 ,1,*, 张坤明1, 薛春雷1, 张瑞霞2
,1,*, 张坤明1, 薛春雷1, 张瑞霞2Analysis of SNP and Allele-specific Expression in Transcriptome of Sorghum bicolor × Sorghum sudanense and Their Parents
DONG Jing1, LU Xiao-Ping ,1,*, ZHANG Kun-Ming1, XUE Chun-Lei1, ZHANG Rui-Xia2
,1,*, ZHANG Kun-Ming1, XUE Chun-Lei1, ZHANG Rui-Xia2通讯作者:
第一联系人:
收稿日期:2017-12-21接受日期:2018-07-20网络出版日期:2018-07-25
| 基金资助: |
Corresponding authors:
Received:2017-12-21Accepted:2018-07-20Online:2018-07-25
| Fund supported: |

摘要
关键词:
Abstract
Keywords:
PDF (1814KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
本文引用格式
董婧, 逯晓萍, 张坤明, 薛春雷, 张瑞霞. 高丹草杂种及其亲本转录组SNP及等位基因特异性表达分析[J]. 作物学报, 2018, 44(12): 1809-1817. doi:10.3724/SP.J.1006.2018.01809
DONG Jing, LU Xiao-Ping, ZHANG Kun-Ming, XUE Chun-Lei, ZHANG Rui-Xia.
高粱(Sorghum bicolor)是一种古老的禾谷类作物, 具有抗旱、耐涝、耐盐碱、适应性强等特点, 苏丹草(S. sudanense)是栽培最普遍的一年生禾本科牧草, 具有高度的适应性、很强的再生性和抗旱能力, 其茎叶品质优良[1]。高丹草是高粱-苏丹草杂交种的简称, 它结合了高粱和苏丹草的优点, 在畜牧业和渔业生产上具有广阔的开发利用前景[2]。这种优良的农艺性状表现可能是由2个亲本基因组互作造成的, 但是具体的遗传机制尚不清楚。
杂交是自然界中普遍存在的现象, 不仅可以对物种形成、适应性进化和生态创新产生重要作用, 而且可能出现大量的等位基因变异[3,4,5,6,7]。有研究表明, 融合这些等位基因变异可能导致新的基因行为方式的出现, 从而产生杂种优势[8,9,10,11]。但是, 以往对于杂种优势机理的研究只针对杂种及亲本基因的表达水平, 而对杂种中不同亲本等位基因差异表达的研究较少。
SNP (single nucleotide polymorphisms)是指在基因组上由单个核苷酸变异形成的遗传标记, 其数量庞大[12]。通常杂交种中的等位基因特异性表达的研究方法有2种[13], 一是基于标记多态性, 利用已知基因组变异获得高质量的等位基因表达结果[14,15]; 另外一种是利用SNP芯片同时获得上万个等位基因特异性表达位点[16,17]。然而, 这两种方法都必须提前知道研究对象的基因组信息。随着第二代高通量测序技术的发展, RNA-Seq技术逐渐被人们所熟悉并应用到等位基因特异性表达的研究中[18]。RNA-Seq技术无须预知研究对象的基因组信息并且分辨率能够达到单碱基水平。应用这个方法能够从全基因组水平无偏估计基因的调控, 而且能同时获得转录丰度和等位基因表达偏向性的信息[19]。
本研究在高丹草遗传图谱构建、产量性状QTL定位、杂种表现遗传模型以及差异表达基因分析与蛋白质组学等[2,20-23]研究的基础上, 比较和分析高丹草杂种中2个亲本等位基因的特异性表达, 旨在了解杂交种中双亲等位基因的不同作用以及可能对杂种优势的贡献, 进一步阐明高丹草杂种优势的分子机制, 为高丹草杂种的遗传改良提供依据。
1 材料与方法
1.1 植株材料及样品采集
以高丹草杂种(11A×白壳苏丹草)一代、母本高粱11A和父本白壳苏丹草的根、茎、叶为试材, 设置3个生物学重复(表1)。在三叶期, 分别取高丹草杂种及其亲本的根、茎、叶样品, 立即投入液氮冷冻, 于-80℃保存备用。Table 1
表 1
表 1材料编号及名称
Table 1
| 编号 No. | 材料名称(组织) Material name (tissue) | 编号 No. | 材料名称(组织) Material name (tissue) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 白壳苏丹草(根I) White shell Sudan grass (root I) | 15 | 高粱11A (叶II) Sorghum 11A (leaf II) |
| 2 | 白壳苏丹草(茎I) White shell Sudan grass (stem I) | 16 | F1 (根II) F1 (root II) |
| 3 | 白壳苏丹草(叶I) White shell Sudan grass (leaf I) | 17 | F1 (茎II) F1 (stem II) |
| 4 | 高粱11A (根I) Sorghum 11A (root I) | 18 | F1 (叶II) F1 (leaf II) |
| 5 | 高粱11A (茎I) Sorghum 11A (stem I) | 19 | 白壳苏丹草(根 III) White shell Sudan grass (root III) |
| 6 | 高粱11A (叶I) Sorghum 11A (leaf I) | 20 | 白壳苏丹草(茎 III) White shell Sudan grass (stem III) |
| 7 | F1 (根I) F1 (root I) | 21 | 白壳苏丹草(叶 III) White shell Sudan grass (leaf III) |
| 8 | F1 (茎I) F1 (stem I) | 22 | 高粱11A (根 III) Sorghum 11A (root III) |
| 9 | F1 (叶I) F1 (leaf I) | 23 | 高粱11A (茎 III) Sorghum 11A (stem III) |
| 10 | 白壳苏丹草(根II) White shell Sudan grass (root II) | 24 | 高粱11A (叶 III) Sorghum 11A (leaf III) |
| 11 | 白壳苏丹草(茎II) White shell Sudan grass (stem II) | 25 | F1 (根III) F1 (root III) |
| 12 | 白壳苏丹草(叶II) White shell Sudan grass (leaf II) | 26 | F1 (茎III) F1 (stem III) |
| 13 | 高粱11A (根II) Sorghum 11A (root II) | 27 | F1 (叶III) F1 (leaf III) |
| 14 | 高粱11A (茎II) Sorghum 11A (stem II) |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
1.2 mRNA高通量测序及SNP分析
利用TRIzol法提取高丹草杂种及其亲本各组织的总RNA, 构建高质量文库后, 使用Illumina Hiseq 2000测序仪测序。由于高丹草和苏丹草均尚未完成基因组测序, 所以使用亲本之中已完成基因组测序的高粱基因组(ftp://ftp.jgi-psf.org/pub/compgen/phytozome/v9.0/early_release/Sbicolor_v2.1/)作为参考进行后续分析。利用TopHat 2[24]软件在Clean Reads和高粱参考基因组之间比对。在各样品读长与参考基因组序列的TopHat2软件比对数据的基础上, 利用GATK软件寻找测序样品与参考基因组间的单碱基错配[25]。根据Nr注释信息, 使用Blast 2 GO软件[26]和WEGO (Web Gene Ontology Annotation Plot)软件[27]得到unigene的GO (Gene Ontology)注释信息和功能分类统计。利用蛋白数据库KEGG (http://www.genome.jp/kegg/)进一步得到unigene的pathway注释[28]。通过blastx (e-value<10-5)将包含SNP位点的unigene比对到COG数据库, 从而获得其COG分类注释[29]。本研究通过比较高丹草杂种及其亲本3种组织所有同源基因测序读长, 按照以下标准筛选单核苷酸多态性位点: (1)所有SNP位点须在高丹草及其亲本3种组织测序的3个重复中均出现; (2)为确保等位基因特异性表达数据的可靠程度, 各SNP位点至少有300条reads的支持。在某SNP位点, 两亲本reads中的碱基互不相同, 子代与亲本之一碱基相同, 则认为高丹草杂种中存在等位基因表达偏向性。符合上述标准的SNPs用于后续分析。如果杂交种中2个亲本等位基因对应的reads支持数的比值偏离1.0, 则认为杂交种中存在等位基因表达偏向性。采用卡方检验方法统计分析。1.3 实时荧光定量PCR (Quantitative real-time PCR, qRT-PCR)
从极显著偏向性等位基因表达偏向性SNP- unigene中选择6个基因进行实时荧光定量PCR验证分析, 使用 E.Z.N.A. Plant RNA Maxi Kit抽提RNA。根据基因序列, 使用Primer Quest Tool (http:// sg.idtdna.com/ Primerquest/Home/Index)设计引物。第1链反转录使用PrimeScrip RT reagent Kit with gDNA Eraser (Perfect Real Time)第1链合成试剂(RR047A)。荧光定量检测使用abm Eva Green qPCR Master Mix-No Dye试剂盒。PCR反应流程为95℃预变性1 min; 95℃变性10 s, 60℃退火30 s, 40个循环。以β-actin为内参, 使用2-ΔΔCt法分析表达量。2 结果与分析
2.1 SNP位点统计
根据碱基替换的不同方式, 可以将SNP位点分为转换(Transition)和颠换(Transversion) 2种类型; 根据SNP位点的等位(Allele)数目, 可以将位点分为纯合型(只有一个等位)和杂合型(两个或多个等位)[30]。计算高丹草杂种及其亲本中的SNP位点数目、转换类型、颠换类型比例和杂合型SNP位点比例, 统计结果见表2。对平均长度达58 122 160 bp的序列, 各测序样品中均检测到不少于58 000个SNP位点, 位于基因内的SNP个数显著多于位于基因间的SNP个数。高丹草杂种及其亲本转录组SNP发生频率为1/741 bp, 即平均每741 bp就有1个SNP位点出现。另外, 各样品中转换类型的SNP均占所有SNP数目的60%以上, 明显多于颠换类型的SNP个数, 平均转换颠换比为1.00:1.53 (表2)。Table 2
表2
表2SNP位点统计表
Table 2
| 材料编号 Material number | 总读长 Total reads | SNP数 SNP number | 基因内SNP Genic SNP | 基因间SNP Intergenic SNP | 转换 Transition (%) | 颠换 Transversion (%) | 杂合型 Heterozygosity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 63 420 052 | 64 836 | 59 809 | 5027 | 60.19 | 39.81 | 10.11 |
| 2 | 59 951 742 | 71 331 | 66 793 | 4538 | 60.20 | 39.80 | 8.32 |
| 3 | 57 812 158 | 61 330 | 57 316 | 4014 | 60.69 | 39.31 | 9.28 |
| 4 | 50 219 934 | 62 583 | 57 875 | 4708 | 60.56 | 39.44 | 23.85 |
| 5 | 50 930 220 | 70 397 | 66 138 | 4259 | 60.25 | 39.75 | 21.43 |
| 6 | 47 779 664 | 58 033 | 54 415 | 3618 | 60.54 | 39.46 | 23.60 |
| 7 | 58 868 406 | 68 886 | 64 489 | 4397 | 60.09 | 39.91 | 22.36 |
| 8 | 64 250 174 | 65 248 | 61 364 | 3884 | 60.25 | 39.75 | 16.52 |
| 9 | 72 335 474 | 64 670 | 60 166 | 4504 | 60.60 | 39.40 | 16.67 |
| 10 | 53 344 576 | 99 040 | 92 057 | 6983 | 60.30 | 39.70 | 31.46 |
| 11 | 58 821 334 | 107 700 | 100 064 | 7636 | 60.35 | 39.65 | 31.87 |
| 12 | 61 991 178 | 84 379 | 78 540 | 5839 | 60.27 | 39.73 | 28.42 |
| 13 | 49 206 246 | 99 539 | 92 695 | 6844 | 60.46 | 39.54 | 34.03 |
| 14 | 54 672 342 | 98 391 | 91 657 | 6734 | 60.39 | 39.61 | 33.68 |
| 15 | 61 319 270 | 81 486 | 75 946 | 5540 | 60.36 | 39.64 | 30.89 |
| 16 | 56 744 190 | 109 658 | 102 075 | 7583 | 60.26 | 39.74 | 31.77 |
| 材料编号 Material number | 总读长 Total reads | SNP数 SNP number | 基因内SNP Genic SNP | 基因间SNP Intergenic SNP | 转换 Transition (%) | 颠换 Transversion (%) | 杂合型 Heterozygosity (%) |
| 17 | 59 733 160 | 95 723 | 89 741 | 5982 | 60.17 | 39.83 | 33.54 |
