 ,1,2,**, 孙如建2,3,**, 李忠峰2, 魏中艳2, 任玉龙2, 王俊
,1,2,**, 孙如建2,3,**, 李忠峰2, 魏中艳2, 任玉龙2, 王俊 ,1,*, 邱丽娟
,1,*, 邱丽娟 ,2,*
,2,*Molecular identification of a new soybean germplasm Zhonghuang 608 lacking of 7S globulin alpha' subunit
LI Jun-Ying ,1,2,**, SUN Ru-Jian2,3,**, LI Zhong-Feng2, WEI Zhong-Yan2, REN Yu-Long2, WANG Jun
,1,2,**, SUN Ru-Jian2,3,**, LI Zhong-Feng2, WEI Zhong-Yan2, REN Yu-Long2, WANG Jun ,1,*, QIU Li-Juan
,1,*, QIU Li-Juan ,2,*
,2,*通讯作者:
第一联系人:
收稿日期:2018-06-2接受日期:2018-10-8网络出版日期:2018-11-06
| 基金资助: |
Received:2018-06-2Accepted:2018-10-8Online:2018-11-06
| Fund supported: |

摘要
关键词:
Abstract
Keywords:
PDF (2058KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
本文引用格式
李俊英, 孙如建, 李忠峰, 魏中艳, 任玉龙, 王俊, 邱丽娟. 大豆7S球蛋白α'亚基缺失新种质中黄608的分子鉴定[J]. 作物学报, 2019, 45(1): 18-25. doi:10.3724/SP.J.1006.2019.84078
LI Jun-Ying, SUN Ru-Jian, LI Zhong-Feng, WEI Zhong-Yan, REN Yu-Long, WANG Jun, QIU Li-Juan.
大豆[Glycine max (L.) Merr.]种子中含有约40%的蛋白, 是人类和动物食用植物蛋白的主要来源之一。大豆富含钙、铁、锌、镁和维生素B等多种重要营养元素[1], 与人体健康密切相关, 具有如降胆固醇[2,3]、降血压[4]、抗癌症[5]等功效。
根据沉降系数大小, 可将大豆蛋白分为2S、7S、11S、15S等组分[9]。大豆蛋白70%为贮藏蛋白, 主要由7S球蛋白(β-conglycinin)与11S大豆球蛋白(glycinin)构成。其中7S球蛋白约占大豆总蛋白的30%, 它的组成亚基α' (~76 kD)、α (~71 kD)、β (~52 kD)等是引起人类和动物过敏的主要致敏源[10]。已有研究发现, α' (~76 kD)蛋白亚基含硫氨基酸较少[11], α'亚基缺失型大豆比α'亚基正常型大豆的蛋白凝胶硬度大[12]。α'亚基缺失不仅有利于豆腐的加工, 而且对大豆制品营养品质、加工特性等具有积极影响[13,14], 因此, 控制7S球蛋白含量、培育α'亚基缺失材料已成为近年来大豆学科的重要研究方向之一。
日本****对大豆α'亚基缺失的研究较早。Kitamura等[15]于1981年从日本大豆种质资源中鉴定出α'亚基缺失种质“Keburi”以及α和β亚基低含量种质。Takahashi等[16]利用γ射线处理“Keburi”, 从诱变后代中筛选出α'和α亚基双缺材料及7S球蛋白低含量材料, 通过遗传分析证明, α'亚基缺失表型由一个单隐性基因cgy-1控制[17]。Teraishi等[18]从野生大豆资源中发现一份包含α'亚基整个7S亚基缺失的材料“QT2”, 并认为该性状由第20染色体上的一个显性位点Scg-1控制。国内****宋波等[19]和刘珊珊[20]等利用引自日本的α'+α亚基双缺失材料日B和当地栽培品种组配, 从后代中筛选出α'亚基、α'+α缺失等亚变异类型。我国关于α'亚基缺失材料的创制和遗传分子机制研究鲜见报道。
本研究利用SDS-PAGE技术, 从中品661的EMS突变体库[21]中筛选和创制α'亚基缺失种质中黄608; 利用该突变体和登科1号构建F2遗传分离群体, 并通过连锁分析将控制α'亚基基因定位在第10染色体上物理长度为1.77 Mb区间内, 进一步序列分析发现, 该突变体的α'亚基缺失可能是由Cgy-1基因新的等位变异控制, 并开发了分子标记。本研究为培育α'亚基缺失大豆新品系提供了优异种质材料和技术支撑。
1 材料与方法
1.1 遗传群体的构建
2016年夏季将大豆品种中品661的1000份M5代EMS诱变家系[21]播种于中国农业科学院作物所北京顺义试验基地。同时在内蒙古呼伦贝尔农业科学研究所试验地用α'亚基缺失突变体中黄608与当地主栽品种登科1号组配杂交组合, 在北京顺义种植获得F1种子, 并于当年冬季在海南加代种植收获F2种子。1.2 α'亚基缺失候选基因定位
从宋启建等[22]开发的SSR标记中, 随机选取均匀覆盖大豆20条染色体的540个标记。利用非变性聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳技术, 筛选出突变体中黄608和登科1号之间具有多态性的标记, 分别鉴定F2个体的基因型, 通过连锁分析确定α'亚基缺失相关基因的候选定位区间。1.3 大豆贮藏蛋白亚基组成聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳(SDS-PAGE)
选取亲本及F2籽粒, 在种脐背部磨取豆粉。称取0.5 mg豆粉放入2.0 mL离心管中, 加入0.5 mL蛋白提取液(0.2% SDS, 0.05 mol L-1 Tris-HCl pH 8.0, 0.01 mol L-1巯基乙醇, 1 g L-1溴酚蓝, 5 mol L-1 Urea)并振荡混匀, 于4℃环境下15,294×g离心10 min, 取上清液。蛋白电泳所需凝胶厚度为1 mm, 浓缩胶浓度和分离胶浓度分别为5%、12%。取5 μL蛋白提取液进行SDS-PAGE, 电泳结束进行考马斯亮蓝染色、脱色。后用5%甘油和玻璃纸封存、照相和分析。1.4 DNA提取、PCR扩增反应及产物测序
取幼嫩三出复叶, 利用CTAB法提取基因组DNA[23], 加200 μL灭菌水溶解, 经浓度检测后稀释为20 ng μL-1, 置-20℃冰箱保存备用。PCR体系包括5 μL DNA (20 ng μL-1)、2 μL dNTPs、2 μL buffer、0.2 μL EasyTaq酶和10.8 μL灭菌水。PCR扩增程序为95℃预变性5 min后, 经过34个循环的95℃变性30 s、55℃退火温度30 s和72℃延伸 20 s, 34个循环, 再经72℃ 5 min。从每个扩增样品分别取2 μL产物进行琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测, 同时将剩余样品送公司进行PCR测序。测序结果通过在线软件Multalin等比对分析(http://multalin. toulouse.inra.fr/multalin/multalin.html)。
1.5 引物设计及dCAPS标记开发
从NCBI数据库(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/)下载靶基因Cgy1的基因组序列, 以其为模板利用Primer3 (http://bioinfo.ut.ee/primer3-0.4.0/)设计引物Cgy1-A和Cgy1-B, 其对应PCR扩增产物长度分别为1598 bp和1702 bp, 可以覆盖Cgy-1基因组序列全长(表1)。Table 1
表1
表1基因Cgy-1 PCR扩增引物
Table 1
| 引物名称 Name | 引物序列 Sequence of primer (5'-3') | PCR产物长度 PCR product size (bp) | 退火温度 Annealing temperature (℃) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cgy1-A | Forward: AGCCCAAAACATTCACCAAC | 1598 | 58 |
| Reverse: AGGACTGTTGAGCTTGAGTGC | |||
| Cgy1-B | Forward: CGCCATACCCGTTAACAAAC | 1702 | 58 |
| Reverse: TTGTGGCAGGACATTGCTAC |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
基于突变体中黄608在基因Cgy1上存在的SNP位点, 利用在线软件dCAPS Finder 2.0 (http://helix. wustl.edu/dcaps/dcaps.html)开发一个分子标记。因含有Taq I内切酶识别位点T↓CGA序列, 以突变体中黄608基因组为PCR模板的扩增产物可被切割为2个片段, 而野生型中品661为模板的扩增产物因不含有此识别位点, 不能为Taq I内切酶切割, 仅有一个条带(表2)。10 μL酶切反应体系包含5 μL PCR产物、3 U Taq I内切酶和1.5 μL Cutsmart缓冲液。将酶切反应体系混匀, 放入37℃水浴锅温浴酶切1 h后, 用琼脂糖凝胶电泳(m V-1, 2%)检测, 80 V电压下运行1.5 h。扩增所需引物及限制性内切酶相关信息如表2所示。
Table 2
表2
表2dCAPS标记的引物序列和内切酶
Table 2
| 标记 Marker | 突变位点 SNP | 酶 Enzyme | 引物序列 Sequence of primer (5'-3') | 退火温度 Tm (℃) | PCR片段长度 PCR product Size (bp) | 酶切后片段长度 Product size after digestion by Taq I |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GM7S-1 | G/A | Taq I | F: TCTCATTTGGCATTGCGTATCG R: TTGACCTTCTTCGCATTCT | 55 | 158 | 158 bp/(138 bp+20 bp) |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
1.6 Western blot
