 ,*, 张雅莉*, 南广慧*河南科技大学农学院/洛阳市作物遗传改良与种质创新重点实验室, 河南洛阳 471023
,*, 张雅莉*, 南广慧*河南科技大学农学院/洛阳市作物遗传改良与种质创新重点实验室, 河南洛阳 471023Molecular and Cytogenetic Identification of Triticum aestivum-Leymus racemosus Translocation Line T5AS-7LrL·7LrS
WANG Lin-Sheng ,*, ZHANG Ya-Li*, NAN Guang-Hui*Key Laboratory of Crop Genetic Improvement and Germplasm Innovation / College of Agriculture, Henan University of Science and Technology, Luoyang 471023, Henan, China
,*, ZHANG Ya-Li*, NAN Guang-Hui*Key Laboratory of Crop Genetic Improvement and Germplasm Innovation / College of Agriculture, Henan University of Science and Technology, Luoyang 471023, Henan, China通讯作者:
收稿日期:2018-03-7接受日期:2018-06-12网络出版日期:2018-07-17
| 基金资助: |
Received:2018-03-7Accepted:2018-06-12Online:2018-07-17
| Fund supported: |

摘要
关键词:
Abstract
Keywords:
PDF (1831KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
本文引用格式
王林生, 张雅莉, 南广慧. 普通小麦-大赖草易位系T5AS-7LrL·7LrS分子细胞遗传学鉴定[J]. 作物学报, 2018, 44(10): 1442-1447. doi:10.3724/SP.J.1006.2018.01442
WANG Lin-Sheng, ZHANG Ya-Li, NAN Guang-Hui.
赤霉病是世界小麦主要病害之一, 随着全球气候的变暖, 在我国由南向北有逐渐蔓延加重趋势, 近几年黄淮麦区的赤霉病大发生已得到证实, 仅河南省年发生面积超过100万公顷。2017年国审通过的20个半冬性小麦品种及河南省审定通过的27个小麦品种全部感赤霉病, 且多为高感, 究其原因是遗传基础狭窄。目前, 生产上使用的赤霉病抗源局限于苏麦3号、Frontana等少数品种及其衍生系, 致使我国小麦主产区存在巨大的安全隐患。寻找与拓宽赤霉病抗性资源, 选育和利用抗赤霉病小麦品种是一条经济有效的措施, 越来越受到重视。
大赖草(Leymus racemosus)是一种与小麦亲缘关系较远的多年生植物, 具有耐盐、抗旱、抗多种病害等多种优良特性[1,2], 尤其高抗赤霉病, 是一种具有潜在应用价值的基因源。自Mujeeb-Kazi和Rodriguez[3]报道大赖草抗小麦赤霉病以来, 许多遗传育种工作者开展了大量的研究工作。南京农业大学细胞研究所通过远缘杂交、回交获得并鉴定出3个高抗赤霉病的普通小麦一大赖草附加系AddLr.2、AddLr.7和AddLr.14 [4], 其中Lr.2和Lr.14分别属于小麦第7和第5部分同源群[5]。由于异附加系携带的是整条大赖草染色体, 在导入有益基因的同时也伴随带入对产量、品质等农艺性状不利的冗余基因。为此研究者利用电离辐射、杀配子染色体诱导和遗传控制体系等方法创造易位系, 以减少不利基因对普通小麦造成的不良影响。刘文轩等[6,7,8]通过辐射Lr.14 (5Lr)二体附加系和Lr.2 (7Lr)、Lr.7单体附加系, 选育了纯合易位系T6BL·6BS-L.14L、T4BS·4BL- 7Lr#1S-1、T02和T08。杨宝军等[9]通过辐射Lr.2和Lr.7单体异附加系获得易位系NAU618和NAU601。袁建华等[10]采用杀配子染色体诱导方法得到3个易位系, 分别为T1DS·Lr7L、T4AL·4AS-Lr7S和T1BL-Lr2S。王林生等[11]通过60Co-γ射线处理小麦-大赖草二体附加系DA5Lr雌配子, 获得普通小麦-大赖草染色体相互易位系T7DS·5LrL/T5LrS·7DL; 崔承齐等[12]通过电离辐射, 得到T7BS·7Lr#1S和T2AS·2AL-7Lr#1S易位系。Wang和Chen[13]证实7Lr#1S上存在抗赤霉病的主效基因, 后人把7Lr#1S携带的抗赤霉病基因Fhb3定位在该染色体的近端部[12,14]。
