 ,*湖南农业大学农学院 / 国家油料改良中心湖南分中心, 湖南长沙 410128
,*湖南农业大学农学院 / 国家油料改良中心湖南分中心, 湖南长沙 410128Cloning and Characterization of Brassinazole-resistant (BnaBZR1 and BnaBES1) CDS from Brassica napus L.
FENG Tao, GUAN Chun-Yun ,*College of Agronomy, Hunan Agricultural University / National Oilseed Crops Improvement Center in Hunan, Changsha 410128, Hunan, China
,*College of Agronomy, Hunan Agricultural University / National Oilseed Crops Improvement Center in Hunan, Changsha 410128, Hunan, China通讯作者:
第一联系人:
收稿日期:2018-05-3接受日期:2018-08-20网络出版日期:2018-09-19
| 基金资助: |
Received:2018-05-3Accepted:2018-08-20Online:2018-09-19
| Fund supported: |

摘要
关键词:
Abstract
Keywords:
PDF (2014KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
本文引用格式
冯韬, 官春云. 甘蓝型油菜芸薹素唑耐受因子(BnaBZR1/BnaBES1)全长CDS克隆与生物信息学分析[J]. 作物学报, 2018, 44(12): 1793-1801. doi:10.3724/SP.J.1006.2018.01793
FENG Tao, GUAN Chun-Yun.
油菜素内酯信号途径是植物中重要的激素途径, 其活性调控与植物生长发育以及抗逆能力息息相关。芸薹素唑耐受因子BZR是油菜素内酯信号与其他信号互作的核心元件, 在油菜素内酯信号转导中BZR1/BES1复合体与PIF4和DELLA等转录因子互作, 分别介导油菜素内酯信号途径与光信号[1]、赤霉素信号[2]、茉莉酸信号[3]等互作。在拟南芥中, AtBZR1与AtBES1形成异源复合体并相互磷酸化, 磷酸化后的异源二聚体与AtPIF4结合, 形成三元复合物介导下游基因表达调控, 从而完成油菜素内酯信号与光信号之间的传递, AtBZR1/AtBES1通过磷酸化修饰结合DELLA蛋白, 从而影响赤霉素的生物合成与赤霉素信号通路产生互作[4]。
拟南芥[5]、水稻[6]等植物中油菜素内酯信号途径的研究比较深入, 不仅完成了信号途径中主要基因的克隆, 而且对信号转导、传递有了较全面的认识。拟南芥和水稻中油菜素内酯信号转导过程基本一致, 油菜素内酯(BRs)结合膜表面受体BRI1激活其激酶活性, 并诱导BRI1结合BAK1形成二聚体后相互磷酸化, BSKs蛋白通过活化的BRI1磷酸化其230位丝氨酸而激活, 活化的BSKs蛋白激活BSU1活性, 进而BSU1阻断BIN2对BZR/BES蛋白的过磷酸化, 去磷酸化的BZR/BES蛋白在细胞核积累并与PIF4和DELLA等转录因子互作, 同时参与下游靶基因转录调控。
有研究表明, 油菜素内酯可以促进油菜对高盐环境耐受性, 调节油菜真菌抗性, 影响油菜脂代谢。油菜素内酯处理可明显改善油菜幼苗对渗透胁迫的抗性[7], 2,4-表油菜素内酯可增强油菜对丁香假单胞菌的抗性[8], 同时2,4-表油菜素内酯影响油菜脂代谢, 调控酯质信号的产生和转导[9]。过表达油菜素内酯合成基因DWF4可以促进油菜提高产量[10], 表明油菜素内酯与甘蓝型油菜生长发育息息相关, 油菜素内酯在油菜生产上有广阔的应用前景。然而甘蓝型油菜中油菜素内酯信号途径的相关研究却比较薄弱, 信号通路的构成元件大部分都还处于未知状态, 严重制约了油菜素内酯信号相关基因筛选在高含油、高抗性油菜新品种选育过程中的作用, 限制了油菜分子育种中相关基因工程的应用, 同时由于理论研究的空白限制了油菜素内酯在油菜生产上的应用。
本文通过甘蓝型油菜基因组数据库中预测的BnaBZR/BnaBES基因序列设计引物, 从甘蓝型油菜品种湘油15号中克隆获得3个BZR基因CDS序列, 一个鉴定为BZR1型, 2个鉴定为BES型, 均位于A染色体组。
1 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
甘蓝型油菜双低品系湘油15号由国家油料改良中心湖南分中心提供。1.2 RNA提取与cDNA合成
将湘油15号在22℃、光周期为16 h/8 h条件下培养至2片真叶, 取幼苗50~100 mg。加液氮充分研磨后, 使用TRIzol RNA提取试剂盒(TransGen生物技术有限公司)按其所示方法提取总RNA, 以此RNA为模板参照Easy Script First-Strand cDNA Synthesis SuperMix试剂盒(TransGen生物技术有限公司)说明书合成第1链cDNA。1.3 BnaBZR基因的克隆及序列分析
从BRAD数据库(http://brassicadb.org/brad/)甘蓝型油菜全转录组中提取BnaBZR1以及BnaBES1的转录本序列。分析比对, 设计含起始密码子的5'端引物和含有终止密码子的3'端引物, 合成备用。设计的引物序列为BnaBZR1-F: 5'-ATGACGTCAGA TGGAGCTAC-3', BnaBZR1-R: 5'-TCAACCACGAG CTTTGCCG-3', BnaBES1-F: 5'-ATGACGTCTGACG GTGCG-3', BnaBES1-R: 5'-CTAACGACCTTTAGCG TTTCC-3'。以1.2所述cDNA为模板进行PCR扩增。PCR体系含50 ng μL-1模板1 μL、10 mmol L-1 dNTPs 0.5 μL、2 μmol L-1 BnaBZR1-F 0.75 μL、2 μmol L-1 BnaBZR1-R 0.75 μL、10×反应缓冲液1 μL、HiFi高保真DNA聚合酶0.5 μL和ddH2O 15.5 μL。程序为预变性95℃ 5 min; 95℃ 50 s, 58℃ 45 s, 72℃ 3 min, 35个循环; 72℃后延伸10 min。PCR产物经1.5%琼脂糖凝胶电泳, 用凝胶成像系统(Bio-Rad)检测和记录结果。将PCR产物回收后与pMD18-T载体(TransGen生物技术有限公司)连接, 转化大肠杆菌感受态细胞Trans1-T1 (北京天根生化有限公司), 筛选阳性克隆进行基因测序, 通过BRAD数据库(http://brassicadb.org/brad/)对获得的克隆序列进行染色体步移分析, 随后使用DNAman对克隆获得的BnaBZR1和BnaBES1基因全长CDS序列进行序列比对。通过NCBI核酸数据库(http://www.ncbi.nlm. nih.gov/nuccore/)下载甘蓝型油菜BZR相关基因转录本序列及植物BZR相关蛋白, 构建HMM文件, 使用HMMER软件检索甘蓝型油菜预测蛋白组, 并就BZR相关转录本在甘蓝型油菜基因组中的分布进行分析。1.4 BnaBZR蛋白生物信息学分析
