 ,1,*, 万建民1,2
,1,*, 万建民1,2Introducing qSS-9 Kas into Ningjing 4 by molecular marker-assisted selection to improve its seed storage ability
ZHANG Ping1, JIANG Yi-Mei1, CAO Peng-Hui1, ZHANG Fu-Lin1, WU Hong-Ming1, CAI Meng-Ying1, LIU Shi-Jia1, TIAN Yun-Lu1, JIANG Ling ,1,*, WAN Jian-Min1,2
,1,*, WAN Jian-Min1,2通讯作者:
第一联系人:
收稿日期:2018-07-6接受日期:2018-12-24网络出版日期:2019-01-03
| 基金资助: |
Received:2018-07-6Accepted:2018-12-24Online:2019-01-03
| Fund supported: |

摘要
关键词:
Abstract
Keywords:
PDF (5779KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
本文引用格式
张平, 姜一梅, 曹鹏辉, 张福鳞, 伍洪铭, 蔡梦颖, 刘世家, 田云录, 江玲, 万建民. 通过分子标记辅助选择将耐储藏主效QTL qSS-9 Kas转入宁粳4号提高其种子贮藏能力 [J]. 作物学报, 2019, 45(3): 335-343. doi:10.3724/SP.J.1006.2019.82035
ZHANG Ping, JIANG Yi-Mei, CAO Peng-Hui, ZHANG Fu-Lin, WU Hong-Ming, CAI Meng-Ying, LIU Shi-Jia, TIAN Yun-Lu, JIANG Ling, WAN Jian-Min.
水稻是我国最重要的粮食作物, 60%以上人口以稻米为主食。众所周知, 稻谷在一般贮藏条件下第2年就会产生陈化变质现象, 随着贮藏过程中温度和湿度的加大, 陈化过程也会加快。而具有良好耐贮藏特性的种子可以在同样条件下保存更长的时间, 并且在长时间贮藏后, 仍会表现出较高的萌发与出苗能力和优良的稻米品质, 可减少稻米陈化引起的损失[1]。种子耐贮性是一个受遗传因素、种子发育成熟度和贮藏期间环境条件影响的复杂数量性状, 与种子寿命和种子活力密切相关[2]。在同等贮藏条件下, 不同水稻品种的成熟种子在耐贮性上存在明显差异, 如贮藏1年的武育粳3号的发芽率只有14%, 而耐贮的W017仍保持87.3%的发芽能力, 表明遗传因素在种子耐贮性上有重要贡献。
目前, 利用自然或人工老化处理方法, 已检测到众多的水稻种子耐贮性相关QTL, 除了第8和第10染色体外, 在其他染色体上均有相关QTL分布, 在第9染色体上存在一个在不同遗传背景、不同生长环境下均稳定表达的主效QTL。Miura等[3]在Nipponbare/Kasalath//Nipponbare衍生的回交重组自交系(backcross inbred lines, BILs)群体中检测到主效QTL, 即qLG-9。Ren等[4]用Zhenshan 97/Minghui 63衍生的重组自交系群体(recombinant inbred lines, RILs)检测到的qAGR9-1与Miura等[3]检测到的qLG-9位置一致, 可能为同一个QTL。Xue等[5]在Asominori/IR24衍生的RIL群体中检测到的qRGR-9与Miura等[3]报道的qLG-9位点位置一致。Li等[6]利用Koshihikari/Kasalath//Koshihikari BIL群体在第9染色体检测到主效QTL qSS-9, 来自Kasalath的qSS-9对耐贮性起增效作用。Lin等[7]用Nipponbare/ Kasalath//Nipponbare BIL群体检测到3个QTL, 其中位于第9染色体上的qSSk-9对表型变异的贡献率最大, 该结果与Miura等[3]检测到的qLG-9位点位置一致。这些结果说明, qLG-9、qAGR9-1、qRGR-9、qSS-9和qSSk-9可能是同一个控制种子耐贮性的稳定的主效QTL。
本实验室Lin等[7]进一步通过自然老化和人工老化两种处理方法, 通过构建次级F2分离群体和一系列近等基因系, 对来自耐贮性极强的籼稻品种Kasalath等位基因qSS-9 (简写为qSS-9Kas)的遗传分析和精细定位, 将qSS-9Kas限定在146 kb之间, 获得了与耐贮性紧密连锁的分子标记Y10、Y11、Y14和Y13。本研究即是在此基础上, 利用这些紧密连锁的分子标记, 以宁粳4号为轮回亲本, 以耐贮性的置换系SL36为供体, 进行杂交和连续回交, 将qSS-9Kas转育宁粳4号, 创制携带qSS-9Kas耐贮的宁粳4号。
1 材料与方法
1.1 供试材料和主要农艺性状调查
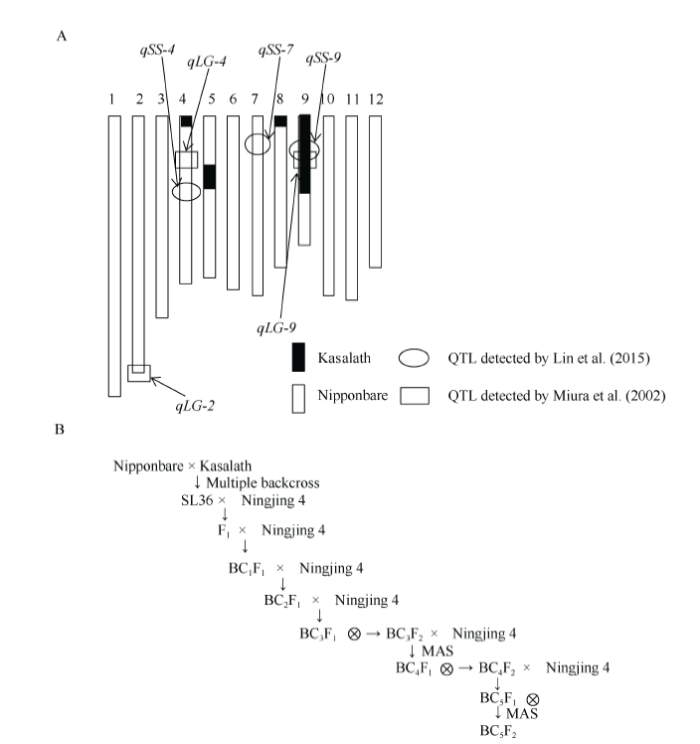
“宁粳4号”是本实验室利用日本优质水稻品种“越光”和我国高产品种“镇稻99”杂交选育而成, 表现出高产稳产、综合抗性较强、适应性广、生育期适中、米质优良等特点[8], 但其耐贮性较弱。为提高宁粳4号的耐贮性, 以宁粳4号为轮回亲本, 以携带qSS-9Kas的日本晴(Nipponbare)为背景的染色体片段置换系SL36为供体(遗传背景见图1-A, 由日本农业生物资源研究所提供), 进行杂交和连续回交, 然后自交获得BC5F2代。图1
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图1染色体片段置换系SL36的基因型示意图(A)和回交育种流程图(B)
Fig. 1Graphical genotypes of chromosome segment substitution line SL36 (A) and backcross breeding scheme between Ningjing 4 and SL36 (B)
如图1-B, 2013年5月中旬将置换系SL36、宁粳4号种植于南京农业大学土桥水稻试验站(南京市江宁区淳化街道土桥社区), 将宁粳4号与置换系SL36杂交获得F1杂交种; 当年冬季南繁获得BC1F1代; 2014年5月中旬回交获得BC2F1代杂交种; 冬季南繁获得BC3F1代杂交种, 在2015年5月于土桥将BC3F1杂交收种后种植获得BC3F2自交种, 下文命名为Y6647。
根据4个与qSS-9紧密连锁的分子标记Y-10、Y-11、Y-14、Y-13[9](表1)对收取119份BC3F2群体进行基因型的筛选, 将BC3F2在温度40℃、湿度80%的人工气候老化箱中处理25 d, 挑选种子活力显著高于宁粳4号的10份进行后代杂交繁育。2015年11月南繁选育获得BC4F1杂交种; 2016年5月于土桥获得BC4F2群体; 2016年11月南繁获得BC5F1杂交种。2017年5月于土桥收获BC5F2群体, 下文命名为Y3059, 均进一步通过MAS和耐储性鉴定, 选育出耐储性较稳定的品系, 成熟期调查株高、单株有效分蘖数、千粒质量等农艺性状。
Table 1
表1
表1本文中qSS-9的筛选标记
Table 1
| 标记 Marker | 正向引物 Forward primer (5°-3°) | 反向引物 Reverse primer (5°-3°) |
|---|---|---|
| Y-10 | ACCTCAAGTTTTCCTATTAGT | TAGAGTGACCTGCTAATGAG |
| Y-11 | ACGATTAGTTCAGTCCTTACAC | AACGGCTCAACGATCAGTAC |
| Y-14 | AAAAAGGATGGGAAACTGACC | TTTGAACTCAGTACCTTGGGG |
| Y-13 | AAAAAGGATGGGAAACTGACC | TACAAATAATCCCGATGCCG |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
1.2 种子耐贮性表型鉴定
1.2.1 自然老化处理 参考Li等[6], 略作改动。将同年正季在南京试验基地种植收获的亲本(置换系SL36、宁粳4号)和119份BC3F2代种子在室温<30℃、湿度40%~60%的环境中存放18个月。1.2.2 人工老化处理 参照Zeng等[10], 略作修改。将同年正季在南京种植收获的置换系SL36和宁粳4号在智能型种子老化试验箱(江苏省南京研奥仪器设备有限公司, 型号为LH-300S)中40℃和80%湿度的条件下分别处理20、25和30 d。根据同年亲本预处理结果, 确定人工老化处理的时间。
1.2.3 发芽率测定 将人工老化处理后的种子发芽率作为种子耐贮性的间接评价指标[3]。随机选取50粒健康饱满经老化处理后的种子, 放入铺有两层滤纸的9 cm培养皿, 加8 mL水, 于30℃光照培养箱中培养7 d。以胚芽超过半粒种子长和胚根超过种子长度为发芽标准, 统计发芽率, 以发芽率的高低来判断种子的耐贮性强弱。设2个重复。
1.3 TTC (2,3,5-氯化三苯基四氮唑)法测定种子生活力
参考Lopez [11]的方法。取50粒脱皮的种子在30℃水中浸泡48 h, 然后在含有0.5% (w/v) TTC (pH 7.0)的PBS (磷酸盐缓冲液)中黑暗染色2 h, 使用红色的强度作为活力的量度。通过改进的测定法测量TTC还原含量[12]。TTC染色后, 将种子在滤纸上干燥并放入盛有10 mL无水乙醇的15 mL试管。在60℃水浴中浸泡6 h将种胚中红色物质提取出来, 在室温下以12,000 r min-1离心2 min, 测定上清液在分光光度计490 nm处OD值。在所有步骤中, 用未经TTC染色的种子作空白对照。设3个重复。
1.4 生理生化指标测定