本研究利用染色体C-分带、荧光原位杂交、分子标记技术和赤霉病抗性鉴定等技术, 对抗赤霉病的普通小麦-大赖草异附加系DA7Lr成熟花粉辐射的后代进行鉴定, 筛选出抗赤霉病的普通小麦-大赖草易位系, 为小麦抗赤霉病育种提供新的基因资源。
1 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
DA7Lr为普通小麦-大赖草二体异附加系[5], 用60Co-γ射线照射其开花期麦穗, 照射剂量为1200 Rad, 剂量率100 Rad min-1。普通小麦中国春去雄, 用上述辐照处理材料的花粉授粉, 其后代种子自交, 获得M2代, 从中鉴定出纯合易位系。抗赤霉病对照品种苏麦3号和感赤霉病品种绵阳85-45均由河南科技大学农学院小麦遗传育种研究室引进保存。1.2 染色体制片
1.2.1 根尖细胞有丝分裂中期 将小麦种子放入垫有湿滤纸的培养皿内发芽(23℃), 待根长至1.0~2.0 cm时, 剪取1~2条种子根在冰水中处理20~24 h。用无水乙醇∶冰醋酸(v:v)为3︰1的固定液固定, 4℃冰箱中保存3 d, 然后于45%醋酸中进行根尖压片, 相差显微镜下观察染色体, 放入-70℃冰箱或液氮中冷冻揭去盖玻片, 脱水备用。1.2.2 花粉母细胞减数分裂中期I 挑取处于减数分裂中期I的花药, 用上述固定液固定, 按根尖细胞有丝分裂中期制片方法压片备用, 用于易位系花粉母细胞染色体配对分析。
1.3 染色体C-分带和荧光原位杂交
参照Gill和Friebe[15]的方法进行染色体C-分带。参照Mukai等[16]描述的荧光原位杂交方法, 并稍加修改。参照Zhang等[17]的方法顺次原位杂交, 首先以荧光素Fluorescein-l2-dUTP标记的大赖草基因组DNA为探针进行GISH (genomic in situ hybridization), 通过SPOT CCD (charge coupled device)获取FISH (fluorescence in situ hybridization)图像, 参照Pedersen和Linde-Laursen[18]描述的方法将信号洗脱, 再以红色荧光素TAMRA (6-carboxytetramethylrhodamine)标记的B组专化探针Oligo- pSc119.2-2 (其寡核苷酸重复序列为6-TAMRA-5′- TTCCA CGATT GACGA TTCCG GGGGT GCGTT TACGT GTCCG TCGTC-3′)和绿色荧光素FAM (6-carboxyfluorescein)标记的D组专化探针Oligo-pAs1-2 (其寡核苷酸重复序列为FAM-5′- CATTT CATCC ACATA GCATG TGCAA GAAAT TTGAG AGGGT TACGG CAAAA ACTGGAT-3′)进行双色荧光原位杂交, 用DAPI (4’,6-diamidino-2- phenylindole)染色; 单色荧光原位杂交用碘化丙锭(propidium iodide, PI)染色。SPOT CCD获取图像, 参考Tang等[19]的标准FISH图谱分析图像结果。所用绿色荧光素和两种专化探针均由上海英骏生物科技有限公司合成。1.4 分子标记鉴定
利用SDS法[20]提取植物基因组DNA。PCR反应体系总体积10 μL, 含1× buffer 10 μL, 1.5 mmol L-1 MgCl2, 模板DNA 20 ng, 200 mmol L-1 dNTP, 终浓度为0.2 μmol L-1的左右引物, 0.5 U Taq DNA聚合酶。反应程序为94℃预变性3 min; 94℃变性30 s, 50~60℃退火40 s, 72℃延伸50 s, 34个循环; 72℃延伸10 min, 4℃保存。扩增产物经8%非变性聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳, 硝酸银染色后照相。从小麦SNP数据库(https://wheat.pw.usda.gov/ SNP/new/pcr_primers.shtml)选择位于小麦第7同源群上的81对EST-STS引物进行PCR扩增, 筛选出可追踪易位系的3对特异引物(表1)。
