 ,1,2,*1
,1,2,*1 2
3
Development and Application of Functional Markers for Rice Blast Resistance Gene Bsr-d1 in Rice
WANG Jun1,2, ZHAO Jie-Yu3, XU Yang1,2, FAN Fang-Jun1,2, ZHU Jin-Yan1,2, LI Wen-Qi1,2, WANG Fang-Quan1,2, FEI Yun-Yan1, ZHONG Wei-Gong1, YANG Jie ,1,2,*1
,1,2,*12
3
通讯作者:
第一联系人:
收稿日期:2018-03-28接受日期:2018-07-20网络出版日期:2018-07-25
| 基金资助: |
Received:2018-03-28Accepted:2018-07-20Online:2018-07-25
| Fund supported: |

摘要
关键词:
Abstract
Keywords:
PDF (1709KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
本文引用格式
王军, 赵婕宇, 许扬, 范方军, 朱金燕, 李文奇, 王芳权, 费云燕, 仲维功, 杨杰. 水稻稻瘟病抗性基因Bsr-d1功能标记的开发和利用[J]. 作物学报, 2018, 44(11): 1612-1620. doi:10.3724/SP.J.1006.2018.01612
WANG Jun, ZHAO Jie-Yu, XU Yang, FAN Fang-Jun, ZHU Jin-Yan, LI Wen-Qi, WANG Fang-Quan, FEI Yun-Yan, ZHONG Wei-Gong, YANG Jie.
危害水稻的侵染性病害有300多种, 有些分布于全世界, 有些局限于部分地区。在我国, 常年发生的水稻病害有29种[1]。其中, 由稻瘟病菌(Magnaporthe oryzae; 无性态, Pyricularia oryzae)[2]引起的稻瘟病是水稻上最具毁灭性的病害之一, 俗称水稻的“癌症”。稻瘟病发生在全球85个水稻种植国家和地区。据统计, 在1975—1990年的16年间, 由稻瘟病引起的全球水稻产量损失高达1.57亿吨[3]。我国每隔7~10年就发生一次较大规模的稻瘟病危害, 受害面积达300~600万公顷, 稻谷损失70~125万吨[4]。稻瘟病的防治途径主要是化学防治和种植抗病品种, 长期实践证明, 选育和推广抗病品种是防治稻瘟病最经济、有效和安全的方法。但由于稻瘟病菌具有高度的变异性, 普通抗病品种种植3~5年后抗性就会逐渐丧失。因此, 选择抗谱广、抗性持久的抗病基因作为抗源来选育新品种, 已经成为抗病育种的最经济有效的策略之一。
传统的稻瘟病抗病育种主要依赖于抗性表型的鉴定, 不仅周期长且极易受环境条件和人为因素的影响, 从而降低了目标基因的选择效率。但受可鉴别不同基因的鉴别菌系的限制, 单纯依赖表型鉴定很难实现多个抗性基因的聚合。分子标记辅助选择是利用与目标基因紧密连锁或共分离的分子标记来选择基因型, 可以在水稻全生育期甚至种子鉴定目标基因及其纯合性, 且不受环境影响, 因而大大提高了选择的效率和准确性。开发与稻瘟病抗性基因紧密连锁的分子标记, 特别是根据抗性基因本身引起抗性变异的DNA序列差异开发出的基因功能标记进行分子标记辅助选择, 不仅可以大大提高抗源筛选、抗性基因鉴定及育种选择效率, 而且使通过基因聚合手段培育持久、广谱抗病良种成为可能。
自20世纪60年代日本系统开展抗稻瘟病基因的遗传研究以来, 国内外研究者已经从不同抗病品种中鉴定出80多个稻瘟病抗性基因, Pi-b[5]、Pi-ta[6]、Pi-d2[7]、Pi9[8]、Pi-21[9]、Pb1[10]等30多个抗稻瘟病基因已经被克隆(http://www.ricedata.cn/gene/index. htm)。Li等[11]利用广谱高抗水稻地谷与基因组已经测序的66份非广谱抗病水稻进行GWAS (全基因组关联)分析, 并应用高抗水稻地谷与高感材料丽江新团黑谷为亲本构建的重组自交系(抗病性经多年田间自然诱发和苗期接种鉴定)进行共相关分析, 发现了编码C2H2类转录因子的基因Bsr-d1的启动子自然变异后对稻瘟病具有抗病性, Bsr-d1基因对ZB-15、ZE-1、NC24等10个稻瘟病生理小种表现出较好的抗性, 是一个广谱的抗病基因。进一步分析发现在地谷中, Bsr-d1基因的启动子区域因一个关键核苷酸变异, 导致上游MYB转录因子对Bsr-d1的启动子结合增强, 从而抑制Bsr-d1响应稻瘟病菌诱导的表达, 并导致BSR-D1直接调控的H2O2降解酶基因表达下调, 使H2O2降解减弱, 细胞内H2O2富集, 提高了水稻的免疫反应和抗病性。该等位变异在提高抗病性的同时, 对产量性状和稻米品质没有明显影响, 具有十分重要的应用价值。获得Bsr-d1基因的功能标记来快捷、准确鉴定Bsr-d1的不同基因型, 是将Bsr-d1基因应用到稻瘟病抗性改良中的前提。
本研究根据Bsr-d1基因的启动子区域关键变异核苷酸设计得到不同类型的与目标基因共分离基因功能标记, 通过PCR产物测序的方法对基因功能标记的检查结果进行了验证, 并利用基因功能标记对不同来源的水稻品种和太湖流域粳稻资源材料进行了Bsr-d1基因型检测。这些基因功能标记的开发和含有Bsr-d1基因品种的筛选, 将有利于广谱抗稻瘟病水稻新品种的选育, 从而提高稻瘟病抗性育种的技术水平。
1 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
包括不同地区籼稻恢复系17份; 常规籼稻品种14份; 籼稻保持系3份; 江苏历年来主要推广的粳稻品种110份; 其他省份粳稻品种13份; 太湖流域地方粳稻资源148份; 太湖流域地方籼稻资源19份; 含有Bsr-d1基因的对照地谷、不含有Bsr-d1基因的对照Nipponbare, 供试水稻种质的类型及来源见附件1。1.2 Bsr-d1基因功能标记的设计和合成
