 ,, 丁仕林, 刘朝雷, 阮班普, 姜洪真, 郭锐, 董国军, 胡光莲, 郭龙彪, 钱前, 高振宇
,, 丁仕林, 刘朝雷, 阮班普, 姜洪真, 郭锐, 董国军, 胡光莲, 郭龙彪, 钱前, 高振宇 ,*中国水稻研究所, 浙江杭州 310006
,*中国水稻研究所, 浙江杭州 310006Genetic analysis of seedling root traits and fine mapping of the QTL qLRL4 for the longest root length in rice
TIAN Biao ,, DING Shi-Lin, LIU Chao-Lei, RUAN Ban-Pu, JIANG Hong-Zhen, GUO Rui, DONG Guo-Jun, HU Guang-Lian, GUO Long-Biao, QIAN Qian, GAO Zhen-Yu
,, DING Shi-Lin, LIU Chao-Lei, RUAN Ban-Pu, JIANG Hong-Zhen, GUO Rui, DONG Guo-Jun, HU Guang-Lian, GUO Long-Biao, QIAN Qian, GAO Zhen-Yu ,*China National Rice Research Institute, Hangzhou 310006, Zhejiang, China
,*China National Rice Research Institute, Hangzhou 310006, Zhejiang, China通讯作者: *高振宇, E-mail:gaozhenyu@caas.cn, Tel: 0571-63370211
收稿日期:2020-12-13接受日期:2021-03-19网络出版日期:2021-04-13
| 基金资助: |
Corresponding authors: *E-mail:gaozhenyu@caas.cn, Tel: 0571-63370211
Received:2020-12-13Accepted:2021-03-19Published online:2021-04-13
| Fund supported: |
作者简介 About authors
E-mail:82101186057@caas.cn,Tel:0571-63370483

摘要
为了解析水培苗期根系相关性状的遗传调控, 以籼稻9311和粳稻日本晴(Nipponbare, NPB)为亲本的148个株系构成的重组自交系群体为材料, 对水稻幼苗根系相关性状开展QTL分析。在2次重复中共检测到26个控制最长根长、总根系长、根表面积、根体积和根直径的QTL, 分布在水稻第1、2、4、7、9、10、11号共7条染色体上, 发现了水稻第2、4、7和10号染色体上的4个QTL簇, 包括第4号染色体上控制最长根长的QTL qLRL4。为了精细定位该QTL, 我们构建了以9311为背景、插入缺失标记IND4-1和IND4-4间来自NPB的近等系NIL-qLRL4。利用NIL-qLRL4和9311构建的F2群体, 最终将qLRL4精细定位在标记IND4-1和IND4-3之间约68.23 kb的区间内并预测了候选基因。此根长QTL的精细定位将有助于水稻根长遗传机理的研究, 为探究水稻根系形态建成的分子机制奠定了基础。
关键词:
Abstract
In order to analyze the genetic basis of root traits at seedling stage, we performed QTL analysis of root morphology with 148 recombinant inbred lines derived from indica variety 9311 and japonica variety Nipponbare (NPB). In two repetitions, a total of 26 QTLs were detected for the longest root length, total root length, root surface area, root volume, and root diameter, distributed on chromosomes 1, 2, 4, 7, 9, 10, and 11 in rice. Four QTL clusters on chromosomes 2, 4, 7, and 10 were found, including a major QTL qLRL4 controlling the longest root length. To fine mapping of the major QTL, we constructed a near isogenic line NIL-qLRL4 with a segment from NPB between markers IND4-1 and IND4-4 with 9311 background. With a F2 population derived from the NIL-qLRL4 and 9311, we fine mapped the qLRL4 within ~68.23 kb region between markers IND4-1 and IND4-3, where eight candidate genes located. Fine mapping of this QTL for root length will help explore genetic mechanism of root elongation and morphogenesis in rice.
Keywords:
PDF (1241KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
本文引用格式
田彪, 丁仕林, 刘朝雷, 阮班普, 姜洪真, 郭锐, 董国军, 胡光莲, 郭龙彪, 钱前, 高振宇. 水稻苗期根部性状的遗传分析和最长根长QTL qLRL4的精细定位[J]. 作物学报, 2021, 47(10): 1863-1873 DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1006.2021.02088
TIAN Biao, DING Shi-Lin, LIU Chao-Lei, RUAN Ban-Pu, JIANG Hong-Zhen, GUO Rui, DONG Guo-Jun, HU Guang-Lian, GUO Long-Biao, QIAN Qian, GAO Zhen-Yu.
