 ,1,2,*
,1,2,*Spatio-temporal Expression of Bt Protein and Stem Borer Resistance of Transgenic Early Japonica Rice with cry1C* or cry2A* Gene
LI Rong-Tian1, WANG Xin-Yu1, TIAN Chong-Bing1, ZHOU Qing1, LIU Chang-Hua ,1,2,*
,1,2,*通讯作者:
第一联系人:
收稿日期:2018-01-23接受日期:2018-08-20网络出版日期:2018-09-29
| 基金资助: |
Received:2018-01-23Accepted:2018-08-20Online:2018-09-29
| Fund supported: |

摘要
关键词:
Abstract
Keywords:
PDF (422KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
本文引用格式
李荣田, 王新宇, 田崇兵, 周青, 刘长华. 转cry1C*及cry2A*基因早粳稻Bt蛋白的时空表达和抗螟虫性[J]. 作物学报, 2018, 44(12): 1829-1836. doi:10.3724/SP.J.1006.2018.01829
LI Rong-Tian, WANG Xin-Yu, TIAN Chong-Bing, ZHOU Qing, LIU Chang-Hua.
水稻(Oryza sativa L.)作为最重要的粮食作物之一, 在其生长和发育的过程中, 常常遭受螟虫的危害, 每年造成的损失占水稻病虫害损失的50%以上[1]。其中, 危害最大的二化螟在我国分布很广, 除少数地区外, 南北稻区都有分布[2]。化学药剂防治螟虫效果较好, 但存在污染环境等问题[3]。培育抗虫水稻品种是防治螟虫最经济有效措施。栽培水稻及其近缘种中缺少抗螟虫基因, 利用转基因技术改良水稻抗虫性已成为抗虫育种的新途径。我国转基因抗虫水稻培育具世界先进水平, 一批转基因抗虫水稻新品系已经进入了环境释放试验和生产性试验阶段, 有的转基因抗虫水稻获得了安全性证书[4]。作物转基因抗虫遗传改良所用的外源基因一般包括凝集素基因[5,6,7,8]、毒素基因[9,10,11,12]、酶抑制剂基因[13]、以及cry等Bt基因[14], 其中以Bt基因应用最普遍、最成功[9,15]。Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt)是革兰氏阳性菌, 在形成芽孢时产生杀虫毒素。Bt杀虫毒素是一类蛋白质, 被称作Bt蛋白, 由cry基因编码[16]。Bt蛋白具有很高的杀虫专一性, 不会对人类及其他动物产生毒害[17]。根据水稻密码子偏爱性, 以cry1C基因和cry2A基因为蓝本经过密码子优化并人工合成了cry1C*基因和cry2A*基因[17,18,19]。转cry1C*或cry2A*基因的籼稻表现出稳定的、较好的抗螟虫性[18,20-22]。另外据研究, 转Bt基因植物Bt蛋白的表达量与环境及遗传背景有关。高温导致转Bt基因棉Bt蛋白含量降低[23,24], 遗传背景会影响Bt抗虫棉Bt蛋白的表达[25]。黑龙江省是我国粳稻最大产区, 具有日照长、气温低及昼夜温差大等独特的环境条件, 水稻生产中受二化螟危害严重[26]。利用在籼稻中抗虫性明确的cry1C*和cry2A*基因转化早粳稻, 培育转基因抗虫早粳稻品种, 有利于黑龙江省水稻生产发展。研究转Bt基因早粳稻田间Bt蛋白质表达特性, 分析不同转化事件形成的转基因早粳稻品系Bt蛋白量差异及其与抗虫性关系, 可为培育农艺性状优良的转基因抗虫早粳稻品种提供参考。
1 材料与方法
1.1 转基因早粳稻及其田间种植
水稻空育131 (cry1C*), 代码HD1。以其为受体, 通过根瘤农杆菌介导法将Ti质粒pBar13-cry1C*的T-DNA区(图1-A)导入水稻核基因组。从不同的遗传转化事件培育了4个遗传稳定的、农艺性状符合育种目标的转基因水稻品系, 即HD1-1、HD1-2、HD1-3和HD1-4。图1
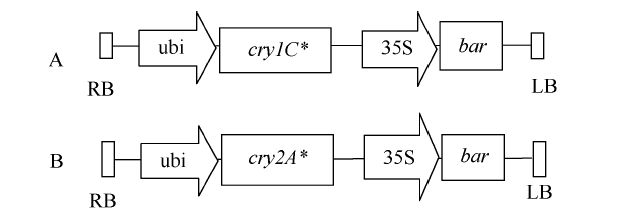 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图1Ti质粒pBar13-cry1C*(A)和pBar13-cry2A*(B)的T-DNA区
RB: 右边界; ubi: ubi启动子; cry1C*: cry1C*基因; cry2A*: cry2A*基因; 35S: CaMV35S启动子; bar: 膦丝菌素乙酰转移酶基因; LB: 左边界。
Fig. 1T-DNA region of Ti plasmid pBar13-cry1C*(A) and pBar13-cry2A*(B)
RB: right border; ubi: ubi promoter; cry1C*: cry1C * gene; cry2A*: cry2A * gene; 35S: CaMV35S promoter; bar: phosphinothricin acetyltransferase gene; LB: left border.
水稻空育131 (cry2A*), 代码HD2。与空育131 (cry2A*)的创制类似, 通过根瘤农杆菌介导法将pBar13-cry2A*的T-DNA区(图1-B)导入早粳稻空育131。来自于不同遗传转化事件的4个遗传稳定的、农艺性状符合育种目标的转基因水稻品系, 即HD2-1、HD2-2、HD2-3和HD2-4。
在黑龙江大学呼兰校区转基因水稻试验基地种植转基因早粳稻HD1-1、HD1-2、HD1-3和HD1-4, 以及HD2-1、HD2-2、HD2-3和HD2-4共8个品系。田间试验设计采用随机区组法, 3次重复。小区6行区, 5 m行长, 插秧规格为行距30 cm、株距12 cm、每蔸插2棵秧苗, 小区面积为9 m2。育苗、插秧、施肥、水管理、防病等与一般生产田相同, 不进行二化螟等虫害防治。