取野生型中品661和突变体中黄608籽粒样品各5 mg, 研磨成豆粉分别加入500 μL提取液(0.05 mol L-1 Tris-HCl pH 8.0)提取总蛋白, 具体流程参考[24]。蛋白电泳需要凝胶厚度为0.75 mm, 分离胶(m V-1, 12.5%)和浓缩胶(m V-1, 5%)各2.5 mL。从制备好的蛋白样品中各取10 μL上样, 浓缩胶120 V电压运行半个小时, 转至140 V电压下运行1 h后结束电泳。随后, 切下分离胶并用半干转膜仪进行转膜, 所需滤纸及NC膜在转膜前用转膜液提前浸泡。25 V电压下转膜1 h, 将NC膜取出放在含有5 mL 5%牛奶的小盒中, 并放置在摇床上封闭1 h; 随后, 在盒子中加入1 μL一抗(1∶5000)(IP-IF小鼠多抗), 孵育1 h后将牛奶倒掉并加入5 mL PBST洗膜液, 置摇床上振荡(100 r min-1) 5 min, 连续洗3次。洗膜后加入5 mL的PBST和1 μL的二抗(1∶10,000), 孵育1 h后加入约5 mL的PBST冲洗, 连续冲洗3遍, 每次5 min; 最后加入光学显色剂显色, 扫描照相。1.7 统计分析
利用理论性卡方适合性测验分析F2群体α'亚基表型分离比例, $\chi^{2}=\sum\frac{(O-E)^{2}}{E}$, 其中O为观测值, E为期望值。利用学生氏t测验对野生型和突变体的11S/7S比值进行差异显著性分析。主要数据分析所用软件为Microsoft Excel 2013和SPSS 19.0。2 结果与分析
2.1 α'蛋白亚基缺突变体筛选及表型鉴定
大豆种子总蛋白电泳(SDS-PAGE)图谱中, 通常有7个蛋白条带比较清晰(图1-a, ZP661), 它们分别对应7S球蛋白的Lox、α、α'、β亚基和11S球蛋白的A3亚基、酸性亚基(Acidic)、碱性亚基(Basic)。利用SDS-PAGE技术, 从中品661的1055份M4代EMS诱变材料中筛选到1份α'亚基缺失材料, 命名为中黄608 (图1-a)。从后代株行表型鉴定结果进一步证实, α'亚基缺失突变体表型可以稳定遗传(图1-b)。图1
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图1α'亚基缺失突变体的表型鉴定
a: α'亚基缺失材料中黄608与野生型中品661的SDS-PAGE电泳结果。b: 中黄608子代株行的α'亚基表型鉴定结果, 1~8分别为8个子代。
Fig. 1Phenotype of the α' protein subunit mutant by SDS-PAGE
a: protein profiles of the α' subunit deletion mutant ZH608 and the wild-type ZP661 by SDS-PAGE. b: α' subunit mutant trait of ten individuals derived from ZH608 validated by SDS-PAGE (lanes 1-8).
2.2 α'亚基缺失突变体中黄608的遗传分析
为了明确中黄608 α'亚基缺失性状的遗传方式, 构建了该突变体与大豆品种登科1号的F2遗传分离群体。SDS-PAGE鉴定结果显示, 杂交F1籽粒均含有α'亚基, 表型与登科1号一致。210个F2籽粒中, α'亚基缺失材料64粒, α'亚基正常146粒。经卡方检验, F2遗传分离群体中, α'亚基正常与缺失籽粒比例符合3∶1 (χ2 = 1.43, P = 0.08), 证明中黄608的籽粒α'亚基缺失性状是由一对隐性单基因控制(表3)。Table 3
表3
表3α'亚基缺失突变体F2群体遗传分析
Table 3
| 表型 Phenotype | 观测值 Observed value | 期望值 Excepted value | χ2(3:1) | P值 P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 突变体(α'亚基缺失) Mutant (α' subunit deletion) | 64 | 53 | 1.43 | 0.08 |
| 野生型 Wild type | 146 | 157 | ||
| 共计 Total | 210 | 210 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
2.3 α'亚基缺失突变体Cgy-1基因定位与候选基因筛选
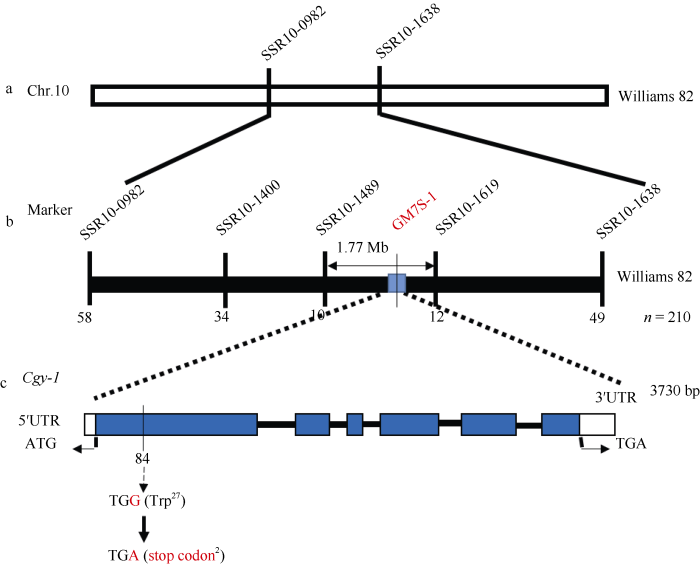
选取均匀覆盖大豆基因组20条染色体540对SSR标记, 通过PCR反应和聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳筛选出亲本间具有多态性的84个标记。利用集团分离分析法(BSA)和F2突变个体, 将α'亚基基因定位在第10染色体标记SSR10_0982和SSR10_1638之间(图2-a)。通过进一步的多态性标记加密和基因型检测, 将定位区间缩小至标记SSR10_1489和SSR10_1612之间, 区间物理长度为1.77 Mb (图2-b)。图2
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图2α'亚基缺失突变体的基因定位
a: 用210个F2单株将候选基因Cgy-1定位到标记SSR10-0982与SSR10-1638之间。b: 通过多态性标记筛选和加密, 将候选基因定位区间缩小至SSR10-1489与SSR10-1619之间。c: 突变体中黄608在Cgy-1基因第1外显子的第84位碱基发生突变(核苷酸G变为A), 造成编码氨基酸序列的提前终止。蓝色方框代表外显子, 白色方框代
Fig. 2Genetic and physical mapping of the α' subunit deletion mutant Zhonghuang 608
a: the candidate gene Cgy-1 was mapped to between SSR marker SSR10-0982 and SSR10-1638 by using 210 F2 individuals. b: the candidate interval was reduced to SSR10-1489 and SSR10-1619 by SSR polymorphic markers. c: the mutation of eighty-fourth bases at the first exon of Cgy-1 gene in the mutant Zhonghuang 608, resulted in pre-terminating of encoding amino acid. Blue boxes, white boxes, and black lines represent exons, 5' UTR/3' UTR and introns, respectively.
查询大豆Williams 82参考基因组, 该定位区间内注释编码蛋白的基因有190个。其中基因Cgy-1 (Glyma.10G264300)在NCBI数据库的功能注释为与α'亚基蛋白编码有关(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ gene/?term=Cgy-1), Harada等[25]研究发现Cgy-1是编码α'亚基的唯一基因, 而且该基因在大豆籽粒中高表达, 推测该基因可能也是引起中黄608 α'亚基缺失的候选基因。
2.4 Cgy-1基因新等位变异位点的鉴定
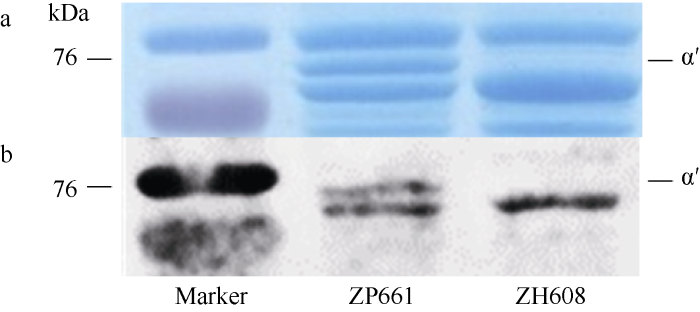
在参考基因组中, Cgy-1 基因全长2730 bp, 包含6个外显子和5个内含子, 其中CDS序列全长1866 bp, 编码621个氨基酸。根据Cgy-1基因组序列, 我们设计2对引物Cgy1-F1和Cgy1-R1, 并对野生型中品661和α'亚基缺失突变体中黄608基因组DNA分别进行PCR扩增。PCR产物测序结果显示, 中黄608与野生型在Cgy-1基因组序列第一外显子上第84位核苷酸发生了变异, 由G变为了A, 导致密码子TGG (色氨酸)变成TGA (终止子), 翻译出氨基酸长度为27个, 显著短于野生型621个。推测基因Cgy-1截短的异常氨基酸序列可能造成了大豆籽粒蛋白中α'亚基缺失(图3-a)。利用合成的抗体对野生型中品661和α'亚基缺失突变体中黄608进行免疫印迹检测(Western blot)也显示, 野生型中品661在76 kD位置有2个条带, 而α'亚基缺失突变体中黄608在76 kD对应位置缺失相应的一条α'亚基蛋白条带(图3-b), 进一步证实Cgy-1的基因组序列改变与中黄608 α'亚基缺失表型相关。图3
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图3野生型和突变体的SDS-PAGE (a)和Western blot (b)实验结果
a: SDS-PAGE电泳结果显示突变体中黄608 (ZH608)缺少α'亚基条带。b: Western blot结果: 抗体杂交结果表明野生型(ZH608)有2条带; 突变体(ZP661)缺失了α'亚基条带。
Fig. 3SDS-PAGE (a) and Western blot (b) results of mutants and wild type
a: the result of SDS-PAGE showed that the mutant ZH608 lacked α' subunit. b: in antibody hybridization results showed that the wild type (ZH608) had two bands and the mutant (ZP661) lacked the α' subunit band.
2.5 dCAPS分子标记开发及其在F2群体中的应用
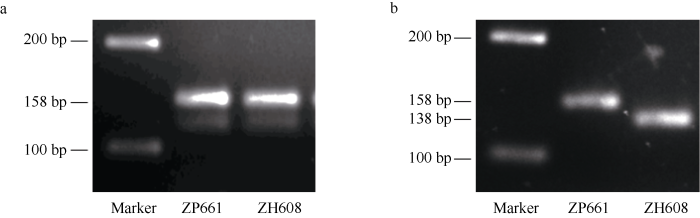
基于中黄608中Cgy-1基因上新的点突变, 本研究开发了一个dCAPS分子标记(命名为GM7S-1)。利用其对应引物(表2)分别扩增中黄608和野生型中品661基因组DNA, PCR产物长度均为158 bp (图4-a), 但是中黄608 的扩增条经Taq I限制性内切酶消化后, 产生长度为138 bp和20 bp (图4-b)的2个片段, 而野生型158 bp的PCR扩增产物不能被该内切酶所消化。因而, 该 dCAPS标记可准确区分野生型和α'亚基缺失突变体中黄608。图4
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图4dCAPS分子标记开发