水稻是人类最主要的粮食作物之一[1], 而根系作为水稻主要的器官, 具有固定水分、吸收养分、合成与分泌激素、酶和有机酸等功能[2]。虽然根系研究与其他性状相比相对薄弱[3], 但是植物学家对根系相关性状已开展了大量遗传研究。徐吉臣等[4]以窄叶青8号和京系17的F1代花培加倍的127个双单倍体(double haploid, DH)群体为材料, 测定了营养液培养条件下亲本及DH株系的最大根长、根干重和根茎干重比, 检测到4个最大根长QTL, 分别位于第2、4、9、10号染色体; 检测到水稻第2号染色体的1个根干重QTL; 根茎干重比共检测到3个QTL, 分别位于第3、5、6号染色体上。滕胜等[5]和胡兴明等[6]也用相同群体进行了根部性状的QTL分析。前者在抽穗期对根系活力进行QTL分析, 在第4号染色体的分子标记RG449和RG809间检测到1个QTL (qRV4)。后者对水稻苗期发根力进行了QTL和上位性分析, 在水稻第3号染色体的C63~CT125之间检测到1个发根力主效QTL; 同时检测到影响水稻发根力的5对上位性效应基因座, 分别位于第2、3、5、6、7、12号染色体上, 其中影响根长和根数的上位性效应各有2对QTL, 有一对QTL同时影响根长和根数。迄今, 国内外科学家已定位了多个水稻根长相关QTL。Mitsuhiro等[7]用粳稻品种Koshihikari和籼稻品种Kasalath杂交和回交得到的38个染色体片段替代系(CSSL)检测生长在5 μmmol L-1或500 μmmol L-1 NH4+中的水稻幼苗根长QTL, 共检测到8个QTL, 分别位于第1、2、4、6、8、11和12号染色体, 并将6号染色体的根长主效QTL qRL6.1精细定位在长臂337 kb区间内。王汝慈等[8]利用协青早B与中恢9308杂交构建的RIL群体在水稻第4号染色体长臂的分子标记RM307与RM1205之间定位到一QTL簇, 控制不同时期的相对根长、相对根冠比、相对根干质量等性状, 其中包括控制水稻根长的主效QTL——qRL4。Obara等[9]以水稻WAB56-104和NERICA7品系的杂交F2群体为材料, 在高NH4+环境下于水稻第1号染色体检测到2个水稻根长相关QTL, 分别命名为qRL1.3- NERICA7和qRL1.4-NERICA7, 其中qRL1.4- NERICA7的定位区间进一步缩小至0.7 Mb。Kitomi等[10]为了鉴定与水稻最大根长相关的基因组区间, 用来自IR64和KinandangPatong间杂交回交得到的26个CSSL进行QTL分析, 得到2个最大根长QTL: 2号染色体的qRO1和6号染色体的qRO2。将qRO1精细定位在SSR标记RM5651和RM6107之间的1.7 Mb区间, 将qRO2定位在SSR标记RM20495和RM3430-1之间884 kb的区间。到目前为止, 科学家已成功克隆了一些控制水稻根系性状的基因[11,12], 如Srt5[13]和OsSPR1[14]基因调控水稻根长, CRL1[15]基因影响冠状根的发生和不定根的形成, ARL1[16]基因影响不定根的形成, WOX11[17]基因促进冠根的起始和伸长, REL2[18]和OsWRKY74[19]基因影响不定根的的数目和长度, SRT6[20]基因抑制初生根的发育, LRT2[21]基因控制侧根发生。为了深入了解水稻根系性状的遗传基础, 我们以9311和日本晴(Nipponbare, NPB)构建的重组自交系(recombinant inbred lines, RIL)群体为材料, 利用水培技术和数量遗传学手段对水稻根系性状相关QTL进行了分析和鉴定。
1 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
研究采用籼稻品种9311和粳稻品种NPB杂交获得的148个株系构成的RIL群体。我们选择了qLRL4区域具有NPB基因型的RIL与亲本9311回交, 并在插入缺失(InDel)标记IND4-1和IND4-4之间选择目标QTL区域携带NPB纯合等位基因的近等基因系(near isogenic lines, NIL) NIL-qLRL4。1.2 试验方法
在黑暗条件下, 水稻种子于37°C去离子水中浸泡2 d, 然后转移至漂浮在去离子水上的网格, 培养3 d。将幼苗培养在正常浓度的Kimura B营养液中(pH 5.4), 每3 d更换一次营养液。然后, 将幼苗转移至30°C温室中培养21 d, 用尺子测量5株幼苗的主根长, 然后用i800扫描仪扫描总根长, 用LA-S根分析系统(万深, 中国杭州)进行分析。用亚甲基蓝比色法(Leagene, 中国北京)测定根系活性(总吸收面积和比表面积), 每3株幼苗为1次重复, 3个重复, 总体进行2次重复实验, 记为重复I (Repeat I)和重复II (Repeat II)。用均匀分布于水稻12条染色体的166个在9311和NPB之间存在多态的SSR和STS标记构建了RIL群体的遗传连锁图谱。使用MultiQTL软件(www. multiqtl.com)对RIL群体采用最大似然区间映射方法进行QTL分析, 根据每个数据集的排列测试(1000个排列, P=0.05)获得LOD阈值。根据McCouch等[22]的方法命名QTL。利用Microsoft Excel软件分析根部形状的表型值与频数分布, 并绘制相关图表; 利用IBM SPSS Statistics 24软件进行显著性差异检验和相关性分析。
通过近等系NIL-qLRL4与9311的杂交和自交, 构建了用于精细定位的830个植株构成的F2群体, 测量了单株根长表型, 在已定位的qLRL4区间内开发了4个InDel标记(表1)检测单株基因型, 用于qLRL4的精细定位。
Table 1
表1
表1qLRL4精细定位的InDel标记引物
Table 1
| 分子标记 Marker | 正向引物 Forward primer (5′-3′) | 反向引物 Reverse primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| IND4-1 | TTGGCAGGTAGAGTCCAAAGG | TGGCTTAAGAGACGTCCCTAAC |
| IND4-2 | TGCCCTGGAAGTATAAGGATG | ATGTCTGCATACCAGAACAAAAG |
| IND4-3 | GCGACCACATAAATACTGTTG | AGGTGGGACTATATATTAATGG |
| IND4-4 | AGTTGTTATTCATCGCCATCGG | TGATATACCCGAGACCAAAAGTAGC |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
采用Axygen公司的AxyPrep总RNA小量制备试剂盒(AP-MD-MS-RNA-50)提取9311、NPB和NIL-q LRL4的根部RNA并使用TOYOBO公司的cDNA逆转录试剂盒(fsq-101)反转录得到cDNA后, 用候选基因引物和内参Histone H3引物(表2)在ABI7900HT Real-time PCR仪上对样品的候选基因表达量进行相对定量检测。
Table 2
表2
表2候选基因实时定量PCR引物
Table 2
| 基因 Gene | 正向序列 Forward primer (5′-3′) | 反向序列 Reverse primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| LOC_Os04g58870 | AATCACTTGAGCAAGCTCTTGG | ATGCAAACATGCACAATGCAG |
| LOC_Os04g58880 | AAGAGCTGCGGTCAAAGAGAG | ACTCACGCAACTCCGTATCTGG |
| LOC_Os04g58890 | TCGTCGCCGACAGGGTG | AGGTCGGTCCCCTCCTCG |
| LOC_Os04g58900 | ACGTATGATTTCCCTGTTGATGTG | ACCTCATCTTCCTTCCCAGTAAATC |
