全文HTML
--> --> --> 我国高等教育水平的不断发展和科研活动的日渐频繁,导致产生了大量的实验废水[1]。而实验废水常含有毒有害的化学物质,直接排放不仅会对环境造成多样性的污染,危害到人们生活健康[2-3],并有可能会对污水处理厂造成损害[4]。不同实验室科研课题不同,实验项目不同,与其他废水相比,实验室废水成分更为复杂[5]。实验室废水不仅具有间歇性强、数量少、危害大等特点[6],而且处理起来难度较大,因此,科研人员一直在寻求一种经济、绿色、高效的处理方法[7-8]。本研究以某高校实验室废水处理站(简称废水站)为研究对象,综合评价了废水站的处理效果、运行情况、生物膜性状,以为高校和科研单位实验室废水的处理提供参考。1.1. 实验室废水来源、水质及工艺介绍
废水站收集的废水为2幢从事生物、环境、食品教学研究的实验楼排放的实验废水,包括强酸强碱溶液、有机废液、清洗废水和一些伴随教学活动间歇排放的低浓度重金属、细菌等实验废液,B/C为0.4~0.5,可生化性较好。高浓度的有机废液、重金属废液等未纳入本废水站,经收集后统一处置。废水站选用的处理工艺为生物膜法,因为生物膜法具有容积负荷高、抗负荷冲击能力强等优点,可以较好地针对实验室废水间歇性强、水质变化较大的特点来进行处理,且占地面积小。