 ,中国农业科学院北京畜牧兽医研究所,北京 100193
,中国农业科学院北京畜牧兽医研究所,北京 100193Application of whole transcriptomics in animal husbandry
Tianpei Shi, Li Zhang ,Institute of Animal Science, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing 100193, China
,Institute of Animal Science, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing 100193, China通讯作者:
编委: 赵要风
收稿日期:2018-07-31修回日期:2018-10-22网络出版日期:2018-11-15
| 基金资助: |
Received:2018-07-31Revised:2018-10-22Online:2018-11-15
| Fund supported: |
作者简介 About authors
石田培,在读硕士研究生,专业方向:动物遗传育种与繁殖E-mail:1337684764@qq.com。

摘要
关键词:
Abstract
Keywords:
PDF (630KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
本文引用格式
石田培, 张莉. 全转录组学在畜牧业中的应用[J]. 遗传, 2019, 41(3): 193-205 doi:10.16288/j.yczz.18-218
Tianpei Shi, Li Zhang.
在后基因组学研究中,转录组学是解读基因组功能元件和揭示细胞及组织分子机制的基础,在生物表型和基因表达研究中占据了重要地位[1]。转录组一般指狭义转录组,即能够编码蛋白的RNA, 而生物学中的转录本概念则为生物体特定细胞或 组织在某一特定条件下的所有转录产物,涵盖了编码RNA (mRNA)和非编码RNA (non-coding RNA, ncRNA)[2]。同相对稳定的基因组比较,转录组会根据生理状态、生长阶段、生长环境的变化而变化[3],具有高度动态可变的特性。除此之外,转录组图谱中含有丰富的生物学信息,包括基因表达丰度及差异、基因结构、反义转录本、选择性剪切、单核苷酸多态性和基因融合等。
生物体是一个错综复杂的网络,构成复杂有机体的任何简单分子都不能孤立存在或行使功能,如转录组中的各类RNA。这些不同类型的RNA生物学功能各异,参与众多信号通路的调控。单一的mRNA或ncRNA研究缺乏关联性,对多种RNA 信息进行整合分析,探索潜在的网络调控机制则成为转录组学研究的趋势。在传统转录组学(以mRNA[4]为主)研究中,样品总RNA的提取通常利用Oligo (dT)磁珠富集法,该方法能有效发掘富含poly (A)尾巴的RNA[5],包括mRNA和一小部分长链非编码RNA (long non-coding RNA, lncRNA),但过滤掉了其他poly (A) minusRNA组分,即无poly (A)尾RNAs,因此导致circRNA (circular RNA)和部分lncRNA的丢失,不能全面地反映转录本的真实情况。Yang等[6]首次提出了基于poly (A) minus富集的RNA-seq方法,可将sno-lncRNAs (small nucleolar RNAs)、ciRNAs (circular intronic RNA)和circRNAs等这类非poly (A)结尾的新型RNA分子富集并保留下来。至此,包括miRNA[7]、lncRNA[8,9]和circRNA[10,11]等非编码RNA的全转录组测序研究应运而生。本文综述了基于RNA-seq 和Small RNA-seq技术的全转录组研究概况,总结了全转录组测序的一般流程和常用策略,最后对畜牧业未来的发展趋势进行展望。
1 全转录组测序概述
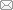
全转录组是指在一定时空状态下有机体特定细胞或组织能够转录出的所有转录本[12],其中蕴含着重要的生物学调控规律。丰富的RNA组学信息可用于开展差异表达ncRNA的靶基因预测、差异表达ncRNA和mRNA的正负相关性分析、ceRNA (competing endogenous RNAs)对靶向mRNA的功能富集分析及关键基因挖掘等研究。全转录测序是通过高通量RNA-seq测序技术对RNA序列进行测序,并通过一些定量平台和技术反应其表达量和表达差异,从而形成表达图谱。全转录组学分析就是以表达谱为基础,对RNA进行鉴定和注释,预测相应靶细胞或编码潜能,并基于GO(Gene Ontology)、COG (Clusters of Orthologous Groups)、KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes)等数据库进行功能富集、聚类分析、信息挖掘和通路探究等。不同于传统转录组学,全转录组学在mRNA研究基础上,涵盖了lncRNA、circRNA、miRNA、siRNA(small interfering RNA)和piRNA(piwi-interacting RNA)等多种非编码RNA及其之间的调控网络分析。目前,转录组测序主要集中在单一RNA的定量表达和注释分析上,而全转录组学测序可同时对多种RNA进行鉴定及关联分析(图1)。图1
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图1全转录组测序一般流程
Fig. 1General process for whole transcriptome sequencing
2 全转录组测序研究的一般技术流程和方法
2.1 测序样品的准备
在样品采集过程中,组织中的RNA 极易受内源或外源RNA酶作用而降解,同样也容易受到蛋白质、DNA、同源和外源酚类等物质的污染,因此,样品质量和保存条件是决定试验结果质量的关键。不同物种不同组织部位的RNA得率大不相同,在动物中,肝脏、脾脏和胰脏组织的得率较大,而肌肉、脑和心脏等组织得率较小。在皮肤、骨骼和毛发中RNA的提取难度较大,效果也较差。在准备样品时,首选新鲜组织,剔除非研究所需的组织类型。若组织体积较大,多管分组置于-80℃或液氮中长期保存。2.2 建库测序
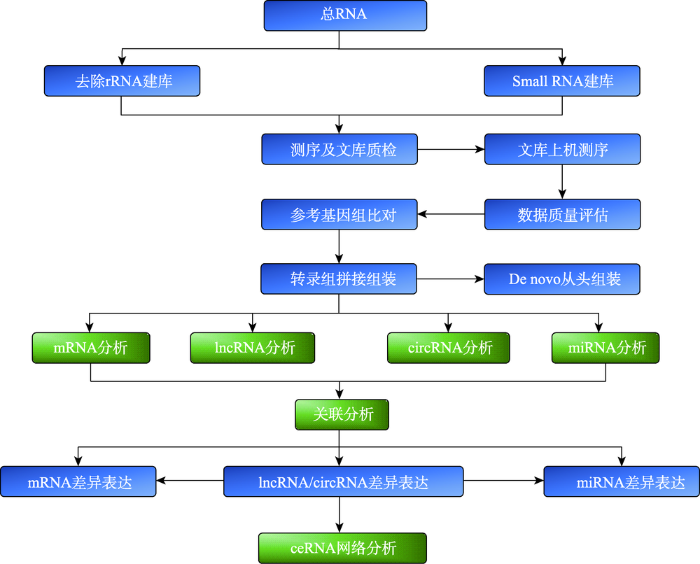
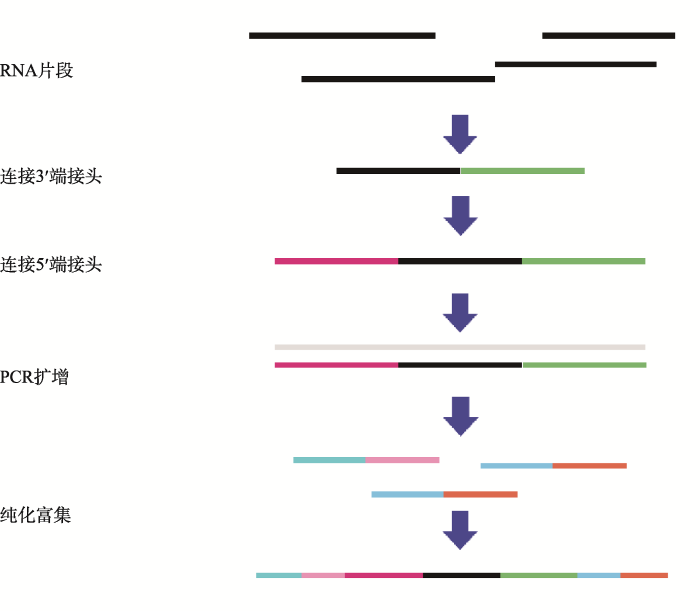
2.2.1 cDNA文库构建和RNA测序总RNA质检后便可建库,由于miRNA与其他3类RNA序列长度差异较大,需要使用SE (single- end)和PE (paired-end)两种测序策略同时建立两个文库。链特异性建库的具体步骤如下(图2):(1)通过试剂盒在样品总RNA中去除rRNA;(2)利用六碱基随机引物合成第一条cDNA链;(3)第二条cDNA链合成时,用dUTP代替dTTP,使链上布满U位点;(4)在3°端加A,加接头;(5)使用USER酶在尿嘧啶位置上产生一个单核苷酸缺口,借此消化掉第二条链,只保留第一条链;(6) PCR扩增。小RNA建库的具体步骤如下(图3):(1)在3°端加接头;(2)在5°端加接头;(3)反转录扩增;(4)用凝胶纯化富集扩增的cDNA后测序。在测序时,理论上数据量越大越利于后续低丰度基因的完整组装,但实际上并非数据量越大越好,需要根据物种情况及相关研究决定数据量的大小。
图2
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图2链特异性建库流程
Fig. 2The construction process for chain-specific library
图3
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图3小RNA建库流程
Fig. 3The construction process for small RNA library
2.2.2 原始数据预处理
测序产生的数据是一系列不能直接使用的原始数据,主要是FASTQ格式的读段(reads)。其中除实验所需的碱基质量信息之外,还包括测序仪器名称、上机次数、试剂型号等信息。原始数据在建库过程或者测序过程中会产生大量低质量读段、较短的序列、含N序列甚至是一些污染序列(如细菌基因序列)[13]、接头序列、载体序列等,因此在数据分析之前,应对原始数据进行过滤、剪切和校正,以确保后期读段定位、转录本组装、基因定量等流程的顺利开展。目前可用的质控软件是FastQC和NGSQC[14]、Qualimap2[15]、HTQC[16]、QCchain[17]、almostSignifican[18]、fastq-clean[19]及FaQCs[20]等,最常用的是FastQC和HTQC。FastQC可作为一个单独的JAVA程序,在速度上远超其他工具,极短时间内就可以运行数千万的读段,输入文件的选择性也较大,如压缩或未压缩的EASTQ或SAM/BAM文件。FastQC除能列出读段的数目及质量编码以外,还能可视化报告碱基内容及质量、读段长度和重复序列等信息。在实际操作中,可联合使用上述质控软件以达最佳过滤效果。
2.2.3 读段定位及转录本重组装
由原始数据进行深度清理及质量控制后获得待分析数据(clean reads),需要通过一系列软件将读段比对到参考基因组或者转录本上,并根据实际定位情况进行转录本组装[21]。在全转录组数据分析时,选择比对程序时还需考虑剪接比对(unspliced aligners)情况[22]。当生物体没有内含子或进行miRNA测序时,可以使用Quality (MAQ)[23]、Burrow-Wheeler Aligner (BWA)[24]和Bowtie[25]等连续比对软件,这些方法用于识别已知外显子和接头,不能识别由可变剪切所产生的新型外显子。但当读段定位至外显子-外显子的交界接头处或作图到有内含子的基因组时,则必须使用剪接比对程序,如TopHat[26]、MapSplice[27]、STAR[28]和GSNAP[29]等。可先将读段分成两个短片段再参与定位,同时还可记录分割数据以供查找后续转录本,该方法能够识别由可变剪切产生的新转录本。一般情况下,先利用Bowtie进行初步匹配,用匹配成功的reads来获取基因组覆盖区域,预测剪接点(splice junction)局域。然后利用Tophat将未成功匹配的reads划分到splice junction序列上。如果研究物种没有参考基因组或转录组时,需要将读段自行组装成可用的参考序列,然后将所有测序读段通过从头组装生成重叠群和单一序列,再进行后续数据分析。目前,有多种组装程序可供分析使用[30,31],如Newbler[32]、MIRA[33]、CAP3[34]、Seq-Man[35]、TGICL[36]、stackPACK[37]、Velvet[38]、AbySS[39]、ALLPATHS2[40]、Oases[41]、SOAPdenovo[42]、Multiple-k method[43]、Scaffolding using translation mapping (STM)、Trinity[44]和PCAP[45]等。
2.2.4 表达量化及差异分析
经过读段定位后,可根据读段在转录本上的分布情况预测基因丰度。一般来说,通过软件分析获得的注释文件中会含有转录本分布信息,能够通过分析读段的匹配情况来识别新的转录本。在高等动物的生命活动调控过程中,存在可变剪切(alternatively splice, AS)等一系列复杂的调控系统,致使全部转录物不能直接对应基因。此外,还存在不同转录本外显子共享、读段不能跨越多个剪接位点等问题。因此,需要先进行可变剪接识别[46]。现阶段,常用转录本识别软件包括Stringtie[47]、cufflinks[48]、CIDANE[49]、GRIT[50]、TransComb[51]、iReckon[52]、SLIDE[53]、Montebello[54]、Augustus[55]、IsoLassociation[56]、Scripture[57]、Traph[58]和MITIE等。人(Homo sapiens)和斑马鱼(Danio rerio)等基因信息注释完整的物种可直接进行基因预测定量分析,但对于一些基因注释信息不完整的物种需要先进行转录本的预测。目前已完成的大量转录组测序数据快速完善了遗传数据库,反复检验校对了基因注释信息,推动了分子生物学的研究进展。
测序过程中测序深度、基因片段大小、运用算法、实验批次等因素极易造成误差,所以在定量时应使用标准化的方法消除差异,最常用的样本内标准化方法包括RPKM[59]、FPKM、TMP[60]和KPKM等。根据比对到基因上的reads或者fragments数目,进行基因长度和测序总量归一化后,即可统计表达量。常用的转录本定量软件包括HTSeq[61]、featureCounts[62]、StringTie、Cufflinks、RSEM[63]、Sailfish[64]、kallisto[65]、IsoLasso和NURD[66]等。为确定在不同条件或平台的表达差异情况,经过量化和标准化表达水平的基因仍需利用测序覆盖度估测表达丰度分布[67,68]。
RNA-seq数据的差异表达(differential expression, DE)分析往往以单变量的方式进行,很难拟合出一个普遍适用的统计模型,因此根据生物统计学原理将DE分析软件进行下列分析对比(表1)。为使表达分布符合统计方法的假设,RNA-seq数据会被某种方式归一化。按照归一化在DE分析中的前后顺序可将常用软件分为两类:第一类是先进行标准化处理再通过统计学原理计算表达差异,包括TMM[69]、DESeq[70]、PoissonSeq[71]和UpperQuartile[72]等;第二类是将归一化作为DE分析的步骤,在处理时直接执行归一化,如FPKM、RPKM和TPM,但可信度较差。
Table 1
表1
表1 差异表达分析软件
Table 1
| 软件名称 | 所属类型 | 原理方法 | 特点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| edgeR | R-Bioconductor | 负二项计数 | 高保守性 |
| DESeq | R-Bioconductor | 负二项计数 | 高保守性,低假阳性 |
| DESeq2 | R-Bioconductor | 负二项计数 | 保守性较高 |
| tweeDESeq | R-Bioconductor | 特威迪分布族计数 | 普适性差 |
| ebSeq | R-Bioconductor | 异构体反褶积 | 可反应差异表达的异构体 |
| Limma[73] | R-Bioconductor | 连续数据的线性模型 | 需要将计数转换成连续的值 |
| SAMSeq[74] | R包 | 非参数检验 | 需要多次重复 |
| Cuffdiff | Linux命令行 | 异构体反褶积 | 可反应差异表达的异构体及基因 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
2.3 基因功能分析
生物信息学主要用数学及统计学的方法对生物信息进行存储、分配、检索及分析,是一门集合生命科学、自然科学与信息科学的新学科。目前,生物信息学在生命科学研究中应用十分广泛,在全转录组研究中也占据重要地位。在全转录组学分析中主要以差异基因的功能富集、候选基因的功能预测、调控网络的构建等分析为主。当前以GO、COG及KEGG数据库为基础的分析工具包、软件和网站众多,如基于R语言的GSA、PADOG、SAFE、Globaltest、Sigpathway、GAGE、GSVA、PLAGE、ZSCORE、SSGSEA、MRGSE、ANCOVA、CAMERA、SPIA、TopoGSA、ToPASeq、NetGSA、NEA和GOGANPA等工具包;DAVID、GOstat、GenMAPP、GOMiner、Onto-Express、EnrichNet和NOA等网站;MetaCore、Cytoscape和GSEA等软件。以上分析软件各有千秋,功能也不尽相同,在数据处理与分析时,应根据实验目选择合适的方法。如需更系统地反映分子调控机制,还可结合其他基因组学手段如全基因组测序、RNA甲基化、表观修饰等数据进行联合分析。3 全转录组学技术在畜牧业中的应用
