 ,1,2, 刘震2, 黄鹏翔2,3, 朱金勇1,2, 李志涛1,2, 马文婧1,2, 张俊莲2,3, 白江平
,1,2, 刘震2, 黄鹏翔2,3, 朱金勇1,2, 李志涛1,2, 马文婧1,2, 张俊莲2,3, 白江平 ,1,2,*, 刘玉汇
,1,2,*, 刘玉汇 ,1,2,*
,1,2,*Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of potato GAUT gene family
NIU Na ,1,2, LIU Zhen2, HUANG Peng-Xiang2,3, ZHU Jin-Yong1,2, LI Zhi-Tao1,2, MA Wen-Jing1,2, ZHANG Jun-Lian2,3, BAI Jiang-Ping
,1,2, LIU Zhen2, HUANG Peng-Xiang2,3, ZHU Jin-Yong1,2, LI Zhi-Tao1,2, MA Wen-Jing1,2, ZHANG Jun-Lian2,3, BAI Jiang-Ping ,1,2,*, LIU Yu-Hui
,1,2,*, LIU Yu-Hui ,1,2,*
,1,2,*通讯作者: * 白江平, E-mail:baijp@gsau.edu.cn;刘玉汇, E-mail:lyhui@gsau.edu.cn
收稿日期:2020-12-9接受日期:2021-04-14网络出版日期:2021-06-03
| 基金资助: |
Corresponding authors: * E-mail:baijp@gsau.edu.cn;E-mail:lyhui@gsau.edu.cn
Received:2020-12-9Accepted:2021-04-14Published online:2021-06-03
| Fund supported: |
作者简介 About authors
E-mail:2413748774@qq.com

摘要
半乳糖醛酸转移酶(GAUT)是一种参与催化糖基化反应的酶类,在植物生长发育过程中发挥着重要作用。本研究鉴定了马铃薯GAUT家族成员,并对其理化性质、染色体定位、基因结构、保守蛋白结构域、基因重复事件和表达模式进行了分析。结果表明,鉴定到的41个GAUT家族成员(StGAUT),不均匀的分布在10条染色体上。根据基因的结构和系统发育蛋白特征,将41个StGAUT分为4个亚组。共线性分析表明,StGAUT基因家族存在12对片段重复基因,均在纯化选择下进化。通过对马铃薯双单倍体(DM)的不同组织部位和非生物胁迫下的RNA-seq数据进行分析,筛选出了组织特异性表达及响应非生物胁迫的StGAUT基因。此外,进一步对不同四倍体栽培种彩色马铃薯的薯皮和薯肉进行RNA-seq测序和分析,获得了可能参与花色素苷生物合成的StGAUT基因。本研究结果为进一步阐明StGAUT基因在马铃薯中的功能提供了有价值的信息。
关键词:
Abstract
Galacturonyltransferases (GAUTs) are enzymes responsible for catalyzing glycosylation reactions and play an important role in the growth and development of plant. In this study, GAUT genes family members in potato (StGAUT) were identified, and their physical and chemical characteristics, distribution on chromosomes, gene structure, conserved motifs, gene duplication events, and expression patterns were analyzed. The results showed that a total of 41 StGAUTs were identified and distributed extensively and unevenly on 10 chromosomes. According to their structural and phylogenetic protein features, these 41 StGAUT genes were divided into four subclasses. Collinearity analysis indicated that 12 pairs of StGAUTs were segmental duplication genes, and these gene pairs evolved under purifying selection. RNA-seq data of different tissues and abiotic stresses were used to analyze tissue-specific and abiotic stress-responses of the StGAUT genes in doubled monoploid potato (DM). Results revealed that StGAUT genes might be involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis in three different-colored potato cultivars based on RNA-seq data. The results provide valuable information regarding further functional elucidation of StGAUT genes in potato.
Keywords:
PDF (3346KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
本文引用格式
牛娜, 刘震, 黄鹏翔, 朱金勇, 李志涛, 马文婧, 张俊莲, 白江平, 刘玉汇. 马铃薯GAUT基因家族的全基因组鉴定及表达分析. 作物学报, 2021, 47(12): 2348-2361 DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1006.2021.04268
NIU Na, LIU Zhen, HUANG Peng-Xiang, ZHU Jin-Yong, LI Zhi-Tao, MA Wen-Jing, ZHANG Jun-Lian, BAI Jiang-Ping, LIU Yu-Hui.
糖基转移酶家族(glycosyltransferase,GTs)是专门负责催化糖基化反应的酶类,它们将活性糖基从糖基供体转移到糖基受体,并形成糖苷键,产物包括寡糖、多糖、各种复合糖(糖蛋白、糖脂)和多种多样的糖苷化合物(如花色苷、黄酮糖苷、白藜芦醇糖苷等)[1]。根据蛋白氨基酸序列的相似性,GTs被分为100多个亚家族[2]。其中一些家族的结构特征及其功能有被报道。Yin等[3]研究发现,糖基转移酶家族8 (GT8)基因家族的蛋白含有一个Glyco-transf-8结构域(约256个氨基酸),其中一些GT8基因参与植物细胞壁的生物合成。
