 ,1,2, 赵小珍1,2, 庞承珂1,2, 彭门路1,2, 王晓东2, 陈锋2, 张维2, 陈松2, 彭琦2, 易斌3, 孙程明
,1,2, 赵小珍1,2, 庞承珂1,2, 彭门路1,2, 王晓东2, 陈锋2, 张维2, 陈松2, 彭琦2, 易斌3, 孙程明 ,2,3,*, 张洁夫
,2,3,*, 张洁夫 ,2,*, 傅廷栋3
,2,*, 傅廷栋3Genome-wide association study of 1000-seed weight in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.)
ZHANG Chun ,1,2, ZHAO Xiao-Zhen1,2, PANG Cheng-Ke1,2, PENG Men-Lu1,2, WANG Xiao-Dong2, CHEN Feng2, ZHANG Wei2, CHEN Song2, PENG Qi2, YI Bin3, SUN Cheng-Ming
,1,2, ZHAO Xiao-Zhen1,2, PANG Cheng-Ke1,2, PENG Men-Lu1,2, WANG Xiao-Dong2, CHEN Feng2, ZHANG Wei2, CHEN Song2, PENG Qi2, YI Bin3, SUN Cheng-Ming ,2,3,*, ZHANG Jie-Fu
,2,3,*, ZHANG Jie-Fu ,2,*, FU Ting-Dong3
,2,*, FU Ting-Dong3通讯作者:
收稿日期:2020-06-22接受日期:2020-09-13网络出版日期:2021-04-12
| 基金资助: |
Received:2020-06-22Accepted:2020-09-13Online:2021-04-12
| Fund supported: |
作者简介 About authors
E-mail:

摘要
关键词:
Abstract
Keywords:
PDF (2798KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
本文引用格式
张春, 赵小珍, 庞承珂, 彭门路, 王晓东, 陈锋, 张维, 陈松, 彭琦, 易斌, 孙程明, 张洁夫, 傅廷栋. 甘蓝型油菜千粒重全基因组关联分析[J]. 作物学报, 2021, 47(4): 650-659. doi:10.3724/SP.J.1006.2021.04136
ZHANG Chun, ZHAO Xiao-Zhen, PANG Cheng-Ke, PENG Men-Lu, WANG Xiao-Dong, CHEN Feng, ZHANG Wei, CHEN Song, PENG Qi, YI Bin, SUN Cheng-Ming, ZHANG Jie-Fu, FU Ting-Dong.
甘蓝型油菜(Brassica napus L., 2n = 38, AACC)是世界上广泛种植的油料作物, 也是我国重要的植物油来源之一, 占总食用植物油40%以上。然而我国植物油料自给率不足四成, 且缺口仍呈扩大趋势, 提高油菜产量、保障油料供给安全已迫在眉睫[1]。千粒重是构成油菜产量的三因素之一, 提高油菜千粒重是增产的直接途径, 因此解析粒重遗传基础和分子机理对油菜产量乃至国家油料供给安全具有重要意义。
千粒重是由多基因控制的数量性状, 受基因型和环境条件共同作用[2]。从细胞学水平看, 种子器官的发育主要受细胞增殖和细胞膨大调节, 两者又分别决定着细胞数目和细胞大小[3], Breuninger等[4]研究认为, 细胞增殖(细胞数目)对种子等器官大小的影响更大。从种子发育进程看, 胚、胚乳及胚珠的协同生长关系着种子重量及大小, 同时发育过程又与母体植株密不可分, 种子大小与母体组织间存在某种内在联系。朱军等[5]研究认为, 粒重遗传模型为胚、胚乳、细胞质和母体基因型的效应, 其中细胞质和母体基因型效应属母体效应。李娜等[6]通过对遗传背景广泛的油菜大小粒种质进行遗传分析, 证明了油菜种子大小主要由母体基因型效应调控, 母体效应值达0.93。母体组织可从多种途径对种子大小产生影响: 一是转录因子调控途径, 如AP2通过限制种皮细胞的延伸控制种子生长[7]; 二是泛素化途径, 如泛素受体DA1和DA2通过限制种皮细胞增殖影响籽粒大小[8,9]; 三是G蛋白途径, 如G蛋白复合物由异源三聚体的Gα、Gβ和Gγ 3个亚基组成, 超表达Gγ (AGG3)的拟南芥通过细胞增殖促进种子生长发育[10]; 四是激素途径, 如BZR1通过油菜素内酯途径影响种子大小[11]; 五是其他类型生长物质, 如EOD3编码细胞色素P450单加氧酶, 通过促进种子株被或种皮细胞的延伸增加种子大小[12]。
分子标记、SNP芯片等技术的出现大大推进了对复杂数量性状如千粒重基因的定位。多数科研工作者利用遗传差异大的双亲构建连锁群体, 进行千粒重QTL定位。Quijada等[13]利用2个DH群体定位到3个千粒重QTL位点, 分别位于A07、C07和C09染色体上。Basunanda等[14]同样利用DH群体, 结合SSR标记和AFLP标记, 检测到34个千粒重QTL, 表型变异贡献率范围为2.4%~23.0%, 其中7个位点能重复检测到。Yang等[15]考察186个RIL群体在2环境下的表型, 检测到9个与千粒重相关的QTL, 分布在5个连锁群A01、A06、A07、A09和C03, 其中贡献率最大的QTL cqSW.A9位于A09染色体, 解释28.2%的表型变异。Zhao等[16]考察DH群体在5个环境下的表型, 定位到40个千粒重QTL位点, 其中位于A06的主效QTL qSN.A6贡献率为20.1%。Fan等[17]考察DH和F2两群体在2环境下的表型, 共检测到9个千粒重QTL, 分别位于在A01、A02、A05、A07、A10和C04, 解释的表型变异范围为27.6%~37.9%。Sun等[18]利用高密度SNP图谱, 考察189个RIL群体在5个环境下的表型, 定位到25个千粒重相关的QTL, 其中QTL uqC2-1解释6.6%~7.6%的表型变异。目前甘蓝型油菜中已精细定位的粒重基因很少, Liu等[19]成功克隆了第1个影响千粒重的基因ARF18, 该基因是控制角果长和千粒重的双效调控因子, 通过延长角果皮细胞长度促进角果伸长, 增加角果皮光合面积, 促进千粒重增加。Shi等[20]利用图位克隆得到1个影响千粒重的基因BnaA9.CYP78A9D, 该基因编码1个P450单加氧酶, 通过促进角果瓣中的细胞伸长来调节角果长度, 影响种子大小。
随着高密度单核苷酸多态性(single nucleotide polymorphism, SNP)基因分型芯片和全基因组测序等技术的发展, 全基因组关联分析(genome-wide association study, GWAS)已广泛应用于油菜复杂性状的遗传结构解析[21,22]。本研究选用496份具有代表性的油菜种质资源为关联群体, 利用60K SNP芯片对群体进行基因型分析, 结合3个环境考察的千粒重表型数据, 对该性状进行全基因组关联分析, 基于检测到的显著SNP位点挖掘候选基因。本研究中筛选出千粒重大的优异种质资源, 为今后的性状改良提供材料; 基于检测到的显著位点, 为开发粒重分子标记提供信息; 挖掘候选基因, 为千粒重基因克隆和调控机理研究奠定基础。
1 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
496份甘蓝型油菜为国内外的地方品种、育成品种及高世代育种材料(附表1)。其中国内资源444份, 主要来自湖北、重庆、江苏、湖南、四川、陕西等油菜主产省市; 国外资源52份, 主要来自德国、瑞典、朝鲜、加拿大等国家。所有材料均由华中农业大学国家油菜工程技术研究中心提供。Table S1
附表1
附表1496份油菜的信息
Table S1
| 材料号 Line No. | 材料名称 Name | 来源 Origin | 材料号Line No. | 材料名称 Name | 来源 Origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 甘油5号 Ganyou 5 | 中国湖北Hubei, China | 2 | 农林42 Nonglin 42 | 日本 Japan |
| 3 | 科里纳 Kelina | 国外Unknown | 4 | 淮油6号 Huaiyou 6 | 中国江苏 Jiangsu, China |
| 5 | 炎81-2 Yan 81-2 | 中国重庆Chongqing, China | 6 | 28887 | 中国重庆Chongqing, China |
| 7 | 黔油4号 Qianyou 4 | 中国贵州Guizhou, China | 8 | 黔油331 Qianyou 331 | 中国贵州 Guizhou, China |
| 9 | 恩油73 Enyou 73-1-2 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 10 | 牛耳朵 Niuerduo | 中国贵州 Guizhou, China |
| 11 | 880101 | 中国重庆Chongqing, China | 12 | SWU40 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China |
| 13 | SWU42 | 中国重庆Chongqing, China | 14 | SWU43 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China |
| 15 | SWU44 | 中国重庆Chongqing, China | 16 | SWU45 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China |
| 17 | SWU46 | 中国重庆Chongqing, China | 18 | SWU47 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China |
| 19 | SWU48 | 中国重庆Chongqing, China | 20 | SWU52 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China |
| 21 | SWU53 | 中国重庆Chongqing, China | 22 | SWU56 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China |
| 23 | SWU59 | 中国重庆Chongqing, China | 24 | SWU65 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China |
| 25 | SWU82 | 中国重庆Chongqing, China | 26 | SWU83 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China |
| 27 | SWU92 | 中国重庆Chongqing, China | 28 | SWU101 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China |
| 29 | SWU106 | 中国重庆Chongqing, China | 30 | SWU108 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China |
| 31 | 川油20 Chuanyou 20 | 中国四川 Sichuan, China | 32 | 川油18 Chuanyou 18 | 中国四川Sichuan, China |
| 33 | CY12NY-7 | 中国四川 Sichuan, China | 34 | CY12Q95406 | 中国四川Sichuan, China |
| 35 | CY12Q8-7 | 中国四川 Sichuan, China | 36 | CY12QSZ06 | 中国四川Sichuan, China |
| 37 | CY12QCWH-1 | 中国四川 Sichuan, China | 38 | CY12Q95108 | 中国四川Sichuan, China |
| 39 | CY12Q21535-N3 | 中国四川 Sichuan, China | 40 | CY12PXW-4 | 中国四川Sichuan, China |
| 41 | CY12PXW-6 | 中国四川 Sichuan, China | 42 | CY12PXW-9 | 中国四川Sichuan, China |
| 43 | CY13PXW-17 | 中国四川 Sichuan, China | 44 | CY14PXW-18 | 中国四川Sichuan, China |
| 45 | CY15PXW-31 | 中国四川 Sichuan, China | 46 | CY16PXW-35 | 中国四川 Sichuan, China |
| 47 | CY17PXW-58 | 中国四川 Sichuan, China | 48 | CY18PXW-62 | 中国四川 Sichuan, China |
| 49 | CY19PXW-65 | 中国四川 Sichuan, China | 50 | CY20PXW-66 | 中国四川 Sichuan, China |
| 51 | CY21PXW-84 | 中国四川 Sichuan, China | 52 | CY12GJ-1 | 中国四川 Sichuan, China |
| 53 | wx1025 | 中国湖南 Hunan, China | 54 | wx10213 | 中国湖南 Hunan, China |
| 55 | wx10296 | 中国湖南 Hunan, China | 56 | wx10315 | 中国湖南 Hunan, China |
| 57 | 10-1043 | 中国湖南 Hunan, China | 58 | 10-1047 | 中国湖南 Hunan, China |
| 59 | 10-1061 | 中国湖南 Hunan, China | 60 | 10-1070 | 中国湖南 Hunan, China |
| 61 | 10-804 | 中国湖南 Hunan, China | 62 | 10-1358 | 中国湖南 Hunan, China |
| 63 | 1472 | 中国湖南 Hunan, China | 64 | 湘油13号 Xiangyou 13 | 中国湖南 Hunan, China |
| 65 | 湘油15号 Xiangyou 15 | 中国湖南 Hunan, China | 66 | 湘油11号 Xiangyou 11 | 中国湖南 Hunan, China |
| 67 | 740 | 中国湖南 Hunan, China | 68 | 631 | 中国湖南 Hunan, China |
| 69 | 613 | 中国湖南 Hunan, China | 70 | 783 | 中国湖南 Hunan, China |
| 71 | 782 | 中国湖南 Hunan, China | 72 | YB3 | 中国湖南 Hunan, China |
| 73 | 1360 | 中国湖南 Hunan, China | 74 | 563 | 中国湖南 Hunan, China |
| 75 | WX10329 | 中国湖南 Hunan, China | 76 | santana | 德国 German |
| 77 | 1281 | 中国湖南 Hunan, China | 78 | 509 | 中国湖南 Hunan, China |
| 79 | 1368 | 中国湖南 Hunan, China | 80 | 1322 | 中国湖南 Hunan, China |
| 81 | 1252 | 中国湖南 Hunan, China | 82 | 1321 | 中国湖南 Hunan, China |