1.4.1 BnaBZR1_A07、BnaBES1_A06F和BnaBES1_ A06R氨基酸序列特征与二级结构预测 通过ANTHEPROT 6.2软件分析来源于甘蓝型油菜的BnaBZR1和BnaBES1基因所编码的蛋白质。统计编码蛋白的氨基酸残基组分、分析编码蛋白的等电点、信号肽序列和亲疏水特征并使用Gariner模型进行二级结构预测。使用PSORT (http://psort.hgc.jp/form. html)和Plant-mPLoc (http://www.csbio.sjtu.edu.cn/ cgi-bin/PlantmPLoc.cgi)进行亚细胞定位预测。1.4.2 BnaBZR蛋白同源结构域分析 使用DNAman对BnaBZR蛋白进行同源比对分析; 同时使用NCBI (http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/)分别对不同的BnaBZR蛋白序列进行保守结构域分析; 使用SMART (http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/)、MOTIF (http://www. genome.jp/tools/motif/)及InterPro (http://www.ebi.ac. uk/interpro/)分析BnaBZR包含的特殊结构域。
1.4.3 BZR蛋白聚类分析 通过NCBI蛋白数据库(http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein)、String数据库(http://string.embl.de/)和PDB数据库(http://www. pdb.org/pdb/home/home.do)检索来源于不同物种的BZR相关蛋白序列, 并使用MEGA6.0对来源不同的BZR1相关蛋白进行聚类分析。
1.5 甘蓝型油菜中BnaBZR1_A07、BnaBES1_ A06F和BnaBES1_A06R基因时空表达分析
以1.2方法提取甘蓝型油菜湘油15号不同时期根、茎、叶、花和角果皮总RNA, 使用宝生物工程(大连)有限公司PrimeScript RTreagent Kit with gDNA Eraser (Perfect Real-time)试剂盒进行反转录, 获得cDNA第1链作为qRT-PCR模板。分析1.3中克隆获得的BnaBZR片段, 根据序列特征设计分型引物, 以BnaUBC21作为内参基因[11], 用于BnaBZR1_ A07、BnaBES1_A06F和BnaBES1_A06R时空表达分析, 每样品进行3次重复。QRT-PCR在ABI 7500荧光定量PCR系统上运行。PCR体系包含1 μL cDNA、10 μL 2×FastStart Universal SYBR GreenMaster with ROX、10 μmol L-1正向引物和反向引物各0.5 μL、8 μL ddH2O。PCR程序为95℃ 10 min; 95℃ 15 s, 60℃ 15 s, 72℃ 32 s, 35个循环。反应完成后进行95℃ 20 s, 60℃ 20 s, 95℃ 20 s, 59℃ 20 s绘制熔解曲线检测扩增产物的正确性和引物二聚体。2 结果与分析
2.1 BnaBZR基因全长CDS序列的克隆
以湘油15 cDNA为模板, 克隆到3个CDS序列, 长度分别为996、993和996 bp (图1), 分别定位于A07、A06和A06染色体上, 分别命名为BnaBZR1_ A07、BnaBES1_A06F和BnaBES1_A06R。通过BRAD数据库比对, 确认3个CDS序列的完整性, 以3条CDS序列为模板分别对BRAD数据库进行检索, 发现1条BnaBZR1_A07同源序列位于C06染色体, 相似度82.5%, 发现1条BnaBES1_A06F和BnaBES1_ A06R共有同源序列位于C08染色体, 相似度分别为85.2%和84.9%; 同时对BnaBZR1_A07、BnaBES1_ A06F和BnaBES1_A06R进行多序列比对发现, BnaBZR1_A07与BnaBES1_A06F和BnaBES1_A06R相似度分别为82.28%和82.26%, BnaBES1_A06F和BnaBES1_A06R相似度98.79%。以上结果表明, 克隆获得的BnaBZR1_A07与BnaBES1_A06F和BnaBE S1_A06R分属2个不同的家族亚类群, 并在C亚基因组上存在对应的同源基因; 甘蓝型油菜基因组具异源多倍性, 其A、C两个亚基因组之间高度同源, 在A染色体组上的基因大多存在C染色体组同源基因, C染色体组基因亦然。图1
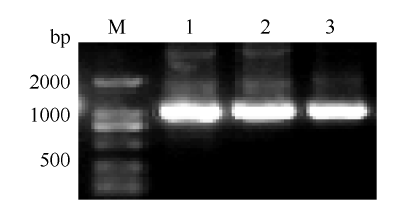 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图1BnaBZR1_A07、BnaBES1_A06F和BnaBES1_A06R 基因克隆
M: 2K DNA marker; 1: BnaBZR1_A07编码序列; 2: BnaBES1_A06F编码序列; 3: BnaBES1_A06R编码序列。
Fig. 1Cloning of BnaBZR1_A07, BnaBES1_A06F, and BnaBES1_A06R
M: 2K DNA marker; 1: BnaBZR1_A07CDS; 2: BnaBES1_A06F CDS; 3: BnaBES1_A06R CDS.
