 ,*, 肖炳光
,*, 肖炳光 ,*云南省烟草农业科学研究院 / 烟草行业烟草生物技术育种重点实验室 / 国家烟草基因工程研究中心, 云南昆明 650021
,*云南省烟草农业科学研究院 / 烟草行业烟草生物技术育种重点实验室 / 国家烟草基因工程研究中心, 云南昆明 650021Mapping of quantitative trait loci conferring resistance to brown spot in cigar tobacco cultivar Beinhart1000-1
TONG Zhi-Jun, ZHANG Yi-Han, CHEN Xue-Jun, ZENG Jian-Min, FANG Dun-Huang ,*, XIAO Bing-Guang
,*, XIAO Bing-Guang ,*Yunnan Academy of Tobacco Agricultural Sciences / Key Laboratory of Tobacco Biotechnological Breeding / National Tobacco Genetic Engineering Research Center, Kunming 650021, Yunnan, China
,*Yunnan Academy of Tobacco Agricultural Sciences / Key Laboratory of Tobacco Biotechnological Breeding / National Tobacco Genetic Engineering Research Center, Kunming 650021, Yunnan, China通讯作者:
收稿日期:2018-03-5接受日期:2018-12-24网络出版日期:2019-01-05
| 基金资助: |
Received:2018-03-5Accepted:2018-12-24Online:2019-01-05
| Fund supported: |
作者简介 About authors
E-mail:tzj861@163.com。