3.1 全转录组测序在猪中的应用
猪(Sus scrofa)的饲养对畜牧业发展乃至民生都至关重要。不同品种猪的肌纤维类型对猪肉品质有很大影响,但潜在的分子机制仍不清楚。近年来,有关猪非编码RNA的功能研究开展得很多。为探究miRNA在猪骨骼肌中的作用,Mcdaneld等[75]分别选取了增殖中的卫星细胞(4~代)、胚胎(60、90、105日龄)、出生胎儿和成年猪组织进行了全转录组研究,发现了12个新型miRNA与肌肉生长发育密切相关,其中肌肉特异性miR-206在卫星细胞中近乎缺失,但在其他发育阶段表达量却很高;miR-1在成年猪中的表达丰度最高;miR-133在胚胎期和初生时的丰度极低甚至检测不到,但miR-368、miR-376和miR-423-5p在初生猪中极高;miR-432表达量在胚胎发育早期最高,随后逐渐降低。该研究是对猪胚胎发育期骨骼肌miRNA较为全面的转录组分析,为深入探究猪骨骼肌miRNA调控机制提供了理论基础。沈一飞[76]利用RNA-seq和Small RNA-seq技术对瘦肉型约克夏猪和脂肪型金华猪进行了甲状腺组织的mRNA、lncRNA和miRNA共表达鉴定与比较,结果发现差异表达mRNA 492个,差异表达lncRNA 48个和miRNA 18个。通过功能分析和聚类,共有256个RNA(其中18个miRNA、1个lncRNA)参与到同一个调控网络中。在整个调控网络中,发现ssc- miRNA-221-5p、ssc-miRNA-708-5p、ssc-miRNA-532- 3p和novel_12等发挥重要调控作用。Li等[77]对从胎儿期到成年期期间获得的组织混合物制备的10个小RNA测序文库中的荣昌猪(Rongchang pigs) miRNA进行全面检测,通过哺乳动物miRNA、前体发夹(pre-miRNA)、高覆盖率猪基因组装配(2009年4月)和表达序列标签(EST)的分析,将猪miRNAome的所有组成部分扩展到867个pre- miRNAs (623个基因组坐标),编码1004个miRNA,其中777个是独特的。对47个组织特异性样品中选定的30个miRNA进行qRT-PCR实验,发现测序数据和试验结果一致。Sun等[78]对长白猪(Landrace)和兰塘猪(Lantang pigs)背最长肌进行了全转录组测序研究,从22 469个编码转录物中筛选出547个差异表达mRNA,通过生物信息学分析挖掘出与肌肉生长发育相关的 17个基因。此外还发现差异表达的5566个lncRNA和4360个circRNA。其中,3376个lncRNA和1401个circRNA在Lantang文库中上调表达,而1590个lncRNA和2959个circRNA下调表达。通过结合匹配的miRNA谱分析测序数据,鉴定出26种参与ceRNA网络的海绵载体,包括19种lncRNA、40种circRNA和9种mRNA。全转录组研究提供了一种全新的分析方法,对解析猪肌肉生长发育规律和疾病发生机制具有重要意义。3.2 全转录组测序在禽类中的应用
我国家禽遗传资源丰富,地方品种各具特色,但由于总体生产水平较低,许多优良性状利用效率不高。随着分子生物学和生物信息学的发展与融合,通过各种技术和手段,已鉴定出一批与生长、繁殖等重要经济性状相关的分子标记和候选基因。Yu等[79,80]选取了6和10日龄的鸡胚左(L)、右(R)卵巢作为样品,通过全转录组测序技术对卵巢的退化进行了研究。在6R样品中产生31 066 414个序列读数,在6L样品中产生31 900 200个序列读数,在10R样品中产生31 400 070个序列读数,在10L样品中读取35 504746个序列。这些数据中,大约73.33%的序列可以定位到鸡胚卵巢的参考基因组序列上。鸡胚卵巢的发育受许多基因和信号通路的调控,通过对差异表达基因比对和通路功能聚类发现了22个与卵巢发育和退化相关的基因。其中转录水平排名前20的卵巢基因可能与碳代谢、吞噬体及钙信号传导密切相关。Glazov等[81]在已发现的miRNA基础上进行了深度挖掘,将3个小RNA文库同时比较并严格区分真正miRNA前体与结构相似的RNA,共鉴定到361个新的miRNA、88个新的miRNA候选物、18个mirtrons (包括6个新的非典型mirtron候选物)和21个mirtron候选物。为识别潜在的禽类特异性miRNA,同时与人、狗(Canis lupus familiaris)、斑马鱼、爪蟾(Xenopus laevis)和蜥蜴(Bachia Oxyrhinas)进行保守进化分析,结果表明只有6种miRNA在非禽类脊椎动物中具有保守性,剩余miRNA可能具有鸟类和/或鸡系特异性。Li等[80]分别从孵育10天、12天、14天和18天的白来航鸡(White Leghorns)蛋胚中收集骨骼肌(胸大肌),经过RNA-seq技术测序并与已发布的数据库进行比对,筛选到281个新型基因间lncRNA,对这些lncRNA进行保守性分析,并利用UCSC数据库评分,结果表明以上lncRNA的保守性均高于随机非编码序列,但远低于蛋白质编码基因。该研究是首例有关白来航鸡骨骼肌lncRNA的分析,鉴定出的新型lncRNA极大丰富了鸡ncRNA数据库。近年来,鹅(Anser cygnoides orientalis)以其适应性强、生长快、营养成分丰富和投入要求低而备受关注。此前,Kang等[82]通过抑制性消减杂交(suppression subtractive hybridization, SSH)方法鉴定了一些与鹅从产卵阶段到产蛋阶段繁殖相关的差异表达基因,Guo等[83]也使用相同的方法在产蛋阶段和育雏阶段发现了若干差异表达的基因。Xu等[84]采用短读序列技术(Illumina)对10只380日龄的雌性浙东白鹅(Goose)的卵巢样本进行了从头转录组装配,使用Illumina RNA-seq和DGE深度测序并绘制出鹅卵巢组织的转录组图谱,得到67 315 996个100 bp的短读数,组装成130 514个独特序列。基于已知蛋白质的BLAST结果,分析鉴定到52 642个目标序列。该研究分析了鹅产蛋、育雏期间的转录变化情况,鉴定出大量与卵泡发育和生殖相关的基因。
病理性肥胖是鸭养殖业所面临的重要问题之一,其分子机制仍然未知。Chen等[85]对家养鸭与野鸭两个品种腹部脂肪进行转录组测序分析,预测了23 699个未注释基因,确定了753个差异表达基因。在北京鸭(Anatinae)中,一些与脂质代谢的相关基因(IGF2、FABP5和BMP7等)和致癌基因(RRM2、AURKA和CYR61等)上调表达,而与肿瘤抑制和免疫相关的基因(TNFRSF19、TNFAIP6、IGSF21和NCF1等)被下调,这些数据表明鸭的肿瘤发生可能与病理性肥胖密切相关。此外,发现280 576个单核苷酸变异在两个品种之间存在差异,包括8641个异构变异,富含参与脂质和免疫相关途径的基因,表明与鸭的代谢功能和免疫相关功能密切相关。
3.3 全转录组测序在反刍动物中的应用
近年来国内牛羊肉市场需求不断增加,这对牛羊的育种和养殖工作提出了更高的要求,只有充分了解牛羊生长发育与繁殖等性状的发生机制,才能提高生产效率,全转录组学则为其提供了全新的研究手段。Di等[86]在滩羊(Tan)和小尾寒羊(STH)的卵巢中鉴定出483个miRNA (包括97个已知的、369个保守的和17个预测的新miRNA)。基于KEGG分析,一些差异表达miRNA的靶基因参与生殖激素相关途径(如类固醇生物合成、雄激素和雌激素代谢和GnRH信号传导途径)以及卵泡和黄体发育相关途 径,这对绵羊的繁育具有重要意义。Chang等[87]使用新一代测序技术(Solexa高通量测序技术)研究了绵羊黄体期卵巢组织,鉴定出267种新的miRNA,并利用qRT-PCR和Northern印迹证实了在绵羊卵巢和睾丸中表达的一种新型miRNA (ovis_aries_ovary m0033_3p)。根据序列和结构的一致性,推测ovis_ aries_ovarym0033_3p具有类似于hsa-miR-214-3p的功能,能够参与细胞存活、胚胎发育、繁育生殖和卵巢癌抗性的精细调节。张世芳等[88]采用Solexa技术对5头特克赛尔羊(Texel)进行miRNA深度测序,获得了16 532 850条原始序列读数。通过与哺乳动物成熟miRNA数据库、miRNA前体序列、绵羊基因组数据库的比对分析,更新miRNA前体序列库至1529条,编码的miRNA成熟体序列增至1999条。Miao等[89]对道赛特绵羊(Dorset)和小尾寒羊(Han)卵巢组织测序,鉴定出可能参与繁殖力调节的候选基因,这些候选基因参与各种细胞活动,如代谢级联、催化功能和信号转导。此外,通过miRNA谱分析鉴定了每组绵羊特有的特异性miRNA,发现若干与生殖力调控相关的miRNA。Billerey等[90]检测了9头利木赞牛犊(Limousin)的胸肌样本,每个文库约获得14~45百万个配对末端读数,发现418种lincRNA (large intergenic non-coding RNAs),与已知的10 775种蛋白编码基因存在显著差异。Sun等[91]利用Ribo-Zero RNA-seq技术深度剖析了胚胎、犊牛和成年牛骨骼肌的转录组谱,发现犊牛和成年牛之间的表达水平高度相关。在胚胎期有数百个基因显著表达,但在出生后至少减少了10倍,表明这些基因在肌肉发育中具有潜在作用。此外,该研究首次分析了牛骨骼肌中全部转录异构体,发掘出36 694个新型异构体,检测到185 036个SNP和12 428个短插入缺失(InDel)位点。研究发现可变剪接事件、SNP和InDel的数量在胚胎中比在犊牛和成年牛中更多,这表明基因表达在胚胎中最活跃。Cánovas等[92]通过转录组学测序对7头荷斯坦奶牛(Holstein cow)的乳样品进行了SNP筛选,共检测到19 175个差异表达基因,100 734个SNP位点,其中33 045个与荷斯坦奶牛SNP位点重合,这些SNP位于泌乳期间表达基因的编码区中,可用于荷斯坦奶牛乳用性状的基因变异分析和关联研究。
在梅花鹿(Cervus nippon taiouanus)的育种研究中,Yao等[93]对鹿茸进行了转录组测序,组装出89 001个独特序列(平均大小450 bp),发现了一些高度表达的基因参与鹿茸快速生长的调节,包括转录因子、信号分子和细胞外基质蛋白。这些数据是当前梅花鹿最全面的序列资源,为鹿的分子遗传学和功能基因组学的研究提供了理论基础。
3.4 全转录组测序在马属动物中的应用
全转录组研究在马属动物中开展得较少,目前主要是通过转录组学测序技术进行基因挖掘、注释和功能预测。Xie等[94]从头组装了驴(Equus africanus asinus)白细胞的转录组,鉴定出264 714个不同序列,预测了38 949个蛋白质片段。通过比较驴、马(E. caballus)和野马(E. przewalskii)的蛋白质序列,将驴蛋白片段与哺乳动物表型相关联。通过比较驴和马的外耳性状相关蛋白,鉴定出3种与耳形大小相关的蛋白质HIC1、PRKRA和KMT2A。Scott等[95]通过转录组测序对马的lncRNA进行注释,发现了20 800新型转录本,证明了lncRNA独有的特征,包括低表达、低外显子多样性和低水平的序列保守性。该研究结果所提供的候选基因可作为日后lncRNA注释的基准。近年来发表了大量关于马运动机能、骨骼发育的文献报道,一部分是通过马组织的RNA-seq数据改进蛋白质编码基因的结构注释,另一部分是对RNA序列的分析。如Park等[96]对6匹纯种马运动前后的血液和肌肉进行全转录测序,通过与前人的研究对比,发现超过19 417个新型单基因簇,鉴定出189 973个单核苷酸位点变异(single nucleotide variants, SNV)。使用差异表达分析,确定了多个运动调节基因:血液中有62个上调基因和80个下调基因,肌肉中有878个上调基因和285个下调基因。结果表明,在差异表达的基因中有91个转录因子编码基因,其中包括56个功能未知的转录因子候选物可能与早期调节运动机制相关;此外,还发现了新型RNA表达模式:同一基因的不同可变剪接形式在运动前后表现出反向表达模式。该研究首次提供了马转录组数据和较为全面的分析结果,包括运动前后表达的基因,以及与运动相关的候选基因:6个运动相关基因和91个早期调节转录因子,3个高SNV密度的基因,以及4个交替表达的剪接体。
3.5 全转录组测序在其他特种经济动物中的应用
特种经济动物养殖已成为调整农村产业结构、发展特色经济的新亮点,为了发挥皮毛的最大经济价值,科研人员开始研究关于被毛颜色的调控机制。牛晓艳等[97]首先对不同毛色的獭兔(Rex rabbit)进行测序和差异基因分析,找到12 408个差异表达基因,然后通过KEGG分析将得到的差异基因聚类富集到相关代谢通路上,结果发现8个与黑素细胞分化相关的差异基因。宋兴超[98]利用RNA-seq技术对水貂(Lutreola)被毛色素沉积机理进行了研究,鉴定出不同时期被毛黑素含量的变化,并根据水貂皮肤组织中成熟黑素细胞的分布特点,开展SNPs检测,将 不同基因突变体与水貂毛色表型进行关联分析。mRNA定量表达验证结果表明,KITLG、LEF1、 DCT、TYRP1、PMEL、TYR、Myo5a、Rab27a和SLC7A11等基因参与了黑素细胞发育、黑素小体前体形成、黑素小体转运和真黑和褐黑色素合成等生物学过程。4 结语与展望
全转录组学以其精准、系统、直观的技术优势为畜禽重要经济性状功能基因的挖掘、鉴定与验证提供了新的技术平台和手段,并已广泛地运用在临床医学、药学、生物学、水产学和农林学等多个领域,为人类疾病研究、新药研发和动植物育种等开辟了新的思路。但是,全转录组学在畜牧领域的研究较其他领域而言起步较晚,研究还不够深入,尤其在羊上,转录组的研究目前还主要集中在小RNA测序和基因注释上。本研究团队将开展绵羊全转录组研究,并对其生长性状、肉用性状等重要经济性状进行解析和应用。参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
URLPMID:10866209 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract Experimental genomics in combination with the growing body of sequence information promise to revolutionize the way cells and cellular processes are studied. Information on genomic sequence can be used experimentally with high-density DNA arrays that allow complex mixtures of RNA and DNA to be interrogated in a parallel and quantitative fashion. DNA arrays can be used for many different purposes, most prominently to measure levels of gene expression (messenger RNA abundance) for tens of thousands of genes simultaneously. Measurements of gene expression and other applications of arrays embody much of what is implied by the term 'genomics'; they are broad in scope, large in scale, and take advantage of all available sequence information for experimental design and data interpretation in pursuit of biological understanding.
URLPMID:19716875 [本文引用: 1]