半乳糖基转移酶基因(GAUT)属于GT8基因家族,它编码的半乳糖醛酸转移酶(GAUT,alpha- galacturonosyltransferase, EC2.4.1.43)与果胶和半纤维素生物合成密切相关[4,5]。Sterling等[6]在拟南芥中共鉴定出15个GAUT家族成员,分为3个分支:GAUT-A (AtGAUT1~AtGAUT7)、GAUT-B (AtGAUT8~AtGAUT11)和GAUT-C (AtGAUT12~AtGAUT15)。Mohnen等[7]研究表明,GAUT1是参与果胶合成的半乳糖醛酸转移酶。GAUT4沉默的番茄植株果实表现出果胶成分的改变,积累的淀粉减少,果胶的数量减少,除其在果胶生物合成中的作用外,GAUT4还干扰了碳的代谢和分配[5]。GAUT13与GAUT14位于高尔基体中,参与了植物的发育过程,例如促进了花粉管壁和营养体细胞壁中果胶和木聚糖的合成[8]。GbGAUT32和GbGAUT04在海岛棉纤维发育过程中发挥着重要作用[9]。然而,GAUT基因在马铃薯中的功能尚不明确。鉴于GAUT基因在植物生长发育中发挥重要的作用,本研究从马铃薯全基因组水平对GAUT基因家族成员的数目、染色体上的分布特征、基因结构、理化性质、蛋白质保守结构域的组成和基因间的亲缘关系进行了全面的鉴定和分析,同时利用RNA-seq数据筛选出可能参与双单倍体马铃薯DM的不同器官发育和响应非生物胁迫的StGAUT基因,并进一步对3个不同颜色马铃薯品种的薯皮及薯肉中的StGAUT基因表达进行分析,获得了可能参与花色素苷生物合成的StGAUT基因,旨在为进一步研究GAUT基因家族成员的功能提供理论基础。
1 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
研究材料为3种不同颜色的马铃薯品种,包括‘黑美人’ (紫皮紫肉)、‘新大坪’ (白皮白肉)和‘铃田红美’ (红皮红肉)。所有试验材料在甘肃省定西市农业科学研究院试验田种植。每个品种取6个新鲜块茎(直径约4~5 cm),蒸馏水冲洗干净后,用手术刀将块茎薯皮分离取样,距离薯皮组织至少5 mm取薯肉,并将薯肉切成薄块。样品立即冷冻在液氮中,存放在-80℃的冰箱中以备使用。1.2 马铃薯基因组中GAUT成员(StGAUT)的鉴定
马铃薯基因组信息、蛋白质和CDS序列及染色体位置等信息均下载自在线数据资源(PGSC,1.3 马铃薯GAUT家族成员的序列和结构特征分析
使用Expasy网站(1.4 马铃薯GAUT家族成员的染色体定位与基因重复事件分析
根据StGAUT家族成员在染色体上的位置信息,利用MapChart软件绘制StGAUT基因的染色体位置图和相对距离。StGAUT基因的串联重复事件由以下2个条件确定:(1) 短序列的长度覆盖了长序列的70%以上;(2) 2个对齐序列的相似性大于70% [16,17]。串联重复是指2个基因位于同一染色体片段中,距离小于100 kb,且它们之间的基因个数≤5[18]。用MCScanX分析了马铃薯基因的重复事件[19],并用Circis v0.69[20]绘图。为进一步估计StGAUT的重复事件,使用KaKs calculator 2.0[21]计算非同义替换率(Ka)和同义替换率(Ks)。1.5 GAUT的进化分析与分类
利用ClustalW软件对新鉴定的马铃薯GAUT氨基酸序列以及已知的15个拟南芥GAUT氨基酸序列[6]进行多序列比对,利用MEGA7.0软件[22]构建无根系统发育树(最大似然法和1000次迭代bootstrap测试)。1.6 总mRNA提取和实时荧光定量PCR (qPCR)
采用RNA提取试剂盒DP419 (天根生化科技(北京)有限公司)提取总RNA,之后利用琼脂糖凝胶电泳和Nanodrop ND-2000 (Nanodrop Technologies,美国)分光光度计检测RNA的完整性和浓度。使用带有gDNase的快速RT试剂盒KR116 (天根生化科技(北京)有限公司)进行基因组DNA污染的消除和第一链cDNA的合成。使用(天根生化科技(北京)有限公司)的SuperReal PreMix Plus (SYBRGreen FP205)试剂盒在CFX96 (Bio-Rad,美国)上进行qPCR,采用3次生物学重复。反应体系为20 μL,包含2 μL cDNA (50 ng μL-1)、上下引物(10 µmol L-1)各0.6 μL、2×SYBRGreen MasterMix 10 μL、ddH2O 6.8 μL。qPCR反应条件为95℃预变性30 s;95℃变性下5 s,60℃退火30 s,40个循环;65~95℃条件下检测熔点曲线。通过分析cDNA梯度稀释的标准曲线获得每个基因的扩增效率,利用2-ΔΔCt方法计算基因的相对表达水平,以StEF-1α (AB061263)作为内参基因[23],使用Origin 2018绘图。由生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司设计并合成引物,引物名称及序列详见表1。Table 1
表1
表1qPCR引物序列
Table 1
| 基因名称 Gene name | 正向引物 Forward sequence (5°-3°) | 反向引物 Reverse sequence (5°-3°) |
|---|---|---|
| StEF-1α | GGTCGTGTTGAGACTGGTGTGATC | GCTTCGTGGTGCATCTCTACAGAC |
| PG0024800 | ACAGAGTATTCGCTTGGCAGGTTC | CTTCCATCCGGCAGCCTCTAAAC |
| PG0024782 | CATTGGAGTGGAGGTGGCAAACC | TGCAAATCATATCGAGCCCAGAGC |
| PG0020103 PG0000827 | CTGATCTCGGCGTCGGAATTACAC AAGCTCCAGCATTCCGCAACG | AGCCAGAACCAATGAACGGTGATC CGGAGGTAAGGGGAGGAGTAATCG |
| PG0003522 | GCCGTTGATGGTGAAGTTGAAGC | GCCGCCGATGGAGCAGTTATG |
| PG0001444 | CAGACAGTTGCCTTCACCAGAGC | GGCAGCCAGGATGTTGTCAGTG |
| PG0001396 | GGGAAACCTTGGGTCAGGCTTG | CATCGCTCTTCGCTCTTGATCGTC |
| PG0001388 | ACTTGCATCGGTCATTGGTGTCAC | TAAGCGGCGTAGGCATTCACAAG |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
1.7 StGAUT家族成员的表达模式分析
利用PGSC的Illumina RNA-seq数据,分析DM马铃薯中的StGAUT基因在非生物胁迫下(盐处理:150 mmol L-1 NaCl;甘露醇诱导干旱胁迫处理:260 µmol L-1甘露醇;热处理:35℃)和不同组织(未成熟果实、成熟果实、心皮、花瓣、叶柄、花、匍匐茎、雄蕊、萼片、块茎、芽、根和叶)中的表达模式。使用TBtools软件绘制表达量的热图[24]。对3个不同颜色马铃薯品种‘新大坪’、‘黑美人’和‘铃田红美’薯皮和薯肉的18个样品进行RNA-seq文库的构建,利用Ilumina HiSeq高通量测序平台对构建的cDNA文库进行测序,由百迈客生物科技有限公司负责完成RNA-seq文库的构建和测序。测序获得的Raw date提交至NCBI (Project ID PRJNA 541919)。
以RNA-seq数据为基础,分析StGAUT基因在‘新大坪’的皮和肉(XDS、XDF)、‘黑美人’的皮和肉(HMS、HMF)以及‘铃田红美’的皮和肉(LTS、LTF)中的表达。
2 结果与分析
2.1 StGAUT的鉴定及染色体分布