从NCBI共获取甘蓝型油菜BZR/BES及BZR/BES类似序列转录本13个, 7个位于C染色体组, 6个位于A染色体组, 主要集中于A06、A07、A08、C06、C08和C09染色体; HMMER检索甘蓝型油菜预测蛋白组数据库共发现31条具有BZR/BES家族特征结构域的序列, 其中17个位于A染色体组, 14个位于C染色体组; 表明具有BZR特征的基因在甘蓝型油菜A/C基因组间分布较均匀, 具有BZR特征的BZR家族基因在甘蓝和白菜2个亚组间可能具有相似的进化规律。
2.2 BnaBZR生物信息学分析
BnaBZR1_A07、BnaBES1_A06F和BnaBES1_ A06R基因各自编码长度331、330和331个氨基酸残基的蛋白, 分别命名为BnaBZR1_A07、BnaBES1_ A06F和BnaBES1_A06R (表1)。Table 1
表1
表1BnaBZR1、BnaBES1_F和BnaBES1_R蛋白信息汇总表
Table 1
| 蛋白编号 Serial number | 氨基酸残基数 Base of amino acid residues | 摩尔质量 Molar mass (Da) | 等电点 Isoelectric point |
|---|---|---|---|
| BnaBZR1_A07 | 331 | 35 895.131 | 9.145 |
| BnaBES1_A06F | 330 | 36 071.176 | 9.745 |
| BnaBES1_A06R | 331 | 36 177.322 | 9.745 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
BnaBZR蛋白主要表现疏水性, 未发现信号肽序列, 暗示其不存在信号肽介导的跨膜转运。PSORT与Plant-mPLoc亚细胞定位预测显示, BnaBZR1_A07与BnaBES1_A06F和BnaBES1_A06 R 均主要定位于细胞核, 可信度0.789, 这与BZR蛋白作为转录因子的功能一致。
二级结构预测结果如图2, BnaBZR1_A07有27% α螺旋、14% β折叠、29% β转角和32%无规卷曲; BnaBES1_A06F分别有24%、16%、29%和31%; BnaBES1_A06R分别有23%、16%、29%和32%。
图2
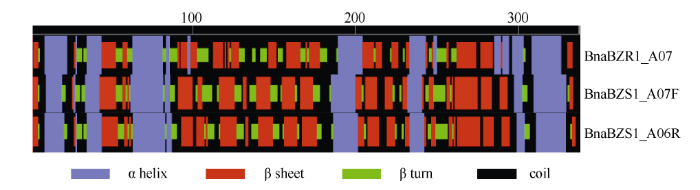 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图2BnaBZR1_A07、BnaBES1_A06F和BnaBES1_A06R蛋白二级结构
Fig. 2Secondary structure of BnaBZR1_A07, BnaBES1_A06F, and BnaBES1_A06R
通过ANTHEPROT分析了BnaBZR1_A07、BnaBES1_A06F和BnaBES1_A06R蛋白具有的序列特异性识别位点。由表2可知, BnaBES1_A06F和BnaBES1_A06R具有仅含微弱差别的特异性识别序列, BnaBES1_A06R相对于BnaBES1_A06F仅175- 177位置识别序列存在一个氨基酸残基的差别, 其他位置的特异性识别序列完全一致, 表明BnaBES1_ A06F和BnaBES1_A06R蛋白相似度极高。BnaBZR1_A07蛋白缺少PS00016特异性序列, 同时PS00006特异性序列数量也更少。3条蛋白序列中特异性识别序列主要为糖基化修饰、磷酸化修饰、酰化修饰和细胞连接序列, 表明BnaBZR蛋白可能受多种激酶介导的糖基化、磷酸化、酰基化修饰调节, 并可能介导细胞间连接, 这与拟南芥BZR蛋白通过磷酸化水平改变实现核质穿梭与互作因子结合, 调控下游靶基因表达的功能相吻合。
Table 2
表2
表2BnaBZR1_A07、BnaBES1_A06F和BnaBES1_A06R蛋白特殊识别位点序列总表
Table 2
| 蛋白编号 Serial number | 位点类型 Domains type | 数量 Number | 位置 Location | 序列 Sequence | 序列模式 Sequence motif | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BnaBZR1_A07 | PS00001 | 2 | 142-145, 143-146 | NNSS, NSST | N-{P}-[ST]-{P} | ||