| 18 | 72 158 580 | 81 267 | 75 641 | 5626 | 60.34 | 39.66 | 29.79 |
| 19 | 78 016 508 | 95 205 | 87 506 | 7699 | 60.50 | 39.50 | 36.17 |
| 20 | 53 568 218 | 82 079 | 77 412 | 4667 | 60.47 | 39.53 | 30.25 |
| 21 | 49 779 342 | 73 905 | 69 659 | 4246 | 60.75 | 39.25 | 30.17 |
| 22 | 59 151 356 | 89 068 | 82 884 | 6184 | 60.36 | 39.64 | 38.21 |
| 23 | 50 348 066 | 75 276 | 70 970 | 4306 | 60.23 | 39.77 | 36.31 |
| 24 | 51 025 424 | 72 978 | 68 695 | 4283 | 60.48 | 39.52 | 36.28 |
| 25 | 55 095 668 | 81 945 | 76 448 | 5497 | 60.75 | 39.25 | 31.16 |
| 26 | 57 676 612 | 87 673 | 82 696 | 4977 | 60.37 | 39.63 | 31.16 |
| 27 | 61 078 424 | 78 864 | 74 174 | 4690 | 60.74 | 39.26 | 30.43 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
2.2 SNP类型
由图1可知, 在所有12种单核苷酸变异类型中, 发生频率最高的前4种分别是C/T、G/A、A/G和T/C, 均大于40 000个, 而其他8种单核苷酸变异C/G、G/C、C/A、G/T、T/G、A/C、A/T和T/A均在20 000以下。12种变异类型中以C/T类型频率最高, 原因可能是CpG二核苷酸上甲基化的胞嘧啶残基易脱去氨基而转化成胸腺嘧啶[31]。图1
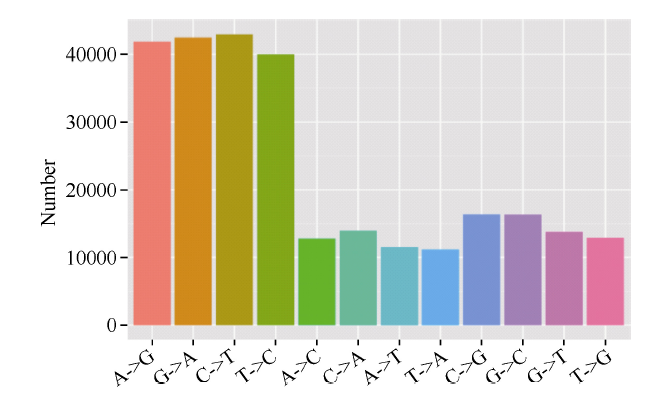 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图1SNP类型统计
Fig. 1SNP type and number
2.3 SNP注释
将SNP-unigene序列与GenBank中的非冗余蛋白数据库Nr数据库进行相似性比对。其中, 比对效率最高的有24 515条unigene (79.12%)与数据库中已知的高粱基因同源; 3806条unigene (12.28%)与数据库中已知的玉米基因组同源; 1435条unigene (4.63%)与数据库中已知的谷子基因组同源(图2)。图2
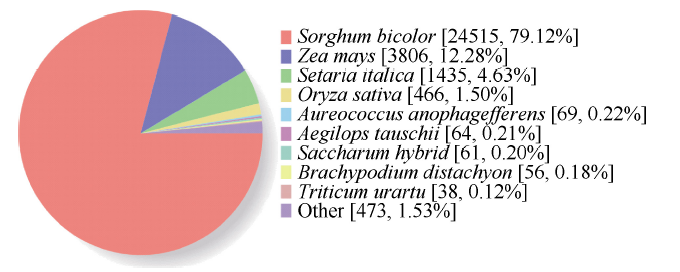 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图2SNP-unigene Nr比对结果
括号内为该类型unigene数及其在所有unigene中所占比例。
Fig. 2SNP-unigene Nr comparison results
Unigene number of this type and its proportion in all unigene are shown in parentheses.
能够在COG中找到10 328条unigene相应的注释信息, 共获得15 799个COG功能注释, 可分为24类(图3中A~Z表示), 并对其进行数量统计。从分析统计结果可以看出, 这10 328条被注释的unigene功能种类较为全面, 涉及大多数生命活动过程或功能。“一般功能预测类”是最大的一个分类, 包含3099 (19.05%)个unigene。其次是“转录”、“复制、重组和修复”、“信号转导机制”和“翻译、核糖体结构和生物转化”分别包含1521 (9.63%)、1430 (9.05%)、1309 (8.29%)和1099 (6.96%)条SNP-unigene。“核结构”分类中包含2 (0.01%)条SNP-unigene, 数量最少(图3)。
图3
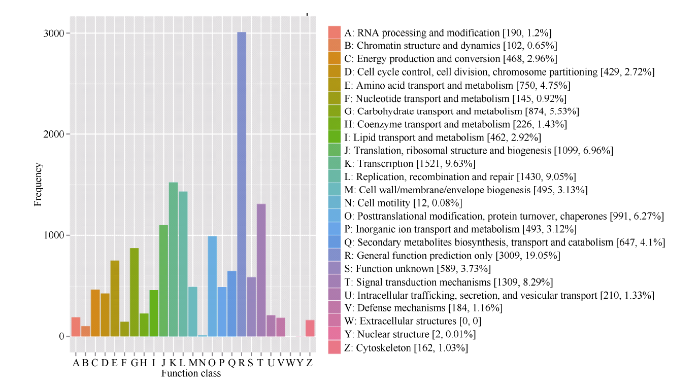 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图3SNP-unigene COG比对结果
Fig. 3SNP-unigene COG comparison results
2.4 等位基因偏向性表达与亲本差异相关
为了分析杂种中的等位基因特异性表达, 比较得到注释的转录本外显子区域的每个碱基并鉴定SNP, 经过筛选后, 将9308个SNP用于后续分析。在本研究中, 如果在一个转录本中同时存在多个SNP, 并且其中2个SNP的表达偏向性不同, 则将该转录本信息直接删除。为了保证分析的准确性和可靠性, 本试验只将表现极显著偏向性(P<0.01)的SNP用于后续分析。图4所示是198个极显著偏向性等位基因表达偏向性SNP在3种不同组织中的表达情况。图4
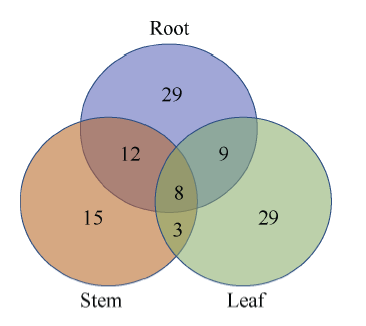 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图4等位基因表达偏向性SNP
Fig. 4Allelic expression bias SNPs
在亲本基因差异表达对高丹草杂种中的等位基因特异性表达方式的影响分析中, 将父本白壳苏丹草与母本高粱11A的基因表达比值命名为P1/P2, 高丹草杂种中的亲本等位基因表达比值命名为F1/P2。结果表明, 很多在白壳苏丹草中具有高水平基因表达的转录本, 在高丹草杂种中的等位基因表达也偏向白壳苏丹草(图5)。
图5
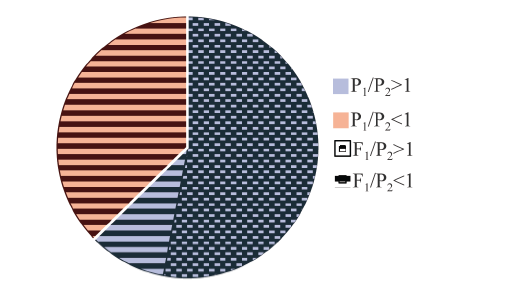 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图5高丹草杂种中等位基因表达偏向性
Fig. 5Allelic biases in Sorghum bicolor×Sorghum sudanense hybrid
在198个SNPs中, 根、茎、叶组织中分别有79个(涉及58个基因)、53个(涉及38个基因)和66个(涉及49个基因)单核苷酸多态性位点具有等位基因表达偏向性。其中, 有10个SNPs (涉及8个转录本)在根、茎、叶中均有表现(表3)。
Table 3
表3
表310个等位基因表达偏向性SNPs
Table 3
| 编号 No. | 基因名称 Gene ID | 位置 Position | ♂ | F1 | ♀ | 深度 Depth | 染色体 Chr. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Sobic.001G191200 | 16936477 | A | A | R | 477 | 1 |
| 2 | Sobic.001G293800 | 50043262 | G | R | R | 394 | 1 |
| 3 | Sobic.002G215700 | 60749644 | C | C | S | 518 | 2 |
| 4 | Sobic.002G215700 | 60750650 | T | T | Y | 476 | 2 |
| 5 | Sobic.003G085700 | 7390162 | T | T | W | 353 | 3 |
| 6 | Sobic.003G206800 | 53754265 | T | Y | Y | 361 | 3 |
| 7 | Sobic.003G314500 | 64282541 | T | T | K | 492 | 3 |
| 8 | Sobic.003G314500 | 64279654 | C | C | Y | 419 | 3 |
| 9 | Sobic.004G225100 | 56832538 | C | C | Y | 476 | 4 |
| 10 | Sobic.004G253000 | 59205755 | T | T | Y | 335 | 4 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
GO功能分析将Sobic.001G191200转录本定位到蔗糖响应机制(response to sucrose)、葡萄糖响应机制(response to glucose)、果糖响应机制(response to fructose)功能; Sobic.001G293800转录本定位到蛋白质磷酸化(protein phosphorylation)、ATP结合(ATP binding)、叶绿体(chloroplast)等32种功能; Sobic.002G215700转录本定位到干旱响应机制(response to desiccation)、醛脱氢酶活性(aldehyde dehydrogenase, NAD)、胞液(cytosol)等17种功能; Sobic.003G085700转录本定位到RNA加工(RNA processing)、基因表达调控 (regulation of gene expression)和核腔(nuclear lumen)等7种功能; Sobic.003G206800转录本定位到脂肪酸β氧化(fatty acid beta-oxidation )、激酶活性(kinase activity)等12种功能; Sobic.003G314500转录本定位到水解酶活性(hydrolase activity)、叶绿体被膜(chloroplast envelope )、有机物质代谢过程(organic substance metabolic process )等5种功能; Sobic.004G225100转录本定位到叶绿体(chloroplast)、吲哚乙酸生物合成过程(indoleacetic acid biosynthetic process )、氰化物代谢过程(cyanide metabolic process)等20种功能; Sobic.004G253000转录本定位到胞膜界小泡(cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle)功能。
KEGG代谢通量分析发现Sobic.001G293800转录本参与β录淀粉酶代谢通路; Sobic.002G215700转录本参与醛脱氢酶家族7成员A1代谢通路; Sobic. 004G225100转录本参与腈水解酶代谢通路; Sobic. 004G253000转录本参与FAM32A (A)蛋白代谢。
2.5 荧光定量PCR验证结果
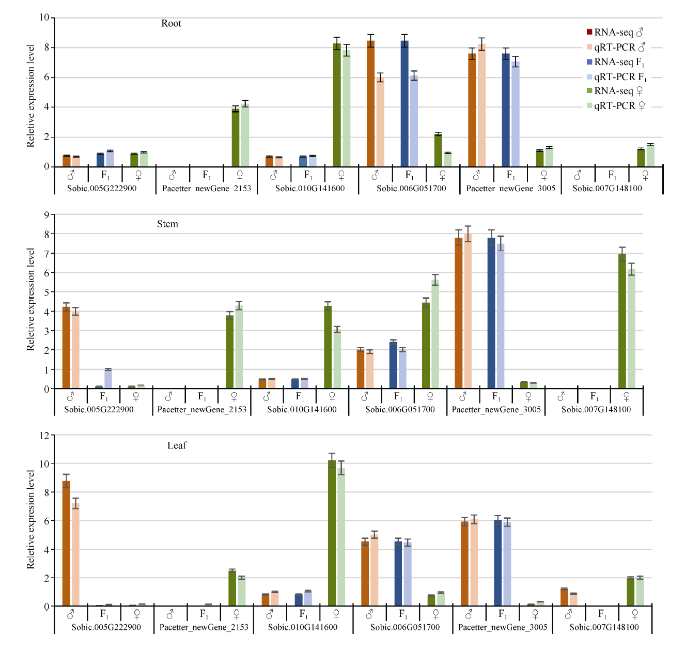
从198个等位基因表达偏向性SNPs中随机选择6个基因进行qRT-PCR验证分析, 4个基因在3种组织中表现相同的偏向性, 2个基因在3种组织中表现不同的偏向性, 均与RNA-Seq分析结果一致(图6)。图6
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图6高丹草杂种及其亲本3个组织中各基因表达量
Fig. 6Expression levels of each gene in three tissues of Sorghum bicolors × Sorghum sudanense hybrid and its parents
3 讨论
本研究表明, Illumina 双端测序技术是同时分析杂交种中基因表达水平和等位基因表达方式的一个强有力工具, 为深入研究杂种优势的分子机制提供了有价值的信息。在高丹草杂种及其亲本之间的SNP类型中, CT和GA为数量最多的类型。研究表明, 胞嘧啶甲基化可能是造成这种现象的原因[32], 发生甲基化的胞嘧啶比没有发生甲基化的胞嘧啶突变频率高, 而且甲基化的胞嘧啶发生脱氨基作用产生胸腺嘧啶T的频率高于其他自发突变的频率[33,34,35]。本研究在根、茎和叶组织中的9308个等位基因表达偏向性一致的SNP中, 仅有198个存在极显著的等位基因表达偏向性, 约占21%。He等[36]发现在日本晴93-11及其杂交种中有398 (22.7%)个存在显著的等位基因表达偏向性。在玉米[37]和杨树[38]的基因中, 分别有73%和57%的基因表现出等位基因表达偏向性。翟蓉蓉等[39]发现在超级稻协优9308及其亲本中有480 (17%)个存在显著的等位基因表达偏向性。本研究中, 至少在一个组织存在等位基因表达偏向性的145个转录本中, 根、茎和叶分别有62% (36)、66% (26)和65% (32)的转录本的等位基因表达偏向白壳苏丹草, 这些转录本编码多种重要功能蛋白。在3种组织中, 与高粱11A的等位基因相比, 白壳苏丹草的等位基因更能维持它们在高丹草杂种中的活性, 并且对杂种优势做出贡献。白壳苏丹草等位基因的功能多样性也可能对高丹草杂种的优良表型起作用。在上述145个转录本中, 49个转录本(约34%)的等位基因表达在不同组织表现出不同的偏向性, 说明杂交种中的等位基因表达具有组织特异性[38, 40]。
顺式作用元件或反式作用因子变异均可能引起等位基因的表达变异[41]。前者可能改变启动子强度、增强子活性或转录稳定性, 而后者可能影响结构、连接和转录因子[42]。顺式和反式调控可以通过比较亲本表达水平的比值和杂交种中亲本等位基因特异性表达的比值来确定[38]。如果变异发生在顺式作用元件, 那么亲本表达水平的比值和杂交种中亲本等位基因特异性表达的比值没有差异。如果变异发生在反式作用因子, 由于杂交种中的两个亲本等位基因处于相同的亚细胞环境中, 杂交种中的双亲等位基因的表达没有差异。本研究发现, 在3种组织中,分别有79%和82%转录本的2个亲本等位基因表现出稳定的表达水平, 说明与顺式作用相比, 反式作用可能更多地影响了等位基因的特异性表达, 这些涉及抗性或者其他重要代谢反应相关转录本的等位基因所受到的差异调控可能与高丹草杂种表现出的杂种优势有关。
4 结论
共鉴定了9308个分布于整个基因组的高质量的SNP位点。Illumina测序技术是分析高丹草杂种中基因表达水平和等位基因表达方式的一个强有力工具, 为深入研究杂种优势形成的分子机制提供了有价值的信息。DNA甲基化现象可能存在于高丹草杂种及其亲本中; 与母本高粱11A相比, 父本白壳苏丹草的等位基因更能维持在高丹草杂种中的表达并对杂种优势形成产生影响; 根、茎和叶组织的高丹草杂种中亲本等位基因具有不同的表达方式, 具有组织特异性; 高丹草杂种中亲本等位基因的差异表达多数由反式作用因子调控。参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0496-3490.2004.01.014URL [本文引用: 1]

