 ,2,*, 方平平
,2,*, 方平平 ,2,*
,2,*Development and verification of CAPS markers based on SNPs from transcriptome of jute (Corchorus L.)
TAO Ai-Fen1,2, YOU Zi-Yi2, XU Jian-Tang2, LIN Li-Hui2, ZHANG Li-Wu2, QI Jian-Min ,2,*, FANG Ping-Ping
,2,*, FANG Ping-Ping ,2,*
,2,*通讯作者:
收稿日期:2019-10-23接受日期:2020-03-24网络出版日期:2020-07-12
| 基金资助: |
Received:2019-10-23Accepted:2020-03-24Online:2020-07-12
| Fund supported: |
作者简介 About authors
E-mail:281770126@qq.com,Tel:0591-83789483。

摘要
关键词:
Abstract
Keywords:
PDF (1034KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
本文引用格式
陶爱芬, 游梓翊, 徐建堂, 林荔辉, 张立武, 祁建民, 方平平. 基于黄麻转录组序列SNP位点的CAPS标记开发与验证[J]. 作物学报, 2020, 46(7): 987-996. doi:10.3724/SP.J.1006.2020.94158
TAO Ai-Fen, YOU Zi-Yi, XU Jian-Tang, LIN Li-Hui, ZHANG Li-Wu, QI Jian-Min, FANG Ping-Ping.
黄麻属于椴树科(Tiliaceae)黄麻属(Corchorus L.)一年生草本植物, 其韧皮纤维具有易降解、透气性强、吸水性好等优点。近年来, 黄麻纤维被广泛应用于建材和可降解地膜等产业[1]。但与苎麻、亚麻等相比, 黄麻韧皮纤维细胞壁木质化程度较高、纤维素含量较低, 导致纤维粗、硬, 品质不佳, 使其只适合加工绳索和包装用麻袋等, 限制了黄麻在纺织业等工业领域的应用[2]。目前, 国内外研究人员已克隆了包括4CL和COMT在内的多个木质素生物合成途径中的关键酶基因[3]。而MYB (V-myb avian myeloblastosis viral oncogene homolog)转录因子是植物转录因子家族中最大的成员之一, 它参与并对植物生长和发育的各个方面产生重大影响, 在植物次生代谢调节、激素和环境因子反应、细胞分化、器官形态发生和细胞周期调节中均有重要作用[4]。若能开发出与黄麻木质素合成和MYB转录因子相关的标记, 则将为黄麻种质资源鉴定、育种亲本选配和遗传学研究等提供重要方法。
生物的遗传因子受到多个因素的影响, 并在基因组水平上产生一定的波动。而分子标记技术是直接反映DNA分子水平多态性的技术, 与其他标记相比, 具有无表型效应、分布广、多态性高等优点, 并且不受环境的影响[5,6]。近年来取得长足发展的转录组测序技术, 具有通量高、分辨率高、不受限制等优点[7,8]。利用该技术可以获得大量潜在的SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism)和SSR (Simple Sequence Repeat)标记, 并用于各种分子生物学研究[9,10]。与其他标记方法相比, SNP标记遗传稳定性高、位点分布广泛且富有代表性, 因此已成为当前研究最多的分子标记之一[11,12]。虽然SNP 的检测方法众多, 但大部分方法均有其不足, 例如操作繁琐或者成本过高, 从而限制了其在植物遗传育种领域的应用[13,14]。其中较经济并且适合常规分子生物学实验的方法, 是把SNP多态转化成酶切扩增多态性(Cleaved Amplified Polymorphic Sequences, CAPS)标记或衍生CAPS (Derived Cleaved Amplified Polymorphic Sequences, dCAPS)标记[15]。王彩芬等[16]和司文洁等[17]研究表明, CAPS标记技术具有多态性高、共显性、所需DNA量少、操作简便、结果稳定可靠等优点。CAPS分子标记技术建立以来, 已经在水稻、小麦、玉米、大豆、番茄、马铃薯等作物中得到广泛应用[18,19,20,21]。
目前, 分子标记技术已广泛应用于黄麻遗传多样性分析、起源与演化、遗传连锁图谱构建等研究上[22,23,24,25,26]。关于黄麻分子标记的开发已取得一些进展, 例如SSR标记[27,28,29]、SNP标记[30,31]都已被开发利用, 但是关于黄麻CAPS标记的开发, 未见有相关文献报道, 而与黄麻木质素合成基因和MYB转录因子相关的CAPS标记的开发与验证, 更是未见报道。鉴于CAPS分子标记的优点及其在黄麻上开发应用的滞后性, 开展该研究是十分必要的。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料
1.1.1 植物材料 用于转录组测序的黄麻材料为黄麻179和爱店野生种。2017年4月种植于福建农林大学田间科技园, 采用盆栽栽培, 每盆10株, 3次重复, 出苗后30 d, 真叶长到7~8片时, 取茎和叶混合进行转录组测序。用于CAPS多态性引物筛选验证的12份黄麻种质资源的名称和类型见表1。所有材料均为盆栽, 于2017年8月份播种, 每盆10株, 置自然条件下生长, 长至5~6片真叶时, 取幼嫩叶片混合后提取DNA。Table 1
表1
表1用于CAPS引物多态性验证的黄麻品种名称和类型
Table 1
| 编号 Number | 名称 Name | 品种类型 Type of accessions |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 梅峰4号 Meifeng 4 | 圆果种 Corchorus capsularis |