| LOC_Os04g58910 | AGAAATGGAAGCCTGTGAACGAC | TCATGCTGGCCTCTGCGTC |
| LOC_Os04g58920 | AGCTGTGCGTGGTGGCGC | CTGCAAGCAGGGCGAGTTCC |
| LOC_Os04g58940 | AGGCTCTTCGGCTACCTGC | ATCAGCTCATCCCCATCACC |
| LOC_Os04g58960 | AGCAGATGACCAATGGTGGG | TGGTTGCTGGGTGAGCTAGAAC |
| Histone H3 | GGTCAACTTGTTGATTCCCCTCT | AACCGCAAAATCCAAAGAACG |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
2 结果与分析
2.1 9311、NPB及其RIL群体的根系性状
亲本9311和NPB之间的根系形态存在显著差异(表3和图1)。9311的最长根长(the longest root length, LRL)、总根系长(total root length, TRL)、根表面积(root surface area, RSA)、根体积(root volume, RV)和根直径(root diameter, RD)均显著大于NPB。考察9311和NPB构建的RIL群体的最长根长、总根系长、根表面积、根体积和根直径这5个性状, 统计2次重复的平均值, 最长根长为14.8 cm和14.3 cm, 总根系长为296.35 cm和331.61 cm, 根表面积为25.26 cm2和25.62 cm2, 根体积为0.22 cm3和0.26 cm3, 根直径为0.25 mm和0.23 mm。RIL的5个性状与两亲本相比, 最长根长和平均直径均小于两亲本。RIL的平均总根系长、根表面积和根体积介于NPB和9311之间(表4)。在2次重复中, 5个根系性状在RIL群体中均呈连续正态分布(图2), 且大部分呈现出明显的超亲分离, 表明这些性状由多基因控制, 适合进行QTL分析。2次重复之间比较后发现, 重复I和重复II的最长根长、根表面积和根体积的分布范围基本一致。然而, 重复I的总根长和平均直径的变化范围大于重复II。Table 3
表3
表39311和NPB的根系性状
Table 3
| 重复 Repeat | 品种 Variety | 最长根长 LRL (cm) | 总根系长 TRL (cm) | 根表面积 RSA (cm2) | 根体积 RV (cm3) | 根直径 RD (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 9311 | 17.3 ± 0.4** | 331.38 ± 30.07** | 34.23 ± 3.93** | 0.36 ± 0.05** | 0.32 ± 0.01** |
| NPB | 15.9 ± 0.8 | 253.08 ± 36.76 | 27.33 ± 1.65 | 0.20 ± 0.06 | 0.25 ± 0.03 | |
| II | 9311 | 17.9 ± 0.5** | 360.36 ± 31.64** | 34.46 ± 0.99** | 0.37 ± 0.01** | 0.33 ± 0.01** |
| NPB | 15.6 ± 0.6 | 277.22 ± 28.44 | 24.44 ± 2.27 | 0.21 ± 0.02 | 0.26 ± 0.01 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
图1
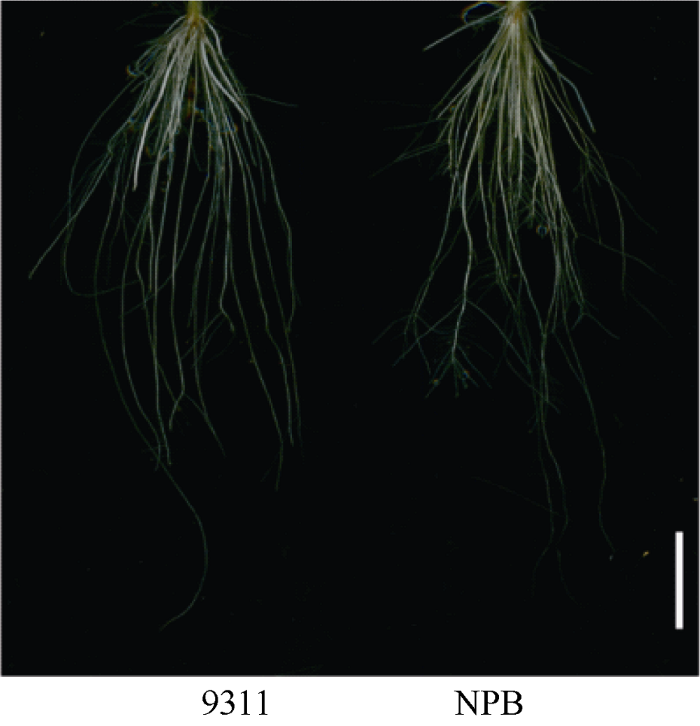 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图19311和NPB在营养液中培养21 d的根系形态
NPB: 日本晴; 标尺为3 cm。
Fig. 1Root morphology of 9311 and NPB cultured in nutrient solution for 21 days
NPB: Nipponbare; Bar: 3 cm.
Table 4
表4
表4RIL群体的根系性状
Table 4
| 重复 Repeat | 统计参数 Parameter | 最长根长 LRL (cm) | 总根系长 TRL (cm) | 根表面积 RSA (cm2) | 根体积 RV (cm3) | 根直径 RD (mm) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 均值 Mean | 14.8 | 296.35 | 25.26 | 0.22 | 0.25 | ||||||||||
| 标准差 SD | 2.3 | 86.90 | 7.40 | 0.08 | 0.04 | |||||||||||
| 变幅 Range | 8.9-24.0 | 132.88-562.92 | 9.26-45.12 | 0.06-0.45 | 0.15-0.34 | |||||||||||
| 偏度 Skewness | 0.50 | 0.85 | 0.40 | 0.31 | -0.44 | |||||||||||
| 峰度 Kurtosis | 0.90 | 0.72 | -0.09 | -0.27 | -0.08 | |||||||||||
| II | 均值 Mean | 14.3 | 331.61 | 25.62 | 0.26 | 0.23 | ||||||||||
| 标准差 SD | 2.9 | 57.19 | 7.27 | 0.08 | 0.07 | |||||||||||
| 变幅 Range | 8.9-24.0 | 186.30-481.50 | 9.82-45.33 | 0.09-0.62 | 0.08-0.59 | |||||||||||
| 偏度 Skewness | 0.39 | 0.01 | 0.39 | 0.62 | 0.85 | |||||||||||
| 峰度 Kurtosis | 0.24 | 0.03 | -0.08 | 1.45 | 3.53 | |||||||||||
新窗口打开|下载CSV
图2
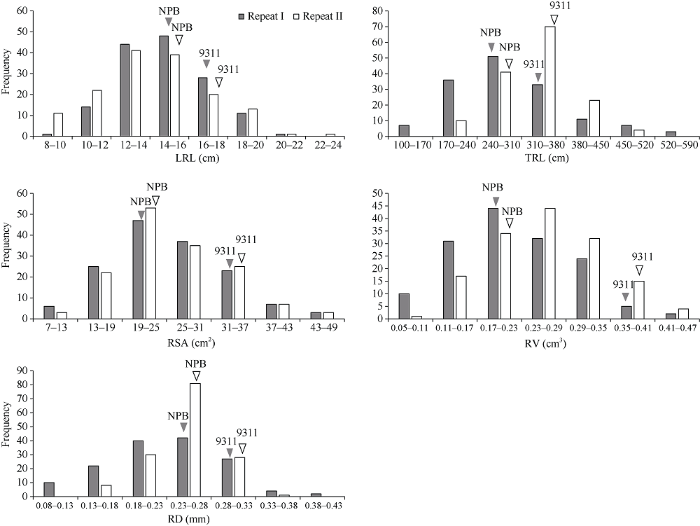 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图2在2次重复中9311和NPB构建的RIL群体5个根系性状的频数分布
NPB: 日本晴; 倒三角指示亲本的平均值; LRL: 最长根长; TRL: 总根系长; RSV: 根表面积; RV: 根体积; RD: 根直径。
Fig. 2Frequency distribution of five root traits in the RIL population from 9311 and NPB in two repetitions
NPB: Nipponbare; the inverted triangle indicates the average value of the parent. LRL: the longest root length; TRL: total root length; RSV: root surface area; RV: root volume; RD: root diameter.