通过生物信息学方法共鉴定出44个候选StGAUT基因,利用Smart和NCBI在线软件剔除不含完整Glyco_transf_8保守结构域的序列,最终确定出41个StGAUT家族成员。由染色体定位(图1)可知,40个StGAUT基因(PG0004427尚未定位)不均匀地分布在10条染色体上,其中1号和2号染色体上StGAUT基因分布最多(分别为8个),4号染色体次之(7个),而在8号和11号染色体上没有StGAUT基因的分布。1号、3号、4号、7号染色体上的StGAUT基因主要分布在染色体的远端。
图1
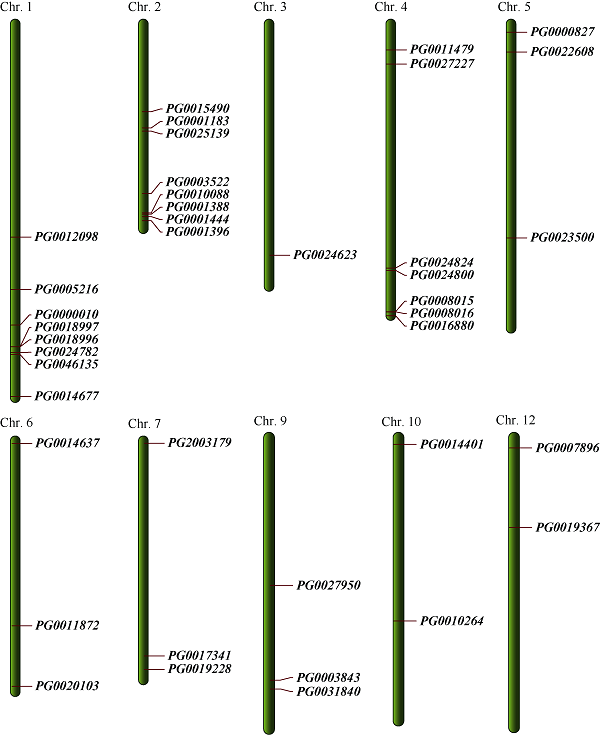 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图1StGAUT基因在马铃薯12条染色体上的分布
Fig. 1Genomic distributions of StGAUT genes on 12 potato chromosomes
2.2 StGAUT进化分析与分类
由图2可知,55个GAUT (除At2G38650外)共分为4个亚组,其中有11个StGAUT属于8亚组,12个StGAUT属于C II亚组,7个StGAUT和4个AtGAUT属于C III亚组,11个StGAUT和10个AtGAUT属于C IV亚组。C I、C II亚组中只包含StGAUT。图2
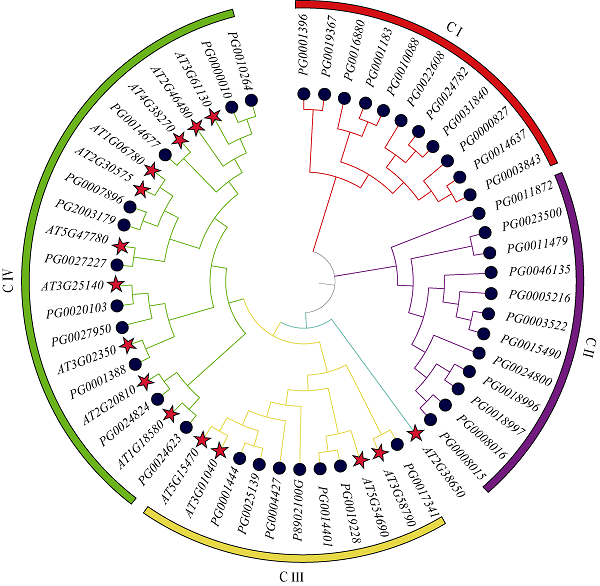 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图2拟南芥和马铃薯GAUT基因家族进化分析
不同颜色的半圆代表不同的亚组。蓝色圆表示StGAUT基因,红色五角星表示AtGAUT基因。
Fig. 2Phylogenic classification of GAUTs between Arabidopsis and potato
The different subgroups were marked with different colors. The blue rounds represent StGAUTs genes, and the red stars represent AtGAUTs genes.
2.3 StGAUT蛋白的理化性质和亚细胞定位
由表2可知,StGAUT家族成员的氨基酸长度和理化性质存在较大的差异。这些蛋白质的氨基酸残基长度为90个(PG0012098)至688个氨基酸(PG0000010),分子量为10,714.47 kD (PG0012098)至78,728.64 kD (PG0014677),等电点(pI)的范围为5.48 (PG0003522)到10.39 (PG0012098)。10个(PG0003522、PG0015490、PG0001183、PG0016880、PG0046135、PG0005216、PG0010088、PG0024800、PG0014401、PG0024623) GAUT氨基酸序列理论等电点在酸性范围内,其余都在碱性范围内,说明StGAUT蛋白质分子富含碱性氨基酸。同时,利用在线软件CELLO v.2.5对41个家族成员的进行亚细胞定位预测发现,4个家族成员定位于细胞核中,17个位于细胞膜中,11个位于线粒体中,6个位于细胞质中,3个位于细胞外。Table 2
表2
表2StGAUT基因家族理化性质及亚细胞定位
Table 2
| 基因名称 Gene name | 染色体定位Chromosome localization | 亚组 分类Subgroup | 氨基酸长度Amino acid length | 等电点 Point isoelectric (pI) | 相对分子量 Molecular weight (kD) | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PG0025139 | ch02 | C III | 533 | 9.30 | 60,619.92 | 线粒体 Mitochondrial |
| PG0003522 | ch02 | C II | 337 | 5.48 | 38,646.39 | 细胞外 Extracellular |
| PG0015490 | ch02 | C II | 327 | 5.52 | 37,560.90 | 细胞外 Extracellular |
| PG0001183 | ch02 | C I | 285 | 5.77 | 31,985.75 | 细胞膜 Plasma membrane |
| PG0001388 | ch02 | C IV | 547 | 8.47 | 63,223.59 | 线粒体 Mitochondrial |
| PG0001396 | ch02 | C I | 365 | 8.84 | 42,038.75 | 细胞膜 Plasma membrane |
| PG0010088 | ch02 | C I | 345 | 6.24 | 38,390.78 | 细胞膜 Plasma membrane |
| PG0001444 | ch02 | C III | 534 | 9.09 | 60,404.61 | 线粒体 Mitochondrial |
| PG0004427 | ch00 | C III | 423 | 9.04 | 48,777.15 | 线粒体 Mitochondrial |
| PG2003179 | ch07 | C IV | 597 | 9.33 | 68,386.80 | 线粒体 Mitochondrial |
| PG0017341 | ch07 | C III | 545 | 7.36 | 61,040.35 | 细胞膜 Plasma membrane |
| PG0019228 | ch07 | C III | 533 | 9.10 | 60,862.53 | 线粒体 Mitochondrial |
| PG0018996 | ch01 | C II | 555 | 8.84 | 65,196.17 | 细胞核 Nuclear |
| 基因名称 Gene name | 染色体定位Chromosome localization | 亚组 分类Subgroup | 氨基酸长度Amino acid length | 等电点 Point isoelectric (pI) | 相对分子量 Molecular weight (kD) | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization |
| PG0046135 | ch01 | C II | 321 | 6.02 | 36,737.36 | 细胞质 Cytoplasmic |
| PG0018997 | ch01 | C II | 504 | 8.56 | 58,979.96 | 细胞质 Cytoplasmic |
| PG0000010 | ch01 | C IV | 688 | 9.46 | 78,276.85 | 线粒体 Mitochondrial |
| PG0005216 | ch01 | C II | 336 | 6.02 | 38,507.42 | 细胞质 Cytoplasmic |
| PG0012098 | ch01 | C III | 90 | 10.39 | 10,714.47 | 线粒体 Mitochondrial |
| PG0024782 | ch01 | C I | 353 | 9.26 | 40,529.85 | 细胞膜 Plasma membrane |
| PG0014677 | ch01 | C IV | 680 | 8.34 | 78,728.64 | 细胞核 Nuclear |
| PG0023500 | ch05 | C II | 533 | 8.96 | 60,350.47 | 细胞膜 Plasma membrane |