| 2 | 越南圆果 Yuenanyuanguo | 圆果种 Corchorus capsularis |
| 3 | 广东独尾麻 Guangdongduweima | 圆果种 Corchorus capsularis |
| 4 | 中黄麻1号 Zhonghuangma 1 | 圆果种 Corchorus capsularis |
| 5 | 日本大分青皮 Japanese Dafenqingpi | 圆果种 Corchorus capsularis |
| 6 | 福农1号 Funong 1 | 长果种 Corchorus olitoris |
| 7 | 马里野生种 Maliyeshengzhong | 长果种 Corchorus olitoris |
| 8 | 广西长果 Guangxichangguo | 长果种 Corchorus olitoris |
| 9 | 日本5号 Japanese 5 | 长果种 Corchorus olitoris |
| 10 | 翠绿 Cuilyu | 长果种 Corchorus olitoris |
| 11 | 龙溪长果 Longxichangguo | 长果种 Corchorus olitoris |
| 12 | 台湾加利麻 Taiwanjialima | 圆果种 Corchorus capsularis |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
1.1.2 试剂及仪器 DNA提取试剂盒、限制性内切酶等购自北京百泰克生物技术有限公司, 其他常用试剂为实验室分析纯常规试剂; PCR仪为德国Eppendorf公司的MC-gradient; 电泳仪购自六一仪器厂(北京), 型号为DYY-6。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 黄麻转录组测序和SNP位点鉴别 基于Illumina HiSeq 4000测序技术平台, 构建黄麻转录组文库并进行建库测序, 获得黄麻转录组数据。在转录组测序的基础上, 采用GATK针对RNA-Seq 的SNP识别流程, 进行SNP多态性位点识别[32], 识别标准是, (1) 35 bp范围内连续出现的单碱基错配不超过3个; (2)经过序列深度标准化的SNP质量值大于2.0。1.2.2 与4CL、COMT和MYB转录因子相关的黄麻SNP引物设计 在黄麻转录组序列中, 寻找与木质素合成酶基因4CL和COMT以及MYB转录因子相关的unigene, 并采用Oligo 8设计SNP引物, 主要参数为: (1)引物长度在18~25 bp 之间; (2) PCR预期扩增产物大小在100~500 bp之间; (3)退火温度(Tm)在53~58℃之间, 上、下游引物的Tm值相差不大于4℃; (4)GC含量在40%~60%之间。
1.2.3 CAPS标记开发及内切酶的选择 采用 dCAPS Finder 2.0 进行CAPS引物开发和内切酶的选择, 主要步骤为, (1)在黄麻unigene序列中寻找与CAPS标记的PCR扩增体系中SNP引物相对应的unigene片段; (2)选取其SNP位点前后各30 bp长度的碱基序列; (3)将SNP位点原序列和突变序列分别输入 dCAPS Finder 2.0的对话框中, 寻找可以对位点进行切割的限制酶, 其对应的标记即为基于SNP的CAPS标记。
1.2.4 黄麻DNA的提取 采用北京百泰克生物公司的BioTeke试剂盒, 按说明书提取DNA。
1.2.5 CAPS标记的PCR扩增体系构建 采用束永俊等[14]的CAPS标记的PCR扩增程序, 反应体系为20 μL, 包含DNA 2 μL、上下游引物各1 μL、PRR MIX 10 μL、无菌水6 μL。PCR程序为95℃预变性3 min; 95℃变性30 s, 53℃退火30 s, 74℃延伸45 s, 共9个循环; 95℃变性30 s, 53℃退火45 s, 72℃延伸45 s, 共14个循环; 最后72℃延伸10 min, 4℃保存。
1.2.6 限制性核酸内切酶的酶切反应 按照内切酶的使用说明书构建限制性酶切反应体系, 反应体系可分为省时酶和非省时酶2种。
1.2.7 琼脂糖凝胶电泳 用1.2%的琼脂糖凝胶检测扩增和酶切产物, 电泳电压为100 V, 电流为100 mA, 电泳时间为40 min, 电泳完成后用培清600型凝胶成像仪观察条带并拍照记录。
1.2.8 数据统计分析 按照扩增和酶切条带的有无计数, 当某一条带出现时赋值为“1”, 不存在时赋值为“0”, 从而把图形资料转换成数据资料。参照Nei等[33]的方法求得品种之间的遗传距离, 然后用DPS软件中的类平均聚类法(UPGMA)对12份黄麻种质进行聚类分析。
2 结果与分析
2.1 黄麻转录组中SNP位点的数量与分布
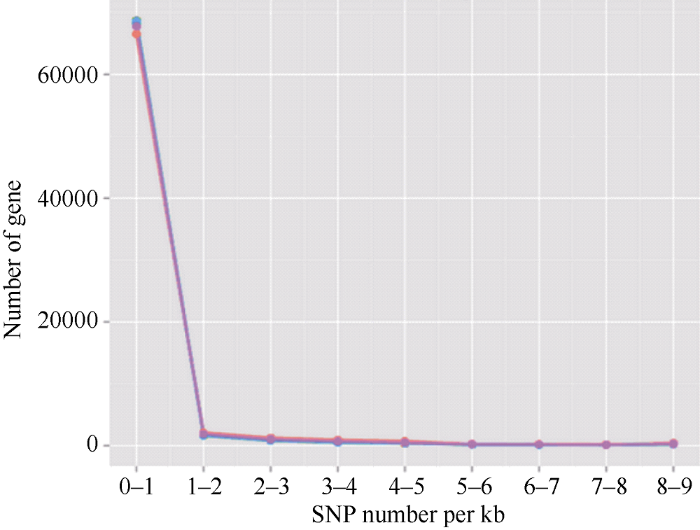
黄麻转录组经组装后共获得72,674条unigene序列, 检测到的SNP位点总数为67,567个, 序列总长度为29,705,997 bp。在黄麻unigene序列中, 平均每440 bp会有一个SNP位点。SNP位点分布密度如表2和图1所示。由表2可知, 含0~1个SNP位点的unigene序列最多, 有66,525条, 占总数的91.53%; 含2个以上SNP位点的unigene序列数目急剧下降, 其中含1~2个SNP位点的unigene序列有2092条, 比例为2.88%; 含2~3个SNP位点的unigene序列有1277条, 占1.76%; 含3个以上SNP位点的unigene序列总数亦较少, 有2780条, 比例为3.81%。表明绝大多数黄麻unigene上含有单个SNP位点, 含有2个及以上SNP位点的unigene数量不多, 总计约8%左右, 其中含5~8个SNP位点的unigene数量尤其少, 比例非常低。图1
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图1黄麻unigene中SNP位点分布的趋势图
