127 [本文引用: 1]

Summary Homologous recombination in embryonic stem cells (ESCs) is widely utilized in genome engineering, particularly in the generation of gene targeted mice. However, genome engineering is often plagued by the problem of low homologous recombination efficiency. In this study, we developed a novel method to increase the efficiency of homologous recombination in ESCs by changing its culture conditions. By comparing the efficiency of different ESCs in various culture conditions, we determined that chemicals that inhibit the MEK and GSK3β pathways (2i condition) enhance homologous recombination and eliminate differences in efficiencies among cell lines. Analysis of gene expression patterns in ESCs maintained in different culture conditions has identified several homologous recombination-related candidates, including the pluripotent markers Eras and Tbx3. The results of this study suggest that homologous recombination is associated with ESC pluripotency. genesis 52:889–896, 2014. 08 2014 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
URL [本文引用: 1]
URLPMID:24503648 [本文引用: 1]

Rosa26-targeted swine models for stable gene over-expression and Cre-mediated lineage tracingCell Research advance online publication, February 7 2014. doi:10.1038/cr.2014.15Author ...
URL [本文引用: 1]

The main DNA repair pathways, nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ) and homology-directed repair (HDR), are complementary to each other; hence, interruptions of the NHEJ pathway can favor HDR. Improving HDR efficiency in animal primary fibroblasts can facilitate the generation of gene knock-in animals with agricultural and biomedical values by somatic cell nuclear transfer. In this study, we used siRNA to suppress the expression of Ku70 and Ku80, which are the key factors in NHEJ pathway, to investigate the effect of Ku silencing on the HDR efficiency in pig fetal fibroblasts. Down-regulation of Ku70 and Ku80 resulted in the promotion of the frequencies of multiple HDR pathways, including homologous recombination, single strand annealing, and single-stranded oligonucleotide-mediated DNA repair. We further evaluated the effects of Ku70 and Ku80 silencing on promoting HR-mediated knock-in efficiency in two porcine endogenous genes and found a significant increase in the amount of knock-in cells in Ku-silenced fibroblasts compared with control. The RNA interference strategy will benefit the generation of cell lines and organisms with precise genetic modifications.
URL [本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
URLPMID:4757933 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract Efficient gene editing is essential to fully utilize human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) in regenerative medicine. Custom endonuclease-based gene targeting involves two mechanisms of DNA repair: homology directed repair (HDR) and non-homologous end joining (NHEJ). HDR is the preferred mechanism for common applications such knock-in, knock-out or precise mutagenesis, but remains inefficient in hPSCs. Here, we demonstrate that synchronizing synchronizing hPSCs in G2/M with ABT phase increases on-target gene editing, defined as correct targeting cassette integration, 3 to 6 fold. We observed improved efficiency using ZFNs, TALENs, two CRISPR/Cas9, and CRISPR/Cas9 nickase to target five genes in three hPSC lines: three human embryonic stem cell lines, neural progenitors and diabetic iPSCs. neural progenitors and diabetic iPSCs. Reversible synchronization has no effect on pluripotency or differentiation. The increase in on-target gene editing is locus-independent and specific to the cell cycle phase as G2/M phase enriched cells show a 6-fold increase in targeting efficiency compared to cells in G1 phase. Concurrently inhibiting NHEJ with SCR7 does not increase HDR or improve gene targeting efficiency further, indicating that HR is the major DNA repair mechanism after G2/M phase arrest. The approach outlined here makes gene editing in hPSCs a more viable tool for disease modeling, regenerative medicine and cell-based therapies.
URLPMID:25497837 [本文引用: 1]

10.7554/eLife.04766.001The CRISPR/Cas9 system is a robust genome editing technology that works in human cells, animals and plants based on the RNA-programmed DNA cleaving activity of the Cas9 enzyme. Building on previous work (Jinek et al., 2013), we show here that new genetic information can be introduced site-specifically and with high efficiency by homology-directed repair (HDR) of Cas9-induced site-specific double-strand DNA breaks using timed delivery of Cas9-guide RNA ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complexes. Cas9 RNP-mediated HDR in HEK293T, human primary neonatal fibroblast and human embryonic stem cells was increased dramatically relative to experiments in unsynchronized cells, with rates of HDR up to 38% observed in HEK293T cells. Sequencing of on- and potential off-target sites showed that editing occurred with high fidelity, while cell mortality was minimized. This approach provides a simple and highly effective strategy for enhancing site-specific genome engineering in both transformed and primary human cells.DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.04766.001
URLPMID:9337851 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract In Chinese hamster embryo fibroblasts (IIC9 cells), platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) stimulated mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular-signal-regulated kinase (MAP kinase/ERK) activity, but not that of c-jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), and induced G1 phase progression. ERK1 activation was biphasic and was sustained throughout the G1 phase of the cell cycle. PDGF induced cyclin D1 protein and mRNA levels in a time-dependent manner. Inhibition of PDGF-induced ERK1 activity by the addition of a selective inhibitor of MEK1 (MAP kinase kinase/ERK kinase 1) activation, PD98059, or transfection with a dominant-negative ERK1 (dnERK-) was correlated with growth arrest. In contrast, growth was unaffected by expression of dominant-negative JNK (dnJNK-). Interestingly, addition of PD98059 or dnERK-, but not dnJNK-, resulted in a dramatic decrease in cyclin D1 protein and mRNA levels, concomitant with a decrease in cyclin D1-cyclin-dependent kinase activity. To investigate the importance of sustained ERK1 activation, ERK1 activity was blocked by the addition of PD98059 throughout G1. Addition of PD98059 up to 4 h after PDGF treatment decreased ERK1 activity to the levels found in growth-arrested IIC9 cells. Loss of cyclin D1 mRNA and protein expression was observed within 1 h after inhibition of the second sustained phase of ERK1 activity. Disruption of sustained ERK1 activity also resulted in G1 growth arrest. These data provide evidence for a role for sustained ERK activity in controlling G1 progression through positive regulation of the continued expression of cyclin D1, a protein known to positively regulate G1 progression.
URL [本文引用: 2]