1.2 Bt蛋白量检测
在水稻分蘖期、抽穗期、灌浆期, 从田间每小区随机选取3蔸水稻, 取每蔸主茎上部叶片、茎鞘及幼穗等3个部位, 用灭菌的锡箔纸包好置液氮中保存, 室内检测水稻各器官样品的Bt蛋白量。成熟期收获小区稻谷, 室内加工糙米, 检测糙米Bt蛋白量。利用武汉上成生物科技有限公司“转基因Bt Cry1C酶联免疫定量检测试剂盒”检测水稻样品cry1C*基因Bt蛋白量, 利用“转基因Bt Cry2A酶联免疫定量检测试剂盒”检测水稻样品cry2A*基因Bt蛋白量。依据武汉上成生物科技有限公司的Cry1C和Cry2A酶联免疫定量检测试剂盒说明书, 用TECAN Infinite200型酶标仪, 检测样品450 nm OD值; 以试剂盒中标准品浓度为横坐标、OD值为纵坐标, 制作标准曲线; 称量、抽提液研磨及稀释水稻样品, 检测稀释后水稻样品OD值, 利用标准曲线计算稀释后水稻样品Bt蛋白浓度; Bt蛋白量(μg g-1) = 稀释后水稻样品Bt蛋白浓度(μg mL-1)×稀释倍数×抽提液体积(mL)/水稻样品鲜重(g)。对每个水稻样品Bt蛋白量检测2次, 2次差异在5%以内为有效数据, 2次的平均值为该小区该时空水稻Bt蛋白量。
1.3 螟虫抗性鉴定
二化螟一龄期的幼虫用于水稻接虫。二化螟虫卵由中国农业科学院植物保护研究所水稻害虫研究室侯茂林教授惠赠。在水稻抽穗期, 随机选每小区3蔸水稻, 取每蔸一茎秆并截取其基部5 cm。于室内将茎秆基部包裹湿纱布, 以保持茎秆新鲜不脱水, 将同一个小区的3个茎秆放在1个试管中。每个试管接二化螟一龄期幼虫30头, 平均每个茎秆接虫10头。封闭试管口防止昆虫逃逸及水分蒸发。在28℃、相对湿度90%以上、光照3000 μmol m-2 s-1、12 h光照/12 h黑暗条件放置, 7 d后统计死虫数, 计算二化螟死亡率及校正死亡率。二化螟死亡率 = (接虫数 - 活虫数)/接虫数×100%, 二化螟校正死亡率 = (转基因早粳稻品系二化螟死亡率 - 对照CK二化螟死亡率)/(100 - 对照CK二化螟死亡率)×100%。对照CK为水稻空育 131。以二化螟校正死亡率高低代表螟虫抗性强弱。
1.4 数据分析
转cry1C*基因或cry2A*基因早粳稻Bt蛋白量和二化螟死亡率及二化螟校正死亡率等性状以小区平均数为基础数据分析比较。各转基因品系Bt蛋白量是3个小区的Bt蛋白量平均值, HD1及HD2不同生长发育阶段及器官的Bt蛋白量是各自4个不同品系的Bt蛋白量平均值。利用Microsoft Excel 2003及SPSS21.0软件进行方差及相关性等统计分析。2 结果与分析
2.1 转不同基因早粳稻Bt蛋白量
由图2可知, 叶片Bt蛋白量, 在分蘖期、抽穗期和灌浆期, 转cry1C*基因早粳稻HD1均明显地低于转cry2A*基因早粳稻HD2; 与叶片类似, 茎鞘中Bt蛋白量, 在水稻各个生长发育阶段, 转基因早粳稻HD1均显著地低于HD2; 幼穗或糙米中Bt蛋白量, 在抽穗期HD1比HD2显著低, 水稻生长发育到灌浆期及成熟期, HD1水稻虽然仍低于HD2水稻, 但是差异变得不明显。这表明, 在早粳稻中cry1C*基因蛋白质表达量低于cry2A*蛋白质表达量, 在营养器官及生长发育前期, 这种差异更加明显。图2
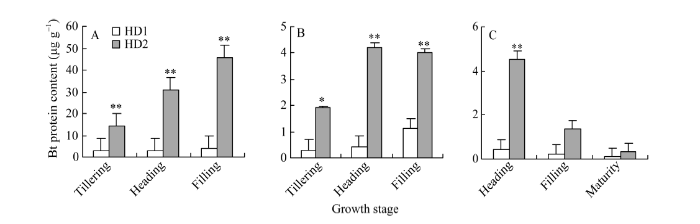 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图2转基因早粳稻HD1和HD2的Bt蛋白量
A: 叶片; B: 茎鞘; C: 幼穗或糙米; BPC: Bt蛋白量。*和**: 差异达0.05和0.01概率显著水平。
Fig. 2Bt protein content of HD1 and HD2 of transgenic early japonica rice
A: leaf blade; B: sheath-culm; C: young panicle or brown rice; BPC: Bt protein content. *, **: significant at P < 0.05 and P < 0.01, respectively.
2.2 不同生长发育阶段Bt蛋白量
从图3可见, 叶片和茎鞘的Bt蛋白量, 除转基因早粳稻HD1叶片从分蘖期、抽穗期到灌浆期有逐渐上升趋势之外, HD1和HD2不同生长发育阶段高低明显不同, 通常情况是分蘖期最低、抽穗期居中、灌浆期最高。幼穗或糙米Bt蛋白量, 不论HD1还是HD2, 不同生长发育阶段高低差异显著, 抽穗期幼穗比灌浆期幼穗高, 最低的是成熟糙米。这说明, 随着生长发育进程叶片及茎鞘等营养器官Bt蛋白量升高; 幼穗及糙米等生殖器官Bt蛋白量降低。图3
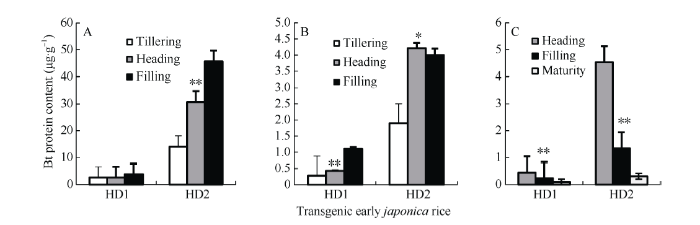 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图3转基因早粳稻不同生长发育阶段的Bt蛋白量
A: 叶片; B: 茎鞘; C: 幼穗或糙米; BPC: Bt蛋白量。*和**: 差异达0.05和0.01概率显著水平。
Fig. 3Bt protein content of the transgenic early japonica rice among the different growth stages
A: leaf blade; B: sheath-culm; C: young panicle or brown rice; BPC: Bt protein content. *, **: significant at P < 0.05 and P < 0.01, respectively.