横坐标为SNP的密度, 即每kb基因序列上的SNP数目; 纵坐标为拥有对应密度的unigene数目。
Fig. 1Trend of SNP loci distribution in the unigenes of jute
The abscissa shows the density of the SNPs, which means the number of SNPs per kb gene sequence in jute; the ordinate shows the number of unigenes with corresponding density of SNPs.
Table 2
表2
表2黄麻unigene中SNP位点的分布密度表
Table 2
| SNP位点的数目 Number of SNP loci | 对应unigene序列的数目 Corresponding number of unigenes | 所占比例 Ratio of SNP (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0-1 | 66,525 | 91.53 |
| 1-2 | 2092 | 2.88 |
| 2-3 | 1277 | 1.76 |
| 3-4 | 948 | 1.30 |
| 4-5 | 735 | 1.01 |
| 5-6 | 258 | 0.35 |
| 6-7 | 234 | 0.32 |
| 7-8 | 174 | 0.24 |
| >8 | 431 | 0.59 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
2.2 与4CL、COMT及MYB转录因子相关的CAPS标记开发
在对与黄麻木质素合成基因4CL、COMT及MYB转录因子相关的unigene分析的基础上, 共获得39对与上述基因及转录因子相关的SNP引物(表3)。其中和4CL相关的SNP引物最少, 仅有6对, 和COMT相关的有15对, 数量居中, 而与MYB转录因子相关的最多, 有18对。在此基础上, 采用dCAPS Finder 2.0软件开发基于SNP位点的CAPS标记, 共获得26对有酶切位点的CAPS标记(表4), 开发比率为66.7%, 这26对CAPS标记分别具有能被Ssp I、Cla I和Mse I等17种内切酶识别的位点。Table 3
表3
表339对SNP引物的编号、名称及序列
Table 3
| 引物名称 Primer name | 正向引物序列 Forward primer sequence (5′-3′) | 反向引物序列 Reverse primer sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| 4CL SNP1-1 | GTGCTTTTCATCGGTGGTTT | TGTCGTAAAACTGCTGCTGG |
| 4CL SNP1-2 | CGATTTTCATCTCGGCATTT | GCCACCCATAGTTTTGGCTA |
| 4CL SNP2-1 | AGCTCCCATGAAAGCAAAGA | AGCTCCCATGAAAGCAAAGA |
| 4CL SNP2-2 | AGCTCCCATGAAAGCAAAGA | CGATTTTCATCTCGGCATTT |
| 4CL SNP3-1 | GAGCTTAGCGCGAGAAGTGT | TGTCGTAAAACTGCTGCTGG |
| 4CL SNP3-2 | TCTCGGCATTTCTAACCACC | GCCACCCATAGTTTTGGCTA |
| COMT SNP1F1 | CACCGTTTTCCGTTGTTCTT | GTTGGAAAGCTAGCCAAACG |
| COMT SNP1F2 | ACACTCCATCTTGGTTTGGC | GCTACCCATGGCGTTAAAAA |
| COMT SNP1F3 | CCAGGTTTTCAACACTGCAA | GCATCTCCATTGGGAACACT |
| COMT SNP1F4 | TGAAGATGACAATAAAGCGAAAA | GTGGACAATCAGTGTGTGGC |
| COMT SNP1F5 | ATGCAAGAAAGCCGAGTTTG | GCAGGATTCCAAGGTTTCAA |
| COMT SNP2F1 | AAGGTGATAGAAACACGCCG | GTTGGAAAGCTAGCCAAACG |
| COMT SNP2F2 | ACTCCATCTTGGTTTGGCAC | GCTACCCATGGCGTTAAAAA |
| 引物名称 Primer name | 正向引物序列 Forward primer sequence (5′-3′) | 反向引物序列 Reverse primer sequence (5′-3′) |
| COMT SNP2F3 | GCTTAACCGGGTTGTTGATG | GCATCTCCATTGGGAACACT |
| COMT SNP2F4 | TGAAGATGACAATAAAGCGAAAA | GCATCTCCATTGGGAACACT |
| COMT SNP2F5 | ATGCAAGAAAGCCGAGTTTG | TTGATTGCATCATGTTGGCT |
| COMT SNP3F1 | AATTTCACCGTTTTCCGTTG | GTTGGAAAGCTAGCCAAACG |
| COMT SNP3F2 | ACTCCATCTTGGTTTGGCAC | AAAAACTGCGGTGGAGATTG |
| COMT SNP3F3 | GCTTAACCGGGTTGTTGATG | CCATTGTCTGGAATGGCTTT |
| COMT SNP3F4 | TGAAGATGACAATAAAGCGAAAA | TGGACAATCAGTGTGTGGCT |
| COMT SNP3F5 | ATGCAAGAAAGCCGAGTTTG | CATAATCCGGGTGGAAAAGA |
