 ), 周滢鑫, 李玉, 李文一, 张号博, 郭彦麟, 胡国庆
), 周滢鑫, 李玉, 李文一, 张号博, 郭彦麟, 胡国庆 西北师范大学心理学院, 兰州 730070
收稿日期:2020-06-10出版日期:2021-03-15发布日期:2021-01-26通讯作者:胡砚冰E-mail:hybpsy2018@163.com基金资助:国家自然科学基金地区项目(31660281);国家自然科学基金地区项目(31860285);西北师范大学研究生科研资助项目(2019KYZZ012016)The neural mechanism of phonagnosia
ZHOU Aibao, HU Yanbing( ), ZHOU Yingxin, LI Yu, LI Wenyi, ZHANG Haobo, GUO Yanlin, HU Guoqing
), ZHOU Yingxin, LI Yu, LI Wenyi, ZHANG Haobo, GUO Yanlin, HU Guoqing School of Psychology, Northwest Normal University, Lanzhou 730070, China
Received:2020-06-10Online:2021-03-15Published:2021-01-26Contact:HU Yanbing E-mail:hybpsy2018@163.com摘要/Abstract
摘要: 人声身份识别对于社交交流的许多方面都至关重要, 大多数个体都能根据声音识别其声源者, 然而人声失认症患者似乎已经丧失了这种能力。人声失认症是指人声身份加工的不同阶段出现障碍, 症状主要包括获得性人声失认症, 发展性人声失认症及其亚型。获得性人声失认症患者受损脑区主要包括颞叶, 赫氏脑回和颞极, 发展性人声失认症主要与右后侧颞上沟的非典型性反应和颞叶与杏仁核间的功能联结障碍有关。以后的研究可以重点关注人声失认症的筛选方法, 界定范围和文化差异等方面。
图/表 2
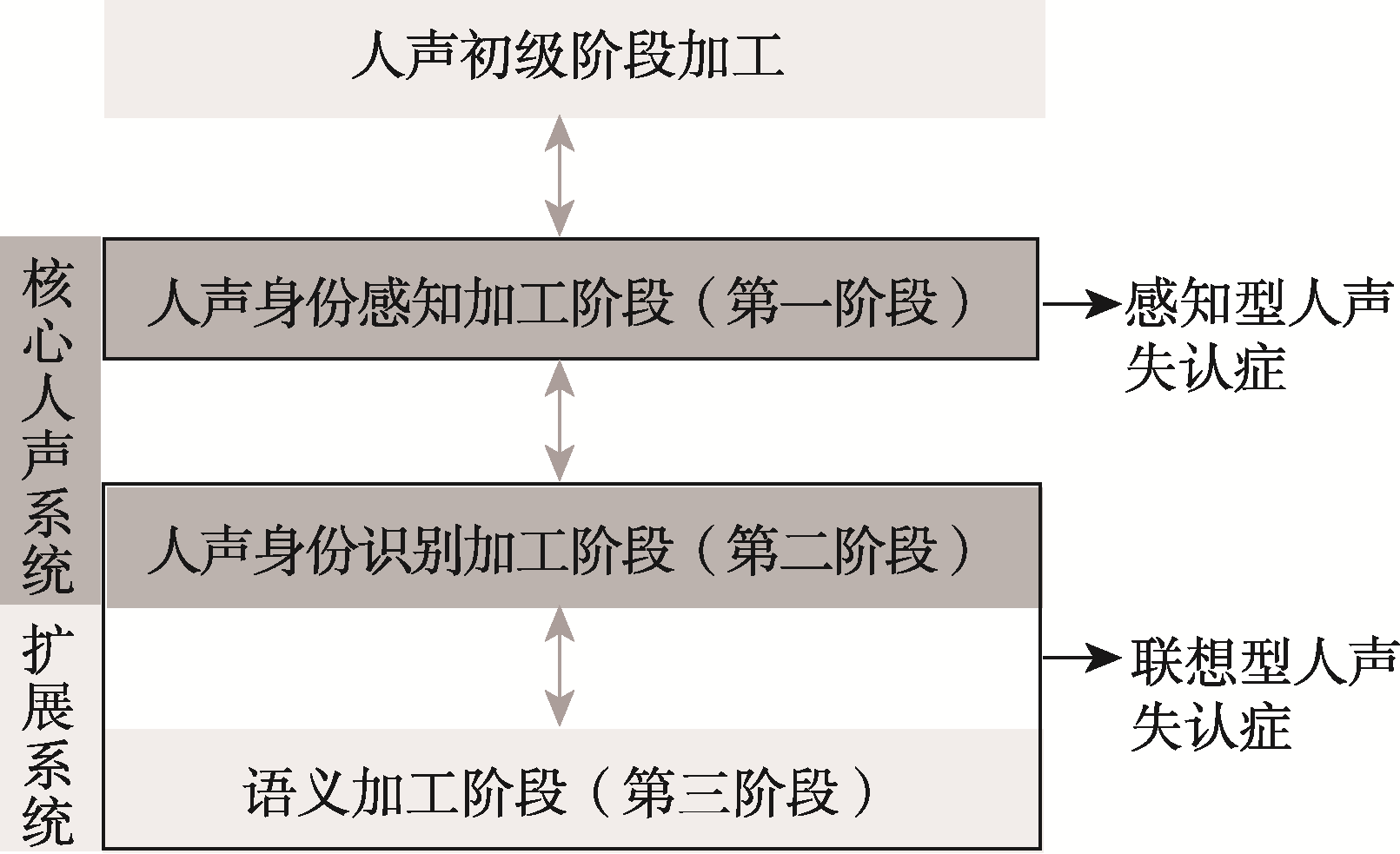
图1人声失认症的认知模型(Roswandowitz, 2017)
 图1人声失认症的认知模型(Roswandowitz, 2017)
图1人声失认症的认知模型(Roswandowitz, 2017)
图1人声失认症的认知模型(Roswandowitz, 2017)
 图1人声失认症的认知模型(Roswandowitz, 2017)
图1人声失认症的认知模型(Roswandowitz, 2017)参考文献 62
| [1] | 林菲菲, 陈旭, 周春霞, 马建苓, 冉光明. (2013). 面孔失认症的神经机制. 心理科学进展, 21(10), 1755-1762. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2013.01755URL |
| [2] | 伍可, 陈杰, 李雯婕, 陈洁佳, 刘雷, 刘翠红. (2020). 人声加工的神经机制. 心理科学进展, 28(5), 752-765. |
| 伍可, 陈杰, 李雯婕, 陈洁佳, 刘雷, 刘翠红. (2020). 人声加工的神经机制. 心理科学进展, 28(5), 752-765. | |
| [3] | 周爱保, 胡砚冰, 鲁小勇, 申莎, 关香丽, 陈大亮, 崔嘉溦. (2020). 我听故我在?自我声音识别机制的探索. 心理科学, 43(3), 564-570. |
| 周爱保, 胡砚冰, 鲁小勇, 申莎, 关香丽, 陈大亮, 崔嘉溦. (2020). 我听故我在?自我声音识别机制的探索. 心理科学, 43(3), 564-570. | |
| [4] | Aglieri, V., Chaminade, T., Takerkart, S., & Belin, P. (2018). Functional connectivity within the voice perception network and its behavioural relevance. Neuroimage, 183, 356-365. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2018.08.011URLpmid: 30099078 |
| Aglieri, V., Chaminade, T., Takerkart, S., & Belin, P. (2018). Functional connectivity within the voice perception network and its behavioural relevance. Neuroimage, 183, 356-365. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2018.08.011URLpmid: 30099078 | |
| [5] | Aglieri, V., Watson, R., Pernet, C., Latinus, M., Garrido, L., & Belin, P. (2017). The Glasgow Voice Memory Test: Assessing the ability to memorize and recognize unfamiliar voices. Behavior Research Methods, 49(1), 97-110. doi: 10.3758/s13428-015-0689-6URLpmid: 26822668 |
| Aglieri, V., Watson, R., Pernet, C., Latinus, M., Garrido, L., & Belin, P. (2017). The Glasgow Voice Memory Test: Assessing the ability to memorize and recognize unfamiliar voices. Behavior Research Methods, 49(1), 97-110. doi: 10.3758/s13428-015-0689-6URLpmid: 26822668 | |
| [6] | Alain, C., Du, Y., Bernstein, L. J., Barten, T., & Banai, K. (2018). Listening under difficult conditions: An activation likelihood estimation meta‐analysis. Human Brain Mapping, 39(7), 2695-2709. doi: 10.1002/hbm.24031URLpmid: 29536592 |
| Alain, C., Du, Y., Bernstein, L. J., Barten, T., & Banai, K. (2018). Listening under difficult conditions: An activation likelihood estimation meta‐analysis. Human Brain Mapping, 39(7), 2695-2709. doi: 10.1002/hbm.24031URLpmid: 29536592 | |
| [7] | Belin, P., Fecteau, S., & Bedard, C. (2004). Thinking the voice: Neural correlates of voice perception. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 8(3), 129-135. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2004.01.008URLpmid: 15301753 |
| Belin, P., Fecteau, S., & Bedard, C. (2004). Thinking the voice: Neural correlates of voice perception. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 8(3), 129-135. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2004.01.008URLpmid: 15301753 | |
| [8] | Belin, P., Zatorre, R. J., Lafaille, P., Ahad, P., & Pike, B. (2000). Voice-selective areas in human auditory cortex. Nature, 403(6767), 309-312. doi: 10.1038/35002078URLpmid: 10659849 |
| Belin, P., Zatorre, R. J., Lafaille, P., Ahad, P., & Pike, B. (2000). Voice-selective areas in human auditory cortex. Nature, 403(6767), 309-312. doi: 10.1038/35002078URLpmid: 10659849 | |