摘要
关键词:
Abstract
Keywords:
PDF (471KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
本文引用格式
童治军, 张谊寒, 陈学军, 曾建敏, 方敦煌, 肖炳光. 雪茄烟品种Beinhart1000-1赤星病抗性基因的QTL定位[J]. 作物学报, 2019, 45(3): 477-482. doi:10.3724/SP.J.1006.2019.84035
TONG Zhi-Jun, ZHANG Yi-Han, CHEN Xue-Jun, ZENG Jian-Min, FANG Dun-Huang, XIAO Bing-Guang.
赤星病由链格孢菌(Alternaria alternate (Fries) Keissl)[1,2,3]引起, 是最具破坏性的烟草(Nicotiana tabacum L.)叶斑病害之一, 在烟草的整个生育期内均有发生, 尤其在烟叶的成熟期更严重[1,2,3,4]。病害通常从烟株下部叶开始发生, 随着叶片的成熟, 病斑自上而下发生[5]。最初在叶片上出现黄褐色圆形小斑点, 而后变成褐色, 并会逐步扩大, 病斑呈圆形或不规则圆形, 有同心轮, 外围有淡黄色晕圈[6,7,8]。严重时, 病斑相互连接合并, 致使病斑焦枯、破碎。在中国, 赤星病在各个烟区广泛发生, 严重影响烟草的产量和质量。
培育抗烟草赤星病的优良品种虽然是预防该病最经济有效的途径, 但其抗性属于受微效多基因控制且极易受环境影响的数量性状[9,10,11,12], 极大地增加了育种的难度。分子标记辅助选择育种(MAS)是利用与目的性状基因连锁的分子标记快捷、有效地选择目标性状基因型, 加快作物育种进程[13]。对数量性状(或微效多基因控制的复杂性状)进行MAS的先决条件是利用分子标记对目的性状扫描定位全基因组的QTL。迄今, QTL定位研究在烟草上虽有较多的报道[14,15,16], 但在烟草赤星病抗性基因QTL定位分析方面的报道较少[17,18,19,20]。究其原因是烟草栽培品种间的多态性水平极其低下[21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29], 高质量的烟草遗传连锁图谱构建工作十分困难[30,31,32,33], 因而已报道的基于不完整(低质量)的烟草遗传图谱进行的赤星病抗性基因QTL定位分析的结果, 不能满足烟草抗赤星病的分子标记辅助育种需求。
本研究旨在利用抗、感烟草赤星病品种Beinhart1000-1和红花大金元经杂交、自交产生的F2作图群体构建一张高质量烟草遗传连锁图谱, 并结合组培快繁形成的F2株系的田间赤星病病情指数进行全基因组QTL定位分析, 检测获得与烟草赤星病抗性相关的QTL, 为下一步开展烟草抗赤星病的分子标记辅助育种工作奠定基础。
1 材料与方法
1.1 植物材料
用于遗传图谱构建的群体是由红花大金元和Beinhart1000-1经杂交、自交产生的362个F2单株构成。其中, 红花大金元是具有优良品质但极易感烟草赤星病的烤烟品种, 而Beinhart1000-1则是由美国引进的具有烟草赤星病抗性的优良雪茄烟品种。2015年种植亲本红花大金元和Beinhart1000-1, 杂交后获得其后代F1; 2016年种植F1和亲本, 自交并收获F2种子; 2017年种植包含亲本、F1、F2各世代材料及抗、感对照品种。其中, 抗感对照品种(净叶黄和Speight G-140)、两亲本和F1各种植3个重复, 每个重复15株, 共计45株; 此外, 用于田间烟草赤星病抗性鉴定的362个F2株系(组培快繁获得), 每个株系含有45个具有相同基因型的组培单株, 即每个株系种植3个重复, 每个重复15个单株。于云南省玉溪市研和实验基地种植以上试验材料, 株行距为0.50 m×1.00 m, 按当地优质烟生产技术措施进行栽培管理。1.2 组培快繁
通过外植体的处理、培养基的配置、组培室培养和再生植株诱导及移栽将362个F2单株进一步扩繁为362个F2株系。1.3 接菌与抗性调查
将赤星病强致病力菌株0-268 (由云南省烟草农业科学研究院提供)接种于PDA培养基上, 在28℃条件下培养15 d, 待菌丝布满培养基表面时, 保存在4℃的冰箱中备用[6]。在田间叶片接近成熟期时, 用1%灭菌葡萄糖溶液洗下菌苔, 过滤获得分生孢子液, 再用1%葡萄糖、1%甘油、0.25%吐温-80组成的水溶液配制10,000个 mL-1的分生孢子悬浮液。利用新配置的烟草赤星病菌分生孢子悬浮液对两亲本、362个F2株系和抗、感病对照品种(净叶黄和Speight G-140)进行接病菌试验[34], 并在对照品种病情指数(DI)达到75%时, 按国家标准GB/T 23222-2008烟草病虫害分级及调查方法进行调查。将3个重复共计45株接种烟株的所有叶片进行分级调查, 并计算出平均病情指数来替代原始F2单株的病情指数。1.4 SSR标记分析
按照Tong等[32]方法提取和纯化亲本和362份F2单株的基因组DNA。参照Bindler等[30,31]和Tong等[33]进行SSR-PCR扩增体系配置和程序设置。参照Xu等[35]的方法进行PCR扩增产物的6%非变性聚丙烯酰胺凝胶(non- denaturing PAGE)电泳检测。1.5 遗传图谱构建
首先, 利用两亲本和F1三份材料对参试的SSR标记进行多态标记筛选, 选取呈共显性多态的SSR标记进行F2群体基因型分析。其次, 将获得的F2群体基因型数据经过偏分离分析(卡方检测), 并将分离比符合1∶2∶1的标记用于遗传连锁图谱的构建。最后, 利用作图软件JoinMap v 4.0[36]分析符合1∶2∶1分离比例的标记间的遗传连锁关系, 并利用软件MapChart v2.22[37]绘制遗传图谱。参照Tong等[32,33] 设置以上软件相关参数。1.6 QTL定位分析
基于构建获得的遗传图谱并结合田间赤星病病情指数(DI), 利用MapQTL v 6软件[38]提供的Restricted Multiple-QTL model Mapping (rMQM)方法进行全基因组QTL扫描定位, 相关参数设置为: Algorithm=Regression, Test statistic=LOD, Fit dominance for F2=Yes, Mapping step size=1.0, Maximum number of neighboring markers=30, Maximum number of iterations=10,000, Number of permutations=10,000。按照McCouch等[39]的方法命名QTL, 即前缀q+性状名称缩写+ LG数目。2 结果与分析
2.1 赤星病抗性鉴定
由田间鉴定结果可知, 两亲本间的赤星病抗性差异较大, Beinhart1000-1和红花大金元的平均病情指数(DI)分别为7.39 (变异范围为2.03~13.96)和91.28 (变异范围为78.85~98.38)。赤星病的病情指数在由组培快繁获得的F2群体中呈连续性分布(变异范围为2.30~98.13), 即呈典型的正态分布且所有的数据均落在两亲本内(图1)。这一结果与已报道的研究结果相符, 即烟草赤星病的抗性是典型的数量性状[9-12,20,40]。同时也表明, 在F2群体中不存在赤星病抗性的超亲分离现象, 这意味着感病(高值病情指数)和抗病(低值病情指数)的等位基因在两亲本间是完全连锁在一起的, 即所有高值病情指数的亲本具有易感病的等位基因, 而所有低值病情指数的亲本具有抗病等位基因。
图1
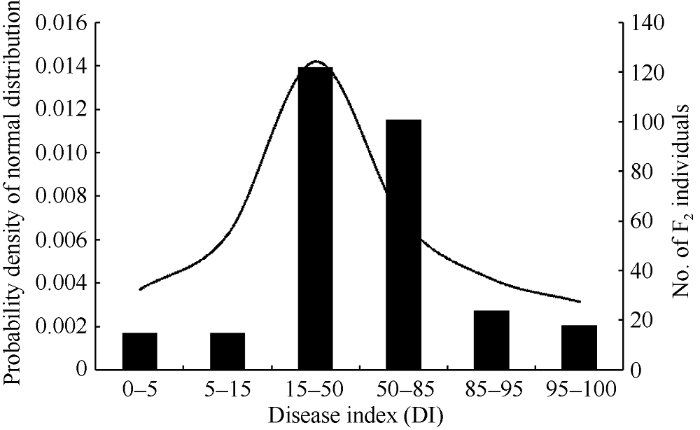 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图1烟草赤星病病情指数在F2群体中的分布频率
Fig. 1Frequency distribution of DI in F2 population
2.2 遗传连锁图谱构建