The dogmatic view of RNA as a mere necessity in the transfer of information between DNA and proteins has during recent years come into question. Novel approaches and new technology has revealed an unprecedented level of inherent complexity in the mammalian transcriptome. Here, the majority of nucleotides are expressed, in sharp contrast to the 65021.2% of the human genome harboring protein coding information. Also, >0250% of genomic loci contain antisense and interleaved transcription, a conservative estimate since non-coding RNA is highly regulated between tissues and developmental stages, which has only been investigated to a limited extent. Subsequent focus on RNA with no coding potential has revealed numerous species with novel functions, and deep sequencing studies imply that many remain to be discovered. This review gives an overview of the plasticity and dynamics of the mammalian transcriptome and the prevailing interpretation of its effect on the complexity of species.
URL [本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
URLPMID:21324177 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract BACKGROUND: RNAs can be physically classified into poly(A)+ or poly(A)- transcripts according to the presence or absence of a poly(A) tail at their 3' ends. Current deep sequencing approaches largely depend on the enrichment of transcripts with a poly(A) tail, and therefore offer little insight into the nature and expression of transcripts that lack poly(A) tails. RESULTS: We have used deep sequencing to explore the repertoire of both poly(A)+ and poly(A)- RNAs from HeLa cells and H9 human embryonic stem cells (hESCs). Using stringent criteria, we found that while the majority of transcripts are poly(A)+, a significant portion of transcripts are either poly(A)- or bimorphic, being found in both the poly(A)+ and poly(A)- populations. Further analyses revealed that many mRNAs may not contain classical long poly(A) tails and such messages are overrepresented in specific functional categories. In addition, we surprisingly found that a few excised introns accumulate in cells and thus constitute a new class of non-polyadenylated long non-coding RNAs. Finally, we have identified a specific subset of poly(A)- histone mRNAs, including two histone H1 variants, that are expressed in undifferentiated hESCs and are rapidly diminished upon differentiation; further, these same histone genes are induced upon reprogramming of fibroblasts to induced pluripotent stem cells. CONCLUSIONS: We offer a rich source of data that allows a deeper exploration of the poly(A)- landscape of the eukaryotic transcriptome. The approach we present here also applies to the analysis of the poly(A)- transcriptomes of other organisms.
URLPMID:19239886 [本文引用: 1]

Over the last decade, 6520–30 nucleotide RNA molecules have emerged as critical regulators in the expression and function of eukaryotic genomes. Two primary categories of these small RNAs—short interfering RNAs (siRNAs) and microRNAs (miRNAs)—act in both somatic and germline lineages in a broad range of eukaryotic species to regulate endogenous genes and to defend the genome from invasive nucleic acids. Recent advances have revealed unexpected diversity in their biogenesis pathways and the regulatory mechanisms that they access. Our understanding of siRNA- and miRNA-based regulation has direct implications for fundamental biology as well as disease etiology and treatment.
URL [本文引用: 1]
URLPMID:22959273 [本文引用: 1]

78 Intron-derived sno-lncRNAs are processed on both ends by the snoRNA machinery 78 Sno-lncRNAs are functionally distinct from classical snoRNAs 78 The genomic region encoding the most abundant sno-lncRNAs is associated with PWS 78 PWS region sno-lncRNAs interact with Fox2 and alter patterns of splicing
URLPMID:24035497 [本文引用: 1]

61Circular intronic RNAs accumulate in human cells owing to escape from debranching61Their processing depends on RNA motifs near 5′ splice site and branchpoint61ciRNAs regulate parent gene expression by modulating elongation Pol II activity
URLPMID:25242744 [本文引用: 1]

The competition of RNA pairing mediated by flanking intronic complementary sequences regulates exon circularization efficiency and alternative circularization.
URLMagsci [本文引用: 1]

转录组是特定组织或细胞在某一发育阶段或功能状态下转录出来的所有RNA的集合。转录组研究能够从整体水平研究基因功能以及基因结构, 揭示特定生物学过程以及疾病发生过程中的分子机理。RNA-Seq作为一种新的高效、快捷的转录组研究手段正在改变着人们对转录组的认识。RNA-Seq利用高通量测序技术对组织或细胞中所有RNA反转录而成的cDNA文库进行测序, 通过统计相关读段(reads)数计算出不同RNA的表达量, 发现新的转录本; 如果有基因组参考序列, 可以把转录本映射回基因组, 确定转录本位置、剪切情况等更为全面的遗传信息, 已广泛应用于生物学研究、医学研究、临床研究和药物研发等。文章主要介绍了RNA-Seq原理、技术特点及其应用, 并就RNA-Seq技术面临的挑战和未来发展前景进行了讨论, 为今后该技术的研究与应用提供参考。
URLMagsci [本文引用: 1]

转录组是特定组织或细胞在某一发育阶段或功能状态下转录出来的所有RNA的集合。转录组研究能够从整体水平研究基因功能以及基因结构, 揭示特定生物学过程以及疾病发生过程中的分子机理。RNA-Seq作为一种新的高效、快捷的转录组研究手段正在改变着人们对转录组的认识。RNA-Seq利用高通量测序技术对组织或细胞中所有RNA反转录而成的cDNA文库进行测序, 通过统计相关读段(reads)数计算出不同RNA的表达量, 发现新的转录本; 如果有基因组参考序列, 可以把转录本映射回基因组, 确定转录本位置、剪切情况等更为全面的遗传信息, 已广泛应用于生物学研究、医学研究、临床研究和药物研发等。文章主要介绍了RNA-Seq原理、技术特点及其应用, 并就RNA-Seq技术面临的挑战和未来发展前景进行了讨论, 为今后该技术的研究与应用提供参考。
URL [本文引用: 1]

伴随高通量测序技术的快速发展,转录组测序(RNA-Seq)技术在各个研究领域已经得到广泛的运用.RNA-Seq通过分析不同细胞或者组织转录组的表达情况来揭示细胞的基因表达情况,结构特点和调控规律.近年来基于高通量测序技术的RNA-Seq分析方法发展迅速,涌现出一大批相关的分析方法和工具,如何根据实际需求选择合适的工具和分析流程,成为广大科研人员面临的问题.本文参照近几年在RNA-seq技术研究领域发表的文献,综述了RNA-Seq应用实际过程中涉及的分析方法、软件工具及其选用标准,为相关的研究和应用提供信息和参考.
URL [本文引用: 1]

伴随高通量测序技术的快速发展,转录组测序(RNA-Seq)技术在各个研究领域已经得到广泛的运用.RNA-Seq通过分析不同细胞或者组织转录组的表达情况来揭示细胞的基因表达情况,结构特点和调控规律.近年来基于高通量测序技术的RNA-Seq分析方法发展迅速,涌现出一大批相关的分析方法和工具,如何根据实际需求选择合适的工具和分析流程,成为广大科研人员面临的问题.本文参照近几年在RNA-seq技术研究领域发表的文献,综述了RNA-Seq应用实际过程中涉及的分析方法、软件工具及其选用标准,为相关的研究和应用提供信息和参考.
URL [本文引用: 1]
URLPMID:26428292 [本文引用: 1]

Motivation:Detection of random errors and systematic biases is a crucial step of a robust pipeline for processing high-throughput sequencing (HTS) data. Bioinformatics software tools capable of performing this task are available, either for general analysis of HTS data or targeted to a specific sequencing technology. However, most of the existing QC instruments only allow processing of one sample at a time. Results:Qualimap 2 represents a next step in the QC analysis of HTS data. Along with comprehensive single-sample analysis of alignment data, it includes new modes that allow simultaneous processing and comparison of multiple samples. As with the first version, the new features are available via both graphical and command line interface. Additionally, it includes a large number of improvements proposed by the user community. Availability and implementation:The implementation of the software along with documentation is freely available athttp://www.qualimap.org. Contact:meyer@mpiib-berlin.mpg.de Supplementary information:Supplementary dataare available atBioinformaticsonline.
URLPMID:23363224 [本文引用: 1]

Background Illumina sequencing platform is widely used in genome research. Sequence reads quality assessment and control are needed for downstream analysis. However, software that provides efficient quality assessment and versatile filtration methods is still lacking. Results We have developed a toolkit named HTQC ??? abbreviation of High-Throughput Quality Control ??? for sequence reads quality control, which consists of six programs for reads quality assessment, reads filtration and generation of graphic reports. Conclusions The HTQC toolkit can generate reads quality assessment faster than existing tools, providing guidance for reads filtration utilities that allow users to choose different strategies to remove low quality reads.
URLPMID:23565205 [本文引用: 1]

Next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies have been widely used in life sciences. However, several kinds of sequencing artifacts, including low-quality reads and contaminating reads, were found to be quite common in raw sequencing data, which compromise downstream analysis. Therefore, quality control (QC) is essential for raw NGS data. However, although a few NGS data quality control tools are publicly available, there are two limitations: First, the processing speed could not cope with the rapid increase of large data volume. Second, with respect to removing the contaminating reads, none of them could identify contaminating sourcesde novo, and they rely heavily on prior information of the contaminating species, which is usually not available in advance. Here we report QC-Chain, a fast, accurate and holistic NGS data quality-control method. The tool synergeticly comprised of user-friendly tools for (1) quality assessment and trimming of raw reads using Parallel-QC, a fast read processing tool; (2) identification, quantification and filtration of unknown contamination to get high-quality clean reads. It was optimized based on parallel computation, so the processing speed is significantly higher than other QC methods. Experiments on simulated and real NGS data have shown that reads with low sequencing quality could be identified and filtered. Possible contaminating sources could be identified and quantifiedde novo, accurately and quickly. Comparison between raw reads and processed reads also showed that subsequent analyses (genome assembly, gene prediction, gene annotation, etc.) results based on processed reads improved significantly in completeness and accuracy. As regard to processing speed, QC-Chain achieves 7 8 time speed-up based on parallel computation as compared to traditional methods. Therefore, QC-Chain is a fast and useful quality control tool for read quality process andde novocontamination filtration of NGS reads, which could significantly facilitate downstream analysis. QC-Chain is publicly available at:http://www.computationalbioenergy.org/qc-chain.html.
URLPMID:27559158 [本文引用: 1]

Motivation:The current generation of DNA sequencing technologies produce a large amount of data quickly. All of these data need to pass some form of quality control (QC) processing and checking before they can be used for any analysis. The large number of samples that are run through Illumina sequencing machines makes the process of QC an onerous and time-consuming task that requires multiple pieces of information from several sources. Results:AlmostSignificant is an open-source platform for aggregating multiple sources of quality metrics as well as run and sample meta-data associated with DNA sequencing runs from Illumina sequencing machines. AlmostSignificant is a graphical platform to streamline the QC of DNA sequencing data, to store these data for future reference together with extra meta-data associated with the sequencing runs not typically retained. This simplifies the challenge of monitoring the volume of data produced by Illumina sequencers. AlmostSignificant has been used to track the quality of over 80 sequencing runs covering over 2500 samples produced over the last three years. Availability and Implementation:The code and documentation for AlmostSignificant is freely available athttps://github.com/bartongroup/AlmostSignificant. Contacts:c.cole@dundee.ac.ukorg.j.barton@dundee.ac.uk Supplementary information:Supplementary dataare available atBioinformatics online.
[本文引用: 1]

The usability of the NGS technologies heavily relies on the accuracy of the data. Many research groups developed different programs to clean the sequenced raw data by removing adapter contamination and trimming low-quality nucleotides. However, they are not optimized to process data from any specific equipment. In this study, we present an optimized pipeline Fastq_clean to clean the DNA-seq and RNA-seq data from the illumina sequencer. Fastq_clean can remove the low quality nucleotides and adapter contamination precisely and keep as many of the qualified nucleotides as possible. Fastq_clean can batchly process sequenced data and export statistics information for the data quality control (QC) by running a single command line. Compared with two most used tools on a published dataset, Fastq_clean reached the best performance. Fastq_clean has already been successfully used in some genome or transcriptome projects and it can also be used to clean the NGS data from other sequencers (e.g. 454), but needs some modification to reach the rest performance.
PMID:4246454 [本文引用: 1]

Background Next generation sequencing (NGS) technologies that parallelize the sequencing process and produce thousands to millions, or even hundreds of millions of sequences in a single sequencing run, have revolutionized genomic and genetic research. Because of the vagaries of any platform???s sequencing chemistry, the experimental processing, machine failure, and so on, the quality of sequencing reads is never perfect, and often declines as the read is extended. These errors invariably affect downstream analysis/application and should therefore be identified early on to mitigate any unforeseen effects. Results Here we present a novel FastQ Quality Control Software (FaQCs) that can rapidly process large volumes of data, and which improves upon previous solutions to monitor the quality and remove poor quality data from sequencing runs. Both the speed of processing and the memory footprint of storing all required information have been optimized via algorithmic and parallel processing solutions. The trimmed output compared side-by-side with the original data is part of the automated PDF output. We show how this tool can help data analysis by providing a few examples, including an increased percentage of reads recruited to references, improved single nucleotide polymorphism identification as well as de novo sequence assembly metrics. Conclusion FaQCs combines several features of currently available applications into a single, user-friendly process, and includes additional unique capabilities such as filtering the PhiX control sequences, conversion of FASTQ formats, and multi-threading. The original data and trimmed summaries are reported within a variety of graphics and reports, providing a simple way to do data quality control and assurance.
URLPMID:21623353 [本文引用: 1]