| [9] | Bestelmeyer, P. E. G., Belin, P., & Grosbras, M.-H. (2011). Right temporal TMS impairs voice detection. Current Biology, 21(20), R838-R839. URLpmid: 22032183 |
| Bestelmeyer, P. E. G., Belin, P., & Grosbras, M.-H. (2011). Right temporal TMS impairs voice detection. Current Biology, 21(20), R838-R839. URLpmid: 22032183 | |
| [10] | Biederman, I., Shilowich, B. E., Herald, S. B., Margalit, E., Maarek, R., Meschke, E. X., & Hacker, C. M. (2018). The cognitive neuroscience of person identification. Neuropsychologia, 116, 205-214. URLpmid: 29408397 |
| Biederman, I., Shilowich, B. E., Herald, S. B., Margalit, E., Maarek, R., Meschke, E. X., & Hacker, C. M. (2018). The cognitive neuroscience of person identification. Neuropsychologia, 116, 205-214. URLpmid: 29408397 | |
| [11] | Blank, H., Kiebel, S. J., & von Kriegstein, K. (2015). How the human brain exchanges information across sensory modalities to recognize other people. Human Brain Mapping, 36(1), 324-339. URLpmid: 25220190 |
| Blank, H., Kiebel, S. J., & von Kriegstein, K. (2015). How the human brain exchanges information across sensory modalities to recognize other people. Human Brain Mapping, 36(1), 324-339. URLpmid: 25220190 | |
| [12] | Bodin, C., & Belin, P. (2020). Exploring the cerebral substrate of voice perception in primate brains. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B, 375(1789), 20180386. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2018.0386URL |
| Bodin, C., & Belin, P. (2020). Exploring the cerebral substrate of voice perception in primate brains. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B, 375(1789), 20180386. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2018.0386URL | |
| [13] | Bonilha, L., Hillis, A. E., Hickok, G., Den Ouden, D. B., Rorden, C., & Fridriksson, J. (2017). Temporal lobe networks supporting the comprehension of spoken words. Brain, 140(9), 2370-2380. doi: 10.1093/brain/awx169URLpmid: 29050387 |
| Bonilha, L., Hillis, A. E., Hickok, G., Den Ouden, D. B., Rorden, C., & Fridriksson, J. (2017). Temporal lobe networks supporting the comprehension of spoken words. Brain, 140(9), 2370-2380. doi: 10.1093/brain/awx169URLpmid: 29050387 | |
| [14] | Bonte, M., Hausfeld, L., Scharke, W., Valente, G., & Formisano, E. (2014). Task-dependent decoding of speaker and vowel identity from auditory cortical response patterns. The Journal of Neuroscience, 34(13), 4548-4557. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4339-13.2014URLpmid: 24672000 |
| Bonte, M., Hausfeld, L., Scharke, W., Valente, G., & Formisano, E. (2014). Task-dependent decoding of speaker and vowel identity from auditory cortical response patterns. The Journal of Neuroscience, 34(13), 4548-4557. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4339-13.2014URLpmid: 24672000 | |
| [15] | Candini, M., Avanzi, S., Cantagallo, A., Zangoli, M., Benassi, M., Querzani, P., ... Frassinetti, F. (2018). The lost ability to distinguish between self and other voice following a brain lesion. NeuroImage: Clinical, 18, 903-911. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2018.03.021URL |
| Candini, M., Avanzi, S., Cantagallo, A., Zangoli, M., Benassi, M., Querzani, P., ... Frassinetti, F. (2018). The lost ability to distinguish between self and other voice following a brain lesion. NeuroImage: Clinical, 18, 903-911. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2018.03.021URL | |
| [16] | Connolly, C. G., Wu, J., Ho, T. C., Hoeft, F., Wolkowitz, O., Eisendrath, S., ... Yang, T. T. (2013). Resting-state functional connectivity of subgenual anterior cingulate cortex in depressed adolescents. Biological Psychiatry, 74(12), 898-907. URLpmid: 23910949 |
| Connolly, C. G., Wu, J., Ho, T. C., Hoeft, F., Wolkowitz, O., Eisendrath, S., ... Yang, T. T. (2013). Resting-state functional connectivity of subgenual anterior cingulate cortex in depressed adolescents. Biological Psychiatry, 74(12), 898-907. URLpmid: 23910949 | |