| 83 | 07022 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 84 | 07094 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 85 | 07016 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 86 | 9F087 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 87 | 97096 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 88 | 97097 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 89 | 07189 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 90 | 07191 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 91 | 07037 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 92 | RQ011 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 93 | RR009 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 94 | RR002 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 95 | 97177 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 96 | 96021 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 97 | 96063 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 98 | 01111 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 99 | 01570 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 100 | 9保22 9Bao 22 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 101 | 01188 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 102 | 02354 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 103 | 02359 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 104 | 02365 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 105 | 93205 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 106 | 93210 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 107 | Nca | 国外 Unknown | 108 | 中双4号 Zhongshuang 4 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 109 | 中双9号 Zhongshuang 9 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 110 | 中双11号 Zhongshuang 11 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 111 | 2011-6200 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 112 | 2011-6308 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 113 | 2011-7103 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 114 | 2012-11526 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 115 | 2012-3448 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 116 | 2012-3546 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 117 | 2012-4531 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 118 | 2012-5086 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 119 | 2012-5113 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 120 | 2012-8327 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 121 | 2012-8355 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 122 | 2012-8380 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 123 | 2012-8998 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 124 | 2012-9323 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 125 | 2012-9354 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 126 | 2012-9380 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 127 | 2012-9478 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 128 | 2012-9542 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 129 | 2012-K8053 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 130 | R2 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 131 | 希望106 Xiwang 106 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 132 | 阳光198 Yangguang 198 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 133 | 阳光2009 Yangguang 2009 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 134 | 中双10号 Zhongshuang 10 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 135 | 中双12号 Zhongshuang 12 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 136 | 中双6号 Zhongshuang 6 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 137 | 中双7号 Zhongshuang 7 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 138 | 中油589 Zhongyou 589 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 139 | 华油2号 Huayou 2 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 140 | Major | 法国 France |
| 141 | 华双2号 Huashuang 2 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 142 | Aurora | 德国 German |
| 143 | 华油13号 Huayou13 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 144 | Rucabo | 德国 German |
| 145 | 华油3号 Huayou 3 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 146 | 华油14 Huayou 14 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 147 | 宁油1号 Ningyou 1 | 中国江苏 Jiangsu, China | 148 | Ceres | 德国 German |
| 149 | 11-9-700 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 150 | 11-9-701 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 151 | 11-9-702 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 152 | 11-9-703 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 153 | 11-9-704 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 154 | 11-9-705 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 155 | 11-9-706 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 156 | 11-9-707 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 157 | 11-P63-5育7 11-P63-5 yu 7 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 158 | 11-P63-8育32 11-P63-8 yu 32 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 159 | 11-P63-3育3 11-P63-3 yu 3 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 160 | 11-P67东 11-P67 Dong | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 161 | 09-P64-1 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 162 | 10-崇23 10-chong23 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 163 | 10-崇24 10-chong 24 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 164 | 10-崇25 10-chong25 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 165 | 10-崇29 10-chong 29 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 166 | 10-崇32 10-chong 32 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 167 | 10-崇33 10-chong 33 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 168 | 10-崇34 10-chong 34 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 169 | 10-江棚2 10-jiangpeng 2 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 170 | 10-江棚3 10-jiangpeng 3 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 171 | 11-育7-103 11-yu 7-103 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 172 | 11-育7-117 11-yu7-117 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 173 | 11-育7-125 11-yu 7-125 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 174 | 11-P74-8 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 175 | 11-P74-13 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 176 | 7-7766-74 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 177 | P18 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 178 | 64棚-1064 peng-10 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 179 | 圣光77 Shengguang 77 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 180 | 甲预17棚 Jiayu17peng | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 181 | 甲预25棚 Jiayu25peng | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 182 | 甲预16棚 Jiayu16peng | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 183 | 甲预31棚 Jiayu31peng | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 184 | 华双5号 Huashuang5 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 185 | 华双4号 Huashuang 4 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 186 | 甲972Jia972 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 187 | 华双128 Huashuang 128 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 188 | 甲904 Jia904 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 189 | 甲908 Jia 908 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 190 | 甲PF190棚 Jia PF190peng | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 191 | 甲915 Jia 915 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 192 | 甲922 Jia 922 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 193 | 甲951棚 Jia951peng | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 194 | 甲917 Jia 917 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 195 | 甲923 Jia923 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 196 | 甲931 Jia 931 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 197 | 甲预05棚 Jiayu05peng | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 198 | 甲963棚 Jia963peng | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 199 | 沪油12号 Huyou 12 | 中国上海 Shanghai, China | 200 | 宁油16号 Ningyou 16 | 中国江苏 Jiangsu, China |