设计每天运行20 h,处理废水水量为0.5 m3·h?1,化学需氧量(COD)为150~800 mg·L?1,生化需氧量(BOD5)为80~400 mg·L?1,悬浮物(SS)为120~520 mg·L?1,氨氮(NH3-N)为6~45 mg·L?1,总铜为2~4 mg·L?1,总锌为5~10 mg·L?1。实验室废水收集后经废水站处理,出水要求达到《污水综合排放标准》(GB 8978-1996)三级标准,内部质控要求达到一级标准。设计处理水质及排放标准见表1,废水站主要构筑物见表2。
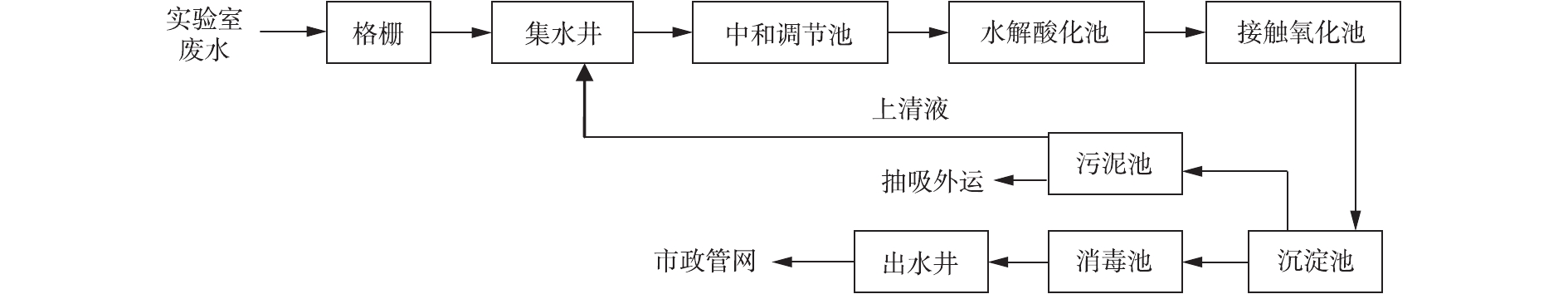
废水经过格栅去除大颗粒不溶解物质后,首先用泵从集水井打入中和调节池调节水质,再进行兼氧(A)和好养(O)两段生物反应。在A段反应过程中,通过微生物兼氧水解,提高废水可生化性并去除部分污染物,该反应于水解酸化池中进行。在O段反应过程中,通过异养菌经好氧代谢进一步分解去除污染物,该过程由2个接触氧化池完成,在水解酸化池和接触氧化池中,悬挂组合填料,以供微生物生长挂膜。随后流入沉淀池,将脱落的生物膜沉淀分离。最后经过消毒池消毒处理排入市政管网。废水站工艺流程见图1,废水站概况见图2。
1.2. 材料与方法