利用双亲(红花大金元和Beinhart1000-1)及其F1三份材料, 对共计38,437对SSR引物(TM、TMt、TMs和PT系列引物分别为11,302、12,016、10,000和5119对)进行多态性分析, 其中, 仅筛选出677对(TM、TMt、TMs和PT系列多态性引物分别为138、187、172和180对)在两亲本间有多态且在F1上呈共显性的SSR引物, 多态率低至1.76% (677/38,437)。利用筛选出的稳定且呈共显性多态的SSR引物在362个F2单株中所获得的基因型数据进行连锁分析, 最终获得一张含有670个SSR标记、较均匀分布于24个连锁群、覆盖烟草基因组总长度为2878.732 cM、相邻标记间的平均距离为4.297 cM的高质量烟草遗传连锁图谱。每条连锁群所包含的SSR 标记数目在13(LG05)~43(LG02)之间, 各染色体的长度范围是43.122 cM (LG19)~186.598 cM (LG22), 各染色体相邻标记间平均间隔的变化在2.398~6.794 cM之间。此外, 受益于共有的180个PT系列标记, 我们参照Bindler等[30,31]公布的图谱将本研究构建获得的连锁群编号, 使二者的连锁群顺序和编号保持一致。2.3 QTL定位分析
最终有2个与烟草赤星病抗性基因相关的QTL被检测到, 分别位于第20(LG20)和第23(LG23)连锁群上 (表1)。其中, qTBS20是2个QTL中具有最大效应值的一个, 可解释18.31%的表型变异。2个QTL均具有显著的加性效应, 但仅有qTBS23表现出显著的显性效应, 这表明, 感病基因(具有较高的DI值)相对于抗病基因(具有较低的DI值)呈现出完全显性。此外, 2个抗病的等位基因全部源自抗病亲本Beinhart1000-1。图2
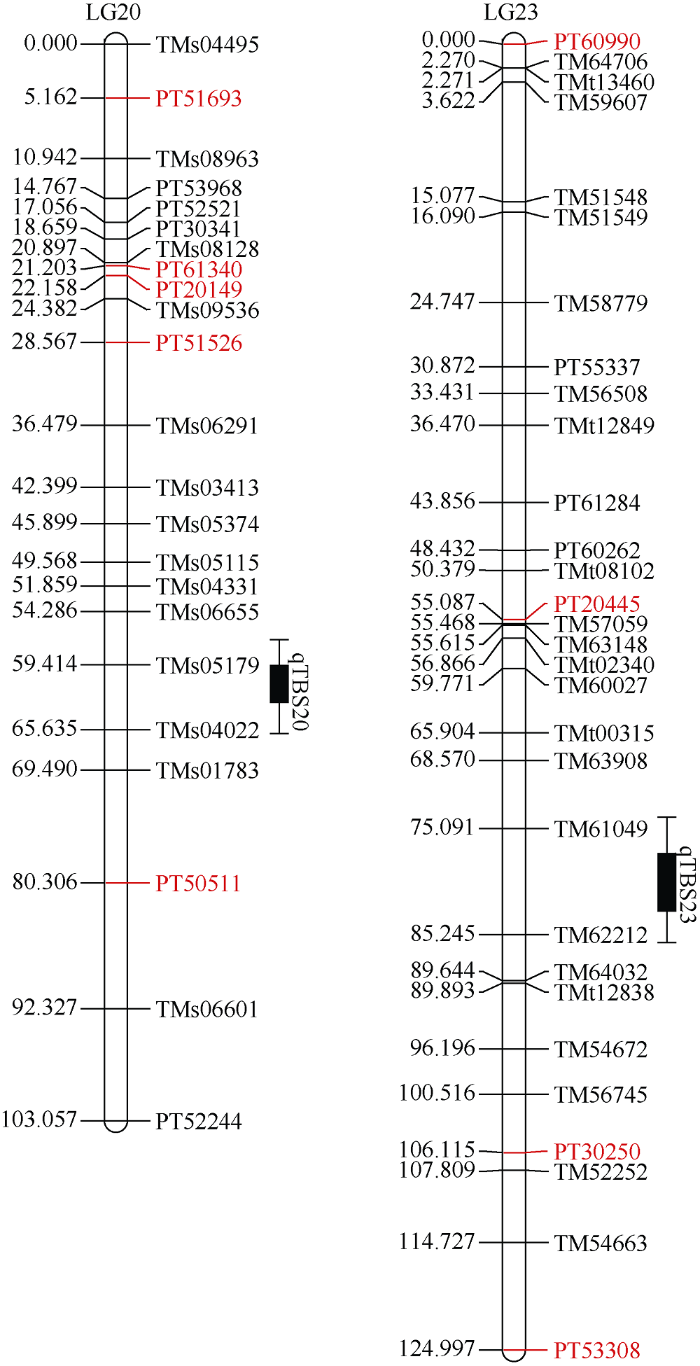 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图2基于362个F2单株(红花大金元×Beinhart1000-1)的烟草赤星病抗性QTL定位结果
图中每条连锁群的左右两侧分别为遗传距离(厘摩尔)和标记名称, 其中, 红色标记表示位于Bindler等[30,31]公布的连锁群上。
Fig. 2QTL mapping of tobacco brown spot (TBS) resistance based on 362 F2 individuals derived from the cross HD × Beinhart-1000
In each linkage group, the positions (cM) and names of markers were shown on the left and right side, respectively. The red markers were mapped in the genetic map constructed by Bindler et al. [30,31]
Table 1
表1
表1烟草赤星病抗性QTL定位结果
Table 1
| QTL | LG | 位置 Position | 两侧标记 Marker interval | LOD | 加性效应a Additive a | 显性效应 Dominant | 贡献率b Exp b(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qTBS20 | LG20 | 62.414 | TMs05179-TMs04022 | 5.82 | -15.874 | -1.819 | 18.31 |
| qTBS23 | LG23 | 79.091 | TM61049-TM62212 | 3.51 | -10.923 | 11.145 | 8.94 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
3 讨论
由于用于构建作图群体的双亲间亲缘关系较近, 因此, 本研究中用于构建遗传连锁图谱的标记较少, 且标记的多态性水平较低(1.76%; 677/38,437), 远低于Bindler等[31]所用标记的多态率(46.16%; 2363/5119)。本研究利用670个多态SSR标记构建的图谱中虽然也包含24个连锁群(与普通栽培烟草中所拥有的24对染色体一致), 但仍然存在标记数目较少的连锁群, 尤其是LG05连锁群其上仅有13个标记。相较于Bindler等[31]公布的含有2363个SSR标记分布在24个连锁群上且覆盖全基因组3270 cM的高密度烟草遗传连锁图谱, 我们构建的图谱有待进一步完善。其差距在于: 1) 作图的亲本材料不同。本研究所用的材料均属于栽培烟草且红花大金元与Beinhart1000-1间具有很近的(或相似的)亲缘关系; 而Bindler等[30,31]使用的2个亲本材料间的亲缘关系较远(双亲间的遗传相似性系数GS≈0.385), 接近于栽培烟草与野生烟草间的亲缘关系。2) 基因型分析所使用的试验检测系统不同。本研究使用的实验检测系统(6%的非变性聚丙烯酰胺凝胶和银染显色)的分辨率及灵敏度均较低; 而Bindler等[30,31]的检测系统(Applied Biosystems 3100 Genetic Analyzers)很灵敏, 因此, 那些具有较小片段长度差异的标记很可能在我们的试验系统中无法检测出来。本研究所使用的2个亲本材料的赤星病抗性表现刚好呈现出2个极端且没有超亲遗传现象在F2群体中表现出来(即, F2群体中的赤星病病情指数变异范围完全包含在抗、感两亲本的赤星病DI值内)。这表明, 所有的抗、感病等位基因分别来自抗、感病亲本。此外, 在不计上位性效应的前提下, 两亲本间不同的DI值(91.28-7.39= 83.89)应该是由加性效应的累积产生的。QTL定位的结果也与赤星病田间表型数据在两亲本和F2群体中的分布相符合, 即所检测到的2个低DI值QTL的等位基因均来自抗病亲本Beinhart1000-1。根据加性效应值且不计上位性效应的前提下, 检测到的2个QTL共同解释了两亲本间53.58 [2×(15.87+10.92)]或约64% (53.58/83.89)的加性效应值。这就意味着, 通过利用在抗病亲本Beinhart1000-1中的2个QTL对应的等位基因与感病亲本红花大金元替换后, 红花大金元的DI值如预期一样地由89.25降低至39.73。因此, 本研究筛选获得的2个QTL可应用于烟草抗赤星病的分子标记辅助育种。
前人关于烟草赤星病抗病基因QTL定位分析的研究主要集中在抗病烤烟品种净叶黄上[17,18,19], 通过对比发现(二者用于QTL定位的标记和连锁群顺序是相同的, 均按照Bindler等[31]公布的连锁群排序), Tong等[17]获得的3个源自净叶黄的赤星病抗性QTL与本研究获得的2个QTL不同, 前者分别位于第3 (LG03)、第4 (LG04)和第17 (LG17) 3个连锁群上, 而后者分别位于第20 (LG20)和第23 (LG23) 2个连锁群上。因此, 源自净叶黄与源自Beinhart1000-1的赤星病抗性基因(QTL)是不同的。目前仅有1篇基于Beinhart1000-1的赤星病抗性QTL定位分析研究[20], 虽也检测获得2个QTL(分别位于第7和第15连锁群上的RBS-1和RBS-2), 但二者因使用的标记和连锁图谱不同而无法进一步将同是源自Beinhart1000-1赤星病抗性的4个QTL间的关系进行比较。
本研究通过对2个QTL两侧的标记进行检测, 在362个F2单株中分别有5株和3株与红花大金元和Beinhart1000-1一致的基因型单株, 其平均DI值分别为85.93 (变异范围为78.38~91.57)和17.96 (变异范围为9.49~26.17)。所以, 这两组的DI值差异为85.93-17.96= 67.97 (占两亲本间DI值差异的81%), 解释了23%的加性效应值(2个QTL共同解释了64%)。这说明, 在2个QTL的加性效应中存在着两两间的互作效应(上位性效应), 这也正解释了两亲本间剩余19% (100%~81%)的DI值。与预期一致, 上位性效应与加性效应均在同一方向上提高两亲本间DI值的差异。因此, 在2个QTLs中与Beinhart1000-1基因型相同的单株可能是赤星病抗性最优的。
参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1080/13102818.2004.10817126URL [本文引用: 2]

