 )
) 上海师范大学人力资源管理系, 上海 200234
收稿日期:2020-10-04发布日期:2021-06-25通讯作者:张辉华E-mail:zhanghuihua2005@126.com基金资助:国家自然科学基金面上项目(71971141)Team emotional intelligence: A social network perspective
ZHANG Hui-hua( )
) Department of Human Resource Management, Shanghai Normal University, Shanghai 200234, China
Received:2020-10-04Published:2021-06-25Contact:ZHANG Hui-hua E-mail:zhanghuihua2005@126.com摘要/Abstract
摘要: 据估计, 60%的团队都没有达到它们的目标, 这给学术界提出了重要且具有挑战性的研究课题。情绪智力(emotional intelligence)是在人际关系基础上发展起来的重要概念。研究发现, 基于微观个体或宏观整体的团队情绪智力在团队成功达到目标过程中起到重要作用。然而, 当前尚无研究探讨基于团队局部成员间情绪智力行为交换而产生的团队情绪智力对团队的影响。为此, 本课题从配对层次(一对一关系中两个人, 即actor-target)这一新角度探讨团队情绪智力, 通过把它看做团队过程中一种产生的状态(emergent state), 在整合团队成员交换理论和社会网络方法基础上对它进行研究。具体围绕团队内配对单元存在的交换关系(指目标者感受到行动者对其实施的情绪智力行为)在团队中形成的网络所代表的团队情绪智力开展实证研究, 以期从理论上揭示团队内情绪智力行为交换的特征, 情绪智力自下而上(bottom-up)由个体发展到团队的过程, 以及配对基础的团队情绪智力的影响效应, 从而为团队管理实践提供具体的改善建议。
图/表 3
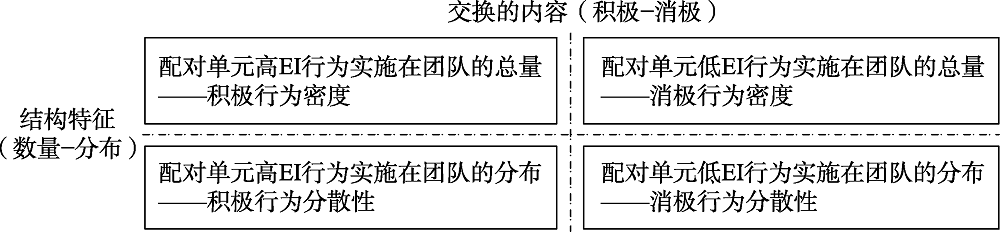
图1团队情绪智力的测量指标(EI代表情绪智力, 下图同)
 图1团队情绪智力的测量指标(EI代表情绪智力, 下图同)
图1团队情绪智力的测量指标(EI代表情绪智力, 下图同)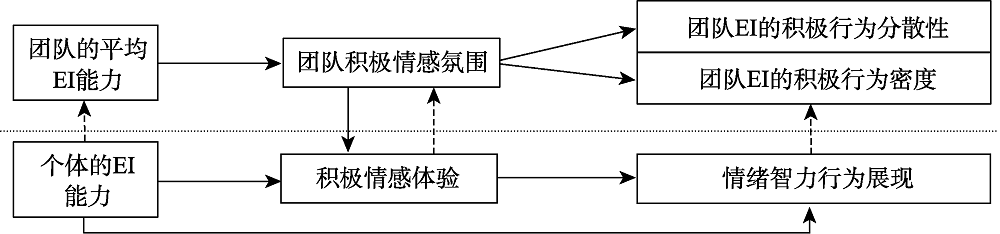
图2团队情绪智力的形成过程(指团队背景下)
 图2团队情绪智力的形成过程(指团队背景下)
图2团队情绪智力的形成过程(指团队背景下)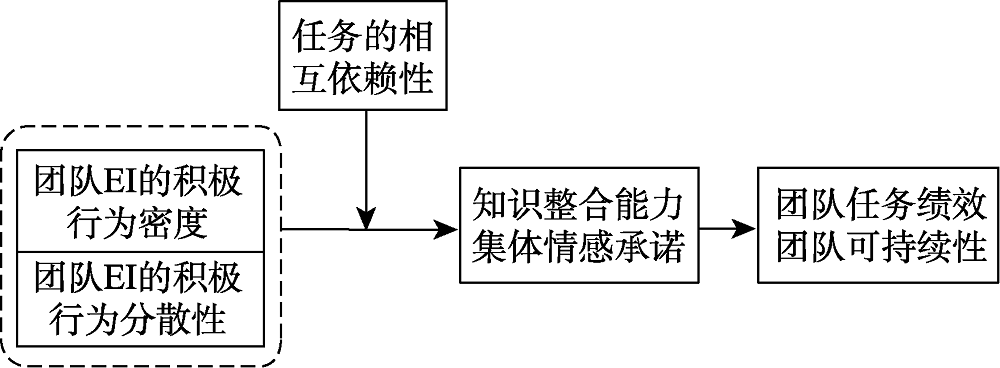
图3团队情绪智力的具体影响
 图3团队情绪智力的具体影响
图3团队情绪智力的具体影响参考文献 70
| [1] | 刘咏梅, 卫旭华, 陈晓红.(2011). 群体情绪智力对群决策行为和结果的影响研究. 管理科学学报, 14(10),11-27. |
| [2] | 梅占军, 马钦海, 沈忻昕.(2014). 临时团队中快速信任对团队情绪智力与绩效关系的中介作用研究. 南大商学评论, 26,106-224. |
| [3] | 容琰, 隋杨, 杨百寅.(2015). 领导情绪智力对团队绩效和员工态度的影响——公平氛围和权力距离的作用. 心理学报, 47(9),1152-1161. |
| [4] | 沈其泰, 黄涓容, 姜定宇.(2014). 领导者的团队情绪领导行为与团队效能:团队社会交换关系与知觉风险程度的干扰效果. 人力资源管理学报(台湾), 14(2),55-80. |
| [5] | 卫旭华, 刘咏梅, 车小玲.(2015). 关系冲突管理:团队效能感和团队情绪智力的调节作用. 系统管理学报, 24(1),138-145, 152. |
| [6] | 张辉华.(2012). 情绪智力与工作相关变量关系的元分析:以中国样本为例. 心理科学, 35(5),1175-1184. |
| [7] | Ayoko, O. B., Callan, V. J., & Hartel, C. E.J.(2008). The influence of team emotional intelligence climate on conflict and team members' reactions to conflict. Small Group Research, 39(2),121-149. doi: 10.1177/1046496407304921URL |
| [8] | Balkundi, P., & Harrison, D. A.(2006). Ties, leaders, and time in teams: Strong inference about network structure's effects on team viability and performance. Academy of Management Journal, 49(1),49-68. doi: 10.5465/amj.2006.20785500URL |
| [9] | Barczak, G., Lassk, F., & Mulki, J.(2010). Antecedents of team creativity: An examination of team emotional intelligence, team trust and collaborative culture. Creativity and Innovation Management, 19(4),332-345. doi: 10.1111/caim.2010.19.issue-4URL |
| [10] | Barney, J.(1991). Firm resources and sustained competitive advantage. Journal of Management, 17(1),99-120. doi: 10.1177/014920639101700108URL |
| [11] | Barsade, S. G.(2002). The ripple effect: Emotional contagion and its influence on group behavior. Administrative Science Quarterly, 47(4),644-675. doi: 10.2307/3094912URL |
| [12] | Barsade, S. G., & Gibson, D. E.(1998). Group emotion: A view from top and bottom. In D. Gruenfeld, B. Mannix, & M. Neale (Eds.), Research on managing on groups and teams (pp.81-102). Stamford, CT: JAI. |