| PS00004 | 1 | 21-24 | RKPS | [RK](2)-x-[ST] | |||
| PS00005 | 5 | 24-26, 84-86, 162-164, 179-181, 221-223 | SWR, TYR, SLR, TSK, THR | [ST]-x-[RK] | |||
| PS00006 | 4 | 24-27, 236-239, 230-233, 240-243 | SWRE, SRGE, TIPE, STVD | [ST]-x(2)-[DE] | |||
| PS00008 | 4 | 5-10, 154-159, 155-160, 325-330 | GATSTS, GGIPSS, GIPSSSL, GNGKAR | G-{EDRKHPFYW}-x(2)-[STAGCN]-{P} | |||
| BnaBES1_A06F | PS00001 | 1 | 138-141 | NIST | N-{P}-[ST]-{P} | ||
| PS00004 | 1 | 20-23 | RKPS | [RK](2)-x-[ST] | |||
| 蛋白编号 Serial number | 位点类型 Domains type | 数量 Number | 位置 Location | 序列 Sequence | 序列模式 Sequence motif | ||
| BnaBES1_A06R | PS00005 | 5 | 18-20, 23-25, 83-85, 99-101, 174-176 | TRR, SWR, TYR, SSR, TNK | [ST]-x-[RK] | ||
| PS00006 | 6 | 23-26, 112-115, 134 -137, 227 -230, 237-240, 305-308 | SWRE, SPFE, SRGD, TIPE, STVD, TPWE | [ST]-x(2)-[DE] | |||
| PS00008 | 5 | 5-10, 149-154, 150-155, 259-264, 325-330 | GATSTS, GGIPSS, GIPSSL, GVSSAV, GNAKGR | G-{EDRKHPFYW}-x(2)-[STAGCN]-{P} | |||
| PS00016 | 1 | 135-137 | RGD | R-G-D | |||
| PS00001 | 1 | 139-142 | NIST | N-{P}-[ST]-{P} | |||
| PS00004 | 1 | 21-24 | RKPS | [RK](2)-x-[ST] | |||
| PS00005 | 5 | 18-20, 24-26, 84-86, 100-102, 175-177 | TRR, SWR, TYR, SSR, TSK | [ST]-x-[RK] | |||
| PS00006 | 6 | 24-27, 113-116, 135-138, 228-231, 238-241, 306-309 | SWRE, SPFE, SRGD, TIPE, STVD, TPWE | [ST]-x(2)-[DE] | |||
| PS00008 | 5 | 5-10, 150-155, 151-156, 260-265, 326-331 | GATSTS, GGIPSS, GIPSSL, GVSSAV, GNAKGR | G-{EDRKHPFYW}-x(2)-[STAGCN]-{P} | |||
| PS00016 | 1 | 136-138 | RGD | R-G-D | |||
新窗口打开|下载CSV
同源比对BnaBZR1_A07、BnaBES1_A06F和BnaBES1_A06R, 同时使用SMART和MOTIF分析结构域发现, 3条BnaBZR蛋白具有基本相同的结构域, N端表现明显的植物BZR/BES结构特征序列, C端结构差异相对明显; 全长蛋白序列与pfam05687、PLN02905、cd00609等结构域相似度高, 3条蛋白序列中均存在多个激酶特征域, 可能参与磷酸化、酰基化, 蛋白本身又具丰富的磷酸化位点, 这与BZR/BES蛋白可以通过结合并相互磷酸化进行构象调控介导核质穿梭的功能一致(图3)。
图3
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图3BnaBZR氨基酸序列比对
Fig. 3Comparison of the amino acid sequences of BnaBZR