1.4.1 直链淀粉含量测定 按照国家标准GB-7648-87法经改进简化, 称取过0.15 mm筛的待测精米粉样品和标准样品0.1000 g放入100 mL容量瓶, 加1 mL 95%乙醇和9 mL 1 mol L-1 NaOH溶液, 沸水浴10 min后, 加蒸馏水定容至100 mL。吸取5 mL 样品溶液至100 mL容量瓶中, 加1 mL 1 mol L-1乙酸溶液和1.5 mL碘液显色并定容, 静止20 min后在620 nm 波长下测定吸光值, 计算宁粳4号和置换系后代的直链淀粉含量。设3个重复。1.4.2 MDA (丙二醛)含量测定 通过以下步骤从过完100目筛的糙米粉中提取MDA。取6粒左右健康饱满的稻谷手工去壳后, 收集胚及糊粉层的混合物。在2.0 mL离心管中, 加入1 mL 0.05 mol L-1 NaH2PO4-Na2HPO4缓冲液(pH 7.4), 在混合仪(Retsch MM301, 德国)上以1/30 s的周期振荡2 min后, 提取0.1 g糙米粉。测定采用MDA测定试剂盒(南京建成生物工程研究所), 以nmol mg-1表示。
2 结果与分析
2.1 携带qSS-9Kas的染色体片段置换系具有强的耐贮性
室温下贮藏18个月的宁粳4号的种子发芽率仅为26.70%±0.03%, 而置换系SL36和F1杂交种(SL36×宁粳4号)的发芽率分别为91.10% ± 0.05%和80.90% ± 0.08%, 均与宁粳4号存在极显著差异(P < 0.01)(图2-A, B), 表明qSS-9位点上的Kasalath等位基因表现为强的耐贮性, 且为显性效应。TTC染色结果表明, 大部分宁粳4号种子的胚部均未染上红色, 部分种子胚部虽已着色, 但着色程度较浅, 表明宁粳4号种子已基本丧失生活力。而置换系SL36和F1种子的种胚大多染上红色且着色程度深, 表现出较强的种子生活力(图2-C)。该结果与种子发芽测定结果一致, 说明两种方法均能检测种子的耐贮性。图2
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图2亲本及F1种子在自然环境下贮藏18个月后的种子发芽率和TTC法测定的种子生活力
A: 亲本及F1种子发芽率测定; B、C: 亲本及F1发芽表现和TTC法种子生活力表现, 从左到右依次是SL36、宁粳4号和F1。**表示与宁粳4号的发芽率相比, 在0.01水平上存在极显著差异。
Fig. 2Germination rates and tetrazolium assay of parents and F1 after natural aging for 18 months
A : Germination rates of parents and F1; B,C: Seed germination and tetrazolium assay of parents SL36, Ningjing 4 and F1 (from left to right). ** means significant at the 0.01 probability level compared with the germination rate of Ningjing 4.
2.2 利用MAS方法, 将控制耐贮性的主效QTL qSS-9Kas导入宁粳4号
利用与qSS-9紧密连锁的分子标记Y-10、Y-11、Y-14、Y-13对各亲本进行基因型分析。分子标记电泳图谱显示宁粳4号与不耐贮的粳稻品种Nipponbare一样, 在qSS-9位点上不同于Kasalath的基因型, 即不携带qSS-9Kas, 而置换系SL36则含有该QTL的Kasalath等位基因qSS-9Kas (图3-A)。在收取的200份置换系后代BC5F2的基因型鉴定和目的单株选育(图3-B)中, 带型和SL36一致的有194个。图3
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图3各亲本和BC5F2在与qSS-9紧密连锁的分子标记Y-10、Y-11、Y-14、Y-13下的基因型鉴定
A: 利用与qSS-9紧密连锁的分子标记Y-10、Y-11、Y-14和Y-13对各亲本的基因型进行鉴定; 其中, 1: DNA marker; 泳道2~5、6~9、10~13和14~17分别代表各品系在Y-10、Y-11、Y-14和Y-13的基因型; 泳道2、6、10和14为Nipponbare; 泳道3、7、11和15为宁粳4号; 泳道4、8、12和16为置换系SL36; 泳道5、9、13和17为Kasalath。B: 利用与qSS-9紧密连锁的分子标记Y-10、Y-11、Y-14和Y-13对宁粳4号、SL36及BC2F1间的基因型进行鉴定: 其中1: DNA marker; 泳道2~6分别代表宁粳4号、SL36及BC2F1在Y-10下的基因型; 7~11分别代表宁粳4号、SL36及BC5F2在Y-11下的基因型; 12~16分别代表宁粳4号、SL36及BC2F1在Y-14下的基因型; 17~21分别代表宁粳4号、SL36及BC2F1在Y-13下的基因型。
Fig. 3Genotype identification of parents and BC5F2 by molecular markers Y-10, Y-11, Y-14, and Y-13 close linked to qSS-9
A: Genotype identification of parents by molecular markers Y11 and Y14 close linkage to qSS-9; 1: DNA marker; 2-5, 6-9, 10-13, and 14-17 indicate genotype of markers Y-10, Y-11, Y-14, and Y-13 respectively; 2, 6, 10, and 14 indicate genotype of Nipponbare; 3, 7, 11, and 15 indicate genotype of Ningjing 4; 4, 8, 12, and 16 indicate genotype of SL36; 5, 9, 13, and 17 indicate genotype of Kasalath, respectively. B: Genotype identification of Ningjing 4, SL36 and BC5F2 by molecular markers Y11 and Y14 close linked to qSS-9; 1: DNA marker; 2-6 : Genotype of Ningjing 4, SL36 and BC5F2 under marker Y-10; 7-11: Genotype of Ningjing 4, SL36 and BC5F2 under marker Y-11; 12-16: Genotype of Ningjing 4, SL36 and BC5F2 under marker Y-14; 17-21: Genotype of Ningjing 4, SL36 and BC5F2 under marker Y-13, respectively.
共选择212个均匀分布于12条染色体的多态性标记对2017年正季BC5F2代单株进行置换系背景鉴定, 发现BC5F2中宁粳4号遗传背景达到约97.6%, 表明经过高代回交, qSS-9Kas已被成功转育到宁粳4号中, 遗传背景已较纯合。
2.3 携带qSS-9Kas的宁粳4号改良系老化后丙二醛含量降低
种子中MDA的含量是衡量脂质过氧化的主要指标, 随着稻米贮藏时间的延长, 种子活性降低, MDA的含量不断增加。自然老化处理一年后测定种子发现, SL36、Y6647中MDA的含量(1.60~1.85 nmol mg-1)明显低于对照宁粳4号(5.65 nmol mg-1)(图4-A), 说明与对照相比, 在常温条件储存下, 携带qSS-9Kas的置换系和改良系种子的劣变及衰老过程延缓, 脂质降解产生的MDA较少。图4
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图4亲本和后代种子在不同老化处理下的发芽率和丙二醛的含量
A: 宁粳4号、SL36、BC3F2 (Y6647)在自然老化一年MDA含量; B: 宁粳4号、SL36、BC3F2在自然老化一年和两年的发芽率; C: 亲本和BC5F1种子在人工老化处理35 d后的发芽率; D: 宁粳4号、Y3059-1-7、Y3059-1-8、Y3059-1-9的发芽率; E~H: 老化处理30 d后的发芽情况。E、F、G、H分别代表宁粳4号、Y3059-1-7、Y3059-1-8、Y3059-1-9。*表示在P = 0.05水平上差异显著; **表示在P = 0.01水平上差异极显著。
Fig. 4Germination rate and MDA contents in seeds of Ningjing 4, SL36, and progenies of different generations
A: Contents of MDA in seeds of Ningjing 4, SL36, and BC3F2 after natural aging for one year; B: Germination rate of Ningjing 4, SL36 and BC3F2 after natural aging forone year and two years; C: Germination rates of parents and BC5F1 after artificial aging for 35 days; D: Seed germination of BC5F2 and Ningjing 4 after accelerated aging for 30 d and storage at 40°C and 80% RH; E-H: Seed viability of the control after aging treatment; E, F, G, and H represent Ningjing 4, Y3059-1-7, Y3059-1-8, Y3059-1-9, respectively. Significant differences relative to the control were assessed by t-tests. * and **, significant at P = 0.05 and P = 0.01, respectively. Values are means ± SD (n = 2).
2.4 携带qSS-9Kas的宁粳4号改良系耐储性显著增强
