 ), 王婧怡, 李昱汝
), 王婧怡, 李昱汝 天津职业技术师范大学职业教育学院, 天津 300222
收稿日期:2020-07-20发布日期:2021-06-25通讯作者:张珊珊E-mail:zhangss945@126.com基金资助:天津市哲学社会科学规划项目(TJJX20-020)Affect spin and its impact on mental health
ZHANG Shanshan( ), WANG Jingyi, LI Yuru
), WANG Jingyi, LI Yuru School of Vocational Education, Tianjin University of Technology and Education, Tianjin 300222, China
Received:2020-07-20Published:2021-06-25Contact:ZHANG Shanshan E-mail:zhangss945@126.com摘要/Abstract
摘要: 情绪自旋是度量核心情绪个体内可变性的一种非认知性的人格特质。其通常采用经验取样法或日间重构法来对个体核心情绪状态进行每日动态跟踪, 并根据测评周期内的核心情绪空间位置的矢量角度的跨时间标准差来反映个体核心情绪状态的时间波动特性。基于情绪事件理论, 日常负性事件经历及其评估导致了个体情绪自旋的产生, 而动态情绪模型进一步解释了情绪自旋对心理健康功能的阻碍作用。未来应在情绪自旋的心理健康作用机制方面进行深入研究。
图/表 1
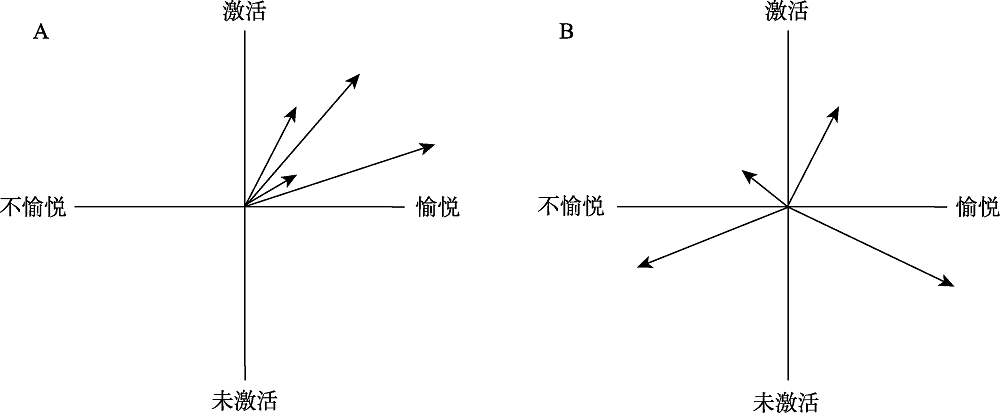
图1低情绪自旋(A)与高情绪自旋(B)的图示 (资料来源:改编自Kuppens et al., 2007)
 图1低情绪自旋(A)与高情绪自旋(B)的图示 (资料来源:改编自Kuppens et al., 2007)
图1低情绪自旋(A)与高情绪自旋(B)的图示 (资料来源:改编自Kuppens et al., 2007)参考文献 39
| [1] | 黄玲玲, 瞿鸿雁, 许远理.(2011). 核心情绪的概念、维度及神经机制. 人力资源管理, 2,77-78. |
| [2] | Beal, D. J., & Ghandour, L.(2011). Stability, change, and the stability of change in daily workplace affect. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 32,526-546. doi: 10.1002/job.v32.4URL |
| [3] | Beal, D. J., Trougakos, J. P., Weiss, H. M., & Dalal, R. S.(2013). Affect spin and the emotion regulation process at work. The Journal of Applied Psychology, 98(4),593-605. doi: 10.1037/a0032559URL |
| [4] | Brose, A., Voelkle, M. C., Lövdén, M., Lindenberger, U., & Schmiedek, F.(2015). Differences in the between-person and within-person structures of affect are a matter of degree. European Journal of Personality, 29(1),55-71. doi: 10.1002/per.1961URL |
| [5] | Cervone, D.(2005). Personality architecture: Within-person structures and processes. Annual Review of Psychology, 56,423-452. pmid: 15709942 |
| [6] | Chester, D. S., Clark, M. A., & DeWall, C. N.(2020). The flux, pulse, and spin of aggression-related affect. Emotion, http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/emo0000730 . |
| [7] | Chester, D. S., Lynam, D. R., Milich, R., & DeWall, C. N.(2018). Neural mechanisms of the rejection-aggression link. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 13,501-512. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsy025pmid: 29618118 |
| [8] | Clark, M. A., Robertson, M. M., & Carter, N. T.(2018). You spin me right round: A within-person examination of affect spin and voluntary work behavior. Journal of Management, 44(8),3176-3199. doi: 10.1177/0149206316662315URL |
| [9] | Dalal, R. S., Lam, H., Weiss, H. M., Welch, E. R., & Hulin, C. L.(2009). A within-person approach to work behavior and performance: Concurrent and lagged citizenship- counterproductivity associations, and dynamic relationships with affect and overall job performance. Academy of Management Journal, 52,1051-1066. doi: 10.5465/amj.2009.44636148URL |
| [10] | Davidson, R. J.(1998). Affective style and affective disorders: Perspectives from affective neuroscience. Cognition & Emotion, 12,307-330. |
| [11] | Dejonckheere, E., Mestdagh, M., Houben, M., Rutten, I., Sels, L., Kuppens, P., & Tuerlinckx, F.(2019). Complex affect dynamics add limited information to the prediction of psychological well-being. Nature Human Behaviour, 3,478-491. doi: 10.1038/s41562-019-0555-0pmid: 30988484 |
| [12] | Denson, T. F., DeWall, C. N., & Finkel, E. J.(2012). Self-control and aggression. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 21,20-25. doi: 10.1177/0963721411429451URL |
| [13] | Eid, M., & Diener, E.(1999). Intraindividual variability in affect: Reliability, validity, and personality characteristics. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 76,662-676. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.76.4.662URL |