Table 1
表1
表1鉴定易位染色体的特异性引物
Table 1
| 引物名称 Primer name | 序列 Sequence (5′-3′) | EST染色体 EST chromosome | 退火温度 Annealing temperature (°C) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 正向 Froward | 反向 Reverse | |||
| BE591127 | GCAGCTCATCTTCATGGTCA | CGTTGCAGCAATCAGTCCTA | 7AS 7BS 7DS | 60 |
| BQ168298 | GCTCTCGCTCATCATCAACA | CTCGCAATGGTACCAAGGTT | 7AS 7BS 7DS | 60 |
| BE591737 | AGCAGCTAGGAGGGTGTCTG | TAACCGCAGCTTTCTCATCC | 7AS 7BS 7DS | 60 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
1.5 赤霉病抗性鉴定
在河南科技大学开元校区农场进行抗性鉴定, 按照随机区组设计, 每个处理3次重复, 每个小区播种20行, 行长2 m, 行距21 cm, 株距5 cm, 开沟点播。采用王裕中等[21]的单花滴注法接种禾谷镰刀菌(由河南科技大学林学院植物病理学系徐建强博士提供菌种), 接种后早、晚2次喷雾, 保证发病湿度。2015—2017年连续3年均使用编号为LHLY-2的高强毒菌株分生孢子悬浮液接种, 每小区接种10穗, 接种21 d后调查接种穗的发病小穗数和总小穗数。病小穗率(%) = (病小穗数/总小数) × 100。采用SPSS20.0软件分析不同材料间的抗病性差异。2 结果与分析
2.1 易位系T5AS-7LrL·7LrS的分子细胞遗传学鉴定
用DA7Lr经辐射处理的花粉, 授给已去雄的中国春, 获得11粒种子, 发现其中编号为NGH-01的单株具有1条普通小麦-大赖草易位染色体。从该材料自交后代(M2代)种子中得到一株含有2条易位染色体的单株, 有丝分裂中期染色体制片观察结果显示2n = 44 (图1)。图1
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图1易位系T5AS-7LrL·7LrS荧光原位杂交(2n=44)
有丝分裂中期的顺次GISH-FISH, A图中绿色信号为Fluorescein-l2-dUTP标记的大赖草基因组DNA, B图中的红色信号为TARAM标记的Oligo-pSc119.2-2, 绿色信号为6-FAM标记的Oligo-pAs1-2, 箭头指示易位染色体。
Fig. 1Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) of translocation line T5AS-7LrL·7LrS (2n = 44)
Sequential GISH-FISH of mitotic metaphase chromosomes. In panel A, L. racemosus genomic DNA was labeled with fluorescein-12-dUTP and visualized with green signals. In panel B, Oligo-pSc119.2-2 was labeled with TARAM and visualized with red signals ,and Oligo-pAs1-2 was labeled with 6-FAM and visualized with green signals. The arrows show translocation chromosomes.