| 201 | 史力佳 Shilijia | 中国江苏 Jiangsu, China | 202 | 杨油6号 Yangyou 6 | 中国江苏 Jiangsu, China |
| 203 | 扬油5号 Yangyou 5 | 中国江苏 Jiangsu, China | 204 | 镇油3号 Zhenyou 3 | 中国江苏 Jiangsu, China |
| 205 | 苏油1号 Suyou 1 | 中国江苏 Jiangsu, China | 206 | 浙油18 Zheyou18 | 中国浙江 Zhejiang, China |
| 207 | 浙双72 Zheshuang 72 | 中国浙江 Zhejiang, China | 208 | 浙双8号 Zheshuang 8 | 中国浙江 Zhejiang, China |
| 209 | 浙油758 Zheyou 758 | 中国浙江 Zhejiang, China | 210 | 沪油14 Huyou 14 | 中国上海 Shanghai, China |
| 211 | 沪油18 Huyou 18-2 | 中国上海 Shanghai, China | 212 | 沪油19 Huyou 19 | 中国上海 Shanghai, China |
| 213 | 浙油19 Zheyou 19 | 中国浙江 Zhejiang, China | 214 | 浙油21 Zheyou 21 | 中国浙江 Zhejiang, China |
| 215 | 浙双6号 Zheshuang 6 | 中国浙江 Zhejiang, China | 216 | 皖油15号 Wanyou 15 | 中国安徽 Anhui, China |
| 217 | 皖油16号 Wanyou 16 | 中国安徽 Anhui, China | 218 | 皖油29 Wanyou 29 | 中国安徽 Anhui, China |
| 219 | AGREV012 | 德国 German | 220 | AGREV019 | 德国 German |
| 221 | AGREV021 | 德国 German | 222 | Topas | 瑞典 Sweden |
| 223 | cyclon | 丹麦 Denmark | 224 | 伟杰 Weijie | 加拿大 Canada |
| 225 | 四达 Sida | 加拿大 Canada | 226 | 至尊 Zhizun | 加拿大 Canada |
| 227 | 海神 Haishen | 加拿大 Canada | 228 | D2 | 丹麦 Denmark |
| 229 | D3 | 丹麦 Denmark | 230 | Qu | 美国 America |
| 231 | 11-985 | 中国青海 Qinghai, China | 232 | 11-504 | 中国青海 Qinghai, China |
| 233 | 11-997 | 中国青海 Qinghai, China | 234 | 11-540 | 中国青海 Qinghai, China |
| 235 | 11-1184 | 中国青海 Qinghai, China | 236 | 10-758 | 中国青海 Qinghai, China |
| 237 | 10-1230 | 中国青海 Qinghai, China | 238 | 10-847 | 中国青海 Qinghai, China |
| 239 | 11-1124 | 中国青海 Qinghai, China | 240 | 垦C1 KenC1 | 中国陕西 Shaanxi, China |
| 241 | P113 | 中国陕西 Shaanxi, China | 242 | P158 | 中国陕西 Shaanxi, China |
| 243 | P310 | 中国陕西 Shaanxi, China | 244 | P312 | 中国陕西 Shaanxi, China |
| 245 | P668 | 中国陕西 Shaanxi, China | 246 | P685 | 中国陕西 Shaanxi, China |
| 247 | A117 | 中国陕西 Shaanxi, China | 248 | A172 | 中国陕西 Shaanxi, China |
| 249 | B250 | 中国陕西 Shaanxi, China | 250 | B265 | 中国陕西 Shaanxi, China |
| 251 | A109 | 中国陕西 Shaanxi, China | 252 | B285 | 中国陕西 Shaanxi, China |
| 253 | C052 | 中国陕西 Shaanxi, China | 254 | GY270 | 中国陕西 Shaanxi, China |
| 255 | GY282 | 中国陕西 Shaanxi, China | 256 | GY284 | 中国陕西 Shaanxi, China |
| 257 | B262 | 中国河南 Henan, China | 258 | A82 | 中国江西 Jiangxi, China |
| 259 | A98 | 中国陕西 Shaanxi, China | 260 | B414 | 中国新疆 Xinjiang, China |
| 261 | B308 | 瑞典 Sweden | 262 | A97 | 中国四川 Sichuan, China |
| 263 | A148 | 瑞典 Sweden | 264 | B431 | 丹麦 Denmark |
| 265 | 08-P35 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 266 | 08-P36 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 267 | 09-P32 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 268 | 09-P36 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 269 | 09-P37 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 270 | 10-P10 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 271 | 10-P29 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 272 | 11-P30 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 273 | 12-P24 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 274 | 12-P25 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 275 | 03ⅡB | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 276 | 03Ⅱ3B | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 277 | 03Ⅰ32B | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 278 | 964 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 279 | DD1 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 280 | 9L302-1 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 281 | 06T9F | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 282 | 03Ⅱ4B | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 283 | 03LF1 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 284 | 9852 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 285 | 9801C | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 286 | 986 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 287 | 876 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 288 | 武164 Wu164 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 289 | 9889 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 290 | 06H7 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 291 | 湖北白花油菜 Hubeibaihuayoucai | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 292 | 南川长角 Nanchuanchangjiao | 中国四川 Sichuan, China |
| 293 | IMC103 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China | 294 | Oscar | 澳大利亚 Australia |
| 295 | Sophia | 德国 German | 296 | campina | 德国 German |
| 297 | Conny | 瑞典 Sweden | 298 | Wesreo | 澳大利亚 Australia |
| 299 | Wase Chousen | 朝鲜 North Korea | 300 | Gogatsuna | 日本 Japan |
| 301 | Nakaee Chousen | 朝鲜 North Korea | 302 | Cat.No.117 | 德国 German |
| 303 | 90750 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China | 304 | 农林43 Nonglin 43 | 日本 |
| 305 | 西藏油菜 Xizangyoucai | 中国西藏 Tibet, China | 306 | 油研2号 Youyan 2 | 中国贵州 |
| 307 | 矮架早 Aijiazao | 中国四川 Sichuan, China | 308 | SWU41 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China |
| 309 | SWU49 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China | 310 | SWU54 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China |
| 311 | SWU57 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China | 312 | SWU60 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China |
| 313 | SWU61 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China | 314 | SWU62 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China |
| 315 | SWU63 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China | 316 | SWU64 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China |
| 317 | SWU66 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China | 318 | SWU67 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China |
| 319 | SWU68 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China | 320 | SWU69 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China |
| 321 | SWU70 | 中国重庆Chongqing, China | 322 | SWU71 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China |
| 323 | SWU74 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China | 324 | SWU75 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China |
| 325 | SWU76 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China | 326 | SWU77 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China |
| 327 | SWU80 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China | 328 | SWU81 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China |
| 329 | SWU84 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China | 330 | SWU85 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China |