| [17] | Cosseddu, M., Gazzina, S., Borroni, B., Padovani, A., & Gainotti, G. (2018). Multimodal face and voice recognition disorders in a case with unilateral right anterior temporal lobe atrophy. Neuropsychology, 32(8), 920-930. doi: 10.1037/neu0000480URLpmid: 30080078 |
| Cosseddu, M., Gazzina, S., Borroni, B., Padovani, A., & Gainotti, G. (2018). Multimodal face and voice recognition disorders in a case with unilateral right anterior temporal lobe atrophy. Neuropsychology, 32(8), 920-930. doi: 10.1037/neu0000480URLpmid: 30080078 | |
| [18] | Djouab, S., Albonico, A., Yeung, S. C., Malaspina, M., Mogard, A., Wahlberg, R., Barton, J. J. S. (2020). Search for face identity or expression: Set size effects in developmental prosopagnosia. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 32(5), 889-905. doi: 10.1162/jocn_a_01519URLpmid: 31905091 |
| Djouab, S., Albonico, A., Yeung, S. C., Malaspina, M., Mogard, A., Wahlberg, R., Barton, J. J. S. (2020). Search for face identity or expression: Set size effects in developmental prosopagnosia. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 32(5), 889-905. doi: 10.1162/jocn_a_01519URLpmid: 31905091 | |
| [19] | Fruhholz, S., & Staib, M. (2017). Neurocircuitry of impaired affective sound processing: A clinical disorders perspective. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 83, 516-524. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2017.09.009URLpmid: 28919431 |
| Fruhholz, S., & Staib, M. (2017). Neurocircuitry of impaired affective sound processing: A clinical disorders perspective. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 83, 516-524. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2017.09.009URLpmid: 28919431 | |
| [20] | Fruhholz, S., Trost, W., & Kotz, S. A. (2016). The sound of emotions-Towards a unifying neural network perspective of affective sound processing. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 68, 96-110. URLpmid: 27189782 |
| Fruhholz, S., Trost, W., & Kotz, S. A. (2016). The sound of emotions-Towards a unifying neural network perspective of affective sound processing. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 68, 96-110. URLpmid: 27189782 | |
| [21] | Gabrieli, J. D. E. (2009). Dyslexia: A new synergy between education and cognitive neuroscience. Science, 325(5938), 280-283. doi: 10.1126/science.1171999URLpmid: 19608907 |
| Gabrieli, J. D. E. (2009). Dyslexia: A new synergy between education and cognitive neuroscience. Science, 325(5938), 280-283. doi: 10.1126/science.1171999URLpmid: 19608907 | |
| [22] | Gainotti, G. (2018). How can familiar voice recognition be intact if unfamiliar voice discrimination is impaired? An introduction to this special section on familiar voice recognition. Neuropsychologia, 116, 151-153. URLpmid: 29627274 |
| Gainotti, G. (2018). How can familiar voice recognition be intact if unfamiliar voice discrimination is impaired? An introduction to this special section on familiar voice recognition. Neuropsychologia, 116, 151-153. URLpmid: 29627274 | |
| [23] | Garrido, L., Eisner, F., McGettigan, C., Stewart, L., Sauter, D., Hanley, J. R., ... Duchaine, B. (2009). Developmental phonagnosia: A selective deficit of vocal identity recognition. Neuropsychologia, 47(1), 123-131. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2008.08.003URL |
| Garrido, L., Eisner, F., McGettigan, C., Stewart, L., Sauter, D., Hanley, J. R., ... Duchaine, B. (2009). Developmental phonagnosia: A selective deficit of vocal identity recognition. Neuropsychologia, 47(1), 123-131. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2008.08.003URL | |
| [24] | Hailstone, J. C., Crutch, S. J., Vestergaard, M. D., Patterson, R. D., & Warren, J. D. (2010). Progressive associative phonagnosia: A neuropsychological analysis. Neuropsychologia, 48(4), 1104-1114. URLpmid: 20006628 |
| Hailstone, J. C., Crutch, S. J., Vestergaard, M. D., Patterson, R. D., & Warren, J. D. (2010). Progressive associative phonagnosia: A neuropsychological analysis. Neuropsychologia, 48(4), 1104-1114. URLpmid: 20006628 | |