以绿色荧光标记的大赖草基因组DNA作为探针, 对NGH-01纯合单株根尖染色体制片进行GISH分析。在450~490 nm激发光波长下观察到易位染色体的大赖草片段有弥散的黄绿色荧光杂交信号, 且染色体末端的荧光杂交信号明显强于其他部分, 小麦染色体的易位片段大约占易位染色体短臂的1/2, 而大赖草染色体易位片段占整个易位染色体的长臂及短臂的1/2区段, 约占易位染色体全长的80%, 属于染色体大片段易位(图1-A)。
将上述片子的信号洗脱干净, 再以红色荧光标记的小麦B组专化探针寡聚核苷酸Oligo-pSc119.2-2和绿色荧光标记的小麦D组专化探针寡聚核苷酸Oligo-pAs1-2为探针进行双色FISH分析, 发现在易位染色体短臂顶端(小麦染色体片段)有两个比较明显的红色点状杂交信号, 但在小麦染色体片段上没有发现绿色杂交信号。参照Tang等[19]的标准图谱, 符合这一荧光杂交信号特征的小麦染色体有5A、2B、4B、6B、2D、3D和4D, 而小麦染色体2D、3D和4D端部或近端部除了有Oligo-pSc119.2-2杂交信号同时还应具有Oligo-pAs1-2荧光信号。该易位染色体小麦片段上只有Oligo-pSc119.2-2的杂交信号, 因此可排除2D、3D和4D染色体(图1-B)。结合C-分带结果, 2B、4B和6B染色体短臂的端部和近端部都有较强的C带, 而易位染色体小麦片段上只有较弱的C带(图2), 故可排除2B、4B和6B染色体, 发生易位的应为5A染色体, 且为5A短臂的端部片段。
图2
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图2易位染色体T5AS-7LrL·7LrS的C-分带及荧光原位杂交
从左至右依次为C-分带的5A、C-分带的T5AS-7LrL·7LrS、荧光原位杂交的T5AS-7LrL·7LrS、Oligo-pSc119.2-2 (红色)杂交的T5AS-7LrL·7LrS、Oligo-pSc119.2-2 (绿色)杂交的5A、荧光原位杂交的7Lr和C分带的7Lr。
Fig. 2C-banding and FISH of translocation chromosome T5AS-7LrL·7LrS
Chromosomes from left to right are C-banded 5A, C-banded T5AS-7LrL·7LrS, FISH T5AS-7LrL·7LrS, T5AS-7LrL·7LrS with red Oligo-pSc119.2-2, 5A with green Oligo-pSc119.2-2, FISH 7Lr, and C-banded 7Lr.
C-分带荧光原位杂交对比发现, 大赖草7LrL顶端有很强的荧光原位杂交信号, 易位的大赖草7Lr染色体片段包含了整个7LrS短臂和一部分7LrL长臂, 荧光原位杂交结果该易位染色体与7Lr相符(图2)。对其花粉母细胞减数分裂中期I染色体配对行为观察, 发现其易位染色体正常配对, 形成稳定的环状二价体(图3)。综上所述, 将该易位系命名为T5AS-7LrL·7LrS。
图3
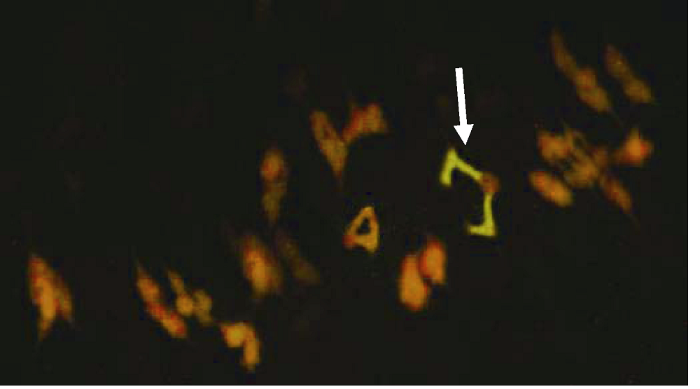 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图3易位系T5AS-7LrL·7LrS花粉母细胞减数分裂中期I染色体的荧光原位杂交
图中绿色信号为荧光素Fluorescein-l2-dUTP标记的大赖草基因组DNA, 箭头指示配对的二价体易位染色体T5AS-7LrL·7LrS。
Fig. 3Chromosome FISH at MI of PMC of translocation line T5AS-7LrL·7LrS
L. racemosus genomic DNA was labeled with Fluorescein-l2-dUTP and visualized with green signals. The arrow shows the ring bivalent formed by a pair of translocation chromosomes T5AS-7LrL·7LrS.