1.2.1 CAPs标记的设计 根据稻瘟病抗性基因Bsr-d1的克隆结果, Bsr-d1抗病基因在LOC_Os03g3 2230启动子618位核苷酸为G, 而感病基因bsr-d1在该位点核苷酸为A, 对该功能区域生物信息学分析表明, 抗病基因单核苷酸变异产生了一个Aiu I限制内切酶位点(AG∧CT), 而感病基因不含Aiu I酶切位点(AACT)。在GenBank (http://www.ncbi.nlm. nih.gov/)下载Bsr-d1基因所在PAC (P1-derived artificial chromosome, PAC)克隆的核酸序列(AP014959), 并分析相关序列, 利用Primer Premier 5.0 (http:// www.premierbiosoft.com/)在单核苷酸变异区域的两侧设计包含该变异位点的引物, 并保证酶切后的片段能较好地在低浓度的琼脂糖凝胶上电泳分析。为明确本研究中Bsr-d1功能标记扩展的PCR产物为Bsr-d1的DNA片段的特异性扩增, 设计测序引物对部分品种Bsr-d1基因的功能区域进行PCR扩增、测序, 进一步验证功能标记的准确性。1.2.2 等位基因特异PCR标记的设计 等位基因特异PCR (allele-specific PCR, AS-PCR)的基本原理是根据目的基因存在的SNP设计的特异引物仅在一种基因型中有扩增产物, 而另一种基因型中没有扩增产物, 因此通过2次PCR扩增就可以区分3种基因型。针对LOC_Os03g32230启动子618位点存在的SNP, 以该位点为引物的3°端设计2条反向引物, 一个与Bsr-d1基因完全匹配, 一个与bsr-d1完全匹配; 而另一条正向引物为相同引物。这样, 2对引物为互补的等位基因特异引物, 可以分别与抗病和感病基因型结合, 进行特异扩增。为增强PCR扩增的特异性, 部分引物在3°端引入了核苷酸错配。本研究所合成引物及相关信息见表1, 引物由Invitrogen中国公司合成。
Table 1
表1
表1基于变异位点设计的功能标记和测序引物
Table 1
| 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列 Primer sequence (5'-3') | 片段长度 Expected size (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| CAPs1F | AGTCTAGCATCCACCGTTCCAC | 313 |
| CAPs1R | GTAGGCAGGCAGTGGGATGA | |
| CAPs2F | TTTTATAGGACAGAGGGAATATGTA | 368 |
| CAPs2R | GCAGTGGGATGAACCTGTAC | |
| Bsr-d1-F | AGTCTAGCATCCACCGTTCCAC | |
| 1Bsr-d1-R | CTTTTCGCTTATACTTATATTTATCAGC | 241 |
| 1bsr-d1-R | CTTTTCGCTTATACTTATATTTATCAGT | 241 |
| 2Bsr-d1-R | CTTTTCGCTTATACTTATATTTATCgGC | 241 |
| 2bsr-d1-R | CTTTTCGCTTATACTTATATTTATCgGT | 241 |
| 3Bsr-d1-R | CTTTTCGCTTATACTTATATTTATCAaC | 241 |
| 3Bsr-d1-R | CTTTTCGCTTATACTTATATTTATCAaT | 241 |
| C1F | AGTCTAGCATCCACCGTTCCAC | 755 |
| C1R | ATGATTTGATGGGATTGATTGC | |
| C2F | TTTTATAGGACAGAGGGAATATGTA | 983 |
| C2R | GCGAGGTACTCCTCCTTGTTGAT |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
1.3 DNA提取
在水稻分蘖盛期选取新鲜幼嫩叶片, 采用CTAB的方法提取水稻基因组DNA。1.4 PCR扩增、酶切和电泳
使用实验室常规PCR扩增技术, 20 μL反应体系包括模板DNA (约15 ng μL-1) 2 μL、引物(4 pmol μL-1) 2 μL、10×缓冲液(25 mmol L-1) 2 μL、MgCl2 (25 mmol L-1) 1.2 μL、dNTP (2.5 mmol L-1) 0.4 μL、Taq DNA聚合酶(5 U μL-1) 0.2 μL、灭菌双蒸水12.2 μL。在Eppendorf PCR仪上扩增, 反应条件为: (1) 94°C, 预变性5 min; (2) 94°C, 30 s; 50°C, 30 s; 72°C, 1 min; 共35个循环; (3) 72°C再延伸10 min。反应产物经1.5%的琼脂糖凝胶电泳分离, 筛选出PCR产物条带最清晰、单一且没有杂带的引物。对筛选出的引物扩增的PCR产物进行Aiu I酶切, 酶切反应体系为10 μL, PCR反应产物5 μL、10×buffer R 1 μL、Aiu I (10 U μL-1) 0.25 μL、ddH2O 3.75 μL。在37°C恒温水浴锅酶切5~8 h, 酶切产物在1.5%琼脂糖凝胶上电泳, DuRed染色, 经紫外凝胶成相系统成像。1.5 Bsr-d1基因的测序和序列比对
为排除假阳性, 即明确Bsr-d1的CAPs基因标记的PCR产物能够被Aiu I酶切开的水稻材料含有Bsr-d1基因, 不能够被Aiu I酶切开的水稻材料含有bsr-d1基因, 对6份水稻品种的PCR 产物测序, PCR反应体系为50 μL, 利用试剂盒回收目标条带, 由上海Invitrogen公司测序。利用测序引物的正反向引物双向测序, 将序列拼接后与地谷的Bsr-d1进行序列比对。2 结果与分析
2.1 Bsr-d1基因CAPs功能标记的筛选和验证
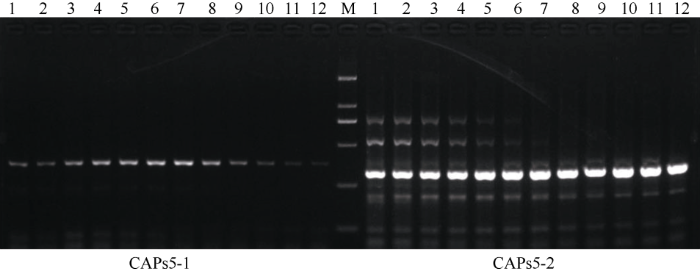
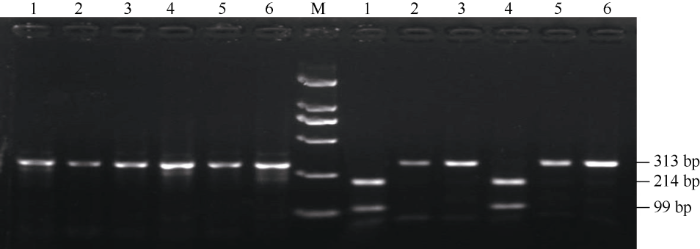
以地谷的DNA为模板, 利用表1设计的2对CAPs功能标记进行梯度PCR扩增, 梯度范围为45~55°C, 扩增产物经1.5%琼脂糖凝胶电泳分析(图1)。由图1可以看出, CAPs5-1在退火温度为50°C扩增的PCR产物条带最清晰、单一且没有杂带, 其产物可以用于进一步的Aiu I酶切分析。以地谷、Nipponbare、南粳9108、广陆矮4号、武育粳3号和南粳45的DNA为模板, 对CAPs5-1扩增的PCR产物进行Aiu I酶切, 并在1.5%琼脂糖凝胶上电泳(图2)。由图2可以看出含有Bsr-d1基因的水稻品种地谷能够被Aiu I酶切, 分别形成99 bp、214 bp的特征条带; 而不含有Bsr-d1基因的水稻品种Nipponbare不能被Aiu I酶切, 只形成313 bp的特征条带; 广陆矮4号扩增产物能够被Aiu I酶切成99 bp、214 bp的特征条带, 说明广陆矮4号含有稻瘟病广谱抗性基因Bsr-d1; 南粳9108、武育粳3号和南粳45等3个品种的扩增产物均不能被Aiu I酶切, 说明这些品种中均不含有Bsr-d1基因。图1
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图12对引物梯度PCR扩增产物在1.5%的琼脂糖胶电泳结果
M: DL2000; 1~12退火温度分别为: 45.1°C, 45.3°C, 45.9°C, 46.8°C, 47.9°C, 49.1°C, 50.4°C, 51.7°C, 52.8°C, 53.8°C, 54.5°C, 54.8°C。