a: 引物GM7S-1分别扩增野生型及突变体, PCR产物为150 bp的单一条带。b: ZH608的扩增产物被Taq I酶酶切为2条更小的片段。
Fig. 4A agarose detection for amplified products and enzyme products
a: the single fragment was detected for the amplified PCR product of both the wild type and the mutant by the primer GM7S-1. b: the PCR product of ZH608 was cleaved into two smaller fragments by the restriction enzyme Taq I.
在此基础之上, 利用标记GM7S-1对中黄608与登科1号杂交组合的210个F2子代进行基因型检测显示, 64个α'亚基缺失个体的PCR产物均可以被酶切为2个片段, 为纯合突变基因型A; 146个α'亚基正常个体中, 80个F2的PCR产物完全不能被酶切, 为纯合野生型基因型G, 另外有66个F2的PCR产物可以部分被Taq I酶切, 为杂合基因型G/A(H)(图5)。由前述结果可知, F2个体的基因型与α'亚基表型表现一致。因此, 该dCAPS分子标记可用于α'亚基缺失表型的分子辅助鉴定。
图5
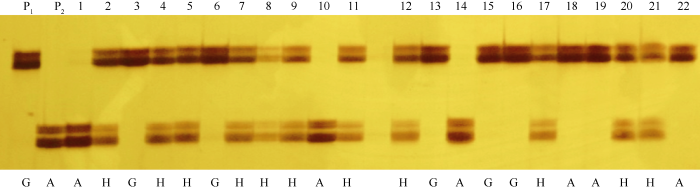 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图5F2代dCAPs标记基因型检测结果
P1, P2为亲本; G为野生型基因型(父本), A为突变基因型(母本), H为杂合基因型。
Fig. 5Genotyping of some F2 individuals by the dCAPS marker
P1 is the female parent, and P2 male parent. G, A, and H represent the wild type, mutant, and heterozygous genotype, respectively.
2.6 α'亚基缺失与11S/7S比值关系
α'亚基缺失材料中黄608的11S/7S比值为2.52, 显著高于野生型中品661 (2.04)(t = 14.7, P < 0.0001)。在中黄608与登科1号杂交组合的F2群体中, 64份α'亚基缺失材料的11S/7S平均值为2.73, 同样要显著高于146份α'亚基正常个体, 后者平均值为1.75 (t = 11.76, P < 0.0001)(图6)。可见, 作为7S大豆球蛋白的重要构成因子, α'亚基的缺失可以引起7S总量的减少, 进而改变11S/7S比值。图6
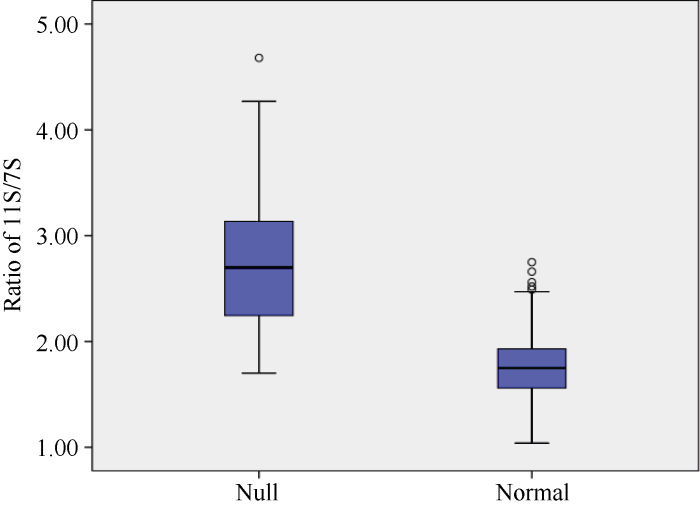 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图6F2群体α'亚基缺失和α'亚基正常材料11S/7S比值分布
Fig. 6Distribution of 11S/7S ratio for materials with and without α' subunit in F2 population
3 讨论
7S球蛋白α'亚基的缺失可以提高豆腐的凝胶硬度[26], 同时也能降低致敏性。因此, 筛选α'亚基缺失材料对提高大豆营养价值利用效率和改善其加工性能均十分重要。目前, 国内创制的大豆α'亚基缺失材料, 主要是利用国外材料与国内品种杂交选育的。例如, 刘珊珊[27]、宋波等[28]利用从日本引进的(α'+α)亚基缺失品种“日B”与黑龙江主栽品种东农47杂交, 从中筛选出α'缺失、A3缺失和α'+α亚基缺失等多种蛋白亚基变异类型材料。研究发现, 这些亚基缺失材料携带了不利基因位点, 多表现为萎黄病, 甚至发生致死, 不利于在大豆育种中进一步利用[29]。我国从α'亚基缺失材料变异中筛选的仅有几例[30,31], 尚不能满足α'亚基缺失品系选育需要。本研究中的α'亚基缺失材料中黄608是从高产、高油优良大豆品种中品661的化学诱变后代中筛选而来, 表现为α'亚基缺失表型但无黄化致死等不良性状, 为大豆蛋白品质改良提供了宝贵的材料。目前, 已报道的α'亚基缺失的等位基因有限。Kim等[32]研究发现, ‘Keburi’ α'亚基缺失表型可能与Cgy-1整个基因及不完整串联重复序列的12,998 bp删除相关。张国敏[33]从2份α'亚基缺失材料中分别克隆Cgy-1基因, 发现二者cDNA序列的361 bp和529 bp处均发生小片段缺失, 推测该基因的突变导致了α'亚基缺失。本研究则发现, Cgy-1基因组因第84位碱基发生了突变, 使编码氨基酸序列提前终止, 导致中黄608的α'亚基缺失表型。在此基础上, 我们利用鉴定出的Cgy-1基因的新等位变异位点开发了分子标记。为α'亚基缺失表型的分子标记辅助育种提供了新材料和技术支持。与前人研究结果类似[34], 本研究发现中黄608因α'亚基缺失, 导致11S/7S比值变大, 并且蛋白质含量较野生型表现一定程度增加, 然而, α'亚基缺失对大豆籽粒总蛋白含量的影响以及二者相互关系还有待进一步研究[35]。
4 结论
利用α'亚基缺失突变体中黄608构建的F2群体, 通过连锁分析将控制α'亚基合成基因Cgy-1定位在Chr10标记SSR10_1489和SSR10_1612之间1.77 Mb的区间内。Cgy-1基因第84位碱基的突变, 导致编码氨基酸的提前终止。推测这是α'亚基的缺失的原因。参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
DOI:10.1080/030144601300119061URLPMID:11352858 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract Many experimental but few epidemiological studies have suggested that soyfoods and their constituents have cancer-inhibitory effects on breast cancer. No epidemiological study has evaluated the association of adolescent soyfood intake with the risk of breast cancer. To evaluate the effect of soyfood intake during adolescence, one of the periods that breast tissue is most sensitive to environmental stimuli, on subsequent risk of breast cancer, we analyzed data from a population-based case-control of 1459 breast cancer cases and 1556 age-matched controls (respective response rates were 91.1% and 90.3%). Information on dietary intake from ages 13-15 years was obtained by interview from all study participants and, in addition, from mothers of subjects less than 45 years of age (296 cases and 359 controls). Odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) derived from unconditional logistic models were used to measure soyfood intake and breast cancer risk. After adjustment for a variety of other risk factors, adolescent soyfood intake was inversely associated with risk, with ORs of 1.0 (reference), 0.75 (95% CI, 0.60-0.93), 0.69 (95% CI, 0.55-0.87), 0.69 (95% CI, 0.55-0.86), and 0.51 (95% CI, 0.40-0.65), respectively, for the lowest to highest quintiles of total soyfood intake (trend test, P < 0.001). The inverse association was observed for each of the soyfoods examined and existed for both pre- and postmenopausal women. Adolescent soyfood intakes reported by participants' mothers were also inversely associated with breast cancer risk (P for trend < 0.001), with an OR of 0.35 (95% CI, 0.21-0.60) for women in the highest soyfood intake group. Adjustment for rice and wheat products, the major energy source in the study population, and usual adult soyfood intake did not change the soyfood associations. Our study suggests that high soy intake during adolescence may reduce the risk of breast cancer in later life.
DOI:10.1021/jf025642fURLPMID:12236704 [本文引用: 1]