| PG0000827 | ch05 | C I | 351 | 8.64 | 40,823.85 | 细胞膜 Plasma membrane |
| PG0022608 | ch05 | C I | 385 | 8.32 | 44,667.17 | 细胞膜 Plasma membrane |
| PG0019367 | ch12 | C I | 116 | 9.45 | 13,445.85 | 细胞膜 Plasma membrane |
| PG0007896 | ch12 | C IV | 579 | 9.00 | 66,706.29 | 线粒体 Mitochondrial |
| PG0014637 | ch06 | C I | 350 | 8.68 | 40,382.78 | 细胞膜 Plasma membrane |
| PG0011872 | ch06 | C II | 465 | 8.68 | 52,580.83 | 细胞膜 Plasma membrane |
| PG0020103 | ch06 | C IV | 557 | 9.23 | 63,946.48 | 线粒体 Mitochondrial |
| PG0003843 | ch09 | C I | 356 | 8.63 | 40,860.88 | 细胞外 Extracellular |
| PG0027950 | ch09 | C IV | 288 | 7.21 | 32,817.57 | 细胞膜 Plasma membrane |
| PG0031840 | ch09 | C I | 353 | 9.02 | 40,214.14 | 细胞膜 Plasma membrane |
| PG0024623 | ch09 | C IV | 536 | 6.95 | 62,348.31 | 细胞膜 Plasma membrane |
| PG0027227 | ch04 | C IV | 678 | 9.26 | 77,430.93 | 细胞核 Nuclear |
| PG0016880 | ch04 | C I | 351 | 5.99 | 39,345.05 | 细胞膜 Plasma membrane |
| PG0008016 | ch04 | C II | 579 | 8.70 | 67,676.72 | 细胞质 Cytoplasmic |
| PG0024824 | ch04 | C IV | 534 | 9.18 | 61,816.85 | 细胞膜 Plasma membrane |
| PG0008015 | ch04 | C II | 564 | 9.02 | 66,085.84 | 细胞核 Nuclear |
| PG0011479 | ch04 | C II | 533 | 9.05 | 60,263.41 | 细胞膜 Plasma membrane |
| PG0024800 | ch04 | C II | 648 | 6.24 | 75,006.44 | 细胞质 Cytoplasmic |
| PG0014401 | ch10 | C III | 533 | 6.58 | 60,586.97 | 细胞质 Cytoplasmic |
| PG0010264 | ch10 | C IV | 635 | 9.24 | 72,635.34 | 线粒体 Mitochondrial |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
2.4 StGAUT基因结构和motif分析
对41条StGAUT基因的氨基酸序列进行系统进化树分析(图3-A),将其分为4个亚组,C I、C II、C III、C IV亚组,分别包含11个、12个、7个和11个基因。基因结构图(图3-B)显示,7个StGAUT基因不含内含子,9个StGAUT基因只含有1个内含子,6个StGAUT基因含有2个内含子,其余基因含有3~9个内含子。此外,同一亚组的StGAUT基因表现出相似的基因结构。图3
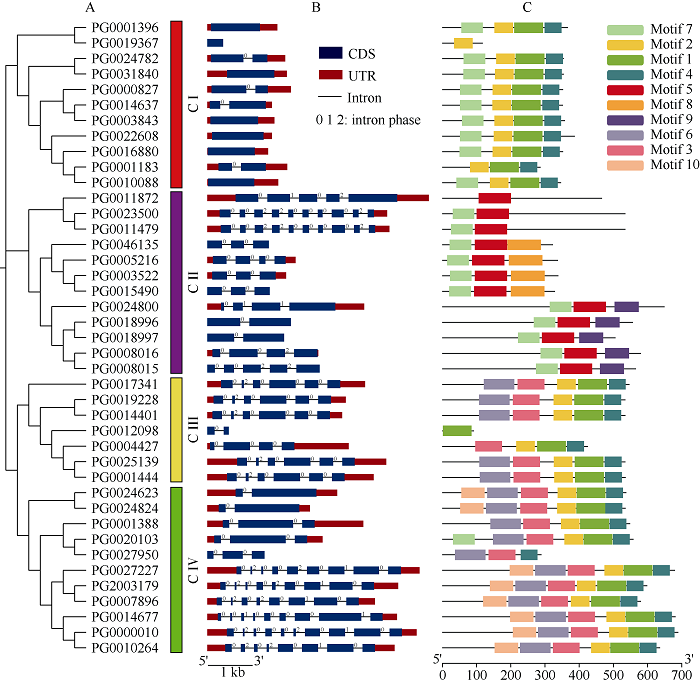 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图3StGAUT的进化关系、基因结构和保守基序分析
A:StGAUT进化树。B:StGAUT基因的外显子/内含子结构;蓝色框表示外显子,相同长度的黑线表示内含子,红色方框表示上游/下游区域,数字0、1和2表示内含子的剪接阶段。C:StGAUT中保守基序的分布;10个不同颜色的框代表了10个不同的基序。
Fig. 3Phylogenetic relationships, gene structure, and conserved motifs analysis of StGAUT
A: the phylogenetic tree of StGAUT. B: exon/intron structure of StGAUT gene; the blue boxes indicate exons, the black lines of the same length indicates the intron, the upstream/downstream area is indicated by a red box, the numbers 0, 1, and 2 represent the splicing phase of the intron. C: the distribution of conserved motifs in StGAUT; the 10 different colored boxes represent 10 different motifs.
使用在线MEME程序对StGAUT成员的氨基酸序列进行分析发现,StGAUT结构域存在多种组成形式,如motif 1和motif 2、motif 3和motif 5。motif 3主要位于GAUT的C端,motif 1主要位于GAUT的N端。由图3-C可知,一个亚组中的大部分StGAUT具有相似的motif组成,motif 5、motif 8、motif 9为C II亚组所特有,motif 10是C IV亚组所特有的。总的来说,一个亚组成员的motif组成相对保守,基因结构则较为相似,可以进一步证明进化分析的可靠性。
2.5 StGAUT基因复制事件分析
在植物基因组进化中,串联重复和片段重复有助于扩展基因家族的新成员和新功能。为研究StGAUT基因的重复事件,本研究分析了StGAUT基因家族中的片段重复和串联重复,共鉴定出12对片段重复基因(21/41,56.09%),其中2号染色体上的片段重复基因最多,共有6个片段重复基因(图4和表3)。每一对片段重复基因均属于同一亚组,其中C I亚组的片段重复基因最多(5对)。表明,片段复制在StGAUT基因家族的扩展中发挥着重要作用。图4
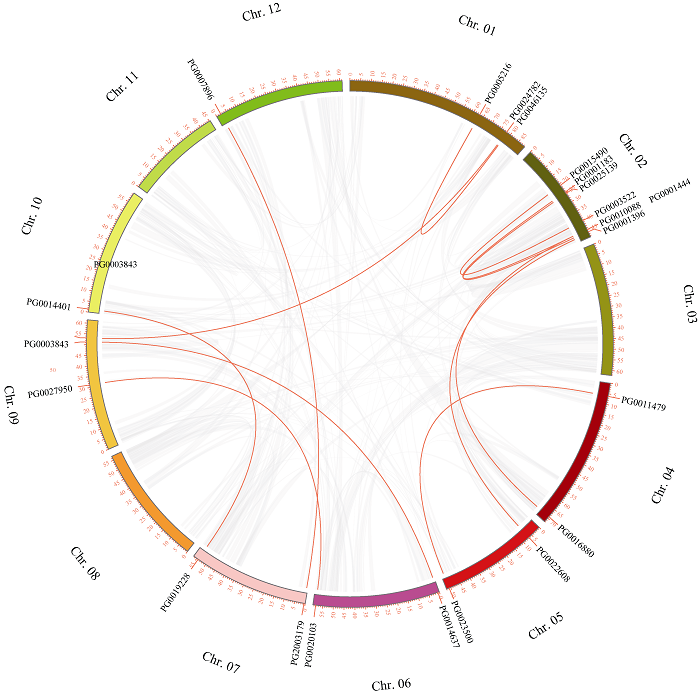 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图4StGAUT基因的片段重复事件
灰色线表示马铃薯基因组中的所有同线性区块,红色线表示StGAUT基因的片段重复。
Fig. 4Segmental replication events of StGAUT genes
The gray lines indicate all the same linear blocks in the potato genome, and the red lines indicate the segmental repeats of StGAUT genes.