自然条件储存一年后, 宁粳4号的发芽率为78.0%±5.7%, 置换系SL36的发芽率为93.0%±1.4%, 置换系后代BC3F2发芽率为73.0%±12.7%, 但是继续储存一年后, 宁粳4号的发芽率降到20%以下, 而置换系SL36的发芽率为77.0%±4.2%, BC3F2的发芽率仍保持在57.7%±8.4%, 活力相比宁粳4号显著提高(图4-B)。2016年海南收获的宁粳4号、置换系SL36和BC5F1代的破除休眠后种子在温度40℃和湿度80%条件下老化35 d后, 宁粳4号的发芽率已降至69% ± 1%, 而置换系SL36和BC5F1的发芽率仍分别保持在95%±2.5%和96.5%±3.0%, 表明qSS-9Kas导入宁粳4号后, 显著提高了其抗人工老化的能力(图4-C)。
将2017年正季收获的宁粳4号、置换系SL36和BC5F2代的种子破除休眠后, 人工老化处理30 d, 宁粳4号的发芽率为55.6%±1.7%, 而置换系SL36的发芽率为85.6%±2.6%, 两者之间存在极显著差异(P<0.01)。从194份含有目的片段的单株中挑选出发芽率较宁粳4号显著提高的186份, 其中农艺性状与宁粳4号基本一致的3份种子发芽率分别为78%± 4%、91%±1%、76%±2% (图4-D, E, F, G, H), 显著高于宁粳4号, 表明qSS-9Kas导入宁粳4号, 显著提高其种子耐贮性。
2.5 携带qSS-9Kas的宁粳4号改良系种子活力增强
TTC在种子脱氢酶的作用下, 可还原产生TTCH (三苯甲簪), 以还原力的高低来判定种子的活力。TTC被还原越多, 产生红色的TTCH就越多, 种子的活力越高, 用无水乙醇将不溶于水的TTCH从种胚中提取出来, 测量提取液在TTCH最大吸收波长490 nm处的吸光值, 以检测种子的活力。取人工老化30 d的宁粳4号及携带qSS-9Kas的宁粳4号改良家系种子, 进行TTC染色, 如图5-A所示, 改良系种子被染色的部分更多更深, 对TTCH含量测定发现, 改良系种子中TTCH的含量是对照宁粳4号的1.5~2.0倍(图5-B)。图5
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图5宁粳4号和Y3059的TTC试验、直链淀粉含量和株型的比较
A: 老化处理30 d后宁粳4号和Y3059的TTC染色情况, 从左到右分别代表宁粳4号、Y3059-1-7、Y3059-1-8、Y3059-1-9; B: Y3059及宁粳4号种子中TTCH的含量; C: 宁粳4号和Y3059老化处理前后表观淀粉含量的变化; D: 抽穗时期宁粳4号(左)和BC5F2 (右)株型; E: 抽穗35 d后宁粳4号(左)和BC5F2 (右)株型。*表示在P = 0.05水平上差异显著; **表示在P = 0.01水平上差异极显著。
Fig. 5Comparison of Ningjing 4 and Y3059 in tetrazolium assays, apparent amylose content and plant types
A: Tetrazolium assay of Ningjing 4 and Y3059; From left to right represent Ningjing 4, Y3059-1-7, Y3059-1-8, Y3059-1-9, respectively; B: The content of TTCH of Y3059 and Ningjing 4; C: The change of apparent amylose content in Ningjing 4 and Y3059; D: Plant type of Ningjing 4 and BC5F2 at heading; E: Plant type of Ningjing 4 and BC5F2 at 35 days after heading; Significant differences relative to the control were assessed by t-tests. * and **, significant at P = 0.05 and P = 0.01, respectively. Values are means ± SD (n = 2).
2.6 携带qSS-9Kas的宁粳4号改良家系的农艺性状表现
由于稻米直链淀粉含量是决定品质的最重要性状之一, 其含量与米饭的黏性、柔软性、光泽和食味品质密切相关。为此, 我们测定了宁粳4号和Y3059-1-7、Y3059-1-8、Y3059-1-9老化处理前后直链淀粉的含量随种子老化程度加深, 伴随着种子发芽率的降低, 种子中直链淀粉的含量也有所降低(图5-C), 但具体的变化机制仍需进一步探究。对改良家系进行农艺性状考察, 如图5-D, E所示, 改良系和宁粳4号的抽穗期、结实率、千粒重、单株产量都没有显著差异(表2)。表明在提高宁粳4号耐贮性的同时并没有影响其主要的农艺性状。
Table 2
表2
表2宁粳4号和Y3059农艺性状的比较
Table 2
| 抽穗期 HD (d) | 株高 PH (cm) | 分蘖数 NT | 结实率 SSR (%) | 千粒重 TGW (g) | 单株产量 YPP (g) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 宁粳4号Ningjing 4 | 87 ± 3 | 95 ± 4 | 11 ± 2 | 80.74 ± 0.02 | 25.50 ± 0.20 | 23 ± 0.18 |
| BC5F2 (Y3059) | 85 ± 3 | 107.5 ± 2.2** | 13 ± 3* | 83.08 ± 0.06 | 25.65 ± 0.90 | 22 ± 0.20 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
3 讨论
本实验室Li等[6]利用Koshihikari/Kasalath// Koshihikari BIL群体在南京、连云港、金湖3个不同地方种植并进行种子耐贮性相关QTL分析, 在第9染色体标记R10783S和R1751区间检测到qSS-9Kas, 并且利用CSSL群体验证了qSS-9Kas的真实性。该位点与Miura等[3]检测到的qLG-9位置一致, 在此基础上, 林秋云[9]利用以Nipponabre为背景, Kasalath为置换片段的染色体片段置换系SL36与Nipponabre回交, 构建次级F2分离群体, 对qSS-9Kas进行遗传分析, 同时进行F3后代验证和构建的近等基因系进行验证, 获得了与qSS-9Kas紧密连锁的Indel标记Y11和Y14, 在Nipponbare基因组上的物理距离约为147 kb。同时用以Koshihikari为背景, Kasalath为置换片段的染色体片段置换系SL226与Koshihikari回交, 构建次级F2分离群体, 对qSS-9Kas进行精细定位, 将qSS-9Kas定位在Indel标记Y7和Y13之间, 在Nipponbare基因组上的物理距离约为478 kb。两种qSS-9Kas的精细定位区间重叠。经过多年多点的检测, 发现qSS-9Kas是真实存在并稳定表达的主效QTL。本研究在前期定位基础上, 利用4个Indel标记Y10、Y11、Y14和Y13, 对本实验室选育的主栽粳稻品种宁粳4号与耐贮性的染色体片段置换系SL36的回交和自交后代单株, 进行分子标记的选择, 再经过老化后种子活力检测及目标性状的选育, 已将qSS-9Kas转育到宁粳4号中, 获得耐贮性的宁粳4号。影响种子耐贮性的因素很多, 如种子自身的遗传因素、种子灌浆成熟时的气候条件、收获干燥条件、种子贮藏时的外界环境等。本研究发现在同一型号的同一台老化箱中, 每次老化的时间均有一定的波动, 如南繁收获的种子, 可能由于海南热带季风气候, 种子灌浆时期温度较高, 收获时较为干燥, 种子的生长状况良好, 耐贮性稍强, 人工老化时间也会相应增加, 说明水稻自身的状况对种子耐贮性有一定的影响。本研究中虽然不同年份不同批次的老化试验结果略有差异, 但总体趋势是一致的, 转育了qSS-9Kas的宁粳4号, 其耐贮性均明显高于背景亲本宁粳4号。同时, 本文使用了两种不同的老化方法, 在短时间内用自然老化方法较难评价种子的耐贮性[13]; 人工老化是在人为控制的环境条件下加快种子老化速率, 高温高湿是目前最常用的人工老化方法[14]。通过人工老化处理后种子在短时间内发芽率下降明显, 因此可以快速评价种子的耐贮性, 弥补自然老化所需较长时间的缺点。Rajjou等[15]认为人工加速老化可以模拟自然老化从而提高鉴定种子耐贮性的效率。许惠滨等[16]认为短时间的高温高湿加速老化条件不能完全替代自然老化。从本文的研究结果看, 人工老化虽然与自然老化结果有一定的差异, 但两种方法均可验证, 在通过不断回交转育的后代中, 种子的耐贮性的确得到提高, 因此, 人工老化同样可适用于分子标记辅助育种。我们已成功地将耐储藏主效QTL qSS-9Kas引入到主栽品种宁粳4号中。
生产上, 人们一般通过改善贮藏条件, 如修建气调库或低温库、选择合适的包装材料和微波处理种子等[17], 虽然可以延缓稻米贮藏期间的陈化, 但需要消耗大量的人力和财力。从遗传角度改良种子本身的耐贮性, 能更加经济、有效地解决种子在贮藏过程中的陈化变质问题。因此, 水稻种子耐贮性的分子育种已经成为水稻育种的重要目标之一。本研究采用人工老化为主, 自然老化为辅, 结合MAS方法, 将来源于Kasalath的控制种子耐贮性的主效QTL qSS-9Kas转移到宁粳4号中, 从种子自身的遗传基因来提高种子的耐贮性, 经过多年多种方法验证, 表明该手段能稳定有效提高其种子的耐贮性。如自然条件下贮藏2年的种子, 宁粳4号的发芽率已低于20%, 而改良家系Y6647的发芽率仍保持在57.7% ± 8.4%。为耐贮性分子育种奠定了基础。
4 结论
利用分子标记辅助选择技术将来源于Kasalath的控制种子耐贮性的主效QTL qSS-9Kas转育到主栽品种宁粳4号中, 获得的宁粳4号改良系表现出更高的耐贮性, 同时大多数农艺性状和宁粳4号无显著差异。参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
DOI:10.2135/cropsci1996.0011183X003600030027xURL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-416X.2005.03.004URL [本文引用: 1]