To know whether isoflavones are responsible for the hypocholesterolemic effect of soy protein, the effect on plasma cholesterol of isoflavone-free soy protein prepared by column chromatography was examined in rats. Five-week-old male Sprague鈭扗awley rats were fed cholesterol-enriched AIN-93G diets containing either 20% casein (CAS), 20% soy protein isolate (SPI), 20% isoflavone-free SPI (IF-SPI), 19.7% IF-SPI + 0.3% isoflavone-rich fraction (isoflavone concentrate, IC), or 20% CAS + 0.3% IC for 2 weeks. Plasma total cholesterol concentrations of rats fed SPI and IF-SPI were comparable and were significantly lower than that of rats fed CAS. The addition of IC to the CAS and IF-SPI did not influence plasma cholesterol level. Fecal steroid excretion of the three SPI groups was higher than that of the two CAS groups, whereas the addition of IC showed no effect. Thus, a significant fraction of the cholesterol-lowering effect of SPI in rats can be attributed to the protein content, but the isoflavones and other ...
DOI:10.1038/sj.ijo.0802967URLPMID:15987841 [本文引用: 1]

Our previous studies showed that intake of 20% alcohol-washed soy protein isolate (SPI) significantly increased hepatic thyroid hormone receptor (TR) beta1 protein content in rats. However, whether SPI influences the binding ability of TR to its target genes is unknown. The purpose of this study was to examine the effect of increasing amounts of dietary SPI on hepatic TRbeta1 content and the binding of TR to thyroid hormone response element (TRE) in rats. Sprague-Dawley rats (28 d old) were fed diets containing casein (20%) with or without isoflavone supplementation (50 mg/kg diet) or alcohol-washed SPI (5, 10, or 20%) for 90 d. The hepatic TRbeta1 protein content was measured by Western blot, and the binding ability of TR to DNA was examined by electrophoretic mobility shift assay. Consumption of the 20% SPI diet increased pancreatic relative weight and decreased spleen relative weight. Intake of SPI markedly elevated TRbeta1 content in both male and female rats compared with a casein-based control diet. The increase in TRbeta1 in females was much higher than that in males. Interestingly, the binding abilities of TR to DNA were significantly inhibited by increasing amounts of dietary SPI in female rats. In conclusion, this study shows for the first time that dietary SPI increases hepatic TRbeta1 protein content and inhibits the binding of TR to target genes. Modulation of hepatic TRbeta1, a key regulator of gene expression involved in lipid metabolism, by SPI may be a novel mechanism by which soy components lower blood lipid level and exert their hypocholesterolemic actions.
DOI:10.1021/jf048174dURLPMID:15853374 [本文引用: 1]

Angiotensin I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory activity was determined in the soy protein isolate (SPI) digest produced by in vitro pepsin-pancreatin sequential digestion. The inhibitory activity was highest within the first 20 min of pepsin digestion and decreased upon subsequent digestion with pancreatin. An IC(50) value of 0.28 +/- 0.04 mg/mL was determined after 180 min of digestion, while no ACE inhibitory activity was measured for the undigested SPI at 0.73 mg/mL. Chromatographic fractionation of the SPI digest resulted in IC(50) values of active fractions ranging from 0.13 +/- 0.03 to 0.93 +/- 0.08 mg/mL. Although many of the fractions showed ACE inhibition, peptides with lower molecular masses and higher hydrophobicities were most active. The findings show that many different peptides with ACE inhibitory activities were produced after in vitro pepsin-pancreatin digestion of SPI and lead to the speculation that physiological gastrointestinal digestion could also yield ACE inhibitory peptides from SPI.
DOI:10.1016/j.peptides.2005.01.010URLPMID:15808899 [本文引用: 1]

Previously, we found that orally administered soymetide-4 (MITL), an immunostimulating peptide derived from soybean β-conglycinin α′ subunit, suppressed alopecia induced by the anti-cancer drug etoposide in neonatal rats. Soymetide-4 has weak affinity for N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine (fMLP) receptor. fMLP showed an anti-alopecia effect after intraperitoneal administration, though it was inactive after oral administration. Anti-alopecia effect of fMLP was blocked by pyrilamine or cimetidine, antagonists for histamine H 1 or H 2 receptor, respectively. However, the anti-alopecia effect of soymetide-4 was not inhibited by the histamine antagonists but by indomethacin, an inhibitor of cyclooxygenase (COX), or AH-23848B, an antagonist of the EP 4 receptor for PGE 2. Anti-alopecia effect of soymetide-4 was also blocked by pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate, an inhibitor of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB). These results suggest that PGE 2, which is produced after activation of COX by soymetide-4, might suppress apoptosis of hair matrix cells and etoposide-induced alopecia by activating NF-κB.
DOI:10.1038/sj.ijo.0802613URLPMID:15113974

Abstract Food allergy is a relatively rare and sometimes violent reaction of the immune system to food proteins. The first report characterizing soy allergy appeared in 1934. The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations includes soy in its list of the 8 most significant food allergens. At least 16 potential soy protein allergens have been identified but their relative clinical significance is unknown. Conversely, soy has a long history of successful use in managing cow's milk allergies in infants. To better predict the utility of soy proteins for controlling food allergy, it is important to understand the relative allergenic reactivity of soy compared with other major food proteins. This can be studied using clinical data, animal models, and biochemical approaches; all show diminished reactivity for soy. Clinical studies using in vitro methods and blinded food challenges have generated substantial information. Study populations include high-risk asymptomatic infants and patients with atopic symptoms, positive food challenges, and specific milk allergies. Generally, these studies show lower allergic reactivity for soy proteins vs. other food allergens. Comparisons of food allergen dose-response relationships for triggering allergic symptoms also demonstrate a higher protein concentration threshold for soy (approximately 100 times), indicating lower allergenic reactivity. Extensive investigations of soy immunological reactivity have also been carried out using animal models. Consistent with clinical results, all of these data show substantially diminished immunological reactivity for soy proteins. Biochemical and immunochemical analyses indicate no striking differences between soy and other food proteins that would explain these unexpected differences in allergenic reactivity.
DOI:10.1080/87559129109540915URL

The most important chemical reactions during the process of soybean protein foods are the intermolecular reactions among the residues exposed on the surface of the protein molecules through the denaturation process. In native soybean protein molecules, most amino acid residues responsible for the reactions—such as cysteine (‐SH), cystine (S‐S), and hydrophobic amino acid residues—are buried in the inside region of the molecule, inaccessible to water. These residues become reactable with each other through the exposure from the inside by heat denaturation during processing. The unique textures of soybean protein foods, such as tofu, kori‐tofu, yuba, and texturized products produced by extruder, etc., are the results of both the intermolecular interchange reaction between the exposed ‐SH and S‐S groups and the intermolecular hydrophobic reaction among the exposed hydrophobic amino acid residues. The exposure of amino acid residues is also important for the hydrolysis of soybean proteins by enzymes, through which soy sauce is produced, because the cleavage of the peptide bonds is carried out after binding between the active sites of the enzymes and the enzyme‐specific amino acid residues exposed through denaturation. These facts indicate the importance of the three‐dimensional structures of soybean protein molecules in the technology of soybean protein foods. Recently great progress has been made in the manufacturing techniques of soybean protein foods, such as soy milk, tofu, abura‐age, textured protein products, and soy sauce. The quality of soy milk and tofu was very much improved by controlling the action of the biologically active substances such as lipoxygenases and β‐glucosidases which are contained in soybeans and responsible for the production of off‐flavor. A new abura‐age, whose texture does not deteriorate during frozen storage or drying, was developed by using soybean protein isolate and oil as materials. A new type of textured protein product was also developed: a deep‐fat‐fried nugget with unique texture and flavor. This product is textured through a twin‐type extruder. For soy sauce manufacturing new biotechnology has been applied on the pilot‐plant scale. This is a system of continuous fermentation through bioreactors with the immobilized whole cells of microorganisms, by which the fermentation term is shortened strikingly. New and important discoveries were made on the nutrition of soybean proteins. According to recent experiments using human beings, the amino acid score of soybean proteins is 100 for persons more than 2 years old, indicating that the nutritive value of soybean proteins is equal to animal proteins. Further, it was elucidated that soybean proteins have cholesterol‐lowering action. A discussion is presented on the future of the soybean protein foods.
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1003-7969.2008.08.009URL

以4个蛋白亚基变异类型大豆品种(系)制备的分离蛋白和南农大黄豆粗7S蛋白为材料,以亚基正常品种南农大黄豆制备的分离蛋白为对照,对其溶解性、凝胶质构特性、乳化性、乳化稳定性以及DSC特性进行了测定。结果表明,11S组分单个亚基缺失对大豆蛋白的溶解性、乳化性、乳化稳定性和热稳定性影响不显著;11S组分含量显著降低或缺失能提高大豆蛋白的乳化性和乳化稳定性,但降低大豆蛋白变性温度和变性焓;在凝胶质构特性方面,7S组分含量与凝胶弹性呈显著正相关,11S组分含量与凝胶内聚性呈极显著正相关,与凝胶硬度、胶黏性和破裂强度呈显著正相关,与凝胶弹性呈极显著负相关。
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1003-7969.2008.08.009URL

以4个蛋白亚基变异类型大豆品种(系)制备的分离蛋白和南农大黄豆粗7S蛋白为材料,以亚基正常品种南农大黄豆制备的分离蛋白为对照,对其溶解性、凝胶质构特性、乳化性、乳化稳定性以及DSC特性进行了测定。结果表明,11S组分单个亚基缺失对大豆蛋白的溶解性、乳化性、乳化稳定性和热稳定性影响不显著;11S组分含量显著降低或缺失能提高大豆蛋白的乳化性和乳化稳定性,但降低大豆蛋白变性温度和变性焓;在凝胶质构特性方面,7S组分含量与凝胶弹性呈显著正相关,11S组分含量与凝胶内聚性呈极显著正相关,与凝胶硬度、胶黏性和破裂强度呈显著正相关,与凝胶弹性呈极显著负相关。
DOI:10.1016/0003-9861(56)90007-8URLPMID:13341041 [本文引用: 1]