High-throughput RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) promises a comprehensive picture of the transcriptome, allowing for the complete annotation and quantification of all genes and their isoforms across samples. Realizing this promise requires increasingly complex computational methods. These computational challenges fall into three main categories: (i) read mapping, (ii) transcriptome reconstruction and (iii) expression quantification. Here we explain the major conceptual and practical challenges, and the general classes of solutions for each category. Finally, we highlight the interdependence between these categories and discuss the benefits for different biological applications.
URLPMID:26865842 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract RNA is a polymeric molecule implicated in various biological processes, such as the coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. Numerous studies have examined RNA features using whole transcriptome sequencing (RNA-seq) approaches. RNA-seq is a powerful technique for characterizing and quantifying the transcriptome and accelerates the development of bioinformatics software. In this review, we introduce routine RNA-seq workflow together with related software, focusing particularly on transcriptome reconstruction and expression quantification.
URL [本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
URLPMID:19289445 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract MOTIVATION: A new protocol for sequencing the messenger RNA in a cell, known as RNA-Seq, generates millions of short sequence fragments in a single run. These fragments, or 'reads', can be used to measure levels of gene expression and to identify novel splice variants of genes. However, current software for aligning RNA-Seq data to a genome relies on known splice junctions and cannot identify novel ones. TopHat is an efficient read-mapping algorithm designed to align reads from an RNA-Seq experiment to a reference genome without relying on known splice sites. RESULTS: We mapped the RNA-Seq reads from a recent mammalian RNA-Seq experiment and recovered more than 72% of the splice junctions reported by the annotation-based software from that study, along with nearly 20,000 previously unreported junctions. The TopHat pipeline is much faster than previous systems, mapping nearly 2.2 million reads per CPU hour, which is sufficient to process an entire RNA-Seq experiment in less than a day on a standard desktop computer. We describe several challenges unique to ab initio splice site discovery from RNA-Seq reads that will require further algorithm development. AVAILABILITY: TopHat is free, open-source software available from http://tophat.cbcb.umd.edu. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION: Supplementary data are available at Bioinformatics online.
URLPMID:20802226 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract The accurate mapping of reads that span splice junctions is a critical component of all analytic techniques that work with RNA-seq data. We introduce a second generation splice detection algorithm, MapSplice, whose focus is high sensitivity and specificity in the detection of splices as well as CPU and memory efficiency. MapSplice can be applied to both short (<75 bp) and long reads ( 75 bp). MapSplice is not dependent on splice site features or intron length, consequently it can detect novel canonical as well as non-canonical splices. MapSplice leverages the quality and diversity of read alignments of a given splice to increase accuracy. We demonstrate that MapSplice achieves higher sensitivity and specificity than TopHat and SpliceMap on a set of simulated RNA-seq data. Experimental studies also support the accuracy of the algorithm. Splice junctions derived from eight breast cancer RNA-seq datasets recapitulated the extensiveness of alternative splicing on a global level as well as the differences between molecular subtypes of breast cancer. These combined results indicate that MapSplice is a highly accurate algorithm for the alignment of RNA-seq reads to splice junctions. Software download URL: http://www.netlab.uky.edu/p/bioinfo/MapSplice.
URL [本文引用: 1]
URLPMID:20147302 [本文引用: 1]

Next-generation sequencing captures sequence differences in reads relative to a reference genome or transcriptome, including splicing events and complex variants involving multiple mismatches and long indels. We present computational methods for fast detection of complex variants and splicing in short reads, based on a successively constrained search process of merging and filtering position lists from a genomic index. Our methods are implemented in GSNAP (Genomic Short-read Nucleotide Alignment Program), which can align both single- and paired-end reads as short as 14 nt and of arbitrarily long length. It can detect short- and long-distance splicing, including interchromosomal splicing, in individual reads, using probabilistic models or a database of known splice sites. Our program also permits SNP-tolerant alignment to a reference space of all possible combinations of major and minor alleles, and can align reads from bisulfite-treated DNA for the study of methylation state.In comparison testing, GSNAP has speeds comparable to existing programs, especially in reads of > or=70 nt and is fastest in detecting complex variants with four or more mismatches or insertions of 1-9 nt and deletions of 1-30 nt. Although SNP tolerance does not increase alignment yield substantially, it affects alignment results in 7-8% of transcriptional reads, typically by revealing alternate genomic mappings for a read. Simulations of bisulfite-converted DNA show a decrease in identifying genomic positions uniquely in 6% of 36 nt reads and 3% of 70 nt reads.Source code in C and utility programs in Perl are freely available for download as part of the GMAP package at http://share.gene.com/gmap.
URLPMID:20950480 [本文引用: 1]

Roche 454 pyrosequencing has become a method of choice for generating transcriptome data from non-model organisms. Once the tens to hundreds of thousands of short (250-450 base) reads have been produced, it is important to correctly assemble these to estimate the sequence of all the transcripts. Most transcriptome assembly projects use only one program for assembling 454 pyrosequencing reads, but there is no evidence that the programs used to date are optimal. We have carried out a systematic comparison of five assemblers (CAP3, MIRA, Newbler, SeqMan and CLC) to establish best practices for transcriptome assemblies, using a new dataset from the parasitic nematode Litomosoides sigmodontis. Although no single assembler performed best on all our criteria, Newbler 2.5 gave longer contigs, better alignments to some reference sequences, and was fast and easy to use. SeqMan assemblies performed best on the criterion of recapitulating known transcripts, and had more novel sequence than the other assemblers, but generated an excess of small, redundant contigs. The remaining assemblers all performed almost as well, with the exception of Newbler 2.3 (the version currently used by most assembly projects), which generated assemblies that had significantly lower total length. As different assemblers use different underlying algorithms to generate contigs, we also explored merging of assemblies and found that the merged datasets not only aligned better to reference sequences than individual assemblies, but were also more consistent in the number and size of contigs. Transcriptome assemblies are smaller than genome assemblies and thus should be more computationally tractable, but are often harder because individual contigs can have highly variable read coverage. Comparing single assemblers, Newbler 2.5 performed best on our trial data set, but other assemblers were closely comparable. Combining differently optimal assemblies from different programs however gave a more credible final product, and this strategy is recommended.
URLPMID:3041503 [本文引用: 1]

Chickpea ranks third among the food legume crops production in the world. However, the genomic resources available for chickpea are still very limited. In the present study, the transcriptome of chickpea was sequenced with short reads on Illumina Genome Analyzer platform. We have assessed the effect of sequence quality, various assembly parameters and assembly programs on the final assembly output. We assembled ???107million high-quality trimmed reads using Velvet followed by Oases with optimal parameters into a non-redundant set of 53 409 transcripts (???100 bp), representing about 28 Mb of unique transcriptome sequence. The average length of transcripts was 523 bp and N50 length of 900 bp with coverage of 25.7 rpkm (reads per kilobase per million). At the protein level, a total of 45 636 (85.5%) chickpea transcripts showed significant similarity with unigenes/predicted proteins from other legumes or sequenced plant genomes. Functional categorization revealed the conservation of genes involved in various biological processes in chickpea. In addition, we identified simple sequence repeat motifs in transcripts. The chickpea transcripts set generated here provides a resource for gene discovery and development of functional molecular markers. In addition, the strategy for de novo assembly of transcriptome data presented here will be helpful in other similar transcriptome studies.<br>
URL [本文引用: 1]
URLPMID:4888495 [本文引用: 1]

ABSTRACT Motivation: This article presents a method for assembling shotgun sequences which primarily uses high confidence regions whilst taking advantage of additional available information such as low confidence regions, quality values or repetitive region tags. Conflict situations are resolved with routines for analysing trace signals.
URLPMID:10508846 [本文引用: 1]

We describe the third generation of the CAP sequence assembly program. The CAP3 program includes a number of improvements and new features. The program has a capability to clip 5′ and 3′ low-quality regions of reads. It uses base quality values in computation of overlaps between reads, construction of multiple sequence alignments of reads, and generation of consensus sequences. The program also uses forward–reverse constraints to correct assembly errors and link contigs. Results of CAP3 on four BAC data sets are presented. The performance of CAP3 was compared with that of PHRAP on a number of BAC data sets. PHRAP often produces longer contigs than CAP3 whereas CAP3 often produces fewer errors in consensus sequences than PHRAP. It is easier to construct scaffolds with CAP3 than with PHRAP on low-pass data with forward–reverse constraints.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
URLPMID:19796385 [本文引用: 1]

Allpaths2, a method for accurately assembling small genomes with high continuity using short paired reads. We demonstrate that genome sequences approaching finished quality can be generated from short paired reads. Using 36 base (fragment) and 26 base (jumping) reads from five microbial genomes of varied GC composition and sizes up to 40 Mb, ALLPATHS2 generated assemblies with long, accurate contigs and scaffolds. Velvet and EULER-SR were less accurate. For example, forEscherichia coli, the fraction of 10-kb stretches that were perfect was 99.8% (ALLPATHS2), 68.7% (Velvet), and 42.1% (EULER-SR).
URLPMID:22368243 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract MOTIVATION: High-throughput sequencing has made the analysis of new model organisms more affordable. Although assembling a new genome can still be costly and difficult, it is possible to use RNA-seq to sequence mRNA. In the absence of a known genome, it is necessary to assemble these sequences de novo, taking into account possible alternative isoforms and the dynamic range of expression values. RESULTS: We present a software package named Oases designed to heuristically assemble RNA-seq reads in the absence of a reference genome, across a broad spectrum of expression values and in presence of alternative isoforms. It achieves this by using an array of hash lengths, a dynamic filtering of noise, a robust resolution of alternative splicing events and the efficient merging of multiple assemblies. It was tested on human and mouse RNA-seq data and is shown to improve significantly on the transABySS and Trinity de novo transcriptome assemblers. AVAILABILITY AND IMPLEMENTATION: Oases is freely available under the GPL license at www.ebi.ac.uk/~zerbino/oases/.
URLPMID:18227114 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract SUMMARY: We have developed a program SOAP for efficient gapped and ungapped alignment of short oligonucleotides onto reference sequences. The program is designed to handle the huge amounts of short reads generated by parallel sequencing using the new generation Illumina-Solexa sequencing technology. SOAP is compatible with numerous applications, including single-read or pair-end resequencing, small RNA discovery and mRNA tag sequence mapping. SOAP is a command-driven program, which supports multi-threaded parallel computing, and has a batch module for multiple query sets. AVAILABILITY: http://soap.genomics.org.cn.
URL [本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
URLPMID:12952883 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract We describe a whole-genome assembly program named PCAP for processing tens of millions of reads. The PCAP program has several features to address efficiency and accuracy issues in assembly. Multiple processors are used to perform most time-consuming computations in assembly. A more sensitive method is used to avoid missing overlaps caused by sequencing errors. Repetitive regions of reads are detected on the basis of many overlaps with other reads, instead of many shorter word matches with other reads. Contaminated end regions of reads are identified and removed. Generation of a consensus sequence for a contig is based on an alignment of reads in the contig, in which both base quality values and coverage information are used to determine every consensus base. The PCAP program was tested on a mouse whole-genome data set of 30 million reads and a human Chromosome 20 data set of 1.7 million reads. The program is freely available for academic use.
[本文引用: 1]
URLPMID:4643835 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract Methods used to sequence the transcriptome often produce more than 200 million short sequences. We introduce StringTie, a computational method that applies a network flow algorithm originally developed in optimization theory, together with optional de novo assembly, to assemble these complex data sets into transcripts. When used to analyze both simulated and real data sets, StringTie produces more complete and accurate reconstructions of genes and better estimates of expression levels, compared with other leading transcript assembly programs including Cufflinks, IsoLasso, Scripture and Traph. For example, on 90 million reads from human blood, StringTie correctly assembled 10,990 transcripts, whereas the next best assembly was of 7,187 transcripts by Cufflinks, which is a 53% increase in transcripts assembled. On a simulated data set, StringTie correctly assembled 7,559 transcripts, which is 20% more than the 6,310 assembled by Cufflinks. As well as producing a more complete transcriptome assembly, StringTie runs faster on all data sets tested to date compared with other assembly software, including Cufflinks.
URLPMID:21697122 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract SUMMARY: We describe a new 'reference annotation based transcript assembly' problem for RNA-Seq data that involves assembling novel transcripts in the context of an existing annotation. This problem arises in the analysis of expression in model organisms, where it is desirable to leverage existing annotations for discovering novel transcripts. We present an algorithm for reference annotation-based transcript assembly and show how it can be used to rapidly investigate novel transcripts revealed by RNA-Seq in comparison with a reference annotation. AVAILABILITY: The methods described in this article are implemented in the Cufflinks suite of software for RNA-Seq, freely available from http://bio.math.berkeley.edu/cufflinks. The software is released under the BOOST license. CONTACT: cole@broadinstitute.org; lpachter@math.berkeley.edu SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION: Supplementary data are available at Bioinformatics online.
URLPMID:26831908 [本文引用: 1]

We present CIDANE, a novel framework for genome-based transcript reconstruction and quantification from RNA-seq reads. CIDANE assembles transcripts efficiently with significantly higher sensitivity and precision than existing tools. Its algorithmic core not only reconstructs transcripts ab initio, but also allows the use of the growing annotation of known splice sites, transcription start and end sites, or full-length transcripts, which are available for most model organisms. CIDANE supports the integrated analysis of RNA-seq and additional gene-boundary data and recovers splice junctions that are invisible to other methods. CIDANE is available at
URLPMID:4037530 [本文引用: 1]

The identification of full length transcripts entirely from short-read RNA sequencing data (RNA-seq) remains a challenge in genome annotation pipelines. Here we describe an automated pipeline for genome annotation that integrates RNA-seq and gene-boundary data sets, which we call generalized RNA integration tool, or GRIT. By applying GRIT to Drosophila melanogaster short-read RNA-seq, cap analysis of gene expression (CAGE) and poly(A)-site-seq data collected for the modENCODE project, we recover the vast majority of previously annotated transcripts and double the total number of transcripts cataloged. We find that 20% of protein coding genes encode multiple protein-localization signals, and that, in 20 day old adult fly heads, genes with multiple poly-adenylation sites are more common than genes with alternate splicing or alternate promoters. When compared to the most widely used transcript assembly tools, GRIT recovers a larger fraction of annotated transcripts at higher precision. GRIT will enable the automated generation of high-quality genome annotations without necessitating extensive manual annotation.
URL [本文引用: 1]

Transcriptome assemblers aim to reconstruct full-length transcripts from RNA-seq data. We present TransComb, a genome-guided assembler developed based on a junction graph, weighted by a bin-packing strategy and paired-end information. A newly designed extension method based on weighted junction graphs can accurately extract paths representing expressed transcripts, whether they have low or high expression levels. Tested on both simulated and real datasets, TransComb demonstrates significant improvements in both recall and precision over leading assemblers, including StringTie, Cufflinks, Bayesembler, and Traph. In addition, it runs much faster and requires less memory on average. TransComb is available athttp://sourceforge.net/projects/transcriptomeassembly/files/. The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s13059-016-1074-1) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
URLPMID:23204306 [本文引用: 1]