| [13] | Barsade, S. G., & Knight, A. P.(2015). Group affect. Annual Review of Organizational Psychology and Organizational Behavior, 2(14),1-26. doi: 10.1146/annurev-orgpsych-032414-111449URL |
| [14] | Beal, D. J., Cohen, R. R., Burke, M. J., & McLendon, C. L.(2003). Cohesion and performance in groups: A meta-analytic clarification of construct relations. Journal of Applied Psychology, 88(6),989-1004. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.88.6.989URL |
| [15] | Bell, S. T.(2007). Deep-level composition variables as predictors of team performance: A meta-analysis. Journal of Applied Psychology, 92(3),595-615. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.92.3.595URL |
| [16] | Berdahl J.L, & Anderson, C.(2005). Men, women, and leadership centralization in groups over time. Group Dynamics: Theory, Research, and Practice, 9(1),45-57. doi: 10.1037/1089-2699.9.1.45URL |
| [17] | Côté, S.(2007). Group emotional intelligence and group performance. In E. A. Mannix, M. A. Neale, & C. P. Anderson (Eds.), Research on managing groups and teams (Vol. 10, pp. 309-336). Oxford, UK: Elsevier/JAI Press. |
| [18] | Côté, S.(2014). Emotional intelligence in organizations. Annual Review of Organizational Psychology and Organizational Behavior, 1(1),459-488. doi: 10.1146/annurev-orgpsych-031413-091233URL |
| [19] | Courtright, S. H., McCormick, B. W., Mistry, S., & Wang, J.(2017). Quality charters or quality members? A control theory perspective on team charters and team performance. Journal of Applied Psychology, 102(10),1462-1470. doi: 10.1037/apl0000229pmid: 28530414 |
| [20] | Courtright, S. H., Thurgood, G. R., Stewart, G. L., & Pierotti, A. J.(2015). Structural interdependence in teams: An integrative framework and meta-analysis. Journal of Applied Psychology, 100(6),1825-1846. doi: 10.1037/apl0000027pmid: 25938722 |
| [21] | Curşeu, P. L., Pluut, H., Boroş, S., & Meslec, N.(2015). The magic of collective emotional intelligence in learning groups: No guys needed for the spell!. British Journal of Psychology, 106(2),217-234. doi: 10.1111/bjop.12075pmid: 24905387 |
| [22] | DeRue, D. S., Nahrgang, J. D., & Ashford, S. J.(2015). Interpersonal perceptions and the emergence of leadership structures in groups: A network perspective. Organization Science, 26(4),1192-1209. doi: 10.1287/orsc.2014.0963URL |
| [23] | Druskat, V., & Wolff, S.(2001). Group emotional intelligence and its influence on group effectiveness. In C. Cherniss & D. Goleman (Eds.), The emotionally intelligent workplace: How to select for, measure, and improve emotional intelligence in individuals, groups, and organizations (pp.132-155). San Francisco: Jossey-Bass. |
| [24] | Elfenbein, H. A.(2006). Team emotional intelligence: What it can mean and how it can affect performance. In V. U. Druskat, F. Sala, & G. Mount (Eds.), Linking emotional intelligence and performance at work: Current research evidence with individuals and groups (pp.165-184). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum. |