Ultracentrifuge studies of the water-extractable soybean proteins reveal the presence of four resolvable fractions having s 20,w values of approximately 2, 7, 11, and 15 S. An unresolvable fraction having an an s 20,w value greater than 15 S is also present. Ultracentrifugal analyses of the proteins extracted by various concentrations of sodium chloride and calcium chloride show that the decreased extractability of soybean protein at intermediate concentrations of salts is due primarily to the decreased solubility of the 11 S and 15 S fractions and of the unresolvable fraction. The decrease in extractability of these fractions is more pronounced with calcium chloride than with sodium chloride. Estimates were made of the amount of each fraction extractable at the different salt concentrations.
DOI:10.1021/jf802451gURLPMID:19138084 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract Soybeans are recognized as one of the "big 8" food allergens. IgE antibodies from soybean-sensitive patients recognize more than 15 soybean proteins. Among these proteins only the alpha-subunit of beta-conglycinin, but not the highly homologous alpha'- and beta-subunits, has been shown to be a major allergenic protein. The objective of this study was to examine if the alpha'- and beta-subunits of beta-conglycinin can also serve as potential allergens. Immunoblot analysis using sera collected from soybean-allergic patients revealed the presence of IgE antibodies that recognized several soy proteins including 72, 70, 52, 34, and 21 kDa proteins. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF) analysis of trypsin-digested 72, 70, and 52 kDa proteins indicated that these proteins were the alpha'-, alpha-, and beta-subunits of beta-conglycinin, respectively. Additionally, purified alpha'-, alpha-, and beta-subunits of beta-conglycinin were recognized by IgE antibodies present in the soybean-allergic patients. The IgE reactivity to the beta-subunit of beta-conglycinin was not abolished when this glycoprotein was either deglycosylated using glycosidases or expressed as a recombinant protein in Escherichia coli . The results suggest that in addition to the previously recognized alpha-subunit of beta-conglycinin, the alpha'- and beta-subunits of beta-conglycinin also are potential food allergens.
URL [本文引用: 1]

主要介绍大豆7S和11S球蛋白的结构和功能性质,大豆蛋白质各个成分的分子量有所不同,按超速离心分离系数可分为2S,7S11S和15S4个组份。7S组份占总蛋白质的30.9%,它是由4种不同大豆蛋白民组成,11S组份占总大豆蛋白质的41%,而且都是单一的11S球蛋白,11S球蛋白的等电点为pH4.64。
URL [本文引用: 1]

主要介绍大豆7S和11S球蛋白的结构和功能性质,大豆蛋白质各个成分的分子量有所不同,按超速离心分离系数可分为2S,7S11S和15S4个组份。7S组份占总蛋白质的30.9%,它是由4种不同大豆蛋白民组成,11S组份占总大豆蛋白质的41%,而且都是单一的11S球蛋白,11S球蛋白的等电点为pH4.64。
DOI:10.1271/bbb.68.1091URLPMID:15170114 [本文引用: 1]

The effects of protein concentration, and heating temperature and time on the gelling properties of soybean β-conglycinin (7S globulins) lacking the α or α′ subunit were compared with those of 7S containing all three subunits (α, α′, and β) to determine whether each subunit contributes equally. In most of the conditions, the relative order of gel hardness was α′-lacking > 7S > α-lacking. From Fourier transform infrared studies, the secondary structure change after heating was very similar among the three samples; thus, the secondary structural change is not the reason for the differences in gel hardness. By using scanning electron microscopy, we observed differences in strand thickness and the density of the gel network among the three samples. These differences correlated well with the differences in gel hardness.
DOI:10.1080/87559129109540916URL [本文引用: 1]

The complete amino acid sequence of plant storage protein molecules has been determined over the past decade by sequence analysis of full‐length cDNA and genomic clones for most cereal and legume seeds. At the same time, knowledge on the biosynthesis of the storage proteins has also been accumulated at the molecular level. According to the data on the gene structures of the plant storage proteins, the homology of their amino acid sequences, and the mechanisms of their accumulation into the protein bodies in the biosynthesis, the storage proteins which are classified as glutelins by a traditional sequential extraction method should be classified as either globulins or prolamins on the basis of the molecular structures. For instance, both orizenin, the rice main storage protein, and glutenin, the most important protein component of wheat proteins, have been classified as glutelins, but they should be classified as globulins and prolamins from the molecular base standpoint, respectively. The amino acid sequences of 7S and 11S globulins of legumes such as soybeans, peas, kidney beans, etc., showed considerable sequence homology and predicted secondary structural identity among 7S globulins or among 11S globulins. In addition, there was a high degree of re‐latedness on the secondary structures, even between the 7S and 11S globulins. The 11S‐type globulins exist widely, not only in legumes, but also in sesame, rape seed, rice, oat, pumpkin, etc. Furthermore, the amino acid sequences of these globulins showed quite a high homology each other. These facts indicate that the 11S globulins, which are distributed very widely among the different species, have all evolved from a common origin. The storage proteins of corn, wheat, rye, and barley are the typical prolamins, of which amino acid sequences are quite different from those of the globulin. The characteristic structural feature of the prolamin molecules is the presence of a repetitive peptide structure in their polypeptide chains. The functional properties of storage proteins and their mechanisms are described at the molecular level both from the gelation of soybean 7S and 11S globulins, and from the viscoelastic properties of the high molecular weight (HMW) subunits of wheat glutenin. In the gel formation of 7S globulins, no ‐SH/S‐S interchange reaction participates and therefore the gels are soft and transparent, whereas in the gel formation of 11S globulins, the interchange reaction participates, which makes the resultant gels firm and turbid. In addition, the subunit compositions of the 11S globulin molecules markedly effect the hardness, turbidity, and rates of gelation of the 11S gels. The viscoelastic properties of wheat HMW subunit are ascribed to the β‐spiral structures of the repetitive central domain, which are assembled into long linear polymers through covalent crosslinks via cysteine residues between the ‐NH2 and ‐COOH termini. A discussion on the improvement of the plant storage proteins as food by genetic engineering techniques is presented.
DOI:10.1080/87559129109540915URL [本文引用: 1]

The most important chemical reactions during the process of soybean protein foods are the intermolecular reactions among the residues exposed on the surface of the protein molecules through the denaturation process. In native soybean protein molecules, most amino acid residues responsible for the reactions—such as cysteine (‐SH), cystine (S‐S), and hydrophobic amino acid residues—are buried in the inside region of the molecule, inaccessible to water. These residues become reactable with each other through the exposure from the inside by heat denaturation during processing. The unique textures of soybean protein foods, such as tofu, kori‐tofu, yuba, and texturized products produced by extruder, etc., are the results of both the intermolecular interchange reaction between the exposed ‐SH and S‐S groups and the intermolecular hydrophobic reaction among the exposed hydrophobic amino acid residues. The exposure of amino acid residues is also important for the hydrolysis of soybean proteins by enzymes, through which soy sauce is produced, because the cleavage of the peptide bonds is carried out after binding between the active sites of the enzymes and the enzyme‐specific amino acid residues exposed through denaturation. These facts indicate the importance of the three‐dimensional structures of soybean protein molecules in the technology of soybean protein foods. Recently great progress has been made in the manufacturing techniques of soybean protein foods, such as soy milk, tofu, abura‐age, textured protein products, and soy sauce. The quality of soy milk and tofu was very much improved by controlling the action of the biologically active substances such as lipoxygenases and β‐glucosidases which are contained in soybeans and responsible for the production of off‐flavor. A new abura‐age, whose texture does not deteriorate during frozen storage or drying, was developed by using soybean protein isolate and oil as materials. A new type of textured protein product was also developed: a deep‐fat‐fried nugget with unique texture and flavor. This product is textured through a twin‐type extruder. For soy sauce manufacturing new biotechnology has been applied on the pilot‐plant scale. This is a system of continuous fermentation through bioreactors with the immobilized whole cells of microorganisms, by which the fermentation term is shortened strikingly. New and important discoveries were made on the nutrition of soybean proteins. According to recent experiments using human beings, the amino acid score of soybean proteins is 100 for persons more than 2 years old, indicating that the nutritive value of soybean proteins is equal to animal proteins. Further, it was elucidated that soybean proteins have cholesterol‐lowering action. A discussion is presented on the future of the soybean protein foods.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1007/BF00266899URLPMID:24259062 [本文引用: 1]

A cultivar lacking the glycinin subunit A 5 A 4 B 3 (‘Raiden’) was crossed with one lacking the α′-subunit of β -conglycinin (‘Keburi’). Analysis of F 2 and F 3 progeny indicated that the missing bands of the A 5 A 4 B 3 and the α′-subunit were each controlled by a recessive allele of two independently segregating genes. Gene symbols Gy 4 / gy 4 and Cgy 1 / cgy 1 were proposed for the genes which confer the presence or absence of the glycinin and conglycinin subunits, respectively.
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1006.2012.02297URL [本文引用: 1]

7S球蛋白α'与α亚基是大豆种子贮藏蛋白的重要组分,是影响大豆营养价值与加工品质的重要因子,同时还是主要的大豆致敏原,降低它们的含量是大豆品质改良育种的最新研究热点之一。以日本育种材料7S球蛋白(α'+α)-亚基双缺失型日B为供体亲本,黑龙江省主栽大豆品种东农47为受体亲本,采用回交转育方法,将α'与(α'+α)-亚基缺失特性导入东农47。结果表明,α'-缺失型(Cc)和(α'+α)-双缺失型(Cd)品系均能正常生长、结实,并能稳定遗传;Cc、Cd产量组分性状的平均值均远高于轮回亲本,蛋白质含量平均值均高于双亲,部分Cd株系籽粒蛋白质总量高达46.7%,脂肪含量平均值介于双亲之间,略高于日B;导入α'-缺失和(α'+α)双缺失性状后,绝大多数氨基酸组分含量和氨基酸总量提高,其中精氨酸和天门冬氨酸平均含量变幅最大。Cd株系籽粒含硫氨基酸含量(蛋氨酸与胱氨酸之和)及氨基酸总量分别比东农47高出0.11和5.56个百分点。说明通过常规育种重组α'-缺失或(α'+α)-双缺失性状即可提高大豆含硫氨基酸含量,并提高其他氨基酸组分含量及氨基酸总量,在Cc、Cd的BC2F3后代群体中有望筛选到α'-缺失或α'与α同时缺失的高产、高含硫氨基酸、优质大豆新品种。
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1006.2012.02297URL [本文引用: 1]