实验中各项指标的检测方法和设备[3,9-11]见表3。实验中所用的生物膜取自废水站接触氧化池组合填料,所用试剂均为分析纯。在实验过程中,每间隔2~3 d,对中和调节池、水解酸化池、接触氧化池和消毒沉淀池的pH、DO、NH3-N、COD、重金属的含量进行1次监测。综合考虑文献中的方法[11-14],本次实验采用效果较好的加热法提取EPS。取50 mL泥水混合液,于3 500 r·min?1离心10 min后,弃去上清液,加蒸馏水,补足体积后混匀,重复3次,制得混合液;将混合液在80 ℃水浴中,加热40 min后,在12 000 r·min?1离心15 min,取上清液,用孔径为0.22 μm的滤膜过滤得到EPS[11-13]。EPS浓度用蛋白质、多糖、DNA之和表示。
2.1. 进水、出水水样表观结果
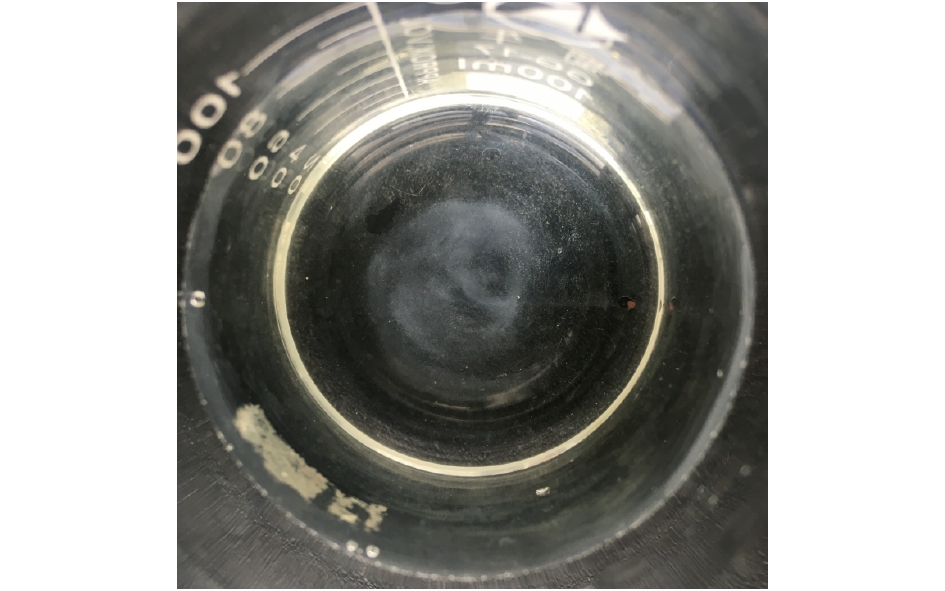
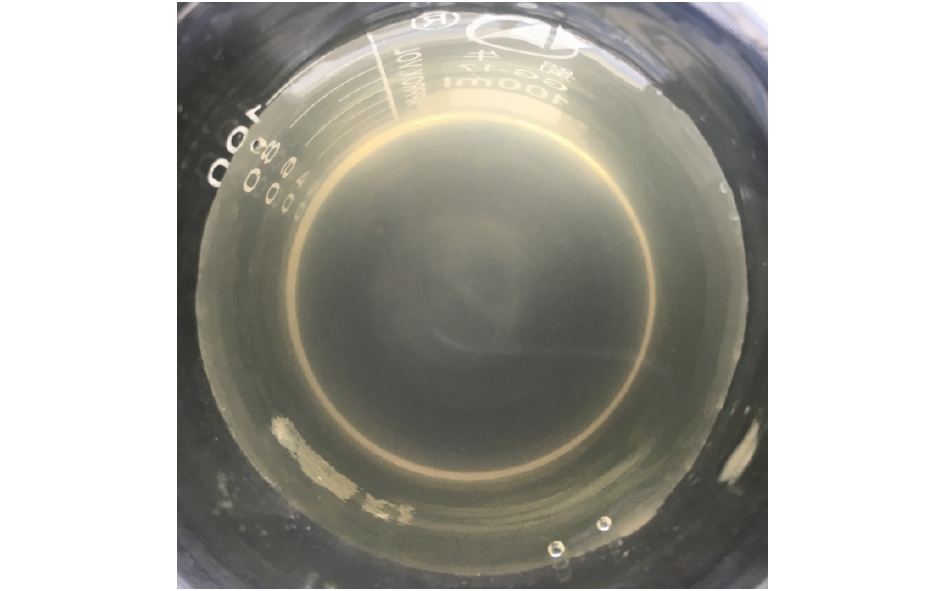
在调试实验1个月期间,废水站的进出水流量、自动监控设备及各项处理设施均运行正常。废水站进水、出水水质见图3和图4。由图3和图4可知,进水水质颜色偏黄,内含较多肉眼可见不溶颗粒,测量显示浊度为62.91 NTU,SS为323.1 mg·L?1;经废水站处理后,出水有了明显的改善,水质澄清透明,无明显的颜色,无肉眼可见不溶性颗粒,出水浊度为2.37 NTU,SS为63.2 mg·L?1。2.2. pH、DO、NH3-N、COD去除效果