通过不同数据库, 共获得70种来源于不同植物的BZR相关蛋白序列, 使用MEGA6.0进行聚类分析, 绘制进化树(图4)。
图4
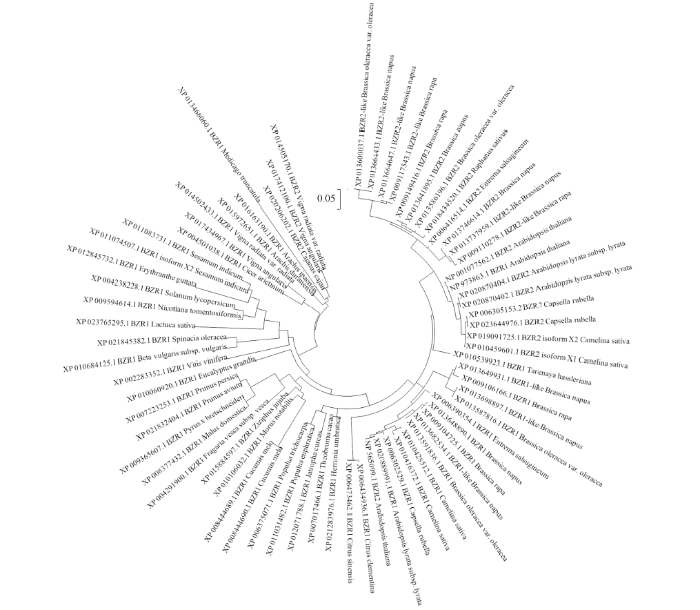 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图4不同植物BZR/BES蛋白的进化树分析
Fig. 4Phylogenetic analysis of BZR/BES in different plant species
BZR/BES相关蛋白聚类表现出了明显单、双子叶植物差异, 十字花科植物BZR/BES蛋白明显聚于同一亚群。对十字花科BZR/BES相关蛋白亚群分析可以发现, BZR1及其相似蛋白明显聚类, BZR2与其相似蛋白明显聚类, 蛋白类别之间的差异远大于物种差异, 同一亚类蛋白在不同的十字花科植物中相似度极高, 分枝距离极近, 然而, 甚至在同一物种中BZR1与BZR2亚群的分枝距离都较远, 相似度相对较低, 表明BZR1与BZR2的分化是一个早期进化事件。但物种亲缘关系极远的单双子叶植物中BZR/BES蛋白同样具有较高的相似度, 较近的亲缘关系, 表明BZR/BES蛋白家族在进化中起源古老且高度保守, 侧面显示BZR/BES家族蛋白可能具有能影响植物生存的重要作用。
2.3 甘蓝型油菜中BnaBZR1时空表达特征
为进一步了解BnaBZR在甘蓝型油菜中的功能, 对甘蓝型油菜不同时期, 不同组织中BnaBZR1_ A07、BnaBES1_A06F和BnaBES1_A06R表达进行了分析, 三基因定量引物为 BZR1_A07-F: 5'-CTCTC ATCTCCAACTTCCAA-3', BZR_A07-R: 5'-GACTC ATCACACTCAGGTAT-3'; BES1_A06F-F: 5'-TTCTC CGACCTTCAACCTA-3', BES1_A06F-R: 5'-TCCTC CATAGCCACATCAT-3°; BES1_A06R-F: 5'-GGCTA CTATACCTGAATGTGA-3', BES1_A06R-R: 5'-GCT GTTGCTGTTGTGAGA-3'; 内参引物为BnUBC21- F: 5'-CCTCTGCAGCCTCCTCAAGT-3', BnUBC21-R: 5'-TATCTCCCCTGTCTTGAAATGC-3'。由图5可知, 湘油15号中BnaBZR1_A07、BnaBE S1_A06F和BnaBES1_A06R具有相似的表达模式, 基因表达均表现一定的组织差异和一定的生长发育时间差异, 在茎叶花果等地上部分表达比地下部分高, 苗期、花期表达比抽薹期和角果成熟期高。BnaBZR1_A07在湘油15号根中的表达在各个生育时期均相对较低且平稳, 在茎叶中表达水平较高, 但在角果成熟过程中茎叶中表达水平显著下降, 同时在花中可以发现高水平的BnaBZR1_A07表达。在湘油15号中BnaBES1_A06F相对于BnaBES1_A06R整体表现较低表达水平, 茎叶与根中表达水平的差异相对较小。在花期BnaBES1_A06F和BnaBES1_ A06R表达水平达到峰值, 根中表达水平随发育时期表现较明显的差异。植物各组织均有油菜素内酯合成能力, 但地上部分组织中油菜素内酯含量高于地下部分, 尤其是花、种子和嫩叶中含量较高, BnaBZR1_ A07、BnaBES1_A06F和BnaBES1_ A06R在甘蓝型油菜中表现的组织差异与此具有相似规律, 这也与油菜素内酯一方面能通过一系列信号转导促进BZR/BES活化, 同时BZR/BES又能对油菜素内酯生物合成形成负反馈的规律吻合, 这一定程度上表明甘蓝型油菜中BnaBZR1_A07、BnaBES1_A06F和BnaBES1_ A06R与油菜素内酯信号具有紧密的关联性。
图5
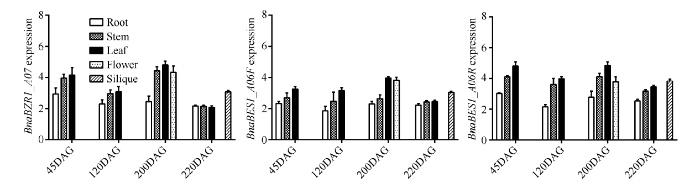 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图5不同发育时期不同组织中BnaBZR1_A07、BnaBES1_A06F和BnaBES1_A06R的表达量
DAG表示种子萌发后天数。
Fig. 5BnaBZR1_A07, BnaBES1_A06F, and BnaBES1_A06R expression in root, stem, leaf, flower, and silique
DAG means days after seed germination.