目的研究人乳腺癌组织、良性肿瘤以及瘤旁乳腺组织中细胞外信号调 节激酶(ERK1、ERK2)及其上游激酶(MEK1、MEK2)的表达,以及术前化疗对MEK1、MEK2、ERK1、ERK2蛋白表达的影响. 方法应用蛋白质印迹法检测56例患者乳腺癌组织、8例乳腺良性肿瘤以及相应瘤旁组织中MEK1、MEK2及ERK1、ERK2蛋白的表达情况,其中16例 患者术前接受环磷酰胺,表阿霉素加5-氟脲嘧啶或泰素加表阿霉素方案化疗.应用免疫组织化学方法检测乳腺癌组织及癌旁组织中MEK1、MEK2及 ERK1、ERK2蛋白的表达. 结果 40例未行术前化疗的乳腺癌组织中MEK2、ERK1、ERK2蛋白表达水平高于癌旁组织,分别为癌旁组织的4.76、1.48和2.09倍(t值分别为 7.244,5.959,3.735,P<0.01);MEK1水平低于相应癌旁组织(t=2.206,P<0.05);未行术前化疗的乳腺 癌组织中MEK2、ERK1、ERK2蛋白表达水平高于乳腺良性肿瘤(t值分别为2.932,2.082,2.021,P<0.05);MEK1水 平低于良性肿瘤(t=2.075,P<0.05);雌激素受体阴性的乳腺癌中MEK2蛋白表达水平高于雌激素受体阳性的肿瘤(t=2.40,P& lt;0.05),MEK1蛋白表达水平低于雌激素受体阳性的肿瘤(t=2.58,P<0.01);术前化疗的乳腺癌组织中MEK2蛋白表达水平明 显低于未化疗组(t=2.485,P<0.05). 结论 MEK-ERK蛋白的过表达可能在人乳腺癌的发生发展中起重要作用,术前化疗对于MEK-ERK蛋白表达有一定的抑制作用.
URL [本文引用: 2]

目的研究人乳腺癌组织、良性肿瘤以及瘤旁乳腺组织中细胞外信号调 节激酶(ERK1、ERK2)及其上游激酶(MEK1、MEK2)的表达,以及术前化疗对MEK1、MEK2、ERK1、ERK2蛋白表达的影响. 方法应用蛋白质印迹法检测56例患者乳腺癌组织、8例乳腺良性肿瘤以及相应瘤旁组织中MEK1、MEK2及ERK1、ERK2蛋白的表达情况,其中16例 患者术前接受环磷酰胺,表阿霉素加5-氟脲嘧啶或泰素加表阿霉素方案化疗.应用免疫组织化学方法检测乳腺癌组织及癌旁组织中MEK1、MEK2及 ERK1、ERK2蛋白的表达. 结果 40例未行术前化疗的乳腺癌组织中MEK2、ERK1、ERK2蛋白表达水平高于癌旁组织,分别为癌旁组织的4.76、1.48和2.09倍(t值分别为 7.244,5.959,3.735,P<0.01);MEK1水平低于相应癌旁组织(t=2.206,P<0.05);未行术前化疗的乳腺 癌组织中MEK2、ERK1、ERK2蛋白表达水平高于乳腺良性肿瘤(t值分别为2.932,2.082,2.021,P<0.05);MEK1水 平低于良性肿瘤(t=2.075,P<0.05);雌激素受体阴性的乳腺癌中MEK2蛋白表达水平高于雌激素受体阳性的肿瘤(t=2.40,P& lt;0.05),MEK1蛋白表达水平低于雌激素受体阳性的肿瘤(t=2.58,P<0.01);术前化疗的乳腺癌组织中MEK2蛋白表达水平明 显低于未化疗组(t=2.485,P<0.05). 结论 MEK-ERK蛋白的过表达可能在人乳腺癌的发生发展中起重要作用,术前化疗对于MEK-ERK蛋白表达有一定的抑制作用.
URLPMID:26463630 [本文引用: 2]