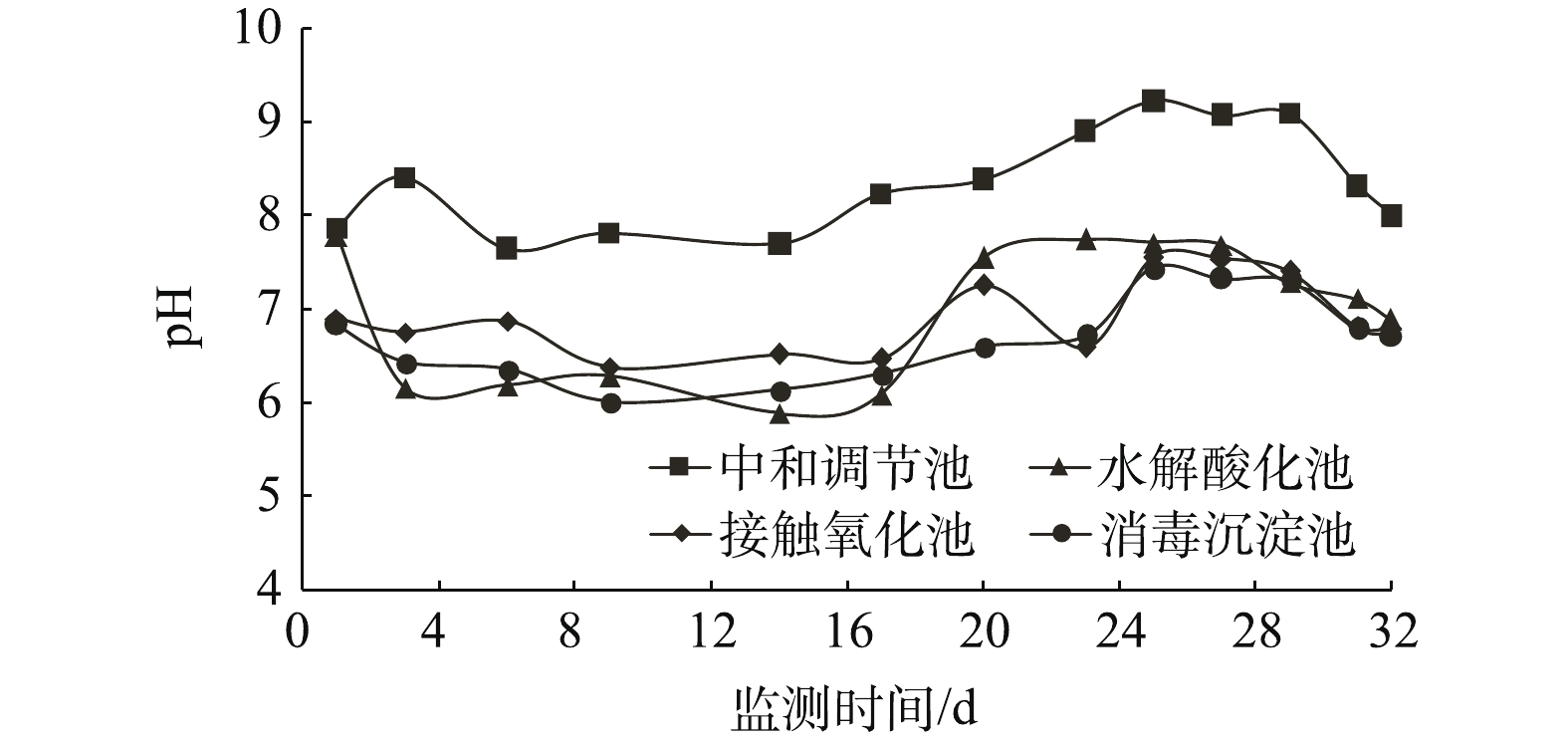
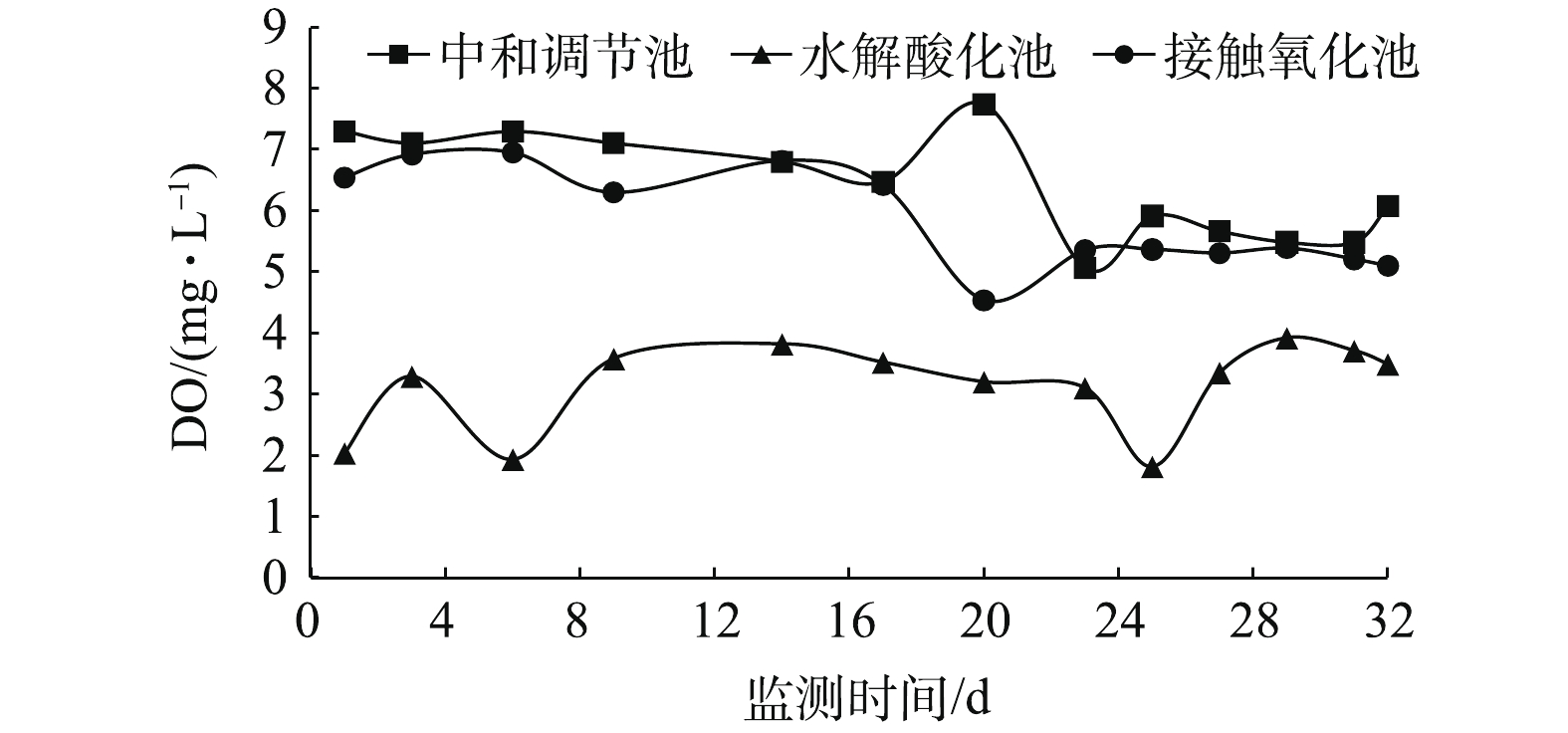
调试实验阶段pH、DO、NH3-N、COD监测情况见图5~图8。水解酸化、接触氧化过程最佳pH分别为6.0~8.0和6.5~9.5[3,15],由图5可见,废水站各单元pH均可保持在最佳范围内。最终出水pH满足《污水综合排放标准》(GB 8978-1996)一级标准(pH=6~9)。水解酸化过程DO须维持在0.2~0.5 mg·L?1[3,16];接触氧化过程DO须维持在2.0 mg·L?1以上[17-18]。由图6可见,水解酸化池DO长期高于2.0 mg·L?1,接触氧化池DO处在5.0~7.0 mg·L?1。究其原因,发现水解酸化池无法维持兼氧环境是由于中和调节池过度曝气的高DO废水(5.0~8.0 mg·L?1)流入所致;而接触氧化池虽能满足氧化条件,但长期过度曝气可能会造成菌胶团破碎,使微生物活性减小[19]。
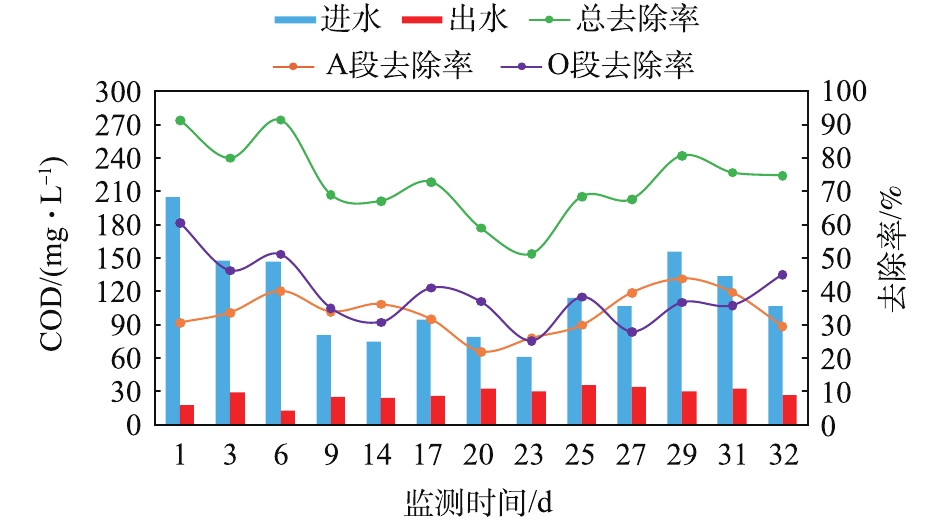