利用珍汕97B/密阳46构建的RIL群体及其相应分子遗传图谱,采用种子加速老化鉴定法,以处理后的相对发芽率(%)作为该材料耐贮藏性的考察指标,分别对老化处理7d和14d后测得的数据进行QTL定位和上位性分析.共检测到2个主效应QTL与控制种子耐贮藏性有关.在老化程度相对较轻时,qSS9-1起忍耐作用;而在老化程度相对较重时,则有qSS4基因在起作用.试验还检测到5对耐贮藏性的上位性互作QTL,其贡献率为8.14%~13.51%,涉及第1、2、3、4、5、6、9、12等8条染色体.其中在7d老化处理试验中,检测到2对效应值相对较小的上位性互作;而在14d老化处理试验中,检测到3对效应值相对较大的上位性互作.
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-416X.2005.03.004URL [本文引用: 1]

利用珍汕97B/密阳46构建的RIL群体及其相应分子遗传图谱,采用种子加速老化鉴定法,以处理后的相对发芽率(%)作为该材料耐贮藏性的考察指标,分别对老化处理7d和14d后测得的数据进行QTL定位和上位性分析.共检测到2个主效应QTL与控制种子耐贮藏性有关.在老化程度相对较轻时,qSS9-1起忍耐作用;而在老化程度相对较重时,则有qSS4基因在起作用.试验还检测到5对耐贮藏性的上位性互作QTL,其贡献率为8.14%~13.51%,涉及第1、2、3、4、5、6、9、12等8条染色体.其中在7d老化处理试验中,检测到2对效应值相对较小的上位性互作;而在14d老化处理试验中,检测到3对效应值相对较大的上位性互作.
URLPMID:11912234 [本文引用: 6]