| [25] | Farh, C. I.C., Lanaj, K., & ILies, R.(2017). Resource-based contingencies of when team member exchange helps member performance in teams. Academy of Management Journal, 60(3),1117-1137. doi: 10.5465/amj.2014.0261URL |
| [26] | Fredrickson, B. L.(1998). What good are positive emotions. Review of General Psychology, 2(3),300-319. pmid: 21850154 |
| [27] | Fredrickson, B. L.(2001). The role of positive emotions in positive psychology: The broaden-and-build theory of positive emotions. American Psychologist, 56(3),218-226. pmid: 11315248 |
| [28] | Frye, C. M., Bennett, R., & Caldwell, S.(2006). Team emotional intelligence and team interpersonal process effectiveness. American Journal of Business, 21(1),49-56. doi: 10.1108/19355181200600005URL |
| [29] | Gardner, H. K., Gino, F., & Staats, B. R.(2012). Dynamically integrating knowledge in teams: Transforming resources into performance. Academy of Management Journal, 55(4),998-1022. doi: 10.5465/amj.2010.0604URL |
| [30] | Grand, J. A., Braun, M. T., Kuljanin, G., Kozlowski, S. W.J., & Chao, G. T.(2016). The dynamics of team cognition: A process-oriented theory of knowledge emergence in teams. Journal of Applied Psychology, 101(10),1353-1385. doi: 10.1037/apl0000136URL |
| [31] | Hamme, C.(2003). Group emotional intelligence: The research and development of an assessment instrument. (Unpublished Doctoral Dissertation). The State University of New Jersey, New Brunswick. |
| [32] | Helfat, G., & Peteraf, M. A.(2003). The dynamic resource-based view: Capability lifecycles. Strategic Management Journal, 24(10),997-1010. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1097-0266URL |
| [33] | Ilgen, D. R., Hollenbeck, J. R., Johnson, M., & Jundt, D.(2005). Teams in organizations: From input-process-output models to IMOI models. Annual Review of Psychology, 56,517-543. doi: 10.1146/annurev.psych.56.091103.070250URL |
| [34] | Jordan, P. J., & Lawrence, S. A.(2009). Emotional intelligence in teams: Development and initial validation of the short version of the Workgroup Emotional Intelligence Profile (WEIP-S). Journal of Management & Organization, 15(4),452-469. |
| [35] | Jordan, P. J., & Troth, A. C.(2004). Managing emotions during team problem solving: Emotional intelligence and conflict resolution. Human Performance, 17(2),195-218. doi: 10.1207/s15327043hup1702_4URL |
| [36] | Knoke, D., & Yang, S.(2008). Social network analysis (2nd ed.). London: Sage Publications. |
| [37] | Kozlowski, S. W.J., & Chao, G. T.(2018). Unpacking team process dynamics and emergent phenomena: Challenges, conceptual advances, and innovative methods. American Psychologist, 73(4),576-592. doi: 10.1037/amp0000245pmid: 29792469 |
| [38] | Lawler, E. J., & Yoon, J.(1996). Commitment in exchange relations: Test of a theory of relational cohesion. American Sociological Review, 61(1),89-108. doi: 10.2307/2096408URL |