由图7可见,废水站进水COD低于200 mg·L?1,经处理后出水COD可低于40 mg·L?1,平均去除率为72.98%,出水可以满足《污水综合排放标准》(GB 8978-1996)一级标准,A段COD平均去除率为33.66%,略低于O段(39.32%)。期间,接触氧化池COD容积负荷为0.09~0.30 kg·(m3·d)?1,长期低负荷运行,不仅导致细菌生长繁殖受到抑制,还会降低生物膜EPS浓度,影响了污染物的吸附和分解[20-21],因此,在20~23 d,COD的去除率低于60%。
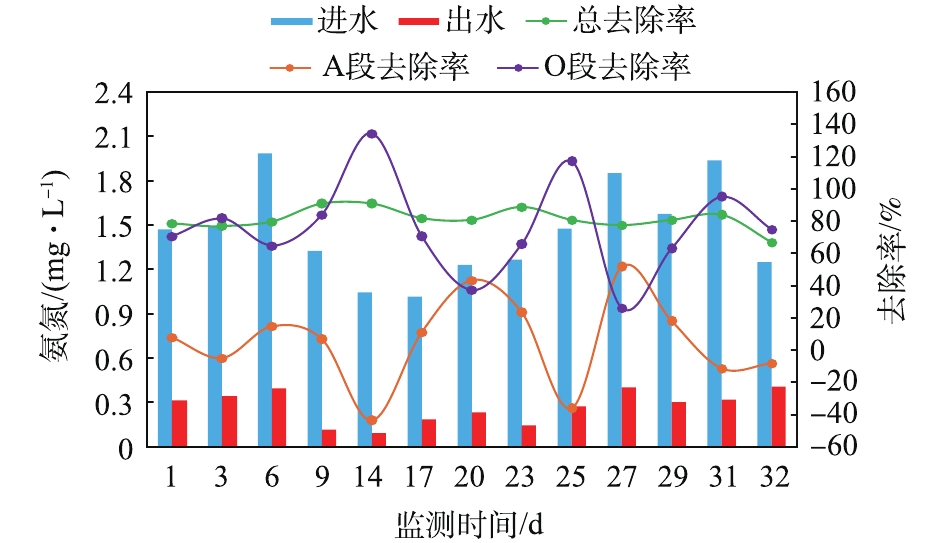
由图8可见,实验室排放的废水NH3-N含量低于2 mg·L?1,经废水站处理后,出水NH3-N含量均小于0.5 mg·L?1,去除率稳定维持在70%~90%,出水满足《污水综合排放标准》(GB 8978-1996)一级标准。且NH3-N主要在O段得到去除,而A段对于NH3-N的去除率较低,甚至时常出现负值,这是由于在兼氧水解过程中,微生物分解含氮有机物,释放大量NH3-N导致[22]。
2.3. 重金属去除效果
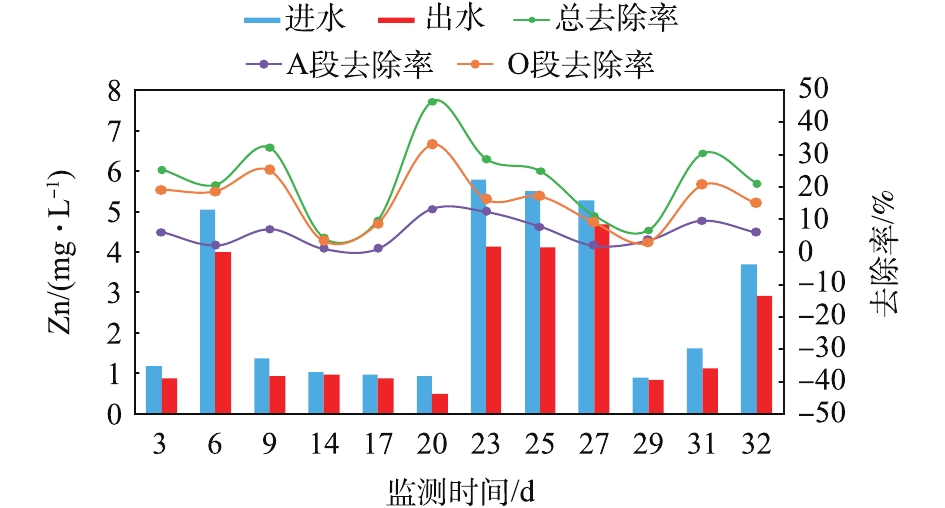
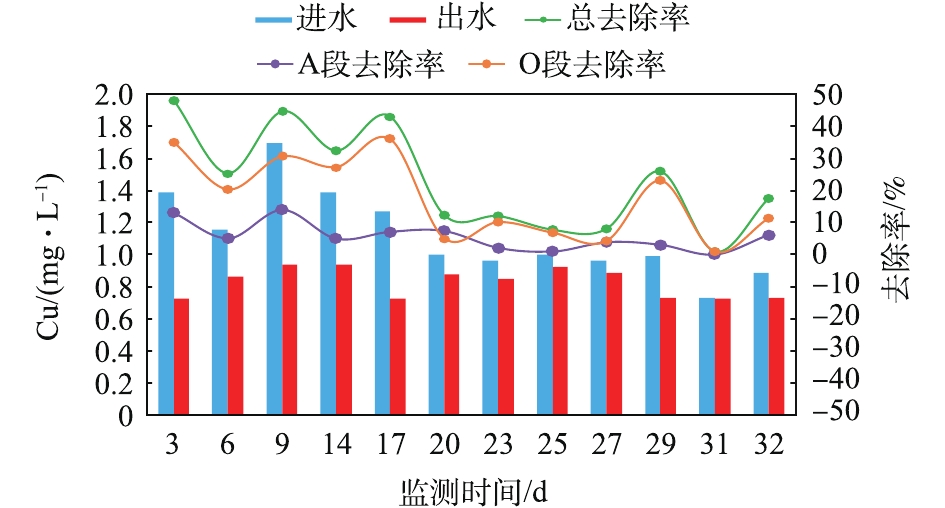
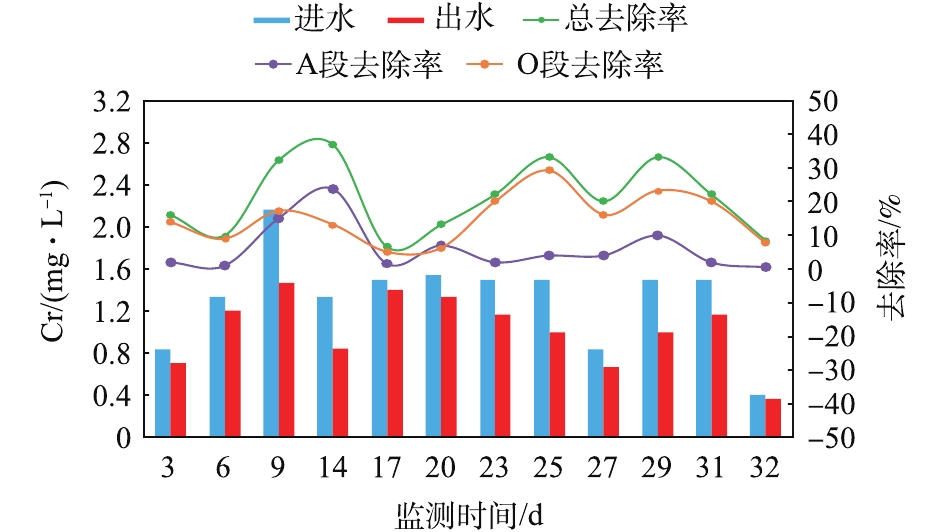
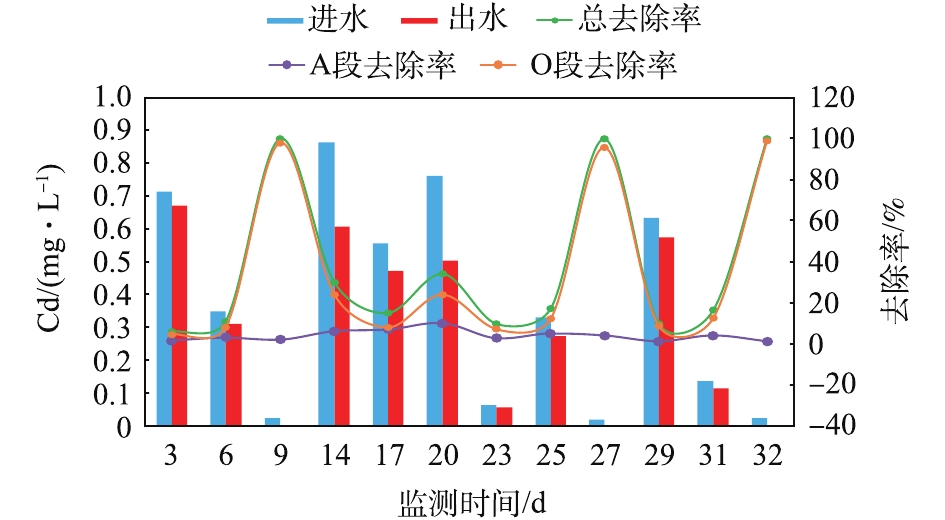
