 ,1,*, 彭振英
,1,*, 彭振英 ,1,2,*
,1,2,*Structure and expression analysis of the members of peanut annexin gene family
WANG Hui-Min1, LI Xin-Guo2, WAN Shu-Bo3, ZHANG Zhi-Meng4, DING Hong4, LI Guo-Wei2, GAO Wen-Wei ,1,*, PENG Zhen-Ying
,1,*, PENG Zhen-Ying ,1,2,*
,1,2,*通讯作者:
收稿日期:2018-04-19接受日期:2018-10-8网络出版日期:2018-11-05
| 基金资助: |
Received:2018-04-19Accepted:2018-10-8Online:2018-11-05
| Fund supported: |
作者简介 About authors
E-mail:whuiminyspa@163.com。

摘要
关键词:
Abstract
Keywords:
PDF (3241KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
本文引用格式
王慧敏, 李新国, 万书波, 张智猛, 丁红, 李国卫, 高文伟, 彭振英. 花生膜联蛋白基因家族成员的结构和表达分析[J]. 作物学报, 2019, 45(3): 390-400. doi:10.3724/SP.J.1006.2019.84056
WANG Hui-Min, LI Xin-Guo, WAN Shu-Bo, ZHANG Zhi-Meng, DING Hong, LI Guo-Wei, GAO Wen-Wei, PENG Zhen-Ying.
膜联蛋白(annexin)是一类钙依赖性磷脂结合蛋白, 广泛存在于除酵母外的真核生物细胞中, 在进化上属于保守的多基因家族[1]。来源于脊椎动物、无脊椎动物、真菌和单细胞真核生物、植物和原生生物的 annexin被分为 A、B、C、D、E五大类[2], 动物annexin属于A类和B类, 参与细胞中的胞饮、胞吐、细胞骨架、离子通道、细胞增殖、细胞凋亡等多种重要的功能调节及多种信号调节[3,4]。植物annexin属于D类, 约占植物总蛋白含量的0.1%[5], 与动物annexin在分子量、氨基酸序列及钙离子与磷脂结合的能力上, 具有较高的同源性[2]。
目前, 动物annexin的研究主要集中在肺癌[6]、胃癌[7]、卵巢癌[8]、结直肠癌(CRC)[5]等相关疾病上, 如研究annexin在肿瘤细胞中的表达水平及其与临床特征的相关性[6]。ANXA3与肿瘤细胞的化疗药物有关, 对新药开发与新疗法探究有重要意义[9]; Annexin A2能够激活纤溶系统, 调控细胞骨架和重肌动蛋白, 在肿瘤侵袭和转移中具有非常重要的作用[10]。
植物annexin研究起步晚于动物, 但是近几年取得了初步进展。研究表明, 植物annexin参与了细胞多个生命过程, 对许多物质的合成途径具有重要的调节作用。如小麦TaAnn10在小麦花药中特异表达, 但是在温敏核不育系中不能被低温诱导表达, 表明TaAnn10特异性下调与小麦雄性不育具有相关性[11]; 棉花GhFAnnxA影响棉纤维的伸长, 并参与次生细胞壁的生物合成[12]。植物annexin基因家族庞大, 其家族成员各自具有不同的功能分工和时空表达模式。植物annexin的表达具有组织特异性, 在植物生长的各个阶段、不同器官、组织中的表达模式各有不同, 并且参与植物代谢和生长发育的调节过程[13]。拟南芥中8个annexin基因在各组织部位的表达水平各不相同, 其中AnnAt4只在幼苗下胚轴表达, 而AnnAt5主要在幼苗胚轴和花丝中表达[14]。
Annexin亚细胞定位的多样性也反应出其功能的多样性, 其定位与胞质中的Ca2+浓度、细胞所处pH值以及外界环境有关[15,16]。Annexin通常为胞质蛋白, 具有可溶型和结合型两种形式。Annexin常常和液泡、细胞核、质膜以及高尔基体等结合在一起[17,18,19]。Annexin也能够可逆地与细胞骨架组成成分或介导细胞和胞外基质间互作的蛋白结合。褚翠萍等[16]研究表明, 拟南芥中annexin2可能通过微丝骨架调节与介导的囊泡运输参与细胞分泌活动。植物annexin的表达受各种生物及非生物胁迫的影响, 且逆境胁迫会影响annexin的亚细胞定位。欧洲甜瓜受到机械损伤时, 薄壁细胞中的annexin 会从胞质中重新定位于质膜上[20]。