7S球蛋白α'与α亚基是大豆种子贮藏蛋白的重要组分,是影响大豆营养价值与加工品质的重要因子,同时还是主要的大豆致敏原,降低它们的含量是大豆品质改良育种的最新研究热点之一。以日本育种材料7S球蛋白(α'+α)-亚基双缺失型日B为供体亲本,黑龙江省主栽大豆品种东农47为受体亲本,采用回交转育方法,将α'与(α'+α)-亚基缺失特性导入东农47。结果表明,α'-缺失型(Cc)和(α'+α)-双缺失型(Cd)品系均能正常生长、结实,并能稳定遗传;Cc、Cd产量组分性状的平均值均远高于轮回亲本,蛋白质含量平均值均高于双亲,部分Cd株系籽粒蛋白质总量高达46.7%,脂肪含量平均值介于双亲之间,略高于日B;导入α'-缺失和(α'+α)双缺失性状后,绝大多数氨基酸组分含量和氨基酸总量提高,其中精氨酸和天门冬氨酸平均含量变幅最大。Cd株系籽粒含硫氨基酸含量(蛋氨酸与胱氨酸之和)及氨基酸总量分别比东农47高出0.11和5.56个百分点。说明通过常规育种重组α'-缺失或(α'+α)-双缺失性状即可提高大豆含硫氨基酸含量,并提高其他氨基酸组分含量及氨基酸总量,在Cc、Cd的BC2F3后代群体中有望筛选到α'-缺失或α'与α同时缺失的高产、高含硫氨基酸、优质大豆新品种。
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1007-9084.2008.03.004URL [本文引用: 1]

以7S球蛋白亚基组成各异的稀有大豆种质为试材,系统分析了7s球蛋白三个主要亚基(α’-、α-和β-亚基)的相对含量与品质性状之问的相关性。结果表明:(1)α’-亚基的相对含量与蛋白质总量呈显著负相关;α’-与α-亚基的相对含量与氨基酸组份间的负相关多数达到显著或极显著水平;β-亚基的相对含量与蛋氨酸、胱氨酸和精氨酸的含量呈显著正相关,与苏氨酸呈极显著正相关。(2)脂肪含量与α’-、β-亚基的相对含量呈显著负相关,与α-亚基的相对含量呈显著正相关;α'-亚基的相对含量与亚麻酸的含量呈极显著正相关;α-亚基的相对含量与棕榈酸呈显著负相关,与亚油酸含量呈显著正相关,与硬脂酸和亚麻酸含量呈极显著正相关。(3)亚基组成表现分别为(α’+α)-亚基缺失和α'-亚基缺失的日B-1和日A-5是具有较大育种潜力的优异种质。(4)通过遗传学的手段调整亚基含量,是选育“双高”(高蛋白、高脂肪)品种的新思路。
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1007-9084.2008.03.004URL [本文引用: 1]

以7S球蛋白亚基组成各异的稀有大豆种质为试材,系统分析了7s球蛋白三个主要亚基(α’-、α-和β-亚基)的相对含量与品质性状之问的相关性。结果表明:(1)α’-亚基的相对含量与蛋白质总量呈显著负相关;α’-与α-亚基的相对含量与氨基酸组份间的负相关多数达到显著或极显著水平;β-亚基的相对含量与蛋氨酸、胱氨酸和精氨酸的含量呈显著正相关,与苏氨酸呈极显著正相关。(2)脂肪含量与α’-、β-亚基的相对含量呈显著负相关,与α-亚基的相对含量呈显著正相关;α'-亚基的相对含量与亚麻酸的含量呈极显著正相关;α-亚基的相对含量与棕榈酸呈显著负相关,与亚油酸含量呈显著正相关,与硬脂酸和亚麻酸含量呈极显著正相关。(3)亚基组成表现分别为(α’+α)-亚基缺失和α'-亚基缺失的日B-1和日A-5是具有较大育种潜力的优异种质。(4)通过遗传学的手段调整亚基含量,是选育“双高”(高蛋白、高脂肪)品种的新思路。
DOI:10.2135/cropsci2009.10.0607URL [本文引用: 2]

Simple sequence repeat (SSR) genetic markers, also referred to as microsatellites, function in map-based cloning and for marker-assisted selection in plant breeding. The objectives of this study were to determine the abundance of SSRs in the soybean genome and to develop and test soybean SSR markers to create a database of locus-specific markers with a high likelihood of polymorphism. A total of 210,990 SSRs with di-, tri-, and tetranucleotide repeats of five or more were identified in the soybean whole genome sequence (WGS) which included 61,458 SSRs consisting of repeat units of di- (≥10), tri- (≥8), and tetranucleotide (≥7). Among the 61,458 SSRs, (AT)n, (ATT)n and (AAAT)n were the most abundant motifs among di-, tri-, and tetranucleotide SSRs, respectively. After screening for a number of factors including locus-specificity using e-PCR, a soybean SSR database (BARCSOYSSR_1.0) with the genome position and primer sequences for 33,065 SSRs was created. To examine the likelihood that primers in the database would function to amplify locus-specific polymorphic products, 1034 primer sets were evaluated by amplifying DNAs of seven diverse Glycine max (L.) Merr. and one wild soybean (Glycine soja Siebold & Zucc.) genotypes. A total of 978 (94.6%) of the primer sets amplified a single polymerase chain reaction (PCR) product and 798 (77.2%) amplified polymorphic amplicons as determined by 4.5% agarose gel electrophoresis. The BARCSOYSSR1.0 SSR markers can be found in Soy- Base (http://soybase.org; verified 21 June 2010) the USDA-ARS Soybean Genome Database.
DOI:10.1111/jipb.12505URLPMID:5248594 [本文引用: 1]

Mutagenized populations have provided impor-tant materials for introducing variation and identifying gene function in plants. In this study, an ethyl methanesul-fonate (EMS)-induced soybean (Glycine max) population, consisting of 21,600 independent M2 lines, was developed. Over 1,000 M4 (5) families, with diverse abnormal pheno-types for seed composition, seed shape, plant morphology and maturity that are stably expressed across different environments and generations were identified. Phenotypic analysis of the population led to the identification of a yellow pigmentation mutant, gyl, that displayed signifi-cantly decreased chlorophyll (Chl) content and abnormal chloroplast development. Sequence analysis showed that gyl is allelic to MinnGold, where a different single?nucleotide polymorphism variation in the Mg-chelatase subunit gene (ChlI1a) results in golden yellow leaves. A cleaved amplified polymorphic sequence marker was developed and may be applied to marker-assisted selection for the golden yellow phenotype in soybean breeding. We show that the newly developed soybean EMS mutant population has potential for functional genomics research and genetic improvement in soybean.
DOI:10.1093/nar/8.19.4321URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1021/jf9604394URL [本文引用: 1]

Soybean isogenic lines having different glycinin subunit compositions are now being bred. To compare the characteristics of the genetically improved soybean proteins, total protein and purified glycinin proteins were investigated in this study. The absence of subunit(s) resulted in marked changes in the proportion of glycinin to -conglycinin. When the pH of the total protein and glycinin solution was changed and NaCl was added to the solution, glycinin consisting of only group I subunits and -conglycinin are highly soluble compared to the A5A4B3 or A3B4 subunit at a NaCl concentration lower than 0.05 M at pH 5.5. Ultracentrifuge analysis showed that the glycinin containing all subunits was able to assemble to form the 11S structure. That consisting of group I subunits formed a uniform 7S structure. Decreasing glycinin/ -conglycinin ratios and structural changes caused by a lack of glycinin subunit(s) are thus expected to influence the food-processing properties of soybeans. Keywords: Soybean; glycinin; ...
DOI:10.2307/3869102URLPMID:2562562 [本文引用: 1]

We investigated the chromosomal organization and developmental regulation of soybean β-conglycinin genes. The β-conglycinin gene family contains at least 15 members divided into two major groups encoding 2.5-kilobase and 1.7-kilobase embryo mRNAs. β-Conglycinin genes are clustered in several DNA regions and are highly homologous along their entire lengths. The two groups differ by the presence or absence of specific DNA segments. These DNA segments account for the size differences in β-conglycinin mRNAs. The 2.5-kilobase and 1.7-kilobase β-conglycinin mRNAs accumulate and decay at different times during embryogenesis. By contrast, genes encoding these mRNAs are transcriptionally activated and repressed at the same time periods. Our studies indicate that the β-conglycinin family evolved by both duplication and insertion/deletion events, and that β-conglycinin gene expression is regulated at both the transcriptional and posttranscriptional levels.
DOI:10.1016/j.foodres.2005.08.003URL [本文引用: 1]

Tofu was made, using two coagulants, from soybean lines which lacked specific glycinin and β-conglycinin protein subunits and the quality evaluated to determine the effects of specific protein subunits. The group IIb (A 3) glycinin subunit played the major role in contributing to tofu firmness, regardless of coagulant, while the group IIa (A 4) subunit had a negative effect on tofu quality in 2002. Soybeans with the group I (A 1A 2) subunit resulted in tofu with textural properties about one-third higher, expressed as a percent of Harovinton’s values, than tofu prepared from soybeans without the group I subunit. The individual components of group I had contradictory effects on GDL tofu quality in 2002, with the A 1 subunit having a negative effect and A 2 having a major positive effect. Lack of the α′ subunit of β-conglycinin increased gel hardness relative to the complete 7S protein.
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1006.2010.01409URL [本文引用: 1]