| 331 | SWU87 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China | 332 | SWU88 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China |
| 333 | SWU89 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China | 334 | SWU90 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China |
| 335 | SWU93 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China | 336 | SWU94 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China |
| 337 | SWU95 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China | 338 | SWU96 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China |
| 339 | SWU99 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China | 340 | SWU100 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China |
| 341 | SWU102 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China | 342 | SWU103 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China |
| 343 | SWU104 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China | 344 | SWU105 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China |
| 345 | SWU107 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China | 346 | SWU110 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China |
| 347 | SWU111 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China | 348 | SWU112 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China |
| 349 | SWU113 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China | 350 | SWU114 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China |
| 351 | 辐油4号 Fuyou 4 | 中国重庆 Chongqing, China | 352 | 镇3736 Zhen3736 | 中国江苏 Jiangsu, China |
| 353 | 镇2609 Zhen 2609 | 中国江苏 Jiangsu, China | 354 | HX0352 | 中国江苏 Jiangsu, China |
| 355 | 阳光2009 Yangguang 2009 | 中国江苏 Jiangsu, China | 356 | 沪油21 Huyou 21 | 中国上海 Shanghai, China |
| 357 | 浙双3号 Zheshuang 3 | 中国浙江 Zhejiang, China | 358 | 浙油21 Zheyou 21 | 中国浙江 Zhejiang, China |
| 359 | 皖油20 Wanyou 20 | 中国安徽 Anhui, China | 360 | 皖油12 Wanyou 12 | 中国安徽 Anhui, China |
| 361 | 皖油7号 Wanyou 7 | 中国安徽 Anhui, China | 362 | 红油3号 Hongyou 3 | 中国江苏 Jiangsu, China |
| 363 | 镇油5号 Zhenyou5 | 中国江苏 Jiangsu, China | 364 | 扬油4号 Yangyou 4 | 中国上海 Shanghai, China |
| 365 | 沪油15 Huyou 15 | 中国上海 Shanghai, China | 366 | 沪油16 Huyou 16 | 中国上海 Shanghai, China |
| 367 | 沪油17 Huyou17 | 中国上海 Shanghai, China | 368 | 浙双72 Zheshuang 72 | 中国浙江 Zhejiang, China |
| 369 | 浙双8号 Zheshuang 8 | 中国浙江 Zhejiang, China | 370 | 浙油50 Zheyou 50 | 中国浙江 Zhejiang, China |
| 371 | 中双11 Zhongshuang 11 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 372 | 阳光198 Yangguang198 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 373 | 华航901 Huahang 901 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 374 | 扬J6711 Yang J6711 | 中国江苏 Jiangsu, China |
| 375 | 盐6055 Yan 6055 | 中国江苏 Jiangsu, China | 376 | 杨鉴8号 Yangjian8 | 中国江苏 Jiangsu, China |
| 377 | 希望106 Xiwang 106 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 378 | 浙油17号 Zheyou 17 | 中国浙江 Zhejiang, China |
| 379 | 中双5号 Zhongshuang 5 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 380 | 中油821 Zhongyou 821 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 381 | 秦油1号 Qinyou 1 | 中国陕西 Shaanxi, China | 382 | 纬隆88 Weilong 88 | 中国陕西 Shaanxi, China |
| 383 | 盐油2号 Yanyou 2 | 中国江苏 Jiangsu, China | 384 | 秦油5号 Qinyou 5 | 中国陕西 Shaanxi, China |
| 387 | 德68-12 De 68-12 | 中国四川 Sichuan, China | 388 | Monty | 澳大利亚 Australia |
| 389 | Oscar | 澳大利亚 Australia | 390 | 宁油12 Ningyou 12-1 | 中国江苏 Jiangsu, China |
| 391 | 宁油14 Ningyou 14 | 中国江苏 Jiangsu, China | 392 | 史力丰-1 Shilifeng-1 | 中国江苏 Jiangsu, China |
| 393 | 宁油18 Ningyou 18 | 中国江苏 Jiangsu, China | 394 | Helios | 丹麦 Denmark |
| 395 | Hector | 加拿大 Canada | 396 | 棉96-203 Mian96-203 | 中国青海 Qinghai, China |
| 397 | 青662A Qing662A | 中国青海 Qinghai, China | 398 | 699 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 399 | 加拿大2号 Jianada 2 | 加拿大 Canada | 400 | 中双2号 Zhongshuang 2 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 401 | WH-12 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 402 | WH-15 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 403 | WH-17 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 404 | WH-19 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 405 | WH-20 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 406 | WH-23 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 407 | WH-24 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 408 | WH-25 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 409 | WH-26 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 410 | WH-27 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 411 | WH-28 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 412 | WH-29 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 413 | WH-30 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 414 | WH-31 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 415 | WH-33 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 416 | WH-37 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 417 | WH-38 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 418 | WH-41 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 419 | WH-42 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 420 | WH-43 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 421 | WH-45 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 422 | WH-49 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 423 | WH-50 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 424 | WH-55 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 425 | WH-56 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 426 | WH-57 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 427 | WH-58 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 428 | WH-59 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 429 | WH-60 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 430 | WH-61 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 431 | WH-62 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 432 | WH-63 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 433 | WH-81 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 434 | WH-83 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 435 | WH-85 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 436 | WH-88 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 437 | WH-93 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 438 | WH-95 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 439 | WH-100 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 440 | WH-127 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 441 | 豫油1号 Yuyou 1 | 中国河南 Henan, China | 442 | COBRA | 德国 German |
| 443 | 宁油7号 Ningyou 7 | 中国江苏 Jiangsu, China | 444 | Tapidor | 法国 France |
| 445 | 华油6号 Huayou 6 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 446 | 华油12 Huayou 12 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 447 | Cubs root | 朝鲜 North Korea | 448 | 华油10 Huayou 10 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China |
| 449 | Bienvenu | 法国 France | 450 | 胜利油菜 Shengliyoucai | 中国四川 Sichuan, China |
| 451 | ERAKE | 波兰 Poland | 452 | Taisetsu | 日本 Japan |
| 453 | cresor | 加拿大 Canada | 454 | Daichousen | 朝鲜 North Korea |
| 455 | comet | 瑞典 Sweden | 456 | Niklas | 丹麦 Denmark |
| 457 | Askari | 德国 German | 458 | chuosenshu | 朝鲜 North Korea |