花生是世界范围内广泛种植的油料和经济作物之一, 在国民经济占有重要地位。目前关于花生的研究多集中在产量和品质上, 而关于抗逆性研究进展缓慢。早期研究主要集中在抗逆性综合评价及抗逆种质筛选上, 而关于抗性机制研究相对较少。目前花生全基因组测序工作已经完成[21], 为系统研究花生的功能基因奠定了基础。本课题组王靖从花生“鲁花14”中克隆了2个花生annexin基因, AnnAh1和AnnAh2, 并用烟草进行了耐盐性检验, 发现AnnAh2在盐胁迫下表达下调[22]。何美敬等[23]从花生中克隆获得6个annexin基因, 发现它们在盐、旱、重金属、低温和激素处理下表达量均发生了改变。然而到目前为止, 有关花生annexin基因在非生物胁迫中的作用机制还没有得以系统研究。本文通过对AnnAh进行全基因组生物信息学分析, 并利用转录组数据分析其表达模式和可变剪接, 以期为深入研究其功能和调控机制奠定基础。
1 材料与方法
1.1 AnnAh全基因组检索以及其他物种annexin获得
运用“annexin”关键词在花生基因组数据库(https://www.peanutbase.org/)中搜索, 获得30个anneixn家族基因(表1), 命名为AnnAh (Annexin of Arachis hypogaea)。运用“annexin”关键词在NCBI (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/)上搜索其他物种annexin基因并下载其蛋白序列。搜索物种为拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana, Ath)、大豆(Glycine max, Gma)、苜蓿(Medicago truncatula, Mtr)、向日葵(Helianthus annuus, Han)、谷子(Setaria italica, Sit)、水稻(Oryza sativa, Osa)、玉米(Zea mays, Zma)、卷柏(Selaginella moellendorffii, Smo)、伪矮海链藻(Thalassiosira pseudonana, Tps)、三角褐指藻(Phaeodactylum tricornutum, Ptr)、绿色鞭毛藻(Ostreococcus lucimarinus, Olu)、水蕨(Ceratopteris richardii, Cri)和小立碗藓(Physcomitrella patens, Ppa), 对以上物种名缩写为大写属的首字母加小写种的前2个字母。命名方法为其蛋白序列号加物种名缩写(图1)。Table 1
表1
表1Anneixn家族基因
Table 1
| 基因名称 Gene name | 染色体位置 Chr. position | 氨基酸个数 Amino acid number | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization | 蛋白完整性 Protein integrity | Annexin 结构域 Annexin domain | 重复序列 Repetitive sequence | 其他结构域 Other domains |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aradu.V26BD | Aradu.A03 | 279 | C | 完整 Complete | 4 | 4 | 0 |
| Aradu.86DER | Aradu.A03 | 286 | – | 不完整 Incomplete | 4 | 3 | 0 |
| Aradu.KJ1YM | Aradu.A04 | 274 | – | 不完整 Incomplete | 3 | 2 | 0 |
| Aradu.3L5NK | Aradu.A05 | 315 | C | 完整 Complete | 4 | 4 | 0 |
| Aradu.WYZ5E | Aradu.A05 | 323 | C | 不完整 Incomplete | 4 | 4 | 0 |
| Aradu.9BC7H | Aradu.A07 | 342 | C | 不完整 Incomplete | 4 | 4 | 0 |
| Aradu.23XWK | Aradu.A08 | 309 | C | 不完整 Incomplete | 3 | 3 | 0 |
| Aradu.N8MUP | Aradu.A08 | 279 | – | 不完整 Incomplete | 3 | 3 | 0 |
| Aradu.4J11T | Aradu.A08 | 339 | – | 不完整 Incomplete | 3 | 3 | 0 |