| MYB SNP F1 | TTGCAATGGATTTGTGCAAT | GATTCCCAGCAAATGGAAGA |
| MYB SNP F2 | TGCCTTGTCCTCTCACTAAGC | TTGAGGCCACATGTTCTAATTG |
| MYB SNP F3 | CCTTGCTATCATTGCCCATT | TTTATGGCCCTCAAAACTGG |
| MYB SNP F4 | CAAAAGCTCATCCTCTTCCG | CAAACTGCTTGGCTCATCAA |
| MYB SNP F5 | AAGTGTTCAAAGAGAAGCAGCA | TTATAGATGGCGATGGAGGC |
| MYB SNP F6 | AAGCAGAAGCAAAATCCCAA | AAGTAGCCATGGAGGTGTGG |
| MYB SNP F7 | GGCCATGAGTTTCAACGACT | GACGGGAAGAGAAAACCCTT |
| MYB SNP F8 | CTGCGTTTGTAACCCCAGAT | GCTTCCTCTTCTGCTTCTCG |
| MYB SNP F9 | CGACTCTTTCGGGACTCAAG | TCGTCGGCGTTTAAGAAGTT |
| MYB SNP F10 | TTACACCACCGTAACCGACA | AGATGTGGATCGGATCAAGG |
| MYB SNP F11 | AAGGAAGCCATGGAAGGACT | ATGCTTCTACCAATGCCAGG |
| MYB SNP F12 | TCGATCATCAGCAACCAAAA | GCATTGAATTTTCCGTGGTT |
| MYB SNP F13 | CCTGATCTTAAGCGTGGCTC | TTTGGTGACGGAGTTGATGA |
| MYB SNP F14 | GGCCATTGGAAAACTCAAAA | TGGATGAAGAGCCTTTCACA |
| MYB SNP F15 | ATCTTTGCCCAAAAATGCTG | GCAATTACCTGCTTCCCAAA |
| MYB SNP F16 | GAGAAGGGAAATGGCATCAA | CTTTGGTGGAACTGGAAGGA |
| MYB SNP F17 | TTCTTCAGCTCTCCAACGCT | GGCTTGTGGTATTGTGAGCA |
| MYB SNP F18 | CCCTTTCTAGCATATGGGCA | AACATCCCTCCATATTCATGTGT |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
由表4可知, 在26对CAPS引物中, 仅有3对与黄麻木质素合成基因4CL相关, 比例为11.5%, 其对应的unigene序列仅有一条, 即unigene_17597, 能识别位点的内切酶种类也仅有一种, 为Ssp I; 有9对CAPS引物与COMT相关, 占34.6%, 数量居中, 它们分别与unigene_04800、unigene_09002和unigene_08713等3条unigene序列相对应, 能识别变异位点的内切酶也分别有3种, 即Cla I、Bsi YI和Ava III; 而与MYB转录因子相关的CAPS标记最多, 有14对, 占总数的53.8%, 其对应的unigene序列有14条, 各不相同, 除MYBCAPS8和MYBCAPS13对应的内切酶均为Sec I之外, 其他内切酶种类也均有所不同。表明在3种CAPS标记中, 与MYB转录因子相关的CAPS标记具有多样化的、可以被多种内切酶识别的SNP变异位点。
Table 4
表4
表4CAPS引物名称、对应的unigene编号及内切酶名称
Table 4
| 序号 Code | 引物名称 Primer name | unigene编号 unigene code | 内切酶的名称 Endonuclease name |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4CL CAPS1-1 | unigene_17597 | Ssp I |
| 2 | 4CL CAPS2-1 | unigene_17597 | Ssp I |
| 3 | 4CL CAPS3-1 | unigene_17597 | Ssp I |
| 4 | COMT CAPS1-1 | unigene_04800 | Cla I |
| 5 | COMT CAPS1-3 | unigene_09002 | Bsi YI |
| 6 | COMT CAPS1-5 | unigene_08713 | Ava III |
| 7 | COMT CAPS2-1 | unigene_04800 | Cla I |
| 8 | COMT CAPS2-3 | unigene_09002 | Bsi YI |
| 9 | COMT CAPS2-5 | unigene_08713 | Ava III |
| 10 | COMT CAPS3-1 | unigene_04800 | Cla I |
| 11 | COMT CAPS3-3 | unigene_09002 | Bsi YI |
| 12 | COMT CAPS3-5 | unigene_08713 | Ava III |
| 13 | MYB CAPS1 | unigene_47261 | Psi I |
| 14 | MYB CAPS2 | unigene_17018 | Mse I |
| 序号 Code | 引物名称 Primer name | unigene编号 unigene code | 内切酶的名称 Endonuclease name |
| 15 | MYB CAPS3 | unigene_53709 | Mbo II |
| 16 | MYB CAPS5 | unigene_64377 | Mnl I |
| 17 | MYB CAPS6 | unigene_10508 | Mbo I |