2.2 RIL群体各根系性状间的相关性分析
将RIL群体各根系性状进行相关性分析发现(表5), 在重复I中, 最长根长与总根系长、根表面积、根体积均呈显著正相关, 相关系数为0.359’0.399, 与根直径没有显著相关性。总根系长与根表面积和根体积的相关系数为0.946和0.859, 远大于与最长根长和根直径的0.359和0.408。同样, 根表面积与根体积间具有显著相关性。总的来说, 这5个性状, 最长根长与根直径没有显著的相关性, 其他性状之间都存在显著正相关。而在重复II中, 最长根长与其他4个性状间均无明显相关性, 其他性状相互之间都存在显著正相关。Table 5
表5
表5RIL群体根系性状间的相关系数
Table 5
| 重复 Repeat | 性状 Trait | 最长根长 LRL (cm) | 总根系长 TRL (cm) | 根表面积 RSA (cm2) | 根体积 RV (cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 总根系长 TRL | 0.359** | |||
| 根表面积 RSA | 0.399** | 0.946** | |||
| 根体积 RV | 0.365** | 0.859** | 0.975** | ||
| 根直径 RD | 0.011 | 0.408** | 0.571** | 0.671** | |
| II | 总根系长 TRL | 0.041 | |||
| 根表面积 RSA | 0.030 | 0.684** | |||
| 根体积 RV | 0.043 | 0.749** | 0.831** | ||
| 根直径 RD | 0.084 | 0.799** | 0.737** | 0.914** |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
2.3 RIL群体根系性状的QTL分析
利用一些SSR和STS标记引物进行QTL定位(表6), 然后对9311和NPB构建的RIL群体的最长根长、总根系长、根表面积、根体积和根直径这5个性状进行QTL分析(图3和表7)。重复I共检测到15个QTL, 分布在水稻第1、2、4、7、10和11染色体上。控制最长根长的QTL有3个, 分布在第1、4和10号染色体, 变异贡献率幅度为4.8%’10.3%。其中, 贡献率超过5%的位点有2个: qLRL1和qLRL10, 贡献率分别为10.3%和6.3%, 前者效应来自NPB, 后者效应来自9311。我们检测到控制总根系长的QTL 4个, 分布在水稻第1、2、7和11号染色体上, LOD值为2.92’8.47。这些QTL的表型变异贡献率均超过5%, 幅度为7.8%’42.5%。qTRL1的效应来自NPB, 其余3个QTL的效应来自9311。控制根表面积的QTL有3个, 分布于水稻第2、7和11号染色体, 3个QTL的表型变异贡献率均超过5%。控制根体积的QTL有4个, 分布于水稻第2、7、10和11号染色体, 贡献率(除qRV10外)都超过5%。控制根直径的QTL有2个, 分布在水稻第1和4号染色体, 这2个QTL的贡献率均超过5%。qRD1的效应来自9311, qRD4的效应来自NPB。Table 6
表6
表6QTL定位的SSR和STS标记引物
Table 6
| 分子标记 Marker | 正向引物 Forward primer (5'-3') | 反向引物 Reverse primer (5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
| M1-2 | ACAATTTGGAGCAAGAAAGA | CTTGTCGCAGTACAGTTTTG |
| M1-4 | AACATCGAGAATGTGAATCC | TGCTGATTCGTATAGCTTTG |
| M1-16 | AGAGAGCTGTACCAAAGCTG | TACATCATATGCCACCAAAC |
| 分子标记 Marker | 正向引物 Forward primer (5'-3') | 反向引物 Reverse primer (5'-3') |
| M1-18 | CCTAAATGACAAAGTTTGGG | TGTTTGGACTTAGAAATCTCG |
| M1-19 | TTTCCATGGCTATTGCTAAC | ATCTTGGGGATCATGAATTG |
| M1-20 | TGCATTTATGCATCTACTGG | TCACTGCATTTGCAAGTTAC |
| M1-21 | AAGATGATGAGGTTCATTGG | TATACGACGTGGCTGTATCA |
| M1-22 | GATGTCACTTTAGCGGTAGC | AAAATTTTCTTTCTCGAGGG |
| M2-10 | TGCTGCTTCTGTCCAGTGAG | GGATCATAACAAGTGCCTCG |
| M2-13 | ACAAGGAAATCCAAAGCTG | CTTCTTCAAAAATTGACGGT |
| M2-14 | GTAGCAGAAACCAATGCTC | ATTCGCGATAAATATGGACT |
| M4-10 | AAAGAAGAAGATGAGTCCCC | AGACATATTCCCGTCTGTTG |
| M4-13 | AATTGGAGCTAGTAGTTGGCT | AGCGAAGTAAACAAGAGCTG |
| M7-1 | TATGTCCTTAGCATGGAAGACC | CGTTGTTGATCATCTGGTACG |
| M7-3 | GTCCATGCATCCATCTCTAG | ACGGAAGGAATACGTCTGTA |
| M9-7 | GATTAATTAAGGAAAAAGTTACACA | TTTAAGAAACACAGTCCATAACA |
| M9-10 | CTCGTTTATTACCTACAGTACC | CTACCTCCTTTCTAGACCGATA |
| M10-4 | TTTGTACTGTGAGTGCCAAG | AACACCCAAACTTGTGAAAC |
| M10-7 | AATGGTGCATATTTAATGGG | ATTGTTTGTTTCCTTGTTGG |
| M11-2 | TTGTCAGGAACAACCTTAGC | ACCGAGCCTAGCAACTTAG |
| M11-6 | CGCTTGAAAGGACTCCAGAC | CCATCTACTCACCAAACGTTCC |
| M11-9 | CGGCATGTCATGGACTACG | CAGGAAATCTGTAACCAGAGG |
| M11-11 | TGAACCCTGCTCTTCTGAGTC | AAAGAAGATATGAAGGCACCG |
| M11-13 | TGCTTGATCTGTGTTCGTCC | TAGCAGCACCAGCATGAAAG |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
图3
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图3RIL群体根系性状QTL的遗传图谱位置
每条染色体的左边列出为分子标记。
Fig. 3Map locations of QTLs for root traits in RIL population
Molecular markers for QTLs are listed on the left along each chromosome.