Quantitative trait loci (QTLs) controlling seed longevity in rice were identified using 98 backcross inbred lines (BILs) derived from a cross between a japonica variety Nipponbare and an indica variety Kasalath. Seeds of each BIL were kept for 12 months at 30 00°C in dry conditions to promote loss of viability. To measure seed longevity, we performed an additional aging-processing treatment for 2 months at 30 00°C maintaining seeds at 15% moisture content. We measured the germination percent of these treated seeds at 25 00°C for 7 days as the degree of seed longevity. The germination of BILs ranged from 0 to 100% with continuous variation. Three putative QTLs for seed longevity, qLG-2, qLG-4 and qLG-9, were detected on chromosome 2, 4 and 9, respectively. Kasalath alleles increased the seed longevity at these QTLs. The QTL with the largest effect, qLG-9, explained 59.5% of total phenotypic variation in BILs. The other two QTLs, qLG-2 and qLG-4, explained 13.4 and 11.6% of the total phenotypic variation, respectively. We also verified the effect of the Kasalath allele of qLG-9 using chromosome segment substitution lines. Furthermore, QTLs for seed dormancy were identified on chromosomes 1, 3, 5, 7 and 11. Based on the comparison of the chromosomal location of QTLs for seed longevity and seed dormancy, these traits seem to be controlled by different genetic factors.
URL [本文引用: 1]