| [39] | Le Blanc, P.M., & González-Romá, V.(2012). A team level investigation of the relationship between leader-member exchange (LMX) differentiation, and commitment and performance. The Leadership Quarterly, 23(3),534-544. doi: 10.1016/j.leaqua.2011.12.006URL |
| [40] | LePine, J. A., Piccolo, R. F., Jackson, C. L., Mathieu, J. E., & Saul, J. R.(2008). A meta-analysis of teamwork processes: Tests of a multidimensional model and relationships with team effectiveness criteria. Personnel Psychology, 61(2),273-307. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-6570.2008.00114.xURL |
| [41] | Mathieu, J. E., Hollenbeck, J. R., van Knippenberg, D., & Ilgen, D. R.(2017). A century of work teams in the Journal of Applied Psychology. Journal of Applied Psychology, 102(3),452-467. doi: 10.1037/apl0000128pmid: 28150984 |
| [42] | Mayer, J. D., Roberts, R. D., & Barsade, S. G.(2008). Human abilities: Emotional intelligence. Annual Review of Psychology, 59,507-536. pmid: 17937602 |
| [43] | Mayo, M., Meindl, J. R., & Pastor, J. C.(2002). Shared leadership in work teams:A social network approach. In C. L. Pearce, & J. A. Conger (Eds.), Shared Leadership: Reframing the Hows and Whys of Leadership (pp.193-214). Sage Publications, Inc. |
| [44] | Menges, J. I., & Kilduff, M.(2015). Group emotions: Cutting the gordian knots concerning terms, levels of analysis, and processes. Academy of Management Annals, 9(1),845-928. doi: 10.5465/19416520.2015.1033148URL |
| [45] | Mesmer-Magnus, J. R., & DeChurch, L. A.(2009). Information sharing and team performance: A meta- analysis. Journal of Applied Psychology, 94(2),535-546. doi: 10.1037/a0013773pmid: 19271807 |
| [46] | Mischel, W.(1976). Towards a cognitive social model learning reconceptualization of personality. In: N. S. Endler & D. Magnusson (Eds.), Interactional psychology and personality (pp.166-207). New York: Wiley. |
| [47] | Neuman, G. A., Wagner, S. H., & Christiansen, N. D.(1999). The relationship between work-team personality composition and the job performance of teams. Group & organization management, 24(1),28-45. |
| [48] | Newman, D. A., & Wang, W.(2019). Social network effects: Computational modeling of network contagion and climate emergence. In S. E. Humphrey, & J. M. LeBreton (Eds.), The handbook of multilevel theory, measurement, and analysis (pp.541-560). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association. |
| [49] | Offermann, L. R., Kennedy, J. K., & Wirtz, P. W.(1994). Implicit leadership theories: Content, structure, and generalizability. The Leadership Quarterly, 5(1),43-58. doi: 10.1016/1048-9843(94)90005-1URL |
| [50] | Paik, Y., Seo, M., & Jin, S.(2019). Affective information processing in self-managing teams: The role of emotional intelligence. The Journal of Applied Behavioral Science, 55(2),235-267. doi: 10.1177/0021886319832013URL |
| [51] | Parke, M. R., Seo, M. -G., & Sherf, E. N.(2015). Regulating and facilitating: The role of emotional intelligence in maintaining and using positive affect for creativity. Journal of Applied Psychology, 100(3),917-934. doi: 10.1037/a0038452URL |