3 讨论
湘油15号是我国第一个通过国家审定并大面积推广的双低油菜品种, 是油菜育种中应用非常广泛的重要种质资源, 但湘油15号未经重测序, 大量基因并未被克隆和研究, 一定程度上制约了种质资源的有效利用。本文从甘蓝型油菜湘油15号中克隆获得3个BnaBZR基因拷贝, 测序比对显示与油菜基因组测序品种中双11中序列一致, 各自编码的BnaBZR蛋白的生物信息学分析显示其具有典型的植物BZR/BES功能结构域, 亚细胞定位于细胞核, 具有多重转录因子功能的核心元件序列, 存在大量磷酸化, 酰基化功能位点, 且本身具有磷酸化酶活性域, 表明BnaBZR基因是重要的涉及磷酸化调控的转录因子, 这与拟南芥[11]、水稻[12]等植物中BZR1/BES1通过形成复合体并相互磷酸化, 介导与PIF4、SMOS1等转录因子的互作, 并调控下游基因表达一致。聚类分析显示, BZR/BES蛋白在进化上具有较高的保守性, BnaBZR1_A07与白菜、甘蓝、拟南芥等植物中BZR1及相似蛋白具有高度同源性, BnaBES1_A06F/R则与白菜、甘蓝、拟南芥等植物中BZR2及相似蛋白高度同源, 同时, 十字花科各近缘种中BZR1与BZR2间分枝距离相对较远, 表明BZR1与BZR2的分化可能先于物种分化, 但进化上又高度保守。另对甘蓝型油菜BZR/BES相关基因染色体分布分析发现A、C亚基因组中BZR/BES出现较平衡, 这显示了甘蓝型油菜A、C亚基因组在进化关系上仍然具有较高的同源性, 也间接证实“禹氏三角”中白菜与甘蓝的近缘关系[13]。
油菜素内酯途径已在多种植物中被证明与植物抗病、种子形成等生物学过程关系密切[14], 油菜素内酯在油菜[15]、水稻[16]、番茄[17]等多种作物中被证实可以用来提高抗逆性, 并有油菜素内酯施用增加玉米[18]、番茄等茄科作物[19]产量的报告。因此阐明甘蓝型油菜中油菜素内酯信号的转化、传递对油菜育种和生产具有重要意义。BZR/BES是油菜素内酯信号与IAA、GA、光信号等多种信号途径互作的节点[20], 是油菜素内酯信号调控植物生长发育的关键转录因子, 对其克隆、表达研究对阐释油菜素内酯信号在油菜中的作用具有重要意义。本文克隆获得3个BnaBZR全长CDS, 分别定位在A07、A06、A06染色体上, 序列相似度较高, 这显示BZR/BES基因起源较早且保守, 在原始的芸薹属植物中即已存在且具有重要功能。其中BnaBES1_A06F和BnaBES1_ A06R同处在A06染色体端部相距不足10 kb的区域内且二者序列相似性超过98%, 表明这很可能是一次基因重复造成。
对湘油15中BnaBZR1_A07、BnaBES1_A06F和BnaBES1_A06R表达研究显示, 三者具有基本一致的表达规律, 表明BZR/BES基因在甘蓝型油菜中可能具有相同或者相似的上游调控因子, 同时可能受到相同或者相似的环境因素、植物内环境等影响。对甘蓝型油菜中BZR/BES基因的表达调控、基因功能有待进一步研究。
4 结论
从甘蓝型油菜湘油15号cDNA中克隆到3个BZR全长编码序列(coding sequence, CDS), 分别定位于A07、A06、A06号染色体, 分别命名为BnaB Z R1_A07、BnaBES1_A06F和BnaBES1_A06R。序列长分别为996、993、996 bp, 各自编码331、330和331个氨基酸。该基因编码蛋白与其他植物BZR/ BES具有较高相似性, 具有典型的BZR/BES结构域, 其起源较早, 但保守性较高。分析了BnaBZR1_A07、BnaBES1_A06F和BnaBES1_A06R在湘油15号中的时空表达模式。参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
DOI:10.1146/annurev-genet-102209-163450URLPMID:23020777 [本文引用: 1]

In plants, the steroidal hormone brassinosteroid (BR) regulates numerous developmental processes, including photomorphogenesis. Genetic, proteomic, and genomic studies in Arabidopsis have illustrated a fully connected BR signal transduction pathway from the cell surface receptor kinase BRI1 to the BZR1 family of transcription factors. Genome-wide analyses of protein-DNA interactions have identified thousands of BZR1 target genes that link BR signaling to various cellular, metabolic, and developmental processes, as well as other signaling pathways. In controlling photomorphogenesis, BR signaling is highly integrated with the light, gibberellin, and auxin pathways through both direct interactions between signaling proteins and transcriptional regulation of key components of these pathways.
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.pbi.2011.02.001URLPMID:21377404 [本文引用: 1]

Plant hormones play central roles in the ability of plants to adapt to changing environments, by mediating growth, development, nutrient allocation, and source/sink transitions. Although ABA is the most studied stress-responsive hormone, the role of cytokinins, brassinosteroids, and auxins during environmental stress is emerging. Recent evidence indicated that plant hormones are involved in multiple processes. Cross-talk between the different plant hormones results in synergetic or antagonic interactions that play crucial roles in response of plants to abiotic stress. The characterization of the molecular mechanisms regulating hormone synthesis, signaling, and action are facilitating the modification of hormone biosynthetic pathways for the generation of transgenic crop plants with enhanced abiotic stress tolerance.
DOI:10.1016/j.pbi.2014.07.012URLPMID:25139830 [本文引用: 1]

Many hormonal and environmental signals regulate common cellular and developmental processes in plants. While the molecular pathways that transduce these signals have each been studied in detail, how these pathways are wired into regulatory networks to provide the coordinated responses has remained an outstanding question. Recent studies of the brassinosteroid signaling network have revealed extensive signal integration through direct interactions between components of different signaling pathways. In particular, a circuit of interacting transcription regulators integrates many signaling pathways to enable coordinated and coherent regulation of seedling morphogenesis by hormonal and environmental signals. The recent studies support an emerging theme that complex networks of highly integrated signaling pathways underlie the high levels of developmental plasticity and environmental adaptability of plants.