采用常规杂交育种方法,人工去雄、授粉,以10份综合农艺性状优良的黑龙江省主栽品种(或优 良品系)为母本、亚基组成为(α'+α+11S酸性亚基)-缺失型育种材料日B为父本进行有性杂交。将F1杂交种南繁,单粒点播、单株收获得到F2代分离 群体。聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳(SDS-PAGE)法分析表明,F1代杂交种子7S球蛋白α'-与α-亚基的表现型全部为正常型。在杂交F2代种子中获得了具 有中国大豆遗传背景的α-缺失、(α+A1aA1bA2)-缺失、A3-缺失、(α'+A4)-缺失和(α'+α)-缺失的贮藏蛋白亚基组成新类型种质, 为我国大豆蛋白组分育种选择提供了重要的中间材料。
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1006.2010.01409URL [本文引用: 1]

采用常规杂交育种方法,人工去雄、授粉,以10份综合农艺性状优良的黑龙江省主栽品种(或优 良品系)为母本、亚基组成为(α'+α+11S酸性亚基)-缺失型育种材料日B为父本进行有性杂交。将F1杂交种南繁,单粒点播、单株收获得到F2代分离 群体。聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳(SDS-PAGE)法分析表明,F1代杂交种子7S球蛋白α'-与α-亚基的表现型全部为正常型。在杂交F2代种子中获得了具 有中国大豆遗传背景的α-缺失、(α+A1aA1bA2)-缺失、A3-缺失、(α'+A4)-缺失和(α'+α)-缺失的贮藏蛋白亚基组成新类型种质, 为我国大豆蛋白组分育种选择提供了重要的中间材料。
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1006.2012.02297URL [本文引用: 1]

7S球蛋白α'与α亚基是大豆种子贮藏蛋白的重要组分,是影响大豆营养价值与加工品质的重要因子,同时还是主要的大豆致敏原,降低它们的含量是大豆品质改良育种的最新研究热点之一。以日本育种材料7S球蛋白(α'+α)-亚基双缺失型日B为供体亲本,黑龙江省主栽大豆品种东农47为受体亲本,采用回交转育方法,将α'与(α'+α)-亚基缺失特性导入东农47。结果表明,α'-缺失型(Cc)和(α'+α)-双缺失型(Cd)品系均能正常生长、结实,并能稳定遗传;Cc、Cd产量组分性状的平均值均远高于轮回亲本,蛋白质含量平均值均高于双亲,部分Cd株系籽粒蛋白质总量高达46.7%,脂肪含量平均值介于双亲之间,略高于日B;导入α'-缺失和(α'+α)双缺失性状后,绝大多数氨基酸组分含量和氨基酸总量提高,其中精氨酸和天门冬氨酸平均含量变幅最大。Cd株系籽粒含硫氨基酸含量(蛋氨酸与胱氨酸之和)及氨基酸总量分别比东农47高出0.11和5.56个百分点。说明通过常规育种重组α'-缺失或(α'+α)-双缺失性状即可提高大豆含硫氨基酸含量,并提高其他氨基酸组分含量及氨基酸总量,在Cc、Cd的BC2F3后代群体中有望筛选到α'-缺失或α'与α同时缺失的高产、高含硫氨基酸、优质大豆新品种。
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1006.2012.02297URL [本文引用: 1]

7S球蛋白α'与α亚基是大豆种子贮藏蛋白的重要组分,是影响大豆营养价值与加工品质的重要因子,同时还是主要的大豆致敏原,降低它们的含量是大豆品质改良育种的最新研究热点之一。以日本育种材料7S球蛋白(α'+α)-亚基双缺失型日B为供体亲本,黑龙江省主栽大豆品种东农47为受体亲本,采用回交转育方法,将α'与(α'+α)-亚基缺失特性导入东农47。结果表明,α'-缺失型(Cc)和(α'+α)-双缺失型(Cd)品系均能正常生长、结实,并能稳定遗传;Cc、Cd产量组分性状的平均值均远高于轮回亲本,蛋白质含量平均值均高于双亲,部分Cd株系籽粒蛋白质总量高达46.7%,脂肪含量平均值介于双亲之间,略高于日B;导入α'-缺失和(α'+α)双缺失性状后,绝大多数氨基酸组分含量和氨基酸总量提高,其中精氨酸和天门冬氨酸平均含量变幅最大。Cd株系籽粒含硫氨基酸含量(蛋氨酸与胱氨酸之和)及氨基酸总量分别比东农47高出0.11和5.56个百分点。说明通过常规育种重组α'-缺失或(α'+α)-双缺失性状即可提高大豆含硫氨基酸含量,并提高其他氨基酸组分含量及氨基酸总量,在Cc、Cd的BC2F3后代群体中有望筛选到α'-缺失或α'与α同时缺失的高产、高含硫氨基酸、优质大豆新品种。
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1007-9084.2007.02.006URL [本文引用: 1]

利用线性梯度SDS-PAGE方法分析了黑龙江省422份大豆资源材料的7S和11S球蛋白 含量、7S球蛋白α′、α和β亚基的含量变化,以及百粒重、蛋白质含量、油分含量、11S球蛋白、7S球蛋白、11S/7S比值的相关性。结果表明大豆种 子贮藏蛋白品种间亚基带型基本一致,但是品种间相同亚基含量差异很大,变异系数均大于10%,变异类型丰富,本实验发现1份α′亚基缺失材料。大豆百粒 重、蛋白质含量、油分含量、11S球蛋白、7S球蛋白以及11S/7S比值之间的相关性结果表明:11S球蛋白含量和7S球蛋白含量间 (r=-1^**)、蛋白质含量和油分含量间(r=-0.776^**)显著负相关;11S/7S比值和百粒重、蛋白质含量以及油分含量间无显著相关性。
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1007-9084.2007.02.006URL [本文引用: 1]

利用线性梯度SDS-PAGE方法分析了黑龙江省422份大豆资源材料的7S和11S球蛋白 含量、7S球蛋白α′、α和β亚基的含量变化,以及百粒重、蛋白质含量、油分含量、11S球蛋白、7S球蛋白、11S/7S比值的相关性。结果表明大豆种 子贮藏蛋白品种间亚基带型基本一致,但是品种间相同亚基含量差异很大,变异系数均大于10%,变异类型丰富,本实验发现1份α′亚基缺失材料。大豆百粒 重、蛋白质含量、油分含量、11S球蛋白、7S球蛋白以及11S/7S比值之间的相关性结果表明:11S球蛋白含量和7S球蛋白含量间 (r=-1^**)、蛋白质含量和油分含量间(r=-0.776^**)显著负相关;11S/7S比值和百粒重、蛋白质含量以及油分含量间无显著相关性。
DOI:10.1007/s10722-005-2434-yURL [本文引用: 1]

Out of 851 soybean accessions from Vietnam, China and Japan analyzed for 7S β-subunit variants, a new β-reduced subunit line with normal growth was collected from the Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Protein of the `β-reduced' line is composed of β-reduced and extremely low-β types. (α-null02+02β-reduced) type and β-null (or extremely low-β) type were screened in the progeny seeds of the Japanese mutant `(α02+02β) null' line. Therefore, recombination between α- and β-subunits was identified. By comparing the nucleotide sequence of the partial β-subunit gene of Enrei (standard), Mo-shi-dou Gong 503 (α02+02β low), β-5 33 seed (β-reduced), β-5 7 seed (extremely low-β), and (α02+02β)-null 16 ((α02+02β) null) seed, we found that the base `T' at 16602bp, in Enrei changed to `G' in Mo-shi-dou Gong 503, β-5 33 and β-5 7 . Using the (α02+02β)-null 16 individual as template, a distinct 30502bp β-subunit gene fragment was identified, instead of a 28502bp fragment.
DOI:10.1007/s10681-010-0251-7URL [本文引用: 1]

The development of soybean varieties that lack the β-conglycinin α′ subunit is an attractive goal because the β-conglycinin α′ subunit exerts a negative influence on nutrition and tofu gelation, and is also a major allergen. We sought to develop a co-dominant DNA marker for the β-conglycinin α′ subunit ( Cgy - 1 ) gene for use in marker-assisted selection (MAS). We identified a deleted sequence responsible for the null allele of Cgy - 1 in a soybean variety lacking the β-conglycinin α′ subunit known as ‘Keburi’. The deletion spanned 12,99802bp and included Cgy - 1 and its incomplete tandem duplicate on chromosome 10. Based on the Cgy - 1 sequence from both the Williams 82 soybean reference sequence and the Keburi variety, a set of three allele-specific primers was designed for multiplex PCR assay. These primers enabled allelic discrimination by the sizes of PCR products. This amplified two distinct DNA fragments of 913 and 64902bp in Williams 82 and Keburi, respectively. The practicality of the developed co-dominant marker for Cgy - 1 was also confirmed by amplification in five other soybean varieties including three wild types and two mutants. The heterozygosity of the F 1 plants at the Cgy - 1 locus was ascertained using our novel co-dominant marker. This PCR-based co-dominant marker is capable of detecting the presence or absence of β-conglycinin α′ subunit for soybean marker assisted breeding system.
URL [本文引用: 1]