The morphological characteristics, heterosis and the forage value of hybrid between sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench] and sudangrass[Sorghum sudanense (Piper) Stapf] were studied. The results showed that the hybrid vigor was obvious, higher than mid-parent, even higher than the high-parent in le
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0496-3490.2004.01.014URL [本文引用: 1]

The morphological characteristics, heterosis and the forage value of hybrid between sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench] and sudangrass[Sorghum sudanense (Piper) Stapf] were studied. The results showed that the hybrid vigor was obvious, higher than mid-parent, even higher than the high-parent in le
[本文引用: 2]
DOI:10.1111/j.1365-294X.2004.02145.xURLPMID:15078439 [本文引用: 1]

The role of natural hybridization in the evolutionary history of numerous species is well recognized. The impact of introgressive hybridization and hybrid speciation has been documented especially in plant and animal assemblages. However, there remain certain areas of investigation for which natural hybridization and its consequences remain under-studied and under-appreciated. One such area involves the evolution of organisms that positively or negatively affect human populations. In this review, I highlight exemplars of how natural hybridization has contributed to the evolution of (i) domesticated plants and animals; (ii) pests; (iii) human disease vectors; and (iv) human pathogens. I focus on the effects from genetic exchange that may lead to the acquisition of novel phenotypes and thus increase the beneficial or detrimental (to human populations) aspects of the various taxa.
DOI:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2004.01253.xURLPMID:15720652 [本文引用: 1]