| [52] | Peña-Sarrionandia, A., Mikolajczak, M., & Gross, J. J.(2015). Integrating emotion regulation and emotional intelligence traditions: A meta-analysis. Frontiers in Psychology, 6,160-186. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2015.00160pmid: 25759676 |
| [53] | Prewett, M. S., Brown, M. I., Goswami, A., & Christiansen, N. D.(2018). Effects of team personality composition on member performance: A multilevel perspective. Group & Organization Management, 43(2),316-348. |
| [54] | Rezvani, A., Barrett, R., & Khosravi, P.(2019). Investigating the relationships among team emotional intelligence, trust, conflict and team performance. Team Performance Management: An International Journal, 25(1/2),120-137. doi: 10.1108/TPM-03-2018-0019URL |
| [55] | Rezvani, A., Khosravi, P., & Ashkanasy, N. M.(2018). Examining the interdependencies among emotional intelligence, trust, and performance in infrastructure projects: A multilevel study. International Journal of Project Management, 36(8),1034-1046. doi: 10.1016/j.ijproman.2018.08.002URL |
| [56] | Schutte, N. S., & Zhang, H. H.(2018). A meta-analytic investigation of the relationship between team emotional intelligence and team outcomes. Unpublished manuscript. |
| [57] | Seers, A.(1989). Team-member exchange quality: A new construct for role-making research. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 43,118-135. doi: 10.1016/0749-5978(89)90060-5URL |
| [58] | Stajkovic, A. D., Lee, D., & Nyberg, A. J.(2009). Collective efficacy, group potency, and group performance: Meta- analyses of their relationships, and test of a mediation model. Journal of Applied Psychology, 94(3),814-828. doi: 10.1037/a0015659URL |
| [59] | Tett, R. P., & Burnett, D. D.(2003). A personality trait-based interactionist model of job performance. Journal of Applied Psychology, 88(3),500-517. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.88.3.500URL |
| [60] | Tett, R. P., & Guterman, H. A.(2000). Situation trait relevance, trait expression, and cross-situational consistency: Testing a principle of trait activation. Journal of Research in Personality, 34(4),397-423. doi: 10.1006/jrpe.2000.2292URL |
| [61] | Thomas, J. S., Loignon, A. C., Woehr, D. J., Loughry, M. L., & Ohland, M. W.(2020). Dyadic viability in project teams: The impact of liking, competence, and task interdependence. Journal of Business and Psychology, 35,573-591. doi: 10.1007/s10869-019-09647-6URL |
| [62] | Troth, A. C., Jordan, P. J., Lawrence, S. A., & Tse, H. H.M.(2012). A multilevel model of emotional skills, communication performance, and task performance in teams. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 33(5),700-722. doi: 10.1002/job.785URL |
| [63] | Tse, H. H.M., & Ashkanasy, N. M.(2015). The dyadic level of conceptualization and analysis: A missing link in multilevel OB research? Journal of Organizational Behavior, 36(8),1176-1180. doi: 10.1002/job.2010URL |