| 459 | WESBROOK | 澳大利亚 Australia | 460 | Suigenshu | 朝鲜 North Korea |
| 461 | 华油4号 Huayou 4 | 中国湖北 Hubei, China | 462 | 胜利青梗 Shengliqinggeng | 中国上海 Shanghai, China |
| 463 | 密角多头油菜 Mijiaoduotouyoucai | 中国上海 Shanghai, China | 464 | 矮箕胜利 Aijishengli | 中国上海 Shanghai, China |
| 465 | 漕泾胜利 Caojingshengli | 中国上海 Shanghai, China | 466 | 沪油三号 Huyou 3 | 中国上海 Shanghai, China |
| 467 | 勺叶青 Shaoyeqing | 中国上海 Shanghai, China | 468 | 非洲油菜乳黄花 Feizhouyoucairuhuanghua | 中国上海 Shanghai, China |
| 469 | 沪激早 Hujizao | 中国上海 Shanghai, China | 470 | 漕油2号 Caoyou 2 | 中国上海 Shanghai, China |
| 471 | 封顶240 Fengding 240 | 中国江苏 Jiangsu, China | 472 | 全紫油菜 Quanziyoucai | 中国江苏 Jiangsu, China |
| 473 | 大花球 Dahuaqiu | 中国江苏 Jiangsu, China | 474 | 荣选 Rongxuan | 中国江苏 Jiangsu, China |
| 475 | 宁油10号 Ningyou 10 | 中国江苏 Jiangsu, China | 476 | 宁油8号 Ningyou 8 | 中国江苏 Jiangsu, China |
| 477 | 宁油六号 Ningyouliu | 中国江苏 Jiangsu, China | 478 | 垛油一号 Duoyou 1 | 中国江苏 Jiangsu, China |
| 479 | 淮油12号 Huaiyou 12 | 中国江苏 Jiangsu, China | 480 | 沛选170 Peixuang 170 | 中国江苏 Jiangsu, China |
| 481 | 广德138 Guangde 138 | 中国安徽 Anhui, China | 482 | 广德8104 Guangde 8104 | 中国安徽 Anhui, China |
| 483 | 当油早1号Dangyouzao 1 | 中国安徽 Anhui, China | 484 | 广德761 Guangde 761 | 中国安徽 Anhui, China |
| 485 | 铜陵花叶 Tonglinghuaye | 中国安徽 Anhui, China | 486 | 滁610 Chu610 | 中国安徽 Anhui, China |
| 487 | 滁107 Chu 107 | 中国安徽 Anhui, China | 488 | 宿84-6 Su 84-6 | 中国安徽 Anhui, China |
| 489 | 皖油早 Wanyouzao | 中国安徽 Anhui, China | 490 | 滁油1号 Chuyou 1 | 中国安徽 Anhui, China |
| 491 | 滁县白花 Chuxianbaihua | 中国安徽 Anhui, China | 492 | 芥65-1 Jie 65-1 | 中国浙江 Zhejiang, China |
| 493 | 申黄1号 Shenhuang 1 | 中国上海 Shanghai, China | 494 | 浙油601 Zheyou 601 | 中国浙江 Zhejiang, China |
| 495 | 三高油菜Three high rape | 中国浙江 Zhejiang, China | 496 | 早丰一号 Zaofeng 1 | 中国四川 Sichuan, China |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
1.2 田间试验与表型调查
试验材料于2014年在江苏南京(14NJ)以及2015年、2016年在泰州(15TZ和16TZ)种植。采用完全随机区组设计, 设置3个重复, 单个材料每重复种2行, 每行15株, 行宽1.5 m, 行距40 cm, 株距15~17 cm。每年10月上旬大田直播, 田间管理按当地常规方式进行。田间材料均是自然成熟时收获, 每小区选择具有代表性的6个单株, 在挂藏室内自然阴干后进行考种分析。千粒重具体测量方法为: 单株全株脱粒后, 随机选择其中500粒种子称重, 重复取样3次, 保证3次称重结果差异小于0.1 g (5%以内)为有效的3个数据, 取平均数后加倍即为测量值。利用RStudio软件对各个环境的千粒重表型进行统计分析和相关性分析, 并计算广义遗传力和最佳线性无偏预测值(best linear unbiased prediction, BLUP) [23,24,25]。1.3 基因型检测与分析
利用Illumina 60K SNP芯片对496份甘蓝型油菜资源进行基因型分析。在Genome Studio软件中对SNP进行质量控制。将过滤后的33,218个SNP序列比对至油菜Darmor-bzh基因组, e-value阈值设为10-12, 得到19,167个单拷贝且位置清楚的SNP标记用于关联分析[26]。1.4 全基因组关联分析
利用软件Structure 2.3.4基于贝叶斯模型进行群体结构, 得到Q矩阵[27], 利用软件SPAGeDi计算不同材料间的亲缘关系, 得到K矩阵[28], 在软件Tassel 5.0中导入基因型、表型、Q矩阵和K矩阵数据文件。以Q矩阵和Q+K矩阵作协变量, 分别进行MLM和GLM 2种模型的全基因组关联分析[29]。对MLM模型设置的显著性阈值(bonferroni threshold)为1/总标记数, 即-lg (P) = 4.28; 对GLM模型设置更为严格的显著性阈值为0.05/总标记数, 即-lg (P) = 5.58。当1 Mb区间内存在多个显著SNP时, 若两两间的r2≥0.1, 则将这些SNP归为1个关联位点, 以最小P值的SNP作为显著性位点代表。用RStudio软件包qqman绘制曼哈顿图和QQ (Quantile-Quantile)图。用RStudio软件lm功能分析关联位点解释的总表型变异。1.5 已报道QTL的信息整理
目前有4篇千粒重关联分析研究, 4个群体分别包含157、192、427和521份油菜资源[30,31,32,33], 整理其检测到的显著位点并与本研究结果进行比较。针对利用SNP芯片进行基因分型的连锁群体, 将检测到的QTL两侧的SNP探针序列比对至油菜Darmor-bzh参考基因组, 以确定QTL的物理区间[34]。对于以SSR和AFLP等传统标记进行基因分型的研究, 搜集QTL两侧标记的引物序列并将其比对至参考基因组, 以确定QTL的物理区间。1.6 候选基因挖掘
对于显著关联位点, 以r2 = 0.1作为衰减阈值, 用软件Tassel 5.0计算显著关联位点的LD衰减距离作为置信区间, 提取置信区间内的基因CDS序列, 与模式植物拟南芥中已报道的千粒重相关基因CDS进行BLAST比对, 设e-value阈值为10-10, 以相似度最高的拟南芥基因信息来注释油菜基因。2 结果与分析
2.1 千粒重表型统计分析
496份油菜种质资源表型千粒重在3个环境中具有广泛的变异, 单个环境的千粒重极差范围为4.63~ 5.36 g。单个环境表型平均值范围为(3.51±0.64)~ (4.27±0.88) g, 变异系数范围为0.16~ 0.21 (表1和图1)。3个环境间的相关系数为0.55, 达到极显著水平(P≤0.001)。这表明本研究考察的表型数据具有较高的可靠性和重复性。利用RStudio软件包lem4计算, 油菜千粒重在3个环境下的广义遗传力为63.12%。Table 1
表1
表1关联群体千粒重性状的统计分析
Table 1
| 年份/环境 Year/Environment | 最小值 Minimum | 最大值 Maximum | 平均值±标准差 Average ± SD | 变异系数 Coefficient of variation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2013/2014 南京Nanjing | 2.27 | 7.63 | 4.27±0.88 | 0.21 |
| 2014/2015 泰州Taizhou | 1.64 | 5.77 | 3.65±0.58 | 0.16 |
| 2015/2016 泰州Taizhou | 1.50 | 6.13 | 3.51±0.64 | 0.18 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
图1
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图1关联群体在3个环境(14NJ、15TZ、16TZ)中的千粒重分布
Fig. 11000-seed weight of the association panel in three environments (14NJ, 15TZ, 16TZ)
2.2 千粒重全基因组关联分析
利用MLM模型对千粒重BLUP值进行关联分析, 显著性阈值为-lg (P) = 4.28时, 共检测到8个显著位点。合并存在连锁不平衡的SNP (r2 ≥ 0.1), 得到6个显著位点, 分布在A01、A02、A03、C06和C09染色体(表2和图2)。6个显著位点的-lg (P)值范围是4.33~5.38, 可解释4.86%~6.06%的表型变异。利用一个简单加性模型计算, 6个位点联合解释28.92%的表型变异。与单环境的关联结果比较, 5个位点被重复检测到。Table 2
表2
表2MLM千粒重显著关联位点(BLUP)
Table 2
| 标记 Marker | 染色体 Chr. | 位置 Position (bp) | -lg (P) | 表型变异 R2 (%) | 环境 Environment | 已报道QTL Reported QTL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bn-A01-p23472380 | A01 | 19,346,196 | 5.34 | 6.03 | 16TZ | |
| Bn-A02-p6300284 | A02 | 3,473,319 | 4.81 | 5.41 | 15TZ | |
| Bn-A02-p6564861 | A02 | 3,784,981 | 5.38 | 6.06 | 14NJ | [32] |
| Bn-A03-p22125583 | A03 | 20,956,967 | 4.77 | 5.36 | [32,35] | |
| Bn-scaff_16874_1-p411591 | C06 | 31,817,621 | 4.33 | 4.86 | 16TZ | [30,36,37] |
| Bn-scaff_17526_1-p1066214 | C09 | 1,488,283 | 4.93 | 5.55 | 16TZ | [32] |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
图2
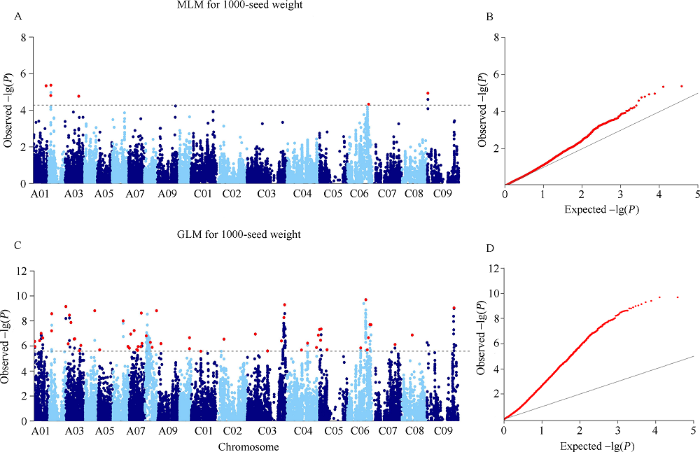 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图2油菜千粒重全基因组关联分析(BLUP)
A: 千粒重MLM曼哈顿图; B: 千粒重MLM QQ图; C: 千粒重GLM曼哈顿图; D: 千粒重GLM QQ图。
Fig. 2Genome-wide association study of 1000-seed weight in rapeseed (BLUP)
A: Manhattan plot of MLM for 1000-seed weight; B: quantile-quantile plot of MLM for 1000-seed weight; C: Manhattan plot of GLM for 1000-seed weight; D: quantile-quantile plot of GLM for 1000-seed weight.
利用GLM模型对千粒重BLUP值进行关联分析, 显著性阈值为-lg (P) = 5.58时, 共检测到226个显著位点。合并存在连锁不平衡的SNP (r2 ≥ 0.1), 得到61个显著位点, 分布在全基因组所有染色体(表3和图2)。其中显著性最高位点Bn-scaff_17526_ 1-p1066214的-lg (P) = 15.98, 对表型变异的贡献率为15.26%。其余位点的-lg (P)值范围是5.58~11.57, 可解释4.89%~11.31%的表型变异。利用一个简单加性模型计算, 61个位点联合解释47.08%的表型变异。与单环境的关联结果比较, 47个位点被检测到, 13个位点在2环境中重复检测到, 7个位点在3个环境中被检测到。
Table 3
表3
表3GLM千粒重显著关联位点(BLUP)
Table 3
| 标记 Marker | 染色体 Chr. | 位置 Position (bp) | -lg (P) | 表型变异 R2 (%) | 环境 Environment | 已报道QTL Reported QTL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bn-A01-p1156979 | A01 | 760,656 | 6.37 | 5.61 | 15TZ | [35] |
| Bn-A01-p1440009 | A01 | 1,036,032 | 5.96 | 5.21 | ||
| Bn-A01-p9621623 | A01 | 8,234,343 | 6.43 | 5.66 | [17,30,36] | |
| Bn-A01-p12222806 | A01 | 10,407,989 | 7.02 | 7.03 | 14NJ | |
| Bn-A01-p15496639 | A01 | 12,941,394 | 6.64 | 6.67 | 16TZ | |
| Bn-A02-p6300284 | A02 | 3,473,319 | 7.22 | 7.23 | 14TZ | |
| Bn-A02-p6564861 | A02 | 3,784,981 | 8.59 | 8.53 | 14NJ/16TZ | [32,35] |
| Bn-A03-p560769 | A03 | 445,706 | 9.16 | 9.08 | 14NJ/16TZ | |
| Bn-A03-p4352837 | A03 | 3,885,180 | 6.18 | 6.22 | ||
| Bn-A03-p6586436 | A03 | 5,884,508 | 8.47 | 8.43 | 16TZ | |
| Bn-A03-p8851142 | A03 | 8,156,299 | 7.88 | 7.86 | 14NJ/15TZ/16TZ | [32] |
| Bn-A03-p13758392 | A03 | 12,893,544 | 6.56 | 6.60 | 15TZ | |
| Bn-A03-p14747263 | A03 | 13,916,047 | 6.57 | 6.60 | 14NJ | [35] |
| Bn-A03-p22125583 | A03 | 20,956,967 | 5.64 | 5.60 | [32,35] | |
| Bn-A03-p24494224 | A03 | 22,999,825 | 6.05 | 6.10 | [32] | |
| Bn-A04-p13705636 | A04 | 14,344,669 | 8.84 | 8.77 | 15TZ | [35] |
| Bn-A05-p2610006 | A05 | 2,720,763 | 5.69 | 5.75 | ||
| Bn-scaff_27198_1-p445589 | A06 | 15,593,147 | 8.01 | 7.99 | 14NJ/15TZ | |
| Bn-A06-p23759352 | A06 | 22,715,814 | 5.97 | 6.01 | ||
| Bn-Scaffold002856-p361 | A07 | 592,982 | 5.84 | 5.89 | 14NJ/16TZ | [14,17,31,36] |