160 recombinant inbred lines from our previous developed population from the cross between Zhenshan 97 and Minghui 63 were used for the genetic analysis of seed aging. Seed germination rate (GR) and seed germination energy (GE) were used as the indices to evaluate the seed aging status. Normal seeds
URL [本文引用: 1]

160 recombinant inbred lines from our previous developed population from the cross between Zhenshan 97 and Minghui 63 were used for the genetic analysis of seed aging. Seed germination rate (GR) and seed germination energy (GE) were used as the indices to evaluate the seed aging status. Normal seeds
DOI:10.1007/s10681-008-9696-3URL [本文引用: 1]

In the present study, quantitative trait loci (QTLs) controlling seed storability based on relative germination rate (%) were dissected using a saturated linkage map and a recombinant inbred lines (RILs) derived from a cross of japonica cultivar Asominori ( Oryza sativa L.) and indica cultivar IR24 ( Oryza sativa L.). A total of three QTLs ( qRGR-1, qRGR-3 and qRGR-9 ) were detected on chromosomes 1, 3 and 9 with LOD score ranging from 3.45 to 6.95 and the phenotypic variance explained from 16.72% to 28.63%. The IR24 alleles were all associated with seed storability at all the three QTLs. The existence of these QTLs was confirmed using IR24 chromosome segment substitution lines (CSSLs) in Asominori genetic background (AIS). By QTL comparative analysis, the QTL, qRGR-9 on chromosomes 9 appeared to be consistent with another rice population, this region may provide an important region for isolating this responsible gene. These results also provide the possibilities of enhancing Seed storability in rice breeding program by marker-assisted selection (MAS) and pyramiding QTLs.
DOI:10.1007/s10681-008-9696-3URL [本文引用: 3]

In the present study, quantitative trait loci (QTLs) controlling seed storability based on relative germination rate (%) were dissected using a saturated linkage map and a recombinant inbred lines (RILs) derived from a cross of japonica cultivar Asominori ( Oryza sativa L.) and indica cultivar IR24 ( Oryza sativa L.). A total of three QTLs ( qRGR-1, qRGR-3 and qRGR-9 ) were detected on chromosomes 1, 3 and 9 with LOD score ranging from 3.45 to 6.95 and the phenotypic variance explained from 16.72% to 28.63%. The IR24 alleles were all associated with seed storability at all the three QTLs. The existence of these QTLs was confirmed using IR24 chromosome segment substitution lines (CSSLs) in Asominori genetic background (AIS). By QTL comparative analysis, the QTL, qRGR-9 on chromosomes 9 appeared to be consistent with another rice population, this region may provide an important region for isolating this responsible gene. These results also provide the possibilities of enhancing Seed storability in rice breeding program by marker-assisted selection (MAS) and pyramiding QTLs.
DOI:10.1111/pbr.12264URL [本文引用: 2]

