 ,1,2, 王瑞莉1, 王刘艳1, 袁芳1,2, 孟丽姣1,2, 邢明礼1,2, 徐璐1,2, 唐章林1,2, 李加纳1,2, 崔翠
,1,2, 王瑞莉1, 王刘艳1, 袁芳1,2, 孟丽姣1,2, 邢明礼1,2, 徐璐1,2, 唐章林1,2, 李加纳1,2, 崔翠 ,1,*, 周清元
,1,*, 周清元 ,1,2,*
,1,2,*Genome-wide association study of seed density and its related traits in Brassica napus L.
LEI Wei ,1,2, WANG Rui-Li1, WANG Liu-Yan1, YUAN Fang1,2, MENG Li-Jiao1,2, XING Ming-Li1,2, XU Lu1,2, TANG Zhang-Lin1,2, LI Jia-Na1,2, CUI Cui
,1,2, WANG Rui-Li1, WANG Liu-Yan1, YUAN Fang1,2, MENG Li-Jiao1,2, XING Ming-Li1,2, XU Lu1,2, TANG Zhang-Lin1,2, LI Jia-Na1,2, CUI Cui ,1,*, ZHOU Qing-Yuan
,1,*, ZHOU Qing-Yuan ,1,2,*
,1,2,*通讯作者: * 崔翠, E-mail:cuicui@swu.edu.cn;周清元, E-mail:qingyuan@swu.edu.cn
收稿日期:2020-10-17接受日期:2021-03-19网络出版日期:2021-04-01
| 基金资助: |
Corresponding authors: * E-mail:cuicui@swu.edu.cn;E-mail:qingyuan@swu.edu.cn
Received:2020-10-17Accepted:2021-03-19Published online:2021-04-01
| Fund supported: |
作者简介 About authors
E-mail:1305600171@qq.com

摘要
种子容重大小反映了作物光合产物在籽粒中的积累特性, 是油菜千粒重重要的组成部分, 筛选高容重种质资源, 研究容重的遗传特性在油菜遗传育种中具有非常重要的作用。本文以不同遗传背景的187份甘蓝型油菜品种(系)构成的自然群体为研究对象, 进行2年种子的容重及其相关性状(千粒重、体积)测定和资源评价, 基于最优模型对各性状进行全基因组关联分析(genome-wide association analysis, GWAS)和候选基因预测。结果显示, 187份材料在2年中容重及其关联性状在品种(系)间差异均达到显著水平(P<0.05), 筛选出3个种子千粒重较大的高容重种质资源。全基因组关联分析共检测到24个与种子容重及其相关性状显著关联的SNP位点, 可解释表型变异的8.21%~10.40%。通过单倍型分析确定关联SNP位点的Block区间, 其所在的Block覆盖了12个与容重、粒重和体积有关的候选基因, 主要编码转录因子(如WOX8、HAIKU1、AP2/ERF转录因子、Dof家族-Zinc finger超家族和BZR1转录因子)、酶类(如BKI1、KAT2、CEL1和UBP15)、DNA结合蛋白和激素响应蛋白(如ARF2和J3)。本研究结果将为进一步解析油菜千粒重的遗传机制、培育高容重油菜品种及后续基因的功能研究提供理论依据。
关键词:
Abstract
Seed density reflects the accumulation characteristics of crop photosynthetic products in the grains, which plays an important role in the thousand-seed weight of rape. Selecting high seed density germplasm resources and studying the genetic characteristics of seed density are very important in the breeding of rapeseed. A natural population containing 187 Brassica napus L. varieties (lines) with different genetic backgrounds was used as plant materials to determine the seed density and its related traits (thousand-seed weight and seed volume) in the two environments. Genome-wide association study was carried out based on the optimal model and the candidate genes associated with seed density, thousand-seed weight, and seed volume was predicted. In the two years, there were significant differences in the seed density and its related traits among 187 materials at P < 0.05, and three materials with high seed density or thousand-seed weight were selected. A total of 24 SNP loci, that were significantly associated with seed density, seed weight, and seed volume, were identified by GWAS, which explained the phenotypic variation of 8.21%-10.40%. Haplotype analysis was used to determine the block interval of the SNP sites. The blocks containing 11 SNPs covered 12 candidate genes, which mainly encoded transcription factors such as WOX8, HAIKU1, AP2/ERF transcription factors, Dof family-zinc finger superfamily, BZR1 transcription factors, enzymes such as BKI1, KAT2, CEL1, UBP15, DNA binding proteins, and hormone response proteins such as ARF2 and J3. These results provide the theoretical basis for the development of high seed density rape varieties and the functional research of subsequent genes.
Keywords:
PDF (6958KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
本文引用格式
雷维, 王瑞莉, 王刘艳, 袁芳, 孟丽姣, 邢明礼, 徐璐, 唐章林, 李加纳, 崔翠, 周清元. 甘蓝型油菜容重及其相关性状的全基因组关联分析. 作物学报, 2021, 47(11): 2099-2110 DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1006.2021.04245
LEI Wei, WANG Rui-Li, WANG Liu-Yan, YUAN Fang, MENG Li-Jiao, XING Ming-Li, XU Lu, TANG Zhang-Lin, LI Jia-Na, CUI Cui, ZHOU Qing-Yuan.