Table 7
表7
表7RIL群体的根系性状QTL
Table 7
| 重复 Repeat | 性状 Trait | 染色体 Chromosome | QTL | LOD | P值 P-value | 分子标记 Marker | 遗传位置 Genetic position (cM) | 贡献率 PEV (%) | 加性效应 Additive effect | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 最长根长 LRL | 1 | qLRL1 | 2.30 | 0.01 | M1-16-M1-19 | 173.3-188.0 | 10.3 | -1.48 | |||||||
| 4 | qLRL4 | 2.38 | 0.01 | M4-10-M4-13 | 161.1-190.6 | 4.8 | 1.47 | |||||||||
| 10 | qLRL10 | 2.33 | 0.01 | M10-4-M10-7 | 15.2-43.4 | 6.3 | 1.16 | |||||||||
| 总根系长 TRL | 1 | qTRL1 | 4.62 | 0.01 | M1-20-M1-22 | 224.4-256.0 | 42.5 | -102.52 | ||||||||
| 2 | qTRL2 | 12.92 | 0.01 | M2-10-M2-13 | 153.9-178.1 | 17.0 | 64.91 | |||||||||
| 7 | qTRL7 | 5.84 | 0.01 | M7-1-M7-3 | 0.0-18.6 | 9.1 | 47.36 | |||||||||
| 11 | qTRL11 | 8.47 | 0.01 | M11-11-M11-13 | 126.5-136.0 | 7.8 | 43.95 | |||||||||
| 根表面积 RSA | 2 | qRSA2 | 4.59 | 0.01 | M2-10-M2-13 | 153.9-178.1 | 15.7 | 5.67 | ||||||||
| 7 | qRSA7 | 3.60 | 0.01 | M7-2-M7-4 | 18.6-62.2 | 17.7 | 6.03 | |||||||||
| 11 | qRSA11 | 3.19 | 0.01 | M11-9-M11-13 | 92.0-136.0 | 7.1 | 3.81 | |||||||||
| 根体积 RV | 2 | qRV2 | 3.49 | 0.01 | M2-10-M2-13 | 153.9-178.1 | 11.3 | 0.05 | ||||||||
| 7 | qRV7 | 3.27 | 0.01 | M7-2-M7-4 | 18.6-62.2 | 15.9 | 0.06 | |||||||||
| 10 | qRV10 | 2.37 | 0.01 | M10-4-M10-7 | 15.2-43.4 | 4.6 | 0.03 | |||||||||
| 11 | qRV11 | 3.77 | 0.01 | M11-2-M11-6 | 24.1-41.2 | 9.4 | 0.05 | |||||||||
| 根直径 RD | 1 | qRD1 | 4.38 | 0.01 | M1-2-M1-4 | 15.1-49.3 | 8.7 | 0.02 | ||||||||
| 4 | qRD4 | 4.04 | 0.01 | M4-10-M4-13 | 161.1-190.6 | 26.3 | -0.04 | |||||||||
| II | 最长根长 LRL | 4 | qLRL4 | 2.03 | 0.04 | M4-10-M4-13 | 161.1-190.6 | 8.3 | 1.99 | |||||||
| 总根系长 TRL | 1 | qTRL1 | 13.53 | 0.01 | M1-18-M1-21 | 185.0-254.8 | 22.1 | -53.10 | ||||||||
| 重复 Repeat | 性状 Trait | 染色体 Chromosome | QTL | LOD | P 值 P-value | 分子标记 Marker | 遗传位置 Genetic position (cM) | 贡献率 PEV (%) | 加性效应 Additive effect | |||||||
| 7 | qTRL7 | 16.84 | 0.01 | M7-2-M7-4 | 18.6-62.2 | 18.6 | 48.80 | |||||||||
| 9 | qTRL9 | 10.29 | 0.01 | M9-7-M9-10 | 86.2-97.6 | 11.7 | -38.67 | |||||||||
| 11 | qTRL11 | 6.95 | 0.01 | M11-9-M11-13 | 92.0-136.0 | 24.7 | 56.19 | |||||||||
| 根表面积RSA | 2 | qRSA2 | 4.61 | 0.01 | M2-10-M2-14 | 153.9-192.0 | 15.6 | 16.63 | ||||||||
| 7 | qRSA7 | 3.64 | 0.01 | M7-2-M7-4 | 18.6-62.2 | 17.9 | 17.84 | |||||||||
| 11 | qRSA11 | 3.36 | 0.01 | M11-9-M11-13 | 92.0-136.0 | 7.4 | 11.48 | |||||||||
| 根体积RV | 10 | qRV10 | 2.00 | 0.04 | M10-4-M10-7 | 15.2-43.4 | 6.5 | 0.03 | ||||||||
| 根直径 RD | 4 | qRD4 | 3.10 | 0.01 | M4-10-M4-13 | 161.1-190.6 | 9.4 | -0.04 | ||||||||
| 11 | qRD11 | 2.83 | 0.01 | M11-4-M11-7 | 29.0-60.2 | 8.1 | 0.04 | |||||||||
新窗口打开|下载CSV
重复II共检测到11个QTL, 分布在第1、2、4、7、9、10和11号染色体上。我们只在4号染色体上发现了一个控制最长根长的QTL, 贡献率为8.3%, 加性效应来自于9311。控制总根长的QTL有4个, 分布在水稻第1、7、9和11号染色体上, LOD值为6.95’16.84。这些QTL的表型变异贡献率均超过5%, 幅度为11.7%’24.7%。qTRL7和qTRL9的效应来自NPB, 其余2个QTL的效应来自9311。控制根表面积的QTL有3个, 分布于水稻第2、7和11号染色体, 3个QTL的表型变异贡献率均超过5%。控制根体积的QTL有1个, 在10号染色体上。控制根直径的QTL有2个, 分布在水稻第4和11号染色体, 这2个QTL的贡献率均超过5%。其中, qRD4的效应来自NPB, qRD11的效应来自9311。
对2个重复进行分析发现, 有5个控制相同性状的QTL在同一位置被重复检测到。包括4号染色体上的qLRL4和qRD4, 7号染色体上的qRSA7, 10号染色体上的qRV10和11号染色体上的qRSA11。qLRL4、qRSA7、qRV10和qRSA11这4个QTL的效应在2个重复中均来自9311, 说明RIL的最长根长、根表面积和根体积的正效应来自9311等位型。qRD4的效应在2个重复中来自NPB, 说明RIL根直径受NPB等位型的正调控。综合2个重复鉴定的QTL来看, 在7条染色体上共分布有4个QTL簇, 分别位于水稻第2、4、7和10号染色体, 只有4号染色体上检测到的最长根长和根直径相关QTL, 在2次重复中定位的染色体相同位置。因此, 我们对QTL qLRL4开展精细定位。
2.4 最长根长QTL qLRL4的精细定位和候选基因确定
位于水稻第4号染色体的QTL qLRL4是控制最长根长的QTL。9311背景下InDel标记IND4-1和IND4-4间约158 kb来自NPB的近等系NIL-qLRL4与9311相比, 最长根长缩短, 根直径略微变大, 总吸收面积和活跃吸收面积减少, 其他性状基本无变化(图4和表8)。利用近等系NIL-qLRL4和9311构建的大规模F2群体, 结合个体的InDel标记基因型和根长表型, 我们进一步精细定位这一最长根长QTL qLRL4, 最终将其定位于标记IND4-1和IND4-3之间约68.23 kb的物理距离内(图5和表1)。依据水稻基因组注释数据库(图4
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图49311和NIL-qLRL4在营养液中培养21 d的根系形态
标尺为3 cm。
Fig. 4Root morphology of 9311 and NIL-qLRL4 cultured in nutrient solution for 21 days
Bar: 3 cm.