High-throughput RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) promises to revolutionize our understanding of genes and their role in human disease by characterizing the RNA content of tissues and cells. The realization of this promise, however, is conditional on the development of effective computational methods for the identification and quantification of transcripts from incomplete and noisy data. In this article, we introduce iReckon, a method for simultaneous determination of the isoforms and estimation of their abundances. Our probabilistic approach incorporates multiple biological and technical phenomena, including novel isoforms, intron retention, unspliced pre-mRNA, PCR amplification biases, and multimapped reads. iReckon utilizes regularized expectation-maximization to accurately estimate the abundances of known and novel isoforms. Our results on simulated and real data demonstrate a superior ability to discover novel isoforms with a significantly reduced number of false-positive predictions, and our abundance accuracy prediction outmatches that of other state-of-the-art tools. Furthermore, we have applied iReckon to two cancer transcriptome data sets, a triple-negative breast cancer patient sample and the MCF7 breast cancer cell line, and show that iReckon is able to reconstruct the complex splicing changes that were not previously identified. QT-PCR validations of the isoforms detected in the MCF7 cell line confirmed all of iReckon's predictions and also showed strong agreement (r(2) = 0.94) with the predicted abundances.
URLPMID:22135461 [本文引用: 1]

Since the inception of next-generation mRNA sequencing (RNA-Seq) technology, various attempts have been made to utilize RNA-Seq data in assembling full-length mRNA isoforms de novo and estimating abundance of isoforms. However, for genes with more than a few exons, the problem tends to be challenging and often involves identifiability issues in statistical modeling. We have developed a statistical method called "sparse linear modeling of RNA-Seq data for isoform discovery and abundance estimation" (SLIDE) that takes exon boundaries and RNA-Seq data as input to discern the set of mRNA isoforms that are most likely to present in an RNA-Seq sample. SLIDE is based on a linear model with a design matrix that models the sampling probability of RNA-Seq reads from different mRNA isoforms. To tackle the model unidentifiability issue, SLIDE uses a modified Lasso procedure for parameter estimation. Compared with deterministic isoform assembly algorithms (e.g., Cufflinks), SLIDE considers the stochastic aspects of RNA-Seq reads in exons from different isoforms and thus has increased power in detecting more novel isoforms. Another advantage of SLIDE is its flexibility of incorporating other transcriptomic data such as RACE, CAGE, and EST into its model to further increase isoform discovery accuracy. SLIDE can also work downstream of other RNA-Seq assembly algorithms to integrate newly discovered genes and exons. Besides isoform discovery, SLIDE sequentially uses the same linear model to estimate the abundance of discovered isoforms. Simulation and real data studies show that SLIDE performs as well as or better than major competitors in both isoform discovery and abundance estimation. The SLIDE software package is available at https://sites.google. com/site/jingyijli/SLIDE.zip.
URLPMID:23888185 [本文引用: 1]

AbstractRNA sequencing is a recent technology which has seen an explosion of methods addressing all levels of analysis, from read mapping to transcript assembly to differential expression modeling. In particular the discovery of isoforms at the transcript assembly stage is a complex problem and current approaches suffer from various limitations. For instance, many approaches use graphs to construct a minimal set of isoforms which covers the observed reads, then perform a separate algorithm to quantify the isoforms, which can result in a loss of power. Current methods also use ad-hoc solutions to deal with the vast number of possible isoforms which can be constructed from a given set of reads. Finally, while the need of taking into account features such as read pairing and sampling rate of reads has been acknowledged, most existing methods do not seamlessly integrate these features as part of the model. We present Montebello, an integrated statistical approach which performs simultaneous isoform discovery and quantification by using a Monte Carlo simulation to find the most likely isoform composition leading to a set of observed reads. We compare Montebello to Cufflinks, a popular isoform discovery approach, on a simulated data set and on 46.3 million brain reads from an Illumina tissue panel. On this data set Montebello appears to offer a modest improvement over Cufflinks when considering discovery and parsimony metrics. In addition Montebello mitigates specific difficulties inherent in the Cufflinks approach. Finally, Montebello can be fine-tuned depending on the type of solution desired.
URLPMID:1538822 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract AUGUSTUS is a software tool for gene prediction in eukaryotes based on a Generalized Hidden Markov Model, a probabilistic model of a sequence and its gene structure. Like most existing gene finders, the first version of AUGUSTUS returned one transcript per predicted gene and ignored the phenomenon of alternative splicing. Herein, we present a WWW server for an extended version of AUGUSTUS that is able to predict multiple splice variants. To our knowledge, this is the first ab initio gene finder that can predict multiple transcripts. In addition, we offer a motif searching facility, where user-defined regular expressions can be searched against putative proteins encoded by the predicted genes. The AUGUSTUS web interface and the downloadable open-source stand-alone program are freely available from http://augustus.gobics.de.
URLPMID:21951053 [本文引用: 1]

The new second generation sequencing technology revolutionizes many biology-related research fields and poses various computational biology challenges. One of them is transcriptome assembly based on RNA-Seq data, which aims at reconstructing all full-length mRNA transcripts simultaneously from millions of short reads. In this article, we consider three objectives in transcriptome assembly: the maximization of prediction accuracy, minimization of interpretation, and maximization of completeness. The first objective, the maximization of prediction accuracy, requires that the estimated expression levels based on assembled transcripts should be as close as possible to the observed ones for every expressed region of the genome. The minimization of interpretation follows the parsimony principle to seek as few transcripts in the prediction as possible. The third objective, the maximization of completeness, requires that the maximum number of mapped reads (or ?expressed segments? in gene models) be explained by (i.e., contained in) the predicted transcripts in the solution. Based on the above three objectives, we present IsoLasso, a new RNA-Seq based transcriptome assembly tool. IsoLasso is based on the well-known LASSO algorithm, a multivariate regression method designated to seek a balance between the maximization of prediction accuracy and the minimization of interpretation. By including some additional constraints in the quadratic program involved in LASSO, IsoLasso is able to make the set of assembled transcripts as complete as possible. Experiments on simulated and real RNA-Seq datasets show that IsoLasso achieves, simultaneously, higher sensitivity and precision than the state-of-art transcript assembly tools.
URL [本文引用: 1]
URLPMID:3622638 [本文引用: 1]

Background: Through transcription and alternative splicing, a gene can be transcribed into different RNA sequences (isoforms), depending on the individual, on the tissue the cell is in, or in response to some stimuli. Recent RNA-Seq technology allows for new high-throughput ways for isoform identification and quantification based on short reads, and various methods have been put forward for this non-trivial problem.Results: In this paper we propose a novel radically different method based on minimum-cost network flows. This has a two-fold advantage: on the one hand, it translates the problem as an established one in the field of network flows, which can be solved in polynomial time, with different existing solvers; on the other hand, it is general enough to encompass many of the previous proposals under the least sum of squares model. Our method works as follows: in order to find the transcripts which best explain, under a given fitness model, a splicing graph resulting from an RNA-Seq experiment, we find a min-cost flow in an offset flow network, under an equivalent cost model. Under very weak assumptions on the fitness model, the optimal flow can be computed in polynomial time. Parsimoniously splitting the flow back into few path transcripts can be done with any of the heuristics and approximations available from the theory of network flows. In the present implementation, we choose the simple strategy of repeatedly removing the heaviest path.Conclusions: We proposed a new very general method based on network flows for a multiassembly problem arising from isoform identification and quantification with RNA-Seq. Experimental results on prediction accuracy show that our method is very competitive with popular tools such as Cufflinks and IsoLasso. Our tool, called Traph (Transcrips in gRAPHs), is available at: http://www.cs.helsinki.fi/gsa/traph/.
URLPMID:18516045 [本文引用: 1]

High read number is relevant for RNA-Seq because our ability to and phage lambda templates (Fig. 2c). These standards comprised reliably detect and measure rare, yet physiologically relevant, RNA long (~10,000 nt), intermediate (~1,500 nt) and short (~300 nt) species (those with abundances of 1-10 RNAs per cell) depends on transcripts, and they were designed to span the range of abundance the number of independent pieces of evidence (sequence reads) (~0.5-50,000 transcripts per cell) typically observed in natural obtained for transcripts from each gene. This constraint influenced transcriptomes. RNA-Seq data for the standards were linear across our sequencing strategy, choice of instrument and choice of the a dynamic range of five orders of magnitude in RNA concentra- 25-bp read length.tion. Sequence coverage over test transcripts was highly reproducibleThe sensitivity of RNA-Seq will be a function of both molar con- and quite uniform (Supplementary Fig. 1c). At current practical centration and transcript length. We therefore quantified transcript sequencing capacity and cost (~40 M mapped reads), transcript levels in reads per kilobase of exon model per million mapped reads detection was robust at 1.0 RPKM and above for a typical 2-kilo- (RPKM) (Fig. 1a,c). The RPKM measure of read density reflects base (kb) mRNA (~80 individual sequence reads resulting in a P the molar concentration of a transcript in the starting sample by value <10-16). Beyond simple detection confidence, we analyzed the normalizing for RNA length and for the total read number in the impact of different amounts of sequencing on our ability to measure measurement. This facilitates transparent comparison of transcript the concentration of a given transcript class (defined on the basis of levels both within and between samples.RPKM) within 5% (Fig. 2d). When these RNA standards are usedin conjunction with information on cellular RNA content, abso- Examination of a well-characterized locuslute transcript levels per cell can also be calculated. For example, on Data from a 21-million-read transcriptome measurement of adult the basis of literature values for the mRNA content of a liver cell19 mouse skeletal muscle (Fig. 1b,c) illustrate some key characteris- and the RNA standards, we estimated that 3 RPKM corresponds to tics of our results. Myf6 (also known as Mrf4) is a much-studied about one transcript per liver cell. For C2C12 tissue culture cells, for myogenic transcription factor gene that is expressed specifically and modestly in mus- cle, as expected, but silent in liver and brain.
URL [本文引用: 1]

RNA-Seq is rapidly becoming the standard technology for transcriptome analysis. Fundamental to many of the applications of RNA-Seq is the quantification problem, which is the accurate measurement of relative transcript abundances from the sequenced reads. We focus on this problem, and review many recently published models that are used to estimate the relative abundances. In addition to describing the models and the different approaches to inference, we also explain how methods are related to each other. A key result is that we show how inference with many of the models results in identical estimates of relative abundances, even though model formulations can be very different. In fact, we are able to show how a single general model captures many of the elements of previously published methods. We also review the applications of RNA-Seq models to differential analysis, and explain why accurate relative transcript abundance estimates are crucial for downstream analyses.
URLPMID:25260700 [本文引用: 1]

Motivation: A large choice of tools exists for many standard tasks in the analysis of high-throughput sequencing (HTS) data. However, once a project deviates from standard workflows, custom scripts are needed. Results: We present HTSeq, a Python library to facilitate the rapid development of such scripts. HTSeq offers parsers for many common data formats in HTS projects, as well as classes to represent data, such as genomic coordinates, sequences, sequencing reads, alignments, gene model information and variant calls, and provides data structures that allow for querying via genomic coordinates. We also present htseq-count, a tool developed with HTSeq that preprocesses RNA-Seq data for differential expression analysis by counting the overlap of reads with genes.
URLPMID:24227677 [本文引用: 1]

Next-generation sequencing technologies generate millions of short sequence reads, which are usually aligned to a reference genome. In many applications, the key information required for downstream analysis is the number of reads mapping to each genomic feature, for example to each exon or each gene. The process of counting reads is called read summarization. Read summarization is required for a great variety of genomic analyses but has so far received relatively little attention in the literature.We present featureCounts, a read summarization program suitable for counting reads generated from either RNA or genomic DNA sequencing experiments. featureCounts implements highly efficient chromosome hashing and feature blocking techniques. It is considerably faster than existing methods (by an order of magnitude for gene-level summarization) and requires far less computer memory. It works with either single or paired-end reads and provides a wide range of options appropriate for different sequencing applications.featureCounts is available under GNU General Public License as part of the Subread (http://subread.sourceforge.net) or Rsubread (http://www.bioconductor.org) software packages.
URLPMID:21816040 [本文引用: 1]

RNA-Seq is revolutionizing the way transcript abundances are measured. A key challenge in transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data is the handling of reads that map to multiple genes or isoforms. This issue is particularly important for quantification with de novo transcriptome assemblies in the absence of sequenced genomes, as it is difficult to determine which transcripts are isoforms of the same gene. A second significant issue is the design of RNA-Seq experiments, in terms of the number of reads, read length, and whether reads come from one or both ends of cDNA fragments. We present RSEM, an user-friendly software package for quantifying gene and isoform abundances from single-end or paired-end RNA-Seq data. RSEM outputs abundance estimates, 95% credibility intervals, and visualization files and can also simulate RNA-Seq data. In contrast to other existing tools, the software does not require a reference genome. Thus, in combination with a de novo transcriptome assembler, RSEM enables accurate transcript quantification for species without sequenced genomes. On simulated and real data sets, RSEM has superior or comparable performance to quantification methods that rely on a reference genome. Taking advantage of RSEM's ability to effectively use ambiguously-mapping reads, we show that accurate gene-level abundance estimates are best obtained with large numbers of short single-end reads. On the other hand, estimates of the relative frequencies of isoforms within single genes may be improved through the use of paired-end reads, depending on the number of possible splice forms for each gene. RSEM is an accurate and user-friendly software tool for quantifying transcript abundances from RNA-Seq data. As it does not rely on the existence of a reference genome, it is particularly useful for quantification with de novo transcriptome assemblies. In addition, RSEM has enabled valuable guidance for cost-efficient design of quantification experiments with RNA-Seq, which is currently relatively expensive.
URLPMID:24752080 [本文引用: 1]

We introduce Sailfish, a computational method for quantifying the abundance of previously annotated RNA isoforms from RNA-seq data. Because Sailfish entirely avoids mapping reads, a time-consuming step in all current methods, it provides quantification estimates much faster than do existing approaches (typically 20 times faster) without loss of accuracy. By facilitating frequent reanalysis of data and reducing the need to optimize parameters, Sailfish exemplifies the potential of lightweight algorithms for efficiently processing sequencing reads.
URL [本文引用: 1]
URLPMID:20167110 [本文引用: 1]

pAbstract/p pBackground/p pHigh-throughput sequencing technologies, such as the Illumina Genome Analyzer, are powerful new tools for investigating a wide range of biological and medical questions. Statistical and computational methods are key for drawing meaningful and accurate conclusions from the massive and complex datasets generated by the sequencers. We provide a detailed evaluation of statistical methods for normalization and differential expression (DE) analysis of Illumina transcriptome sequencing (mRNA-Seq) data./p pResults/p pWe compare statistical methods for detecting genes that are significantly DE between two types of biological samples and find that there are substantial differences in how the test statistics handle low-count genes. We evaluate how DE results are affected by features of the sequencing platform, such as, varying gene lengths, base-calling calibration method (with and without phi X control lane), and flow-cell/library preparation effects. We investigate the impact of the read count normalization method on DE results and show that the standard approach of scaling by total lane counts (e.g., RPKM) can bias estimates of DE. We propose more general quantile-based normalization procedures and demonstrate an improvement in DE detection./p pConclusions/p pOur results have significant practical and methodological implications for the design and analysis of mRNA-Seq experiments. They highlight the importance of appropriate statistical methods for normalization and DE inference, to account for features of the sequencing platform that could impact the accuracy of results. They also reveal the need for further research in the development of statistical and computational methods for mRNA-Seq./p
URLPMID:23837734 [本文引用: 1]