| [14] | Harmon-Jones, E.(2000). Cognitive dissonance and experienced negative affect: Evidence that dissonance increases experienced negative affect even in the absence of aversive consequences. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 26,1490-1501. doi: 10.1177/01461672002612004URL |
| [15] | Hsieh, C. S., & Lee, L. F.(2014). A social interactions model with endogenous friendship formation and selectivity. Journal of Applied Econometrics, 31(2),301-319. doi: 10.1002/jae.2426URL |
| [16] | Ilies, R., Keeney, J., & Scott, B. A.(2011). Work-family interpersonal capitalization: Sharing positive work events at home. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 114,115-126. doi: 10.1016/j.obhdp.2010.10.008URL |
| [17] | In-Jo, P.(2015). The role of affect spin in the relationships between proactive personality, career indecision, and career maturity. Frontiers in Psychology, 18(6),1754-1764. |
| [18] | Judge, T. A., Woolf, E. F., & Hurst, C.(2010). Is emotional labor more difficult for some than for others? A multilevel, experience-sampling study. Personnel Psychology, 62(1),57-88. doi: 10.1111/peps.2009.62.issue-1URL |
| [19] | Jung, H., Park, I. J., & Rie, J.(2015). Future time perspective and career decisions: The moderating effects of affect spin. Journal of Vocational Behavior, 89,46-55. doi: 10.1016/j.jvb.2015.04.010URL |
| [20] | Kring, A. M., Feldman Barrett, L., & Gard, D. E.(2003). On the broad applicability of the affective circumplex: Representations of affective knowledge among schizophrenia patients. Psychological Science, 14,207-214. pmid: 12741742 |
| [21] | Kuppens, P., Mechelen, I. V., Nezlek, J. B., Dossche, D., & Timmermans, T.(2007). Individual differences in core affect variability and their relationship to personality and psychological adjustment. Emotion, 7(2),262-274. doi: 10.1037/1528-3542.7.2.262URL |
| [22] | Kuppens, P., Oravecz, Z., & Tuerlinckx, F.(2010). Feelings change: Accounting for individual differences in the temporal dynamics of affect. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 99:1042-1060. doi: 10.1037/a0020962pmid: 20853980 |
| [23] | Larsen, R. J., & Kasimatis, M.(1990). Individual differences in entrainment of mood to the weekly calendar. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 58,164-171. pmid: 2308073 |
| [24] | Liu, H., Xie, Q. W., & Lou, V. W. Q.(2018). Everyday social interactions and intra-individual variability in affect: A systematic review and meta-analysis of ecological momentary assessment studies. Motivation & Emotion, 43,339-353. |
| [25] | Moskowitz, D. S., & Zuroff, D. C.(2004). Flux, pulse, and spin: Dynamic additions to the personality lexicon. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 86,880-893. pmid: 15149261 |
| [26] | Ohly, S., & Schmitt, A.(2015). What makes us enthusiastic, angry, feeling at rest or worried? Development and validation of an affective work events taxonomy using concept mapping methodology. Journal of Business and Psychology, 30,15-35. doi: 10.1007/s10869-013-9328-3URL |
| [27] | Park, I. J., & Min, K. H.(2015). Making a list of Korean emotion terms and exploring dimensions underlying them. Korean Journal of Social & Personality Psychology, 19,109-129. |
| [28] | Ram, N., Gerstorf, D., Lindenberger, U., & Smith, J.(2011). Developmental change and intraindividual variability: Relating cognitive aging cognitive plasticity, cardiovascular lability, and emotional diversity. Psychology and Aging, 26(2),363-371. doi: 10.1037/a0021500URL |
| [29] | Richels, K. A., Day, E. A., Jorgensen, A. G., & Huck, J. T.(2020). Keeping calm and carrying on: Relating affect spin and pulse to complex skill acquisition and adaptive performance. Frontiers in Psychology, doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.00377. |