2.2 易位系T5AS-7LrL·7LrS的分子标记鉴定
利用位于小麦第7部分同源群不同区段的81对EST-STS引物进行多态性分析, 发现BE591127、BQ168298和BE591737在大赖草、DA7Lr和易位系T5AS-7LrL·7LrS上有特异扩增。这3个标记分别定位在7AS、7BS和7DS上, 可用于追踪大赖草染色体片段, 特异扩增条带大小分别为1000、1733和398 bp (图4)。图4
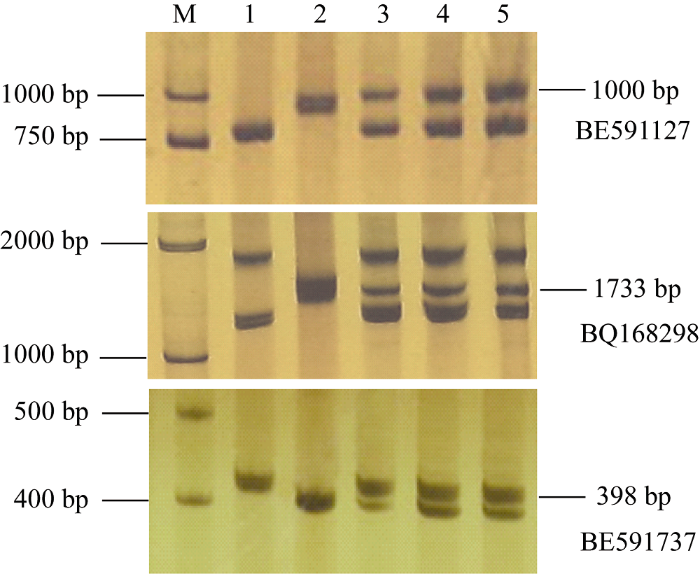 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图4引物BE591127、BQ168298和BE591737的PCR扩增结果
1: 中国春; 2: 大赖草; 3: DA7Lr; 4: T5AS-7LrL·7LrS。
Fig. 4PCR profiles amplified with primers BE591127, BQ168298, and BE591737
1: Chinese Spring; 2: Leymus racemosus (Lr); 3: DA7Lr; 4: T5AS-7LrL·7LrS.
2.3 易位系T5AS-7LrL·7LrS的赤霉病抗性鉴定
经过连续3年的赤霉病接种鉴定结果表明, 易位系T5AS-7LrL·7LrS的病小穗率显著低于感病亲本中国春和感病对照绵阳8545, 但稍高于抗病对照苏麦3号(表1和图5), 表现出较好的赤霉病抗性。Table 1
表1
表1不同材料赤霉病抗性(病小穗率)的田间鉴定
Table 1
| 材料 Material | 大田鉴定 Identified in field | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | |
| 中国春 Chinese Spring | 35.27 | 39.58±7.96 | 30.90±8.92 |
| T5AS-7LrL·7LrS | 8.70 | 11.22±5.12** | 9.67±7.51** |
| 苏麦3号Sumai 3 | 3.90 | 6.35±3.12** | 5.69±2.14** |
| 绵阳85-45 Mianyang 85-45 | 49.23 | 56.32±11.26** | 47.83±13.25** |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
图5
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图5易位系T5AS-7LrL·7LrS的赤霉病抗性鉴定
A: T5AS-7LrL·7LrS; B: 中国春; C: 绵阳85-45; D: 苏麦3号。
Fig. 5Evaluation of scab resistance of translocation line T5AS-7LrL·7LrS
A: T5AS-7LrL·7LrS; B: Chinese Spring; C: Mianyang 85-45; D: Sumai 3.