| Aradu.S16C5 | Aradu.A08 | 321 | – | 完整 Complete | 4 | 4 | 0 |
| Aradu.SCC75 | Aradu.A10 | 266 | C | 不完整 Incomplete | 3 | 3 | 0 |
| Aradu.IZQ3Z | Aradu.A10 | 315 | C | 完整 Complete | 4 | 4 | 0 |
| Aradu.MBZ2M | Aradu.A10 | 333 | – | 完整 Complete | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| Araip.1LR8I | Araip.B02 | 89 | C | 不完整 Incomplete | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| Araip.KR6F4 | Araip.B03 | 323 | – | 完整 Complete | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Araip.X0F2S | Araip.B03 | 317 | – | 完整 Complete | 4 | 4 | 0 |
| Araip.CCM9G | Araip.B03 | 286 | – | 不完整 Incomplete | 4 | 3 | 0 |
| Araip.RGY04 | Araip.B04 | 142 | C | 不完整 Incomplete | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Araip.R8WRM | Araip.B04 | 207 | – | 不完整 Incomplete | 3 | 2 | 0 |
| Araip.HD6QL | Araip.B05 | 316 | C | 完整 Complete | 4 | 4 | 0 |
| Araip.0MR1X | Araip.B05 | 315 | C | 完整 Complete | 4 | 4 | 0 |
| Araip.FX5SI | Araip.B07 | 316 | C | 完整 Complete | 4 | 4 | 0 |
| Araip.J58EQ | Araip.B08 | 135 | C | 不完整 Incomplete | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| Araip.YGP4J | Araip.B08 | 315 | – | 完整 Complete | 3 | 3 | 0 |
| Araip.6KP6U | Araip.B08 | 295 | – | 完整 Complete | 3 | 3 | 0 |
| Araip.Y8EDR | Araip.B08 | 321 | – | 完整 Complete | 4 | 4 | 0 |
| Araip.X9BIG | Araip.B10 | 317 | C | 完整 Complete | 4 | 4 | 0 |
| Araip.Z0Q6Q | Araip.B10 | 311 | C | 完整 Complete | 4 | 3 | 0 |
| Araip.WA456 | Araip.B10 | 315 | C | 完整 Complete | 4 | 3 | 0 |
| Araip.RPP1M | Araip.B10 | 364 | – | 完整 Complete | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| Aradu.V26BD | Aradu.A03 | 279 | C | 完整 Complete | 4 | 4 | 0 |
| Aradu.86DER | Aradu.A03 | 286 | – | 不完整 Incomplete | 4 | 3 | 0 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
图1
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图1植物annexin蛋白聚类分析
红色: 双子叶植物; 绿色: 单子叶植物; 黑色: 低等植物; 黑色圆点: AnnAhs。
Fig. 1Phylogenetic analysis of plant annexins
Red: dicotyledonous; green: monocotyledonous; black: lower plants; black dot: AnnAhs.