Abrupt speciation through interspecific hybridisation is an important mechanism in angiosperm evolution. Flowering plants therefore offer excellent opportunities for studying genetic processes associated with hybrid speciation. Novel molecular approaches are now available to examine these processes at the level of both genome organization and gene expression transcriptomics. Here, we present an overview of the molecular technologies currently used to study hybrid speciation and how they are providing new insights into this mode of speciation in flowering plants. We begin with an introduction to hybrid speciation in plants, followed by a review of techniques, such as isozymes and other markers, which have been used to study hybrid species in the past. We then review advances in molecular techniques that have the potential to be applied to studies of hybrid species, followed by an overview of the main genomic and transcriptomic changes suspected, or known, to occur in newly formed hybrids, together with commentary on the application of advanced molecular tools to studying these changes.
DOI:10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.28.1.359URL [本文引用: 1]

The origin of new homoploid species via hybridization is theoretically difficult because it requires the development of reproductive isolation in sympatry. Nonetheless, this mode is often and carelessly used by botanists to account for the formation of species that are morphologically intermediate with respect to related congeners. Here, I review experimental, theoretical, and empirical studies of homoploid hybrid speciation to evaluate the feasibility, tempo, and frequency of this mode. Theoretical models, simulation studies, and experimental syntheses of stabilized hybrid neospecies indicate that it is feasible, although evolutionary conditions are stringent. Hybrid speciation appears to be promoted by rapid chromosomal evolution and the availability of a suitable hybrid habitat. A selfing breeding system may enhance establishment of hybrid species, but this advantage appears to be counterbalanced by lower rates of natural hybridization among selfing taxa. Simulation studies and crossing experiments also suggest that hybrid speciation can be rapid--a prediction confirmed by the congruence observed between the genomes of early generation hybrids and ancient hybrid species. The frequency of this mode is less clear. Only eight natural examples in plants have been rigorously documented, suggesting that it may be rare. However, hybridization rates are highest in small or peripheral populations, and hybridization may be important as a stimulus for the genetic or chromosomal reorganization envisioned in founder effect and saltational models of speciation.
DOI:10.1126/science.1086949URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1105/tpc.151030URLPMID:14523245 [本文引用: 1]

Many free-swimming unicellular organisms show negative gravitaxis, i.e. tend to swim upward, although their specific densities are higher than the medium density. To obtain clues to the mechanism of this behavior, we examined how a mutation in motility or behavior affects the gravitaxis in Chlamydomonas. A phototaxis mutant, ptx3, deficient in membrane excitability showed weakened gravitaxis, whereas another phototaxis mutant, ptx1, deficient in regulation of flagellar dominance displayed normal gravitaxis. Two mutants that swim backwards only, mbo1 and mbo2, did not show any clear gravitaxis. We also isolated two novel mutants deficient in gravitaxis, gtx1 and gtx2. These mutants displayed normal motility and physical characteristics of cell body as assessed by the behavior of anesthetized cells. However, these cells were found to have defects in physiological responses involving membrane excitation. These observations are consistent with the idea that the gravitaxis in Chlamydomonas involves a physiological signal transduction system, which is at least partially independent of the system used for phototaxis.
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1006.2014.01914URL [本文引用: 1]

Flavonoids as the secondary metabolites play a crucial role in colour changing process of flower, leaf, fruit and seed.yellow- and black-seeded
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1006.2014.01914URL [本文引用: 1]

Flavonoids as the secondary metabolites play a crucial role in colour changing process of flower, leaf, fruit and seed.yellow- and black-seeded
DOI:10.1016/j.aquatox.2007.07.004URLPMID:17255553 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract In this review, we discuss the recent research on allelic variation in maize and possible implications of this work toward our understanding of heterosis. Heterosis, or hybrid vigor, is the increased performance of a hybrid relative to the parents, and is a result of the variation that is present within a species. Intraspecific comparisons of sequence and expression levels in maize have documented a surprisingly high level of allelic variation, which includes variation for the content of genic fragments, variation in repetitive elements surrounding genes, and variation in gene expression levels. There is evidence that transposons and repetitive DNA play a major role in the generation of this allelic diversity. The combination of allelic variants provides a more comprehensive suite of alleles in the hybrid that may be involved in novel allelic interactions. A major unresolved question is how the combined allelic variation and interactions in a hybrid give rise to heterotic phenotypes. An understanding of allelic variation present in maize provides an opportunity to speculate on mechanisms that might lead to heterosis. Variation for the presence of genes, the presence of novel beneficial alleles, and modified levels of gene expression in hybrids may all contribute to the heterotic phenotypes.
DOI:10.1534/genetics.106.060699URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.7666/d.Y2787474URL [本文引用: 1]

单核苷酸多态性(SNP)是近年来被认为最有发展潜力的第三代分子标记。本实验室利用Illumina RNA-seq技术,从淀粉含量、薯干产量和茎线虫病抗性差异明显的徐781和徐薯18测序结果中已获得1,386个SNP候选位点。为开发实用的SNP标记,本研究采用等位基因特异性PCR(AS-PCR)和四引物扩增受阻突变体系PCR(Tetra-primer ARMS-PCR)两种特异性扩增的方法以及酶切扩增多态性序列(CAPS)酶切的方法,检测候选SNP位点,确定合适的甘薯SNP分子标记检测方法,对其反应条件进行优化,包括反应退火温度、内外引物浓度之比和Taq DNA聚合酶用量,并根据候选SNP位点,设计引物,检测SNP位点和开发SNP分子标记。主要研究结果如下:1.通过AS-PCR、Tetra-primer ARMS-PCR和CAPS三种常用的SNP检测方法,对甘薯SNP位点进行检测,比较其检测可行性和有效性,并对适宜检测方法的反应体系进行优化。结果表明,Tetra-primer ARMS-PCR方法能准确、快速检测甘薯SNP位点并进行分型,操作步骤简单,费用低廉,使用25μL的反应体系,在每一组引物的最适退火温度下,内外引物浓度之比为0.4μmol/L:0.2μmol/L,Taq DNA聚合酶用量为1.25 U时,可以达到良好的检测效果。2.利用徐781和徐薯18转录组测序获得的候选SNP位点共设计了153组Tetra-primer ARMS-PCR引物,对徐781和徐薯18候选SNP位点进行检测,其中103组引物的PCR产物有差异,差异检出率为67.97%。研究结果表明,Tetra-primer ARMS-PCR适合甘薯SNP分子标记的检测,可以用于甘薯SNP分子标记的开发。Tetra-primer ARMS-PCR不要求特殊的设备,操作步骤简单,能准确检测甘薯SNP位点,费用低廉,该方法能有效地检测甘薯SNP位点和开发SNP标记,可以用于甘薯分子连锁图谱的构建和实用SNP标记的开发。
DOI:10.7666/d.Y2787474URL [本文引用: 1]

单核苷酸多态性(SNP)是近年来被认为最有发展潜力的第三代分子标记。本实验室利用Illumina RNA-seq技术,从淀粉含量、薯干产量和茎线虫病抗性差异明显的徐781和徐薯18测序结果中已获得1,386个SNP候选位点。为开发实用的SNP标记,本研究采用等位基因特异性PCR(AS-PCR)和四引物扩增受阻突变体系PCR(Tetra-primer ARMS-PCR)两种特异性扩增的方法以及酶切扩增多态性序列(CAPS)酶切的方法,检测候选SNP位点,确定合适的甘薯SNP分子标记检测方法,对其反应条件进行优化,包括反应退火温度、内外引物浓度之比和Taq DNA聚合酶用量,并根据候选SNP位点,设计引物,检测SNP位点和开发SNP分子标记。主要研究结果如下:1.通过AS-PCR、Tetra-primer ARMS-PCR和CAPS三种常用的SNP检测方法,对甘薯SNP位点进行检测,比较其检测可行性和有效性,并对适宜检测方法的反应体系进行优化。结果表明,Tetra-primer ARMS-PCR方法能准确、快速检测甘薯SNP位点并进行分型,操作步骤简单,费用低廉,使用25μL的反应体系,在每一组引物的最适退火温度下,内外引物浓度之比为0.4μmol/L:0.2μmol/L,Taq DNA聚合酶用量为1.25 U时,可以达到良好的检测效果。2.利用徐781和徐薯18转录组测序获得的候选SNP位点共设计了153组Tetra-primer ARMS-PCR引物,对徐781和徐薯18候选SNP位点进行检测,其中103组引物的PCR产物有差异,差异检出率为67.97%。研究结果表明,Tetra-primer ARMS-PCR适合甘薯SNP分子标记的检测,可以用于甘薯SNP分子标记的开发。Tetra-primer ARMS-PCR不要求特殊的设备,操作步骤简单,能准确检测甘薯SNP位点,费用低廉,该方法能有效地检测甘薯SNP位点和开发SNP标记,可以用于甘薯分子连锁图谱的构建和实用SNP标记的开发。
DOI:10.1038/nrg2815URLPMID:20567245 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract Functional genomics is rapidly progressing towards the elucidation of elements that are crucial for the cis-regulatory control of gene expression, and population-based studies of disease and gene expression traits are yielding widespread evidence of the influence of non-coding variants on trait variance. Recently, genome-wide allele-specific approaches that harness high-throughput sequencing technology have started to allow direct evaluation of how these cis-regulatory polymorphisms control gene expression and affect chromatin states. The emerging data is providing exciting opportunities for comprehensive characterization of the allele-specific events that govern human gene regulation.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0513-353X.2014.02.016URL [本文引用: 1]

利用SNP分析软件从辣椒(Capsicum annuum L.)251068条Unigenes中筛选出18159个SNP,其中有1781个SNP位点被匹配在1291个注释基因上,基因功能分类和代谢途径分析表明,其中有853个基因参与初生代谢(28.7%)、细胞代谢(17.3%)、生物合成过程(15.7%),另有125个(9.7%)基因序列参与新陈代谢途径,53条(4.1%)序列参与次生代谢产物合成途径,31条(2.4%)序列参与植物激素合成途径。EST-SNP序列中4172条(22.9%)满足设计CAPS引物条件,为了验证EST-SNP正确性,并选取了15对CAPS引物对5份辣椒材料进行扩增,结果发现有8对(53.3%)引物表现出多态性。表明筛选出这些EST-SNP标记可作为辣椒基因分型、图谱构建等的候选分子标记。
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0513-353X.2014.02.016URL [本文引用: 1]