Abstract Seed storability in rice ( Oryza sativa L.) is an important agronomic trait. We previously showed a quantitative trait locus of seed storability, qSS-9 , on chromosome 9 in a backcross population of ‘Koshihikari’ ( japonica ) / ‘Kasalath’ ( indica ) // ‘Koshihikari’. In this study, fine mapping of the chromosomal location of qSS-9 was performed. Effect of ‘Kasalath’ allele of qSS-9 was validated using a chromosome segment substitution line, SL36, which harboured the target quantitative trait loci (QTL) from ‘Kasalath’ in the genetic background of ‘Nipponbare’ under different ageing treatments in different environments. Subsequently, an F2 population from a cross between ‘Nipponbare’ and SL36 was used for fine mapping of qSS-9 . Simultaneously, four subnear isogenic lines (sub-NILs) that represented different recombination breakpoints across the qSS-9 region were developed from F3 progeny. Finally, the qSS-9 locus was located between the Indel markers Y10 and Y13, which delimit a region of 14702kb in the ‘Nipponbare’ genome. These results provide a springboard for map-based cloning of qSS-9 and possibilities for breeding rice varieties with strong seed storability.
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1008-2239.2010.05.032URL [本文引用: 1]

"宁粳4号"是南京农业大学利用日本优质水稻越光与高产水稻镇稻99杂交选育而成,审定编号为2009040。2010年,南京农业大学在姜堰市娄庄镇布点建立69.23 hm2高产机插示范方;同时,在姜堰市沈高镇河横村省水稻科技综合展示基地参与品种大区展示和小区示范,
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1008-2239.2010.05.032URL [本文引用: 1]

"宁粳4号"是南京农业大学利用日本优质水稻越光与高产水稻镇稻99杂交选育而成,审定编号为2009040。2010年,南京农业大学在姜堰市娄庄镇布点建立69.23 hm2高产机插示范方;同时,在姜堰市沈高镇河横村省水稻科技综合展示基地参与品种大区展示和小区示范,
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
DOI:10.1111/j.1439-0523.2006.01169.xURL [本文引用: 1]

A double haploid population, which consists of 127 lines derived from anther culture of a typical indica and japonica hybrid 'ZYQ8'/'JX17', was used in this study. Seed storability was investigated by using the storage property measured by the difference of seed germination rates before and after treatment of the rice seeds under 40 C and 95% relative humidity for 10 days in a phytotron. Three QTLs related to rice seed storability were detected on chromosomes 9, 11 and 12, with the LOD scores 2.76, 4.83 and 2.54, respectively, together explaining 35.4% of the genetic variation. The 'JX17' allele at qLS-9 and the 'ZYQ8' alleles at qLS-11 and qLS-12 could enhance the rice seed storability. The effects of the 'ZYQ8' alleles of qLS-11 and qLS-12 were also verified using chromosome segment substitution lines.
DOI:10.3389/fpls.2017.00747URLPMID:5433298 [本文引用: 1]

A comparative analysis was carried out of published methods to assess seed viability using 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride (TTC) based assays of seed batches. The tests were carried out on seeds of barley (Hordeum vulgarecv. Optic) as a model. We established that 10% [w/v] trichloroacetic acid (TCA)/methanol is superior to the acetone and methanol-only based methods: allowing the highest recovery of formazan and the lowest background optical density (OD) readings, across seed lots comprising different ratios of viable and dead seeds. The method allowed a linear-model to accurately capture the statistically significant relationship between the quantity of formazan that could be extracted using the method we developed and the seed temperature-response, and seed viability as a function of artificially aged seed lots. Other quality control steps are defined to help ensure the assay is robust and these are reported in a Standard Operating Procedure.
DOI:10.1007/s11738-009-0457-2URL [本文引用: 1]

The triphenyl tetrazolium chloride (TTC) reduction assay was evaluated and improved with maize seed ( Zea mays cv. Zhengdan958). The reduced TTC in embryo was extracted with three kinds of organic solvents: trichloroacetic acid (TCA)/acetone, ethanol, and acetone. The absorbance spectra of the three extracts were similar, with a maximum at 485 nm. The efficiency of TCA/acetone in extracting the reduced TTC was higher than that of acetone and ethanol. A negative correlation between TTC reduction and malondialdehyde content in embryo was demonstrated. The TCA/acetone extraction may be used as a routine protocol for TTC reduction assay of seed vigor in cereal (e.g. maize, rice, wheat and barley) seeds.
DOI:10.1111/j.1439-0523.2005.01109.xURL [本文引用: 1]

Seed longevity varies considerably in cultivated rice ( Oryza sativa L.), but the underlying genetic mechanism of longevity has not been well elucidated. Quantitative trait loci (QTL) that control seed longevity after various periods of seed storage were sought using recombinant inbred lines derived from a combination involving 'Milyang23'(Indica-type) and 'Akihikari' (Japonica-type). In all, 12 QTLs for germination and normal seedling growth were detected as indices of seed longevity on chromosome 7 (one region) and chromosome 9 (two regions) in treated seeds that had been stored under laboratory conditions for 1, 2 or 3 years.'Milyang23' alleles of all QTLs promoted germination and normal seedling growth after all durations of storage. These QTL regions were detected repeatedly in more than one seed condition. Therefore, we infer that these regions control seed longevity.
DOI:10.1007/s10681-014-1304-0URL [本文引用: 1]