调试实验阶段重金属(Zn、Cu、Cr、Cd)的监测情况见图9~图12。可以看出,实验室废水的排放间歇性强,废水站对4种重金属的去除率均未高于50%。Zn出水浓度可以满足《污水综合排放标准》(GB 8978-1996)三级标准(Zn≤5 mg·L?1),但与要求的一级标准(Zn≤2 mg·L?1)仍有差距;Cu出水浓度可以满足《污水综合排放标准》(GB 8978-1996)二级标准(Cu≤1 mg·L?1),略高于要求的一级标准(Cu≤0.5 mg·L?1);Cr、Cd出水浓度均可满足《污水综合排放标准》(GB 8978-1996)第一类污染物最高允许排放标准(Cr≤1.5 mg·L?1、Cd≤0.1 mg·L?1),其中有3 d的Cd出水浓度过小,未有检出。且大部分重金属在O段得到去除,在A段的去除率很小。这是由于生物膜主要通过EPS的吸附作用来去除重金属离子,而O段生物膜EPS及其所带的负电荷高于A段,因而更易吸附重金属离子[23-25]。此外,废水站对4种重金属的去除率均未高于50%。影响生物膜EPS吸附重金属离子的主要因素为pH、吸附时间、温度、EPS浓度及组成 [23-31]。废水站接触氧化池pH(pH=6.0~8.0)在最佳范围内,HRT(HRT =13.8 h)可以满足生物膜对重金属的吸附时间要求,而温度的影响并不大[26-32],故废水站重金属去除率低的原因可能为生物膜EPS浓度或组成异常所致。2.4. 生物膜镜检结果