本研究以聚合杂交育种方法获得的亚基特异种质为材料,通过对亚基缺失类型的鉴定、亚基含量年份间的稳定性、亚基缺失类型的品质性状和农艺性状的差异比较,以及α’亚基缺失分子机制等方面进行了初步研究。为大豆优质品种的培育和加工利用提供理论依据与实践指导。主要研究结果如下:1、经聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳法(SDS-PAGE)分析鉴定,获得A3+α'亚基缺失、只含有p亚基、只含有α+β亚基、只含有α'+β亚基、只含有7 S亚基和A5A4B3亚基缺失、A2A1aA1b含量极低、B1aB1bB2含量极低等系列单缺、双缺、多缺的贮藏蛋白亚基组成类型新种质。2、分析了具有遗传稳定性的只含7 S亚基、只含α+β亚基、A3+α'亚基缺失三种类型大豆种子7 S和11 S组分及其各亚基含量间的差异。结果表明只含7 S亚基类型大豆种子贮藏蛋白的7 S组分总量含量最高;A3+a'亚基缺失类型大豆种子贮藏蛋白11 S组分总含量最高;在11 S+7 S组分总量上由高到低依次是A3+α'亚基缺失类型、只含7 S亚基类型和只含α+β亚基类型,11 S/7 S比值的变异总范围在0.14~1.27之间。3、分析了遗传稳定性的A3+α'亚基缺失、只含有αα+p亚基、只含有7 S亚基三种类型种子的农艺性状和品质性状,结果为:三种类型种质生育期在105~111 d;百粒重基本一致;A3+α'亚基缺失类型大豆平均单株产量最高为55.12 g;只含a+p亚基类型蛋脂总量最低为57.6%,蛋白质含量由高到低依次为只含7 S亚基类型、A3+α'亚基缺失类型和只含α+β亚基类型,脂肪含量由高到低依次为只含α+β亚基类型、只含7S亚基类型和A3+α'亚基缺失类型。4、三种种子贮藏蛋白亚基缺失类型大豆种质(只含7 S亚基类型、只含a+β亚基类型和A3+α'亚基缺失类型)的蛋白质功能性质,分析表明,只含α+β亚基类型大豆蛋白疏水性强、起泡性质和乳化性质好、持油能力高、持水能力低,硬度、弹性、内聚性、胶粘性、咀嚼性、回弹性和破裂强度低的特性;只含7 S亚基类型大豆蛋白具有乳化性质好、持水能力高、持油能力低,弹性、内聚性、回弹性高的特性;A3+α'亚基缺失类型大豆蛋白功能性质与不缺的种质差异不明显。5、大豆种子贮藏蛋白各组分和亚基与蛋白功能性质之间的相关性分析表明,大豆种子蛋白的持水性与α亚基含量呈极显著负相关;持油性与α'亚基呈显著负相关,与碱性亚基呈显著正相关;起泡能力与p亚基含量极显著正相关,与7 S+11 S总量呈显著负相关;乳化稳定性指数与11 S亚基含量,与酸性亚基含量呈显著负相关,与11 S/7S比值之间呈极显著负相关;蛋白凝胶的破裂强度与7 S+11 S组分总量呈极显著正相关。6、分别分析了两年在同一地区、同一年在不同地域种植的三种不同亚基缺失类型大豆种子中7 S和11 S组分含量的差异及其大豆种子贮藏蛋白的功能特异差异。结果表明,不同亚基类型间的7 S组分、11 S组分、7 S+11 S组分总量以及11 S/7 S比值的差异均达极显著水平。不同年份间的7 S组分和7 S+11 S组分总量的差异达极显著水平,11 S组分和11 S/7 S比值的差异不显著;年份和亚基类型互作对7 S组分、11 S组分、7 S+11 S组分总量以及11 S/7 S比值的影响均不显著。同一年不同地点的11 S组分、7 S+11 S组分总量以及11 S/7 S比值的差异均达极显著水平,7 S组分的差异不显著;种植地点和亚基类型互作对大豆7 S组分、11 S组分和11 S/7 S比值的影响达显著水平,对7 S+11 S组分总量的影响不显著。不同年份间大豆蛋白EAI、AH和蛋白凝胶弹性、破裂强度的差异达极显著水平,对ESI、凝胶内聚性的差异达显著水平;年份和亚基类型互作对大豆蛋白的△H、EAI、蛋白凝胶内聚性、回弹性和破裂强度的影响达极显著水平,对蛋白变性温度的影响达显著水平。同一年不同种植地点间大豆蛋白EAI、ESI和蛋白凝胶破裂强度的差异达极显著水平,其他蛋白功能性质差异不显著;种植地点和亚基类型互作对EAI、ESI的影响达极显著水平,对其他蛋白功能性质影响不显著。7、以只含有时α+β亚基类型、A3+α'亚基缺失类型、只含7 S亚基类型以及桂阳紫金豆(对照)为研究材料,采用SDS-PAGE方法确定其播期间亚基带型的稳定之后,分段克隆缺失亚基(α'亚基)所对应的Cgyl基因DNA和cDNA序列全长,发现a'亚基缺失类型扩增出Cgy1基因后半段序列,而无法扩增出Cgyl基因的前半段序列;αα'亚基缺失类型的cDNA序列在361 bp处缺失长达36 bp的片段,在529 bp处缺失12 bp的片段,同时在361 bp与543 bp之间有多个碱基存在差异。
URL [本文引用: 1]

本研究以聚合杂交育种方法获得的亚基特异种质为材料,通过对亚基缺失类型的鉴定、亚基含量年份间的稳定性、亚基缺失类型的品质性状和农艺性状的差异比较,以及α’亚基缺失分子机制等方面进行了初步研究。为大豆优质品种的培育和加工利用提供理论依据与实践指导。主要研究结果如下:1、经聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳法(SDS-PAGE)分析鉴定,获得A3+α'亚基缺失、只含有p亚基、只含有α+β亚基、只含有α'+β亚基、只含有7 S亚基和A5A4B3亚基缺失、A2A1aA1b含量极低、B1aB1bB2含量极低等系列单缺、双缺、多缺的贮藏蛋白亚基组成类型新种质。2、分析了具有遗传稳定性的只含7 S亚基、只含α+β亚基、A3+α'亚基缺失三种类型大豆种子7 S和11 S组分及其各亚基含量间的差异。结果表明只含7 S亚基类型大豆种子贮藏蛋白的7 S组分总量含量最高;A3+a'亚基缺失类型大豆种子贮藏蛋白11 S组分总含量最高;在11 S+7 S组分总量上由高到低依次是A3+α'亚基缺失类型、只含7 S亚基类型和只含α+β亚基类型,11 S/7 S比值的变异总范围在0.14~1.27之间。3、分析了遗传稳定性的A3+α'亚基缺失、只含有αα+p亚基、只含有7 S亚基三种类型种子的农艺性状和品质性状,结果为:三种类型种质生育期在105~111 d;百粒重基本一致;A3+α'亚基缺失类型大豆平均单株产量最高为55.12 g;只含a+p亚基类型蛋脂总量最低为57.6%,蛋白质含量由高到低依次为只含7 S亚基类型、A3+α'亚基缺失类型和只含α+β亚基类型,脂肪含量由高到低依次为只含α+β亚基类型、只含7S亚基类型和A3+α'亚基缺失类型。4、三种种子贮藏蛋白亚基缺失类型大豆种质(只含7 S亚基类型、只含a+β亚基类型和A3+α'亚基缺失类型)的蛋白质功能性质,分析表明,只含α+β亚基类型大豆蛋白疏水性强、起泡性质和乳化性质好、持油能力高、持水能力低,硬度、弹性、内聚性、胶粘性、咀嚼性、回弹性和破裂强度低的特性;只含7 S亚基类型大豆蛋白具有乳化性质好、持水能力高、持油能力低,弹性、内聚性、回弹性高的特性;A3+α'亚基缺失类型大豆蛋白功能性质与不缺的种质差异不明显。5、大豆种子贮藏蛋白各组分和亚基与蛋白功能性质之间的相关性分析表明,大豆种子蛋白的持水性与α亚基含量呈极显著负相关;持油性与α'亚基呈显著负相关,与碱性亚基呈显著正相关;起泡能力与p亚基含量极显著正相关,与7 S+11 S总量呈显著负相关;乳化稳定性指数与11 S亚基含量,与酸性亚基含量呈显著负相关,与11 S/7S比值之间呈极显著负相关;蛋白凝胶的破裂强度与7 S+11 S组分总量呈极显著正相关。6、分别分析了两年在同一地区、同一年在不同地域种植的三种不同亚基缺失类型大豆种子中7 S和11 S组分含量的差异及其大豆种子贮藏蛋白的功能特异差异。结果表明,不同亚基类型间的7 S组分、11 S组分、7 S+11 S组分总量以及11 S/7 S比值的差异均达极显著水平。不同年份间的7 S组分和7 S+11 S组分总量的差异达极显著水平,11 S组分和11 S/7 S比值的差异不显著;年份和亚基类型互作对7 S组分、11 S组分、7 S+11 S组分总量以及11 S/7 S比值的影响均不显著。同一年不同地点的11 S组分、7 S+11 S组分总量以及11 S/7 S比值的差异均达极显著水平,7 S组分的差异不显著;种植地点和亚基类型互作对大豆7 S组分、11 S组分和11 S/7 S比值的影响达显著水平,对7 S+11 S组分总量的影响不显著。不同年份间大豆蛋白EAI、AH和蛋白凝胶弹性、破裂强度的差异达极显著水平,对ESI、凝胶内聚性的差异达显著水平;年份和亚基类型互作对大豆蛋白的△H、EAI、蛋白凝胶内聚性、回弹性和破裂强度的影响达极显著水平,对蛋白变性温度的影响达显著水平。同一年不同种植地点间大豆蛋白EAI、ESI和蛋白凝胶破裂强度的差异达极显著水平,其他蛋白功能性质差异不显著;种植地点和亚基类型互作对EAI、ESI的影响达极显著水平,对其他蛋白功能性质影响不显著。7、以只含有时α+β亚基类型、A3+α'亚基缺失类型、只含7 S亚基类型以及桂阳紫金豆(对照)为研究材料,采用SDS-PAGE方法确定其播期间亚基带型的稳定之后,分段克隆缺失亚基(α'亚基)所对应的Cgyl基因DNA和cDNA序列全长,发现a'亚基缺失类型扩增出Cgy1基因后半段序列,而无法扩增出Cgyl基因的前半段序列;αα'亚基缺失类型的cDNA序列在361 bp处缺失长达36 bp的片段,在529 bp处缺失12 bp的片段,同时在361 bp与543 bp之间有多个碱基存在差异。
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.2135/cropsci2005.0454URL [本文引用: 1]