Background RNA-Seq technology has been used widely in transcriptome study, and one of the most important applications is to estimate the expression level of genes and their alternative splicing isoforms. There have been several algorithms published to estimate the expression based on different models. Recently Wu et al. published a method that can accurately estimate isoform level expression by considering position-related sequencing biases using nonparametric models. The method has advantages in handling different read distributions, but there hasn???t been an efficient program to implement this algorithm. Results We developed an efficient implementation of the algorithm in the program NURD. It uses a binary interval search algorithm. The program can correct both the global tendency of sequencing bias in the data and local sequencing bias specific to each gene. The correction makes the isoform expression estimation more reliable under various read distributions. And the implementation is computationally efficient in both the memory cost and running time and can be readily scaled up for huge datasets. Conclusion NURD is an efficient and reliable tool for estimating the isoform expression level. Given the reads mapping result and gene annotation file, NURD will output the expression estimation result. The package is freely available for academic use at http://bioinfo.au.tsinghua.edu.cn/software/NURD/ webcite.
URLPMID:19371405 [本文引用: 1]

Background Several recent studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of deep sequencing for transcriptome analysis (RNA-seq) in mammals. As RNA-seq becomes more affordable, whole genome transcriptional profiling is likely to become the platform of choice for species with good genomic sequences. As yet, a rigorous analysis methodology has not been developed and we are still in the stages of exploring the features of the data. Results We investigated the effect of transcript length bias in RNA-seq data using three different published data sets. For standard analyses using aggregated tag counts for each gene, the ability to call differentially expressed genes between samples is strongly associated with the length of the transcript. Conclusion Transcript length bias for calling differentially expressed genes is a general feature of current protocols for RNA-seq technology. This has implications for the ranking of differentially expressed genes, and in particular may introduce bias in gene set testing for pathway analysis and other multi-gene systems biology analyses. Reviewers This article was reviewed by Rohan Williams (nominated by Gavin Huttley), Nicole Cloonan (nominated by Mark Ragan) and James Bullard (nominated by Sandrine Dudoit).
URLPMID:2864565 [本文引用: 1]

The fine detail provided by sequencing-based transcriptome surveys suggests that RNA-seq is likely to become the platform of choice for interrogating steady state RNA. In order to discover biologically important changes in expression, we show that normalization continues to be an essential step in the analysis. We outline a simple and effective method for performing normalization and show dramatically improved results for inferring differential expression in simulated and publicly available data sets.
URLPMID:3218662 [本文引用: 1]

High-throughput sequencing assays such as RNA-Seq, ChIP-Seq or barcode counting provide quantitative readouts in the form of count data. To infer differential signal in such data correctly and with good statistical power, estimation of data variability throughout the dynamic range and a suitable error model are required. We propose a method based on the negative binomial distribution, with variance and mean linked by local regression and present an implementation, DESeq, as an R/Bioconductor package.
URLPMID:3372940 [本文引用: 1]

We discuss the identification of genes that are associated with an outcome in RNA sequencing and other sequence-based comparative genomic experiments. RNA-sequencing data take the form of counts, so models based on the Gaussian distribution are unsuitable. Moreover, normalization is challenging because different sequencing experiments may generate quite different total numbers of reads. To overcome these difficulties, we use a log-linear model with a new approach to normalization. We derive a novel procedure to estimate the false discovery rate (FDR). Our method can be applied to data with quantitative, two-class, or multiple-class outcomes, and the computation is fast even for large data sets. We study the accuracy of our approaches for significance calculation and FDR estimation, and we demonstrate that our method has potential advantages over existing methods that are based on a Poisson or negative binomial model. In summary, this work provides a pipeline for the significance analysis of sequencing data.
URL [本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
URLPMID:22127579 [本文引用: 1]

We discuss the identification of features that are associated with an outcome in RNA-Sequencing (RNA-Seq) and other sequencing-based comparative genomic experiments. RNA-Seq data takes the form of counts, so models based on the normal distribution are generally unsuitable. The problem is especially challenging because different sequencing experiments may generate quite different total numbers of reads, or 0900sequencing depths0964. Existing methods for this problem are based on Poisson or negative binomial models: they are useful but can be heavily influenced by 0900outliers0964 in the data. We introduce a simple, non-parametric method with resampling to account for the different sequencing depths. The new method is more robust than parametric methods. It can be applied to data with quantitative, survival, two-class or multiple-class outcomes. We compare our proposed method to Poisson and negative binomial-based methods in simulated and real data sets, and find that our method discovers more consistent patterns than competing methods.
URLPMID:2646747 [本文引用: 1]

MicroRNA (miR) are a class of small RNAs that regulate gene expression by inhibiting translation of protein encoding transcripts. To evaluate the role of miR in skeletal muscle of swine, global microRNA abundance was measured at specific developmental stages including proliferating satellite cells, three stages of fetal growth, day-old neonate, and the adult. Twelve potential novel miR were detected that did not match previously reported sequences. In addition, a number of miR previously reported to be expressed in mammalian muscle were detected, having a variety of abundance patterns through muscle development. Muscle-specific miR-206 was nearly absent in proliferating satellite cells in culture, but was the highest abundant miR at other time points evaluated. In addition, miR-1 was moderately abundant throughout developmental stages with highest abundance in the adult. In contrast, miR-133 was moderately abundant in adult muscle and either not detectable or lowly abundant throughout fetal and neonate development. Changes in abundance of ubiquitously expressed miR were also observed. MiR-432 abundance was highest at the earliest stage of fetal development tested (60 day-old fetus) and decreased throughout development to the adult. Conversely, miR-24 and miR-27 exhibited greatest abundance in proliferating satellite cells and the adult, while abundance of miR-368, miR-376, and miR-423-5p was greatest in the neonate. These data present a complete set of transcriptome profiles to evaluate miR abundance at specific stages of skeletal muscle growth in swine. Identification of these miR provides an initial group of miR that may play a vital role in muscle development and growth.
[D].
URL [本文引用: 1]

猪的脂肪代谢是一个十分复杂的过程,涉及多个组织器官的调控,其中甲状腺分泌的甲状腺激素在脂质代谢过程中发挥着重要的作用。目前对甲状腺激素调控的研究主要集中在DNA和mRNA层面,对非编码RNA介导的基因表达调控的研究还比较匮乏。长链非编码RNA (long non-coding RNA, lncRNA)和microRNA都是重要的调控性非编码RNA。约克夏猪是瘦肉型猪,生长快且脂肪率低,而金华猪是脂肪型猪,生长慢但脂肪率高,它们在脂肪代谢方面有很大的差异。本研究以阉割的120日龄的约克夏猪和金华猪为研究对象,比较它们的血清甲状腺激素水平,并利用RNA-seq和small RNA-seq技术筛选出了大量在约克夏猪和金华猪甲状腺组织中差异表达的mRNA、lncRNA和miRNA,并对差异表达的mRNA及差异表达的lncRNA和miRNA的靶基因进行了功能注释和通路分析,利用荧光定量PCR技术对筛选出的部分差异基因进行了验证,此外,还将获得的RNA-seq结果和small RNA-seq结果进行了联合分析。主要研究内容和结果如下:(1)约克夏猪的体重和甲状腺重均显著高于金华猪(P0.05),但两者比值不变。约克夏猪的血清TT4和TT3水平显著高于金华猪(P0.05),约克夏猪的血清FT4和FT3水平高于金华猪,但差异不显著(P0.05)。(2) RNA-seq共获得约351 M (million)高质量的读长为125 nt的双末端原始读段,其中约83%可以比对到猪参考基因组。共鉴定到22,435个已知mRNA在猪甲状腺组织中表达,其中分别有1,492、2,479个在约克夏猪和金华猪特异性表达。并筛选得到1,018个lncRNA,包括760个lincRNA,140个intronic lncRNA和118个anti-sense lncRNA,此外还筛选到1189个新mRNA。本研究鉴定到的lncRNA与猪已知的蛋白编码基因相比,lncRNA具有更短的转录本和ORF长度、更少的外显子和更低的序列保守性。差异表达分析共筛选出492个mRNA的表达量在两个品种间存在显著差异,其中275个mRNA在约克夏猪甲状腺中高表达,217个在金华猪甲状腺中高表达,差异基因被注释到酪氨酸代谢、钙离子信号通路、甲状腺激素合成等生物学通路,主要富集在细胞周期和基于微管的过程。差异表达分析还筛选出48个lncRNA在约克夏猪和金华猪的甲状腺中差异表达,其中10个经cis预测找到13个靶基因。在猪甲状腺组织中共发现了12类可变剪切,其中TSS(转录起始位点)与TTS(转录终止位点)两种剪切类型所占的比例最大,分别约占38%和30%的百分比。(3) small RNA-seq共获得约44 M (million)高质量的单末端原始读段,其中约74%可以比对到猪参考基因组。共鉴定到293条已知的miRNA在猪甲状腺组织中表达,对应266个miRNA的前体,属于146个miRNA家族,此外还鉴定到60个新miRNA.差异表达分析共筛选出18个miRNA在两个品种间差异表达,其中12个miRNA在约克夏猪甲状腺中高表达,6个在金华猪甲状腺中高表达,生物信息学分析显示差异miRNA参与甲状腺激素调控相关通路,如内吞、甲状腺激素合成、钙离子信号通路、过氧化物酶体、溶酶体等。(4)荧光定量PCR检测了18个差异基因在约克夏猪和金华猪甲状腺组织的表达情况,结果表明与测序结果基本一致,说明本实验的分析结果基本可以反映猪甲状腺组织内基因的真实表达情况。(5)对差异表达的mRNA、lncRNA和miRNA进行联合分析,结果得到的网络调控图中包括237个mRNA、18个miRNA和1个lncRNA。
[学位论文].
URL [本文引用: 1]

猪的脂肪代谢是一个十分复杂的过程,涉及多个组织器官的调控,其中甲状腺分泌的甲状腺激素在脂质代谢过程中发挥着重要的作用。目前对甲状腺激素调控的研究主要集中在DNA和mRNA层面,对非编码RNA介导的基因表达调控的研究还比较匮乏。长链非编码RNA (long non-coding RNA, lncRNA)和microRNA都是重要的调控性非编码RNA。约克夏猪是瘦肉型猪,生长快且脂肪率低,而金华猪是脂肪型猪,生长慢但脂肪率高,它们在脂肪代谢方面有很大的差异。本研究以阉割的120日龄的约克夏猪和金华猪为研究对象,比较它们的血清甲状腺激素水平,并利用RNA-seq和small RNA-seq技术筛选出了大量在约克夏猪和金华猪甲状腺组织中差异表达的mRNA、lncRNA和miRNA,并对差异表达的mRNA及差异表达的lncRNA和miRNA的靶基因进行了功能注释和通路分析,利用荧光定量PCR技术对筛选出的部分差异基因进行了验证,此外,还将获得的RNA-seq结果和small RNA-seq结果进行了联合分析。主要研究内容和结果如下:(1)约克夏猪的体重和甲状腺重均显著高于金华猪(P0.05),但两者比值不变。约克夏猪的血清TT4和TT3水平显著高于金华猪(P0.05),约克夏猪的血清FT4和FT3水平高于金华猪,但差异不显著(P0.05)。(2) RNA-seq共获得约351 M (million)高质量的读长为125 nt的双末端原始读段,其中约83%可以比对到猪参考基因组。共鉴定到22,435个已知mRNA在猪甲状腺组织中表达,其中分别有1,492、2,479个在约克夏猪和金华猪特异性表达。并筛选得到1,018个lncRNA,包括760个lincRNA,140个intronic lncRNA和118个anti-sense lncRNA,此外还筛选到1189个新mRNA。本研究鉴定到的lncRNA与猪已知的蛋白编码基因相比,lncRNA具有更短的转录本和ORF长度、更少的外显子和更低的序列保守性。差异表达分析共筛选出492个mRNA的表达量在两个品种间存在显著差异,其中275个mRNA在约克夏猪甲状腺中高表达,217个在金华猪甲状腺中高表达,差异基因被注释到酪氨酸代谢、钙离子信号通路、甲状腺激素合成等生物学通路,主要富集在细胞周期和基于微管的过程。差异表达分析还筛选出48个lncRNA在约克夏猪和金华猪的甲状腺中差异表达,其中10个经cis预测找到13个靶基因。在猪甲状腺组织中共发现了12类可变剪切,其中TSS(转录起始位点)与TTS(转录终止位点)两种剪切类型所占的比例最大,分别约占38%和30%的百分比。(3) small RNA-seq共获得约44 M (million)高质量的单末端原始读段,其中约74%可以比对到猪参考基因组。共鉴定到293条已知的miRNA在猪甲状腺组织中表达,对应266个miRNA的前体,属于146个miRNA家族,此外还鉴定到60个新miRNA.差异表达分析共筛选出18个miRNA在两个品种间差异表达,其中12个miRNA在约克夏猪甲状腺中高表达,6个在金华猪甲状腺中高表达,生物信息学分析显示差异miRNA参与甲状腺激素调控相关通路,如内吞、甲状腺激素合成、钙离子信号通路、过氧化物酶体、溶酶体等。(4)荧光定量PCR检测了18个差异基因在约克夏猪和金华猪甲状腺组织的表达情况,结果表明与测序结果基本一致,说明本实验的分析结果基本可以反映猪甲状腺组织内基因的真实表达情况。(5)对差异表达的mRNA、lncRNA和miRNA进行联合分析,结果得到的网络调控图中包括237个mRNA、18个miRNA和1个lncRNA。
URLPMID:20634961 [本文引用: 1]

The domestic pig is of enormous agricultural significance and valuable models for many human diseases. Information concerning the pig microRNAome (miRNAome) has been long overdue and elucidation of this information will permit an atlas of microRNA (miRNA) regulation functions and networks to be constructed. Here we performed a comprehensive search for porcine miRNAs on ten small RNA sequencing libraries prepared from a mixture of tissues obtained during the entire pig lifetime, from the fetal period through adulthood. The sequencing results were analyzed using mammalian miRNAs, the precursor hairpins (pre-miRNAs) and the first release of the high-coverage porcine genome assembly (Sscrofa9, April 2009) and the available expressed sequence tag (EST) sequences. Our results extend the repertoire of pig miRNAome to 867 pre-miRNAs (623 with genomic coordinates) encoding for 1,004 miRNAs, of which 777 are unique. We preformed real-time quantitative PCR (q-PCR) experiments for selected 30 miRNAs in 47 tissue-specific samples and found agreement between the sequencing and q-PCR data. This broad survey provides detailed information about multiple variants of mature sequences, precursors, chromosomal organization, development-specific expression, and conservation patterns. Our data mining produced a broad view of the pig miRNAome, consisting of miRNAs and isomiRs and a wealth of information of pig miRNA characteristics. These results are prelude to the advancement in pig biology as well the use of pigs as model organism for human biological and biomedical studies.
URLPMID:28380516 [本文引用: 1]