利用SNP分析软件从辣椒(Capsicum annuum L.)251068条Unigenes中筛选出18159个SNP,其中有1781个SNP位点被匹配在1291个注释基因上,基因功能分类和代谢途径分析表明,其中有853个基因参与初生代谢(28.7%)、细胞代谢(17.3%)、生物合成过程(15.7%),另有125个(9.7%)基因序列参与新陈代谢途径,53条(4.1%)序列参与次生代谢产物合成途径,31条(2.4%)序列参与植物激素合成途径。EST-SNP序列中4172条(22.9%)满足设计CAPS引物条件,为了验证EST-SNP正确性,并选取了15对CAPS引物对5份辣椒材料进行扩增,结果发现有8对(53.3%)引物表现出多态性。表明筛选出这些EST-SNP标记可作为辣椒基因分型、图谱构建等的候选分子标记。
DOI:10.1126/science.1169766URLPMID:19407207 [本文引用: 1]

During evolution, novel phenotypes emerge through changes in gene expression, but the genetic basis is poorly understood. We compared the allele-specific expression of two yeast species and their hybrid, which allowed us to distinguish changes in regulatory sequences of the gene itself (cis) from changes in upstream regulatory factors (trans). Expression divergence between species was generally due to changes in cis. Divergence in trans reflected a differential response to the environment and explained the tendency of certain genes to diverge rapidly. Hybrid-specific expression, deviating from the parental range, occurred through novel cis-trans interactions or, more often, through modified trans regulation associated with environmental sensing. These results provide insights on the regulatory changes in cis and trans during the divergence of species and upon hybridization.
DOI:10.1534/genetics.109.103499URLPMID:19474198 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract Gene expression is a complex trait determined by various genetic and nongenetic factors. Among the genetic factors, allelic difference may play a critical role in gene regulation. In this study we globally dissected cis (allelic) and trans sources of genetic variation in F(1) hybrids between two Arabidopsis thaliana wild accessions, Columbia (Col) and Vancouver (Van), using a new high-density SNP-tiling array. This array tiles the whole genome with 35-bp resolution and interrogates 250,000 SNPs identified from resequencing of 20 diverse A. thaliana strains. Quantitative assessment of 12,311 genes identified 3811 genes differentially expressed between parents, 1665 genes with allele-specific expression, and 1688 genes controlled by composite trans-regulatory variation. Loci with cis- or trans-regulatory variation were mapped onto sequence polymorphisms, epigenetic modifications, and transcriptional specificity. Genes regulated in cis tend to be located in polymorphic chromosomal regions, are preferentially associated with repressive epigenetic marks, and exhibit high tissue expression specificity. Genes that vary due to trans regulation reside in relatively conserved chromosome regions, show activating epigenetic marks and generally constitutive gene expression. Our findings demonstrate a method of global functional characterization of allele-specific expression and highlight that chromatin structure is intertwined with evolution of cis- and trans-regulatory variation.
DOI:10.1186/1471-2164-14-19URLPMID:23324257 [本文引用: 1]

Background: Heterosis is a phenomenon in which hybrids exhibit superior performance relative to parental phenotypes. In addition to the heterosis of above-ground agronomic traits on which most existing studies have focused, root heterosis is also an indispensable component of heterosis in the entire plant and of major importance to plant breeding. Consequently, systematic investigations of root heterosis, particularly in reproductive-stage rice, are needed. The recent advent of RNA sequencing technology (RNA-Seq) provides an opportunity to conduct in-depth transcript profiling for heterosis studies.Results: Using the Illumina HiSeq 2000 platform, the root transcriptomes of the super-hybrid rice variety Xieyou 9308 and its parents were analyzed at tillering and heading stages. Approximately 391 million high-quality paired-end reads (100-bp in size) were generated and aligned against the Nipponbare reference genome. We found that 38,872 of 42,081 (92.4%) annotated transcripts were represented by at least one sequence read. A total of 829 and 4186 transcripts that were differentially expressed between the hybrid and its parents (DG(HP)) were identified at tillering and heading stages, respectively. Out of the DG(HP), 66.59% were down-regulated at the tillering stage and 64.41% were up-regulated at the heading stage. At the heading stage, the DG(HP) were significantly enriched in pathways related to processes such as carbohydrate metabolism and plant hormone signal transduction, with most of the key genes that are involved in the two pathways being up-regulated in the hybrid. Several significant DG(HP) that could be mapped to quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for yield and root traits are also involved in carbohydrate metabolism and plant hormone signal transduction pathways.Conclusions: An extensive transcriptome dataset was obtained by RNA-Seq, giving a comprehensive overview of the root transcriptomes at tillering and heading stages in a heterotic rice cross and providing a useful resource for the rice research community. Using comparative transcriptome analysis, we detected DG(HP) and identified a group of potential candidate transcripts. The changes in the expression of the candidate transcripts may lay a foundation for future studies on molecular mechanisms underlying root heterosis.
DOI:10.1111/tpj.13116URLPMID:26718755 [本文引用: 1]

Summary Imprinting is an epigenetic phenomenon referring to allele-biased expression of certain genes depending on their parent of origin. Accumulated evidence suggests that, while imprinting is a conserved mechanism across kingdoms, the identities of the imprinted genes are largely species-specific. Using deep RNA sequencing of endosperm 1402days after pollination in sorghum, 5683 genes (29.27% of the total 1902418 expressed genes) were found to harbor diagnostic single nucleotide polymorphisms between two parental lines. The analysis of parent-of-origin expression patterns in the endosperm of a pair of reciprocal F1 hybrids between the two sorghum lines led to identification of 101 genes with ≥ fivefold allelic expression difference in both hybrids, including 85 maternal expressed genes (MEGs) and 16 paternal expressed genes (PEGs). Thirty of these genes were previously identified as imprinted in endosperm of maize ( Zea mays ), rice ( Oryza sativa ) or Arabidopsis, while the remaining 71 genes are sorghum-specific imprinted genes relative to these three plant species. Allele-biased expression of virtually all of the 14 tested imprinted genes (nine MEGs and five PEGs) was validated by pyrosequencing using independent sources of RNA from various developmental stages and dissected parts of endosperm. Forty-six imprinted genes (30 MEGs and 16 PEGs) were assayed by quantitative RT–PCR, and the majority of them showed endosperm-specific or preferential expression relative to embryo and other tissues. DNA methylation analysis of the 5’ upstream region and gene body for seven imprinted genes indicated that, while three of the four PEGs were associated with hypomethylation of maternal alleles, no MEG was associated with allele-differential methylation.
DOI:10.7668/hbnxb.2007.04.019URLMagsci [本文引用: 1]

利用分子标记技术,在许多作物上已获得了高密度的分子遗传图谱,并定位了许多主要农艺性状的QTL,而在牧草上这方面的研究尚属空白。为提高育种中对牧草产量性状优良基因型选择的效率,对高丹草的单株产量及其构成因素(株高、分蘖数、叶片数)进行QTL定位,确定其在染色体的位置及其遗传效应,探讨其杂种优势产生原因。在以高粱413A和棕壳苏丹草杂交获得的248个F<sub>2:3</sub>家系构建的作图群体中,应用AFLP和RAPD两种标记技术构建了高丹草(Sorghum×Sudan grass)的遗传连锁图谱。共包含18个标记,分布于10个连锁群,图谱总长度为83 cM,标记间平均图距为4.98 cM。采用Joinmap/QTL4.0对高丹草单株产量及其三大构成因素进行QTL定位。共检测到QTLs19个,分布在8个连锁群上,其中,第1和3连锁群最多,各为4个和3个。单个QTL解释性状表型变异的5.20%~51.50%。检测到的19个QTL中,表现加性效应的有1个,占5.2%,部分显性效应的有3个,占15.79%,显性效应的有个,占31.58%,超显性效应的有9个,占47.3%。超显性效应和显性效应在高丹草杂种优势的遗传基础中占主导地位。
DOI:10.7668/hbnxb.2007.04.019URLMagsci [本文引用: 1]

利用分子标记技术,在许多作物上已获得了高密度的分子遗传图谱,并定位了许多主要农艺性状的QTL,而在牧草上这方面的研究尚属空白。为提高育种中对牧草产量性状优良基因型选择的效率,对高丹草的单株产量及其构成因素(株高、分蘖数、叶片数)进行QTL定位,确定其在染色体的位置及其遗传效应,探讨其杂种优势产生原因。在以高粱413A和棕壳苏丹草杂交获得的248个F<sub>2:3</sub>家系构建的作图群体中,应用AFLP和RAPD两种标记技术构建了高丹草(Sorghum×Sudan grass)的遗传连锁图谱。共包含18个标记,分布于10个连锁群,图谱总长度为83 cM,标记间平均图距为4.98 cM。采用Joinmap/QTL4.0对高丹草单株产量及其三大构成因素进行QTL定位。共检测到QTLs19个,分布在8个连锁群上,其中,第1和3连锁群最多,各为4个和3个。单个QTL解释性状表型变异的5.20%~51.50%。检测到的19个QTL中,表现加性效应的有1个,占5.2%,部分显性效应的有3个,占15.79%,显性效应的有个,占31.58%,超显性效应的有9个,占47.3%。超显性效应和显性效应在高丹草杂种优势的遗传基础中占主导地位。
DOI:10.13430/j.cnki.jpgr.2016.04.020URL