1.2 AnnAh生物信息学分析
利用Mega5.0软件构建annexin蛋白序列进化树, 构建方法为邻近法。用GSDS (http://gsds.cbi.pku.edu.cn/)在线软件分析AnnAhs基因结构。利用TMHMM (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TMHMM/)在线软件分析AnnAhs跨膜结构域。在NCBI的Protein BLAST (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi)上进行AnnAhs蛋白序列完整性分析。利用MEME (http://meme-suite.org/)和NCBI的Conserved domains (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih. gov/Structure/cdd/wrp)在线软件分析AnnAhs保守结构域。利用Softberry (http://linux1.softberry.com/berry)在线软件进行AnnAhs亚细胞定位预测。1.3 AnnAhs的表达模式和可变剪切分析
分别取花生品种“丰花1号”根、叶、果针入土30 d种子(seed1)、果针入土50 d种子(seed2)材料提取总RNA构建cDNA文库, 用链特异性测序方法测序。目前已将原始测序数据上传至NCBI数据库(编号为PRJNA354652)。用Cufflinks软件(http://cufflinks. cbcb.umd.edu/)计算各基因或转录本的表达丰度, 用FPKM 来表示[24]。根据各AnnAhs的FPKM值, 用HemI软件进行表达模式分析。用ASprofile[25]软件对AnnAhs的可变剪切分别进行分类和数量统计。预测的可变剪切形式为TSS, 即转录起始位点可变剪切; TTS为转录终止位点可变剪切; SKIP为外显子跳跃; IR为内含子滞留; AE为可变外显子5'或3'端可变剪切。2 结果与分析
2.1 AnnAh在染色体上的分布
从花生基因组中共检索到30个AnnAhs基因, 其中有12个序列不完整(表1)。它们不均匀地分布在13条染色体上, 其中A基因组中有13个, B基因组中17个。在Araip.B08、Aradu.A08、Araip.B10最多, 各有4个; 在Aradu.A10、Araip.B03各有3个; 在其他8条染色体上分布较少, 分别有1~2个。2.2 植物annexin聚类分析
将AnnAhs与其他植物annexin构建进化树(图10)显示, 植物annexin聚类关系比较复杂, 低等植物、单子叶、双子叶植物annexin间隔分布, AnnAhs穿插其中, 分布于各个分支中, 显示出annexin进化关系的复杂性。在一些次级分支中, 单、双子叶植物annexin聚在一起, 低等植物annexin聚为另一分支; 而在有些小分支中, 高等植物annexin直接和低等植物annexin聚在一起, 如玉米NP_001266716.1和绿色鞭毛藻XP_001420377.1聚在一起, 显示出二者的高度相似性。在各个小分支中, AnnAhs基本上都与双子叶植物annexin聚在一起, 其中与大豆、苜蓿、向日葵亲缘关系较近, 其次是拟南芥。个别AnnAhs与单子叶植物玉米和谷子聚在一起, 如Araip.WA456与玉米XP_008656201.2聚在一起, Araip.R8WRM与谷子XP_004986983.2聚在一起。这些分析结果显示出AnnAhs家族成员的复杂性。
2.3 AnnAhs基因结构分析
由于Araip.J58EQ、Araip.RGY04和Araip.1LR8I序列太短, 故只分析其余27个AnnAhs的基因结构(图2)。分析结果表明, AnnAhs基因序列中至少有2个内含子, 最多有8个内含子, 多数含有5~6个内含子。Aradu.N8MUP、Aradu.WYZ5E、Araip.0MR1X和Araip.6KP6U内含子特别长, 而其外显子序列与其他基因相差并不大, 保守性较强。图2
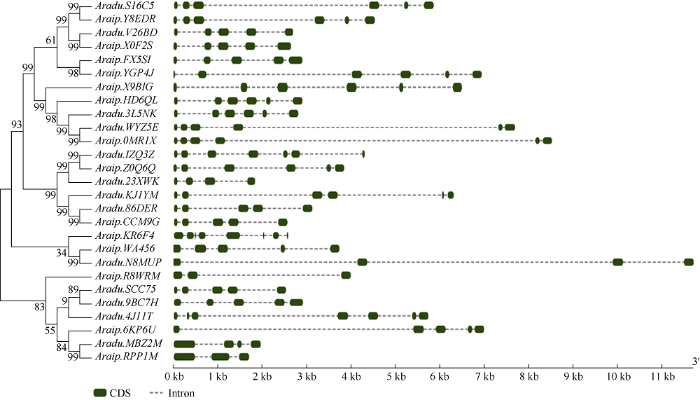 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图2AnnAhs基因结构分析
因部分AnnAhs无UTR, 故均用ORF进行基因结构分析。
Fig. 2Gene structure analysis of AnnAhs
Some of AnnAhs have no UTRs, so the ORF is used to analyze the gene structures.