Table 8
表8
表89311和NIL-qLRL4的根系性状和活性
Table 8
| 品种/品系 Variety/Line | 最长根长 Longest root length (cm) | 总根系长 Total root length (cm) | 根表面积 Root surface area (cm2) | 根体积 Root volume (cm3) | 根直径 Root diameter (mm) | 总吸收面积 Total absorbing area (m2) | 比表面积 Specific surface area (cm2 cm-3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9311 | 17.3 ± 0.4 | 331.38 ± 30.07 | 34.23 ± 3.93 | 0.36 ± 0.05 | 0.32 ± 0.01 | 0.636 ± 0.032 | 4243.3 ± 210.2 |
| NIL-qLRL4 | 14.6 ± 0.1** | 340.40 ± 19.91 | 34.44 ± 3.15 | 0.36 ± 0.04 | 0.35 ± 0.02 | 0.535 ± 0.023** | 3566.9 ± 150.3** |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
图5
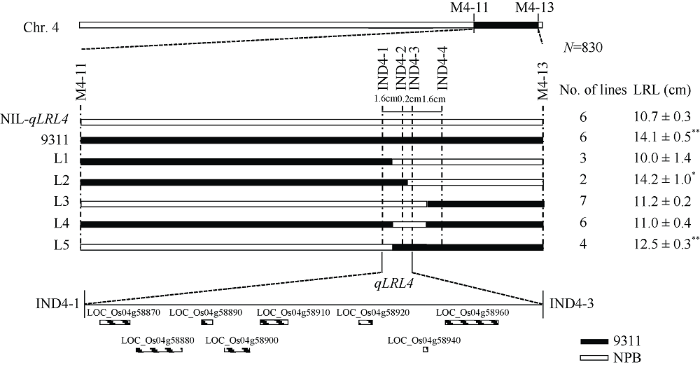 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图5qLRL4的精细定位
qLRL4被缩小到标记IND4-1和IND4-3之间的68.23 kb区间内。图例的黑色条块代
Fig. 5Fine mapping of qLRL4
qLRL4 was narrowed down to a 68.23 kb interval defined by markers IND4-2 and IND4-3. Black box represents 9311 genotype, and white box represents NPB genotype. NPB: Nipponbare. Values represent means ± SD. * and ** indicate significant difference at the 0.05 and 0.01 probability levels compared with NIL-qLRL4, respectively. LRL: the longest root length.
Table 9
表9
表9qLRL4精细定位区间的候选基因和候选基因中引起氨基酸改变的序列变化
Table 9
| 基因 Gene | 注释 Annotation | SNP | INDEL | NPB | 9311 | CDS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOC_Os04g58870 | exo70 exocyst complex subunit, putative, expressed | 4 | 0 | G | T | 487 |
| T | C | 514 | ||||
| A | G | 632 | ||||
| T | G | 1529 | ||||
| LOC_Os04g58880 | exo70 exocyst complex subunit, putative, expressed | 1 | 0 | A | G | 1279 |
| LOC_Os04g58890 | Expressed protein | 1 | 0 | T | G | 416 |
| LOC_Os04g58900 | Hydrolase, NUDIX family, domain containing protein, expressed | 1 | 0 | C | T | 142 |
| LOC_Os04g58910 | Receptor protein kinase TMK1 precursor, putative, expressed | 3 | 1 | G | T | 223 |
| A | G | 1630 | ||||
| A | G | 1909 | ||||
| +TCC | 0 | 14 | ||||
| LOC_Os04g58920 | U-box domain-containing protein, putative, expressed | 1 | 0 | G | T | 338 |
| LOC_Os04g58940 | Expressed protein | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| LOC_Os04g58960 | Regulator of chromosome condensation, putative, expressed | 3 | 0 | T | G | 1148 |
| C | T | 1116 | ||||
| C | T | 2582 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
图6
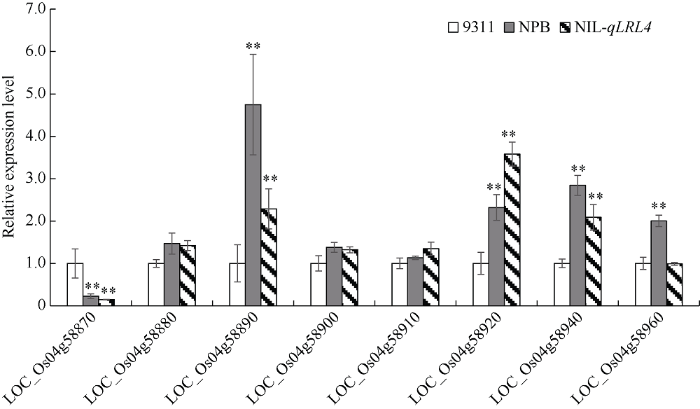 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图6候选基因的相对表达量
相对表达量数据为平均数±标准差, n = 3。**表示与9311比较达到0.01的差异显著水平。
Fig. 6Relative expression level of candidate genes
Data represent means ± SD of three biological replicates. ** indicates significant difference at the 0.01 probability level compared with 9311.