| [25] | Hailstone, J. C., Ridgway, G. R., Bartlett, J. W., Goll, J. C., Buckley, A. H., Crutch, S. J., & Warren, J. D. (2011). Voice processing in dementia: A neuropsychological and neuroanatomical analysis. Brain, 134(9), 2535-2547. doi: 10.1093/brain/awr205URL |
| Hailstone, J. C., Ridgway, G. R., Bartlett, J. W., Goll, J. C., Buckley, A. H., Crutch, S. J., & Warren, J. D. (2011). Voice processing in dementia: A neuropsychological and neuroanatomical analysis. Brain, 134(9), 2535-2547. doi: 10.1093/brain/awr205URL | |
| [26] | Herald, S. B., Xu, X., Biederman, I., Amir, O., & Shilowich, B. E. (2014). Phonagnosia: A voice homologue to prosopagnosia. Visual Cognition, 22(8), 1031-1033. doi: 10.1080/13506285.2014.960670URL |
| Herald, S. B., Xu, X., Biederman, I., Amir, O., & Shilowich, B. E. (2014). Phonagnosia: A voice homologue to prosopagnosia. Visual Cognition, 22(8), 1031-1033. doi: 10.1080/13506285.2014.960670URL | |
| [27] | Kanske, P., & Kotz, S. A. (2012). Auditory affective norms for German: Testing the influence of depression and anxiety on valence and arousal ratings. Plos One, 7(1), e30086. URLpmid: 22276146 |
| Kanske, P., & Kotz, S. A. (2012). Auditory affective norms for German: Testing the influence of depression and anxiety on valence and arousal ratings. Plos One, 7(1), e30086. URLpmid: 22276146 | |
| [28] | Khalfa, S., Guye, M., Peretz, I., Chapon, F., Girard, N., Chauvel, P., & Liégeois-Chauvel, C. (2008). Evidence of lateralized anteromedial temporal structures involvement in musical emotion processing. Neuropsychologia, 46(10), 2485-2493. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2008.04.009URL |
| Khalfa, S., Guye, M., Peretz, I., Chapon, F., Girard, N., Chauvel, P., & Liégeois-Chauvel, C. (2008). Evidence of lateralized anteromedial temporal structures involvement in musical emotion processing. Neuropsychologia, 46(10), 2485-2493. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2008.04.009URL | |
| [29] | Kristinsson, S., Thors, H., Yourganov, G., Magnusdottir, S., Hjaltason, H., Stark, B. C., ... Fridriksson, J. (2020). Brain damage associated with impaired sentence processing in acute aphasia. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 32(2), 256-271. URLpmid: 31596169 |
| Kristinsson, S., Thors, H., Yourganov, G., Magnusdottir, S., Hjaltason, H., Stark, B. C., ... Fridriksson, J. (2020). Brain damage associated with impaired sentence processing in acute aphasia. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 32(2), 256-271. URLpmid: 31596169 | |
| [30] | Leitman, D. I., Laukka, P., Juslin, P. N., Saccente, E., Butler, P. D., & Javitt, D. C. (2010). Getting the Cue: Sensory contributions to auditory emotion recognition impairments in schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 36(3), 545-556. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbn115URLpmid: 18791077 |
| Leitman, D. I., Laukka, P., Juslin, P. N., Saccente, E., Butler, P. D., & Javitt, D. C. (2010). Getting the Cue: Sensory contributions to auditory emotion recognition impairments in schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 36(3), 545-556. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbn115URLpmid: 18791077 | |
| [31] | Leitman, D. I., Wolf, D. H., Laukka, P., Ragland, J. D., Valdez, J. N., Turetsky, B. I., ... Gur, R. C. (2011). Not pitch perfect: Sensory contributions to affective communication impairment in schizophrenia. Biological Psychiatry, 70(7), 611-618. URLpmid: 21762876 |
| Leitman, D. I., Wolf, D. H., Laukka, P., Ragland, J. D., Valdez, J. N., Turetsky, B. I., ... Gur, R. C. (2011). Not pitch perfect: Sensory contributions to affective communication impairment in schizophrenia. Biological Psychiatry, 70(7), 611-618. URLpmid: 21762876 | |
| [32] | Luzzi, S., Coccia, M., Polonara, G., Reverberi, C., Ceravolo, G., Silvestrini, M., ... Gainotti, G. (2018). Selective associative phonagnosia after right anterior temporal stroke. Neuropsychologia, 116, 154-161. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2017.05.016URLpmid: 28506806 |