Fig. 1Gradient PCR amplification products of Digu using two new designed primers
M: DL2000; Annealing temperature of 1-12: 45.1°C, 45.3°C, 45.9°C, 46.8°C, 47.9°C, 49.1°C, 50.4°C, 51.7°C, 52.8°C, 53.8°C, 54.5°C, 54.8°C.
图2
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图2CAPs5-1 PCR扩增产物和酶切结果
M左侧为PCR扩增产物; M右侧为酶切后的产物; M: DL2000; 1~6: 地谷, Nipponbare, 南粳9108, 广陆矮4号,武育粳3号, 南粳45。
Fig. 2Enzyme digestion results of PCR amplification products using CAPs5-1
Left of M is PCR amplification products; Right of M is enzyme-digested products; M: DL2000; 1-6: Digu, Nipponbare, Nanjing 9108, Guanglu,ai 4, Wuyujing 3, Nanjing 45.
图3
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图3部分水稻品种Bsr-d1基因位点功能区的序列比对结果
Fig. 3Sequence alignment of Bsr-d1 functional domain for partial rice varieties
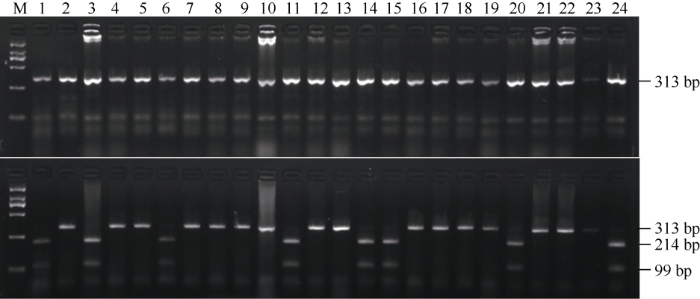
为了进一步验证Bsr-d1基因功能标记CAPs5-1检测结果的准确性, 我们对6个水稻品种(地谷、Nipponbare、南粳9108、广陆矮4号、武育粳3号、南粳45)进行了Bsr-d1基因功能位点的全长测序, 通过序列比对发现, 能够被Aiu I酶切的广陆矮4号与地谷中Bsr-d1功能区域序列完全一致, 即在Bsr-d1基因启动子的618 bp处核苷酸为G; 不能够被酶切的3个品种(南粳9108、武育粳3号和南粳45)中bsr-d1序列与Nipponbare完全一致, 即在Bsr-d1基因启动子的618 bp处核苷酸为A (图4)。因此, 利用CAPs5-1标记的PCR扩增结合Aiu I酶切的方法可以准确鉴定出水稻品种中是否含有稻瘟病广谱抗性基因Bsr-d1。
图4
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图4CAPs5-1对部分水稻品种的分子检测结果
M: DL2000; 1~24: 地谷, Nipponbare, 南京1号, 绵恢501, 浙恢7954, 盐恢559, 镇恢084, BG90-2, 圭630, 明恢63, 青四矮16B, 辐恢718, 扬稻6号, 冈46B, 陆财号, 明恢78, IRBB21, 蜀恢527, 多恢1号, 桂朝2号, 绵恢725, 乐恢188, 广恢128, 珍汕97B。
Fig. 4Molecular detection of partial rice varieties by CAPs5-1
M: DL2000; 1-24: Digu, Nipponbare, Nanjing 1, Mianhui 501, Zhehui 7954, Yanhui 559, Zhenhui 084, BG90-2, Gui 630, Minghui 63, Qingsi’ai 16B, Fuhui 718, Yangdao 6, Gang 46B, Lucaihao, Minghui 78, IRBB21, Shuhui 527, Duohui 1, Guichao 2, Mianhui 725, Yuehui 188, Guanghui 128, Zhenshan 97B.
2.2 CAPs5-1对水稻品种的Bsr-d1基因型鉴定
利用分子标记CAPs5-1对来自不同地区的22份水稻品种进行PCR扩增, PCR扩增产物经Aiu I酶切后电泳检测表明: 15个品种(绵恢501、浙恢7954、镇恢084、BG90-2、圭630、明恢63、辐恢718、扬稻6号、明恢78、IRBB21、蜀恢527、多恢1号、绵恢725、乐恢188、广恢128) CAPs5-1 PCR产物不能够被Aiu I酶切, 形成313 bp的特征条带, 与Nipponbare一致, 因此这些品种中均不含有Bsr-d1基因; 7个品种(南京1号、盐恢559、青四矮16B、冈46B、陆财号、桂朝2号、珍汕97B)的CAPs5-1 PCR产物能够被Aiu I酶切, 形成99 bp、214 bp的特征条带, 与地谷的带型完全一致, 说明这7个水稻品种中均含有稻瘟病广谱抗性基因Bsr-d1, 这些水稻品种在育种中可以作为优异亲本用于水稻稻瘟病的抗性改良(图4)。因此, 通过CAPs5-1标记的PCR扩增结合Aiu I酶切能准确鉴定水稻稻瘟病抗性种质资源。2.3 Bsr-d1基因AS-PCR功能标记的筛选
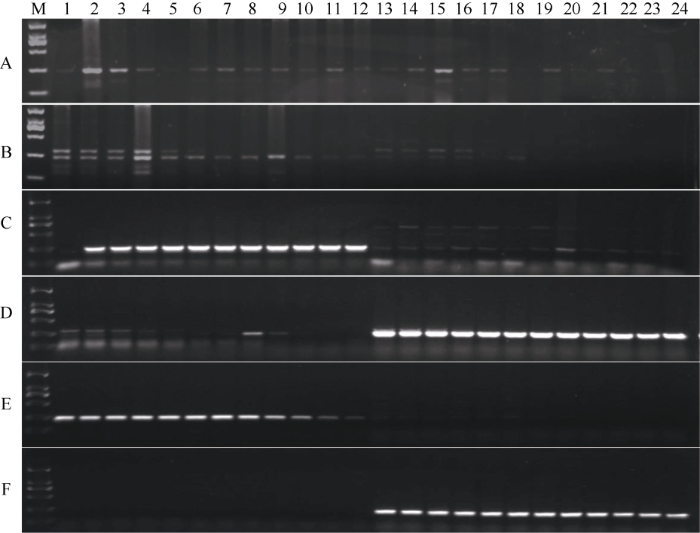
以地谷与Nipponbare的DNA为模板, 利用表1设计的3对AS-PCR标记进行梯度PCR扩增及1.5%琼脂糖凝胶电泳分析(图5)。图5-A为Bsr-d1基因型设计引物1Bsr-d1 (Bsr-d1-F和1Bsr-d1-R), 1Bsr-d1引物可以扩增出地谷中Bsr-d1基因型特异条带, 但也能够扩增出Nipponbare中bsr-d1基因型非特异条带; 图5-B为bsr-d1基因型设计引物1bsr-d1 (Bsr-d1 -F和1bsr-d1-R), 1bsr-d1引物可以扩增出Nipponbare中bsr-d1基因型特异条带, 但也能够扩增出地谷中Bsr-d1基因型非特异条带; 图5-C为Bsr-d1基因型设计引物2Bsr-d1 (Bsr-d1-F和2Bsr-d1-R), 2Bsr-d1引物可以扩增出地谷中Bsr-d1基因型特异条带, 但也能够扩增出Nipponbare中bsr-d1基因型非特异条带; 图5-D为bsr-d1基因型设计引物2bsr-d1 (Bsr-d1 -F和2bsr-d1-R), 2bsr-d1引物既能扩增出Nipponbare中bsr-d1基因型特异条带又能扩增出非特异性条带, 同时也能够扩增出地谷中Bsr-d1基因型非特异条带。图5-E为Bsr-d1基因型设计引物3Bsr-d1 (Bsr-d1-F和3Bsr-d1-R), 3Bsr-d1引物可以扩增出地谷中Bsr-d1基因型特异条带, 同时不能够扩增出Nipponbare中bsr-d1基因型非特异条带; 图5-F为bsr-d1基因型设计引物3bsr-d1(Bsr-d1-F和3bsr-d1-R), 3bsr-d1引物可以扩增出Nipponbare中 bsr-d1基因型特异条带, 同时不能够扩增出地谷中Bsr-d1基因型非特异条带。图5