Table 3
表3
表3StGAUT片段重复基因的Ka/Ks比值
Table 3
| 序号 No. | 基因1 Gene 1 | 基因2 Gene 2 | 非同义替换率 Ka | 同义替换率 Ks | 非同义替换率/同义替换率 Ka/Ks | P值 P-value | 类型 Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PG0001396 | PG0022608 | 0.946754 | 1.20121 | 0.788168 | 4.76E-08 | 片段重复Segmental repeat |
| 2 | PG0024782 | PG0031840 | 0.291121 | 3.40619 | 0.0854681 | 0 | 片段重复Segmental repeat |
| 3 | PG0003843 | PG0014637 | 0.121239 | 1.39384 | 0.0869818 | 1.54E-98 | 片段重复Segmental repeat |
| 4 | PG0010088 | PG0016880 | 0.179392 | 4.47249 | 0.0401102 | 0 | 片段重复Segmental repeat |
| 5 | PG0001183 | PG0010088 | 0.0740382 | 2.24318 | 0.0330059 | 2.71E-125 | 片段重复Segmental repeat |
| 6 | PG0011479 | PG0023500 | 0.103092 | 0.542081 | 0.190177 | 1.53E-47 | 片段重复Segmental repeat |
| 7 | PG0005216 | PG0046135 | 0.264587 | 3.85123 | 0.0687019 | 0 | 片段重复Segmental repeat |
| 8 | PG0003522 | PG0015490 | 0.103439 | 1.30535 | 0.0792418 | 1.55E-87 | 片段重复Segmental repeat |
| 9 | PG0014401 | PG0019228 | 0.077988 | 0.755095 | 0.103282 | 3.94E-89 | 片段重复Segmental repeat |
| 10 | PG0001444 | PG0025139 | 0.0574037 | 0.557829 | 0.102906 | 6.74E-66 | 片段重复Segmental repeat |
| 11 | PG0020103 | PG0027950 | 0.957665 | 1.1718 | 0.817262 | 1.33E-05 | 片段重复Segmental repeat |
| 12 | PG0007896 | PG2003179 | 0.172114 | 0.703844 | 0.244535 | 2.81E-54 | 片段重复Segmental repeat |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
非同义替换率(Ka)和同义替换率(Ks)是评价重复事件正向选择压力的基础。Ka/Ks值为1表示自然选择,Ka/Ks<1表示纯化选择,Ka/Ks>1表示正选择。重复基因的结果表明,片段重复基因Ka/Ks在0.0330~0.8173之间,平均值是0.2199。所有重复事件基因的Ka/Ks值均小于1,说明这些基因均在纯化选择的作用下进化(表3)。
2.6 StGAUT基因在不同组织部分中的表达分析
由图5可知,PG0000827、PG0017341、PG0020 103、PG0024800在所有的组织中表达量均很高(FPKM>5),PG0018996、PG0018997在所有的组织中均低表达(FPKM<2)。一些StGAUT基因表现出组织特异性的表达模式,例如PG0007896在雄蕊中特异性高表达(FPKM>100);PG0001396和PG0001444在匍匐茎中高表达(FPKM>80);PG0003843只在雄蕊和成熟的花中特异性表达(FPKM>30),而在其他的组织中则完全不表达(FPKM=0)。图5
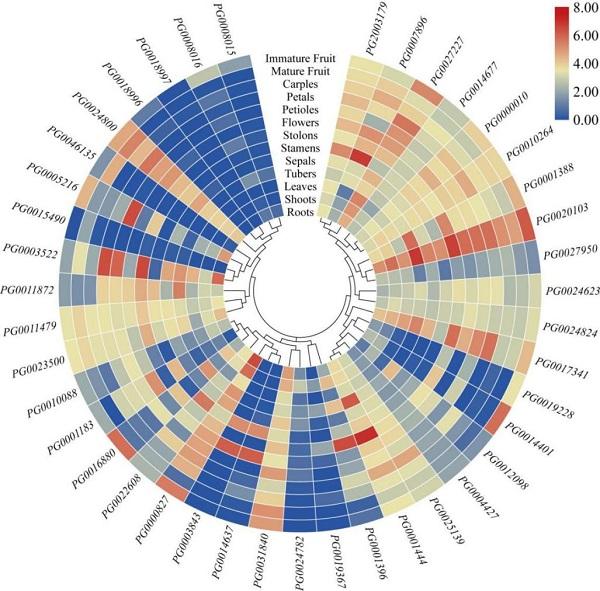 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图5StGAUT基因在不同组织中的表达
对41个StGAUT基因表达量取以2为底的对数进行标准化处理,不同颜色的色块表示基因在不同组织中的表达水平。
Fig. 5Relative expression profiles of StGAUT genes in different tissues
The relative expression levels of 41 StGAUT genes are taken as the logarithm with base 2 for standardization, and the color patches of different colors indicate the relative expression levels of genes in different tissues.