27个AnnAhs中有9对同源基因, 同源基因间具有类似的基因结构(图2)。如Aradu.S16C5和Araip.Y8EDR为一对同源基因, 它们都具有6个外显子, 但是第3个内含子长度差异较大。Aradu.MBZ2M和Araip.RPPIM分别具有4个和3个外显子, 如果Aradu.MBZ2M第2个内含子发生了滞留, 则会产生一个大外显子, 该大外显子与Araip.RPPIM第2个外显子大小相同。
2.4 AnnAhs跨膜结构域与保守结构域分析
对AnnAhs进行跨膜结构域分析, 发现这30 个AnnAhs均无跨膜结构域, 表明它们均为胞质可溶性蛋白。图3显示, 在motif2中有一个保守“isoleucine- arginine-isoleucine” motif, 即IRI基序[26], 27个AnnAhs均有IRI基序; 在motif4中有一个GXGT基序[27], 15个AnnAhs含有GXGT基序。
图3
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图3AnnAhs的保守结构域分析
Fig. 3Conservative domain analysis of AnnAhs
利用NCBI中Conserved domains 进行分析(表1), 发现大多数AnnAhs有4个annexin结构域, 即4个功能结构域[22]。Aradu.SCC75、Aradu.23XWK、Aradu.N8MUP、Araip.YGP4J、Aradu.4J11T、Araip. 6KP6U、Aradu.KJ1YM和Araip.R8WRM各有3个, Aradu.MBZ2M、Araip.RPP1M、Araip.KR6F4各有2个。另外, Araip.KR6F4还含有2个不同的结构域, 即ALDH_F10_BADH结构域和Ribosomal_L18结构域。前者属于ALDH-SF超家族, 即醛脱氢酶家族, 具有氧化还原酶活性。后者是一个核糖体蛋白, 属于L18家族, 在细胞中与RNA分子的核心结构域结合, 以发挥功能。Araip.KR6F4有此2个结构域说明该基因可能具有这方面的功能。
2.5 AnnAhs亚细胞定位预测分析
对30个AnnAhs进行亚细胞定位预测分析显示, 有16个AnnAhs定位于细胞质(表1), 分别是Aradu.3L5NK、Araip.HD6QL、Aradu.WYZ5E、Araip.0MR1X、Aradu.SCC75、Araip.X9BIG、Aradu.9BC7H、Araip.FX5SI、Aradu.23XWK、Aradu.IZQ3Z、Araip.Z0Q6Q、Araip.WA456、Araip.J58EQ、Araip.RGY04、Araip.1LR8I和Aradu.V26BD, 其余14个定位不明确。2.6 AnnAhs可变剪切分析
根据“丰花1号”转录组数据分析AnnAhs的可变剪接情况(表2)表明, 有11个具有可变剪接现象, 占38%。共检测到TSS、TTS、AE和ES四种可变剪接类型, 分别占15.4%、30.8%、30.8%和23.0%。没有发现IR类型。在根中发生的可变剪切数目最多, 其次是叶中, 种子中最少, 显示出AnnAhs的可变剪接在根系发育以及在应对环境胁迫中的重要作用。Aradu.IZQ3Z在4个组织中均发生了可变剪接, Aradu.KJ1YM在3个组织中均发生了可变剪接, 其余9个只在1~2个组织中发生了可变剪接。Table 2
表2
表2AnnAhs可变剪切分析
Table 2
| 基因名称 Name | 种子前期 Seed1 | 种子后期 Seed2 | 根 Root | 叶 Leaf |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aradu.S16C5 | — | — | TSS | — |
| Aradu.N8MUP | — | — | TSS | — |
| Aradu.3L5NK | — | — | — | TTS |
| Araip.CCM9G | — | TTS, AE | — | TTS, AE |
| Araip.WA456 | — | — | TTS, AE | — |
| Aradu.IZQ3Z | TTS, AE | AE | AE | AE |