甘蓝型油菜(Brassica napus L.)是世界四大油料作物之一, 也是食用植物油与动物饲料的重要来源[1,2], 提高油菜籽粒产量是油菜遗传育种研究最重要的方向之一。千粒重是油菜籽粒产量构成的重要组成, 与单株产量有显著正相关关系[3,4,5,6]。而千粒重(thousand-seed weight, TSW)主要由油菜种子体积(seed volume, SV)和容重(seed density, SD)来决定。油菜籽粒体积越大, 库容量也越大, 能贮藏更多的灌浆物质, 这就为粒重的形成创造了条件[7]。而油菜籽粒容重大小体现了籽粒内容物的充实程度, 与光合产物的形成、运输、转化和储存有关, 对千粒重大小和油菜产量具有非常重要的影响。因此, 定位油菜籽粒容重关联的QTL (数量性状基因座)并找到相关候选基因, 对筛选高容重油菜种质、培育油菜高产品种具有非常重要的作用。
近年来, 数量遗传学和现代生物技术的发展为作物育种带来新的活力, 借助DNA分子标记和QTL作图, 复杂的数量性状可被剖分为若干离散的孟德尔因子所决定的组分, 进而确定其在染色体上的位置及其与其他基因的关系。千粒重是油菜产量构成的主要要素(每公顷单株数、单株角果数、每果粒数和千粒重)之一, 是油菜高产育种的关键因子, 被大家广泛重视, 很多****利用不同的分子标记和不同的研究群体, 对不同环境条件下油菜千粒重进行QTL定位, 获得了不同的研究结果[8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16], 为油菜分子育种奠定了一定基础。虽然容重在小麦[17,18,19]、玉米[20,21,22,23]、大豆[24]等多种农作物中都被作为重要的品质性状, 与千粒重(百粒重)具有非常重要的相关性, 但是在油菜中研究极少。随着一些植物全基因组测序的完成, 分子标记和生物信息学的迅速发展, 全基因组关联分析(genome-wide association study, GWAS)已经成为植物数量性状研究的热点之一。同时甘蓝型油菜全基因组序列的公布和芸薹属SNP芯片的开发, 很多****已经通过全基因组关联分析鉴定出与油菜重要农艺、品质和抗性等复杂性状的QTL位点, 解析其遗传结构并预测其候选基因[25,26,27,28,29]。迄今, 利用GWAS筛选甘蓝型油菜容重关联SNP位点, 并充分利用已知物理位置SNP位点筛选候选基因未见报道。
本文以187份遗传来源不同的油菜品种(品系)构建的自然群体为研究对象, 对该群体内各品种(系)容重、千粒重和体积进行比较和评价, 筛选容重、千粒重都较大的种质资源; 利用60K SNP芯片对该群体材料进行基因型分析, 并对千粒重、体积、容重进行GWAS, 挖掘显著的SNP位点, 预测其候选基因, 以期为控制容重性状的遗传解析奠定基础以及高产优质甘蓝型油菜新品种的选育提供重要的理论依据。
1 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
用于全基因组关联分析的自然群体为187份具有不同遗传背景和广泛地理来源的常规品种、品系(附表1), 均由重庆市油菜工程技术研究中心收集并提供。1.2 田间试验
试验材料于2018—2019、2019—2020年度连续2年种植于重庆市北碚区歇马镇油菜基地。采用随机区组试验设计, 3次重复, 每个材料重复种3行, 每行10株。田间管理遵循常规生产方式, 在油菜初花期套袋自交, 种子完全成熟后每家系收取3株正常植株的种子, 自然风干后保存。1.3 性状测定
将每个品种的种子充分混匀, 随机选取1000粒大小相似、饱满的油菜籽粒(随机取到的杂质或干瘪籽粒均去除), 并用万分之一电子天平称其质量, 重复3次, 取其平均值。将挑选出来的油菜种子, 平铺于扫描仪的底片支架上(种子之间相隔一定距离, 不能重叠)。再利用爱普生扫描仪V850对油菜种子进行扫描拍照, 保存图片文件。参考韩光明等[30]的方法, 得到油菜种子的数量以及油菜种子所占面积的百分比, 计算出每一颗油菜种子所占的面积、半径以及体积。在Excel表中按照公式(容重=质量/体积)对每个材料的容重、粒重、体积进行计算。采用Microsoft Excel 2016软件对187份种质资源进行初步筛选排序, 并计算其平均数、标准差和变异系数。1.4 基因型分析
利用油菜基因组60K Illumina Infinium SNP芯片, 参照Chen等[26]和Qu等[31]方法, 对187份材料进行基因型分析, 排除掉最小基因型频率(minor allele frequency, MAF)低于5%和SNP得率(call frequency)小于80%的SNP标记, 最终获得15,436个SNP标记用于关联分析。1.5 群体结构分析与亲缘关系
利用Structure 2.3.4软件进行群体结构分析, 参照Wan等[32]确定最终亚群数目。利用Tassel 5.1.0软件对自然群体进行亲缘关系评估, 计算亲缘关系K矩阵[33]。利用Tassel 5.1.0软件分析连锁不平衡(linkage disequilibrium, LD)在甘蓝型油菜A、C染色体组上的分布, 绘制各染色体的LD衰减图[28]。1.6 全基因组关联分析
采用基于一般线性模型和混合线性模型共6种模型进行关联分析。利用SAS软件检验这6种模型的运算结果, 对-log10(P)的观测值和-log10(P)期望值绘制Quantile-Quantile散点图。在此基础上确定3个性状的最佳模型, 利用haploview软件绘制Manhattan图[34]。本试验使用的SNP数据为26,673个, P值大于阈值(-log10(1/26,673) = 4.4)的位点为显著关联位点。1.7 单倍型分析及候选基因筛选
利用haploview软件对显著性标记所在LD区间的SNP进行单倍型分析[34], 参照Qu等[31]方法设定参数。根据法国公布的甘蓝型油菜“Darmor-Bzh”基因组注释信息获取显著性标记所在的Block区间的基因及序列, 通过BLAST与拟南芥基因进行同源性比对, 将E-value阈值设定为10-10, 以相似度最高的拟南芥基因信息来注释油菜基因。2 结果与分析
2.1 187份甘蓝型油菜的表型特征及其容重评价
统计187份甘蓝型油菜容重、体积及千粒重3个性状的最大值、最小值、均值和变异系数, 并对每年品种(系)间进行方程分析(表1)。3个性状在2年各品种(系)间差异达到极显著水平(P<0.01), 变异系数介于7.11%~35.93%之间, 其中籽粒大小(体积)变异系数最高、容重变异系数最低。差异显著性检验和变异系数结果都表明187份材料具有广泛的遗传变异范围。通过频次分布(图1)可以看到, 3个性状均呈现出连续性分布, 符合数量性状的遗传特点, 适合进行GWAS分析。图1
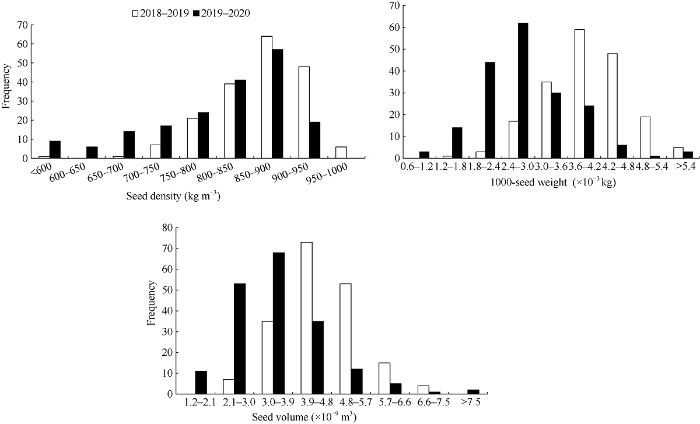 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图1群体容重、千粒重和体积在2种环境下的频率分布
Fig. 1Frequency distribution of seed density, 1000-seed weight, and seed volume in two environments
Table 1