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图5Bsr-d1基因等位基因特异标记的梯度PCR扩增结果
M: DL2000; A: 1Bsr-d1引物梯度PCR扩增产物; B: 1bsr-d1引物梯度PCR扩增产物; C: 2Bsr-d1引物梯度PCR扩增产物; D: 2bsr-d1引物梯度PCR扩增产物; E: 3Bsr-d1引物梯度PCR扩增产物; F: 3bsr-d1引物梯度PCR扩增产物; 1~12为地谷的不同引物对在退火温度分别为45.1°C、45.3°C、45.9°C、46.8°C、47.9°C、49.1°C、50.4°C、51.7°C、52.8°C、53.8°C、54.5°C、54.8°C时的扩增产物; 13~24为Nipponbare的不同引物对在退火温度分别为45.1°C、45.3°C、45.9°C、46.8°C、47.9°C、49.1°C、50.4°C、51.7°C、52.8°C、53.8°C、54.5°C、54.8°C时的扩增产物。
Fig. 5Gradient PCR amplification products of Digu and Nipponbare using allelic-specific PCR markers
M: DL2000; A: Gradient PCR amplification products by 1Bsr-d1; B: Gradient PCR amplification products by 1bsr-d1; C: Gradient PCR amplification products by 2Bsr-d1; D: Gradient PCR amplification products by 2bsr-d1; E: Gradient PCR amplification products by 3Bsr-d1; F: Gradient PCR amplification products by 3bsr-d1; 1-12: amplification products of Didu by different primers in annealing temperatures of 45.1°C, 45.3°C, 45.9°C, 46.8°C, 47.9°C, 49.1°C, 50.4°C, 51.7°C, 52.8°C, 53.8°C, 54.5°C, 54.8°C; and 13-24: amplification products of Nipponbare by different primers in annealing temperatures of 45.1°C, 45.3°C, 45.9°C, 46.8°C, 47.9°C, 49.1°C, 50.4°C, 51.7°C, 52.8°C, 53.8°C, 54.5°C, 54.8°C.
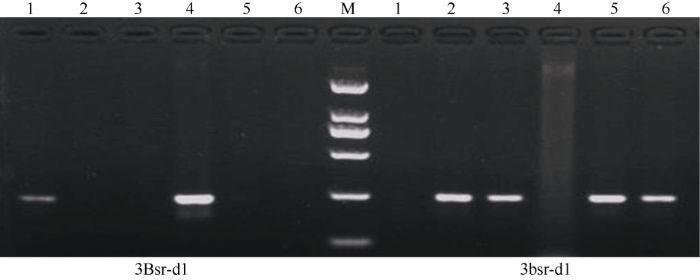
以地谷、Nipponbare、南粳9108、广陆矮4号、武育粳3号和南粳45的DNA为模板, 筛选出的引物3Bsr-d1和3bsr-d1进行PCR扩增, 退火温度为52°C, 扩增产物在1.5%琼脂糖凝胶电泳分析(图6)。由图6可以看出, 以3Bsr-d1为引物, 地谷和广陆矮4号能够扩增出241 bp的特异条带, 同时以3bsr-d1为引物, 地谷和广陆矮4号不能够扩增出241 bp的非特异条带, 说明地谷和广陆矮4号含有稻瘟病广谱抗性基因Bsr-d1; 以3Bsr-d1为引物, Nipponbare、南粳9108、武育粳3号和南粳45不能够扩增出241 bp的非特异条带, 同时以3bsr-d1为引物, Nipponbare、南粳9108、武育粳3号和南粳45能够扩增出241 bp的特异条带, 说明这些品种中均不含有Bsr-d1基因, 3Bsr-d1和3bsr-d1检测结果与测序完全一致。因此, 利用3Bsr-d1和3bsr-d1分子标记可以准确鉴定出水稻品种中是否含有稻瘟病广谱抗性基因Bsr-d1。
图6
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图6Bsr-d1基因等位基因特异标记3Bsr-d1和3bsr-d1扩增结果
M: DL2000; 1~6: 地谷, Nipponbare, 南粳9108, 广陆矮4号, 武育粳3号, 南粳45。
Fig. 6PCR amplification products using allelic-specific PCR markers 3Bsr-d1 and 3bsr-d1
M: DL2000; 1-6: Digu, Nipponbare, Nanjing 9108, Guanglu’ai 4, Wuyujing 3, Nanjing 45.
2.4 AS-PCR功能标记对水稻品种的Bsr-d1基因型鉴定
利用分子标记3Bsr-d1/3bsr-d1对来自不同地区的22份水稻品种进行PCR扩增, PCR扩增产物经1.5%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测分析表明: 15个品种(绵恢501、浙恢7954、镇恢084、BG90-2、圭630、明恢63、辐恢718、扬稻6号、明恢78、IRBB21、蜀恢527、多恢1号、绵恢725、乐恢188和广恢128)在以3bsr-d1为引物时都能够扩增出241 bp的特征条带, 在以3Bsr-d1为引物时都不能够扩增出241 bp的非特征条带, 与Nipponbare一致, 因此这些品种中均不含有Bsr-d1基因; 7个品种(南京1号、盐恢559、青四矮16B、冈46B、陆财号、桂朝2号、珍汕97B)在以3Bsr-d1为引物时都能够扩增出241 bp的特征条带, 在以3bsr-d1为引物时都不能够扩增出241 bp的非特征条带, 与地谷的带型完全一致, 说明这7个水稻品种中均含有稻瘟病广谱抗性基因Bsr-d1 (图7)。AS-PCR功能标记检测结果与CAPs功能标记检测结果完全一致, 因此, 用3Bsr-d1和3bsr-d1分子标记也能准确鉴定水稻稻瘟病抗性种质资源。图7
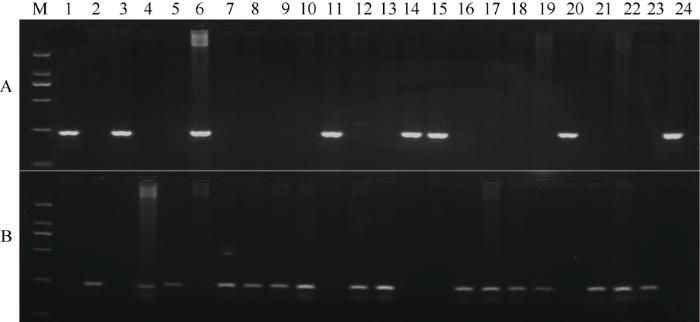 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图73Bsr-d1和3bsr-d对部分水稻品种的分子检测结果