3 讨论
通过电离辐射将外源遗传物质导入普通小麦已成为拓宽小麦育种遗传基础的有效途径。自从1956年Sears [22]获得小麦-小伞山羊草易位系以来, 采用电离辐射创造了许多具有外源有益基因的小麦新种质[23,24,25,26,27,28], 为小麦育种开拓了新视野。但由于电离辐射造成染色体断裂重接完全是随机的, 产生的易位染色体补偿性往往较差, 直接利用还存在一定困难, 因此, 创造携带外源有益基因的补偿性易位, 尤其是中间插入小片段易位, 已成为研究者追求的目标。Chen等[29]通过电离辐射选育的小麦一簇毛麦T6AL/6VS补偿性易位系, 目前已经成为我国小麦抗白粉病育种的重要亲本, 以此易位系为亲本, 已选育出20 余个小麦新品种并在生产上大面积推广[30]。本研究利用C-分带结合顺序GISH-FISH, 从普通小麦-大赖草7Lr二体异附加系辐射后代中选育出的易位系T5AS-7LrL·7LrS, 属于非补偿性易位, 且易位染色体具有较长的大赖草染色体片段, 超过整条染色体的80%, 携带大赖草许多冗余基因, 对小麦的农艺性状造成一定的负面效应, 主要表现为植株偏高、晚熟、穗部顶端有秃尖、千粒重低、结实性差等问题。但该易位系经鉴定对赤霉病有较高的抗性, 3年的病小穗率分别为8.70%、11.22%和9.67%, 显著低于感病品种中国春和绵阳85-45, 表明其具有抗赤霉病的主效基因, 可以作为抗赤霉病的新资源。本课题组正在以该易位系为材料, 采用辐射、杀配子染色体诱导等手段创造小片段易位系, 同时与当前黄淮海主推骨干品种回交, 以期选育出农艺性状优良, 在生产上可利用的抗赤霉病小麦新品系。
本研究分析了易位染色体5AS-7LrL·7LrS的配子传递特性, 发现该易位染色体具有花粉的优先传递性, 但对其易位系所产生的花粉育性观察发现, 没有大量的不育花粉, 育性基本正常, 表明该易位染色体具有与杀配子染色体不同的花粉优先传递基因。
Subbarao等[29]研究发现大赖草第7部分同源群染色体上携有生物硝化抑制基因, 将其导入栽培小麦, 可延缓铵态氮(NH4+-N)向硝态氮(NO3–)的转化,减少土壤中氮的损失, 改善作物氮素营养, 提高氮素利用率。同时也减少地表水和地下水的污染。本研究创造的易位系T5AS-7LrL·7LrS, 是大赖草第7部分同源群染色体与普通小麦染色体发生的易位, 因此, 在易位系获得抗赤霉病的同时有可能又具有生物硝化抑制特性, 成为有双重利用价值的种质资源, 在小麦生产中发挥更大的作用。
4 结论
采用电离辐射的方法创造普通小麦大赖草易位系, 利用C-分带、GISH-FISH双色荧光原位杂交技术鉴定出易位系T5AS-7LrL·7LrS, 并筛选出3个在易位系T5AS-7LrL·7LrS上有特异扩增的EST-STS多态性标记, 可用于追踪大赖草染色体片段。参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
DOI:10.2135/cropsci1981.0011183X002100050018xURL [本文引用: 1]

To determine the potential of various species of wheatgrasses (Elytrigia Desv.) as gene sources for the improvement of salt tolerance in wheat (Triticum aestivum L. em. Thell.), six wheat accessions, previously identified as salt-tolerant, and 36 wheatgrass accessions, representing 13 species, were grown from the seedling stage. Plants were grown in gradually increasing concentrations of NaCl in hydroculture with one-half strength Hoagland's solution. Tolerance to the NaCl was determined for the wheat plants by scoring survival in 250 mM NaCl and for the wheatgrass plants by scoring survival in 500 mM NaCl and in 750 mM NaCl. while no wheat plants survived the stress with 250 nM NaCl, several wheatgrass accessions had large percentages of surviving individuals in 750 MM NaCl. The four most tolerant species were: Elytrigia scirpea (Presl) Holub, E. pontica (Podp.) Holub, E. junceiformis Love et Love, and E. diae (Runemark) nom. nud. Since these species are also among those most easily hybridizable with wheat, they are the best candidates for sources of salt tolerance.