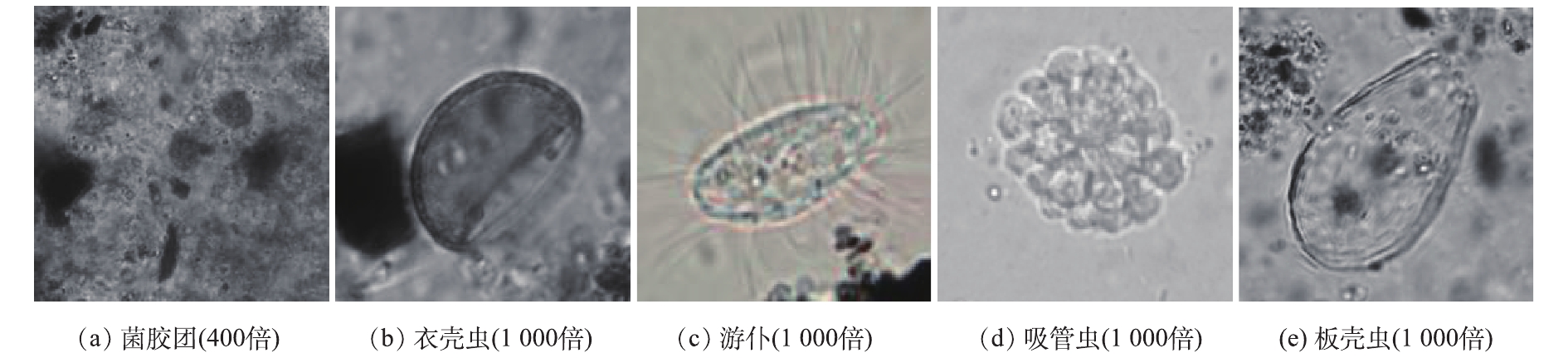
废水站在1个月的运行过程中,出现接触氧化池曝气过度和COD去除率较低的情况,因此,有必要对生物膜进行镜检。由图13可知,菌胶团体积大、结构紧密,大多数无色透明,生物膜性状较好;另外还发现了较多衣壳虫、吸管虫、板壳虫、游仆等标志型微生物。吸管虫、衣壳虫的存在是优质出水的标志,但吸管虫大量存在表示生物膜可能处于老化、解体等不利状态;衣壳虫、板壳虫、游仆大量出现表明存在负荷较低、停留时间过长和溶解氧浓度高的情况[33]。可见目前生物膜性状还较好,但确实存在负荷低和曝气过度的情况,且正处在向老化过度的状态。2.5. 生物膜EPS浓度及组成
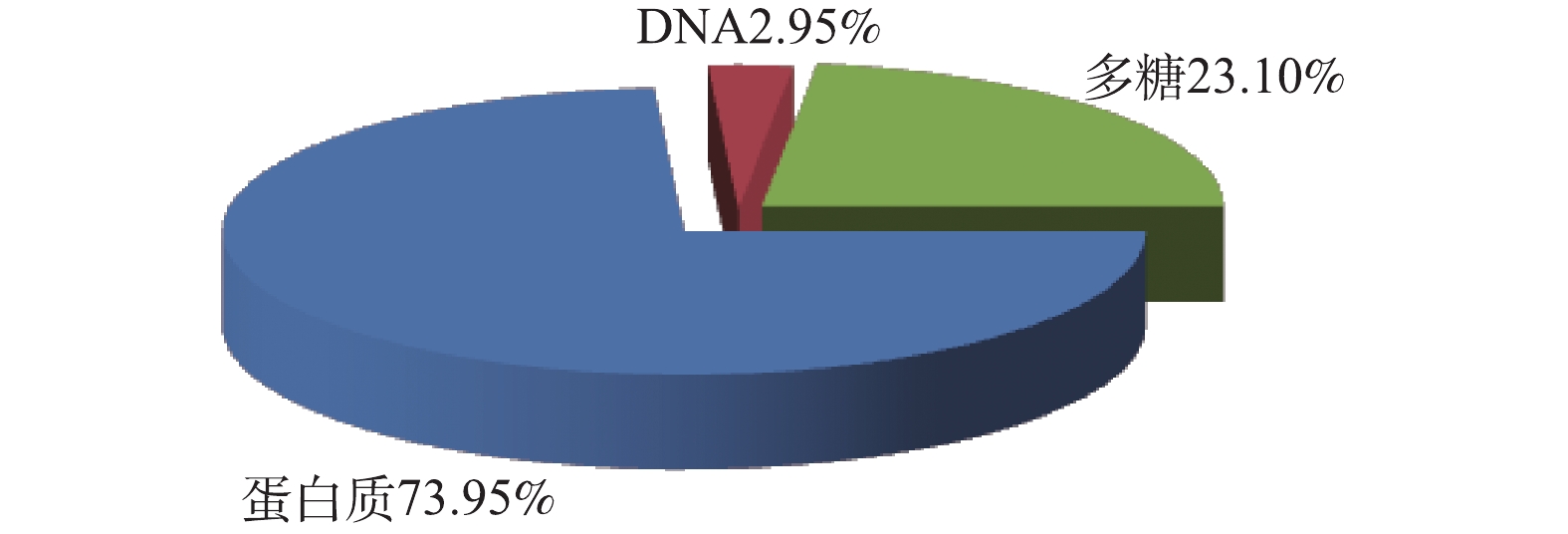
废水站在1个月运行中,COD和重金属的去除效率不高的原因可能为生物膜EPS浓度或组分异常,为分析出现异常的原因,提取生物膜EPS并分析其浓度及组分。生物膜EPS浓度为230.27 mg·g?1,由图14可见,蛋白质含量最高(73.95%)、多糖次之(23.10%)、DNA最低(2.95%),这说明加热法对细胞的破坏程度较小,提取效果较好[13]。