表1
表1187份甘蓝型油菜品种(系)籽粒容重、千粒重和体积的表型统计
Table 1
| 性状 Trait | 年份 Year | 最大值 Max. | 最小值 Min. | 均值 Average | 标准差 SD | 变异系数 CV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 籽粒容重Seed density (kg m-3) | 2018-2019 | 969.05 | 527.31 | 859.96** | 61.16 | 7.11 |
| 2019-2020 | 946.00 | 433.93 | 804.35** | 99.47 | 12.37 | |
| 体积Seed volume (×10-9 m3) | 2018-2019 | 7.30 | 2.58 | 4.60** | 0.89 | 19.38 |
| 2019-2020 | 11.97 | 1.28 | 3.52** | 1.27 | 35.93 | |
| 千粒重Thousand-seed weight (×10-3 kg) | 2018-2019 | 5.75 | 1.73 | 3.95** | 0.76 | 19.24 |
| 2019-2020 | 7.39 | 0.70 | 2.80** | 0.89 | 31.79 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
分别对187份材料的2年容重进行排序(附表1), 容重较均值859.96 kg m-3和804.35 kg m-3的品种(系)分别有112份和115份, 2年均高于均值的有81份, 均低于均值的有41份。2年容重均高于均值的81份甘蓝型油菜品种(系) 2018—2019年度千粒重变化幅度为2.36×10-3~5.75×10-3 kg, 体积介于2.69× 10-9~6.36×10-9 m3; 2019—2020年度千粒重变化幅度为1.16×10-3~5.01×10-3 kg, 体积介于1.28×10-9~ 6.01×10-9 m3; 从81份变异范围和变异系数分析, 虽然较原始群体(187份种质)相比, 变异范围变窄, 变异系数变小, 但是容重大的油菜品种(系)籽粒千粒重不一定大。对两年度的81份种质资源结果进行统计(表2)发现, 2018—2019年度千粒重从大到小依次为2012-9542 (5.75×10-3 kg)、中双11号(5.30×10-3 kg)、秦油5号(5.55×10-3 kg)、红油3号(5.29×10-3 kg)、青662A (5.15×10-3 kg)、2012-5086 (5.12×10-3 kg)、SWU75 (4.99×10-3 kg)、浙油18 (4.99×10-3 kg)、盐6055 (4.97×10-3 kg)和沪油17号(4.93×10-3 kg); 2019—2020年度平均千粒重仅2.78×10-3 kg, 较2018—2019年度下降1.28×10-3 kg, 千粒重5.0×10-3 kg以上的品种为黔油331 (5.01×10-3 kg), 大于4.0× 10-3 kg的有秦油5号(4.78×10-3 kg)、红油3号(4.43× 10-3 kg); 综合两年度结果来看, 秦油5号、红油3号和黔油331为容重高和籽粒大(千粒重)的3个品种。
Table 2
表2
表281份高容重甘蓝型油菜品种(系)体积和千粒重的表型统计
Table 2
| 性状 Trait | 年度 Year | 最大值 Max. | 最小值 Min. | 均值 Average | 标准差 SD | 变异系数 CV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 籽粒容重Seed density (kg m-3) | 2018-2019 | 969.05 | 860.09 | 901.76** | 26.41 | 2.93 |
| 2019-2020 | 946.00 | 806.90 | 875.16** | 31.35 | 3.58 | |
| 体积Seed volume (×10-9 m3) | 2018-2019 | 6.36 | 2.69 | 4.51** | 0.78 | 17.30 |
| 2019-2020 | 6.01 | 1.28 | 3.19** | 0.87 | 27.26 | |
| 千粒重Thousand-seed weight (×10-3 kg) | 2018-2019 | 5.75 | 2.36 | 4.06** | 0.69 | 16.87 |
| 2019-2020 | 5.01 | 1.16 | 2.78** | 0.74 | 26.54 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
在2018—2019年度, 千粒重与容重及体积存在着统计学意义上的极显著正相关(P<0.01) (表3), 相关系数分别为0.31和0.93, 体积与容重的相关性不显著; 在2019—2020年度, 体积与容重及千粒重均表现为极显著相关(P<0.01), 其中体积与容重两性状之间表现为极显著负相关, 相关系数为-0.29, 体积与千粒重表现为极显著正相关, 相关系数分别为0.90。两年度中, 种子体积和千粒重均存在着显著正相关, 说明油菜种子光合产物积累的“库” (体积)越大, 越有利于获得更大的千粒重; 容重与体积存在着负相关, 与千粒重存在着正相关, 说明在育种中筛选油菜籽粒容重更高的品种, 对油菜高产育种具有非常重要的意义。
Table 3
表3
表3油菜3种种子各性状间的相关性分析
Table 3
| 性状 Trait | 容重 Seed density | 体积 Seed volume | 千粒重 Thousand-seed weight |
|---|---|---|---|
| 容重Seed density | 1 | -0.29** | 0.1 |
| 体积Seed volume | -0.03 | 1 | 0.90** |
| 千粒重Thousand-seed weight | 0.31** | 0.93** | 1 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
2.2 容重及其相关性状的6种模型比较
利用SAS软件对容重、千粒重和体积关联分析6种模型下的运算结果绘制Quantile-Quantile (Q-Q)散点图。通过比较6种模型下Q-Q图的分布可以看出(图2), 容重(SD)及体积(SV)的最佳模型都为K+PCA模型, 千粒重的最佳模型均为K模型。在最优模型基础上绘制Manhattan图(图3)。以P值小于阈值(1/26673 = 3.74911E-05)确定显著关联SNP位点(表4)。图2
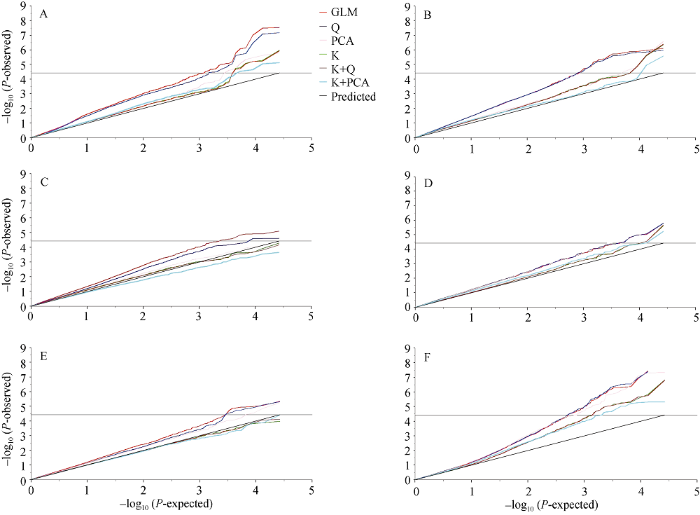 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图2两年度中容重、千粒重和体积在各模型下的QQ图
A: 2018-2019年度容重; B: 2019-2020年度容重; C: 2018-2019年度千粒重; D: 2019-2020年度千粒重; E: 2018-2019年度体积; F: 2019-2020年度体积。