| Luzzi, S., Coccia, M., Polonara, G., Reverberi, C., Ceravolo, G., Silvestrini, M., ... Gainotti, G. (2018). Selective associative phonagnosia after right anterior temporal stroke. Neuropsychologia, 116, 154-161. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2017.05.016URLpmid: 28506806 | |
| [33] | Maguinness, C., Roswandowitz, C., & von Kriegstein, K. (2018). Understanding the mechanisms of familiar voice-identity recognition in the human brain. Neuropsychologia, 116, 179-193. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2018.03.039URLpmid: 29614253 |
| Maguinness, C., Roswandowitz, C., & von Kriegstein, K. (2018). Understanding the mechanisms of familiar voice-identity recognition in the human brain. Neuropsychologia, 116, 179-193. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2018.03.039URLpmid: 29614253 | |
| [34] | Maguinness, C., & von Kriegstei, K. (2017). Cross-modal processing of voices and faces in developmental prosopagnosia and developmental phonagnosia. Visual Cognition, 25(4-6), 644-657. doi: 10.1080/13506285.2017.1313347URL |
| Maguinness, C., & von Kriegstei, K. (2017). Cross-modal processing of voices and faces in developmental prosopagnosia and developmental phonagnosia. Visual Cognition, 25(4-6), 644-657. doi: 10.1080/13506285.2017.1313347URL | |
| [35] | McGettigan, C., Jasmin, K., Eisner, F., Agnew, Z. K., Josephs, O. J., Calder, A. J., ... Scott, S. K. (2017). You talkin’ to me? Communicative talker gaze activates left-lateralized superior temporal cortex during perception of degraded speech. Neuropsychologia, 100, 51-63. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2017.04.013URLpmid: 28400328 |
| McGettigan, C., Jasmin, K., Eisner, F., Agnew, Z. K., Josephs, O. J., Calder, A. J., ... Scott, S. K. (2017). You talkin’ to me? Communicative talker gaze activates left-lateralized superior temporal cortex during perception of degraded speech. Neuropsychologia, 100, 51-63. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2017.04.013URLpmid: 28400328 | |
| [36] | Mitchell, R. L. C., Elliott, R., Barry, M., Cruttenden, A., & Woodruff, P. W. R. (2004). Neural response to emotional prosody in schizophrenia and in bipolar affective disorder. British Journal of Psychiatry, 184(3), 223-230. doi: 10.1192/bjp.184.3.223URL |
| Mitchell, R. L. C., Elliott, R., Barry, M., Cruttenden, A., & Woodruff, P. W. R. (2004). Neural response to emotional prosody in schizophrenia and in bipolar affective disorder. British Journal of Psychiatry, 184(3), 223-230. doi: 10.1192/bjp.184.3.223URL | |
| [37] | Muhl, C., & Bestelmeyer, P. E. (2019). Assessing susceptibility to distraction along the vocal processing hierarchy. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 72(7), 1657-1666. doi: 10.1177/1747021818807183URL |
| Muhl, C., & Bestelmeyer, P. E. (2019). Assessing susceptibility to distraction along the vocal processing hierarchy. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 72(7), 1657-1666. doi: 10.1177/1747021818807183URL | |
| [38] | Muhl, C., Sheil, O., Jarutyt?, L., & Bestelmeyer, P. E. G. (2018). The Bangor Voice Matching Test: A standardized test for the assessment of voice perception ability. Behavior Research Methods, 50(6), 2184-2192. URLpmid: 29124718 |
| Muhl, C., Sheil, O., Jarutyt?, L., & Bestelmeyer, P. E. G. (2018). The Bangor Voice Matching Test: A standardized test for the assessment of voice perception ability. Behavior Research Methods, 50(6), 2184-2192. URLpmid: 29124718 | |
| [39] | Neuner, F., & Schweinberger, S. R. (2000). Neuropsychological impairments in the recognition of faces, voices, and personal names. Brain and Cognition, 44(3), 342-366. doi: 10.1006/brcg.1999.1196URLpmid: 11104530 |
| Neuner, F., & Schweinberger, S. R. (2000). Neuropsychological impairments in the recognition of faces, voices, and personal names. Brain and Cognition, 44(3), 342-366. doi: 10.1006/brcg.1999.1196URLpmid: 11104530 | |