2.3 不同器官Bt蛋白量
图4显示, 转基因早粳稻HD1和HD2的叶片、茎鞘、幼穗或糙米等不同器官间Bt蛋白量差异极显著, 在分蘖期、抽穗期和灌浆期等各生长发育阶段, Bt含量最高的器官均为叶片, 其次为茎鞘及幼穗, 糙米Bt蛋白量最低。转Bt基因早粳稻, 目的基因表达蛋白高低次序为叶片、茎鞘及幼穗、糙米。图4
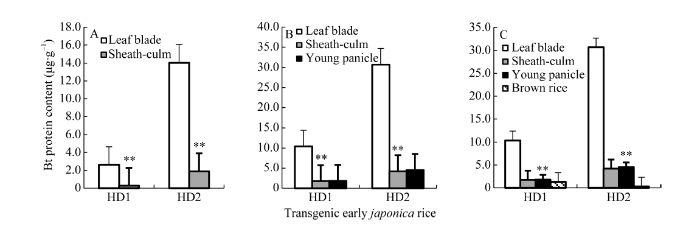 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图4转基因早粳稻器官的Bt蛋白量
A: 分蘖期; B: 抽穗期; C: 灌浆期及成熟期; BPC: Bt蛋白量。**差异达0.01概率显著水平。
Fig. 4Bt protein content of the transgenic early japonica rice at different growth stages
A: tillering stage; B: heading stage; C: filling stage and maturity; BPC: Bt protein content. **: significant at P < 0.01.
2.4 不同品系抽穗期各器官及成熟期糙米Bt蛋白量与螟虫抗性
室内抗虫性实验结果显示对照CK水稻品种空育131的3个重复二化螟幼虫死亡率均在5%以下, 分别为3.33%、6.67%和3.33%, 平均为4.44%± 1.93%。同时, 转基因早粳稻HD1及HD2各品系二化螟幼虫死亡率均在90%以上, 且未死亡幼虫表现出发育迟缓、生长缓慢的特征(数据未在本文提供)。说明室内抗虫性实验可以有效地鉴定区分水稻抗螟虫性。由表1可知, 转基因早粳稻HD1不同品系, 抽穗期叶片、茎鞘和幼穗Bt蛋白量、成熟期糙米Bt蛋白量、以及螟虫抗性强弱等差异极显著。与HD1情况类似, 抽穗期各器官Bt蛋白量、糙米Bt蛋白量、螟虫抗性等在HD2不同品系间存在显著或极显著差异。
Table 1
表1
表1转基因早粳稻不同品系Bt蛋白量及抗虫性
Table 1
| 品系 Line | 叶片Bt蛋白量 BPC of leaf blade (μg g-1) | 茎鞘Bt蛋白量 BPC of sheath-culm (μg g-1) | 幼穗Bt蛋白量 BPC of young panicle (μg g-1) | 糙米Bt蛋白量 BPC of brown rice (μg g-1) | 校正幼虫死亡率 Adjusted larval mortality rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HD1-1 | 5.33±0.04** | 0.50±0.03** | 0.52±0.02** | 0.09±0.01** | 96.46±1.42** |
| HD1-2 | 2.74±0.03** | 0.49±0.02** | 0.51±0.03** | 0.15±0.02** | 91.34±1.02** |
| HD1-3 | 1.16±0.02** | 0.44±0.03** | 0.43±0.03** | 0.06±0.02** | 92.08±2.70** |
| HD1-4 | 1.16±0.02** | 0.31±0.03** | 0.36±0.02** | 0.10±0.02** | 96.20±1.06** |
| HD2-1 | 21.81±0.02** | 2.87±0.04** | 3.95±0.02** | 0.33±0.03** | 94.21±1.05** |
| HD2-2 | 29.65±0.02** | 5.69±0.02** | 4.73±0.02** | 0.24±0.02** | 93.73±3.55** |
| HD2-3 | 21.63±0.04** | 3.63±0.02** | 4.02±0.05** | 0.55±0.03** | 91.56±4.10** |
| HD2-4 | 49.63±0.06** | 4.64±0.02** | 5.43±0.04** | 0.13±0.03** | 98.06±0.88** |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
转基因早粳稻HD1不同品系间抽穗期叶片、茎鞘及幼穗Bt蛋白量与校正二化螟幼虫死亡率间相关性未达到显著水平, 叶片、茎鞘及幼穗等器官目的基因蛋白表达量高低与螟虫抗性强弱没有关系(表2)。HD2不同品系抽穗期叶片、茎鞘及幼穗Bt蛋白量与校正幼虫死亡率存在显著正相关或正相关趋势(表2)。结合表1, HD1和HD2品系校正幼虫死亡率均在90%以上, 表现出高抗螟虫。这表明, 在本研究范围内, 目的基因及其表达框完全可以满足培育转基因早粳稻品种的要求。
Table 2
表2
表2转基因早粳稻不同品系抽穗期Bt蛋白量和糙米Bt蛋白量及螟虫抗性关系
Table 2
| 转基因早粳稻 Transgenic early japonica rice | 抽穗期性状 Characteristic at heading stage | 成熟期糙米Bt蛋白量 BPC of brown rice at maturity | 校正幼虫死亡率 Adjusted larval mortality rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| HD1 | 叶片Bt蛋白量 BPC of leaf blade | 0.233 | 0.375 |
| 茎鞘Bt蛋白量 BPC of sheath-culm | 0.254 | -0.389 | |
| 幼穗Bt蛋白量 BPC of young panicle | 0.381 | -0.267 | |