Fig. 2Quantile-Quantile plot for six models of association analysis using the optimal model for seeds density and its component trait in two years
A: seed density in 2018 and 2019; B: seed density in 2019 and 2020; C: thousand-seed weight in 2018 and 2019; D: thousand-seed weight in 2019 and 2020; E: seed volume in 2018 and 2019; F: seed volume in 2019 and 2020.
图3
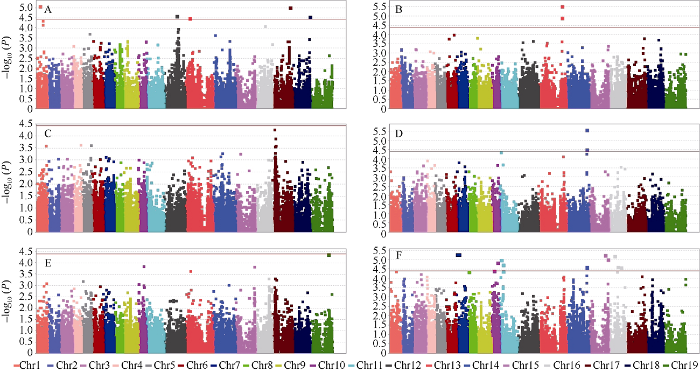 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图3两年度中容重及其相关性状的Manhattan图
A: 2018-2019年度容重; B: 2019-2020年度容重; C: 2018-2019年度千粒重; D: 2019-2020年度千粒重; E: 2018-2019年度体积; F: 2019-2020年度体积。
Fig. 3Manhattan plot of seeds density and its component trait in two years
A: seed density in 2018 and 2019; B: seed density in 2019 and 2020; C: thousand-seed weight in 2018 and 2019; D: thousand-seed weight in 2019 and 2020; E: seed volume in 2018 and 2019; F: seed volume in 2019 and 2020.
Table 4
表4
表4容重、千粒重、体积相关性状的显著关联标记
Table 4
| 性状 Trait | 环境 Environment | 模型 Model | 位点 SNP | 染色体 Chr. | 位置 Position | 阈值 -log10(P) | 贡献率 R2 (%) | 基因型 Loci |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 容重 Seed density | 2018-2019 | K+PCA | Bn-A01-p6774837 | A01 | 6194252 | 5.12 | 9.52 | T/C |
| Bn-scaff_17067_1-p175366 | C02 | 27613356 | 5.06 | 8.64 | T/C | |||
| Bn-A03-p8112016 | C03 | 9899295 | 4.64 | 8.43 | A/G | |||
| Bn-scaff_16069_1-p1916253 | C07 | 38327703 | 4.59 | 9.39 | A/G | |||
| Bn-scaff_21269_1-p313587 | C08 | 37159594 | 4.53 | 8.54 | A/G | |||
| 2019-2020 | K+PCA | Bn-scaff_16394_2-p777469 | C03 | 50479817 | 5.58 | 10.36 | T/C | |
| Bn-scaff_16394_2-p510062 | C03 | 50830988 | 4.95 | 9.20 | T/C | |||
| 体积 Seed volume | 2018-2019 | K+PCA | Bn-A10-p9973634 | C09 | 40023501 | 4.41 | 8.22 | A/C |
| 2019-2020 | K+PCA | Bn-Scaffold000232-p58128 | A07 | 826353 | 5.32 | 9.88 | A/G | |
| 性状 Trait | 环境 Environment | 模型 Model | 位点 SNP | 染色体 Chr. | 位置 Position | 阈值 -log10(P) | 贡献率 R2 (%) | 基因型 Loci |
| Bn-A07-p3618045 | A07 | 5593584 | 5.32 | 9.88 | T/C | |||
| Bn-A10-p5210204 | A10 | 4798717 | 4.43 | 8.25 | T/G | |||
| Bn-A10-p12933288 | A10 | 12981101 | 4.88 | 9.07 | A/C | |||
| Bn-scaff_15838_5-p603655 | C01 | 3432942 | 5.03 | 9.34 | T/C | |||
| Bn-scaff_17731_1-p749457 | C01 | 7033263 | 4.41 | 8.21 | A/C | |||
| Bn-scaff_17731_1-p979512 | C01 | 7260158 | 4.76 | 8.84 | A/G | |||
| Bn-scaff_21186_1-p36313 | C04 | 43747053 | 4.65 | 8.65 | A/G | |||
| Bn-scaff_21566_1-p5088 | C04 | 43859433 | 4.60 | 8.56 | A/C | |||
| Bn-scaff_16770_1-p306276 | C05 | 35633542 | 5.26 | 9.78 | T/C | |||
| Bn-scaff_20270_1-p1211632 | C05 | 41648492 | 5.04 | 9.37 | T/C | |||
| Bn-scaff_18439_1-p633449 | C06 | 12752920 | 5.22 | 9.70 | T/C | |||
| Bn-scaff_15763_1-p595094 | C06 | 20165181 | 4.65 | 8.64 | T/G | |||
| Bn-A07-p16045526 | C06 | 26606197 | 4.63 | 8.62 | A/C | |||
| 千粒重Thousand-seed weight | 2018-2019 | K | — | |||||
| 2019-2020 | K | Bn-scaff_21186_1-p36313 | C04 | 43747053 | 4.55 | 8.43 | A/G | |
| Bn-scaff_21566_1-p5088 | C04 | 43859433 | 5.62 | 10.40 | A/C |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
2.3 全基因组关联分析