| Bn-A10-p11601681 | A07 | 2,573,087 | 6.95 | 6.15 | 16TZ | [33] |
| Bn-A07-p5877587 | A07 | 7,824,442 | 7.24 | 6.42 | 14NJ/15TZ | [13,32] |
| Bn-A07-p10557557 | A07 | 11,738,166 | 5.71 | 5.77 | 16TZ | |
| Bn-A02-p305007 | A07 | 12,930,679 | 5.66 | 4.93 | 14NJ/15TZ/16TZ | |
| Bn-A07-p11611255 | A07 | 13,756,170 | 5.95 | 6.00 | [35] | |
| Bn-A07-p16095589 | A07 | 17,996,553 | 5.96 | 6.01 | ||
| Bn-scaff_15743_1-p590955 | A07 | 18,512,786 | 8.64 | 8.58 | 14NJ/15TZ/16TZ | |
| Bn-A07-p17804261 | A07 | 19,646,053 | 6.20 | 5.45 | [32,38] | |
| Bn-A08-p2675098 | A08 | 2,098,808 | 6.81 | 6.83 | 16TZ | |
| Bn-A08-p10443959 | A08 | 8,372,628 | 6.30 | 6.34 | [32] | |
| Bn-A08-p13284369 | A08 | 11,051,828 | 5.89 | 5.94 | ||
| Bn-A08-p20343735 | A08 | 17,811,886 | 8.82 | 7.90 | 15TZ | |
| Bn-A09-p7329993 | A09 | 5,542,361 | 6.20 | 6.24 | 14NJ/15TZ | [14,32] |
| Bn-A10-p15021776 | A10 | 14,967,128 | 5.78 | 5.83 | 15TZ | |
| Bn-A10-p15167470 | A10 | 15,100,392 | 6.67 | 6.69 | 15TZ | |
| Bn-scaff_15803_1-p837307 | C01 | 14,780,320 | 5.58 | 5.64 | 14NJ | |
| Bn-scaff_20942_1-p52095 | C02 | 11,201,048 | 6.54 | 6.58 | 14NJ | |
| Bn-scaff_16002_1-p1803014 | C03 | 12,573,756 | 6.95 | 6.97 | 15TZ | |
| Bn-scaff_26320_1-p269450 | C03 | 30,924,988 | 5.61 | 4.89 | ||
| Bn-scaff_16182_1-p296671 | C03 | 51,992,967 | 6.41 | 6.44 | 14NJ | |
| Bn-scaff_15794_3-p89166 | C03 | 55,716,441 | 8.28 | 7.39 | 14NJ/15TZ | |
| Bn-scaff_17119_1-p148890 | C03 | 56,814,587 | 9.28 | 9.19 | 14NJ/15TZ | [35] |
| Bn-scaff_16217_1-p597569 | C04 | 21,919,412 | 5.68 | 4.96 | 14NJ | |
| Bn-scaff_18062_1-p229981 | C04 | 31,112,520 | 6.23 | 5.47 | 14NJ/16TZ | |
| 标记 Marker | 染色体 Chr. | 位置 Position (bp) | -lg (P) | 表型变异 R2 (%) | 环境 Environment | 已报道QTL Reported QTL |
| Bn-scaff_15585_1-p1089867 | C04 | 44,500,243 | 5.88 | 5.14 | 16TZ | |
| Bn-scaff_18903_1-p371596 | C04 | 47,531,676 | 6.87 | 6.89 | 16TZ | |
| Bn-scaff_16414_1-p1774629 | C05 | 279,059 | 7.33 | 7.33 | 14NJ | |
| Bn-scaff_20901_1-p2029631 | C05 | 1,973,973 | 6.47 | 6.50 | 14NJ/16TZ | |
| Bn-scaff_20901_1-p1279675 | C05 | 2,707,564 | 7.36 | 7.36 | 14NJ | |
| Bn-scaff_15763_1-p596396 | C05 | 11,699,136 | 5.71 | 4.98 | 16TZ | |
| Bn-scaff_15763_1-p588874 | C06 | 20,160,298 | 5.85 | 5.90 | 16TZ | |
| Bn-scaff_16064_1-p938130 | C06 | 24,703,441 | 11.57 | 11.31 | 14NJ/15TZ/16TZ | [35] |
| Bn-scaff_15743_1-p599416 | C06 | 27,808,971 | 9.80 | 8.80 | 14NJ/15TZ/16TZ | |
| Bn-scaff_18807_1-p747016 | C06 | 30,110,394 | 5.69 | 4.96 | [36] | |
| Bn-scaff_16874_1-p411591 | C06 | 31,817,621 | 6.66 | 6.69 | 14NJ/16TZ | [30,36,37] |
| Bn-scaff_17799_1-p2391172 | C06 | 34,110,582 | 7.71 | 6.87 | 14NJ/16TZ | |
| Bn-scaff_17799_1-p853567 | C06 | 35,737,877 | 7.70 | 7.69 | 14NJ | [35] |
| Bn-scaff_15705_1-p2279820 | C07 | 35,285,037 | 6.12 | 6.16 | 16TZ | |
| Bn-A08-p10452462 | C08 | 16,678,522 | 6.88 | 6.08 | 14NJ/15TZ/16TZ | |
| Bn-scaff_17526_1-p1066214 | C09 | 1,488,283 | 15.98 | 15.26 | 14NJ/15TZ/16TZ | [32] |
| Bn-scaff_15576_1-p614226 | C09 | 41,707,720 | 9.03 | 8.96 | 14NJ/16TZ |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
综合2个模型关联结果, 5个MLM模型的显著位点与GLM重叠, 合并重叠位点后共得到62个显著位点, 联合解释47.31%的表型变异。这些位点分布在全基因组所有染色体上, 其中A07染色体上检测到的数目最多, 达9个位点, A03和C06染色体上分别检测到8个和7个位点。分析显著位点的分布, 58.06%的位点分布在A亚基因组, 41.94%位于C亚基因组(表2和表3)。
2.3 与前人报道 QTL 的比较
综合MLM和GLM模型检测结果, 与已报道的千粒重QTL结果比较, 本研究中21个显著位点与前人研究结果重叠, 其中有8个位点得到至少2个群体的验证(表2和表3)。位于A02染色体的位点Bn-A02-p6564861位置为3.78 Mb, 与Shahid等[32]通过关联分析检测到的位点Bn-A02-p6564861和Luo等[35]通过DH群体定位到的千粒重QTL qSW.A2-4 (位置: 3.78~3.83 Mb)重叠。位于A07染色体的位点Bn-Scaffold002856-p361位置为0.59 Mb, 与Cai等[31]、Fan等[17]和Shi等[36]采用不同策略检测到位点BrGMS3983、QTL TSWA7b和qSW.A7-2 (位置: 0.83 Mb)重叠。位于A09染色体的位点Bn-A09- p7329993位置为5.54 Mb, 与Basunanda等[14]定位到QTL TH-tsm07、TH-tsm06和Shahid等[32]检测到位点Bn-A09-p7327691 (位置: 5.54~5.74 Mb)重叠。位于C06染色体的位点Bn-scaff_16874_1-p411591位置为31.82 Mb, 与Dong等[30]、Shi等[36]和Li等[37]通过不同策略检测到的位点(位置: 31.18 Mb)重叠。GLM模型中效应最大的位点Bn-scaff_ 17526_1-p1066214位于C09染色体1.49 Mb, -lg (P) = 15.98, 解释15.26%的表型变异, 与Shahid等[32]检测到的效应最大位点Bn-scaff_17526_1-p1063974 (位置: 1.49 Mb)一致。该模型中效应次高的位点Bn-scaff_16064_1-p938130位于C06染色体24.70 Mb, -lg (P) = 11.57, 解释11.31%的表型变异, 与Luo等[35]定位到的千粒重QTL qSW.C6-3 (位置: 24.52 Mb)重叠。此外有16个位点与前人检测的QTL位点重叠或相邻(表3), 以上QTL比较验证了本研究结果的可靠性。2.4 候选基因挖掘
基于油菜基因组的注释信息, 在Bn-A03-p221 25583位点下游244 kb处找到候选基因BnaA03g4 1350D, 该基因的拟南芥同源基因DGAT编码二酰甘油酰基转移酶, 其过表达促进种子中甘油三酯含量和种子重量增加[39] (表4)。在Bn-A03-p8851142位点下游118 kb处找到候选基因BnaA03g17130D, 该基因的拟南芥同源基因TTG2编码WRKY转录因子, 通过增加种皮细胞延伸促进种子粒重增加[40]。在Bn-A05-p2610006位点下游7.5 kb处找到候选基因BnaA05g36830D, 该基因的拟南芥同源基因AGL61编码I型MADS结构域蛋白, 在中央细胞发育过程和种子胚乳形成过程中起调节作用, 影响种子大小[41]。在Bn-A07-p11611255位点上游115 kb处找到候选基因BnaA07g16350D, 该基因的拟南芥同源基因WRI1调节编码糖酵解途径和脂肪酸相关酶基因的表达, WRI1通过增大种子体积引起种子重量增加[42]。在Bn-scaff_18062_1-p229981位点上游323 kb找到候选基因BnaC04g33070D, 该基因的拟南芥同源基因RAV1是植物生长的负调控因子, 其高表达的转基因植株表现出异常胚珠, 导致种子大小、重量和数量减少[43]。此外, 本研究还找到其他6个候选基因, 包括拟南芥已知调控粒重相关基因NPC6[44]、CLV3[45]、GRF2[46]、EOD3[12]、GW5[47]、DA2[9]、SHB1[48]等在油菜中的同源拷贝。Table 4
表4
表4千粒重关联位点候选基因信息
Table 4
| 标记 Marker | 油菜基因 Rapeseed gene | 染色体 Chr. | 位置 Position | 拟南芥同源基因Arabidopsis homolog gene | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 基因名称Gene name | 基因号Gene ID | ||||
| Bn-A01-p15496639 | BnaA01g20420D | A01 | 12,306,073 | NPC6 | AT3G48610 |
| Bn-A03-p22125583 | BnaA03g41350D | A03 | 20,713,211 | DGAT | AT3G51520 |
| Bn-A03-p8851142 | BnaA03g17130D | A03 | 8,038,181 | TTG2 | AT2G37260 |
| Bn-A05-p2610006 | BnaA05g36830D | A05 | 2,713,236 | AGL61 | AT5G60440 |
| Bn-A07-p11611255 | BnaA07g16350D | A07 | 13,870,810 | WRI1 | AT3G54320 |
| Bn-A09-p7329993 | BnaA09g12210D | A09 | 6,402,925 | GW5 | AT1G64500 |
| Bn-scaff_20942_1-p52095 | BnaA08g15580D | C02 | 12,923,783 | CLV3 | AT2G27250 |
| Bn-scaff_18903_1-p371596 | BnaC04g50960D | C04 | 48,343,005 | EOD3 | AT2G46660 |
| Bn-scaff_18062_1-p229981 | BnaC04g33070D | C04 | 31,436,211 | RAV1 | AT1G13260 |
| Bn-scaff_17799_1-p853567 | BnaC06g38800D | C06 | 36,244,755 | GRF2 | AT1G78300 |
| Bn-scaff_17799_1-p853567 | BnaC06g38900D | C06 | 36,295,477 | DA2 | AT1G78420 |
| Bn-A08-p10452462 | BnaC08g12050D | C08 | 17,299,420 | SHB1 | AT4G25350 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
3 讨论
本研究对496份油菜资源千粒重进行考察, 分析其在3个环境下的千粒重表型, 其中材料2012-8998、甲904、WH-59和CY19PXW-65等千粒重大且稳定, 其平均千粒重分别为5.63、5.59、5.09和5.06 g, 上述材料值得作为改良千粒重的优良亲本。比较MLM和GLM模型的关联分析, MLM将群体结构Q矩阵作为固定效应, 亲缘关系K矩阵作为随机效应, 很好地控制了假阳性, 位点可靠性更高。MLM模型检测到6个显著位点, 联合解释了28.92%的表型变异, 其中4个位点得到前人验证。但MLM检测功效偏低, 容易造成假阴性。因此, 引入了检测功效高, 同时假阳性更高的模型GLM; 但对GLM模型设置更为严格的显著性阈值为0.05/总标记数, 以减小GLM中可能存在的假阳性位点。GLM检测到61个显著位点, 联合解释了47.08%的表型变异, 其中21个位点得到前人验证。合并两模型位点后共得到62个显著位点, 联合解释47.31%的表型变异。21个位点与前人定位的QTL重叠, 包括Bn-scaff_ 17526_1-p1066214和Bn-scaff_16064_1-p938130等大效应位点, 其中Bn-A01-p9621623、Bn-Scaffold 002856-p361和Bn-scaff_16874_1-p411591等位点得到多个群体的验证。在后续研究中值得对上述可靠性高的位点可进行精细定位和基因克隆, 为油菜千粒重的改良提供基因资源。本研究共收集了26篇已发表的油菜千粒重QTL信息, 包含了3~159个QTL, 分布在19条染色体上, 解释的表型变异范围为2.40%~41.46%。与前人QTL位点比较, 本研究中41个显著位点尚未得到验证(表2和表3)。多个位点效应值较高且在多环境中被检测到, 如位点Bn-A03-p560769、Bn-scaff_ 15743_1-p599416和Bn-scaff_15743_1-p590955的表型贡献值分别为9.08%、8.80%和8.58%, 以上位点在3个单环境中均被检测到。此外, 在多个新位点附近找到候选基因, 如在Bn-A01-p15496639、Bn- A05-p2610006和Bn-A08-p10452462等位点附近分别找到拟南芥粒重已知基因NPC6、AGL61和SHB1等的同源基因。这些新位点可靠性高, 值得进一步研究与验证。鉴于千粒重是受多基因调控的复杂数量性状, 在育种上可针对上述位点设计分子标记, 通过分子标记辅助选择聚合有利等位基因, 选育出高产油菜新品种。