| HD2 | 叶片Bt蛋白量 BPC of leaf blade | -0.796 | 0.910* |
| 茎鞘Bt蛋白量 BPC of sheath-culm | -0.533 | 0.250 | |
| 幼穗Bt蛋白量 BPC of young panicle | -0.827 | 0.838 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
表2还显示, HD1和HD2转基因早粳稻抽穗期植株各器官Bt蛋白量与糙米Bt蛋白量间相关不显著, 生长发育阶段水稻植株外源Bt蛋白表达量与糙米中Bt蛋白量没有必然联系。在培育转基因抗虫早粳稻品种工作中, 在定性地鉴定选择Bt蛋白存在同时, 更多的精力可以集中于农艺性状的鉴定选择。
3 讨论
迄今为止, 序列已知及命名的Cry毒素蛋白有300多种。根据氨基酸序列同一性程度, 把Cry毒素分为74个一级类别((Cry1~Cry74)[27,28]。转cry1C*早粳稻HD1与转cry2A*早粳稻HD2, 受体品种均为空育131水稻, 用于遗传转化的Ti质粒T-DNA区差异仅在于Bt基因的不同。HD1或HD2不同品系, Bt蛋白表达量高低不同。不过, 在田间整个生长期的各个器官, HD1所有品系Bt蛋白量均极显著地低于HD2各品系。不同cry基因在植物细胞蛋白质层面的表达量(或最高表达量)应该是有差别的。植物细胞内cry1C基因蛋白质表达量低于cry2A基因, 至少在转cry1C*早粳稻和转cry2A*早粳稻中的情况是这样的。Bt植物的目的基因蛋白表达量在不同生长发育阶段是不同的。Bt棉花田间生长过程中同一组织的Bt蛋白质含量呈动态下降趋势[29], Bt玉米随生育期的延长Bt蛋白的表达量降低[30,31,32]。在本研究中, 转cry1C*或cry2A*基因早粳稻的幼穗或糙米的Bt蛋白量随生长发育的推进而降低, 但是, 叶片及茎鞘的Bt蛋白量随生长发育的推进而升高。本研究Bt蛋白量检测是以样品鲜重为基础的, 叶片及茎鞘等营养器官生长发育前期含水量比生长发育后期含水量要高得多, 这可能是转基因早粳稻营养器官Bt蛋白量生长发育前期低、后期高的原因之一。
Bt植物的目的基因蛋白表达量在不同器官是不同的。Bt玉米[31]、Bt水稻[33,34,35]等作物叶片中Bt蛋白表达量总是高于其他器官。但是, Bt大豆叶片Bt蛋白表达量低于茎及根, 是营养器官中Bt蛋白量最低的[36]。本研究结果显示, 不论转cry1C*还是转cry2A*基因早粳稻, 生殖器官Bt蛋白量都低于营养器官, 营养器官中叶片Bt蛋白量最高。这说明, 以淀粉为主要储存物质的玉米和水稻等作物, 组成型启动子调控下的外源基因在“源器官”叶片表达量高于“库器官”穗及稻谷中的表达。谷蛋白是水稻糙米中最重要的储存蛋白, 稻谷中贮藏蛋白基因的表达通常具有组织与时空特异性及特定的靶向元件[37,38]。ubi等组成型启动子调控下的cry1C*或cry2A*基因在穗及糙米等器官中Bt蛋白量低是有分子依据的。
在Bt棉花中, Bt蛋白含量与棉铃虫幼虫死亡率呈正相关, 含量越高, 抗虫性越好[25]。Bt玉米与Bt棉花类似, Bt蛋白的表达量与玉米对亚洲玉米螟抗性呈正相关[32]。本研究结果显示转cry1C*基因早粳稻HD1各器官Bt蛋白量和螟虫抗性没有关系, 转cry2A*基因早粳稻HD2各器官Bt蛋白量和螟虫抗性虽有正相关趋势, 但是没有达到显著水平。同时, HD1品系和HD2品系均高抗螟虫。其原因可能在于, 本研究所使用的抗虫基因是针对水稻密码子偏爱性进行了密码子优化的Bt基因, 其启动子是单子叶植物细胞高效启动子ubi, 该Bt基因及其表达框在水稻细胞中的表达量完全可以达到抗虫育种的要求。
转基因植物即使外源基因是单拷贝的、插入位点是基因间区的转化事件形成的品种(品系), 由于外源基因表达消耗能量, 往往导致受体品种农艺性状的变劣[39,40]。在没有害虫胁迫条件下, 转cry1C*基因籼稻明恢63 (1C*)和转cry2A*基因明恢63 (2A*)比明恢63产量降低, 明恢63 (1C*)比明恢(2A*)Bt蛋白量低, 但减产幅度更大[41,42]。本研究结果显示在早粳稻细胞中cry2A*基因比cry1C*基因蛋白表达量高, 暗示外源基因引进植物细胞及增加了细胞能量负担, 导致农艺性状变劣不是必然的。如果增加遗传转化事件, 扩大转基因育种群体及田间鉴定选择压力, 应该能够培育出具有外源目标性状、同时农艺性状与受体品种类似或相同的纯系。不同Cry蛋白杀虫谱不同[43]。对同一靶标幼虫, Cry2A与靶标昆虫幼虫肠道细胞受体结合位点与Cry1C及Vip3A也不同[28,43]。培育高抗螟虫、农艺性状与空育131水稻类似的HD1及HD2, 在生产上混合或轮换应用HD1和HD2, 把Cry2A与Cry1C结合起来用于转基因早粳稻品种, 理论上可以推迟黑龙江省水稻二化螟对Bt蛋白抗性的产生。
4 结论
以早粳稻空育 131为受体, 遗传转化创制了早粳稻空育131 (cry1C*)和空育131 (cry2A*)等转基因早粳稻。其叶片、茎鞘、幼穗和糙米中的Cry2A蛋白量在各生长发育阶段均极显著高于Cry1C表达量。叶片及茎鞘等营养器官Bt蛋白量随生长发育动态而增加, 幼穗或糙米等生殖器官Bt蛋白量在生长发育早期较高、晚期较低。Bt蛋白量在叶片中最高、茎鞘及幼穗中较低、糙米中最低。同一抗虫基因不同转基因品系间抽穗期各器官Bt蛋白量与室内抗螟虫性及成熟期糙米Bt蛋白量之间未见相关性, 本研究所使用的Bt基因及其表达框可以满足培育抗虫转基因早粳稻品种的要求。参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
DOI:10.1073/pnas.0708013104URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-7731.2012.06.014URL [本文引用: 1]