以4份高粱不育系和5种类型苏丹草为亲本,按照NCⅡ设计配制成20个杂交组合,分析各组合及亲本的表型值和中亲及超亲优势并筛选出8个优势强的组合为试材,利用cDNA-AFLP技术,分析杂种与亲本苗期叶片基因差异表达类型与主要产量性状的杂种表现及杂种优势的关系。研究表明:(1)12对引物共扩增出315条TDFs,杂种与亲本间基因表达类型有:单亲表达一致一型(P1F1型)和二型(P2F1型)、杂种特异表达类型(F1型)、单亲表达沉默一型(P1型)和二型(P2型)、双亲共沉默类型(P1P2型)和杂种亲本表达一致型(P1F1P2型)7种。(2)在差异展示类型与产量构成因素的相关分析中,有效分蘖数与P1F1型(0.726**)呈极显著正相关,单株鲜重与P1P2型(0.659*)、叶长与P2型(0.647*)呈显著正相关,成株期叶片数与F1型(-0.81**)呈极显著负相关。在与中亲优势相关分析中发现,单株鲜重与P1(0.695*)、P2(0.637*)呈显著正相关,单株鲜重与P1F1P2型(0.743**)呈极显著正相关,叶宽与P1P2型(-0.619*)呈显著负相关。在与超亲优势进行相关分析后发现,穗长与P2F1型(0.732**)呈极显著正相关,叶宽与P2F1型(-0.731**)以及P1P2型(-0.731**)呈极显著负相关。(3)差异展示类型P1F1、P2F1、P1和P2是显性效应类型,共占总检测的91.4%。差异展示类型F1和P1P2表现超显性,共占总检测的4.8%,说明各个性状的杂种表现主要受到的是(超)显性效应影响。(4)对8个与高丹草杂种优势相关的TDFs进行回收及BLAST分析均得到同源核苷酸,并且找到7个同源蛋白,这些蛋白质在控制植物生长发育方面具有重要作用。(5)将克隆测序获得差异片段的核苷酸序列,采用半定量RT-PCR进行了验证。本研究为进一步揭示高丹草杂种优势的分子机制和提高高丹草强优势组合的筛选效率以及种质17
DOI:10.13430/j.cnki.jpgr.2016.04.020URL

以4份高粱不育系和5种类型苏丹草为亲本,按照NCⅡ设计配制成20个杂交组合,分析各组合及亲本的表型值和中亲及超亲优势并筛选出8个优势强的组合为试材,利用cDNA-AFLP技术,分析杂种与亲本苗期叶片基因差异表达类型与主要产量性状的杂种表现及杂种优势的关系。研究表明:(1)12对引物共扩增出315条TDFs,杂种与亲本间基因表达类型有:单亲表达一致一型(P1F1型)和二型(P2F1型)、杂种特异表达类型(F1型)、单亲表达沉默一型(P1型)和二型(P2型)、双亲共沉默类型(P1P2型)和杂种亲本表达一致型(P1F1P2型)7种。(2)在差异展示类型与产量构成因素的相关分析中,有效分蘖数与P1F1型(0.726**)呈极显著正相关,单株鲜重与P1P2型(0.659*)、叶长与P2型(0.647*)呈显著正相关,成株期叶片数与F1型(-0.81**)呈极显著负相关。在与中亲优势相关分析中发现,单株鲜重与P1(0.695*)、P2(0.637*)呈显著正相关,单株鲜重与P1F1P2型(0.743**)呈极显著正相关,叶宽与P1P2型(-0.619*)呈显著负相关。在与超亲优势进行相关分析后发现,穗长与P2F1型(0.732**)呈极显著正相关,叶宽与P2F1型(-0.731**)以及P1P2型(-0.731**)呈极显著负相关。(3)差异展示类型P1F1、P2F1、P1和P2是显性效应类型,共占总检测的91.4%。差异展示类型F1和P1P2表现超显性,共占总检测的4.8%,说明各个性状的杂种表现主要受到的是(超)显性效应影响。(4)对8个与高丹草杂种优势相关的TDFs进行回收及BLAST分析均得到同源核苷酸,并且找到7个同源蛋白,这些蛋白质在控制植物生长发育方面具有重要作用。(5)将克隆测序获得差异片段的核苷酸序列,采用半定量RT-PCR进行了验证。本研究为进一步揭示高丹草杂种优势的分子机制和提高高丹草强优势组合的筛选效率以及种质17
DOI:10.1093/abbs/gmv126URLPMID:26792642 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract Sorghum-sudangrass hybrids are widely used for forage and silage in the animal husbandry industry due to their hardiness. The heterozygous first generation of sorghum-sudangrass hybrids displays performance superior to their homozygous, parental inbred lines. In order to study the molecular details underlying its heterosis, the leaves of sorghum-sudangrass hybrids and their parents were compared using mass spectrometry-based proteomics. Results showed that among the 996 proteins that were identified, 32 proteins showed 'additive accumulation expression patterns', indicating that the protein abundance in sorghum-sudangrass hybrids showed no significant difference from the average of their parents. Additionally, 74 proteins showed 'nonadditive accumulation expression patterns' (the proteins abundance in the hybrids showed significant difference from the average of their parents). Both additive and nonadditive proteins were mainly involved in photosynthesis and carbohydrate metabolism. More upregulated additive and nonadditive proteins were in the hybrids than in their parents, suggesting that additive and nonadditive proteins are essential to the vigor of sorghum-sudangrass hybrids. The nonadditive proteins were enriched in photosynthesis, carbohydrate metabolism, and protein oligomerization, but the additive proteins were not enriched in any pathway, which indicated that the nonadditive proteins could be greater contributors to heterosis than additive proteins. Furthermore, the highly activated photosynthetic pathway in nonadditive proteins implies that photosynthesis in hybrids is heightened to assimilate more organic matter, resulting in an increased yield. Our results provide a proof-of-concept that reveals the molecular components of heterosis in sorghum-sudangrass hybrid leaves and serves as an important step for future genetic manipulation of specific proteins to improve the performance of hybrids. The Author 2016. Published by ABBS Editorial Office in association with Oxford University Press on behalf of the Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
DOI:10.1186/gb-2013-14-4-r36URLPMID:4053844 [本文引用: 1]

TopHat is a popular spliced aligner for RNA-sequence (RNA-seq) experiments. In this paper, we describe TopHat2, which incorporates many significant enhancements to TopHat. TopHat2 can align reads of various lengths produced by the latest sequencing technologies, while allowing for variable-length indels with respect to the reference genome. In addition to de novo spliced alignment, TopHat2 can align reads across fusion breaks, which can occur after genomic translocations. TopHat2 combines the ability to identify novel splice sites with direct mapping to known transcripts, producing sensitive and accurate alignments, even for highly repetitive genomes or in the presence of pseudogenes. TopHat2 is available at http://ccb.jhu.edu/software/tophat .
DOI:10.1101/gr.107524.110URLPMID:20644199 [本文引用: 1]

Next-generation DNA sequencing (NGS) projects, such as the 1000 Genomes Project, are already revolutionizing our understanding of genetic variation among individuals. However, the massive data sets generated by NGS he 1000 Genome pilot alone includes nearly five terabases ake writing feature-rich, efficient, and robust analysis tools difficult for even computationally sophisticated individuals. Indeed, many professionals are limited in the scope and the ease with which they can answer scientific questions by the complexity of accessing and manipulating the data produced by these machines. Here, we discuss our Genome Analysis Toolkit (GATK), a structured programming framework designed to ease the development of efficient and robust analysis tools for next-generation DNA sequencers using the functional programming philosophy of MapReduce. The GATK provides a small but rich set of data access patterns that encompass the majority of analysis tool needs. Separating specific analysis calculations from common data management infrastructure enables us to optimize the GATK framework for correctness, stability, and CPU and memory efficiency and to enable distributed and shared memory parallelization. We highlight the capabilities of the GATK by describing the implementation and application of robust, scale-tolerant tools like coverage calculators and single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) calling. We conclude that the GATK programming framework enables developers and analysts to quickly and easily write efficient and robust NGS tools, many of which have already been incorporated into large-scale sequencing projects like the 1000 Genomes Project and The Cancer Genome Atlas.
DOI:10.1093/nar/25.17.3389URLPMID:9254694 [本文引用: 1]

The BLAST programs are widely used tools for searching protein and DNA databases for sequence similarities. For protein comparisons, a variety of definitional, algorithmic and statistical refinements described here permits the execution time of the BLAST programs to be decreased substantially while enhancing their sensitivity to weak similarities. A new criterion for triggering the extension of word hits, combined with a new heuristic for generating gapped alignments, yields a gapped BLAST program that runs at approximately three times the speed of the original. In addition, a method is introduced for automatically combining statistically significant alignments pro- duced by BLAST into a position-specific score matrix, and searching the database using this matrix. The resulting Position-Specific Iterated BLAST (PSI- BLAST) program runs at approximately the same speed per iteration as gapped BLAST, but in many cases is much more sensitive to weak but biologically relevant sequence similarities. PSI-BLAST is used to uncover several new and interesting members of the BRCT superfamily.
DOI:10.1038/75556URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1093/nar/gkh063URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1093/nar/28.1.33URLPMID:102395 [本文引用: 1]

Rational classification of proteins encoded in sequenced genomes is critical for making the genome sequences maximally useful for functional and evolutionary studies. The database of Clusters of Orthologous Groups of proteins (COGs) is an attempt on a phylogenetic classification of the proteins encoded in 21 complete genomes of bacteria, archaea and eukaryotes (http://www. ncbi.nlm. nih.gov/COG). The COGs were constructed by applying the criterion of consistency of genome-specific best hits to the results of an exhaustive comparison of all protein sequences from these genomes. The database comprises 2091 COGs that include 56-83% of the gene products from each of the complete bacterial and archaeal genomes and approximately 35% of those from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome. The COG database is accompanied by the COGNITOR program that is used to fit new proteins into the COGs and can be applied to functional and phylogenetic annotation of newly sequenced genomes.
URL [本文引用: 1]