ABSTRACTSome fungi of Alternaria spp. are known as foliar pathogens. Essential for this host range is the production of host-specific toxins, which are involved in the development in a few destructive diseases. A. alternata tobacco pathotype also produces host-specific and nonhost specific toxins. Toxic substances with host specific toxicity were released from germinating spores of this pathogen in 24 hr after germination. AT-toxin was partially purified from culture filtrate the fungus. It was shown to have host specific toxicity at cultivar level in leaf bioassay with tobacco cultivars Beinhart 1000.1, Shiroenshu 601 and Shiroenshu 1.
DOI:10.1046/j.1365-313X.2001.01399.xURLPMID:12366799 [本文引用: 1]

Our previous observation that host plant extracts induce production and secretion of mannitol in the tobacco pathogen Alternaria alternata suggested that, like their animal counterparts, plant pathogenic fungi might produce the reactive oxygen quencher mannitol as a means of suppressing reactive oxygen-mediated plant defenses. The concurrent discovery that pathogen attack induced mannitol dehydrogenase (MTD) expression in the non-mannitol-containing host tobacco suggested that plants, unlike animals, might be able to counter this fungal suppressive mechanism by catabolizing mannitol of fungal origin. To test this hypothesis, transgenic tobacco plants constitutively expressing a celery Mtd cDNA were produced and evaluated for potential changes in resistance to both mannitol- and non-mannitol-secreting pathogens. Constitutive expression of the MTD transgene was found to confer significantly enhanced resistance to A. alternata , but not to the non-mannitol-secreting fungal pathogen Cercospora nicotianae . These results are consistent with the hypothesis that MTD plays a role in resistance to mannitol-secreting fungal plant pathogens.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]