通过分析两年度数据, 共检测到24个与容重及其相关性状(千粒重和体积)关联的SNP位点(图3和表4)。其中, 与容重关联的SNP位点共有7个, 分别位于A01、C02、C03、C07和C08染色体上, 可解释8.43%~10.36%的表型变异, 其中2019—2020年度C03染色体上的Bn-scaff_16394_2-p777469位点贡献率最大。与体积关联的SNP位点共有15个, 2018—2019年度C09染色体上只检测到1个SNP位点, 2019—2020年度共检测到14个SNP, 分别位于A07 (2个)、A10 (2个)、C01 (3个)、C04 (2个)、C05 (2个)和C06 (3个)染色体, 可解释8.21%~9.88%的表型变异, 其中2019—2020年度A07染色体上的Bn-Scaffold000232-p58128和Bn-A07-p3618045位点贡献率最大。与千粒重关联的SNP位点仅在2019—2020年度的C04染色体上检测到2个, 分别解释8.43%和10.40%的表型变异, 这2个位点也在体积中被检测到。2.4 单倍型分析
对24个显著性标记所在LD区间的SNP进行单倍型分析表明, 显著性标记Bn-scaff_17067_1- p175366、Bn-scaff_17731_1-p749457、Bn-scaff_ 18439_1-p633449与至少1个SNP标记位于同一Block, 显著性标记Bn-scaff_21186_1-p36313和Bn- scaff_21566_1-p5088与其他7个SNP位于同一个112 kb跨度的Block, Bn-A03-p8112016、Bn-scaff_ 16069_1-p1916253、Bn-scaff_15838_5-p603655和Bn-A10-p9973634未与其他SNP形成Block (图4)。由于在后续分析中未筛选到候选基因,因此Bn- A01-p6774837、Bn-scaff_21269_1-p313587、Bn-scaff_ 16394_2-p777469、Bn-scaff_16394_2-p510062、Bn- Scaffold000232-p58128、Bn-A07-p3618045、Bn-A10- p5210204、Bn-A10-p12933288、Bn-scaff_17731_1- p979512、Bn-scaff_16770_1-p306276、Bn-scaff_ 20270_1-p1211632、Bn-scaff_15763_1-p595094和Bn-A07-p16045526未在图4中列出。图4
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图4显著性标记所在的Block及候选基因
Fig. 4Blocks including significant SNP markers and their candidate genes
2.5 容重及其相关性状的候选基因筛选
本研究对容重及其相关性状进行全基因组关联分析, 共检测到24个显著相关的SNP位点, 可解释8.21%~10.40%的表型变异。基于甘蓝型油菜参考基因组序列, 显著性标记所在Block区间共筛选出12个候选基因(图4和表5), 其中, 与容重显著关联SNP标记的Block区间找到了6个重要候选基因; 在与体积显著关联SNP标记的Block区间中筛选出5个候选基因; 在与千粒重显著关联SNP标记的Block区间筛选出1个候选基因, 它们均在种子体积显著关联SNP标记的Block区间中找到。以上候选基因主要编码转录因子(如BnaC03g18850D、BnaC03g19320D、BnaC03g19550D、BnaC07g36540D和BnaC01g11380D)、酶类(如BnaC02g28720D、BnaC03g18470D、BnaC04g43460D和BnaC01g06800D)、DNA结合蛋白(如BnaC06g10480D)和激素响应蛋白(如BnaC09g35740D和BnaC09g36560D)。其中, BnaC02g28720D 和BnaC01g11380D均是BR信号通路的调控因子, 前者是BRI1的负调控因子, 通过调控BR信号途径的来改变性状表型[35]; 后者是BR的下游转录因子, 它直接结合到多个调控种子大小的基因启动子上, 促进种子发育[35]。BnaC03g18470D (KAT2)通过影响脂肪酸β氧化过程来影响用于生长与繁殖的营养物质之间的平衡导致种子数减少[36]。BnaC03g18850D (WOX)8已被证实通过监管早期胚的发育形成以及与CLE8共同促进细胞生长和大小[37]。Table 5
表5
表5甘蓝型油菜容重相关性状的候选基因
Table 5
| 性状 Trait | 物理区间 Physical interval | 甘蓝型油菜基因编号 Gene ID in B. napus | 拟南芥基因 Arabidopsis gene | 基因 Gene | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SD | 26393356-28833356 | BnaC02g28720D | AT5G42750 | BKI1 | [35] |
| 9439295-10359295 | BnaC03g18470D | AT2G33150 | KAT2 | [36] | |
| BnaC03g18850D | AT5G45980 | WOX8 | [37] | ||
| BnaC03g19320D | AT2G35230 | IKU1 | [38] | ||
| BnaC03g19550D | AT2G35700 | ERF38 | [39] | ||
| 37927703-38727703 | BnaC07g36540D | AT4G21030 | ATDOF4.2 | [40-41] | |
| TSW | 43147053-44459433 | BnaC04g43460D | AT1G70710 | CEL1 | [42] |
| SV | 2632942-4232942 | BnaC01g06800D | AT1G17110 | UBP15 | [43] |
| 6233263-7833263 | BnaC01g11380D | AT1G75080 | BZR1 | [35] | |
| 43147053-44459433 | BnaC04g43460D | AT1G70710 | CEL1 | [42] | |
| 12082920-13422920 | BnaC06g10480D | AT1G54060 | ASIL1 | [44] | |
| 39083501-40963501 | BnaC09g35740D | AT3G61830 | ARF2 | [45] | |
| BnaC09g36560D | AT3G44110 | J3 | [46] |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
3 讨论