M: DL2000; 1~24: 地谷, Nipponbare, 南京1号, 绵恢501, 浙恢7954, 盐恢559, 镇恢084, BG90-2, 圭630, 明恢63, 青四矮16B, 辐恢718, 扬稻6号, 冈46B, 陆财号, 明恢78, IRBB21, 蜀恢527, 多恢1号, 桂朝2号, 绵恢725, 乐恢188, 广恢128, 珍汕97B。
Fig. 7Molecular detection of partial rice varieties by 3Bsr-d1 and 3bsr-d
M: DL2000; 1-24: Digu, Nipponbare, Nanjing1, Mianhui 501, Zhehui 7954, Yanhui 559, Zhenhui 084, BG90-2, Gui 630, Minghui 63, Qingsi,ai 16B, Fuhui 718, Yangdao 6, Gang 46B, Lucaihao, Minghui 78, IRBB21, Shuhui 527, Duohui 1, Guichao 2, Mianhui 725, Yuehui 188, Guanghui 128, Zhenshan 97B.
利用3Bsr-d1和3bsr-d1标记进一步对34份籼稻品种、江苏历年来主要推广的110份粳稻品种、其他省份的13份粳稻品种、148份太湖流域地方粳稻资源和19份太湖流域地方籼稻资源进行Bsr-d1基因型检测表明, 11个籼稻品种和资源中含有Bsr-d1基因, 而271份粳稻品种和资源中均不含有Bsr-d1基因。
3 讨论
推广种植抗稻瘟病水稻品种可以大大减少农药的使用量, 达到安全、经济、环境友好的目标。目前, 选育抗稻瘟病水稻新品种的最主要手段就是利用与稻瘟病抗病基因紧密连锁或共分离的分子标记进行辅助选择[12,13,14,15,16]。利用分子标记对目的基因进行准确的选择, 在加速稻瘟病抗源筛选、抗病基因的鉴定和快速培育抗病品种等研究方面都具有重大意义。根据分子标记检测到的多态性与功能的相关性水平, 分子标记辅助选择中的标记技术被分为DNA标记、基因标记和功能标记3种类型。Andersen等[17]最早提出了功能标记的概念, 是根据目的基因内部引起表型性状变异的DNA序列差异开发出来的一种新型分子标记。由于是来自基因内的功能性基序, 功能标记不需要进一步验证就可以在不同的遗传背景下确定目标基因的有无。随着分子生物学和功能基因组学的飞速发展, 水稻重要性状的功能标记已经在分子标记辅助育种和品种鉴定中发挥了重要作用[18,19,20,21]。在与稻瘟病紧密连锁的分子标记开发研究方面, Hayashi等[22]根据稻瘟病抗病基因Piz、Piz-t、Pit、Pik、Pik-m、Pik-p、Pita、Pita-2和Pib所在区间内存在的SNP和InDel, 设计了一系列的等位基因特异PCR引物和InDel引物, 通过不同群体分别筛选出这9个抗病基因两侧和共分离的分子标记, 实现了对这9个抗病基因的准确选择。随着越来越多的稻瘟病抗病基因被克隆, 可以根据抗病基因与感病基因在序列上差异开发基因的功能标记对目标基因实现100%准确的选择。在稻瘟病抗病基因功能标记的研究方面, Jia等[23]和王忠华等[24]根据抗病基因Pi-ta和感病等位基因pi-ta在功能区域存在的差异设计了Pi-ta的功能标记, 利用该标记可以准确地鉴定出分离群体和品种资源中是否含有Pi-ta基因。Fjellstrom等[25]针对稻瘟病抗病基因Pib抗感等位基因功能基序的差异, 开发了Pib基因的显性功能标记Pibdom, 可以检测不同品种中是否含有Pib抗病基因, 但不能区分杂合基因型; 刘洋等[26]在此基础上开发了检测感病等位基因Pib的显性标记Lys145, 同时利用Pibdom和Lys145就可以准确鉴定出不同品种中是否含有Pib基因且能够区分不同基因型。Wang等[27]根据稻瘟病抗性基因Pi25不同等位基因编码区序列差异开发了4套CAPS功能标记(CAP1/ Hinc II、CAP3/Bgl II、CAP3/Nde I和CAP3/Hpy99 I), 均能准确检测Pi25/pi25座位。王军等[28]根据Pi-kh感病基因和抗病基因序列存在143 bp插入的特征, 设计了InDel功能标记FM143, 并利用该标记对65份江苏省历年来大面积推广的粳稻品种和64份粳稻品系进行基因型检测。
广谱持久抗稻瘟病基因Bsr-d1与其感病等位基因仅在启动子618位核苷酸处存在一核苷酸的差异(G/A), 该差异产生了一个Aiu I限制内切酶位点(AG∧CT), 本研究筛选获得了Bsr-d1基因的CAPs功能标记CAPs5-1, 结合测序结果验证, CAPs5-1能够准确鉴定出Bsr-d1不同基因型, 鉴定过程要对水稻DNA进行PCR扩增, 然后用限制性内切酶对PCR 扩增产物进行酶切, 再通过凝胶电泳进行检测。CAPs5-1具有共显性、位点特异性高的优点, 但由于需要用到限制性内切酶酶切, 存在着操作略繁琐、成本略高的缺点。本研究同时基于AS-PCR原理, 根据Bsr-d1基因启动子618位核苷酸处的SNP设计3对AS-PCR标记, 通过梯度PCR扩增筛选, 获得了Bsr-d1基因的AS-PCR功能标记3Bsr-d1/3bsr- d1及其特异性扩增的退火温度, 3Bsr-d1/3bsr-d1可以准确鉴定出Bsr-d1的不同基因型, 鉴定过程要对水稻DNA进行2次PCR扩增, 再通过凝胶电泳进行检测。与CAPs5-1相比, 3Bsr-d1/3bsr-d1检测过程更加简单, 成本更加低, 但扩增条件要求相对更严格。
利用3Bsr-d1/3bsr-d对324份不同类型的水稻品种和资源检测发现, 11个籼稻品种和资源中含有Bsr-d1基因, 而271份粳稻品种和资源中均不含有Bsr-d1基因, 说明Bsr-d1基因在籼稻品种中存在一定的分布, 粳稻种质资源中几乎都不含有Bsr-d1基因, 这可能是该基因的功能位点突变发生在籼粳分化以后的原因。利用功能标记进行Bsr-d1基因型选择结合回交转育的方法, 将籼稻资源中的Bsr-d1基因快速准确地转育到粳稻品种中, 可能是粳稻育种中提高稻瘟病持久抗性的一条有效途径。
4 结论
根据广谱持久抗稻瘟病基因Bsr-d1功能区域存在的单核苷酸差异, 筛选获得了该基因的2种不同类型的基因功能标记CAPs5-1和3Bsr-d1/3bsr-d, 均可准确鉴定Bsr-d1的不同基因型, 用于稻瘟病抗病基因Bsr-d1的分子标记辅助选择育种和资源筛选鉴定。利用3Bsr-d1/3bsr-d对324份不同类型的水稻品种和资源检测, 获得了11个含有Bsr-d1基因的水稻品种和资源, 可作为Bsr-d1基因供体应用于稻瘟病抗性改良育种。参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0006-3193.2004.11.002URL [本文引用: 1]