DOI:10.1016/j.devcel.2010.10.010URLPMID:3018842 [本文引用: 1]

76 Genomic targets of brassinosteroid identified by BZR1 ChIP-chip 76 Some BZR1 target genes mediate cell elongation 76 Brassinosteroid regulates other hormone pathways 76 Brassinosteroid regulates light signaling and light-responsive gene expression
DOI:10.1016/j.jgg.2011.12.001URLPMID:22293112 [本文引用: 1]

Combined approaches with genetics, biochemistry, and proteomics studies have greatly advanced our understanding of brassinosteroid (BR) signaling in Arabidopsis. However, in rice, a model plant of monocot and as well an important crop plant, BR signaling is not as well characterized as in Arabidopsis. Recent studies by forward and reverse genetics have identified a number of either conserved or specific components of rice BR signaling pathway, bringing new ideas into BR signaling regulation mechanisms. Genetic manipulation of BR level or BR sensitivity to improve rice yield has established the great significance of BR research achievements.
DOI:10.1134/S1021443714060053URL [本文引用: 1]

The ability of brassinosteroids, such as 24-epibrassinolide (EBL) to increase the resistance of oilseed rape plants ( Brassica napus L.) to salt stress (175 mM NaCl) was investigated along with the possible mechanisms of their protective action. Seedlings were grown for three weeks on the Hoagland-Snyder medium under controlled conditions. The experimental plants were treated with either (1) 175 mM NaCl, or (2) 10 6110 M EBL, or (3) 175 mM NaCl plus 10 6110 M EBL by adding the corresponding components to the growth medium. The exposure was 7 and 14 days. As compared to the control, salinization inhibited plant height by 33–35%, reduced leaf area by 2.0–2.5 times, reduced 2.5- and 2-fold plant fresh and dry weight, respectively, reduced water content of plant tissues by 26–31% and, twofold, the content of chlorophylls a and b . Plants responded to NaCl by developing oxidative stress conditions, lowering the osmotic potential of the cell contents down to 612 MPa, accumulating proline (by 43–52 times) and low-molecular-weight phenolics (by 1.9–2.7 times). Oilseed rape plants were shown to respond to salinization with an increase of endogenous content of steroid hormones: 24-epibrassinosteroids (24-epibrassinolide and 24-epicastasterone), 24S-methyl-brassinosteroids (brassinolide and castasterone), and 28-homobrassinosteroids (28-homobrassinolide and 28-homocastasterone); such evidence indirectly confirms the involvement of brassinosteroids in the development of salt tolerance. Adding EBL to the nutrient medium under optimal growth conditions did not significantly affect the indices under study. Under salt stress, EBL showed a pronounced protective effect: stem growth was fully restored, plant assimilation area increased by as much as 67–76% as compared to the control index, fresh and dry weight largely recovered (up to 85–92% of the control values), and the inhibitory effect of NaCl on photosynthetic pigments was diminished. Exogenous EBL impeded the development of NaCl-dependent lipid peroxidation and increased the osmotic potential of the leaf cell contents. The protective effect of EBL under salt stress was probably associated with EBL antioxidant effect, rather than the hormone-induced accumulation of proline and of low-molecula-weight phenolics, as well as with the ability to regulate water status by maintaining intracellular ion homeostasis.
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1007/s10725-013-9863-yURL [本文引用: 1]

Due to the increasing demand for biofuel production, it is an important goal to optimize the seed productivity and quality of oilseed plants even in adverse conditions. Acting on signalling mechanisms might provide means to attain such goals. In this study, we were interested in the effect of a brassinosteroid hormone 24-epibrassinolide (24-EBR) on Brassica napus cultivated in salt stress condition. We show that salt stress leads to a 60 % decrease in seed production in B. napus . This is accompanied by a 50 % decrease in seed oil content. Treatment with 24-EBR had no effect on seed and oil productivity in control plants. However, it could rescue half of the seed production and all the oil production in salt-treated plants. The fatty acid composition of seed oil in B. napus was selectively affected by salt stress, 24-EBR or combined treatment. Besides these long-term actions of 24-EBR, we have also investigated its short-term actions in cell signalling. We did so by in vivo labelling of plantlets with fluorescently labelled phosphatidylcholine. A treatment of 2 h with 24-EBR was sufficient to induce a substantial increase in the content of diacylglycerol and phosphatidic acid, two lipid mediators. Non-specific phospholipases C and phospholipases D are involved in these increases. Therefore, brassinosteroid treatments appear as promising way to gain oil productivity when plants have to grow in unfavourable conditions such as salt stress. The link between long-term actions and short-term signalling of 24-EBR is discussed.