甘蓝型油菜单株种子产量取决于单株角果数、每果粒数和千粒重[47]。在产量性状中, 千粒重有很高的遗传力, 千粒重位点更容易被稳定的选择, 从而达到增产的目的[48]。容重虽然是影响千粒重大小的重要影响因素, 但由于其测定相对较难, 在油菜上对其关注度相对较低。相同体积下, 提高籽粒容重, 可以提高油菜千粒重, 而容重提高必然有利于提高单株产量, 从而提高群体产量。籽粒体积大小反应了油菜光合产物积累的“库”容量, 容重大小则可以认为其与光合产物积累的特性有关。因此, 在油菜高产和高光效育种过程中, 除关注千粒重外, 还应该关注容重大小和影响因素。本文对具有不同遗传背景和来源的187份油菜资源的容重、千粒重、体积进行2个年度研究, 最终筛选出3个容重高、籽粒大(千粒重)的甘蓝型油菜种质, 为下一步选育高产优质甘蓝型油菜新品种提供参考依据和理论支持, 具有非常重要的实践和理论意义。全基因组关联分析可以快速鉴定与目标性状关联的分子标记和基因, 是非常有效的定位候选基因的方法。随着SNP芯片技术的出现, 利用GWAS定位甘蓝型油菜复杂的数量性状如千粒重[49]、每角粒数[50]、主花序角果密度[51]、角果长度[52]等方面已取得重要进展。Li等[15]利用60K油菜芯片进行关联分析, 分别在A07和A09上找到2个千粒重位点, 解释了4.9%和11.4%的表型变异。荐红举等[16]通过包含2795个SNP位点的RILs群体连锁图谱在5个环境中共检测到14个QTL, 分布在A03、A05、A06、A07、A08、A10、C01、C02和C03共9条染色体上。本文通过对187份材料的千粒重进行全基因组关联分析, 仅在2019—2020年度中检测到位于C04染色体上2个关联位点, 与Shi等[6]检测到的千粒重QTLq0913和q0914位于同一染色体, 两者相距较近。本文检测到的油菜千粒重位点较少, 可能和群体遗传组成、环境因素有关。油菜种子千粒重可进一步分解为种子体积大小和种子内容物充实程度(种子容重), 解析千粒重形成的遗传机制将为选育大粒油菜新品种奠定分子基础。本文中检测到的与容重关联的7个SNP位点和与体积关联的15个SNP位点为进一步研究油菜籽粒这2个性状的QTL奠定基础, 为挖掘与油菜容重和大小有关的基因提供重要参考。另外, 在2019—2020年度, 本研究在C04染色体43.75 Mb和43.86 Mb区间连续检测到千粒重位点Bn-scaff_21186_1-p36313、Bn-scaff_21566_ 1-p5088, 也同时检测到种子体积大小位点, 表明这些位点具有“一因多效”作用。
本研究通过关联分析, 扫描与性状关联的SNP位点的LD区间并进行单倍型分析, 借助甘蓝型油菜“Darmor-Bzh”基因组注释信息和拟南芥基因组数据库, 结果共筛选出12个与种子发育相关的候选基因。这些基因可能通过转录因子途径、泛素途径、IKU途径和激素等通路来调控种子发育[53,54]。本研究检测到的QTL区域是依据每条染色体LD衰减距离及显著性峰值SNP位点确定的, 通过对显著性标记所在LD区间的SNP进行单倍型分析, 再利用基因注释筛选显著性标记所在的Block区间的基因, 这大大增加了候选基因筛选的效率及可靠性。本文筛选到的这些候选基因在油菜种子容重及其相关性状形成的具体作用还有待进一步研究验证。
4 结论
本文筛选出3个种子千粒重较大的高容重种质资源; 通过全基因组关联分析检测到与容重及其关联性状显著关联的24个SNP位点, 其所在的Block筛选到12个候选基因, 主要编码转录因子、酶类、DNA结合蛋白和激素响应蛋白等, 均与种子大小与内容物充实有关。附表 请见网络版: 1) 本刊网站
参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
PMID [本文引用: 1]

Backcross populations are often used to study quantitative trait loci (QTL) after they are initially discovered in balanced populations, such as F(2), BC(1), or recombinant inbreds. While the latter are more powerful for mapping marker loci, the former have the reduced background genetic variation necessary for more precise estimation of QTL effects. Many populations of inbred backcross lines (IBLs) have been developed in plant and animal systems to permit simultaneous study and dissection of quantitative genetic variation introgressed from one source to another. Such populations have a genetic structure that can be used for linkage estimation and discovery of QTL. In this study, four populations of IBLs of oilseed Brassica napus were developed and analyzed to map genomic regions from the donor parent (a winter-type cultivar) that affect agronomic traits in spring-type inbreds and hybrids. Restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs) identified among the IBLs were used to calculate two-point recombination fractions and LOD scores through grid searches. This information allowed the enrichment of a composite genetic map of B. napus with 72 new RFLP loci. The selfed and hybrid progenies of the IBLs were evaluated during two growing seasons for several agronomic traits. Both pedigree structure and map information were incorporated into the QTL analysis by using a regression approach. The number of QTL detected for each trait and the number of effective factors calculated by using biometrical methods were of similar magnitude. Populations of IBLs were shown to be valuable for both marker mapping and QTL analysis.