| [40] | Omar, R., Henley, S. M. D., Bartlett, J. W., Hailstone, J. C., Gordon, E., Sauter, D., ... Warren, J. D. (2011). The structural neuroanatomy of music emotion recognition: Evidence from frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Neuroimage, 56(3), 1814-1821. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.03.002URL |
| Omar, R., Henley, S. M. D., Bartlett, J. W., Hailstone, J. C., Gordon, E., Sauter, D., ... Warren, J. D. (2011). The structural neuroanatomy of music emotion recognition: Evidence from frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Neuroimage, 56(3), 1814-1821. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.03.002URL | |
| [41] | Papagno, C., Mattavelli, G., Casarotti, A., Bello, L., & Gainotti, G. (2018). Defective recognition and naming of famous people from voice in patients with unilateral temporal lobe tumours. Neuropsychologia, 116, 194-204. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2017.07.021URLpmid: 28733246 |
| Papagno, C., Mattavelli, G., Casarotti, A., Bello, L., & Gainotti, G. (2018). Defective recognition and naming of famous people from voice in patients with unilateral temporal lobe tumours. Neuropsychologia, 116, 194-204. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2017.07.021URLpmid: 28733246 | |
| [42] | Patel, S., Oishi, K., Wright, A., Sutherland-Foggio, H., Saxena, S., Sheppard, S. M., & Hillis, A. E. (2018). Right hemisphere regions critical for expression of emotion through prosody. Frontiers in Neurology, 9, 224. URLpmid: 29681885 |
| Patel, S., Oishi, K., Wright, A., Sutherland-Foggio, H., Saxena, S., Sheppard, S. M., & Hillis, A. E. (2018). Right hemisphere regions critical for expression of emotion through prosody. Frontiers in Neurology, 9, 224. URLpmid: 29681885 | |
| [43] | Perrachione, T. K., del Tufo, S. N., & Gabrieli, J. D.-E.(2011). Human voice recognition depends on language ability. Science, 333(6042), 595-595. doi: 10.1126/science.1207327URLpmid: 21798942 |
| Perrachione, T. K., del Tufo, S. N., & Gabrieli, J. D.-E.(2011). Human voice recognition depends on language ability. Science, 333(6042), 595-595. doi: 10.1126/science.1207327URLpmid: 21798942 | |
| [44] | Rohrer, J. D., Sauter, D., Scott, S. K., Rossor, M. N., & Warren, J. D. (2012). Receptive prosody in nonfluent primary progressive aphasias. Cortex, 48(3), 308-316. doi: 10.1016/j.cortex.2010.09.004URL |
| Rohrer, J. D., Sauter, D., Scott, S. K., Rossor, M. N., & Warren, J. D. (2012). Receptive prosody in nonfluent primary progressive aphasias. Cortex, 48(3), 308-316. doi: 10.1016/j.cortex.2010.09.004URL | |
| [45] | Roswandowitz, C. (2017). Voice-identity processing deficit: The cognitive and neural mechanisms of phonagnosia (Unpublished doctorial dissertation), Humboldt University of Berlin. |
| Roswandowitz, C. (2017). Voice-identity processing deficit: The cognitive and neural mechanisms of phonagnosia (Unpublished doctorial dissertation), Humboldt University of Berlin. | |
| [46] | Roswandowitz, C., Kappes, C., Obrig, H., & von Kriegstein, K. (2018). Obligatory and facultative brain regions for voice-identity recognition. Brain, 141(1), 234-247. doi: 10.1093/brain/awx313URLpmid: 29228111 |
| Roswandowitz, C., Kappes, C., Obrig, H., & von Kriegstein, K. (2018). Obligatory and facultative brain regions for voice-identity recognition. Brain, 141(1), 234-247. doi: 10.1093/brain/awx313URLpmid: 29228111 | |
| [47] | Roswandowitz, C., Mathias, S. R., Hintz, F., Kreitewolf, J., Schelinski, S., & von Kriegstein, K. (2014). Two cases of selective developmental voice-recognition impairments. Current Biology, 24(19), 2348-2353. URLpmid: 25264258 |
| Roswandowitz, C., Mathias, S. R., Hintz, F., Kreitewolf, J., Schelinski, S., & von Kriegstein, K. (2014). Two cases of selective developmental voice-recognition impairments. Current Biology, 24(19), 2348-2353. URLpmid: 25264258 | |
| [48] | Roswandowitz, C., Schelinski, S., & von Kriegstein, K. (2017). Developmental phonagnosia: Linking neural mechanisms with the behavioural phenotype. Neuroimage, 155, 97-112. URLpmid: 28254454 |