| [30] | Röcke, C., & Brose, A.(2013). Intraindividual variability and stability of affect and well-being. Journal of Gerontopsychology and Geriatric Psychiatry, 26(3),185-199. |
| [31] | Russell, J. A.(2003). Core affect and the psychological construction of emotion. Psychological Review, 110(1),145-172. pmid: 12529060 |
| [32] | Russell, J. A., Weiss, A., & Mendelsohn, G. A.(1989). Affect grid: A single-item scale of pleasure and arousal. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 57,493-502. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.57.3.493URL |
| [33] | Scherer, K. R.(2009). The dynamic architecture of emotion: Evidence for the component process model. Cognition & Emotion, 23,1307-1351. |
| [34] | Scott, L. N., Wright, A. G. C., Beeney, J. E., Lazarus, S. A., Pilkonis, P. A., & Stepp, S. D.(2017). Borderline personality disorder symptoms and aggression: A within-person process model. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 126,429-440. doi: 10.1037/abn0000272pmid: 28383936 |
| [35] | Sun, J. Q., Wayne, S. J., & Liu, Y.(2017). Perceived leader affect and employee work engagement: The moderating role of affect spin. Academy of Management Annual Meeting Proceedings, 1,14611. |
| [36] | Timmermans, T., van Mechelen, I., & Kuppens, P.(2010). The relationship between individual differences in intraindividual variability in core affect and interpersonal behavior. European Journal of Psychology, 24,623-638. |
| [37] | Uy, M. A., Sun, S. H., & Foo, M. D.(2017). Affect spin, entrepreneurs' well-being, and venture goal progress: The moderating role of goal orientation. Journal of Business Venturing, 32(4),443-460. doi: 10.1016/j.jbusvent.2016.12.001URL |
| [38] | Vansteelandt, K., Probst, M., & Pieters, G.(2013). Assessing affective variability in eating disorders: Affect spins less in anorexia nervosa of the restrictive type. Eating Behaviors, 14(3),263-268. doi: 10.1016/j.eatbeh.2013.03.004pmid: 23910763 |
| [39] | Weiss, H. M., & Cropanzano, R.(1996). Affective events theory:A theoretical discussion of the structure, causes and consequences of affective experiences at work. In B. M. Staw & L. L. Cummings (Eds.), Research in organizational behavior (pp.1-74). Greenwich,CT: JAI Press. |
相关文章 15
| [1] | 徐潞杰, 张镇. 老年人的消极交往与心理健康[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(8): 1472-1483. |
| [2] | 黄骐, 陈春萍, 罗跃嘉, 伍海燕. 好奇心的机制及作用[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(4): 723-736. |
| [3] | 俞国良, 陈婷婷, 赵凤青. 气温与气温变化对心理健康的影响[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(8): 1282-1292. |
| [4] | 陈子晨, 姜鹤. 心理健康服务的文化胜任力:理论取向与实践策略[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(4): 661-672. |
| [5] | 明志君, 陈祉妍. 心理健康素养:概念、评估、干预与作用[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(1): 1-12. |
| [6] | 辛素飞, 姜文源, 辛自强. 1993至2016年医学生心理健康变迁的横断历史研究[J]. 心理科学进展, 2019, 27(7): 1183-1193. |
| [7] | 曹 奔, 夏勉, 任志洪, 林秀彬, 徐升, 赖丽足, 王 琪, 江光荣. 大数据时代心理学文本分析技术 ——“主题模型”的应用[J]. 心理科学进展, 2018, 26(5): 770-780. |
| [8] | 徐富明, 张慧, 马红宇, 邓颖, 史燕伟, 李欧. 贫困问题:基于心理学的视角[J]. 心理科学进展, 2017, 25(8): 1431-1440. |
| [9] | 吕小康;王丛. 空气污染对认知功能与心理健康的损害[J]. 心理科学进展, 2017, 25(1): 111-120. |
| [10] | 王勍;俞国良. 群体认同与个体心理健康的关系:调节变量与作用机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2016, 24(8): 1300-1308. |
| [11] | 李艳青;任志洪;江光荣. 中国公安机关警察心理健康状况的元分析[J]. 心理科学进展, 2016, 24(5): 692-706. |
| [12] | 张镇;郭博达. 社会网络视角下的同伴关系与心理健康[J]. 心理科学进展, 2016, 24(4): 591-602. |
| [13] | 熊猛;叶一舵. 相对剥夺感:概念、测量、影响因素及作用[J]. 心理科学进展, 2016, 24(3): 438-453. |
| [14] | 范会勇;李晶晶;赵曼璐;李红. 幼儿园教师的心理健康:对基于SCL-90量表研究的元分析[J]. 心理科学进展, 2016, 24(1): 9-20. |
| [15] | 高爽;张向葵;徐晓林. 大学生自尊与心理健康的元分析 ——以中国大学生为样本[J]. 心理科学进展, 2015, 23(9): 1499-1507. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlkxjz/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=5523