2.7 StGAUT基因在非生物胁迫下的表达分析
为研究StGAUT基因对非生物胁迫的响应,进一步分析了盐胁迫(150 mmol L-1 NaCl)、干旱胁迫(260 µmol L-1甘露醇)和热胁迫(35℃)下StGAUT的表达模式(图6)。结果表明,与对照相比,在盐胁迫、干旱胁迫和热胁迫处理下,分别有5个、6个、14个StGAUT基因差异表达(FPKM>1和|log2 FC|>1),其中4个StGAUT基因(PG0001396、PG0005216、PG0012098和PG0022608)在3种非生物胁迫下均差异表达,2个StGAUT基因(PG0008015、PG0007896)在2种非生物胁迫下差异表达,9个StGAUT基因只响应一种非生物胁迫。这些StGAUT可能参与了马铃薯对非生物胁迫的响应,值得我们进一步研究。图6
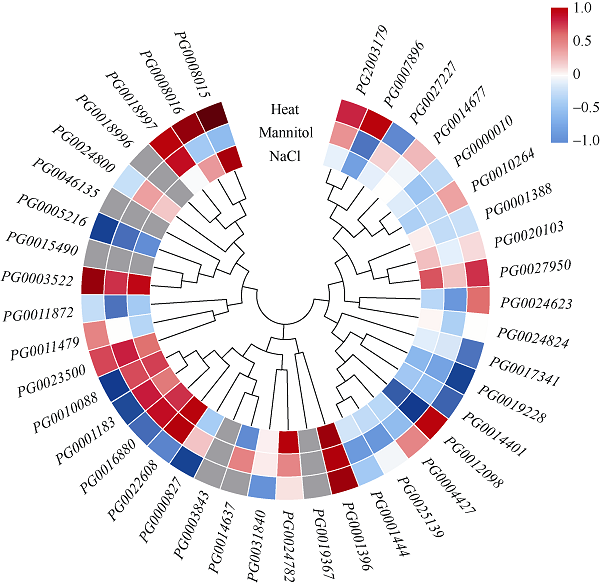 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图6StGAUT基因在盐、干旱、热胁迫下的表达量
盐胁迫、甘露醇胁迫和高温胁迫下StGAUT基因在DM马铃薯中的表达量。标尺表示与对照相比各基因的表达倍数(log2 FC)。
Fig. 6Relative expression profiles of StGAUT under salt, drought, and heat stress
The relative expression profiles of StGAUT genes under salt, mannitol, and heat stress in DM potato. The log2 mean of each gene FPKM is used to draw a color scale.
2.8 StGAUT基因在彩色马铃薯中的表达分析
由图7可知,在薯皮中有6个StGAUT基因不表达(FPKM=0),5个StGAUT基因表达水平较低(FPKM<1)。与‘新大坪’的白色薯皮(XDS)相比,有6个StGAUT基因在红色和紫色薯皮中差异表达(FPKM>1和|log2 FC|>1),其中4个StGAUT基因在彩色薯皮中上调表达,PG0005216、PG0007896和PG0027950在‘黑美人’的紫色薯皮(HMS)中上调表达,PG0008015在‘铃田红美’的红色薯皮(LTS)中上调表达;2个StGAUT基因在彩色薯皮中下调表达,其中PG0024782在HMS和LTS中下调表达,PG0017341只在HMS中下调表达。图7
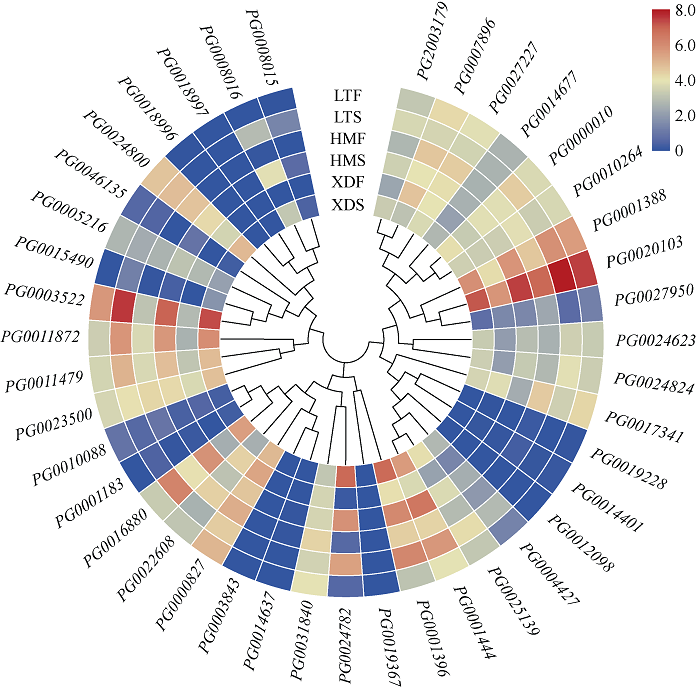 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图7StGAUT基因在不同薯皮薯肉颜色中的表达
对41个StGAUT基因表达量取以2为底的对数进行标准化处理,不同颜色的色块表示基因在不同颜色薯皮薯肉中的表达水平。XDS、HMS和LTS分别代表‘新大坪’、‘黑美人’和‘铃田红美’的薯皮。XDF、HMF和LTF分别代表‘新大坪’、‘黑美人’和‘铃田红美’的薯肉。
Fig. 7Relative expression profile of StGAUT genes in different potato skin and potato flesh colours
The relative expression levels of 41 StGAUT genes ars taken as the logarithm with base 2 for standardization, and the color patches of different colors indicate the expression levels of genes in different color potato skin and flesh. XDS, HMS, and LTS represent the white skin of the white potato cultivar (Xindaping), the purple skin of the purple potato cultivar (Heimeiren), and the red skin of the red potato cultivar (Lingtianhongmei), respectively. XDF, HMF, and LTF represent the white flesh of Xindaping, the purple flesh of Heimeiren, and the red flesh of Lingtianhongmei, respectively.
在薯肉中有4个StGAUT基因未表达(FPKM=0),11个StGAUT基因的FPKM值小于1。与‘新大坪’的薯肉(XDF)相比,在‘黑美人’的薯肉(HMF)和‘铃田红美’的薯肉(LTF)中,分别有5个和8个StGAUT基因表达上调(FPKM>1和|log2 FC|>1),其中2个基因(PG0020103、PG0024800)在HMF和LTF均上调表达,3个基因(PG0011872、PG0016880、PG0027950)在HMF中上调表达,6个基因(PG0001388、PG0003522、PG0024623、PG0024824、PG0025139、PG2003179)在LTF中上调表达。此外,与XDF相比LTF中有2个基因(PG0022608、PG0001396)下调表达(FPKM>1和|log2 FC|>1),这2个基因都属于C I亚组。
为验证RNA-seq数据的可靠性,我们选取了8个在彩色马铃薯薯皮和薯肉中FPKM值较高的StGAUT基因进行qPCR分析(图8)。结果表明,qPCR表达模式与RNA-Seq数据集一致,彩色马铃薯品种RNA-seq数据集与qPCR的线性关系为y = 1.7097x+0.3585,R2 = 0.8268,呈现了较高的相关性。
图8
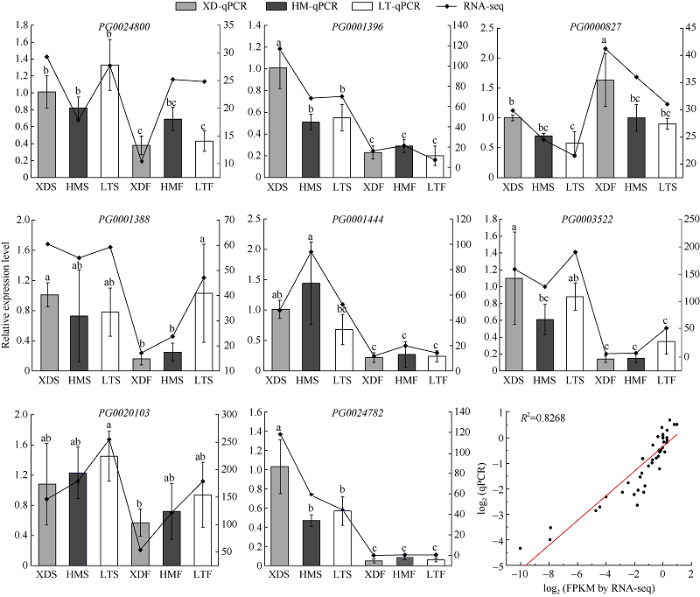 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图88个StGAUT基因在白色和彩色薯皮和薯肉中的定量表达分析
XDS、HMS和LTS分别代表‘新大坪’、‘黑美人’和‘铃田红美’的薯皮。XDF、HMF和LTF分别代表‘新大坪’、‘黑美人’和‘铃田红美’的薯肉。
Fig. 8Relative expression profile of eight StGAUT genes in white and pigmented skin and flesh
XDS, HMS, and LTS represent the white skin of the white potato cultivar (Xindaping), the purple skin of the purple potato cultivar (Heimeiren), and the red skin of the red potato cultivar (Lingtianhongmei), respectively. XDF, HMF, and LTF represent the white flesh of Xindaping, the purple flesh of Heimeiren, and the red flesh of Lingtianhongmei, respectively.