PMID [本文引用: 1]

To develop an efficient mustard (Brassica juncea) breeding programme, a better knowledge of the genetic control and relationships of the main selected characters is needed. Thus, doubled haploid (DH) lines were evaluated over 2 years in the field. Days to flowering, plant height, thousand-seed weight, fatty acid composition, seed oil content, sinigrin, gluconapin and total glucosinolate contents were determined in the DH population. The influence of seed coat colour was estimated. Results showed significant differences between yellow and brown seeds only for oil and fatty acid contents. Molecular analysis revealed that seed coat colour is associated with two Mendelian trait loci: Bjc1 [on linkage group (LG) 3] and Bjc2 (on LG6). The quantitative trait loci associated with characters-detected by composite interval mapping-were not co-localised and revealed a genetic independence. The results obtained in this study show that the most important agronomic and quality traits of brown mustard could be bred independently. Correlation between the studied traits is also discussed.
DOIURL [本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
PMID [本文引用: 1]

The introgression of winter germplasm into spring canola (Brassica napus L.) represents a novel approach to improve seed yield of hybrid spring canola. In this study, quantitative trait loci (QTL) for seed yield and other traits were genetically mapped to determine the effects of genomic regions introgressed from winter germplasm into spring canola. Plant materials used comprised of two populations of doubled haploid (DH) lines having winter germplasm introgression from two related French winter cultivars and their testcrosses with a spring line used in commercial hybrids. These populations were evaluated for 2 years at two locations (Wisconsin, USA and Saskatchewan, Canada). Genetic linkage maps based on RFLP loci were constructed for each DH population. Six QTL were detected in the testcross populations for which the winter alleles increased seed yield. One of these QTL explained 11 and 19% of the phenotypic variation in the two Canadian environments. The winter allele for another QTL that increased seed yield was linked in coupling to a QTL allele for high glucosinolate content, suggesting that the transition of rapeseed into canola could have resulted in the loss of favorable seed yield alleles. Most QTL for which the introgressed allele decreased seed yield of hybrids mapped to genomic regions having homoeologous non-reciprocal transpositions. This suggests that allelic configurations created by these rearrangements might make an important contribution to genetic variation for complex traits in oilseed B. napus and could account for a portion of the heterotic effects in hybrids.
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIPMID [本文引用: 1]

Silique length (SL) and seed weight (SW) are two important yield-related traits controlled by quantitative trait loci (QTL) in oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). The genetic bases underlying these two traits are largely unknown at present. In this study, we conducted QTL analyses for SL and SW using 186 recombinant inbred lines (RILs) derived from a cross between S1, an EMS mutant with extremely long siliques and large seeds, and S2, an inbred line with regular silique length and seed size. RILs were grown in Wuhan in the 2008/09 (SS09) and 2009/10 (SS10) growing seasons, and mean SL and SW for each line were investigated. Ten non-redundant QTL were identified for SL. Of these, a major QTL, cqSLA9, consistently explained as much as 53.4% of SL variation across environments. The others are minor QTL and individually explained less than 10% of the SL variation. Nine non-redundant QTL were identified for SW. Of which, one major QTL, cqSWA9, explained as much as 28.2% of the total SW variation in the SS09 and SS10 environments. In addition, three additive by additive interactions with small effects were detected for SL, and no interactions were detected for SW. Interestingly, the two major QTL, cqSLA9 for SL and cqSWA9 for SW colocalized in the same chromosomal region and were integrated into a unique QTL, uqA9. The S1 allele at this locus increases both SL and SW, suggesting that uqA9 has pleiotropic effects on both SL and SW. The existence and effect of uqA9 was confirmed in genetically different RILs derived from the cross between S1 and No2127, a resynthesized DH line having regular silique length and seed size. Individuals in one residual heterozygous line for cqSLA9 showed significant difference in silique length. The results in this study revealed that silique length in the S1 mutant is mainly controlled by the cqSLA9 locus, which will be suitable for fine mapping and marker-assisted selection in rapeseed breeding for high yield.
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 2]
DOIPMID [本文引用: 1]

Rapid and uniform seed germination is a crucial prerequisite for crop establishment and high yield levels in crop production. A disclosure of genetic factors contributing to adequate seed vigor would help to further increase yield potential and stability. Here we carried out a genome-wide association study in order to define genomic regions influencing seed germination and early seedling growth in oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). A population of 248 genetically diverse winter-type B. napus accessions was genotyped with the Brassica 60k SNP Illumina genotyping array. Automated high-throughput in vitro phenotyping provided extensive data for multiple traits related to germination and early vigor, such as germination speed, absolute germination rate and radicle elongation. The data obtained indicate that seed germination and radicle growth are strongly environmentally dependent, but could nevertheless be substantially improved by genomic-based breeding. Conditions during seed production and storage were shown to have a profound effect on seed vigor, and a variable manifestation of seed dormancy appears to contribute to differences in germination performance in B. napus. Several promising positional and functional candidate genes could be identified within the genomic regions associated with germination speed, absolute germination rate, radicle growth and thousand seed weight. These include B. napus orthologs of the Arabidopsis thaliana genes SNOWY COTYLEDON 1 (SCO1), ARABIDOPSIS TWO-COMPONENT RESPONSE REGULATOR (ARR4), and ARRGINYL-t-RNA PROTEIN TRANSFERASE 1 (ATE1), which have been shown previously to play a role in seed germination and seedling growth in A. thaliana.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 2]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
PMID [本文引用: 1]

Association analyses that exploit the natural diversity of a genome to map at very high resolutions are becoming increasingly important. In most studies, however, researchers must contend with the confounding effects of both population and family structure. TASSEL (Trait Analysis by aSSociation, Evolution and Linkage) implements general linear model and mixed linear model approaches for controlling population and family structure. For result interpretation, the program allows for linkage disequilibrium statistics to be calculated and visualized graphically. Database browsing and data importation is facilitated by integrated middleware. Other features include analyzing insertions/deletions, calculating diversity statistics, integration of phenotypic and genotypic data, imputing missing data and calculating principal components.