表4列举了几种选用不同条件加热法提取生物膜EPS的结果,由于工艺流程和提取条件的不同,因此,结果中EPS浓度及成分含量的变化很大[34]。可以看出,在李继宏等[11]的研究中,提取时的加热温度、时间与本研究一致,且废水处理工艺相近,而EPS浓度是本研究的1.31倍,主要差别为蛋白质含量。也有研究[35-38]认为,DO升高使微生物代谢加快,当污水中底物被消耗殆尽时,处在饥饿状态的微生物会将部分EPS作为有机底物利用,造成EPS浓度下降,而废水站同样存在进水负荷低、曝气过度的问题。李延军等[38]还指出,EPS含量的变化主要来自蛋白质,这也与本研究得到的结果一致。因此可以推测,废水站COD和重金属去除率低是由于低负荷运行和过度曝气引起的生物膜EPS含量下降所致。
2)废水站运行期间,水解酸化池DO过高,主要是由中和调节池过度曝气的高DO废水流入导致,因此,可通过降低中和调节池曝气量,为后续水解酸化提供兼氧环境。
3)废水站运行期间,出现COD和重金属去除率低的情况,通过生物膜镜检和EPS浓度及成分测定,确定是由接触氧化池过度曝气和低负荷运行造成的,可通过降低废水站接触氧化池的曝气量,并适当提高进水负荷来解决。
参考文献

 下载:
下载: 

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图