Production of high-quality meat is important to satisfy the consumer and allow the pork industry to be competitive. It is evident that different muscle fiber types in different breeds greatly influence the pork quality, but the underlying molecular mechanism remains unclear. We used Ribo-Zero RNA-Seq and miRNA-Seq to examine global expressions of protein-coding transcripts and non-coding RNAs including miRNA, lncRNA, and circRNA in the longissimus dorsi of Landrace and Lantang pigs. Of the 22,469 identified coding transcripts, only 547 candidates were differentially expressed, including 461 upregulated and 86 downregulated transcripts in the Lantang pigs compared with Landrace. Gene ontology analysis of these differentially-expressed transcripts further revealed 17 genes involved in myogenesis. In addition, 5,566 lncRNA and 4,360 circRNA candidates were found to be differentially expressed. Of these, 3,976 lncRNAs and 1,401 circRNAs were upregulated in the Lantang library, while 1,590 lncRNAs and 2,959 circRNAs were downregulated. Of the differentially expressed circRNAs, 236 candidates were edited from 93 functional hosting-genes related to myogenesis. We found 96 showed upregulation and 140 showed downregulation. By analyzing Ribo-Zero RNA-Seq data in combination with matched miRNA profiles, we identified 68 sponge modulators participating in 26 miRNA-mediated ceRNA interactions, including 19 lncRNAs, 40 circRNAs, and 9 mRNAs. Our study uncovered a novel post-transcriptional regulation layer which could help in the understanding of the mechanisms that underlie porcine myofiber development in different breeds.
URLPMID:5481632 [本文引用: 1]

In asymmetric chick gonads, the left and right female gonads undergo distinct programs during development, generating a functional ovary on the left side only. Despite some progress being made in recent years, the mechanisms of molecular regulation remain incompletely understood, and little genomic information is available regarding the degeneration of the right ovary in the chick embryo testis. In this study, we performed transcriptome sequencing to investigate differentially expressed genes in the left and right ovaries and gene functions at two critical time points; embryonic days 6 (E6) and 10 (E10). Using high-throughput RNA-sequencing technologies, 539 and 1046 genes were identified as being significantly differentially expressed between 6R-VS-6L and 10R-VS-10L. Gene ontology analysis of the differentially expressed genes revealed enrichment in functional pathways. Among these, candidate genes associated with degeneration of the right ovary in the chick embryo were identified. Identification of a pathway involved in ovarian degeneration provides an important resource for the further study of its molecular mechanisms and functions.
URLPMID:22374175 [本文引用: 2]

78 The first systematic identification of lncRNAs during chicken muscle development was reported. 78 Using the computational approach, 281 new lncRNAs were identified in the chicken genome. 78 The novel lncRNAs are slightly more conserved than random noncoding sequences. 78 The presented pipeline will be useful for characterizing lncRNAs from deep sequencing data.sd
.
[本文引用: 1]
URLPMID:19687284 [本文引用: 1]

The identification of the differential expression of genes in the ovaries of egg-laying and prelaying Zi geese is required to improve the laying performance of the geese. In the present study, suppression subtractive hybridization and reverse dot-blot were employed to identify such genes, using the ovary as a model. Furthermore, expression profiling of estrogen receptor 1, estrogen receptor 2, follicle stimulating hormone receptor, prolactin receptor, ferritin H chain, and ovary differentially expressed unknown gene 08 in ovaries from geese was performed by quantitative real-time PCR. Total RNA from the ovaries of laying and prelaying Zi geese was pooled and the mRNA was isolated. The cDNA that was reverse-transcribed from the ovarian mRNA of the prelaying geese was subtracted from the cDNA isolated from the laying geese. Four hundred sixty-five clones containing putative differentially expressed gene fragments were further identified by reverse dot-blot. Ninety-seven clones were subjected to sequencing and further analysis. Sequence analysis showed that the expression of 18 known (including a mitochondrial gene) and 8 unknown gene fragments was higher in the ovaries of laying geese compared with prelaying geese. Seventeen of the known genes encode proteins that belong to groups involved with binding, catalytic activity, enzyme regulatory activity, signal transducer activity, structural molecule, and transporter activity. The results of the quantitative real-time PCR showed that the expression of estrogen receptor 1, estrogen receptor 2, follicle stimulating hormone receptor, prolactin receptor, ferritin H chain, and ovary differentially expressed unknown gene 08 was higher in the ovaries of the laying geese than in those of the prelaying geese (P<0.05). These differentially expressed genes may be relevant to the progression of prelaying geese to the egg-laying stage. Further study is required to elucidate the molecular mechanism that controls egg-laying in geese, to improve the productivity of laying geese.
URLMagsci [本文引用: 1]

<FONT face=Verdana>旨在利用抑制消减杂交技术构建鹅就巢与产蛋cDNA基因文库,筛选就巢母鹅上调与下调表达的基因。以就巢期和产蛋期鹅卵巢组织互为检测子和驱动子, 进行正反双向消减杂交, 获得鹅卵巢差异表达基因文库。从双向文库随机挑选单菌落进行PCR验证,结果表明文库质量良好。选取654个阳性克隆进行测序分析,获得641条表达序列标签(ESTs)。对ESTs进行去除载体序列、质量检测、聚类及拼接,经BLASTn比对,有166条ESTs找到与之匹配的同源序列,其中92个是功能基因。比较就巢与产蛋SSH文库,发现就巢SSH库中参与细胞凋亡、信号转导及细胞结构的基因出现频率较高;产蛋特异性基因文库中参与物质能量代谢、细胞防御的基因较多;尚有许多差异片段属于未知功能蛋白或理论推定蛋白。结果提示,催乳素受体、抗苗勒管激素以及雌激素受体基因在就巢期上调表达可能与鹅就巢行为的启动与维持有关。该结果为进一步研究鹅就巢行为分子调控机制奠定基础。</FONT>
URLMagsci [本文引用: 1]

<FONT face=Verdana>旨在利用抑制消减杂交技术构建鹅就巢与产蛋cDNA基因文库,筛选就巢母鹅上调与下调表达的基因。以就巢期和产蛋期鹅卵巢组织互为检测子和驱动子, 进行正反双向消减杂交, 获得鹅卵巢差异表达基因文库。从双向文库随机挑选单菌落进行PCR验证,结果表明文库质量良好。选取654个阳性克隆进行测序分析,获得641条表达序列标签(ESTs)。对ESTs进行去除载体序列、质量检测、聚类及拼接,经BLASTn比对,有166条ESTs找到与之匹配的同源序列,其中92个是功能基因。比较就巢与产蛋SSH文库,发现就巢SSH库中参与细胞凋亡、信号转导及细胞结构的基因出现频率较高;产蛋特异性基因文库中参与物质能量代谢、细胞防御的基因较多;尚有许多差异片段属于未知功能蛋白或理论推定蛋白。结果提示,催乳素受体、抗苗勒管激素以及雌激素受体基因在就巢期上调表达可能与鹅就巢行为的启动与维持有关。该结果为进一步研究鹅就巢行为分子调控机制奠定基础。</FONT>
URLPMID:3566205 [本文引用: 1]

The geese have strong broodiness and poor egg performance. These characteristics are the key issues that hinder the goose industry development. Yet little is known about the mechanisms responsible for follicle development due to lack of genomic resources. Hence, studies based on high-throughput sequencing technologies are needed to produce a comprehensive and integrated genomic resource and to better understand the biological mechanisms of goose follicle development.In this study, we performed de novo transcriptome assembly and gene expression analysis using short-read sequencing technology (Illumina). We obtained 67,315,996 short reads of 100 bp, which were assembled into 130,514 unique sequences by Trinity strategy (mean size = 753 bp). Based on BLAST results with known proteins, these analyses identified 52,642 sequences with a cut-off E-value above 10(-5). Assembled sequences were annotated with gene descriptions, gene ontology and clusters of orthologous group terms. In addition, we investigated the transcription changes during the goose laying/broodiness period using a tag-based digital gene expression (DGE) system. We obtained a sequencing depth of over 4.2 million tags per sample and identified a large number of genes associated with follicle development and reproductive biology including cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme gene and dopamine beta-hydroxylas gene. We confirm the altered expression levels of the two genes using quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR).The obtained goose transcriptome and DGE profiling data provide comprehensive gene expression information at the transcriptional level that could promote better understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying follicle development and productivity.
URLPMID:25917302 [本文引用: 1]

Summary Excessive adiposity is a major problem in the duck industry, but its molecular mechanisms remain unknown. Genetic comparisons between domestic and wild animals have contributed to the exploration of genetic mechanisms responsible for many phenotypic traits. Significant differences in body fat mass have been detected between domestic and wild ducks. In this study, we used the Peking duck and Anas platyrhynchos as the domestic breed and wild counterpart respectively and performed a transcriptomic comparison of abdominal fat between the two breeds to comprehensively analyze the transcriptome basis of adiposity in ducks. We obtained approximately 35002million clean reads; assembled 6102250 transcripts, including 2302699 novel ones; and identified alternative 5′ splice sites, alternative 3′ splice sites, skipped exons and retained intron as the main alternative splicing events. A differential expression analysis between the two breeds showed that 753 genes exhibited differential expression. In Peking ducks, some lipid metabolism-related genes ( IGF2 , FABP5 , BMP7 , etc.) and oncogenes ( RRM2 , AURKA , CYR61 , etc.) were upregulated, whereas genes related to tumor suppression and immunity ( TNFRSF19 , TNFAIP6 , IGSF21 , NCF1 , etc.) were downregulated, suggesting adiposity might closely associate with tumorigenesis in ducks. Furthermore, 28002576 single-nucleotide variations were found differentiated between the two breeds, including 8641 non-synonymous ones, and some of the non-synonymous ones were found enriched in genes involved in lipid-associated and immune-associated pathways, suggesting abdominal fat of the duck undertakes both a metabolic function and immune-related function. These datasets enlarge our genetic information of ducks and provide valuable resources for analyzing mechanisms underlying adiposity in ducks.
URLPMID:4287553 [本文引用: 1]

Background Seasonal estrus is a critical limiting factor of animal fecundity, and it involves changes in both ovarian biology and hormone secretion in different seasons. Previous studies indicate that two classes of small RNAs (miRNAs and piRNAs) play important regulatory roles in ovarian biology. To understand the roles of small RNA-mediated post-transcriptional regulation in ovine seasonal estrus, the variation in expression patterns of ovarian small RNAs during anestrus and the breeding season were analyzed using Solexa sequencing technology. In addition, reproductive hormone levels were determined during ovine anestrus and the breeding season. Results A total of 483 miRNAs (including 97 known, 369 conserved and 17 predicated novel miRNAs), which belong to 183 different miRNA families, were identified in ovaries of Tan sheep and Small Tail Han (STH) sheep. Compared with the three stages of the breeding season, 25 shared significantly differentially expressed (including 19 up- and six down-regulated) miRNAs were identified in ovine anestrus. KEGG Pathway analysis revealed that the target genes for some of the differentially expressed miRNAs were involved in reproductive hormone related pathways (e.g. steroid biosynthesis, androgen and estrogen metabolism and GnRH signaling pathway) as well as follicular/luteal development related pathways. Moreover, the expression of the differentially expressed miRNAs and most of their target genes were negatively correlated in the above pathways. Furthermore, the levels of estrogen, progesterone and LH in ovine anestrus were significantly lower than those in the breeding season. Combining the results of pathway enrichment analysis, expression of target genes and hormone measurement, we suggest that these differentially expressed miRNAs in anestrus might participate in attenuation of ovarian activity by regulating the above pathways. Besides miRNAs, a large and unexpectedly diverse set of piRNAs were also identified. Conclusions The miRNA profiles of ovine ovaries in anestrus were presented for the first time. The identification and characterization of miRNAs that are differentially expressed between ovine anestrus and the breeding season will help understanding of the role of miRNAs in the regulation of seasonal estrus, and provides candidates for determining miRNAs which could be potentially used to regulate ovine seasonal estrus.
URLPMID:4710718 [本文引用: 1]

MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of short endogenous, single-stranded, non-coding small RNA molecules, about 19 25 nucleotides in length that regulate gene expression at the translation level and influence many physiological process, such apoptosis, metabolism, signal transduction, and occurrence and development of diseases. In this study, we constructed a library from the ovine luteal phase ovary by using next-generation sequencing technology (Solexa high-throughput sequencing technique) and identified 267 novel miRNAs by bioinformatics. One of the novel miRNAs (ovis_aries_ovary-m0033_3p), which expressed in the sheep ovary and testis, was confirmed by real time PCR and northern blot. Ovis_aries_ovary-m0033_3p was 21 nucleotides in length and located on chromosome 12, and it had 100% similarity to hsa-miR-214-3p, mmu-miR-214-3p, dre-miR-214and ssc-miR-214. Meanwhile, the pre-miRNA was 82 nucleotides in length and had a standard hairpin stem-loop structure. From the consistency of the sequence and structure, we speculated that ovis_aries_ovary-m0033_3p had a function similar to hsa-miR-214-3p, which is involved in the fine regulation of cell survival, embryonic development, breeding activities and resistance to ovarian cancer, so we defined it as oar-miR-214-3p. These experimental results will enrich the miRNA database forovis ariesand provide the basis for researching the regulation mechanism of miRNA in relation to breeding activities of seasonal breeding animals.
URLMagsci [本文引用: 1]

本研究采集的Texel绵羊胎儿的背最长肌样品包括5个发育阶段:70、85、100、120和135 d。通过采用Solexa测序技术对混池样品进行了microRNA(miRNA)深度测序,获得了16532850条原始序列读数。使用ACGT101-miR v4.2分析软件对miRNA测序数据进行了深度发掘;通过与最新的哺乳动物成熟miRNA序列(miRNA数据库:miRBase v17.0)、miRNA前体序列、绵羊基因组序列(绵羊基因组数据库,2010年2月)的比对分析,对绵羊microRNA转录组数据库进行了大幅更新,pre-miRNA(miRNA前体)序列增至1529条,编码的miRNA成熟体序列增至1999条。通过实时荧光定量PCR技术对深度测序获得的5个miRNA在混池样品中进行了验证。绵羊miRNA的研究起步较晚,而miRNA的发现与鉴定将促进基因调控机制及miRNA功能的研究。
URLMagsci [本文引用: 1]