DOI:10.1038/srep28298URLPMID:4915011 [本文引用: 1]

As a resource allocation strategy, plant growth and defense responses are generally mutually antagonistic. Brassinosteroid (BR) regulates many aspects of plant development and stress responses, however, genetic evidence of its integrated effects on plant growth and stress tolerance is lacking. We overexpressed theArabidopsisBR biosynthetic geneAtDWF4in the oilseed plantBrassica napusand scored growth and stress response phenotypes. The transgenicB. napusplants, in comparison to wild type, displayed increased seed yield leading to increased overall oil content per plant, higher root biomass and root length, significantly better tolerance to dehydration and heat stress, and enhanced resistance to necrotrophic fungal pathogensLeptosphaeria maculansandSclerotinia sclerotiorum.Transcriptome analysis supported the integrated effects of BR on growth and stress responses; in addition to BR responses associated with growth, a predominant plant defense signature, likely mediated by BES1/BZR1, was evident in the transgenic plants. These results establish that BR can interactively and simultaneously enhance abiotic and biotic stress tolerance and plant productivity. The ability to confer pleiotropic beneficial effects that are associated with different agronomic traits suggests that BR elated genes may be important targets for simultaneously increasing plant productivity and performance under stress conditions.
[本文引用: 2]
DOI:10.1105/tpc.16.00611URLPMID:28100707 [本文引用: 1]

Brassinosteroids (BRs) are plant-specific steroid hormones that control plant growth and development. Recent studies have identified key components of the BR signaling pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana and in rice (Oryza sativa); however, the mechanism of BR signaling in rice, especially downstream of GSK3/SHAGGY-like kinase (GSK2), remains unclear. Here, we identified a BR-insensitive rice mutant, reduced leaf angle1 (rla1), and cloned the corresponding gene. RLA1 was identical to the previously reported SMALL ORGAN SIZE1 (SMOS1), which was cloned from another allele. RLA1/SMOS1 encodes a transcription factor with an APETALA2 DNA binding domain. Genetic analysis indicated that RLA1/SMOS1 functions as a positive regulator in the BR signaling pathway and is required for the function of BRASSINAZOLE-RESISTANT1 (OsBZR1). In addition, RLA1/SMOS1 can interact with OsBZR1 to enhance its transcriptional activity. GSK2 can interact with and phosphorylate RLA1/SMOS1 to reduce its stability. These results demonstrate that RLA1/SMOS1 acts as an integrator of the transcriptional complex directly downstream of GSK2 and plays an essential role in BR signaling and plant development in rice.
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1007/s00299-013-1438-xURL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1093/mp/sst056URLPMID:23589608 [本文引用: 1]

Plant hormones have been extensively studied for their importance in innate immunity particularly in the dicotyledonous model plant Arabidopsis thaliana. However, only in the last decade, plant hormones were demonstrated to play conserved and divergent roles in fine-tuning immune in rice (Oryza sativa L.), a monocotyledonous model crop plant. Emerging evidence showed that salicylic acid (SA) plays a role in rice basal defense but is differentially required by rice pattern recognition receptor (PRR) and resistance (R) protein-mediated immunity, and its function is likely dependent on the signaling pathway rather than the change of endogenous levels. Jasmonate (JA) plays an important role in rice basal defense against bacterial and fungal infection and may be involved in the SA-mediated resistance. Ethylene (ET) can act as a positive or negative modulator of disease resistance, depending on the pathogen type and environmental conditions. Brassinosteroid (BR) signaling and abscisic acid (ABA) either promote or defend against infection of pathogens with distinct infection/ colonization strategies. Auxin and gibberellin (GA) are generally thought of as negative regulators of innate immunity in rice. Moreover, GA interacts antagonistically with JA signaling in rice development and immunity through the DELLA protein as a master regulator of the two hormone pathways. In this review, we summarize the roles of plant hormones in rice immunity and discuss their interplay/crosstalk mechanisms and the complex regulatory network of plant hormone pathways in fine-tuning rice immunity and growth.
DOI:10.1007/s11104-015-2712-1URL [本文引用: 1]

Aims This study examined brassinosteroids-induced enhancement of plant salt resistance of tomato.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.sjbs.2012.03.005URLPMID:23961193 [本文引用: 1]

The presence of cadmium in the soil above a particular level is proposed to check not only plant growth but also productivity and fruit quality. Therefore, in the present study investigations are directed to evaluate the effect of four levels of cadmium (3, 6, 9, 12mgkg611) in interaction with two analogs of brassinosteroids on the growth, fruit yield and quality of tomato. Under greenhouse conditions plants were analyzed for antioxidant system activity and photosynthetic assimilation efficiency. Cd stressed plants exhibited poor growth and biological yield. The metal also had a negative impact on the antioxidant system of the resulting fruits. However, the follow up application of BRs (10618M) neutralized the damaging effects of the metal on the plants.
DOI:10.1016/j.plantsci.2013.04.002URLPMID:23759100 [本文引用: 1]

The steroid hormones brassinosteroids take on critical roles during various plant growth processes, including control of cell proliferation and cell elongation. In this review, we discuss different strategies that have advanced our understanding of brassinosteroid function. Approaches observing whole-plant responses uncovered regulatory brassinosteroids-dependent modules controlling cell elongation. In these regulatory modules, downstream components of the brassinosteroid signaling pathway directly interact with other hormonal and environmental pathways. In alternative approaches, brassinosteroid activity has been dissected at the tissue and cellular level of above- and below-ground organs. These studies have determined the importance of brassinosteroids in cell cycle progression and in timing of cell differentiation. In addition, they have demonstrated that local reduction of the hormone sets organ boundaries. Finally, these studies uncovered the capacity of the epidermal-derived brassinosteroid signaling to control organ growth. Thus, inter-cellular communication is intimately involved in brassinosteroid-mediated growth control. The current challenge is therefore to decipher the spatiotemporal distribution of brassinosteroid activity and its impact on coherent growth and development.