| [64] | Tse, H. H.M., Troth, A. C., Ashkanasy, N. M., & Collins, A. L.(2018). Affect and leader-member exchange in the new millennium: A state-of-art review and guiding framework. The Leadership Quarterly, 29(1),135-149. doi: 10.1016/j.leaqua.2017.10.002URL |
| [65] | Walter, F., & Bruch, H.(2008). The positive group affect spiral: A dynamic model of the emergence of positive affective similarity in work groups. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 29(2),239-261. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1099-1379URL |
| [66] | Wang, S.(2015). Emotional intelligence, information elaboration, and performance: The moderating role of informational diversity. Small Group Research, 46(3),324-351. doi: 10.1177/1046496415578010URL |
| [67] | Wei, X., Liu, Y., & Allen, N. J.(2016). Measuring team emotional intelligence: A multimethod comparison. Group Dynamics: Theory, Research, and Practice, 20(1),34-50. doi: 10.1037/gdn0000039URL |
| [68] | Zhang, H., Ding, C., Schutte, N. S., & Li, R.(2020). How team emotional intelligence connects to task performance: A network approach. Small Group Research, 51(4),492-516. doi: 10.1177/1046496419889660URL |
| [69] | Zhang, Z., & Peterson, S. J.(2011). Advice networks in teams: The role of transformational leadership and members' core self-evaluations. Journal of Applied Psychology, 96(5),1004-1017. doi: 10.1037/a0023254pmid: 21463014 |
| [70] | Zohar, D., & Tenne-Gazit, O.(2008). Transformational leadership and group interaction as climate antecedents: A social network analysis. Journal of Applied Psychology, 93(4),744-757. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.93.4.744pmid: 18642981 |
相关文章 15
| [1] | 李铭泽, 叶慧莉, 张光磊. 自恋型领导对团队创造力形成过程的多视角研究[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(9): 1437-1453. |
| [2] | 龚艳萍, 陈卓, 谢菊兰, 谢笑春. 手机冷落行为的前因、后果与作用机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2019, 27(7): 1258-1267. |
| [3] | 陈维扬, 谢天. 社会规范的动态过程[J]. 心理科学进展, 2018, 26(7): 1284-1293. |
| [4] | 邓小平, 徐晨, 程懋伟, 张向葵. 青少年偏差行为的同伴选择和影响效应:基于纵向社会网络的元分析[J]. 心理科学进展, 2017, 25(11): 1898-1909. |
| [5] | 尹奎;李秀凤;孙健敏;于浩瀛. 大学生的社会网络[J]. 心理科学进展, 2016, 24(8): 1279-1289. |
| [6] | 张镇;郭博达. 社会网络视角下的同伴关系与心理健康[J]. 心理科学进展, 2016, 24(4): 591-602. |
| [7] | 葛红宁;周宗奎;牛更枫;陈武. 社交网站使用能带来社会资本吗?[J]. 心理科学进展, 2016, 24(3): 454-463. |
| [8] | 赵丹;余林. 社会交往对老年人认知功能的影响[J]. 心理科学进展, 2016, 24(1): 46-54. |
| [9] | 陈武英;刘连启. 情境对共情的影响[J]. 心理科学进展, 2016, 24(1): 91-100. |
| [10] | 李永强;黄 姚. 个性特征与社会网络特征的关系及其本土化发展[J]. 心理科学进展, 2014, 22(11): 1801-1813. |
| [11] | 韦雪艳. 中国背景下农民工创业成长的过程机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2012, 20(2): 197-207. |
| [12] | 马绍奇;焦璨;张敏强. 社会网络分析在心理研究中的应用[J]. 心理科学进展, 2011, 19(5): 755-764. |
| [13] | 杨林佩;石伟. 青少年恋爱关系:研究取向、方法与影响因素[J]. 心理科学进展, 2011, 19(3): 372-381. |
| [14] | 刘金婷;蔡强;王若菡;吴寅. 催产素与人类社会行为[J]. 心理科学进展, 2011, 19(10): 1480-1492. |
| [15] | 张建新;周明洁. 中国人人格结构探索——人格特质六因素假说[J]. 心理科学进展, 2006, 14(4): 574-585. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlkxjz/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=5518