| 18 | MYB CAPS7 | unigene_21631 | Mfe I |
| 19 | MYB CAPS8 | unigene_31305 | Sec I |
| 20 | MYB CAPS9 | unigene_16840 | Hpy99 I |
| 21 | MYB CAPS11 | unigene_02399 | Alu I |
| 22 | MYB CAPS12 | unigene_02162 | Asu I |
| 23 | MYB CAPS13 | unigene_46122 | Sec I |
| 24 | MYB CAPS14 | unigene_10460 | Tsp RI |
| 25 | MYB CAPS17 | unigene_59879 | Rsa I |
| 26 | MYB CAPS18 | unigene_49512 | Mae I |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
2.3 多态性CAPS引物的筛选
对上述26对CAPS引物进行PCR扩增和酶切处理表明, 有11对CAPS引物的PCR产物可以被酶切开来, 得到多态性条带(表4中黑体字标注, 扩增结果见图2), 占总数的42.31%, 而另外15对引物的PCR产物无法被酶切开, 虽然有清晰的条带但没有多态性。在多态性CAPS引物中, 与木质素合成酶基因COMT相关的引物有6对(54.5%), 与MYB转录因子相关的引物有5对(45.5%), 二者数量相当, 而未获得和4CL相关的多态性CAPS标记引物。图2
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图2COMT CAPS1-3引物扩增和酶切结果
M: marker; 1~12表示试验所用的12份黄麻种质资源的代号。
Fig. 2Amplified and enzyme digestion result of CAPS primer COMT CAPS1-3
M: marker; 1-12: the code of 12 jute accessions used in this study.
2.4 多态性CAPS标记的验证
以12个黄麻品种为材料, 对所筛选的11对CAPS标记的有效性进行验证。聚类分析表明(图3), 在遗传相似系数为0.5处画线时, 12个黄麻品种被区分为2个不同的类群, 第I个类群包括7个品种, 除“日本5号”外, 其他6个品种均为圆果种黄麻; 第II个类群包括5个黄麻品种, 均为长果种黄麻。由此可见, 所用的黄麻材料大致有按2个不同栽培类型, 即长果种和圆果种黄麻区分的趋势。来自日本的圆果种黄麻“日本大分青皮”和长果种黄麻“日本5号”被聚在一起, 推测这2个品种虽然属于不同的栽培类型, 但其木质素合成相关的基因以及MYB转录因子均可能有很高的相似性, 因而聚在同一个小类群中。同时进一步细分发现, 在第I个类群中, “台湾加利麻”和“龙溪长果”又各自成一类, 没有和其他品种的黄麻聚在一起, 推测这2个品种的木质素合成相关的基因以及MYB转录因子较为特殊, 与其他品种有所区别。综上所述, 所筛选出来的11对CAPS多态性标记, 可以将12份不同类型的黄麻品种较好地区别开来, 验证了所开发的CAPS标记的有效性和可行性。图3
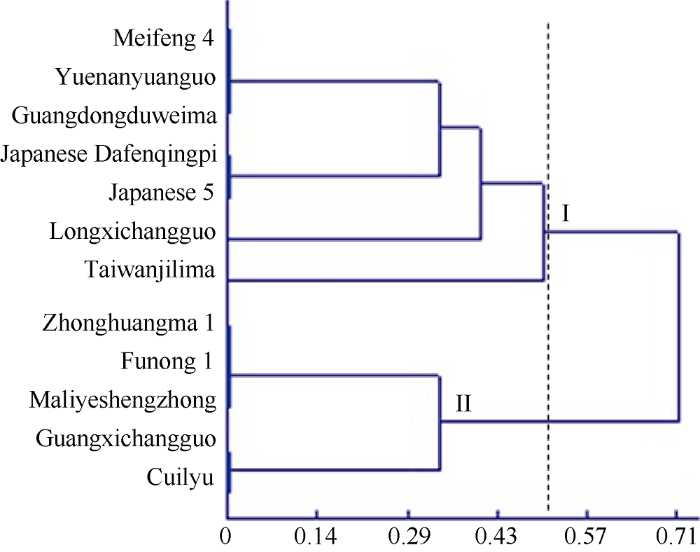 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图312份黄麻品种基于CAPS标记的聚类图
Fig. 3Dendrogram of 12 jute accessions based on CAPS markers
3 讨论
3.1 黄麻转录组中SNP位点的分布
SNP是由单碱基突变引起的DNA序列多态性, 具有数量丰富、分布广泛、覆盖度高等特点[34]。黄麻转录组序列中共检测到67,567个SNP位点, 平均每440 bp出现一个SNP位点, 与其他作物相比较, 出现的频率较低。前人研究表明, 水稻基因组中约268 bp存在1个SNP[35], 玉米基因组中每60~120 bp就存在1个SNP[36], 大豆基因组中每185~266 bp有1个SNP[37], 而茶树基因组中平均每172 bp有1个SNP[38]。SNP出现的频率, 第一, 与物种本身基因组的差异有关, 不同物种不同。第二, 存在于非编码序列中的SNP会提高SNP出现的频率[39], 而黄麻中存在于非编码序列的SNP位点较少, 导致其出现的频率降低。第三, 试验样本大小及测序长度也会影响SNP的频率[40], 今后应进一步增加黄麻转录组的测序长度, 以提高SNP的频率。3.2 所开发CAPS标记的多态性
本试验的CAPS标记是在前期黄麻转录组序列中SNP位点的基础上开发的。SNP标记因为在基因组中分布广泛、遗传稳定等特点, 在植物遗传育种研究方面有巨大的优势, 但是由于检测手段的限制, 阻碍了SNP标记的广泛应用。而CAPS方法无需昂贵的设备、操作简单, 可以实现中通量的 SNP 检测, 因而可以大大促进SNP标记在植物遗传育种中的应用[38]。本研究以39对SNP引物为基础, 获得了26对CAPS标记, 开发成功的比率为66.7%, 与柑橘(65%)和水稻(67.8%)的成功率相似[17,41], 但低于茶树和大豆SNP快速转化为CAPS方法的比例(81.8%和86.21%), 高于大豆传统方法转化的比例(52.51%)[14]。造成这种差异的原因, 首先与酶切位点选择和分析的标准有关, 严格的酶切位点选择和分析标准, 可以提高转化的成功率[38]; 其次, 由于某些SNP并未引起限制性内切酶识别位点的改变, 不能直接使用内切酶进行检测; 再次, 若在同一扩增产物中存在多个与SNP所在酶切识别位点相同的酶切位点, 直接使用内切酶检测难以分辨[19]。另外, 多态性CAPS引物所占的比率为42.3%, 也比较低。原因可能是本研究开发的CAPS引物是和4CL、COMT等木质素合成酶基因及MYB转录因子相关的, 针对性和目的性较强, 而所用的供试材料在这些位点仅有部分多态性, 从而导致多态性引物的比率降低。也有可能是物种本身的特异性引起的, 潜宗伟等研究亦表明, 分子标记引物的多态性比率因物种不同而有所差异[42]。3.3 所开发CAPS标记的有效性