Seed aging or deterioration in rice ( Oryza sativa L.) is a major problem for agronomic production and germplasm preservation. Deciphering the genetic mechanism involved in seed aging and improving seed storability is therefore a vital goal for rice breeding. A set of 85 backcross inbred lines derived from the backcross ‘Sasanishiki’ ( japonica cv.)/‘Habataki’ (an indica cv. with strong seed storability)//‘Sasanishiki’ was used here to detect quantitative trait locus (QTL) controlling seed storability. Seeds were treated under natural (conventional storage for 4802months) and artificial aging storage conditions (i.e. increased temperature and relative humidity) and germination rate was used to evaluate seed storability. A total of thirteen QTLs for seed storability were identified on chromosomes 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 11 and 12, respectively. Among them, two QTLs, viz. qSSh - 2 - 1 and qSSh - 2 - 2 , were repeatedly detected in both treatment conditions. In contrast, four ( qSSh - 4 , qSSs - 5 - 1 , qSSs - 5 - 2 and qSSh - 12 ) and seven QTLs ( qSSh - 1 , qSSh - 3 - 1 , qSSh - 3 - 2 , qSSh - 3 - 3 , qSSh - 7 - 1 , qSSh - 7 - 2 and qSSh - 11 ) were detected only once in natural and artificial aging treatments, respectively. The ‘Habataki’-derived alleles were observed to increase seed storability at all the loci except qSSs - 5 - 1 and qSSs - 5 - 2 . The existence of QTLs qSSh - 1 , qSSh - 3 - 1 , qSSh - 3 - 2 , qSSh - 3 - 3 , qSSh - 4 , qSSh - 7 - 1 , qSSh - 7 - 2 and qSSh - 11 was confirmed using Habataki chromosome segment substitution lines in a Sasanishiki genetic background. These results provide an opportunity for map-based cloning of major QTLs for seed storability, thereby gaining an understanding of seed storability in rice and possibilities for its improvement.
DOI:10.1104/pp.108.123141URLPMID:18599647 [本文引用: 1]

A variety of mechanisms have been proposed to account for the extension of life span in seeds (seed longevity). In this work, we used Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) seeds as a model and carried out differential proteomics to investigate this trait, which is of both ecological and agricultural importance. In our system based on a controlled deterioration treatment (CDT), we compared seed samples treated for different periods of time up to 7 d. Germination tests showed a progressive decrease of germination vigor depending on the duration of CDT. Proteomic analyses revealed that this loss in seed vigor can be accounted for by protein changes in the dry seeds and by an inability of the low-vigor seeds to display a normal proteome during germination. Furthermore, CDT strongly increased the extent of protein oxidation (carbonylation), which might induce a loss of functional properties of seed proteins and enzymes and /or enhance their susceptibility toward proteolysis. These results revealed essential mechanisms for seed vigor, such as translational capacity, mobilization of seed storage reserves, and detoxification efficiency. Finally, this work shows that similar molecular events accompany artificial and natural seed aging.
DOI:10.3969/mpb.011.000552URL [本文引用: 1]

人工老化和自然老化是目前研究水稻种子耐储藏性常用的两种方法。本研究分别采用人工老化和自然老化对4个不同水稻品种"(航1号"",航2号",福恢653和云恢290)的种子进行处理。结果表明,进行人工老化后4个水稻品种种子的发芽率都随着老化时间的延长而降低,但不同品种降低的幅度不一样,其中"航1号"和"航2号"降幅最大,人工老化30 d后发芽率降至约8.7%;而福恢653和云恢290降幅相对较小,人工老化30 d后发芽率分别约为24.0%和25.3%。进行自然老化后,"航1号"和"航2号"的发芽率随着自然老化时间的延长而降低,但是福恢653和云恢290自然老化12个月后的发芽率与自然老化6个月后的发芽率相比反而提高。另外,通过比较分析发现人工老化相同时间后不同品种间发芽率差异都显著,但是自然老化6个月后不同品种间的发芽率差异并不显著。因此,人工老化与自然老化的效果并不完全一致,在这两种老化过程中,水稻种子各发生怎样的生理变化且有何差异等问题都有待于进一步的研究和探讨。
DOI:10.3969/mpb.011.000552URL [本文引用: 1]

人工老化和自然老化是目前研究水稻种子耐储藏性常用的两种方法。本研究分别采用人工老化和自然老化对4个不同水稻品种"(航1号"",航2号",福恢653和云恢290)的种子进行处理。结果表明,进行人工老化后4个水稻品种种子的发芽率都随着老化时间的延长而降低,但不同品种降低的幅度不一样,其中"航1号"和"航2号"降幅最大,人工老化30 d后发芽率降至约8.7%;而福恢653和云恢290降幅相对较小,人工老化30 d后发芽率分别约为24.0%和25.3%。进行自然老化后,"航1号"和"航2号"的发芽率随着自然老化时间的延长而降低,但是福恢653和云恢290自然老化12个月后的发芽率与自然老化6个月后的发芽率相比反而提高。另外,通过比较分析发现人工老化相同时间后不同品种间发芽率差异都显著,但是自然老化6个月后不同品种间的发芽率差异并不显著。因此,人工老化与自然老化的效果并不完全一致,在这两种老化过程中,水稻种子各发生怎样的生理变化且有何差异等问题都有待于进一步的研究和探讨。
URL [本文引用: 1]

react-text: 429 Endogenous tocochromanols in extracted lipids from rice brans of the five cultivars were determined by high-performance liquid chromatography, and were investigated in relation to the fatty acid (FA) distribution of triacylglycerols (TAG) and phospholipids (PL). The dominant tocols were α-tocopherol and γ-tocotrienol, followed by α-tocotrienol and with much smaller amounts of γ-tocopherol and... /react-text react-text: 430 /react-text [Show full abstract]