本文选用赤星病 (Alternariaalternata)抗感程度不同的7个烟草品种,采用双亲交和双列交的交配设计,于1994~1996年间对其田间抗性的遗传进 行了分析。结果表明,品种间抗病性差异显著,尽管环境因素对发病程度影响很大,各抗病品种的抗性基本稳定。双列分析和世代方差分析结果表明,抗病性呈部分 显性,受多基因控制。基因表达的加性效应和显性效应同时存在,以加性为主。各抗性亲本的抗病基因的显隐性方向不同。遗传分析和配合力分析表明,狭义遗传率 变幅为21.2%~78.1%,所有的抗性亲本均表现出较高的负效应一般配合力,具有较好的特殊配合力的组合有:宾哈特1000-1×NC82、宾哈特 1000-1
.
URL [本文引用: 1]

本文选用赤星病 (Alternariaalternata)抗感程度不同的7个烟草品种,采用双亲交和双列交的交配设计,于1994~1996年间对其田间抗性的遗传进 行了分析。结果表明,品种间抗病性差异显著,尽管环境因素对发病程度影响很大,各抗病品种的抗性基本稳定。双列分析和世代方差分析结果表明,抗病性呈部分 显性,受多基因控制。基因表达的加性效应和显性效应同时存在,以加性为主。各抗性亲本的抗病基因的显隐性方向不同。遗传分析和配合力分析表明,狭义遗传率 变幅为21.2%~78.1%,所有的抗性亲本均表现出较高的负效应一般配合力,具有较好的特殊配合力的组合有:宾哈特1000-1×NC82、宾哈特 1000-1
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-5119.2000.04.012URL [本文引用: 2]

对烟草赤星病两个抗性因素遗传的 1/ 2 7( 7+1)双列杂交分析表明 ,病斑数量和病斑大小的遗传都符合加性 显性模型。病斑数量的遗传属部分显性类型 ,显性基因主要表现为减效 ;病斑大小的遗传属完全显性类型 ,显性基因为增效基因。 1996、1997两年的田间试验结果和苗期离体叶片接种的结果基本一致。烟草对赤星病病菌侵入的抗性较抗病斑扩展的能力更容易通过品种间杂交传递给后代。配合力分析表明 ,一些组合具有较好的抗侵入特殊配合力 ,另一些组合具有良好的抗扩展特殊配合力。抗×感组合Beinhart10 0 0 - 1×NC82两个抗性因素特殊配合力均较好 ,在抗病育种中有较高的利用价值
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-5119.2000.04.012URL [本文引用: 2]

对烟草赤星病两个抗性因素遗传的 1/ 2 7( 7+1)双列杂交分析表明 ,病斑数量和病斑大小的遗传都符合加性 显性模型。病斑数量的遗传属部分显性类型 ,显性基因主要表现为减效 ;病斑大小的遗传属完全显性类型 ,显性基因为增效基因。 1996、1997两年的田间试验结果和苗期离体叶片接种的结果基本一致。烟草对赤星病病菌侵入的抗性较抗病斑扩展的能力更容易通过品种间杂交传递给后代。配合力分析表明 ,一些组合具有较好的抗侵入特殊配合力 ,另一些组合具有良好的抗扩展特殊配合力。抗×感组合Beinhart10 0 0 - 1×NC82两个抗性因素特殊配合力均较好 ,在抗病育种中有较高的利用价值
DOI:10.2135/cropsci1987.0011183X002700040006xURL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1007/s00122-002-1096-9URLPMID:12596008 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract Bacterial wilt caused by Ralstonia solanacearum is one of the most destructive soil-borne diseases in the world. Breeding resistant commercial varieties of tobacco is difficult because most donor candidates' resistance is controlled by polygenes. In this paper, we demonstrate the identification of useful DNA markers for bacterial wilt-resistant tobacco breeding. One hundred and seventeen markers were identified by the amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) method between W6, a burley variety with resistance originating from a Japanese domestic variety, Hatano, and Michinoku 1, a commercial burley wilt-susceptible variety, using 3,072 primer combinations. These markers were analyzed in 125 doubled haploid lines, derived from F(1) hybrids between W6 and Michinoku 1, and a linkage map consisting of ten linkage groups was drawn. The resistance phenotype of each of these lines was investigated on the basis of the average of disease severity obtained from field trials over two growing cycles. Quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis was performed on the marker phenotypes and the resistance phenotype of each line. One QTL for the bacterial wilt resistance of W6 and DNA markers associated with this QTL were identified on a linkage group consisting of 15 markers, 32 cM in length. This QTL explained more than 30% of the variance in resistance among these lines.
DOI:10.1007/s11032-006-9019-0URL [本文引用: 1]

Quantitative trait loci (QTLs) were investigated in a recombinant inbred line (RIL) population descended from a cross between two flue-cured Nicotiana tabacum L. inbred lines with unrelated breeding origins. A total of 59 traits, related to diverse agronomic, leaf quality, chemical composition and smoke properties were assessed. Chemical traits and smoke mutagenicity were estimated by near infrared reflectance spectroscopy (NIRS) analyses of leaf lamina powders. Physical properties of cigarettes made from each RIL, and the total particulate matter (tar and nicotine yields), benzo[a]pyrene and CO contents of the main smoke stream generated by the cigarettes in mechanical smoking tests under a standard ISO regime were also analyzed. The RILs were screened for 184 amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP), inter simple sequence repeat (ISSR), sequence specific amplified polymorphism (SSAP), sequence characterized amplified region (SCAR) and biological markers. A partial genetic map including 18 linkage groups was constructed based on 138 of the markers. Substantial segregation distortion (47%) was observed in linkage groups throughout the genome. Seventy-five QTLs associated with 8鈥41.5% of the variation in the examined traits were identified on 12 linkage groups by simple and composite interval mapping. Nineteen QTLs had opposite effects to those expected from the ranking of parental means.
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1111/j.1439-0523.2011.01940.xURL [本文引用: 3]