所开发的CAPS标记引物可以将供试的12份黄麻种质较好地区别开来, 供试材料有大致按栽培类型, 即长果种黄麻和圆果种黄麻聚类的趋势。同时, 来自日本的2个品种聚在一起, 体现了按种质地理来源聚类的特点。另外, 基于CAPS标记的聚类分析也能鉴别出个别特异的种质类型, 如台湾加利麻。以上结果均表明, 所开发的CAPS标记在黄麻遗传多样性分析上是有效和可行的, 且可用于黄麻种质资源鉴定等研究, 为黄麻杂交育种亲本选配提供理论依据。综上所述, 本试验所开发的黄麻CAPS标记是黄麻遗传育种研究中的一项理想的分子标记方法, 可为黄麻分子标记辅助育种和性状改良提供有效方法。4 结论
对黄麻转录组序列中的SNP位点进行了分析, 发现平均每440 bp出现一个SNP位点, 其分布频率低于其他作物, 推测与物种之间的基因组差异性有关, 而黄麻中存在于非编码序列的SNP位点较少也是影响因素之一。同时, 设计了与黄麻木质素合成基因4CL、COMT及转录因子MYB相关的39对SNP引物, 并以此为基础开发了26对CAPS标记, 开发成功率为66.7%, 其中11对CAPS标记具有多态性, 多态性比例为43.2%。开发的CAPS标记能较好地将12份不同类型的黄麻种质按栽培类型区分开来, 同时亦能鉴别出特异种质, 表明所开发的CAPS是适用于黄麻种质资源鉴定的较理想的分子标记方法, 可为黄麻杂交育种亲本选配提供理论依据, 同时也为黄麻分子标记辅助选择育种提供了有效方法。参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
URLPMID:31084451 [本文引用: 1]

Plants face various stresses during the growth and development processes. The specific transcription factors bind to the cis-acting elements upstream of the stress resistance genes, specifically regulating the expression of the gene in plants and increasing the adaptability of plants to environmental stress. The transcription factor-mediated gene expression regulatory networks play an important role in plant stress response pathways. MYB (v-myb avian myeloblastosis viral oncogene homolog) transcription factor is one of the largest members of the transcription factor family in plants. It participates and has a great influence on all aspects of plant growth and development. It plays an important role in plant secondary metabolic regulation, hormone and environmental factor responses, cell differentiation, organ morphogenesis, and cell cycle regulation. This review mainly introduces the characteristics, structure, and classification of MYB transcription factors, as well as the abiotic stress resistance to drought, salt, temperature, and other functions in breeding, and provides a reference for the research and utilization of transcription factors in the future.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1006.2014.00397URL [本文引用: 1]

提出了一种基于基因组简约法开发SNP标记的方法, 即利用特定限制性内切酶酶切降低基因组复杂度, 利用高通量测序平台对酶切位点周围的目标片段进行富集测序, 设计一个生物信息学流程进行序列分析和SNP鉴定。以烤烟DH群体为例, 通过基因组简约法收集烟草基因组代表性片段和高通量测序产生11.4 Gb数据, 经生物信息学分析获得了1015个高质量SNP位点。以SSR标记为骨架, 绘制包括SNP标记在内、标记总数为1307的烤烟遗传连锁图。最后利用该遗传图谱和普通烟草2个祖先种的基因组序列, 分析烟草24个连锁群(染色体)之间的同源关系, 发现了大量染色体之间的重组或交换事件以及部分染色体之间的共线性。
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1006.2014.00397URL [本文引用: 1]