概述了国内外水稻抗病育种基础理论研究、育种新战略和新技术及其应用的进展,分析了水稻抗病育种研究的问题与发展趋势。
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0006-3193.2004.11.002URL [本文引用: 1]

概述了国内外水稻抗病育种基础理论研究、育种新战略和新技术及其应用的进展,分析了水稻抗病育种研究的问题与发展趋势。
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1126/science.276.5313.726URLPMID:9115193 [本文引用: 1]

Analysis of viral and bacterial pathogenesis has revealed common themes in the ways in which plants and animals respond to pathogenic agents. Pathogenic bacteria use macromolecule delivery systems (types III and IV) to deliver microbial avirulence proteins and transfer DNA-protein complexes directly into plant cells. The molecular events that constitute critical steps of plant-pathogen interactions seem to involve ligand-receptor mechanisms for pathogen recognition and the induction of signal transduction pathways in the plant that lead to defense responses. Unraveling the molecular basis of disease resistance pathways has laid a foundation for the rational design of crop protection strategies.
URL [本文引用: 1]

react-text: 182 We construct an index that track the extent to which countries have developed a modern industrial or services based economy that protects the environment and provides equal opportunities. Following…" /react-text react-text: 183 /react-text [more]
[本文引用: 1]
.
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02739.xURLPMID:16709195 [本文引用: 1]

Rice blast, caused by the fungal pathogen Magnaporthe grisea , is one of the most devastating diseases in rice worldwide. The dominant resistance gene, Pi-d2 [previously named Pi-d(t)2 ], present in the rice variety Digu, confers gene-for-gene resistance to the Chinese blast strain, ZB15. Pi-d2 was previously mapped close to the centromere of chromosome 6. In this study, the Pi-d2 gene was isolated by a map-based cloning strategy. Pi-d2 encodes a receptor-like kinase protein with a predicted extracellular domain of a bulb-type mannose specific binding lectin (B-lectin) and an intracellular serine hreonine kinase domain. Pi-d2 is a single-copy gene that is constitutively expressed in the rice variety Digu. Transgenic plants carrying the Pi-d2 transgene confer race-specific resistance to the M. grisea strain, ZB15. The Pi-d2 protein is plasma membrane localized. A single amino acid difference at position 441 of Pi-d2 distinguishes resistant and susceptible alleles of rice blast resistance gene Pi-d2 . Because of its novel extracellular domain, Pi-d2 represents a new class of plant resistance genes.
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1126/science.1175550URLPMID:19696351 [本文引用: 1]

Blast disease is a devastating fungal disease of rice, one of the world's staple foods. Race-specific resistance to blast disease has usually not been durable. Here, we report the cloning of a previously unknown type of gene that confers non--race-specific resistance and its successful use in breeding. Pi21 encodes a proline-rich protein that includes a putative heavy metal--binding domain and putative protein-protein interaction motifs. Wild-type Pi21 appears to slow the plant's defense responses, which may support optimization of defense mechanisms. Deletions in its proline-rich motif inhibit this slowing. Pi21 is separable from a closely linked gene conferring poor flavor. The resistant pi21 allele, which is found in some strains of japonica rice, could improve blast resistance of rice worldwide.
.
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.cell.2017.06.008URLPMID:28666113 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract Rice feeds half the world's population, and rice blast is often a destructive disease that results in significant crop loss. Non-race-specific resistance has been more effective in controlling crop diseases than race-specific resistance because of its broad spectrum and durability. Through a genome-wide association study, we report the identification of a natural allele of a C 2 H 2 -type transcription factor in rice that confers non-race-specific resistance to blast. A survey of 3,000 sequenced rice genomes reveals that this allele exists in 10% of rice, suggesting that this favorable trait has been selected through breeding. This allele causes a single nucleotide change in the promoter of the bsr-d1 gene, which results in reduced expression of the gene through the binding of the repressive MYB transcription factor and, consequently, an inhibition of H 2 O 2 degradation and enhanced disease resistance. Our discovery highlights this novel allele as a strategy for breeding durable resistance in rice. Copyright 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1001-7216.2008.01.004URL [本文引用: 1]