随着抗虫转基因植物的推广和大面积商业化种植,Bt毒蛋白在转基因植物中的表达引起了人们的重视。综述了玉米、棉花、水稻等抗虫转基因植物的Bt毒蛋白表达及其时空变化规律。
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-7731.2012.06.014URL [本文引用: 1]

随着抗虫转基因植物的推广和大面积商业化种植,Bt毒蛋白在转基因植物中的表达引起了人们的重视。综述了玉米、棉花、水稻等抗虫转基因植物的Bt毒蛋白表达及其时空变化规律。
URL [本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1111/j.1570-7458.1996.tb00837.xURL [本文引用: 1]

Abstract Potato plants ( Solanum tuberosum ) cv. Desire were transformed with the genes encoding the proteins bean chitinase (BCH), snowdrop lectin (GNA) and wheat -amylase inhibitor (WAI) under the control of the constitutive CaMV 35S promoter. Transgenic plants with detectable levels of foreign RNA were then selected for further characterisation with respect to protein expression levels by immunodot blot analysis using polyclonal antibodies raised against the respective protein. With the exception of WAI, plants expressing high levels of RNA, expressed correspondingly high levels of the foreign protein (1.5 2.0% of the total soluble protein). Although high levels of WAI mRNA were detected in some of the transformants, the protein could not be detected. On the bases of expression levels, two lines, designated PWG6#85 (transformed with the double construct WAI/GNA) and PBG6#47 (transformed with the double construct BCH/GNA), were selected for testing in aphid trials for enhanced levels of resistance. Both transgenic lines had a marked and significant effect on fecundity. The number of nymphs produced per female per day peaked at 4.1 and 4.2 for lines PBG6#47 and PWG6#85 respectively, compared to a value of 5.4 on control plants. Total nymphal production was also significantly lower on either of the transgenic lines compared to control plants (P<0.001) with the differences between the lines being only just significant (P=0.058). On line PBG6#47 there was a delay in nymphal production of 1.6 days, representing a delay of 1 5%, and on line PWG6#85 this was 3.2 days, representing a delay of ca. 30%. The intrinsic rates of increase (r m ) were also significantly lower on both of the transgenic lines in comparison to that on control plants (P<0.001), however the differences between the lines were not significant. The potential of using such genes as part of an over all strategy for the control of aphid populations is discussed.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 2]
DOI:10.1007/BF02007173URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1007/BF02007173URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1111/j.1574-6976.2012.00341.xURLPMID:22540421 [本文引用: 1]

Bacillus thuringiensis bacteria are insect pathogens that produce different Cry and Cyt toxins to kill their hosts. Here we review the group of three-domain Cry (3d-Cry) toxins. Expression of these 3d-Cry toxins in transgenic crops has contributed to efficient control of insect pests and a reduction in the use of chemical insecticides. The mode of action of 3d-Cry toxins involves sequential interactions with several insect midgut proteins that facilitate the formation of an oligomeric structure and induce its insertion into the membrane, forming a pore that kills midgut cells. We review recent progress in our understanding of the mechanism of action of these Cry toxins and focus our attention on the different mechanisms of resistance that insects have evolved to counter their action, such as mutations in cadherin, APN and ABC transporter genes. Activity of Cry1AMod toxins, which are able to form toxin oligomers in the absence of receptors, against different resistant populations, including those affected in the ABC transporter and the role of dominant negative mutants as antitoxins, supports the hypothesis that toxin oligomerization is a limiting step in the Cry insecticidal activity. Knowledge of the action of 3d-Cry toxin and the resistance mechanisms to these toxins will set the basis for a rational design of novel toxins to overcome insect resistance, extending the useful lifespan of Cry toxins in insect control programs.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
Magsci [本文引用: 1]

通过PCR从克隆载体pUC18-3Z/Cry2A*上扩增水稻偏爱型密码子优化的抗虫基因cry2A*,经限制性内切酶NdeI和BamHI双酶切定向插入到原核表达载体pET-28a(+),成功构建了在表达蛋白的N端只带有6个组氨酸标签的融合蛋白表达载体pET-28a(+)/Cry2A*,并转入大肠杆菌BL21(DE3)中。通过对其表达条件进行优化,发现在IPTG浓度为0.05mmol/L、诱导时间为3h、诱导温度为20℃的表达条件下目的蛋白大部分以可溶形式进行表达。采用Ni-NTA亲和柱纯化得到高纯度目的蛋白,薄层扫描分析蛋白纯度达到95%。
Magsci [本文引用: 1]

通过PCR从克隆载体pUC18-3Z/Cry2A*上扩增水稻偏爱型密码子优化的抗虫基因cry2A*,经限制性内切酶NdeI和BamHI双酶切定向插入到原核表达载体pET-28a(+),成功构建了在表达蛋白的N端只带有6个组氨酸标签的融合蛋白表达载体pET-28a(+)/Cry2A*,并转入大肠杆菌BL21(DE3)中。通过对其表达条件进行优化,发现在IPTG浓度为0.05mmol/L、诱导时间为3h、诱导温度为20℃的表达条件下目的蛋白大部分以可溶形式进行表达。采用Ni-NTA亲和柱纯化得到高纯度目的蛋白,薄层扫描分析蛋白纯度达到95%。
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11963/issn.1002-7807.201702002URL [本文引用: 2]

抗虫棉的培育和利用则是防治棉花虫害最有效的措施。棉铃虫是棉花生长发育过程中的主要害虫。苏云金芽孢杆菌(Bacillus thuringiensis,Bt)在芽孢形成过程中产生1种具有特异杀虫活性的伴孢晶体即Bt蛋白,可致鳞翅目昆虫死亡。随着抗虫棉的应用,人们发现抗虫棉的抗虫性存在较大差异,甚至出现"抗虫棉不抗虫"的现象。因而抗虫棉抗虫差异性原因的研究将为抗虫育种提供重要的理论依据。
DOI:10.11963/issn.1002-7807.201702002URL [本文引用: 2]

抗虫棉的培育和利用则是防治棉花虫害最有效的措施。棉铃虫是棉花生长发育过程中的主要害虫。苏云金芽孢杆菌(Bacillus thuringiensis,Bt)在芽孢形成过程中产生1种具有特异杀虫活性的伴孢晶体即Bt蛋白,可致鳞翅目昆虫死亡。随着抗虫棉的应用,人们发现抗虫棉的抗虫性存在较大差异,甚至出现"抗虫棉不抗虫"的现象。因而抗虫棉抗虫差异性原因的研究将为抗虫育种提供重要的理论依据。
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-6737.2002.02.001URL [本文引用: 1]

一、水稻在农业生产中的地位自80年代初开始,全国水稻播种面积开始减少,到2000年减少近250万hm2,约减7.3%。但我国方水稻播种面积时反而增长,其东北地区增长最快,约占整个北方水稻增加面积的83.8%(见图1)。东北三省中又以我省增加最快,播种面积
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-6737.2002.02.001URL [本文引用: 1]

一、水稻在农业生产中的地位自80年代初开始,全国水稻播种面积开始减少,到2000年减少近250万hm2,约减7.3%。但我国方水稻播种面积时反而增长,其东北地区增长最快,约占整个北方水稻增加面积的83.8%(见图1)。东北三省中又以我省增加最快,播种面积
URL [本文引用: 1]

The crystal proteins of have been extensively studied because of their pesticidal properties and their high natural levels of production. The increasingly rapid characterization of new crystal protein genes, triggered by an effort to discover proteins with new pesticidal properties, has resulted in a variety of sequences and activities that no longer fit the original nomenclature system proposed in 1989. pesticidal crystal protein (Cry and Cyt) nomenclature was initially based on the insecticidal activity for the primary ranking criterion. Many exceptions to this systematic arrangement have become apparent, however, making the nomenclature system inconsistent. Additionally, the original nomenclature, with four activity-based primary ranks for 13 genes, did not anticipate the current 73 holotype sequences that form many more than the original four subgroups. A new nomenclature, based on hierarchical clustering using amino acid sequence identity, is proposed. Roman numerals have been exchanged for Arabic numerals in the primary rank (e.g., Cry1Aa) to better accommodate the large number of expected new sequences. In this proposal, 133 crystal proteins comprising 24 primary ranks are systematically arranged.
[本文引用: 2]
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0496-3490.2005.02.011URL [本文引用: 1]