PMID [本文引用: 2]

Research over the last few years has revealed significant haplotype structure in the human genome. The characterization of these patterns, particularly in the context of medical genetic association studies, is becoming a routine research activity. Haploview is a software package that provides computation of linkage disequilibrium statistics and population haplotype patterns from primary genotype data in a visually appealing and interactive interface.http://www.broad.mit.edu/mpg/haploview/jcbarret@broad.mit.edu
DOIURL [本文引用: 4]
PMID [本文引用: 2]

The enzyme 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase (KAT) (EC 2.3.1.16) catalyses a key step in fatty acid beta-oxidation. In Arabidopsis thaliana, expression of the KAT2 gene is known to be required for the efficient mobilization of triacylglycerol during germination and seedling establishment. Here, data from the Arabidopsis kat2-1 mutant are presented, showing that perturbation of beta-oxidation also affects vegetative growth and reproductive success. In the wild type, the KAT2 protein was detected in all organs tested. In the kat2-1 mutant, rosette leaf area and dry weight, but not leaf number, were greatly increased relative to wild type. Global proliferative arrest of flowering was delayed, resulting in increased silique production in kat2-1 plants. However, total silique dry weight was not increased. kat2-1 siliques were smaller and had a reduced seed number caused by increased ovule abortion. In kat2-1 ovules, carbon flow into sugars via gluconeogeneis and respiration were both reduced in comparison to the wild type. In conclusion, these data indicate that a functional beta-oxidation pathway is required to maintain the balance between silique development and the continued initiation of floral meristems.
DOIURL [本文引用: 2]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
PMID [本文引用: 2]

The isolation of an elongation-specific endo-1,4-beta-glucanase-cel1 from Arabidopsis thaliana was made possible by the fact that considerable homology exists between different endo-1,4-beta-glucanase (EGase) genes from different plants. Degenerate primers were synthesized based on two conserved regions from the avocado and tomato cellulase amino acid sequences. The A.thaliana cel1 cDNA gene was found to encode a 54kDa protein; sequence comparison with the avocado EGase revealed 56% identity. Northern blot analysis of cel1 suggested its developmental regulation. RNA transcripts were undetectable in fully expanded leaves as well as at the basal internode of flowering stems. However, a strong transcript signal was detected in the elongating zone of flowering stems of normal plants. The RNA transcript level of cel1 in the elongating zone of dwarf flowering stems was significantly lower than in the corresponding zone in normal plants. This suggests cel1's involvement in cell elongation in A. thaliana. Transgenic tobacco plants transformed with the putative cel1 promoter region fused to the gus reporter gene, showed a significant GUS staining both in shoot and root elongating zones. These results further substantiate the link between cel1 expression and plant cell elongation.
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
PMID [本文引用: 1]

Control of seed size involves complex interactions among the zygotic embryo and endosperm, the maternally derived seed coat, and the parent plant. Here we describe a mutant in Arabidopsis, megaintegumenta (mnt), in which seed size and weight are dramatically increased. One factor in this is extra cell division in the integuments surrounding mnt mutant ovules, leading to the formation of enlarged seed coats. Unusually for integument mutants, mnt does not impair female fertility. The mnt lesion also has pleiotropic effects on vegetative and floral development, causing extra cell division and expansion in many organs. mnt was identified as a mutant allele of AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR 2 (ARF2), a member of a family of transcription factors that mediate gene expression in response to auxin. The mutant phenotype and gene expression studies described here provide evidence that MNT/ARF2 is a repressor of cell division and organ growth. The mutant phenotype also illustrates the importance of growth of the ovule before fertilization in determining final size of the seed.
[本文引用: 1]
PMID [本文引用: 1]

The inheritance of yield-related traits in rapeseed (Brassica napus) is poorly understood, and the investigations on mapping of quantitative trait loci (QTL) for such traits are only few. QTL related to six traits were mapped which include plant height (PH), height of lowest primary effective branch (HPB), length of main inflorescence (LMI), silique length (SL), number of primary branches (FB) and silique density (SD). A set of 258 doubled haploid (DH) lines derivatives of a cross between a canola variety Quantum and a resynthesized B. napus line No.2127-17, and a fixed immortalized F(2) (designated as IF(2)) population generated by randomly permutated intermating of these DHs were investigated. A genetic linkage map was constructed using 208 SSR and 189 SRAP markers for the DH population. Phenotypic data were collected from three environments for the two populations. Using composite interval mapping analyses, 30 and 22 significant QTL were repeatedly detected across environments for the six traits in the DH and IF(2) populations, respectively. Twenty-nine QTL were common between the two populations. The directions of parental contribution for all common QTL were the same, showing a great potential for marker-assisted selection in improving these traits. Some chromosomal regions harbor QTL for multiple traits, which were consistent with significant phenotypic correlations observed among traits. The results provided a better understanding of the genetic factors controlling yield-related traits in rapeseed.
DOIPMID [本文引用: 1]

Background: There is an urgent need to increase global crop production. Identifying and combining specific genes controlling distinct biological processes holds the potential to enhance crop yields. Transcriptomics is a powerful tool to gain insights into the complex gene regulatory networks that underlie such traits, but relies on the availability of a high-quality reference sequence and accurate gene models. Previously, we identified a grain weight QTL on wheat chromosome 5A (5A QTL) which acts during early grain development to increase grain length through cell expansion in the pericarp. In this study, we performed RNA-sequencing on near isogenic lines (NILs) segregating for the 5A QTL and used the latest gene models to identify differentially regulated genes and pathways that potentially influence pericarp cell size and grain weight in wheat.Results: We sampled grains at 4 and 8 days post anthesis and found that genes associated with metabolism, biosynthesis, proteolysis and the defence response are upregulated during this stage of grain development in both NILs. We identified a specific set of 112 transcripts differentially expressed (DE) between 5A NILs at either time point, including eight potential candidates for the causal 5A gene and its downstream targets. The 112 DE transcripts had functional annotations including non-coding RNA, transposon-associated, cell-cycle control, ubiquitin-related, heat-shock, transcription and histone-related. Many of the genes identified belong to families that have been previously associated with seed/grain development in other species. Notably, we identified DE transcripts at almost all steps of the pathway associated with ubiquitin-mediated protein degradation. In the promoters of a subset of DE transcripts we identified enrichment of binding sites associated with C2H2, MYB/SANT, YABBY, AT-HOOK and Trihelix transcription factor families.Conclusions: In this study, we identified DE transcripts with a diverse range of predicted biological functions, reflecting the complex nature of the pathways that control early grain development. Few of these are the direct orthologues of grain size genes in other species and none have been previously characterised in wheat. Further functional characterisation of these candidates and how they interact will provide novel insights into the control of grain size in cereals.
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