| Araip.HD6QL | TSS, ES | TSS, ES | — | — |
| Aradu.KJ1YM | TTS | — | TTS | TTS, AE, ES |
| Araip.Z0Q6Q | — | — | ES | — |
| Araip.R8WRM | — | — | ES | — |
| Araip.RPP1M | — | — | ES | — |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
2.7 AnnAhs表达模式分析
利用“丰花1号”转录组数据中各基因的FPKM值对其表达模式进行分析。其中Aradu.WYZ5E、Araip.0MR1X、Aradu.SCC75、Araip.X9BIG、Aradu.4J11T、Araip.KR6F4、Araip.RGY04在4个组织中FPKM值均为0, 故不予分析。其余23个基因按照FPKM值作图(图4)表明, 各AnnAhs在不同组织中的表达量存在显著差异。总体而言, 各AnnAhs在seed2和根中表达量较高, 其次是seed1, 在叶中表达量较低。其中Aradu.IZQ3Z和Araip.Z0Q6Q在种子中特异性高表达, 说明二者对种子发育的重要性。各AnnAhs基因在根中的表达量显著高于叶中, 显示出AnnAhs在根系发育中的重要作用。图4
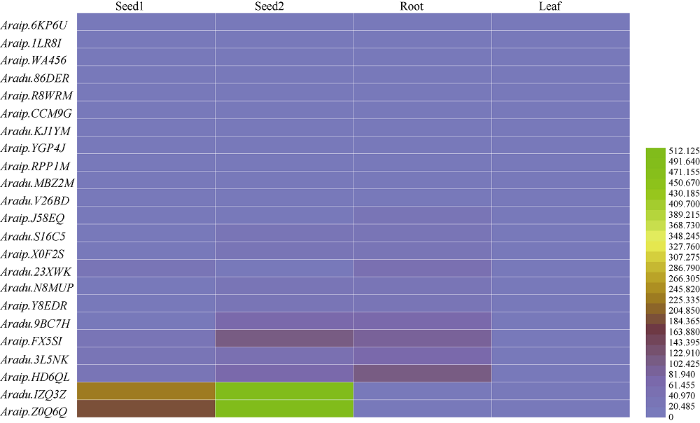 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图4AnnAhs表达模式分析
Fig. 4Expression pattern analysis of AnnAhs
3 讨论
植物anneixn是一个庞大而保守的基因家族[28], 不仅在植物的生长发育中具有重要功能, 还参与抗寒、抗旱及耐盐等多种反应[29]。目前关于植物annexin应对非生物胁迫的研究取得一定进展, 但是其作用机制研究还比较少。本文主要利用花生基因组和转录组数据对AnnAhs进行全基因组系统分析, 可为研究AnnAhs的生理机制与功能提供一定的理论基础。在聚类分析中发现, 植物annexin聚类关系比较复杂, 各类annexin间隔分布, AnnAhs穿插其中。AnnAhs基本上都与双子叶植物annexin聚在一起, 个别AnnAhs与单子叶植物聚在一起, 说明AnnAhs家族基因的复杂性。Jami等[27]对149个植物annexin构建进化树, 并将其分成9个组。并发现, annexin多基因家族似乎随着基因组的复杂而扩大, 可能是与基因复制相关, 而这种扩增意味着该家族可能在植物应对环境胁迫中具有重要作用[27,30]。花生是异源四倍体, 遗传背景复杂, 在整个基因组中含有30个annexin基因, 比其他植物中annexin个数都要多, 可能是在进化过程中通过复制形成的, 类似情况在苔藓、大豆中也有报道[30,31]。
在保守结构域分析中发现AnnAhs都含有 IRI基序, 大部分AnnAhs含有GXGT基序。有研究认为 IRI 可以促成植物annexin与F-actin的结合, F-actin在植物生长发育过程中参与许多重要生命活动, 如细胞分泌、细胞分裂、细胞极性生长、细胞形态维持及物质运输等[32]。含有IRI基序说明这部分annexin可能是通过F-actin而起作用的。在拟南芥annexin家族的8个成员中有3个(AtANN3、AtANN4和AtANN4)不含有IRI基序[33], 说明并不是所有成员都具有IRI 基序, 这部分annexin可能具有其他的调控方式。Araip.KR6F4比较特殊, 还含有ALDH _F10_BADH和Ribosomal_L18结构域。这种现象在annexin蛋白家族中少见, Araip.KR6F4的功能也需要进一步验证与探究。