西瓜(Citrullus lanatus),属葫芦科西瓜属一年生蔓性草本植物,原产于非洲。西瓜是世界上重要的水果之一。随着生活水平的提高,人们对西瓜品质要求也越高。西瓜品质包括外观、口感及营养等。西瓜果皮的色泽是西瓜果实的品质评价以及种质改良的重要经济性状,是现代社会人们在西瓜消费中参考的重要商品特性,因此,优质、高产和外观美丽的西瓜新品种有利于西瓜品种结构的丰富和商品质量的提高,同时也对西瓜的商品性具有很大的影响。本试验从西瓜黄皮突变型材料、绿皮野生型材料的果实座果期、膨大期及成熟期6份样品中提取果皮色泽相关基因,运用转录组测序技术研究基因的生物学功能。基于转录组测序数据,我们进行了转录组文库的评估、基因的分析、各个时期差异表达基因的分析结论如下:(1)经过电泳检测、微量紫外分光光度计定量检测获得了符合建库标准的西瓜果皮总RNA。使用Qubit2.0、Aglient2100对文库的浓度和插入片段大小进行检测,用qPCR方法对文库的有效浓度进行准确定量,检测和定量确定文库质量合格。6份样品转录组测序完成之后,除去其中接头序列及低质量Reads共获得34.27Gb Clean Data,且各样品Clean Data均达到4.67Gb,Q30碱基比均在86.85%及以上,转录组测序数据质量较好。将各样品的Clean Reads与制定的参考基因组进行序列对比,其比对效率为83.75%到88.11%不等,该转录组数据能够满足信息分析的需求及后期数据分析的可靠性,结果比较理想。(2)基于参考基因组序列比对结果,进行了可变剪接预测分析,对10550个基因结构进行了基因结构优化分析,共发现基因958个,其中有678个已有功能注释。(3)在同一时期不同颜色的差异表达基因COG功能分类中,通用功能预测,转录,复制、重组和修复,氨基酸转运和代谢,碳水化合物的运输和代谢这五种功能的基因数量较多,其中核结构、细胞运动、细胞外结构在三个时期的对比中均无对应的差异表达基因。GO注释中,主要是注释到细胞组成部分中的细胞外基质的组成部分、外区部分、外区、细胞外基质,分子功能部分中的核酸结合的转录因子的活性、电子载体活动,生物过程部分中的发育、多生物过程、细胞外基质、蛋白结合的转录因子的活性等功能。KEGG注释中,主要集中注释到环境信息处理的植物激素信号转导、代谢部分中的苯丙合成、代谢部分中的光合作用、代谢部分中的淀粉和蔗糖代谢这几个通路中。(4)同种颜色不同时期差异表达基因在COG功能分类中,差异表达基因主要为通用功能预测,转录,复制、重组和修复,碳水化合物的运输和代谢,信号转导机制等基因,而核结构、细胞运动、细胞外结构等在COG功能分类中并无对应的基因。G O注释中,主要几种表现在细胞组分的细胞外基质的组成部分和细胞部分,分子功能的蛋白标签和转录因子活性,生物学过程中的细胞杀伤和多生物过程。KEGG注释中,主要集中注释在环境信息处理部分中的植物激素信号转导、代谢部分中的淀粉和蔗糖代谢、代谢部分的光合作用、代谢部分中的苯丙合成、遗传信息处理部分中的核糖体、代谢部分中的苯丙氨酸代谢。(5)基于TopHat2比对打分大于等于50;单碱基错配位点间隔不小于5个碱基;变体识别质量值不低于20;序列测序深度,不低于5x且不高于100x的SNP筛选条件,T01、T02、T03、T04、T05、T06分别获得了13853个、15617个、14163个、12155个、15108个、18297个可靠的SNP位点。6个样品转录组的SNP分析,在T01中有13852个可靠的SNP位点,在T02中有15617个可靠的SNP位点,在T03中有14163个可靠的SNP位点,在T04中有12155个可靠的SNP位点,在T05中有15108个可靠的SNP位点,在T06中有18279个可靠的SNP位点。
URL [本文引用: 1]

西瓜(Citrullus lanatus),属葫芦科西瓜属一年生蔓性草本植物,原产于非洲。西瓜是世界上重要的水果之一。随着生活水平的提高,人们对西瓜品质要求也越高。西瓜品质包括外观、口感及营养等。西瓜果皮的色泽是西瓜果实的品质评价以及种质改良的重要经济性状,是现代社会人们在西瓜消费中参考的重要商品特性,因此,优质、高产和外观美丽的西瓜新品种有利于西瓜品种结构的丰富和商品质量的提高,同时也对西瓜的商品性具有很大的影响。本试验从西瓜黄皮突变型材料、绿皮野生型材料的果实座果期、膨大期及成熟期6份样品中提取果皮色泽相关基因,运用转录组测序技术研究基因的生物学功能。基于转录组测序数据,我们进行了转录组文库的评估、基因的分析、各个时期差异表达基因的分析结论如下:(1)经过电泳检测、微量紫外分光光度计定量检测获得了符合建库标准的西瓜果皮总RNA。使用Qubit2.0、Aglient2100对文库的浓度和插入片段大小进行检测,用qPCR方法对文库的有效浓度进行准确定量,检测和定量确定文库质量合格。6份样品转录组测序完成之后,除去其中接头序列及低质量Reads共获得34.27Gb Clean Data,且各样品Clean Data均达到4.67Gb,Q30碱基比均在86.85%及以上,转录组测序数据质量较好。将各样品的Clean Reads与制定的参考基因组进行序列对比,其比对效率为83.75%到88.11%不等,该转录组数据能够满足信息分析的需求及后期数据分析的可靠性,结果比较理想。(2)基于参考基因组序列比对结果,进行了可变剪接预测分析,对10550个基因结构进行了基因结构优化分析,共发现基因958个,其中有678个已有功能注释。(3)在同一时期不同颜色的差异表达基因COG功能分类中,通用功能预测,转录,复制、重组和修复,氨基酸转运和代谢,碳水化合物的运输和代谢这五种功能的基因数量较多,其中核结构、细胞运动、细胞外结构在三个时期的对比中均无对应的差异表达基因。GO注释中,主要是注释到细胞组成部分中的细胞外基质的组成部分、外区部分、外区、细胞外基质,分子功能部分中的核酸结合的转录因子的活性、电子载体活动,生物过程部分中的发育、多生物过程、细胞外基质、蛋白结合的转录因子的活性等功能。KEGG注释中,主要集中注释到环境信息处理的植物激素信号转导、代谢部分中的苯丙合成、代谢部分中的光合作用、代谢部分中的淀粉和蔗糖代谢这几个通路中。(4)同种颜色不同时期差异表达基因在COG功能分类中,差异表达基因主要为通用功能预测,转录,复制、重组和修复,碳水化合物的运输和代谢,信号转导机制等基因,而核结构、细胞运动、细胞外结构等在COG功能分类中并无对应的基因。G O注释中,主要几种表现在细胞组分的细胞外基质的组成部分和细胞部分,分子功能的蛋白标签和转录因子活性,生物学过程中的细胞杀伤和多生物过程。KEGG注释中,主要集中注释在环境信息处理部分中的植物激素信号转导、代谢部分中的淀粉和蔗糖代谢、代谢部分的光合作用、代谢部分中的苯丙合成、遗传信息处理部分中的核糖体、代谢部分中的苯丙氨酸代谢。(5)基于TopHat2比对打分大于等于50;单碱基错配位点间隔不小于5个碱基;变体识别质量值不低于20;序列测序深度,不低于5x且不高于100x的SNP筛选条件,T01、T02、T03、T04、T05、T06分别获得了13853个、15617个、14163个、12155个、15108个、18297个可靠的SNP位点。6个样品转录组的SNP分析,在T01中有13852个可靠的SNP位点,在T02中有15617个可靠的SNP位点,在T03中有14163个可靠的SNP位点,在T04中有12155个可靠的SNP位点,在T05中有15108个可靠的SNP位点,在T06中有18279个可靠的SNP位点。
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1073/pnas.0730835100URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1073/pnas.1209297109URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1074/jbc.M407695200URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1021/bi00045a016URLPMID:7578083 [本文引用: 1]

Sites of cytosine methylation are known to be hot spots for C.G to T.A mutations in a number of systems, including human cells. Traditionally, spontaneous hydrolytic deamination of 5-methylcytosine to thymine has been invoked as the cause of this phenomenon. We show here that a bacterial cytosine methyltransferase can convert 5-methylcytosine in DNA to thymine and that this reaction creates a mutational hot spot at a site of DNA methylation. The reaction is fairly insensitive to the methyl donor in the reaction, S-adenosylmethionine. In many cancers, the most frequent class of mutations is C to T changes within CG dinucleotides of the tumor suppressor gene p53. Because of the similarities of the reaction mechanisms of mammalian and bacterial enzymes and the physiology of the cancer cells, this reaction is expected to contribute to mutations at CG dinucleotides in precancerous cells.
DOI:10.1105/tpc.109.072041URLPMID:20086188 [本文引用: 1]

The behavior of transcriptomes and epigenomes in hybrids of heterotic parents is of fundamental interest. Here, we report highly integrated maps of the epigenome, mRNA, and small RNA transcriptomes of two rice (Oryza sativa) subspecies and their reciprocal hybrids. We found that gene activity was correlated with DNA methylation and both active and repressive histone modifications in transcribed regions. Differential epigenetic modifications correlated with changes in transcript levels among hybrids and parental lines. Distinct patterns in gene expression and epigenetic modifications in reciprocal hybrids were observed. Through analyses of single nucleotide polymorphisms from our sequence data, we observed a high correlation of allelic bias of epigenetic modifications or gene expression in reciprocal hybrids with their differences in the parental lines. The abundance of distinct small RNA size classes differed between the parents, and more small RNAs were downregulated than upregulated in the reciprocal hybrids. Together, our data reveal a comprehensive overview of transcriptional and epigenetic trends in heterotic rice crosses and provide a useful resource for the rice community.
DOI:10.1105/tpc.022087URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1534/genetics.107.080325URL [本文引用: 3]

ABSTRACTHybridization between plant species can induce speciation as well as phenotypic novelty...
URL [本文引用: 1]