Brown spot (BS) caused by Alternaria alternata is one of the most destructive foliar diseases affecting tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) production and quality in China. Breeding of BS-resistant cultivars is difficult because the resistance has proved to be quantitatively inherited. To facilitate marker-assisted selection, we carried out a study of mapping quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for BS resistance. We developed an F2 population consisting of 213 individuals from a cross between a BS-susceptible cultivar ‘Changbohuang’ (CBH) and a BS-resistant cultivar ‘Jinyehuang’ (JYH) and constructed a genetic map consisting of 196 simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers based on this population. Using disease index (DI) as the indicator of BS resistance, we detected three QTLs located between SSR markers TM20534 and TM10737, TM10589 and TM10216, and TM10443 and PT60669, respectively. The resistant alleles of the three QTLs were all from the resistant parent JYH. The three QTLs together could explain 6586% of the DI difference between the two parents in total, with 6561% explained by their additive effects. Therefore, the three QTLs will be useful for BS-resistance breeding.
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-5119.2012.01.004URL [本文引用: 2]

为了在分子水平上弄清烟草赤星病抗性的遗传规律,并进行遗传定位,以抗赤星病品种净叶黄和感赤星病品种NC82为亲本,构建了F1、F2、BC1代群体。通过对该群体进行赤星病接种鉴定和抗性遗传分析,发现净叶黄对赤星病的抗性由显性多基因控制。通过分子标记群体扩增,在第M号连锁群上,筛选到一个与净叶黄的赤星病抗性基因紧密连锁的SSR标记,它与抗性基因间的遗传距离为4 cM。该标记可用于抗赤星病育种的辅助选择。
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-5119.2012.01.004URL [本文引用: 2]

为了在分子水平上弄清烟草赤星病抗性的遗传规律,并进行遗传定位,以抗赤星病品种净叶黄和感赤星病品种NC82为亲本,构建了F1、F2、BC1代群体。通过对该群体进行赤星病接种鉴定和抗性遗传分析,发现净叶黄对赤星病的抗性由显性多基因控制。通过分子标记群体扩增,在第M号连锁群上,筛选到一个与净叶黄的赤星病抗性基因紧密连锁的SSR标记,它与抗性基因间的遗传距离为4 cM。该标记可用于抗赤星病育种的辅助选择。
DOI:10.3969/mpb.011.000566URL [本文引用: 2]

为筛选到与抗赤星病基因连锁更加紧密的SSR标记,并绘制出抗病基因的SSR标记连锁图。本 研究以一个位于M号连锁群上且与净叶黄抗赤星病基因有连锁关系的SSR标记为基础,将高密度遗传连锁图谱中位于M号连锁群上的130对SSR引物进行合成 及扩增筛选,通过数据分析,获得了一个抗赤星病基因的SSR标记连锁群。该连锁群包括12个标记,全长181.5cM,平均间距15.1cM,抗性基因被 定位在标记J4与J9之间,其中与J9的遗传距离仅为4cM,为下一步抗性基因的精细定位奠定了良好的基础。
DOI:10.3969/mpb.011.000566URL [本文引用: 2]

为筛选到与抗赤星病基因连锁更加紧密的SSR标记,并绘制出抗病基因的SSR标记连锁图。本 研究以一个位于M号连锁群上且与净叶黄抗赤星病基因有连锁关系的SSR标记为基础,将高密度遗传连锁图谱中位于M号连锁群上的130对SSR引物进行合成 及扩增筛选,通过数据分析,获得了一个抗赤星病基因的SSR标记连锁群。该连锁群包括12个标记,全长181.5cM,平均间距15.1cM,抗性基因被 定位在标记J4与J9之间,其中与J9的遗传距离仅为4cM,为下一步抗性基因的精细定位奠定了良好的基础。
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-5708.2014.02.018URLMagsci [本文引用: 3]

<p>为了研究赤星病抗性的遗传规律,筛选与抗性基因紧密连锁的SSR标记,并将抗性基因进行QTL定位,用抗赤星病品种Beinhart1000-1作母本,感病品种G140作父本,构建了F1及F2代群体,并对其进行了抗性鉴定和遗传分析。结果表明,Beinhart1000-1的赤星病抗病性是由显性多基因控制的。利用混合群体分组分析法,从2653对SSR引物中,得到83对在抗感池间表现多态且扩增条带稳定清晰的SSR标记。以F2代群体115个单株为作图群体,将该83对引物进行扩增,并用WinQTLCart2.5分析数据。这83个标记分别连锁到18个连锁群上,同时定位到两个抗赤星病的QTL位点,分别位于7号和15号连锁群上。</p>
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-5708.2014.02.018URLMagsci [本文引用: 3]

<p>为了研究赤星病抗性的遗传规律,筛选与抗性基因紧密连锁的SSR标记,并将抗性基因进行QTL定位,用抗赤星病品种Beinhart1000-1作母本,感病品种G140作父本,构建了F1及F2代群体,并对其进行了抗性鉴定和遗传分析。结果表明,Beinhart1000-1的赤星病抗病性是由显性多基因控制的。利用混合群体分组分析法,从2653对SSR引物中,得到83对在抗感池间表现多态且扩增条带稳定清晰的SSR标记。以F2代群体115个单株为作图群体,将该83对引物进行扩增,并用WinQTLCart2.5分析数据。这83个标记分别连锁到18个连锁群上,同时定位到两个抗赤星病的QTL位点,分别位于7号和15号连锁群上。</p>
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1134/S1022795406060123URLPMID:16871787 [本文引用: 1]