亚细胞定位对研究蛋白质功能具有重要作用[28,34], 植物annexin在细胞质、质膜、内膜系统以及核膜均有定位, 但是定位于细胞质中的较多些, 可能与其家族蛋白基因在膜功能中起重要作用相关[15]。而且植物annexin的亚细胞定位与细胞质中的Ca2+浓度、细胞所处pH值以及外界环境均有关系[15,16]。拟南芥Ann At2、Ann At3和Ann At6定位于细胞质和细胞核; Ann At5 定位于过氧化物酶体; Ann At7定位于细胞质[33,34]。棉花中AnnGh3和AnnGh6定位于细胞质[35]; MeAnn1定位于木薯体胚细胞的细胞质和细胞核[36]。小麦中的annexin在低温胁迫下, 以p39和p22.5的形式定位于质膜[37]。蒺藜苜蓿MtANN1定位于核膜[38]。芹菜VCaB42 在 Ca2+ 存在时定位于液泡膜[19]。本研究中预测的AnnAhs大部分定位在细胞质中, 少数部分定位不明确, 因此需要进一步用实验来验证。这些结果暗示Annexin成员在不同的细胞生理过程和不同的环境条件下发挥不同作用。
可变剪接是调控真核生物转录组和蛋白质组多样性的重要分子机制, 也是一种在转录后 RNA 水平调控基因表达的重要机制, 在生物发育中具有重要作用[39]。本研究发现有11个AnnAhs在不同组织中发生了可变剪切, 这种现象在苔藓、拟南芥和水稻的annexin中也有报道[27]。据统计, 单子叶植物annexin发生AS的情况较双子叶植物多。水稻中2个annexin的转录本(Os09g23160, Os02g51750)发生了AS, 而玉米种至少有5个annexin基因发生AS。在双子叶植物中, 拟南芥annexin (At5g65020, AnnAt2)发生AS。当然, 关于AS调控annexin的作用机制仍需进一步研究。
表达模式对基因的功能研究具有重要作用。植物annexin在不同组织中的表达模式具有显著差异。褚翠萍[14]对拟南芥中8个annexin基因的表达模式分析表明, Ann At1、Ann At6、Ann At7在幼苗、花和种子中都有表达; Ann At2主要在子叶、胚轴和花萼中表达; Ann At3主要在叶片、幼苗下胚轴和花萼中表达; Ann At4 只在幼苗下胚轴表达; Ann At5主要在幼苗胚轴和花丝中表达; Ann At8 在叶片、花萼和种子中表达; Ann At3、Ann At6、Ann At7、Ann At8 在保卫细胞中表达[34]。这种表达模式的差异反应了不同annexin成员功能分工的差异。又有研究表明, 许多annexin是在根中发挥功能的。例如玉米annexin能够加强玉米根冠原生质体的胞吐作用[40]; Annexin P35在豌豆胚芽和根部的幼嫩区液泡细胞和根冠外围分泌粘液细胞中含量最高[41]; 烟草Ntann12能够调节根的极性运输[42]; MtAnn3在根毛发育中可被细胞分裂素诱导表达[43]。本研究表明, 除了7个AnnAhs没有表达外, 剩余23个AnnAhs的表达模式各不相同, 但是总体而言它们在seed2和根中的表达水平较高, seed1次之, 而在叶片中的表达量最低。这说明不同AnnAhs成员的功能分工是不同的, 如Aradu.IZQ3Z和Araip.Z0Q6Q在seed1和seed2特异性高表达, 显示出二者对种子发育的重要性; Araip.HD6QL在根中的表达量最高, 表明其在根发育中具有重要作用; 不同AnnAhs在种子发育不同阶段所起的作用也是不同的, 随着种子发育的日趋成熟, 种子内部各个器官逐渐分化出来, 越来越多的AnnAhs参与其中, 表达量也随之增加。
4 结论
本文利用生物信息学方法探讨了花生膜联蛋白基因家族成员的基因结构、跨膜结构域、保守结构域与亚细胞定位的特点, 并利用转录组数据对其进行了可变剪接以及表达模式分析, 为以后进行花生膜联蛋白基因的克隆与功能验证提供了一定的理论基础。参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
DOI:10.1007/s10142-018-0614-zURL [本文引用: 1]

Annexins are multifunctional proteins with roles in plant development and alleviation of stress tolerance. In the present communication, we report on the effect of heterologous expression of Brassica...