3 讨论
在QTL分析中, 同一染色体区间存在多个QTL控制多个根系性状, 这可能是一因多效的作用。姜树坤等[23]以笹锦和北陆129杂交衍生的重组自交系群体为材料, 对水稻移栽后的新生根相关性状进行研究, 共检测到10个QTL, 分别控制根平均直径、总根长、平均根表面积、平均根长和根数等性状。并且对第11号染色体的分子标记C477和G320B之间的新主效QTL——同时控制根长、根表面积和根数的QTL qRL11.1、qRSA11和qRN11.1进行了验证。这些QTL簇体现了QTL的一因多效作用。由于一因多效QTL/基因的存在, 在开展水稻分子育种时, 我们可以考虑选择单个QTL/基因同时改良多个性状。徐晓明等[24]以超级稻协优9308衍生的重组自交系与轮回亲本中恢9308回交多代群体为材料, 采用琼脂无土栽培技术开展了水稻根长主效QTL qRL4的精细定位, 最终将其定位在水稻第4号染色体分子标记RM5687与InDel149之间约624.6 kb的范围内。我们定位的qLRL4是控制最长根长的新QTL, 其位置与报道的qRL4在4号染色体上的位置并不相同, 这可能是所用亲本和群体不同所致。幼苗期根的生长为作物获取水和营养物质提供了保障[25]。近等系NIL-qLRL4在发芽后根的生长受到抑制, 根的总吸收面积和活跃吸收面积相对9311也显著减小(图4和表8)。Raffaele等[26,27]在拟南芥中研究发现, 具有较大根分生组织的突变体往往根较长, 而根分生组织的大小受生长素和细胞分裂素的共同调节。水稻中已克隆了一些与根发育相关的基因, 例如CRL1基因调控不定根的数目[15], REL2基因调控不定根的数目与长短[18], OsCKI1基因调控侧根和不定根的数量[28], SOR1通过根系与乙烯的特异性反应来影响根的生长发育[29]。调控水稻根长的基因也有报道, Rf1a/Rf-1/Rf5基因影响水稻主根长短[30]; Srt5基因通过外源性蔗糖、葡萄糖和果糖的调控影响水稻根系的长短[13]; OsSPR1基因通过影响根细胞的长短与数目影响水稻根系的长短[14]; SRT6基因影响水稻苗期根长与直径的作用可能与ABA的感知或信号传导有关[20]。我们的研究最终将最长根长QTL qLRL4精细定位到约68.23 kb的区间内, 依据基因注释发现该区间包含8个候选基因, 其中有7个基因存在引起氨基酸改变的SNP或InDel, 包括编码水解酶、受体蛋白激酶和染色质结构调节因子的基因。根部转录水平的表达分析显示, 4个候选基因的相对表达量在NIL-qLRL4或NPB与9311之间存在显著差异。因此, 这4个基因作为qLRL4候选基因的可能性更大。当然, 候选基因的最终确定还有待进一步基因克隆和功能验证。4 结论
利用籼稻9311和粳稻日本晴为亲本的RIL群体对水稻苗期根系相关性状开展QTL分析, 共检测到26个控制最长根长、总根系长、根表面积、根体积和根直径的QTL, 发现水稻第2、4、7和10号染色体上的4个QTL簇, 包括第4号染色体上控制最长根长的QTL qLRL4。精细定位将qLRL4定位于InDel标记IND4-1和IND4-3之间约68.23 kb的区间, 包含了8个候选基因。其中7个基因在亲本间有引起氨基酸改变的SNP或InDel, 4个基因在近等基因系NIL-qLRL4和9311之间的转录水平相对表达量上存在显著差异。此最长根长QTL的精细定位为水稻根系发育相关基因的克隆奠定了基础。参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOIPMID [本文引用: 1]

Root system development is an important target for improving yield in cereal crops. Active root systems that can take up nutrients more efficiently are essential for enhancing grain yield. In this study, we attempted to identify quantitative trait loci (QTL) involved in root system development by measuring root length of rice seedlings grown in hydroponic culture. Reliable growth conditions for estimating the root length were first established to renew nutrient solutions daily and supply NH4(+) as a single nitrogen source. Thirty-eight chromosome segment substitution lines derived from a cross between 'Koshihikari', a japonica variety, and 'Kasalath', an indica variety, were used to detect QTL for seminal root length of seedlings grown in 5 or 500 microM NH4(+). Eight chromosomal regions were found to be involved in root elongation. Among them, the most effective QTL was detected on a 'Kasalath' segment of SL-218, which was localized to the long-arm of chromosome 6. The 'Kasalath' allele at this QTL, qRL6.1, greatly promoted root elongation under all NH4(+) concentrations tested. The genetic effect of this QTL was confirmed by analysis of the near-isogenic line (NIL) qRL6.1. The seminal root length of the NIL was 13.5-21.1% longer than that of 'Koshihikari' under different NH4(+) concentrations. Toward our goal of applying qRL6.1 in a molecular breeding program to enhance rice yield, a candidate genomic region of qRL6.1 was delimited within a 337 kb region in the 'Nipponbare' genome by means of progeny testing of F2 plants/F3 lines derived from a cross between SL-218 and 'Koshihikari'.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI [本文引用: 1]

根系作为水稻(Oryza sativa)植株的重要组成部分, 在水稻生长发育过程中发挥多种作用, 包括植物的固定、水分和营养物质的获取以及氨基酸和激素的生物合成等, 其形态结构和生理功能与水稻产量和稻米品质以及抗性等密切相关。目前, 通过遗传及生化等诸多手段, 已挖掘到较多水稻根系QTLs与控制基因。该文综述了水稻根系QTL和基因的研究进展, 并对未来根系研究进行展望, 以期为进一步克隆水稻根系基因和完善水稻理想株型模型提供参考。
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 2]
DOIURL [本文引用: 2]
DOIURL [本文引用: 2]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIPMID [本文引用: 1]

In rice (Oryza sativa), the shoot-borne crown roots are the major root type and are initiated at lower stem nodes as part of normal plant development. However, the regulatory mechanism of crown root development is poorly understood. In this work, we show that a WUSCHEL-related Homeobox (WOX) gene, WOX11, is involved in the activation of crown root emergence and growth. WOX11 was found to be expressed in emerging crown roots and later in cell division regions of the root meristem. The expression could be induced by exogenous auxin or cytokinin. Loss-of-function mutation or downregulation of the gene reduced the number and the growth rate of crown roots, whereas overexpression of the gene induced precocious crown root growth and dramatically increased the root biomass by producing crown roots at the upper stem nodes and the base of florets. The expressions of auxin- and cytokinin-responsive genes were affected in WOX11 overexpression and RNA interference transgenic plants. Further analysis showed that WOX11 directly repressed RR2, a type-A cytokinin-responsive regulator gene that was found to be expressed in crown root primordia. The results suggest that WOX11 may be an integrator of auxin and cytokinin signaling that feeds into RR2 to regulate cell proliferation during crown root development.