目前已商品化生产的国内外抗虫棉品种在生产上均存在“苗期抗性强 ,后期抗性减弱”的现象。从DNA、mRNA和蛋白质 3个水平上对双价抗虫棉 139 2 0R4 代植株中Bt杀虫基因及其在整个生长发育期的时空表达进行了系统研究。研究结果表明 ,Bt杀虫基因在抗虫棉中的表达具有时空特异性。同一组织中 ,Bt杀虫蛋白含量在整个生长发育期呈动态下降趋势。这种现象是由于发育前期Bt杀虫基因表达量过高 ,导致转录后水平的基因表达调控引起的 ,是一种发育调控的体细胞转基因沉默现象。同时 ,Bt杀虫基因在抗虫棉生长发育后期的表达变化与 35S启动子的甲基化程度提高有关。这些研究为进一步采取相应措施 ,提高抗虫棉发育后期的抗虫性提供了依据。
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0496-3490.2005.02.011URL [本文引用: 1]

目前已商品化生产的国内外抗虫棉品种在生产上均存在“苗期抗性强 ,后期抗性减弱”的现象。从DNA、mRNA和蛋白质 3个水平上对双价抗虫棉 139 2 0R4 代植株中Bt杀虫基因及其在整个生长发育期的时空表达进行了系统研究。研究结果表明 ,Bt杀虫基因在抗虫棉中的表达具有时空特异性。同一组织中 ,Bt杀虫蛋白含量在整个生长发育期呈动态下降趋势。这种现象是由于发育前期Bt杀虫基因表达量过高 ,导致转录后水平的基因表达调控引起的 ,是一种发育调控的体细胞转基因沉默现象。同时 ,Bt杀虫基因在抗虫棉生长发育后期的表达变化与 35S启动子的甲基化程度提高有关。这些研究为进一步采取相应措施 ,提高抗虫棉发育后期的抗虫性提供了依据。
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0578-1752.2003.11.008URL [本文引用: 1]

采用ELISA定量法对比研究了美国和中国 4种Bt玉米品种 (34B2 4、NK5 8 D1、R× 6 0 1RR/YG和农大 6 1)不同器官Bt蛋白表达的季节动态 ;应用室内 2 5℃恒温模拟分解试验对比了 4个Bt玉米品种秸秆分解释放的Bt蛋白的土壤降解规律。结果表明 ,4种Bt玉米不同器官不同生育期Bt蛋白含量表现出较大的差异 ,总体趋势为随生育期的延长Bt蛋白的表达量降低 ,农大 6 1后期表达量衰退不明显。室内模拟分解试验显示 ,4种Bt玉米秸秆中的Bt蛋白在水中的降解过程呈现初期大量释放 ,前期大量快速降解和后期极低量稳定 3个阶段 ,农大 6 1、34B2 4、NK5 8 D1分解 7d时含量达到最大 ,但R× 6 0 1RR/YG分解 14d达最大。 4种Bt玉米秸秆中的Bt蛋白在室内 2 5℃恒温条件下均能在土壤中快速降解 ,降解过程均呈现前期负指数大量快速降解和中后期极少量稳定两个阶段 ,其DT50 依次为NK5 8 D1(2 .0 9d) <R× 6 0 1RR/YG(2 .6 1d) <农大 6 1(2 .73d) <34B2 4 (3.4 3d) ,DT90 为农大 6 1(10 .5 3d)<R× 6 0 1RR/YG(11.0 9d) <34B2 4 (13.5 2d) <NK5 8 D1(14 .6 7d)。农大 6 1秸秆中ICP在灭菌与未灭菌土壤中降解的对比发现 ,土壤微生物的分解与利用是Bt蛋白快速降解的原因之一
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0578-1752.2003.11.008URL [本文引用: 1]

采用ELISA定量法对比研究了美国和中国 4种Bt玉米品种 (34B2 4、NK5 8 D1、R× 6 0 1RR/YG和农大 6 1)不同器官Bt蛋白表达的季节动态 ;应用室内 2 5℃恒温模拟分解试验对比了 4个Bt玉米品种秸秆分解释放的Bt蛋白的土壤降解规律。结果表明 ,4种Bt玉米不同器官不同生育期Bt蛋白含量表现出较大的差异 ,总体趋势为随生育期的延长Bt蛋白的表达量降低 ,农大 6 1后期表达量衰退不明显。室内模拟分解试验显示 ,4种Bt玉米秸秆中的Bt蛋白在水中的降解过程呈现初期大量释放 ,前期大量快速降解和后期极低量稳定 3个阶段 ,农大 6 1、34B2 4、NK5 8 D1分解 7d时含量达到最大 ,但R× 6 0 1RR/YG分解 14d达最大。 4种Bt玉米秸秆中的Bt蛋白在室内 2 5℃恒温条件下均能在土壤中快速降解 ,降解过程均呈现前期负指数大量快速降解和中后期极少量稳定两个阶段 ,其DT50 依次为NK5 8 D1(2 .0 9d) <R× 6 0 1RR/YG(2 .6 1d) <农大 6 1(2 .73d) <34B2 4 (3.4 3d) ,DT90 为农大 6 1(10 .5 3d)<R× 6 0 1RR/YG(11.0 9d) <34B2 4 (13.5 2d) <NK5 8 D1(14 .6 7d)。农大 6 1秸秆中ICP在灭菌与未灭菌土壤中降解的对比发现 ,土壤微生物的分解与利用是Bt蛋白快速降解的原因之一
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-4831.2014.05.020URL [本文引用: 2]

采用双抗夹心酶联免疫法(ELISA)定量检测转mCry1 Ac 基因抗虫玉米Bt799 在不同生育期不同植株部位的mCry1Ac 蛋白含量.结果显示:mCry1 Ac 基因在整个生育期玉米叶、茎、根和种子中均能表达,mCry1Ac 蛋白含量为(0. 82±0. 10) ~(15. 83±1. 77) μg·g^-1;随着生育期和植株部位的不同,mCry1Ac 蛋白含量呈现明显的时空动态变化,其中,叶、茎和根中mCry1Ac 蛋白含量随转基因玉米生育期的推移均呈增加趋势,并均在完熟期达最高;在除苗期外的其他各生育期叶中mCry1Ac 蛋白含量均显著高于其他植株部位,而在完熟期种子中mCry1Ac 蛋白含量在各植株部位中最低,为(2. 86±1. 71) μg·g^-1.
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-4831.2014.05.020URL [本文引用: 2]