Nicotiana tabacum (2n = 48) is a natural amphidiploid and shows a distribution over a geographical area in eastern anatolia. Random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) technique was used to evaluate both genetic diversity among 21 primitive tobacco accessions comparing flue cure virginia genotype (FCV) and their geographical polymorphism as a source of genetic variations for breeding programs. Only 13 of all the 60 random primers used in RAPD showed polymorphism acceptable for characterization of these accessions. Totally 118 RAPD fragments were generated from thirteen decamer primer and sixtyfour of them were found polymorphic (54.2%). Mus and FCV showed the smallest genetic distance among accessions cultivated in the eastern anatolia. These results shows that the RAPD assay is a powerful approach for identifying genetic and geographic polymorphism.
DOI:10.1007/s00122-005-0132-yURLPMID:16283232 [本文引用: 1]

Amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) was conducted on a set of 92 Nicotiana tabacum L. accessions from diverse types (flue-cured, dark air-cured, burley, oriental, and cigar wrapper) and breeding origins to identify markers associated with disease resistances. Eleven primer combinations were required to identify 33 polymorphic fragments. This allowed the identification of 92% of these accessions, and yielded sufficient information for building a neighbor joining tree. Clusters of accessions with common traits or breeding origins were observed. An important part of this polymorphism could be related to interspecific introgressions from other Nicotiana species, performed during the breeding history of N. tabacum to confer resistance to pathogens. Seven fragments were associated with three different resistances: two for the blue-mold ( Peronospora tabacina Adam) resistance derived from Nicotiana debneyi Domin, two for the Va gene (Potato Virus Y susceptibility), and three for the black root rot ( Chalara elegans ) resistance of N. debneyi origin. Some of these markers were converted into sequence characterized amplified region markers, and validated on recombinant inbred lines or doubled-haploid lines.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.2135/cropsci2008.05.0253URL [本文引用: 1]

Plant breeding methodologies have been applied to flue-cured tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) for approximately seven decades. As has been observed in several other crops, stringent quality requirements have resulted in use of conservative breeding strategies in the development of new cultivars. The impact of breeding practices on genetic diversity within U.S. flue-cured tobacco germplasm has not...
.
DOI:10.2135/cropsci2009.01.0024URL [本文引用: 1]

Little is currently known about the genetic variation within diverse gene pools of cultivated tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.). Knowledge in this area could aid in future germplasm maintenance activities, provide additional information in the area of N. tabacum population genetics, and assist in selection of materials for breeding or genetic investigations. To this end, 702 N. tabacum accessions ...
DOI:10.1007/s00122-006-0437-5URLPMID:17115128 [本文引用: 7]

We report the first linkage map of tobacco ( Nicotiana tabacum L.) generated through microsatellite markers. The microsatellite markers were predominantly derived from genomic sequences of the Tobacco Genome Initiative (TGI) through bioinformatics screening for microsatellite motives. A total of 684 primer pairs were screened for functionality in a panel of 16 tobacco lines. Of those, 637 primer pairs were functional. Potential parents for mapping populations were evaluated for their polymorphism level through genetic similarity analysis. The similarity analysis revealed that the known groups of tobacco varieties (Burley, Flue-cured, Oriental and Dark) form distinct clusters. A mapping population, based on a cross between varieties Hicks Broad Leaf and Red Russian, and consisting of 186 F2 individuals, was selected for mapping. A total of 282 functional microsatellite markers were polymorphic in this population and 293 loci could be mapped together with the morphological trait flower color. Twenty-four tentative linkage groups spanning 1,920 cM could be identified. This map will provide the basis for the genetic mapping of traits in tobacco and for further analyses of the tobacco genome.
DOI:10.1007/s00122-011-1578-8URLPMID:21461649 [本文引用: 10]

Tobacco (Nicotiana tabacumL.) is a species in the large family of the Solanaceae and is important as an agronomic crop and as a model system in plant biotechnology. Despite its importance, only limited molecular marker resources are available that can be used for genome analysis, genetic mapping and breeding. We report here on the development and characterization of 5,119 new and functional microsatellite markers and on the generation of a high-resolution genetic map for the tetraploid tobacco genome. The genetic map was generated using an F2 mapping population derived from the intervarietal cross of Hicks Broadleaf02×02Red Russian and merges the polymorphic markers from this new set with those from a smaller set previously used to produce a lower density map. The genetic map described here contains 2,317 microsatellite markers and 2,363 loci, resulting in an average distance between mapped microsatellite markers which is less than 202million base pairs or 1.502cM. With this new and expanded marker resource, a sufficient number of markers are now available for multiple applications ranging from tobacco breeding to comparative genome analysis. The genetic map of tobacco is now comparable in marker density and resolution with the best characterized genomes of the Solanaceae: tomato and potato. The online version of this article (doi:10.1007/s00122-011-1578-8) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
DOI:10.1111/j.1439-0523.2012.01984.xURL [本文引用: 3]