| Roswandowitz, C., Schelinski, S., & von Kriegstein, K. (2017). Developmental phonagnosia: Linking neural mechanisms with the behavioural phenotype. Neuroimage, 155, 97-112. URLpmid: 28254454 | |
| [49] | Savitz, J., &Drevets, W. C. (2009). Bipolar and major depressive disorder: Neuroimaging the developmental- degenerative divide. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 33(5), 699-771. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2009.01.004URLpmid: 19428491 |
| Savitz, J., &Drevets, W. C. (2009). Bipolar and major depressive disorder: Neuroimaging the developmental- degenerative divide. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 33(5), 699-771. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2009.01.004URLpmid: 19428491 | |
| [50] | Schall, S., Kiebel, S. J., Maess, B., & von Kriegstein, K. (2013). Early auditory sensory processing of voices is facilitated by visual mechanisms. Neuroimage, 77, 237-245. URLpmid: 23563227 |
| Schall, S., Kiebel, S. J., Maess, B., & von Kriegstein, K. (2013). Early auditory sensory processing of voices is facilitated by visual mechanisms. Neuroimage, 77, 237-245. URLpmid: 23563227 | |
| [51] | Scott, S. K. (2019). From speech and talkers to the social world: The neural processing of human spoken language. Science, 366(6461), 58-62. URLpmid: 31604302 |
| Scott, S. K. (2019). From speech and talkers to the social world: The neural processing of human spoken language. Science, 366(6461), 58-62. URLpmid: 31604302 | |
| [52] | Shilowich, B. E., & Biederman, I. (2016). An estimate of the prevalence of developmental phonagnosia. Brain and Language, 159, 84-91. doi: 10.1016/j.bandl.2016.05.004URLpmid: 27376464 |
| Shilowich, B. E., & Biederman, I. (2016). An estimate of the prevalence of developmental phonagnosia. Brain and Language, 159, 84-91. doi: 10.1016/j.bandl.2016.05.004URLpmid: 27376464 | |
| [53] | Stevenage, S. V. (2018). Drawing a distinction between familiar and unfamiliar voice processing: A review of neuropsychological, clinical and empirical findings. Neuropsychologia, 116, 162-178. URLpmid: 28694095 |
| Stevenage, S. V. (2018). Drawing a distinction between familiar and unfamiliar voice processing: A review of neuropsychological, clinical and empirical findings. Neuropsychologia, 116, 162-178. URLpmid: 28694095 | |
| [54] | Tian, X., Wang, R., Zhao, Y., Zhen, Z., Song, Y., & Liu, J. (2019). Multi-item discriminability pattern to faces in developmental prosopagnosia reveals distinct mechanisms of face processing. Cerebral Cortex, 30(5), 2986-2996. URLpmid: 31813985 |
| Tian, X., Wang, R., Zhao, Y., Zhen, Z., Song, Y., & Liu, J. (2019). Multi-item discriminability pattern to faces in developmental prosopagnosia reveals distinct mechanisms of face processing. Cerebral Cortex, 30(5), 2986-2996. URLpmid: 31813985 | |
| [55] | van Lancker, D. R, & Canter, G. J. (1982). Impairment of voice and face recognition in patients with hemispheric damage. Brain and Cognition, 1(2), 185-195. URLpmid: 6927560 |
| van Lancker, D. R, & Canter, G. J. (1982). Impairment of voice and face recognition in patients with hemispheric damage. Brain and Cognition, 1(2), 185-195. URLpmid: 6927560 | |
| [56] | van Lancker, D. R., Cummings, J. L., Kreiman, J., & Dobkin, B. H. (1988). Phonagnosia: A dissociation between familiar and unfamiliar voices. Cortex, 24(2), 195-209. URLpmid: 3416603 |
| van Lancker, D. R., Cummings, J. L., Kreiman, J., & Dobkin, B. H. (1988). Phonagnosia: A dissociation between familiar and unfamiliar voices. Cortex, 24(2), 195-209. URLpmid: 3416603 | |
| [57] | van Lancker, D. R, & Kreima, J. (1987). Voice discrimination and recognition are separate abilities. Neuropsychologia, 25(5), 829-834. URLpmid: 3431677 |
| van Lancker, D. R, & Kreima, J. (1987). Voice discrimination and recognition are separate abilities. Neuropsychologia, 25(5), 829-834. URLpmid: 3431677 | |
| [58] | van Lancker, D. R., Kreiman, J., & Cummings, J. (1989). Voice perception deficits: Neuroanatomical correlates of phonagnosia. Journal of Clinical & Experimental Neuropsychology, 11(5), 665-674. URLpmid: 2808656 |