In:
URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]

大赖草比抗病品种“苏麦3号”更抗小麦赤霉病。经离体和活体赤霉病抗性单花滴注鉴定和有丝分裂中期及减数分裂中期Ⅰ的C-分带分析,选育出添加了1对第2染色体的抗赤霉病异附加系,其44条染色体在MI配成0.12—0.40ⅠI+21.70—21.93Ⅱ+0.01—0.04Ⅳ。经C-分带和生物素标记的染色体组DNA作探针的分子原位杂交分析证实添加的1对外源染色体在MI配成二价体,在细胞学上已基本稳定。
URL [本文引用: 1]

大赖草比抗病品种“苏麦3号”更抗小麦赤霉病。经离体和活体赤霉病抗性单花滴注鉴定和有丝分裂中期及减数分裂中期Ⅰ的C-分带分析,选育出添加了1对第2染色体的抗赤霉病异附加系,其44条染色体在MI配成0.12—0.40ⅠI+21.70—21.93Ⅱ+0.01—0.04Ⅳ。经C-分带和生物素标记的染色体组DNA作探针的分子原位杂交分析证实添加的1对外源染色体在MI配成二价体,在细胞学上已基本稳定。
[本文引用: 2]
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1672-9072.1999.05.003URL [本文引用: 1]

采用600-1125R剂量的^60Co-γ射线对小麦-大赖草Lr.7单体异附加系在减数 分裂期进行成株辐射处理,经过M1代根尖细胞有丝分裂中期(RTC,M期)染色体GiemsaC-分带粗筛,M2代RTC M期染色体C-分带和荧光原位杂交鉴定,选育出2个小麦-大赖草Lr.7异易位系。其中T02易位系是由Lr.7染色体绝大部分与一小片段小麦染色体接在 一起组成的易位类型(TLr.7·Lr.7-W);T08
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1672-9072.1999.05.003URL [本文引用: 1]

采用600-1125R剂量的^60Co-γ射线对小麦-大赖草Lr.7单体异附加系在减数 分裂期进行成株辐射处理,经过M1代根尖细胞有丝分裂中期(RTC,M期)染色体GiemsaC-分带粗筛,M2代RTC M期染色体C-分带和荧光原位杂交鉴定,选育出2个小麦-大赖草Lr.7异易位系。其中T02易位系是由Lr.7染色体绝大部分与一小片段小麦染色体接在 一起组成的易位类型(TLr.7·Lr.7-W);T08
DOI:10.1007/BF02983442URL [本文引用: 1]

将小麦-大赖草Lr.2和Lr.14染色体二体异附加系 94G15和 94G45即将成熟花粉经(60)Co-γ射线辐射处理,然后分别给普通小麦品种扬麦 5号和绵阳11授粉。辐射 M1的 PMC MI期染色体经 Chemsa C-分带和基因组DNA荧光原位杂交处理后进行染色体配对分析,从 17株 MI单株中筛选到5株PMC MI期大赖草染色体与小麦配对的个体。根据这5株单株自交M1种子根尖细胞有丝分裂中期染色体C-分带和原位杂交检测,筛选并鉴定出了LW8(3)1和LW11(3)12个涉及大赖草Lr.14染色体的小麦-大赖草易位系。还就花粉辐射在诱发小麦-亲缘物种染色体易位的可行性及有效性,以及所获2个易位系的利用价值进行了讨论。
DOI:10.1007/BF02983442URL [本文引用: 1]

将小麦-大赖草Lr.2和Lr.14染色体二体异附加系 94G15和 94G45即将成熟花粉经(60)Co-γ射线辐射处理,然后分别给普通小麦品种扬麦 5号和绵阳11授粉。辐射 M1的 PMC MI期染色体经 Chemsa C-分带和基因组DNA荧光原位杂交处理后进行染色体配对分析,从 17株 MI单株中筛选到5株PMC MI期大赖草染色体与小麦配对的个体。根据这5株单株自交M1种子根尖细胞有丝分裂中期染色体C-分带和原位杂交检测,筛选并鉴定出了LW8(3)1和LW11(3)12个涉及大赖草Lr.14染色体的小麦-大赖草易位系。还就花粉辐射在诱发小麦-亲缘物种染色体易位的可行性及有效性,以及所获2个易位系的利用价值进行了讨论。
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0496-3490.2000.03.009URL [本文引用: 1]

After pollinating a scab susceptible T. aestivum cultivar Yangmai 5 with the 60 Co-γ irradiated pollens of a scab-resistant T. aestivum-L.racemosus Lr.2 addition line, an alien translocation line was developed through two continuous years′ scab-resistance identification. On the basis of Giemsa
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0496-3490.2000.03.009URL [本文引用: 1]

After pollinating a scab susceptible T. aestivum cultivar Yangmai 5 with the 60 Co-γ irradiated pollens of a scab-resistant T. aestivum-L.racemosus Lr.2 addition line, an alien translocation line was developed through two continuous years′ scab-resistance identification. On the basis of Giemsa
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1139/g04-042URLPMID:15499412 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) is widely used in the physical mapping of genes and chromosome landmarks in plants and animals. Bacterial artificial chromosomes (BACs) contain large inserts, making them amenable for FISH mapping. In our BAC-FISH experiments, we selected 56 restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP)-locus-specific BAC clones from the libraries of Triticum monococcum and Aegilops tauschii, which are the A- and D-genome donors of wheat (Triticum aestivum, 2n = 6x = 42), respectively. The BAC clone 676D4 from the T. monococcum