采用双抗夹心酶联免疫法(ELISA)定量检测转mCry1 Ac 基因抗虫玉米Bt799 在不同生育期不同植株部位的mCry1Ac 蛋白含量.结果显示:mCry1 Ac 基因在整个生育期玉米叶、茎、根和种子中均能表达,mCry1Ac 蛋白含量为(0. 82±0. 10) ~(15. 83±1. 77) μg·g^-1;随着生育期和植株部位的不同,mCry1Ac 蛋白含量呈现明显的时空动态变化,其中,叶、茎和根中mCry1Ac 蛋白含量随转基因玉米生育期的推移均呈增加趋势,并均在完熟期达最高;在除苗期外的其他各生育期叶中mCry1Ac 蛋白含量均显著高于其他植株部位,而在完熟期种子中mCry1Ac 蛋白含量在各植株部位中最低,为(2. 86±1. 71) μg·g^-1.
URL [本文引用: 2]

分析不同转化体Bt蛋白表达量和评估其抗虫性,进而筛选优异转化事件是转基因玉米新品种培育研究中的重要环节.为分析转cry1Ab/Gc基因玉米中Bt蛋白表达特性与抗虫性的关系,筛选优秀转化事件,研究以三个转化事件HG-1、HG-2、HG-3为试验材料,利用ELISA检测、玉米螟生测等技术,在室内和田间详细分析心叶期和抽丝期玉米抗虫蛋白表达量,并评估抗虫性.研究结果表明,同一转化事件不同组织或器官Cry1Ab/Gc蛋白含量存在显著差异,均表现为叶〉茎〉根;不同时期叶片Cry1Ab/Gc蛋白含量存在显著差异,表现为抽丝期〉心叶期;不同转化事件间,心叶期转化事件HG-1的叶片、抽丝期转化事件HG-1和HG-2的茎中Cry1Ab/Gc蛋白的含量明显高于其他材料.室内和田间亚洲玉米螟生测试验结果表明:不同转化事件抗虫性差异显著,转化事件HG-1在心叶期和抽丝期亚洲玉米螟抗性显著高于其他两个玉米转化事件,与该时期Cry1Ab/Gc蛋白高表达的试验结果一致.本研究结果证实不同玉米转化事件Bt蛋白表达量显著差异,心叶期和抽丝期Bt蛋白表达量与亚洲玉米螟抗性呈正相关,可以作为抗虫转基因玉米优秀转化体初步筛选的重要技术指标,具有可操作性强、技术稳定性好、节省时间等优势,为抗虫转基因玉米新品种培育研发提供数据参考.
URL [本文引用: 2]

分析不同转化体Bt蛋白表达量和评估其抗虫性,进而筛选优异转化事件是转基因玉米新品种培育研究中的重要环节.为分析转cry1Ab/Gc基因玉米中Bt蛋白表达特性与抗虫性的关系,筛选优秀转化事件,研究以三个转化事件HG-1、HG-2、HG-3为试验材料,利用ELISA检测、玉米螟生测等技术,在室内和田间详细分析心叶期和抽丝期玉米抗虫蛋白表达量,并评估抗虫性.研究结果表明,同一转化事件不同组织或器官Cry1Ab/Gc蛋白含量存在显著差异,均表现为叶〉茎〉根;不同时期叶片Cry1Ab/Gc蛋白含量存在显著差异,表现为抽丝期〉心叶期;不同转化事件间,心叶期转化事件HG-1的叶片、抽丝期转化事件HG-1和HG-2的茎中Cry1Ab/Gc蛋白的含量明显高于其他材料.室内和田间亚洲玉米螟生测试验结果表明:不同转化事件抗虫性差异显著,转化事件HG-1在心叶期和抽丝期亚洲玉米螟抗性显著高于其他两个玉米转化事件,与该时期Cry1Ab/Gc蛋白高表达的试验结果一致.本研究结果证实不同玉米转化事件Bt蛋白表达量显著差异,心叶期和抽丝期Bt蛋白表达量与亚洲玉米螟抗性呈正相关,可以作为抗虫转基因玉米优秀转化体初步筛选的重要技术指标,具有可操作性强、技术稳定性好、节省时间等优势,为抗虫转基因玉米新品种培育研发提供数据参考.
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2012.06.014URL [本文引用: 1]

[目的]对转基因抗虫水稻中Bt蛋白表达量进行研究。[方法]应用酶联免疫吸附测定法(ELISA)定量检测转基因抗虫水稻生相同生长时期不同部位的Bt蛋自表达量。[结果]转基因水稻灌浆期不同组织中Bt蛋白表达绝对含量的高低顺序为:叶片未成熟种子及颖壳根茎杆;在水稻不同的生长发育(分蘖期、抽穗期和灌浆期)阶段,转基因Bt水稻中Bt蛋白的含量有一些变化;一般在水稻生长后期Bt蛋白的浓度有所下降,但幅度不大,对其抗性不会造成太大影响。[结论]该试验对田间害虫的防治以及转基因水稻的育种都具有重要意义。
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2012.06.014URL [本文引用: 1]

[目的]对转基因抗虫水稻中Bt蛋白表达量进行研究。[方法]应用酶联免疫吸附测定法(ELISA)定量检测转基因抗虫水稻生相同生长时期不同部位的Bt蛋自表达量。[结果]转基因水稻灌浆期不同组织中Bt蛋白表达绝对含量的高低顺序为:叶片未成熟种子及颖壳根茎杆;在水稻不同的生长发育(分蘖期、抽穗期和灌浆期)阶段,转基因Bt水稻中Bt蛋白的含量有一些变化;一般在水稻生长后期Bt蛋白的浓度有所下降,但幅度不大,对其抗性不会造成太大影响。[结论]该试验对田间害虫的防治以及转基因水稻的育种都具有重要意义。
URL [本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/S2095-3119(14)60897-2URL [本文引用: 1]