Triple-negative breast cancers (TNBCs) are aggressive cancers that do not benefit from hormonal therapy or therapies that target HER2 receptors. Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF-1R), which has been shown to be overexpressed in breast cancer, activates numerous downstream kinases that associate with cell proliferation and survival. This study compared the effects caused by dual treatments targeting IGF-1R, PI3K, mTORC, or MEK with those by single treatments in a TNBC cell line, MDA-MB-231. We used small-molecule kinase inhibitors, namely, NVP-AEW541, NVP-BKM120, KU0063794, and PD0325901 to target IGF-1R, PI3K, mTORC, and MEK, respectively. Combination treatments of PD0325901 with NVP-AEW541, NVP-BKM120 or KU0063794 and NVP-AEW541 with KU0063794 demonstrated a significant synergistic growth inhibition. These dual treatments increased apoptosis and/or cell cycle arrest at G0/G1 phase and enhanced the inhibition of phosphorylation of Akt or downstream molecules of mTORC1, as compared to the single treatments. Our study suggests that targeting multiple kinases in IGF-1R signaling may be a promising therapeutic approach.
URLPMID:3632057 [本文引用: 1]

Nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ) refers to a set of genome maintenance pathways in which two DNA double-strand break (DSB) ends are (re)joined by apposition, processing, and ligation without the use of extended homology to guide repair. Canonical NHEJ (c-NHEJ) is a well-defined pathway with clear roles in protecting the integrity of chromosomes when DSBs arise. Recent advances have revealed much about the identity, structure, and function of c-NHEJ proteins, but many questions exist regarding their concerted action in the context of chromatin. Alternative NHEJ (alt-NHEJ) refers to more recently described mechanism(s) that repair DSBs in less-efficient backup reactions. There is great interest in defining alt-NHEJ more precisely, including its regulation relative to c-NHEJ, in light of evidence that alt-NHEJ can execute chromosome rearrangements. Progress toward these goals is reviewed.
URLPMID:3494418

78 The rate of DSB repair depends on the cell-cycle stage at time of damage 78 NHEJ dominates in G1 and in G2 even in the presence of a functional HR pathway 78 NHEJ and HR are used during S and G2, and the balance between them changes gradually 78 Highest HR use is at the peak of active replication, correlating with slower repair
URL [本文引用: 1]
URLPMID:26437586 [本文引用: 1]

Of the four known pathways for repairing DNA DSBs, some evolved towards high-fidelity processes (HR and C-NHEJ), while others are intrinsically mutagenic (alt-EJ and SSA). Some repair pathways are end resection-independent (C-NHEJ), while others are end resection-dependent (HR, alt-EJ, and SSA). End resection likely plays a key role in dictating DNA repair pathway choice. Homology-based repair pathways (HR, alt-EJ, and SSA) are competitive and mutually regulated around the RAD51 presynaptic and postsynaptic steps of HR. Error-prone repair pathways can compensate for the loss of HR. Pol (an alt-EJ polymerase) is upregulated in HR-deficient cancers: loss of the HR and Pol胃-mediated alt-EJ pathways is synthetic lethal.
URLPMID:3087377 [本文引用: 1]

相应再结合(HR ) 包括在脱氧核糖核酸双 stranded 裂缝(DSB ) 的修理工作的一系列互连的小径并且内部海滨交叉连接(ICL ) 。另外,再结合在阻止或碎的复制叉的恢复为 DNA 提供批评支持,贡献脱氧核糖核酸损坏的忍耐。蛋白质的一个中央核心,最非常 RecA 相当或相同的事物 Rad51,催化代表 HR 的关键反应:相同搜索和脱氧核糖核酸海滨侵略。再结合的多样的功能在对与核心蛋白质一起执行补加的功能的上下文特定的因素的需要被反映。适当地修理复杂脱氧核糖核酸损坏并且解决 DNA 应力的无能导致 genomic 不稳定性并且贡献癌症病原学。在 BRCA2 重组基因的变化引起倾向到胸和卵巢的癌症以及 Fanconi 贫血症,癌症倾向症候群在脱氧核糖核酸的修理由一个缺点描绘了内部海滨交叉连接。再结合的细胞的功能对癌症的基于 DNA 的治疗形式也适切,它指向由是为再结合小径的底层的脱氧核糖核酸损害的直接或间接的正式就职复制房间。这评论集中于关于 DSB 和 ICL 修理以及复制叉支持的 HR 的机械学的方面。
URL [本文引用: 1]