DOIURL [本文引用: 2]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 2]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
PMID [本文引用: 1]

Plant postembryonic development takes place in the meristems, where stem cells self-renew and produce daughter cells that differentiate and give rise to different organ structures. For the maintenance of meristems, the rate of differentiation of daughter cells must equal the generation of new cells: How this is achieved is a central question in plant development. In the Arabidopsis root meristem, stem cells surround a small group of organizing cells, the quiescent center. Together they form a stem cell niche [1, 2], whose position and activity depends on the combinatorial action of two sets of genes - PLETHORA1 (PLT1) and PLETHORA2 (PLT2)[3, 4] and SCARECROW (SCR) and SHORTROOT (SHR)[2] - as well as on polar auxin transport. In contrast, the mechanisms controlling meristematic cell differentiation remain unclear. Here, we report that cytokinins control the rate of meristematic cell differentiation and thus determine root-meristem size via a two-component receptor histidine kinase-transcription factor signaling pathway. Analysis of the root meristems of cytokinin mutants, spatial cytokinin depletion, and exogenous cytokinin application indicates that cytokinins act in a restricted region of the root meristem, where they antagonize a non-cell-autonomous cell-division signal, and we provide evidence that this signal is auxin.
DOIPMID [本文引用: 1]

Plant growth and development are sustained by meristems. Meristem activity is controlled by auxin and cytokinin, two hormones whose interactions in determining a specific developmental output are still poorly understood. By means of a comprehensive genetic and molecular analysis in Arabidopsis, we show that a primary cytokinin-response transcription factor, ARR1, activates the gene SHY2/IAA3 (SHY2), a repressor of auxin signaling that negatively regulates the PIN auxin transport facilitator genes: thereby, cytokinin causes auxin redistribution, prompting cell differentiation. Conversely, auxin mediates degradation of the SHY2 protein, sustaining PIN activities and cell division. Thus, the cell differentiation and division balance necessary for controlling root meristem size and root growth is the result of the interaction between cytokinin and auxin through a simple regulatory circuit converging on the SHY2 gene.
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
相关话题/基因 控制 遗传 材料 日本
小麦穗发芽性状的全基因组关联分析
谢磊,1,2,任毅1,2,张新忠1,3,王继庆1,2,张志辉1,2,石书兵1,2,耿洪伟,1,2,*1新疆农业大学农学院,新疆乌鲁木齐8300522新疆农业大学生物技术重点实验室,新疆乌鲁木齐8300523新疆农业科学院粮食作物研究所,新疆乌鲁木齐830091Genome-wideassociati ...中国农业科学院科研学术 本站小编 Free考研考试 2021-12-26叉柱棉sHSP基因家族的鉴定与特征分析
范凯,,潘鑫峰,毛志君,叶方婷,李兆伟,林伟伟,林文雄,*福建农林大学农学院作物遗传育种与综合利用教育部重点实验室,福建福州350002IdentificationandanalysisofsHSPgenefamilyinGossypioideskirkiiFANKai,,PANXin-Feng,M ...中国农业科学院科研学术 本站小编 Free考研考试 2021-12-26玉米籽粒缺陷突变基因dek54的精细定位及候选基因分析
周练,,刘朝显,陈秋栏,王文琴,姚顺,赵子堃,朱思颖,洪祥德,熊雨涵,蔡一林,*西南大学玉米研究所/农业科学研究院/南方山地作物逆境生物学国家级培育基地,重庆400715Finemappingandcandidategeneanalysisofmaizedefectivekernelmutantde ...中国农业科学院科研学术 本站小编 Free考研考试 2021-12-26半夏PtPAL基因的克隆、表达与酶动力学分析
何潇,1,2,刘兴3,辛正琦1,2,谢海艳1,2,辛余凤1,2,吴能表,1,2,*1西南大学生命科学学院,重庆4007152三峡库区生态环境教育部重点实验室,重庆4007153重庆市大足中学,重庆402360Molecularcloning,expression,andenzymekinetican ...中国农业科学院科研学术 本站小编 Free考研考试 2021-12-26大环内酯类和高表达玉米C4-PEPC基因对水稻耐旱性的影响
宋凝曦,1,2,李霞,1,2,3,*,王净1,2,吴博晗1,4,曹悦1,5,杨杰1,3,谢寅峰21江苏省农业科学院粮食作物研究所/江苏省优质水稻工程技术研究中心/国家水稻改良中心南京分中心,江苏南京2100142南京林业大学生物与环境学院,江苏南京2100373江苏省粮食作物现代产业技术协同创新中心 ...中国农业科学院科研学术 本站小编 Free考研考试 2021-12-26水稻基因OsATS的克隆及功能鉴定
李晓旭,**,王蕊,**,张利霞,宋亚萌,田晓楠,葛荣朝,*河北师范大学生命科学学院,河北石家庄050024CloningandfunctionalidentificationofgeneOsATSinriceLIXiao-Xu,**,WANGRui,**,ZHANGLi-Xia,SONGYa-Me ...中国农业科学院科研学术 本站小编 Free考研考试 2021-12-26青藏春冬麦区93份小麦地方种质条锈病抗性评价及抗病基因分子鉴定
赵旭阳,1,姚方杰1,龙黎1,王昱琦1,康厚扬1,2,蒋云峰1,2,李伟3,邓梅1,李豪1,陈国跃,1,2,*1四川农业大学小麦研究所,四川成都6111302西南作物基因资源发掘与利用国家重点实验室,四川成都6111303四川农业大学农学院,四川成都611130Evaluationofresista ...中国农业科学院科研学术 本站小编 Free考研考试 2021-12-26利用WGCNA鉴定花生主茎生长基因共表达模块
汪颖,,高芳,刘兆新,赵继浩,赖华江,潘小怡,毕晨,李向东,杨东清,*山东农业大学农学院/作物生物学国家重点实验室,山东泰安271018Identificationofgeneco-expressionmodulesofpeanutmainstemgrowthbyWGCNAWANGYing,,GAO ...中国农业科学院科研学术 本站小编 Free考研考试 2021-12-26花生AhFAD2-1基因启动子及5'-UTR内含子功能验证及其低温胁迫应答
石磊,1,2,苗利娟1,2,黄冰艳1,2,高伟3,张忠信1,2,齐飞艳1,2,刘娟3,董文召1,2,张新友,1,2,*1河南省农业科学院河南省作物分子育种研究院/农业农村部黄淮海油料作物重点实验室/河南省油料作物遗传改良重点实验室/花生遗传改良国家地方联合工程实验室,河南郑州4500022河南生物育 ...中国农业科学院科研学术 本站小编 Free考研考试 2021-12-26小麦lncRNA27195及其靶基因TaRTS克隆及表达分析
王娜,1,2,**,白建芳2,**,马有志1,郭昊宇2,王永波2,陈兆波2,赵昌平,2,*,张立平,2,*1中国农业科学院作物科学研究所,北京1000872北京市农林科学院北京杂交小麦工程技术研究中心/杂交小麦分子遗传北京市重点实验室,北京100097Cloningandexpressionanal ...中国农业科学院科研学术 本站小编 Free考研考试 2021-12-26