| van Lancker, D. R., Kreiman, J., & Cummings, J. (1989). Voice perception deficits: Neuroanatomical correlates of phonagnosia. Journal of Clinical & Experimental Neuropsychology, 11(5), 665-674. URLpmid: 2808656 | |
| [59] | von Kriegstein, K, & Girau, A.-L. (2006). Implicit multisensory associations influence voice recognition. PLoS Biology, 4(10), e326. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0040326URLpmid: 17002519 |
| von Kriegstein, K, & Girau, A.-L. (2006). Implicit multisensory associations influence voice recognition. PLoS Biology, 4(10), e326. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0040326URLpmid: 17002519 | |
| [60] | von Kriegstein, K., Kleinschmidt, A., Sterzer, P., & Giraud, A. (2005). Interaction of face and voice areas during speaker recognition. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 17(3), 367-376. doi: 10.1162/0898929053279577URLpmid: 15813998 |
| von Kriegstein, K., Kleinschmidt, A., Sterzer, P., & Giraud, A. (2005). Interaction of face and voice areas during speaker recognition. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 17(3), 367-376. doi: 10.1162/0898929053279577URLpmid: 15813998 | |
| [61] | Xu, X., Biederman, I., Shilowich, B. E., Herald, S. B., Amir, O., & Allen, N. E. (2015). Developmental phonagnosia: Neural correlates and a behavioral marker. Brain and Language, 149, 106-117. doi: 10.1016/j.bandl.2015.06.007URLpmid: 26197259 |
| Xu, X., Biederman, I., Shilowich, B. E., Herald, S. B., Amir, O., & Allen, N. E. (2015). Developmental phonagnosia: Neural correlates and a behavioral marker. Brain and Language, 149, 106-117. doi: 10.1016/j.bandl.2015.06.007URLpmid: 26197259 | |
| [62] | Young, A. W., Frühholz, S., & Schweinberger, S. R. (2020). Face and voice perception: Understanding commonalities and differences. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 24(5), 398-410. URLpmid: 32298625 |
| Young, A. W., Frühholz, S., & Schweinberger, S. R. (2020). Face and voice perception: Understanding commonalities and differences. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 24(5), 398-410. URLpmid: 32298625 |
相关文章 15
| [1] | 张照, 张力为, 龚然. 视觉工作记忆的过滤效能[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(4): 635-651. |
| [2] | 赵小红, 童薇, 陈桃林, 吴冬梅, 张蕾, 陈正举, 方晓义, 龚启勇, 唐小蓉. 敬畏的心理模型及其认知神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(3): 520-530. |
| [3] | 魏真瑜, 邓湘树, 赵治瀛. 亲社会行为中的从众效应[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(3): 531-539. |
| [4] | 岳童, 黄希庭, 傅安国. 人们何以能够“舍生取义”?基于保护性价值观认知神经机制的解释[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(3): 540-548. |
| [5] | 王葛彤, 席洁, 陈霓虹, 黄昌兵. 双眼视差的神经机制与知觉学习效应[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(1): 56-69. |
| [6] | 郭滢, 龚先旻, 王大华. 错误记忆产生的认知与神经机制:信息加工视角[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(1): 79-92. |
| [7] | 刘启鹏, 赵小云, 王翠艳, 徐艺雅, 王淑燕. 反刍思维与注意脱离损坏的关系及其神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(1): 102-111. |
| [8] | 翁纯纯, 王宁. 时距知觉的动物研究范式及相关神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(9): 1478-1492. |
| [9] | 杨晓梦, 王福兴, 王燕青, 赵婷婷, 高春颍, 胡祥恩. 瞳孔是心灵的窗口吗?——瞳孔在心理学研究中的应用及测量[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(7): 1029-1041. |
| [10] | 程士静, 何文广. 语义认知的习得、发展和老化及其神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(7): 1156-1163. |
| [11] | 张晶晶, 梁啸岳, 陈伊笛, 陈庆荣. 音乐句法加工的认知机制与音乐结构的影响模式[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(6): 883-892. |
| [12] | 杨国春, 伍海燕, 齐玥, 刘勋. 人类性别加工的认知神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(12): 2008-2017. |
| [13] | 李灵, 侯晓旭, 张亚, 隋雪. 食物线索注意偏向及其神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(12): 2040-2051. |
| [14] | 岳童, 黄希庭, 徐颖, 潘思存. 价值观的稳定性与可变性:基于认知神经科学的视角[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(12): 2091-2101. |
| [15] | 王鑫, 杭明丽, 梁丹丹. 动词论元结构复杂性加工的认知神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(1): 62-74. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlkxjz/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=5377