library contains a dispersed repeat that preferentially hybridizes to A-genome chromosomes, and two BAC clones, 9I10 and 9M13, from the Ae. tauschii library contain a dispersed repeat that preferentially hybridizes to the D-genome chromosomes. These repeats are useful in simultaneously discriminating the three different genomes in hexaploid wheat, and in identifying intergenomic translocations in wheat or between wheat and alien chromosomes. Sequencing results show that both of these repeats are transposable elements, indicating the importance of transposable elements, especially retrotransposons, in the genome evolution of wheat.
DOI:10.1007/BF01539456URLPMID:8162323 [本文引用: 1]

Four minor rDNA loci have been mapped physically to barley ( Hordeum vulgare L.) chromosomes 1 (7I), 2 (2I), 4 (4I), and 5 (1I) by a two-step in situ hybridization procedure including a GAA microsatellite sequence. Reprobing with the microsatellite resulted in a distinct banding pattern, resembling the C-banding pattern, which enabled unequivocal chromosome identification. This study suggests that gene mapping accuracy may be improved by using probes with well-characterized and narrow hybridization sites as cytological markers which are situated close to the gene locus. One of the rDNA loci is located about 54% out on the short arm of chromosome 4 and it has not previously been reported in barley. We have disignated the new locus Nor -16. rDNA loci on homoeologous group 4 chromosomes have not yet been reported in other Triticeae species. The origin of these 4 minor rDNA loci is discussed in relation to their equilocal distribution on the chromosomes.
DOI:10.1007/s13353-014-0215-zURL [本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.2135/cropsci1993.0011183X003300050004xURL [本文引用: 1]

Ionizing radiation can accomplish the transfer of genetic information from species so distantly related to wheat (Triticum aestivum L. em Thell.) that their chromosomes pair very little, if at all, with those of wheat, even in the absence of the homoeologous-pairing suppressor Ph1. In a successful transfer, the alien segment must almost always replace a homoeologous wheat segment, but radiation induces translocations largely at random; therefore automatic selection in favor of desirable translocations must be provided if the size of the project is to be kept within reasonable limits. Pollen selection will occur if seeds or plants monosomic for both an alien chromosome and one of its wheat homoeologues are irradiated. Making the plants also deficient for Ph1 may increase the number of suitable transfers. High-frequency occurrence of the desired alien character in M2 head-rows from plants grown from irradiated seed can identify favorable transfers with little cytological work. Irradiation of plants shortly before meiosis, using them to pollinate ditelosomics or double ditelosomics for the wheat arm or chromosome concerned, and cytologically examining offspring which have the alien character can not only identify the desirable transfers, but also reveal the lengths of the alien segments involved
DOI:10.1007/BF00035277URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1093/aob/mcs230URL