协优9308是农业部推荐的第一批超级稻品种。该品种株型挺拔、根系发达、产量潜力大。本研究以协优9308及双亲协青早B和中恢9308、协优9308衍生的重组自交系(RIL)为材料,深入开展了协优9308根系杂种优势的分子机制研究,主要结果如下: 1.以超级杂交稻协优9308衍生的234个重组自交系(RIL)为材料,在正常水分和20%聚乙二醇(PEG-6000)模拟水分胁迫处理下对水稻苗期最大根长(MRL)、总根长(TRL)、根表面积(RSA)、根体积(RV)、根平均直径(RAD)、根尖数(RTN)、根鲜重(RFW)和根冠比(RS)进行QTL定位分析,共检测到影响8个根部性状的21个QTL。其中,在正常水分和胁迫条件下分别检测到7个和14个QTL。两种水分条件下检测到的QTL位点差异很大,表明两种水分条件下的遗传机制不同。在第3和第6染色体上各检测到1个根部性状的QTL簇,尤其在第3染色体RM6283-RM7370区间发现苗期根系性状与抗旱性及产量相关性状之间存在连锁关系,利用这些与QTL紧密连锁的分子标记可望同时对多个相关性状进行遗传改良。除此之外,本研究结果也为挖掘可能与根系发育相关的关键基因及深入研究杂种优势遗传机制提供重要信息。 2.基于Illumina HiSeq2000平台,本研究分析了分蘖期和抽穗期超级稻协优9308及双亲根系的转录谱。我们将双端测序产生的约3.91亿条高质量的reads比对到日本晴参考基因组,在已经注释的42081个转录本中,38872(92.4%)个至少有一条测序的read能够比对到日本晴参考基因组。分蘖期和抽穗期分别有829个和4186个在杂种一代(F_1)与亲本之间存在表达差异的转录本(DG_(HP))。在分蘖期,F_1中66.59%的DG_(HP)下调表达,而在抽穗期F_1中约64.41%的DG_(HP)上调表达。在抽穗期,DG_(HP)主要集中在碳代谢和植物激素信号转导途径,并且参与这两个途径的多数关键基因在F_1中上调表达;其中涉及上述两个途径的部分DG_(HP)能够比对到控制产量和根系性状的QTL区间。这些候选基因的表达变化为将来研究根系杂种优势的潜在机制奠定了基础,本研究获得的大量转录组数据也为其他水稻研究团队提供了有用的资源。 3.应用RNA-Seq技术分析了超级稻协优9308中的等位基因特异性表达(ASGE),共鉴定9325个可靠的SNP位点,这些SNPs分布于整个基因组。中恢9308与协青早B相比,约68%的SNP类型是CT和GA,表明协优9308和亲本中可能存在DNA甲基化。本研究发现,在分蘖期和抽穗期的2793个等位基因表达偏向性一致的转录本中,仅有480个存在显著的等位基因表达偏向性,约占17%,说明杂交种中亲本等位基因的差异表达多数是由反式作用因子调控。在上述480个转录本中,分蘖期和抽穗期分别有67%和62%转录本的等位基因表达偏向中恢9308。很多转录本在中恢9308中具有高水平表达,在杂交种中它们的等位基因表达也偏向中恢9308。除此之外,在两个时期同时存在等位基因表达偏向性的125个转录本中,约74%的等位基因表达偏向中恢9308。中恢9308的等位基因可能更能维持它们在杂交种中的活性并且对杂种优势作出贡献。355个转录本的等位基因在不同的发育时期表现出不同的表达偏向性,具有很高的时期特异性。杂交种中等位基因表达具有严重偏向性的转录本多与胁迫反应有关,这些转录本可能受到差异调控。本研究结果对深入研究杂种优势的分子机制提供了重要见解。
URL [本文引用: 1]

协优9308是农业部推荐的第一批超级稻品种。该品种株型挺拔、根系发达、产量潜力大。本研究以协优9308及双亲协青早B和中恢9308、协优9308衍生的重组自交系(RIL)为材料,深入开展了协优9308根系杂种优势的分子机制研究,主要结果如下: 1.以超级杂交稻协优9308衍生的234个重组自交系(RIL)为材料,在正常水分和20%聚乙二醇(PEG-6000)模拟水分胁迫处理下对水稻苗期最大根长(MRL)、总根长(TRL)、根表面积(RSA)、根体积(RV)、根平均直径(RAD)、根尖数(RTN)、根鲜重(RFW)和根冠比(RS)进行QTL定位分析,共检测到影响8个根部性状的21个QTL。其中,在正常水分和胁迫条件下分别检测到7个和14个QTL。两种水分条件下检测到的QTL位点差异很大,表明两种水分条件下的遗传机制不同。在第3和第6染色体上各检测到1个根部性状的QTL簇,尤其在第3染色体RM6283-RM7370区间发现苗期根系性状与抗旱性及产量相关性状之间存在连锁关系,利用这些与QTL紧密连锁的分子标记可望同时对多个相关性状进行遗传改良。除此之外,本研究结果也为挖掘可能与根系发育相关的关键基因及深入研究杂种优势遗传机制提供重要信息。 2.基于Illumina HiSeq2000平台,本研究分析了分蘖期和抽穗期超级稻协优9308及双亲根系的转录谱。我们将双端测序产生的约3.91亿条高质量的reads比对到日本晴参考基因组,在已经注释的42081个转录本中,38872(92.4%)个至少有一条测序的read能够比对到日本晴参考基因组。分蘖期和抽穗期分别有829个和4186个在杂种一代(F_1)与亲本之间存在表达差异的转录本(DG_(HP))。在分蘖期,F_1中66.59%的DG_(HP)下调表达,而在抽穗期F_1中约64.41%的DG_(HP)上调表达。在抽穗期,DG_(HP)主要集中在碳代谢和植物激素信号转导途径,并且参与这两个途径的多数关键基因在F_1中上调表达;其中涉及上述两个途径的部分DG_(HP)能够比对到控制产量和根系性状的QTL区间。这些候选基因的表达变化为将来研究根系杂种优势的潜在机制奠定了基础,本研究获得的大量转录组数据也为其他水稻研究团队提供了有用的资源。 3.应用RNA-Seq技术分析了超级稻协优9308中的等位基因特异性表达(ASGE),共鉴定9325个可靠的SNP位点,这些SNPs分布于整个基因组。中恢9308与协青早B相比,约68%的SNP类型是CT和GA,表明协优9308和亲本中可能存在DNA甲基化。本研究发现,在分蘖期和抽穗期的2793个等位基因表达偏向性一致的转录本中,仅有480个存在显著的等位基因表达偏向性,约占17%,说明杂交种中亲本等位基因的差异表达多数是由反式作用因子调控。在上述480个转录本中,分蘖期和抽穗期分别有67%和62%转录本的等位基因表达偏向中恢9308。很多转录本在中恢9308中具有高水平表达,在杂交种中它们的等位基因表达也偏向中恢9308。除此之外,在两个时期同时存在等位基因表达偏向性的125个转录本中,约74%的等位基因表达偏向中恢9308。中恢9308的等位基因可能更能维持它们在杂交种中的活性并且对杂种优势作出贡献。355个转录本的等位基因在不同的发育时期表现出不同的表达偏向性,具有很高的时期特异性。杂交种中等位基因表达具有严重偏向性的转录本多与胁迫反应有关,这些转录本可能受到差异调控。本研究结果对深入研究杂种优势的分子机制提供了重要见解。
DOI:10.1105/tpc.107.052258URLPMID:17693532 [本文引用: 1]

We employed allele-specific expression (ASE) analyses to document biased allelic expression in maize (Zea mays). A set of 316 quantitative ASE assays were used to profile the relative allelic expression in seedling tissue derived from five maize hybrids. The different hybrids included in this study exhibit a range of heterosis levels; however, we did not observe differences in the frequencies of allelic bias. Allelic biases in gene expression were consistently observed for 50% of the genes assayed in hybrid seedlings. The relative proportion of genes that exhibit cis- or trans-acting regulatory variation was very similar among the different genotypes. The cis-acting regulatory variation was more prevalent and resulted in greater expression differences than trans-acting regulatory variation for these genes. The ASE assays were further used to compare the relative expression of the B73 and Mo17 alleles in three tissue types (seedling, immature ear, and embryo) derived from reciprocal hybrids. These comparisons provided evidence for tissue-specific cis-acting variation and for a slight maternal expression bias in 20% of genes in embryo tissue. Collectively, these data provide evidence for prevalent cis-acting regulatory variation that contributes to biased allelic expression between genotypes and between tissues.
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.cbpc.2011.03.012URLPMID:3178741 [本文引用: 1]

Variations in gene expression are essential for the evolution of novel phenotypes and for speciation. Studying allelic specific gene expression (ASGE) within interspecies hybrids provides a unique opportunity to reveal underlying mechanisms of genetic variation. Using Xiphophorus interspecies hybrid fishes and high-throughput next generation sequencing technology, we were able to assess variations between two closely related vertebrate species, Xiphophorus maculatus and Xiphophorus couchianus, and their F 1 interspecies hybrids. We constructed transcriptome-wide SNP polymorphism sets between two highly inbred X. maculatus lines (JP 163 A and B), and between X. maculatus and a second species, X. couchianus. The X. maculatus JP 163 A and B parental lines have been separated in the laboratory for 70 years and we were able to identify SNPs at a resolution of 1 SNP per 49 kb of transcriptome. In contrast, SNP polymorphisms between X. couchianus and X. maculatus species, which diverged 5 10 million years ago, were identified about every 700 bp. Using 6524 transcripts with identified SNPs between the two parental species ( X. maculatus and X. couchianus), we mapped RNA-seq reads to determine ASGE within F 1 interspecies hybrids. We developed an in silico X. couchianus transcriptome by replacing 90,788 SNP bases for X. maculatus transcriptome with the consensus X. couchianus SNP bases and provide evidence that this procedure overcomes read mapping biases. Employment of the in silico reference transcriptome and tolerating 5 mismatches during read mapping allow direct assessment of ASGE in the F 1 interspecies hybrids. Overall, these results show that Xiphophorus is a tractable vertebrate experimental model to investigate how genetic variations that occur during speciation may affect gene interactions and the regulation of gene expression.