3 讨论
本研究对马铃薯GAUT基因家族进行了全基因组分析,共鉴定了41个StGAUT,多于拟南芥(15个)、番茄(17个)和棉花(37个) GAUT基因家族成员。分析了马铃薯和拟南芥的GAUT基因之间的进化关系,以鉴定StGAUT基因的进化和可能的功能。进一步分析了StGAUT基因成员的基因结构、保守基序组成、染色体定位和基因重复事件,以及GAUT基因在马铃薯不同组织部位、非生物胁迫下和彩色马铃薯品种薯皮和薯肉中的表达模式。对StGAUT基因的功能分化有了更深入的了解,为进一步研究马铃薯基因家族提供了综合信息。3.1 StGAUT基因家族成员的扩展和进化关系
StGAUT基因家族发生了扩张,可能是导致StGAUT基因家族比拟南芥和番茄的庞大的原因。串联重复和片段复制是植物基因家族扩张的主要方式[25]。这些基因通过串联重复和片段复制保留在植物基因组中,在对环境刺激的适应性反应中起重要作用[26,27]。本研究发现,片段重复是StGAUT基因家族主要的扩张方式。我们对StGAUT基因家族中的基因重复事件进行分析,共鉴定出12对片段重复基因,大多片段重复基因位于C I亚组,并且在2号染色体上的片段重复基因最多。因此,片段重复可能对StGAUT基因家族的扩张起主导作用。基因重复事件中一些正在进化的新成员可能失去其原有的功能成为伪基因,或获得新功能已增强植物适应性[28]。在本研究中,我们发现了一些片段重复基因,存在截然不同的表达模式,如PG0003522和PG0015490是一对片段重复基因,PG0003522在LTF中上调表达(FPKM>1和|log2 FC|>1),而PG0015490在LTF中则完全不表达(FPKM=0)。PG0001396和PG0022608是一对片段重复基因,它们在盐胁迫和干旱胁迫下均上调表达。
3.2 StGAUT的系统发育分析和进化
我们可以通过了解已知家族成员的功能来确认直系和旁系同源基因的功能,因为同一个亚组成员可能具有共同的进化起源和保守功能。根据系统发育比较分析,一些StGAUT基因与AtGAUT基因的直系同源物在不同的亚组中聚集在一起。例如,PG0019228、PG0014401与GAUT12 (At5G54690)聚集在一起,表明可能参与细胞壁多糖的合成。PG0020103、PG0001388、PG0024824、PG0024623与GAUT8 (AT3G25140)、GAUT9 (At3G02350)、GAUT10 (At2G20810)、GAUT11 (At1G18580)聚集在一起,表明可能参与果胶或木聚糖的生物合成[29]。通过对外显子和内含子的研究,有助于我们进一步了解家族成员基因结构和功能的差异[30]。StGAUT基因家族的外显子数量介于1~10之间,且位于同一分支的StGAUT基因具有相似的外显子数量和排列模式。StGAUT蛋白保守结构域也表现出类似的结果。说明同一亚组内的成员较为保守。3.3 StGAUT基因的表达分析
基因的组织特异性表达可初步预测其相应的功能[31]。通过对StGAUT基因在马铃薯不同组织中的表达谱分析发现,有的基因只在某一组织中表达,例如PG0003843和PG0014637是C I亚组中同一簇的一对片段重复基因,他们均在雄蕊和成熟的花中特异性表达;PG2003179和PG0007896属于C IV亚组同一簇的一对片段重复基因,它们在雄蕊里面特异性表达。因此,这些基因可能与马铃薯雄蕊的生长发育有关。Fabiana等[5]研究发现,SlGAUT4基因在发育器官中的表达水平较高,是决定番茄植株生长和果实产量的关键。与SlGAUT4同源的马铃薯PG0027227在花瓣中特异性表达,说明PG0027227可能与马铃薯植株生长发育有关。AtGAUT12 (At5G 54690)参与拟南芥细胞壁多糖的合成[32],在本研究中,与AtGAUT12同源的一对片段重复基因PG0014401和PG0019228在匍匐茎和未成熟的果实中特异性表达,它们的功能有待进一步研究。GAUT基因参与非生物胁迫的相关研究尚未见报道。本研究发现了一些响应多种非生物胁迫(盐、甘露醇、热)的StGAUT基因,如PG0001396和PG0022608是C I亚组的一对片段重复基因,它们在盐胁迫和干旱胁迫下均上调表达(FPKM>1和|log2 FC|>1),PG0001396在热胁迫下上调表达,而PG0022608则下调表达。此外,我们发现34.15% (14/41)的StGAUT基因在热胁迫下差异表达。这些StGAUT基因可能参与了对非生物胁迫的响应,它们的功能有待进一步研究。
同时,本研究发现了一些StGAUT基因可能参与花色素苷的合成,例如一对片段重复基因PG0001396和PG0022608在红色的薯肉中均下调表达(FPKM>1和|log2 FC|>1),PG0027950在紫色薯皮薯肉中都上调表达(FPKM>1和|log2 FC|>1)。综上所述,StGAUT基因家族成员可能在马铃薯的器官发育、抵御非生物胁迫和花色素苷的合成方面发挥着重要的作用。
4 结论
本研究在全基因组水平上鉴定并分析了41个StGAUT基因,不均匀的分布在10条染色体上。基于高度保守的基因结构和基序,把StGAUT基因划分为4个亚组。共线性分析表明,片段重复事件在StGAUT基因家族的扩展中起着至关重要的作用。根据Ka/Ks比率,这些基因对在纯化选择下进化。参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 3]
DOIURL [本文引用: 3]
DOIPMID [本文引用: 1]

Pectin is structurally and functionally the most complex polysaccharide in plant cell walls. Pectin has functions in plant growth, morphology, development, and plant defense and also serves as a gelling and stabilizing polymer in diverse food and specialty products and has positive effects on human health and multiple biomedical uses. Pectin is a family of galacturonic acid-rich polysaccharides including homogalacturonan, rhamnogalacturonan I, and the substituted galacturonans rhamnogalacturonan II (RG-II) and xylogalacturonan (XGA). Pectin biosynthesis is estimated to require at least 67 transferases including glycosyl-, methyl-, and acetyltransferases. New developments in understanding pectin structure, function, and biosynthesis indicate that these polysaccharides have roles in both primary and secondary cell walls. Manipulation of pectin synthesis is expected to impact diverse plant agronomical properties including plant biomass characteristics important for biofuel production.