此外, 本研究在11个显著位点附近找到千粒重相关的候选基因及其拟南芥同源基因(表4), 根据基因功能注释, 多数候选基因归类于转录因子, 如TTG2、AGL61、WRI1、RAV1和GRF2等。这些基因还影响除粒重外的其他性状, 如EOD3功能缺失后对粒重和角果长均有抑制作用[12]; DGAT编码二酰甘油酰基转移酶, 对籽粒含油量和籽粒均有重要调节作用[39]; CLV3双突变产生多室角果, 每角粒数和千粒重均增加[45], 这些基因调控范围广, 利用价值大, 后期可重点关注。目前很多研究通过CRISPR/Cas9基因编辑技术改良油菜的性状, 如改良抗裂角[49]、株高和分枝数[50]、高油酸[51]等。本研究在Bn-scaff_18062_1-p229981位点附近找到候选基因BnaC04g33070D, 其拟南芥同源基因RAV1为负调控因子, 可与MINI3和IKU2的启动子直接结合, 导致后者表达受抑制, 进而影响粒重, 后续研究可通过CRISPR/Cas9敲除提高油菜的千粒重。
4 结论
本研究利用496份油菜种质资源对千粒重进行全基因组关联分析, 群体在3个环境中千粒重的广义遗传力为63.12%。MLM模型检测到6个显著位点, GLM模型检测到61个显著位点, 合并共同位点后得到62个显著位点, 联合解释47.31%的表型变异。此外, 21个位点与前人研究定位的QTL重叠, 其中8个位点得到至少2个群体验证, 其余41个为新检测到的位点。在11个位点附近发现拟南芥粒重基因DGAT、EOD3、AGL61、WRI1、DA2和RAV1等的同源拷贝。附表请见网络版: 1) 本刊网站
参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
.
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/S0070-2153(10)91007-7URLPMID:20705183 [本文引用: 1]

Plant organs grow to characteristic, species-specific sizes and shapes. At the cellular level, organ growth is initially characterized by cell proliferation, which gives way to cell expansion at later stages. Using mainly Arabidopsis thaliana as a model species, a number of factors have been isolated in recent years that promote or restrict organ growth, with the altered organ size being associated with changes in cell number, in cell size, or in both. However, cells in an organ do not appear to follow a strictly autonomous program of proliferation and expansion, and their behavior is coordinated in at least three different respects: normally sized organs can be formed consisting of altered numbers of cells with compensatory changes in the size of the individual cells, suggesting that cellular behavior is subject to organ-wide control; the growth of cells derived from more than one clonal origin is coordinated within a plant lateral organ with its different histological layers; and growth of cells in different regions of an organ is coordinated to generate a reasonably flat leaf or floral organ. Organ growth is strongly modulated by environmental factors, and the molecular basis for this regulation is beginning to be understood. Given the complexity of organ growth as a dynamic four-dimensional process, precise quantification of growth parameters and mathematical modeling are increasingly used to understand this fascinating problem of plant biology.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
.
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
URLPMID:22251317 [本文引用: 3]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 2]
.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
URLPMID:20574694 [本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1073/pnas.1423244112URLPMID:25838284 [本文引用: 1]

Among the variety of tissue-resident NK-like populations recently distinguished from recirculating classical NK (cNK) cells, liver innate lymphoid cells (ILC) type 1 (ILC1s) have been shown to represent a distinct lineage that originates from a novel promyelocytic leukaemia zinc finger (PLZF)-expressing ILC precursor (ILCP) strictly committed to the ILC1, ILC2, and ILC3 lineages. Here, using PLZF-reporter mice and cell transfer assays, we studied the developmental progression of ILC1s and demonstrated substantial overlap with stages previously ascribed to the cNK lineage, including pre-pro-NK, pre-NK precursor (pre-NKP), refined NKP (rNKP), and immature NK (iNK). Although they originated from different precursors, the ILC1 and cNK lineages followed a parallel progression at early stages and diverged later at the iNK stage, with a striking predominance of ILC1s over cNKs early in ontogeny. Although a limited set of ILC1 genes depended on PLZF for expression, characteristically including Il7r, most of these genes were also differentially expressed between ILC1s and cNKs, indicating that PLZF together with other, yet to be defined, factors contribute to the divergence between these lineages.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
.
URLPMID:30858362 [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 4]
URLPMID:24510440 [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1038/nature08800URLPMID:20336072 [本文引用: 1]

Although pioneered by human geneticists as a potential solution to the challenging problem of finding the genetic basis of common human diseases, genome-wide association (GWA) studies have, owing to advances in genotyping and sequencing technology, become an obvious general approach for studying the genetics of natural variation and traits of agricultural importance. They are particularly useful when inbred lines are available, because once these lines have been genotyped they can be phenotyped multiple times, making it possible (as well as extremely cost effective) to study many different traits in many different environments, while replicating the phenotypic measurements to reduce environmental noise. Here we demonstrate the power of this approach by carrying out a GWA study of 107 phenotypes in Arabidopsis thaliana, a widely distributed, predominantly self-fertilizing model plant known to harbour considerable genetic variation for many adaptively important traits. Our results are dramatically different from those of human GWA studies, in that we identify many common alleles of major effect, but they are also, in many cases, harder to interpret because confounding by complex genetics and population structure make it difficult to distinguish true associations from false. However, a-priori candidates are significantly over-represented among these associations as well, making many of them excellent candidates for follow-up experiments. Our study demonstrates the feasibility of GWA studies in A. thaliana and suggests that the approach will be appropriate for many other organisms.
URLPMID:28455767 [本文引用: 2]
URLPMID:19414564 [本文引用: 2]
.
URLPMID:24779415 [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1104/pp.126.2.861URLPMID:11402213 [本文引用: 2]

We recently reported the cloning and characterization of an Arabidopsis (ecotype Columbia) diacylglycerol acyltransferase cDNA (Zou et al., 1999) and found that in Arabidopsis mutant line AS11, an ethyl methanesulfonate-induced mutation at a locus on chromosome II designated as Tag1 consists of a 147-bp insertion in the DNA, which results in a repeat of the 81-bp exon 2 in the Tag1 cDNA. This insertion mutation is correlated with an altered seed fatty acid composition, reduced diacylglycerol acyltransferase (DGAT; EC 2.3.1.20) activity, reduced seed triacylglycerol content, and delayed seed development in the AS11 mutant. The effect of the insertion mutation on microsomal acyl-coenzyme A-dependent DGAT is examined with respect to DGAT activity and its substrate specificity in the AS11 mutant relative to wild type. We demonstrate that transformation of mutant AS11 with a single copy of the wild-type Tag1 DGAT cDNA can complement the fatty acid and reduced oil phenotype of mutant AS11. More importantly, we show for the first time that seed-specific over-expression of the DGAT cDNA in wild-type Arabidopsis enhances oil deposition and average seed weight, which are correlated with DGAT transcript levels. The DGAT activity in developing seed of transgenic lines was enhanced by 10% to 70%. Thus, the current study confirms the important role of DGAT in regulating the quantity of seed triacylglycerols and the sink size in developing seeds.