提出了一种基于基因组简约法开发SNP标记的方法, 即利用特定限制性内切酶酶切降低基因组复杂度, 利用高通量测序平台对酶切位点周围的目标片段进行富集测序, 设计一个生物信息学流程进行序列分析和SNP鉴定。以烤烟DH群体为例, 通过基因组简约法收集烟草基因组代表性片段和高通量测序产生11.4 Gb数据, 经生物信息学分析获得了1015个高质量SNP位点。以SSR标记为骨架, 绘制包括SNP标记在内、标记总数为1307的烤烟遗传连锁图。最后利用该遗传图谱和普通烟草2个祖先种的基因组序列, 分析烟草24个连锁群(染色体)之间的同源关系, 发现了大量染色体之间的重组或交换事件以及部分染色体之间的共线性。
DOI:10.1186/s12864-017-3712-8URLPMID:28482802 [本文引用: 1]

BACKGROUND: Genetic mapping and quantitative trait locus (QTL) detection are powerful methodologies in plant improvement and breeding. White jute (Corchorus capsularis L.) is an important industrial raw material fiber crop because of its elite characteristics. However, construction of a high-density genetic map and identification of QTLs has been limited in white jute due to a lack of sufficient molecular markers. The specific locus amplified fragment sequencing (SLAF-seq) strategy combines locus-specific amplification and high-throughput sequencing to carry out de novo single nuclear polymorphism (SNP) discovery and large-scale genotyping. In this study, SLAF-seq was employed to obtain sufficient markers to construct a high-density genetic map for white jute. Moreover, with the development of abundant markers, genetic dissection of fiber yield traits such as plant height was also possible. Here, we present QTLs associated with plant height that were identified using our newly constructed genetic linkage groups. RESULTS: An F8 population consisting of 100 lines was developed. In total, 69,446 high-quality SLAFs were detected of which 5,074 SLAFs were polymorphic; 913 polymorphic markers were used for the construction of a genetic map. The average coverage for each SLAF marker was 43-fold in the parents, and 9.8-fold in each F8 individual. A linkage map was constructed that contained 913 SLAFs on 11 linkage groups (LGs) covering 1621.4 cM with an average density of 1.61 cM per locus. Among the 11 LGs, LG1 was the largest with 210 markers, a length of 406.34 cM, and an average distance of 1.93 cM between adjacent markers. LG11 was the smallest with only 25 markers, a length of 29.66 cM, and an average distance of 1.19 cM between adjacent markers. 'SNP_only' markers accounted for 85.54% and were the predominant markers on the map. QTL mapping based on the F8 phenotypes detected 11 plant height QTLs including one major effect QTL across two cultivation locations, with each QTL accounting for 4.14-15.63% of the phenotypic variance. CONCLUSIONS: To our knowledge, the linkage map constructed here is the densest one available to date for white jute. This analysis also identified the first QTL in white jute. The results will provide an important platform for gene/QTL mapping, sequence assembly, genome comparisons, and marker-assisted selection breeding for white jute.