以C101LAC和C101A51为稻瘟病抗性基因的供体亲本,金23B为受体亲本,通过杂交、复交及一次回交,在分离世代,利用分子标记辅助选择技术结合特异稻瘟病菌株接种鉴定和农艺性状筛选,获得6个导入Pi-1、Pi-2和Pi-33基因的金23B导入系,其中导入系W1对稻瘟病的抗病频率为96.7%,明显高于携带单个基因的C104LAC(Pi-1)、C101A51(Pi-2)和北京糯(Pi-33)。基因聚合后抗病频率提高,说明基因聚合是培育稻瘟病持久抗性的有效方法之一。
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1001-7216.2008.01.004URL [本文引用: 1]

以C101LAC和C101A51为稻瘟病抗性基因的供体亲本,金23B为受体亲本,通过杂交、复交及一次回交,在分离世代,利用分子标记辅助选择技术结合特异稻瘟病菌株接种鉴定和农艺性状筛选,获得6个导入Pi-1、Pi-2和Pi-33基因的金23B导入系,其中导入系W1对稻瘟病的抗病频率为96.7%,明显高于携带单个基因的C104LAC(Pi-1)、C101A51(Pi-2)和北京糯(Pi-33)。基因聚合后抗病频率提高,说明基因聚合是培育稻瘟病持久抗性的有效方法之一。
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1006.2011.00975URL [本文引用: 1]

水稻稻瘟病和条纹叶枯病是长江中下游粳稻稻区两大主要病害,选育 抗病品种是防治这两大病害最有效的方法.以同时含有稻瘟病抗病基因Pi-ta和Pi-b的武运粳8号,含有条纹叶枯病抗病基因Sty-bi的镇稻42为基 因供体配置杂交组合.利用Pi-ta和Pi-b的基因标记和Sty-bi紧密连锁的分子标记对分离世代进行基因位点的检测,结合田间多代选育、抗性鉴定将 3个抗病基因同时转育到高产品种中,选育出高产、优质、多抗水稻新品系74121.利用分子标记辅助选择,为选育多抗水稻新品种提供了一种简单、快捷的选 择方法,同时也为水稻抗病育种提供了新的遗传资源.
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1006.2011.00975URL [本文引用: 1]

水稻稻瘟病和条纹叶枯病是长江中下游粳稻稻区两大主要病害,选育 抗病品种是防治这两大病害最有效的方法.以同时含有稻瘟病抗病基因Pi-ta和Pi-b的武运粳8号,含有条纹叶枯病抗病基因Sty-bi的镇稻42为基 因供体配置杂交组合.利用Pi-ta和Pi-b的基因标记和Sty-bi紧密连锁的分子标记对分离世代进行基因位点的检测,结合田间多代选育、抗性鉴定将 3个抗病基因同时转育到高产品种中,选育出高产、优质、多抗水稻新品系74121.利用分子标记辅助选择,为选育多抗水稻新品种提供了一种简单、快捷的选 择方法,同时也为水稻抗病育种提供了新的遗传资源.
DOI:10.1007/s11032-012-9751-6URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.tplants.2003.09.010URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1006.2009.02000URL [本文引用: 1]

Wide compatibility varieties (WCVs) with are able to produce highly fertile hybrids when crossed to both japonica is to test the fertility of F hybrid. However, this method is labour-consuming, time-consuming and. difficult in operation. The technically simplified approach of marker-assisted selection(MAS) has directly and practically used in rice breeding. Therefore, it is urgent to find a convenient and efficient way in WCV breeding with MAS. The wide compatibility gene () has 136 bp deletion compared with the , we developed the functional marker S5136 based on the deletion in the DNA sequence of . The differentiation for S5-j.The results indicated that this marker was low-cost, robust technique that can be utilized to identify the in WCVs like 02428, Dular and CPSLO17. The S5136 could distinguish the homozygous population derived from 3037 and 02428. From the tested materials, 13 germplasms with were identified and conformed by sequencing the S5136 PCR products, and 2 restore lines with germplasm screening, perfect marker-assisted selection breeding and seed purity testing for the two line hybrids with Pei’ai 64S as maternal parent.
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1006.2009.02000URL [本文引用: 1]

Wide compatibility varieties (WCVs) with are able to produce highly fertile hybrids when crossed to both japonica is to test the fertility of F hybrid. However, this method is labour-consuming, time-consuming and. difficult in operation. The technically simplified approach of marker-assisted selection(MAS) has directly and practically used in rice breeding. Therefore, it is urgent to find a convenient and efficient way in WCV breeding with MAS. The wide compatibility gene () has 136 bp deletion compared with the , we developed the functional marker S5136 based on the deletion in the DNA sequence of . The differentiation for S5-j.The results indicated that this marker was low-cost, robust technique that can be utilized to identify the in WCVs like 02428, Dular and CPSLO17. The S5136 could distinguish the homozygous population derived from 3037 and 02428. From the tested materials, 13 germplasms with were identified and conformed by sequencing the S5136 PCR products, and 2 restore lines with germplasm screening, perfect marker-assisted selection breeding and seed purity testing for the two line hybrids with Pei’ai 64S as maternal parent.
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-7216.2011.01.006URL [本文引用: 1]

水稻酚反应是水稻分类的重要依据。控制水稻酚反应的多酚氧化酶基因(PPO)已经克隆,根据其等位基因的DNA序列差异设计了InDel功能标记FMppo-18和FMppo-29。利用这两个标记对45份材料进行了标记基因型分析和酚反应鉴定。结果发现3份普通野生稻为非缺失带型;8份籼稻材料中6份为非缺失带型,而Dular为缺失29 bp带型,龙晴为缺失18bp带型,表明Dular和龙晴分别携带29 bp和18 bp缺失的PPO等位基因;11份粳稻材料中9份携带18 bp缺失的PPO等位基因,2份携带29 bp缺失的PPO等位基因。对23份杂草稻鉴定的结果表明,7份早年发现的杂草稻,即3份江苏省连云港穞稻和4份安徽省怀远、来安、全椒、肥东的塘稻为非缺失带型;而16份近年来发现的杂草稻中14份不缺失,2份表现为18 bp缺失的PPO等位基因,与江苏省大面积推广的栽培粳稻品种携带相同的PPO基因。酚反应结果表明带29 bp或18bp缺失的PPO等位基因的材料酚反应呈阴性,而不缺失的材料酚反应呈阳性。标记基因型与酚反应表现型完全对应。表明这两个功能标记可用于水稻种质资源鉴定、进化研究以及多酚氧化酶基因的分子标记辅助选择育种。
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-7216.2011.01.006URL [本文引用: 1]