本研究采集的Texel绵羊胎儿的背最长肌样品包括5个发育阶段:70、85、100、120和135 d。通过采用Solexa测序技术对混池样品进行了microRNA(miRNA)深度测序,获得了16532850条原始序列读数。使用ACGT101-miR v4.2分析软件对miRNA测序数据进行了深度发掘;通过与最新的哺乳动物成熟miRNA序列(miRNA数据库:miRBase v17.0)、miRNA前体序列、绵羊基因组序列(绵羊基因组数据库,2010年2月)的比对分析,对绵羊microRNA转录组数据库进行了大幅更新,pre-miRNA(miRNA前体)序列增至1529条,编码的miRNA成熟体序列增至1999条。通过实时荧光定量PCR技术对深度测序获得的5个miRNA在混池样品中进行了验证。绵羊miRNA的研究起步较晚,而miRNA的发现与鉴定将促进基因调控机制及miRNA功能的研究。
URLPMID:25573241 [本文引用: 1]

A variety of sheep species with diverse fecundities are kept as livestock and make up the global agricultural economy. A mutation in the FecB gene has been implicated to be essential and additive for ovulation rate. To uncover potential regulators of fecundity, we performed a genome-wide analysis of mRNAs and miRNAs from Dorset sheep (Dorset), Small Tail Han sheep FecB(B)FecB(B) genotype (Han BB) and Small Tail Han sheep FecB(+)FecB(+) genotype (Han ++). Here we present detailed analyses at both the mRNA and miRNA levels to aid in the identification of candidate genes that might regulate fecundity. We found differentially expressed genes between each of the groups, which are involved in various cellular activities, such as metabolic cascades, catalytic function and signal transduction. Moreover, the miRNA profiling identified specific miRNAs unique to each group of sheep, which may play a role in the controlling fecundity differences. By exploring the miRNA-regulated gene expression network in the different sheep species we can create a stronger profile for regulation of fecundity. Furthermore, quantitative real-time PCR verified the reliability of the RNA-Seq data. To our knowledge, this is the first analysis of intravariety and intervariety in any species in this area. Taken together, this genome-wide analysis of mRNAs and miRNAs in sheep will aid in the ability to identify fecundity regulators between different sheep species. (C) 2014 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
URLPMID:4073507 [本文引用: 1]

Background The advent of large-scale gene expression technologies has helped to reveal in eukaryotic cells, the existence of thousands of non-coding transcripts, whose function and significance remain mostly poorly understood. Among these non-coding transcripts, long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are the least well-studied but are emerging as key regulators of diverse cellular processes. In the present study, we performed a survey in bovine Longissimus thoraci of lincRNAs (long intergenic non-coding RNAs not overlapping protein-coding transcripts). To our knowledge, this represents the first such study in bovine muscle. Results To identify lincRNAs, we used paired-end RNA sequencing (RNA-Seq) to explore the transcriptomes of Longissimus thoraci from nine Limousin bull calves. Approximately 14???45 million paired-end reads were obtained per library. A total of 30,548 different transcripts were identified. Using a computational pipeline, we defined a stringent set of 584 different lincRNAs with 418 lincRNAs found in all nine muscle samples. Bovine lincRNAs share characteristics seen in their mammalian counterparts: relatively short transcript and gene lengths, low exon number and significantly lower expression, compared to protein-encoding genes. As for the first time, our study identified lincRNAs from nine different samples from the same tissue, it is possible to analyse the inter-individual variability of the gene expression level of the identified lincRNAs. Interestingly, there was a significant difference when we compared the expression variation of the 418 lincRNAs with the 10,775 known selected protein-encoding genes found in all muscle samples. In addition, we found 2,083 pairs of lincRNA/protein-encoding genes showing a highly significant correlated expression. Fourteen lincRNAs were selected and 13 were validated by RT-PCR. Some of the lincRNAs expressed in muscle are located within quantitative trait loci for meat quality traits. Conclusions Our study provides a glimpse into the lincRNA content of bovine muscle and will facilitate future experimental studies to unravel the function of these molecules. It may prove useful to elucidate their effect on mechanisms underlying the genetic variability of meat quality traits. This catalog will complement the list of lincRNAs already discovered in cattle and therefore will help to better annotate the bovine genome.
URLPMID:26641174 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract Ribonucleic acid sequencing (RNA-Seq) libraries are normally prepared with oligo(dT) selection of poly(A)+ mRNA, but it depends on intact total RNA samples. Recent studies have described Ribo-Zero technology, a novel method that can capture both poly(A)+ and poly(A)- transcripts from intact or fragmented RNA samples. We report here the first application of Ribo-Zero RNA-Seq for the analysis of the bovine embryonic, neonatal, and adult skeletal muscle whole transcriptome at an unprecedented depth. Overall, 19,893 genes were found to be expressed, with a high correlation of expression levels between the calf and the adult. Hundreds of genes were found to be highly expressed in the embryo and decreased at least 10-fold after birth, indicating their potential roles in embryonic muscle development. In addition, we present for the first time the analysis of global transcript isoform discovery in bovine skeletal muscle and identified 36,694 transcript isoforms. Transcriptomic data were also analyzed to unravel sequence variations; 185,036 putative SNP and 12,428 putative short insertions-deletions (InDel) were detected. Specifically, many stop-gain, stop-loss, and frameshift mutations were identified that probably change the relative protein production and sequentially affect the gene function. Notably, the numbers of stage-specific transcripts, alternative splicing events, SNP, and InDel were greater in the embryo than in the calf and the adult, suggesting that gene expression is most active in the embryo. The resulting view of the transcriptome at a single-base resolution greatly enhances the comprehensive transcript catalog and uncovers the global trends in gene expression during bovine skeletal muscle development.
URLPMID:21057797 [本文引用: 1]

High-throughput sequencing of RNA (RNA-Seq) was developed primarily to analyze global gene expression in different tissues. However, it also is an efficient way to discover coding SNPs. The objective of this study was to perform a SNP discovery analysis in the milk transcriptome using RNA-Seq. Seven milk samples from Holstein cows were analyzed by sequencing cDNAs using the Illumina Genome Analyzer system. We detected 19,175 genes expressed in milk samples corresponding to approximately 70% of the total number of genes analyzed. The SNP detection analysis revealed 100,734 SNPs in Holstein samples, and a large number of those corresponded to differences between the Holstein breed and the Hereford bovine genome assembly Btau4.0. The number of polymorphic SNPs within Holstein cows was 33,045. The accuracy of RNA-Seq SNP discovery was tested by comparing SNPs detected in a set of 42 candidate genes expressed in milk that had been resequenced earlier using Sanger sequencing technology. Seventy of 86 SNPs were detected using both RNA-Seq and Sanger sequencing technologies. The KASPar Genotyping System was used to validate unique SNPs found by RNA-Seq but not observed by Sanger technology. Our results confirm that analyzing the transcriptome using RNA-Seq technology is an efficient and cost-effective method to identify SNPs in transcribed regions. This study creates guidelines to maximize the accuracy of SNP discovery and prevention of false-positive SNP detection, and provides more than 33,000 SNPs located in coding regions of genes expressed during lactation that can be used to develop genotyping platforms to perform marker-trait association studies in Holstein cattle.
URLPMID:22198337 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract value of 10. Assembled sequences were then annotated using Gene ontology terms, Clusters of Orthologous Groups classifications, and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathways. In addition, we found a number of highly expressed genes involved in the regulation of Sika deer antler rapid growth, including transcription factors, signaling molecules, and extracellular matrix proteins. Our data represent the most comprehensive sequence resource available for the deer antler and provide a basis for new research on deer antler molecular genetics and functional genomics.
URLPMID:4514889 [本文引用: 1]

Prior to the mechanization of agriculture and labor-intensive tasks, humans used donkeys (Equus africanus asinus) for farm work and packing. However, as mechanization increased, donkeys have been increasingly raised for meat, milk, and fur in China. To maintain the development of the donkey industry, breeding programs should focus on traits related to these new uses. Compared to conventional marker-assisted breeding plans, genome- and transcriptome-based selection methods are more efficient and effective. To analyze the coding genes of the donkey genome, we assembled the transcriptome of donkey white blood cells de novo. Using transcriptomic deep-sequencing data, we identified 264,714 distinct donkey unigenes and predicted 38,949 protein fragments. We annotated the donkey unigenes by BLAST searches against the non-redundant (NR) protein database. We also compared the donkey protein sequences with those of the horse (E. caballus) and wild horse (E. przewalskii), and linked the donkey protein fragments with mammalian phenotypes. As the outer ear size of donkeys and horses are obviously different, we compared the outer ear size-associated proteins in donkeys and horses. We identified three ear size-associated proteins, HIC1, PRKRA, and KMT2A, with sequence differences among the donkey, horse, and wild horse loci. Since the donkey genome sequence has not been released, the de novo assembled donkey transcriptome is helpful for preliminary investigations of donkey cultivars and for genetic improvement.
URLPMID:5496257 [本文引用: 1]

Efforts to resolve the transcribed sequences in the equine genome have focused on protein-coding RNA. The transcription of the intergenic regions, although detected via total RNA sequencing (RNA-seq), has yet to be characterized in the horse. The most recent equine transcriptome based on RNA-seq from several tissues was a prime opportunity to obtain a concurrent long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) database. This lncRNA database has a breadth of eight tissues and a depth of over 20 million reads for select tissues, providing the deepest and most expansive equine lncRNA database. Utilizing the intergenic reads and three categories of novel genes from a previously published equine transcriptome pipeline, we better describe these groups by annotating the lncRNA candidates. These lncRNA candidates were filtered using an approach adapted from human lncRNA annotation, which removes transcripts based on size, expression, protein-coding capability and distance to the start or stop of annotated protein-coding transcripts. Our equine lncRNA database has 20,800 transcripts that demonstrate characteristics unique to lncRNA including low expression, low exon diversity and low levels of sequence conservation. These candidate lncRNA will serve as a baseline lncRNA annotation and begin to describe the RNA-seq reads assigned to the intergenic space in the horse. The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s12864-017-3884-2) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
URLPMID:3472166 [本文引用: 1]

pAbstract/p pBackground/p pThoroughbred horses are the most expensive domestic animals, and their running ability and knowledge about their muscle-related diseases are important in animal genetics. While the horse reference genome is available, there has been no large-scale functional annotation of the genome using expressed genes derived from transcriptomes./p pResults/p pWe present a large-scale analysis of whole transcriptome data. We sequenced the whole mRNA from the blood and muscle tissues of six thoroughbred horses before and after exercise. By comparing current genome annotations, we identified 32,361 unigene clusters spanning 51.83 b that contained 11,933 (36.87%) annotated genes. More than 60% (20,428) of the unigene clusters did not match any current equine gene model. We also identified 189,973 single nucleotide variations (SNVs) from the sequences aligned against the horse reference genome. Most SNVs (171,558 SNVs; 90.31%) were novel when compared with over 1.1 million equine SNPs from two SNP databases. Using differential expression analysis, we further identified a number of exercise-regulated genes: 62 up-regulated and 80 down-regulated genes in the blood, and 878 up-regulated and 285 down-regulated genes in the muscle. Six of 28 previously-known exercise-related genes were over-expressed in the muscle after exercise. Among the differentially expressed genes, there were 91 transcription factor-encoding genes, which included 56 functionally unknown transcription factor candidates that are probably associated with an early regulatory exercise mechanism. In addition, we found interesting RNA expression patterns where different alternative splicing forms of the same gene showed reversed expressions before and after exercising./p pConclusion/p pThe first sequencing-based horse transcriptome data, extensive analyses results, deferentially expressed genes before and after exercise, and candidate genes that are related to the exercise are provided in this study./p
URL [本文引用: 1]

利用转录组测序方法分析了不同毛色(白色和海狸色)獭兔皮肤组织中基因的表达差异,旨在找到影响獭兔毛色的候选基因。采用Illumina Hi Seq ^TM2500测序平台对不同毛色獭兔耳组织中所有m RNA进行高通量测序,所得序列经质控、组装后比对到GO、COG、SWISS-PROT数据库中注释,并进行差异表达基因聚类分析和KEGG通路分析。结果表明:测序共获得Unigene 275 625个,差异表达基因12 408个,其中上调表达基因4 904个,下调表达基因7 504个。KEGG通路分析发现,这些差异基因显著地富集在13个代谢通路中,并在细胞色素代谢通路(metabolism of xenobiotics by cytochrome P450)中有8个差异表达的基因,其中CP2F1和CP2BB属于细胞色素P450家族成员,而GSTA4与黑素细胞分化有关,可能在獭兔毛色中发挥作用。
URL [本文引用: 1]

利用转录组测序方法分析了不同毛色(白色和海狸色)獭兔皮肤组织中基因的表达差异,旨在找到影响獭兔毛色的候选基因。采用Illumina Hi Seq ^TM2500测序平台对不同毛色獭兔耳组织中所有m RNA进行高通量测序,所得序列经质控、组装后比对到GO、COG、SWISS-PROT数据库中注释,并进行差异表达基因聚类分析和KEGG通路分析。结果表明:测序共获得Unigene 275 625个,差异表达基因12 408个,其中上调表达基因4 904个,下调表达基因7 504个。KEGG通路分析发现,这些差异基因显著地富集在13个代谢通路中,并在细胞色素代谢通路(metabolism of xenobiotics by cytochrome P450)中有8个差异表达的基因,其中CP2F1和CP2BB属于细胞色素P450家族成员,而GSTA4与黑素细胞分化有关,可能在獭兔毛色中发挥作用。
[D].
[本文引用: 1]

水貂(Neovison vison),是一种珍贵毛皮动物,其毛皮主要用于制裘,因此,被毛颜色是决定貂皮质量与价值的一种重要经济性状,深入解析水貂被毛色素沉积机理在新型毛色品种培育过程中具有重要的理论与实践意义。为了更好地明确水貂被毛颜色表型形成的遗传调控机制,本研究以具有显著毛色差异的金州黑水貂(黑色)、吉林白水貂(白色)、银蓝水貂(灰色)、咖啡水貂(棕褐色)和珍珠水貂(珍珠色)为研究对象,利用组织学、细胞学、分子生物学及高通量RNA-seq转录组测序技术,系统开展了水貂被毛黑色素含量差异分析、成熟黑色素细胞组织学定位检测、毛色关联基因克隆及其...
[学位论文].
[本文引用: 1]

水貂(Neovison vison),是一种珍贵毛皮动物,其毛皮主要用于制裘,因此,被毛颜色是决定貂皮质量与价值的一种重要经济性状,深入解析水貂被毛色素沉积机理在新型毛色品种培育过程中具有重要的理论与实践意义。为了更好地明确水貂被毛颜色表型形成的遗传调控机制,本研究以具有显著毛色差异的金州黑水貂(黑色)、吉林白水貂(白色)、银蓝水貂(灰色)、咖啡水貂(棕褐色)和珍珠水貂(珍珠色)为研究对象,利用组织学、细胞学、分子生物学及高通量RNA-seq转录组测序技术,系统开展了水貂被毛黑色素含量差异分析、成熟黑色素细胞组织学定位检测、毛色关联基因克隆及其...