URLPMID:19597725 [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 3]
[本文引用: 3]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
URLPMID:22546823 [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
URLPMID:30813897 [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1073/pnas.76.10.5269URLPMID:291943 [本文引用: 1]

A mathematical model for the evolutionary change of restriction sites in mitochondrial DNA is developed. Formulas based on this model are presented for estimating the number of nucleotide substitutions between two populations or species. To express the degree of polymorphism in a population at the nucleotide level, a measure called
DOI:10.11963/issn.1002-7807.201604012URL [本文引用: 1]

单核苷酸多态性标记已在农作物研究中得到广泛应用并取得重大进展。为了便利棉花SNP(Single nucleotide polymorphism)标记的研究和应用,介绍了利用基因芯片、简化基因组测序、重测序等在棉花中开发SNP标记的方法,综述了SNP标记在棉花遗传图谱构建、数量位点的定位和分子标记辅助育种、基因组测序以及系统进化等研究中的应用。并对异源四倍体棉花中SNP标记开发时,同源序列位点和部分同源序列位点上的SNP标记辨别问题进行了系统探讨,对其快捷的开发、检测方式和在数量基因定位中的应用前景进行了展望。
DOI:10.11963/issn.1002-7807.201604012URL [本文引用: 1]

单核苷酸多态性标记已在农作物研究中得到广泛应用并取得重大进展。为了便利棉花SNP(Single nucleotide polymorphism)标记的研究和应用,介绍了利用基因芯片、简化基因组测序、重测序等在棉花中开发SNP标记的方法,综述了SNP标记在棉花遗传图谱构建、数量位点的定位和分子标记辅助育种、基因组测序以及系统进化等研究中的应用。并对异源四倍体棉花中SNP标记开发时,同源序列位点和部分同源序列位点上的SNP标记辨别问题进行了系统探讨,对其快捷的开发、检测方式和在数量基因定位中的应用前景进行了展望。
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1186/1471-2156-3-19URLPMID:12366868 [本文引用: 1]

BACKGROUND: Recent studies of ancestral maize populations indicate that linkage disequilibrium tends to dissipate rapidly, sometimes within 100 bp. We set out to examine the linkage disequilibrium and diversity in maize elite inbred lines, which have been subject to population bottlenecks and intense selection by breeders. Such population events are expected to increase the amount of linkage disequilibrium, but reduce diversity. The results of this study will inform the design of genetic association studies. RESULTS: We examined the frequency and distribution of DNA polymorphisms at 18 maize genes in 36 maize inbreds, chosen to represent most of the genetic diversity in U.S. elite maize breeding pool. The frequency of nucleotide changes is high, on average one polymorphism per 31 bp in non-coding regions and 1 polymorphism per 124 bp in coding regions. Insertions and deletions are frequent in non-coding regions (1 per 85 bp), but rare in coding regions. A small number (2-8) of distinct and highly diverse haplotypes can be distinguished at all loci examined. Within genes, SNP loci comprising the haplotypes are in linkage disequilibrium with each other. CONCLUSIONS: No decline of linkage disequilibrium within a few hundred base pairs was found in the elite maize germplasm. This finding, as well as the small number of haplotypes, relative to neutral expectation, is consistent with the effects of breeding-induced bottlenecks and selection on the elite germplasm pool. The genetic distance between haplotypes is large, indicative of an ancient gene pool and of possible interspecific hybridization events in maize ancestry.
DOI:10.1038/ng.715URLPMID:21076406 [本文引用: 1]

We report a large-scale analysis of the patterns of genome-wide genetic variation in soybeans. We re-sequenced a total of 17 wild and 14 cultivated soybean genomes to an average of approximately x5 depth and >90% coverage using the Illumina Genome Analyzer II platform. We compared the patterns of genetic variation between wild and cultivated soybeans and identified higher allelic diversity in wild soybeans. We identified a high level of linkage disequilibrium in the soybean genome, suggesting that marker-assisted breeding of soybean will be less challenging than map-based cloning. We report linkage disequilibrium block location and distribution, and we identified a set of 205,614 tag SNPs that may be useful for QTL mapping and association studies. The data here provide a valuable resource for the analysis of wild soybeans and to facilitate future breeding and quantitative trait analysis.
[本文引用: 3]
[本文引用: 3]
DOI:10.1007/s00122-004-1833-3URLPMID:15650816 [本文引用: 1]

Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) are the most abundant type of DNA polymorphism found in animal and plant genomes. They provide an important new source of molecular markers that are useful in genetic mapping, map-based positional cloning, quantitative trait locus mapping and the assessment of genetic distances between individuals. Very little is known on the frequency of SNPs in cassava. We have exploited the recently-developed collection of cassava expressed sequence tags (ESTs) to detect SNPs in the five cultivars of cassava used to generate the sequences. The frequency of intra-cultivar and inter-cultivar SNPs after analysis of 111 contigs was one polymorphism per 905 and one per 1,032 bp, respectively; totaling 1 each 509 bp. We have obtained further information on the frequency of SNPs in six cassava cultivars by analysis of 33 amplicons obtained from 3' EST and BAC end sequences. Overall, about 11 kb of DNA sequence was obtained for each cultivar. A total of 186 SNPs (136 and 50 from ESTs and BAC ends, respectively) were identified. Among these, 146 were intra-cultivar polymorphisms, while 80 were inter-cultivar polymorphisms. Thus the total frequency of SNPs was one per 62 bp. This information will help to develop new strategies for EST mapping as well as their association with phenotypic characteristics.
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1007/s11032-014-0129-9URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