DOI:10.1105/tpc.001404URLPMID:12084832 [本文引用: 1]

Mutants of a new gene, TRANSPARENT TESTA GLABRA2 (TTG2), show disruptions to trichome development and to tannin and mucilage production in the seed coat. The gene was tagged by the endogenous transposon Tag1 and shown to encode a WRKY transcription factor. It is the first member of this large, plant-specific family known to control morphogenesis. The functions of all other WRKY genes revealed to date involve responses to pathogen attack, mechanical stress, and senescence. TTG2 is strongly expressed in trichomes throughout their development, in the endothelium of developing seeds (in which tannin is later generated) and subsequently in other layers of the seed coat, and in the atrichoblasts of developing roots. TTG2 acts downstream of the trichome initiation genes TTG1 and GLABROUS1, although trichome expression of TTG2 continues to occur if they are inactivated. Later, TTG2 shares functions with GLABRA2 in controlling trichome outgrowth. In the seed coat, TTG2 expression requires TTG1 function in the production of tannin. Finally, TTG2 also may be involved in specifying atrichoblasts in roots redundantly with other gene(s) but independently of TTG1 and GLABRA2.
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1007/s11816-015-0351-xURL [本文引用: 1]
URLPMID:30518173 [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1111/nph.16473URLPMID:32176333 [本文引用: 1]

Plant oils are valuable commodities for food, feed, renewable industrial feedstocks and biofuels. To increase vegetable oil production, here we show that the nonspecific phospholipase C6 (NPC6) promotes seed oil production in the Brassicaceae seed oil species Arabidopsis, Camelina and oilseed rape. Overexpression of NPC6 increased seed oil content, seed weight and oil yield both in Arabidopsis and Camelina, whereas knockout of NPC6 decreased seed oil content and seed size. NPC6 is associated with the chloroplasts and microsomal membranes, and hydrolyzes phosphatidylcholine and galactolipids to produce diacylglycerol. Knockout and overexpression of NPC6 decreased and increased, respectively, the flux of fatty acids from phospholipids and galactolipids into triacylglycerol production. Candidate-gene association study in oilseed rape indicates that only BnNPC6.C01 of the four homeologues NPC6s is associated with seed oil content and yield. Haplotypic analysis indicates that the BnNPC6.C01 favorable haplotype can increase both seed oil content and seed yield. These results indicate that NPC6 promotes membrane glycerolipid turnover to accumulate TAG production in oil seeds and that NPC6 has a great application potential for oil yield improvement.
DOI:10.1111/pbi.12872URLPMID:29250878 [本文引用: 2]

Multilocular silique is a desirable agricultural trait with great potential for the development of high-yield varieties of Brassica. To date, no spontaneous or induced multilocular mutants have been reported in Brassica napus, which likely reflects its allotetraploid nature and the extremely low probability of the simultaneous random mutagenesis of multiple gene copies with functional redundancy. Here, we present evidence for the efficient knockout of rapeseed homologues of CLAVATA3 (CLV3) for a secreted peptide and its related receptors CLV1 and CLV2 in the CLV signalling pathway using the CRISPR/Cas9 system and achieved stable transmission of the mutations across three generations. Each BnCLV gene has two copies located in two subgenomes. The multilocular phenotype can be recovered only in knockout mutations of both copies of each BnCLV gene, illustrating that the simultaneous alteration of multiple gene copies by CRISPR/Cas9 mutagenesis has great potential in generating agronomically important mutations in rapeseed. The mutagenesis efficiency varied widely from 0% to 48.65% in T0 with different single-guide RNAs (sgRNAs), indicating that the appropriate selection of the sgRNA is important for effectively generating indels in rapeseed. The double mutation of BnCLV3 produced more leaves and multilocular siliques with a significantly higher number of seeds per silique and a higher seed weight than the wild-type and single mutant plants, potentially contributing to increased seed production. We also assessed the efficiency of the horizontal transfer of Cas9/gRNA cassettes by pollination. Our findings reveal the potential for plant breeding strategies to improve yield traits in currently cultivated rapeseed varieties.
DOI:10.1093/jxb/ers066URL [本文引用: 1]

Seed yield and oil content are two important agricultural characteristics in oil crop breeding, and a lot of functional gene research is being concentrated on increasing these factors. In this study, by differential gene expression analyses between rapeseed lines (zy036 and 51070) which exhibit different levels of seed oil production, BnGRF2 (Brassica napus growth-regulating factor 2-like gene) was identified in the high oil-producing line zy036. To elucidate the possible roles of BnGRF2 in seed oil production, the cDNA sequences of the rapeseed GRF2 gene were isolated. The Blastn result showed that rapeseed contained BnGRF2a/2b which were located in the A genome (A1 and A3) and C genome (Cl and C6), respectively, and the dominantly expressed gene BnGRF2a was chosen for transgenic research. Analysis of 35S-BnGRF2a transgenic Arabidopsis showed that overexpressed BnGRF2a resulted in an increase in seed oil production of >50%. Moreover, BnGRF2a also induced a >20% enlargement in extended leaves and >40% improvement in photosynthetic efficiency because of an increase in the chlorophyll content. Furthermore, transcriptome analyses indicated that some genes associated with cell proliferation, photosynthesis, and oil synthesis were up-regulated, which revealed that cell number and plant photosynthesis contributed to the increased seed weight and oil content. Because of less efficient self-fertilization induced by the longer pistil in the 35S-BnGRF2a transgenic line, Napin-BnGRF2a transgenic lines were further used to identify the function of BnGRF2, and the results showed that seed oil production also could increase >40% compared with the wild-type control. The results suggest that improvement to economically important characteristics in oil crops may be achieved by manipulation of the GRF2 expression level.
DOI:10.1038/cr.2008.307URLPMID:19015668 [本文引用: 1]

Grain weight is a major determinant of crop grain yield and is controlled by naturally occurring quantitative trait loci (QTLs). We earlier identified a major QTL that controls rice grain width and weight, GW5, which was mapped to a recombination hotspot on rice chromosome 5. To gain a better understanding of how GW5 controls rice grain width, we conducted fine mapping of this locus and uncovered a 1 212-bp deletion associated with the increased grain width in the rice cultivar Asominori, in comparison with the slender grain rice IR24. In addition, genotyping analyses of 46 rice cultivars revealed that this deletion is highly correlated with the grain-width phenotype, suggesting that the GW5 deletion might have been selected during rice domestication. GW5 encodes a novel nuclear protein of 144 amino acids that is localized to the nucleus. Furthermore, we show that GW5 physically interacts with polyubiquitin in a yeast two-hybrid assay. Together, our results suggest that GW5 represents a major QTL underlying rice width and weight, and that it likely acts in the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway to regulate cell division during seed development. This study provides novel insights into the molecular mechanisms controlling rice grain development and suggests that GW5 could serve as a potential tool for high-yield breeding of crops.Cell Research (2008) 18:1199-1209. doi: 10.1038/cr.2008.307; published online 18 November 2008.
DOI:10.1105/tpc.108.064972URLPMID:19141706 [本文引用: 1]

Seed development in Arabidopsis thaliana undergoes an initial phase of endosperm proliferation followed by a second phase in which the embryo grows at the expense of the endosperm. As mature seed size is largely attained during the initial phase, seed size is coordinately determined by the growth of the maternal ovule, endosperm, and embryo. Here, we identify SHORT HYPOCOTYL UNDER BLUE1 (SHB1) as a positive regulator of Arabidopsis seed development that affects both cell size and cell number. shb1-D, a gain-of-function overexpression allele, increases seed size, and shb1, a loss-of-function allele, reduces seed size. SHB1 is transmitted zygotically. The increase in shb1-D seed size is associated with endosperm cellurization, chalazal endosperm enlargement, and embryo development. SHB1 is required for the proper expression of two other genes that affect endosperm development, MINISEED3 (MINI3) and HAIKU2 (IKU2), a WRKY transcription factor gene and a leucine-rich repeat receptor kinase gene. SHB1 associates with both MINI3 and IKU2 promoters in vivo. SHB1 may act with other proteins that bind to MINI3 and IKU2 promoters to promote a large seed cavity and endosperm growth in the early phase of seed development. In the second phase, SHB1 enhances embryo cell proliferation and expansion through a yet unknown IKU2-independent pathway.
[本文引用: 1]
.
DOI:10.1111/pbi.13228URLPMID:31373135 [本文引用: 1]

Plant height and branch number are essential components of rapeseed plant architecture and are directly correlated with its yield. Presently, improvement of plant architecture is a major challenge in rapeseed breeding. In this study, we first verified that the two rapeseed BnaMAX1 genes had redundant functions resembling those of Arabidopsis MAX1, which regulates plant height and axillary bud outgrowth. Therefore, we designed two sgRNAs to edit these BnaMAX1 homologs using the CRISPR/Cas9 system. The T0 plants were edited very efficiently (56.30%-67.38%) at the BnaMAX1 target sites resulting in homozygous, heterozygous, bi-allelic and chimeric mutations. Transmission tests revealed that the mutations were passed on to the T1 and T2 progeny. We also obtained transgene-free lines created by the CRISPR/Cas9 editing, and no mutations were detected in potential off-target sites. Notably, simultaneous knockout of all four BnaMAX1 alleles resulted in semi-dwarf and increased branching phenotypes with more siliques, contributing to increased yield per plant relative to wild type. Therefore, these semi-dwarf and increased branching characteristics have the potential to help construct a rapeseed ideotype. Significantly, the editing resources obtained in our study provide desirable germplasm for further breeding of high yield in rapeseed.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