A synthetic cry2A* gene encoding Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) 未-endotoxin that resistance to lepidopteran pest was transformed into japonica rice variety Jijing 88, which is the most widely cultivated variety in Jilin Province, Northeast China, by Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. A total of 106 independent transformants overexpressing cry2A* gene driven by ubiquitin (Ubi) promoter was produced. Three single-copy homozygous transgenic lines were finally selected based on the results of PCR analysis, segregation ratio of Basta resistance, and Southern hybridization analyses. RT-PCR and enzyme linked immune sorbent assay (ELISA) revealed that cry2A* transcripts and protein were highly expressed in these lines. The high level of Cry2A* protein expression resulted in high resistance to rice striped stem borer as evidenced by insect feeding bioassays. Our results demonstrate that cry2A* transgenic japonica rice confers resistance to the rice striped stem borer in the laboratory conditions.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1038/35037633URLPMID:11048726 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract Rice seeds, a rich reserve of starch and protein, are a major food source in many countries. Unlike the seeds of other plants, which typically accumulate one major type of storage protein, rice seeds use two major classes, prolamines and globulin-like glutelins. Both storage proteins are synthesized on the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and translocated to the ER lumen, but are then sorted into separate intracellular compartments. Prolamines are retained in the ER lumen as protein bodies whereas glutelins are transported and stored in protein storage vacuoles. Mechanisms responsible for the retention of prolamines within the ER lumen and their assembly into intracisternal inclusion granules are unknown, but the involvement of RNA localization has been suggested. Here we show that the storage protein RNAs are localized to distinct ER membranes and that prolamine RNAs are targeted to the prolamine protein bodies by a mechanism based on RNA signal(s), a process that also requires a translation initiation codon. Our results indicate that the ER may be composed of subdomains that specialize in the synthesis of proteins directed to different compartments of the plant endomembrane system.
DOI:10.1105/tpc.113.121376URLPMID:24488962 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract In seed plants, a major pathway for sorting of storage proteins to the protein storage vacuole (PSV) depends on the Golgi-derived dense vesicles (DVs). However, the molecular mechanisms regulating the directional trafficking of DVs to PSVs remain largely elusive. Here, we report the functional characterization of the rice (Oryza sativa) glutelin precursor accumulation3 (gpa3) mutant, which exhibits a floury endosperm phenotype and accumulates excess proglutelins in dry seeds. Cytological and immunocytochemistry studies revealed that in the gpa3 mutant, numerous proglutelin-containing DVs are misrouted to the plasma membrane and, via membrane fusion, release their contents into the apoplast to form a new structure named the paramural body. Positional cloning of GPA3 revealed that it encodes a plant-specific kelch-repeat protein that is localized to the trans-Golgi networks, DVs, and PSVs in the developing endosperm. In vitro and in vivo experiments verified that GPA3 directly interacts with the rice Rab5a-guanine exchange factor VPS9a and forms a regulatory complex with Rab5a via VPS9a. Furthermore, our genetic data support the notion that GPA3 acts synergistically with Rab5a and VPS9a to regulate DV-mediated post-Golgi traffic in rice. Our findings provide insights into the molecular mechanisms regulating the plant-specific PSV pathway and expand our knowledge of vesicular trafficking in eukaryotes.
DOI:10.7606/j.issn.1000-7601.2017.02.17URL [本文引用: 1]

对9个经PCR检测确定为转Bt基因阳性的海岛棉品系的农艺性状和产量性状考察结果表明,外源基因Bt的导入对9个海岛棉品系的农艺性状和产量性状有不同程度的影响。① 受体为K222时,Bt基因导入使得株高、始节高、始节数、有效果枝数、铃数、有效铃数差异达到极显著水平(P<0.01)。当受体为XH25和XH30时,转基因品系农艺性状与对照差异无显著水平;② 9个转基因品系间株高、始节高、始节数和铃数差异达到极显著水平(P<0.01),有效果枝数和有效铃数差异达到显著水平(P<0.05);③ 9个转基因品系的产量性状与对照差异均无显著性;④ 株高、始节高、始节数、果枝数、有效果枝数、铃数和有效铃数与籽棉产量呈显著相关;⑤ 两年(2014和2015)和两点(北疆和南疆)间农艺性状及产量性状差异达到显著水平。
DOI:10.7606/j.issn.1000-7601.2017.02.17URL [本文引用: 1]

对9个经PCR检测确定为转Bt基因阳性的海岛棉品系的农艺性状和产量性状考察结果表明,外源基因Bt的导入对9个海岛棉品系的农艺性状和产量性状有不同程度的影响。① 受体为K222时,Bt基因导入使得株高、始节高、始节数、有效果枝数、铃数、有效铃数差异达到极显著水平(P<0.01)。当受体为XH25和XH30时,转基因品系农艺性状与对照差异无显著水平;② 9个转基因品系间株高、始节高、始节数和铃数差异达到极显著水平(P<0.01),有效果枝数和有效铃数差异达到显著水平(P<0.05);③ 9个转基因品系的产量性状与对照差异均无显著性;④ 株高、始节高、始节数、果枝数、有效果枝数、铃数和有效铃数与籽棉产量呈显著相关;⑤ 两年(2014和2015)和两点(北疆和南疆)间农艺性状及产量性状差异达到显著水平。
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2005.06.006URL [本文引用: 1]

田间调查发现,为害TT9-4和IR72两种水稻品种的螟虫主要为大螟、二化螟和稻纵卷叶螟.转基因水稻TT9-4对螟虫的控制作用显著优于对照IR72(P0.05),TT9-4平均每穗所结谷粒数显著多于对照IR72(P<0.05),但结实率不若IR72高,分别为56.32%和65.14%,使得TT9-4的田间产量低于对照水稻IR72.化学农药的使用对IR72水稻螟害控制有一定的作用,但控害效果不如TT9-4.
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2005.06.006URL [本文引用: 1]

田间调查发现,为害TT9-4和IR72两种水稻品种的螟虫主要为大螟、二化螟和稻纵卷叶螟.转基因水稻TT9-4对螟虫的控制作用显著优于对照IR72(P0.05),TT9-4平均每穗所结谷粒数显著多于对照IR72(P<0.05),但结实率不若IR72高,分别为56.32%和65.14%,使得TT9-4的田间产量低于对照水稻IR72.化学农药的使用对IR72水稻螟害控制有一定的作用,但控害效果不如TT9-4.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.procbio.2014.01.008URL [本文引用: 2]

We modeled Cry1C toxin and its Aminopeptidase-N receptor and in silico docking analysis was performed. Further, we utilized biopanning against Cry1C followed by blocking assays and mutagenesis analysis to identify the binding epitope of SlAPN. We have identified a putative SlAPN binding region, APN-CRY (128HLHFHLP134). A derivative of SlAPN carrying the 128HLHFHLP134 region termed as binding region of APN (BR-APN) was cloned and its involvement in Cry1C binding and toxicity was checked. Cry1C-BR-APN binding was competed by synthetic peptides homologous to loop2 and loop3 of domain II but not by that of loop伪. Additionally, alanines substitution of residues H128, H130, H132 and P134 affect the binding efficiency of receptor to Cry1C toxin (upto 4-fold lower affinity).These residues are also implicated in Cry1C toxicity as shown by the reduced ability to affect the mortality of Cry1C on S. litura larvae when toxin was preincubated with a fragment of the receptor.