Molecular markers and genetic maps are useful tools for genetic research and molecular breeding. Although significant progress has been made recently on molecular marker development and genetic map construction in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum), more efforts are still required to meet the needs of genetic research and breeding in this allotetraploid species. In this study, based on the expressed sequence tag (EST) data and genome sequence data of N. tabacum, we developed a total of 4886 simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers (including 1365 genomic SSRs and 3521 EST-SSRs), which were functional in a set of eight tobacco varieties of four different types and were basically novel. Using these newly developed SSR markers as well as published SSR markers and a population of 207 double haploid (DH) lines derived from a cross between two flue-cured tobacco varieties ‘Honghua Dajinyuan’ and ‘Hicks Broad Leaf’, we constructed a genetic map consisting of 611 SSR loci distributed on 24 tentative linkage groups and covering a total length of 1882.1 cM with an average distance of 3.1 cM between adjacent markers.
DOI:10.1270/jsbbs.15129URLPMID:4902457 [本文引用: 3]

Tobacco (Nicotiana tabacumL.), particularly flue-cured tobacco, is one of the most economically important nonfood crops and is also an important model system in plant biotechnology. Despite its importance, only limited molecular marker resources are available for genome analysis, genetic mapping, and breeding. Simple sequence repeats (SSR) are one of the most widely-used molecular markers, having significant advantages including that they are generally co-dominant, easy to use, abundant in eukaryotic organisms, and produce highly reproducible results. In this study, based on the genome sequence data of flue-cured tobacco (K326), we developed a total of 13,645 mostly novel SSR markers, which were working in a set of eighteen tobacco varieties of four different types. A mapping population of 213 backcross (BC1) individuals, which were derived from an intra-type cross between two flue-cured tobacco varieties, Y3 and K326, was selected for mapping. Based on the newly developed SSR markers as well as published SSR markers, we constructed a genetic map consisting of 626 SSR loci distributed across 24 linkage groups and covering a total length of 1120.45 cM with an average distance of 1.79 cM between adjacent markers, which is the highest density map of flue-cured tobacco till date.
URL [本文引用: 1]

国外赤星病抗源Beinbart1000-1和国内抗病品种净叶黄及许金4号的抗病性分属两种不同的类型,本文对7个赤星病抗感程度不同的烟草品种的抗病性分别进行了以下测定:1.通过观察病斑和病斑大小测定抗侵入和抗扩展能力;2.测定各品种对两种Alternaria毒素,AT毒素和细交各孢酮酸(TA)处理的反应;3.双列杂交法分析法抗性遗传规律,重点对Beinhart1000-1和净叶黄的抗性特点进行比较,
URL [本文引用: 1]

国外赤星病抗源Beinbart1000-1和国内抗病品种净叶黄及许金4号的抗病性分属两种不同的类型,本文对7个赤星病抗感程度不同的烟草品种的抗病性分别进行了以下测定:1.通过观察病斑和病斑大小测定抗侵入和抗扩展能力;2.测定各品种对两种Alternaria毒素,AT毒素和细交各孢酮酸(TA)处理的反应;3.双列杂交法分析法抗性遗传规律,重点对Beinhart1000-1和净叶黄的抗性特点进行比较,
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0253-9772.2002.03.027URL [本文引用: 1]

本文介绍了一套简单快速的DNA银染以及胶保存的方法,整个过程仅需10~15分钟,而且背景浅,条带清楚,灵敏度高,稳定性好.胶保存采用双层玻璃纸夹心法,可长久地保存胶显色时的原貌.以常规PAG胶检测和HLA的SSCP分型为例,利用该套方法进行了银染以及胶的保存,均得到了满意的结果.该方法具有推广价值.
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0253-9772.2002.03.027URL [本文引用: 1]

本文介绍了一套简单快速的DNA银染以及胶保存的方法,整个过程仅需10~15分钟,而且背景浅,条带清楚,灵敏度高,稳定性好.胶保存采用双层玻璃纸夹心法,可长久地保存胶显色时的原貌.以常规PAG胶检测和HLA的SSCP分型为例,利用该套方法进行了银染以及胶的保存,均得到了满意的结果.该方法具有推广价值.
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1093/jhered/93.1.77URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.13496/j.issn.1007-5119.2015.05.001URL [本文引用: 1]

以高抗赤星病烟草品种净叶黄(JYH)、Beinhart1000-1(Beinhart)和感病品种NC82为材料分别构建了2个杂交组合的P1、P2、F1、F2四世代群体,成熟期赤星病菌人工接种鉴定后,采用主基因+多基因混合遗传模型对JYH和Beinhart两个材料进行抗性分析,结果表明,两者的赤星病抗性均受两对加性-完全显性主基因+加性-显性多基因控制。组合1的加性效应以第1对主基因为主,且多基因的加性效应大于显性效应;组合2的两对主基因负向加性效应相等,且多基因的显性效应大于加性效应;2个组合F2群体主基因遗传率分别为64.72%和63.88%,表明赤星病的抗性遗传以主基因效应为主,并且受环境影响较大。
DOI:10.13496/j.issn.1007-5119.2015.05.001URL [本文引用: 1]

以高抗赤星病烟草品种净叶黄(JYH)、Beinhart1000-1(Beinhart)和感病品种NC82为材料分别构建了2个杂交组合的P1、P2、F1、F2四世代群体,成熟期赤星病菌人工接种鉴定后,采用主基因+多基因混合遗传模型对JYH和Beinhart两个材料进行抗性分析,结果表明,两者的赤星病抗性均受两对加性-完全显性主基因+加性-显性多基因控制。组合1的加性效应以第1对主基因为主,且多基因的加性效应大于显性效应;组合2的两对主基因负向加性效应相等,且多基因的显性效应大于加性效应;2个组合F2群体主基因遗传率分别为64.72%和63.88%,表明赤星病的抗性遗传以主基因效应为主,并且受环境影响较大。