水稻酚反应是水稻分类的重要依据。控制水稻酚反应的多酚氧化酶基因(PPO)已经克隆,根据其等位基因的DNA序列差异设计了InDel功能标记FMppo-18和FMppo-29。利用这两个标记对45份材料进行了标记基因型分析和酚反应鉴定。结果发现3份普通野生稻为非缺失带型;8份籼稻材料中6份为非缺失带型,而Dular为缺失29 bp带型,龙晴为缺失18bp带型,表明Dular和龙晴分别携带29 bp和18 bp缺失的PPO等位基因;11份粳稻材料中9份携带18 bp缺失的PPO等位基因,2份携带29 bp缺失的PPO等位基因。对23份杂草稻鉴定的结果表明,7份早年发现的杂草稻,即3份江苏省连云港穞稻和4份安徽省怀远、来安、全椒、肥东的塘稻为非缺失带型;而16份近年来发现的杂草稻中14份不缺失,2份表现为18 bp缺失的PPO等位基因,与江苏省大面积推广的栽培粳稻品种携带相同的PPO基因。酚反应结果表明带29 bp或18bp缺失的PPO等位基因的材料酚反应呈阴性,而不缺失的材料酚反应呈阳性。标记基因型与酚反应表现型完全对应。表明这两个功能标记可用于水稻种质资源鉴定、进化研究以及多酚氧化酶基因的分子标记辅助选择育种。
DOI:10.1007/s00122-006-0290-6URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.2135/cropsci2002.2145URL [本文引用: 1]

Abstract Incorporation of resistance genes into existing rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars is a powerful strategy and is commonly applied in breeding rice resistance to blast disease [caused by Pyricularia grisea Sacc. = P. oryzae Cavara (teleomorph: Magnaporthe grisea (Hebert) Barr)]. The rice blast resistance gene, Pi-ta, originally introgressed into japonica from indica rice is important in breeding for rice blast resistance worldwide. In the southern USA, the rice cultivar Katy contains Pi-ta and is resistant to the predominant blast M. grisea races IB-49 and IC-17 and has been used as the blast resistant breeding parent. Three pairs of DNA primers specific to the dominant indica Pi-ta gene were designed to amplify the Pi-ta DNA fragments by polymerase chain reaction (PCR). PCR products amplified by these Pi-ta specific primers were cloned and sequenced. Sequence analysis confirmed the presence of the dominant indica Pi-ta allele. These Pi-ta primers were used to examine the presence of Pi-ta alleles in advanced Arkansas rice breeding lines. The Pi-ta containing rice lines, as determined by PCR analysis, were resistant to both IB-49 and IC-17 in standard pathogenicity assays. In contrast, lines lacking the Pi-ta genes failed to protect rice plants against both races IB-49 and IC-17. The presence of Pi-ta markers correlated with the Pi-ta resistance spectrum. Thus, the Pi-ta gene markers provide a basis for stacking other blast resistance genes into high yielding and good quality advanced breeding rice lines.
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0496-3490.2004.12.015 [本文引用: 1]

利用已建立的水稻抗稻瘟病基因Pi ta显性分子标记对 30个品系和 1 57个来自不同国家的一些水稻品种进行分子鉴定 ,并采用稻瘟病菌菌株ZN57(IC 1 7)和ZN6 1 (IB 4 9)人工接种试验进行致病性测试。结果表明 ,大部分品系和少数水稻品种含抗病基因Pi ta ,且对稻瘟病菌菌株ZN57和ZN6 1表现抗病反应。除此之外 ,利用两对显性分子标记YL1 55 YL87和YL1 83 YL87对 350个杂交F3代株系进行早期筛选 ,得到 1 1 8个抗病基因Pi ta纯合的株系。这些株系田间抗性调查结果表明 ,抗病基因存在与否与田间抗性相吻合。因Pi ta基因与许多其他抗病基因紧密连锁 ,而使含有Pi ta基因的品种具有广谱抗性 ,由此确立了Pi ta基因显性分子标记在育种辅助选择中的应用价值。
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0496-3490.2004.12.015 [本文引用: 1]

利用已建立的水稻抗稻瘟病基因Pi ta显性分子标记对 30个品系和 1 57个来自不同国家的一些水稻品种进行分子鉴定 ,并采用稻瘟病菌菌株ZN57(IC 1 7)和ZN6 1 (IB 4 9)人工接种试验进行致病性测试。结果表明 ,大部分品系和少数水稻品种含抗病基因Pi ta ,且对稻瘟病菌菌株ZN57和ZN6 1表现抗病反应。除此之外 ,利用两对显性分子标记YL1 55 YL87和YL1 83 YL87对 350个杂交F3代株系进行早期筛选 ,得到 1 1 8个抗病基因Pi ta纯合的株系。这些株系田间抗性调查结果表明 ,抗病基因存在与否与田间抗性相吻合。因Pi ta基因与许多其他抗病基因紧密连锁 ,而使含有Pi ta基因的品种具有广谱抗性 ,由此确立了Pi ta基因显性分子标记在育种辅助选择中的应用价值。
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.10017216.2014.02.005URL [本文引用: 1]

Pikhis a vital non racespecific resistance gene for rice blast. In this study, one InDel marker, FM143 was developed based on the 143 bp insertion between the susceptible and resistant Pikh alleles. Previous studies showed that Tetep carried resistant Pikh allele and had the noneinsertion genotype for PCR by FM143. F2 population, derived from Tetep and Ning 9108, were detected by marker FM143 and the result indicated that FM143 could effectively identify Pikh/Pikh, Pikh/pikh and pikh/pikh genotypes with the expected segregation ratio 1:2:1. Sixtyfive japonica varieties widely grown in Jiangsu Province over years and sixtyfour japonica lines were genotyped by FM143. Among them, 19 japonica varieties and 22 japonica lines showed noneinsertion genotype. Further sequencing at the target Pikh locus for these noneinsertion genotype showed that there was one highly conserved singlebase mutation (G→C) at 102 bp location compared with the whole target gene sequence in Tetep and public Pikh GeneBank leading to the changes from glutamic acid to asparaginic acid. This new allele in Jiangsu japonica rice was termed as PikhJSJ.
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.10017216.2014.02.005URL [本文引用: 1]

Pikhis a vital non racespecific resistance gene for rice blast. In this study, one InDel marker, FM143 was developed based on the 143 bp insertion between the susceptible and resistant Pikh alleles. Previous studies showed that Tetep carried resistant Pikh allele and had the noneinsertion genotype for PCR by FM143. F2 population, derived from Tetep and Ning 9108, were detected by marker FM143 and the result indicated that FM143 could effectively identify Pikh/Pikh, Pikh/pikh and pikh/pikh genotypes with the expected segregation ratio 1:2:1. Sixtyfive japonica varieties widely grown in Jiangsu Province over years and sixtyfour japonica lines were genotyped by FM143. Among them, 19 japonica varieties and 22 japonica lines showed noneinsertion genotype. Further sequencing at the target Pikh locus for these noneinsertion genotype showed that there was one highly conserved singlebase mutation (G→C) at 102 bp location compared with the whole target gene sequence in Tetep and public Pikh GeneBank leading to the changes from glutamic acid to asparaginic acid. This new allele in Jiangsu japonica rice was termed as PikhJSJ.