DOIPMID [本文引用: 1]

Cell wall biosynthesis is indispensable for pollen tube growth. Despite its importance to sexual reproduction, the molecular mechanisms of pollen tube wall biosynthesis remain poorly understood. Here, we report functional characterization of two putative Arabidopsis galacturonosyltransferase genes, GAUT13 and GAUT14, which are essential for pollen tube growth. GAUT13 and GAUT14 encode the proteins that share a high amino acid sequence identity and are located in the Golgi apparatus. The T-DNA insertion mutants, gaut13 and gaut14, did not exhibit any observable defects, but the gaut13 gaut14 double mutants were defective in pollen tube growth; 35.2-37.3% pollen tubes in the heterozygous double mutants were swollen and defective in elongation. The outer layer of the cell wall did not appear distinctly fibrillar in the double mutant pollen tubes. Furthermore, distribution of homogalacturonan labeled with JIM5 and JIM7 in the double mutant pollen tube wall was significantly altered compared to wild-type. Our results suggest that GAUT13 and GAUT14 function redundantly in pollen tube growth, possibly through participation in pectin biosynthesis of the pollen tube wall.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
PMID [本文引用: 1]

The BLAST programs are widely used tools for searching protein and DNA databases for sequence similarities. For protein comparisons, a variety of definitional, algorithmic and statistical refinements described here permits the execution time of the BLAST programs to be decreased substantially while enhancing their sensitivity to weak similarities. A new criterion for triggering the extension of word hits, combined with a new heuristic for generating gapped alignments, yields a gapped BLAST program that runs at approximately three times the speed of the original. In addition, a method is introduced for automatically combining statistically significant alignments produced by BLAST into a position-specific score matrix, and searching the database using this matrix. The resulting Position-Specific Iterated BLAST (PSI-BLAST) program runs at approximately the same speed per iteration as gapped BLAST, but in many cases is much more sensitive to weak but biologically relevant sequence similarities. PSI-BLAST is used to uncover several new and interesting members of the BRCT superfamily.
PMID [本文引用: 1]

The focusing positions in narrow range immobilized pH gradients of 29 polypeptides of known amino acid sequence were determined under denaturing conditions. The isoelectric points of the proteins calculated from their amino acid sequences matched with good accuracy the experimentally determined pI values. We show the advantages of being able to predict the position of a protein of known structure within a two-dimensional gel.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIPMID [本文引用: 1]

We created a visualization tool called Circos to facilitate the identification and analysis of similarities and differences arising from comparisons of genomes. Our tool is effective in displaying variation in genome structure and, generally, any other kind of positional relationships between genomic intervals. Such data are routinely produced by sequence alignments, hybridization arrays, genome mapping, and genotyping studies. Circos uses a circular ideogram layout to facilitate the display of relationships between pairs of positions by the use of ribbons, which encode the position, size, and orientation of related genomic elements. Circos is capable of displaying data as scatter, line, and histogram plots, heat maps, tiles, connectors, and text. Bitmap or vector images can be created from GFF-style data inputs and hierarchical configuration files, which can be easily generated by automated tools, making Circos suitable for rapid deployment in data analysis and reporting pipelines.
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIPMID [本文引用: 1]

Real-time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) is the most commonly used method for accurately detecting gene expression patterns. As part of RT-qPCR analysis, normalization of the data requires internal control gene(s) that display uniform expression under different biological conditions. However, no invariable internal control gene exists, and therefore more than one reference gene is needed to normalize RT-qPCR results. Identification of stable reference genes in potato will improve assay accuracy for selecting stress-tolerance genes and identifying molecular mechanisms conferring stress tolerance in this species.In the experiment, we assessed the expression of eight candidate internal control genes, namely elongation factor-1alpha (),,, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (), adenine phosphoribosyl transferase (), 60S ribosomal protein L8 (), Cullin 3A (), and exocyst complex component sec3 (), in a diverse set of potato samples representing drought stress and osmotic stress challenges, and using geNorm, NormFinder, BestKeeper and RefFinder softwares.The results indicated that and were the most stably expressed genes in the potato under drought and osmotic stress conditions. This work will facilitate future work on gene expression studies in potato and also benefit other species of the, such as tomato.
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIPMID [本文引用: 1]

The trihelix gene family is a plant-specific transcription factor family that plays important roles in plant growth, development, and responses to abiotic stresses. However, to date, no systemic characterization of the trihelix genes has yet been conducted in wheat and its close relatives.We identified a total of 94 trihelix genes in wheat, as well as 22 trihelix genes in Triticum urartu, 29 in Aegilops tauschii, and 31 in Brachypodium distachyon. We analyzed the chromosomal locations and orthology relations of the identified trihelix genes, and no trihelix gene was found to be located on chromosome 7A, 7B, or 7D of wheat, thereby reflecting the uneven distributions of wheat trihelix genes. Phylogenetic analysis indicated that the 186 identified trihelix proteins in wheat, rice, B. distachyon, and Arabidopsis were clustered into five major clades. The trihelix genes belonging to the same clades usually shared similar motif compositions and exon/intron structural patterns. Five pairs of tandem duplication genes and three pairs of segmental duplication genes were identified in the wheat trihelix gene family, thereby validating the supposition that more intrachromosomal gene duplication events occur in the genome of wheat than in that of other grass species. The tissue-specific expression and differential expression profiling of the identified genes under cold and drought stresses were analyzed by using RNA-seq data. qRT-PCR was also used to confirm the expression profiles of ten selected wheat trihelix genes under multiple abiotic stresses, and we found that these genes mainly responded to salt and cold stresses.In this study, we identified trihelix genes in wheat and its close relatives and found that gene duplication events are the main driving force for trihelix gene evolution in wheat. Our expression profiling analysis demonstrated that wheat trihelix genes responded to multiple abiotic stresses, especially salt and cold stresses. The results of our study built a basis for further investigation of the functions of wheat trihelix genes and provided candidate genes for stress-resistant wheat breeding programs.
[本文引用: 1]