URL [本文引用: 2]

植物膜联蛋白属于D类膜联蛋白是在植物中的一类钙和磷脂结合蛋白。植物膜联蛋白约占植物总蛋白含量的0.1%,与动物膜联蛋白在分子量、氨基酸序列及Ca~(2+)与磷脂结合的能力上,都拥有较高的同源性。植物膜联蛋白的亚细胞定位具有多样性,与胞质Ca~(2+)浓度、细胞所处pH、植物组织及外界环境有关。植物膜联蛋白的表达具有组织特异性,且受到各种生物及非生物因子在转录及翻译后水平的调控。植物膜联蛋白具有与植物肌动蛋白结合、参与钙离子通道形成、膜动力学功能、具有ATPase/GTPase及过氧化物酶活性等生物功能,在植物生长发育及响应逆境胁迫过程中起重要作用。本综述从植物膜联蛋白的进化、结构、亚细胞定位、表达调控和生物学功能方面进行综述,旨在为深入研究植物膜联蛋白的功能及其应用提供参考。
URL [本文引用: 2]

植物膜联蛋白属于D类膜联蛋白是在植物中的一类钙和磷脂结合蛋白。植物膜联蛋白约占植物总蛋白含量的0.1%,与动物膜联蛋白在分子量、氨基酸序列及Ca~(2+)与磷脂结合的能力上,都拥有较高的同源性。植物膜联蛋白的亚细胞定位具有多样性,与胞质Ca~(2+)浓度、细胞所处pH、植物组织及外界环境有关。植物膜联蛋白的表达具有组织特异性,且受到各种生物及非生物因子在转录及翻译后水平的调控。植物膜联蛋白具有与植物肌动蛋白结合、参与钙离子通道形成、膜动力学功能、具有ATPase/GTPase及过氧化物酶活性等生物功能,在植物生长发育及响应逆境胁迫过程中起重要作用。本综述从植物膜联蛋白的进化、结构、亚细胞定位、表达调控和生物学功能方面进行综述,旨在为深入研究植物膜联蛋白的功能及其应用提供参考。
.
[本文引用: 1]
.
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1002/eji.201646551URLPMID:27995621 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract Gout is a self-limited inflammatory disease caused by deposition of monosodium urate (MSU) crystals in the joints. Resolution of inflammation is an active process leading to restoration of tissue homeostasis. Here, we studied the role of Annexin A1 (AnxA1), a glucocorticoid-regulated protein that has anti-inflammatory and proresolving actions, in resolution of acute gouty inflammation. Injection of MSU crystals in the knee joint of mice induced inflammation that was associated with expression of AnxA1 during the resolving phase of inflammation. Neutralization of AnxA1 with antiserum or blockade of its receptor with BOC-1 (nonselective) or WRW 4 (selective) prevented the spontaneous resolution of gout. There was greater neutrophil infiltration after challenge with MSU crystals in AnxA1 knockout mice (AnxA1 -/- ) and delayed resolution associated to decreased neutrophil apoptosis and efferocytosis. Pretreatment of mice with AnxA1-active N-terminal peptide (Ac 2-26 ) decreased neutrophil influx, IL-10205, and CXCL1 production in periarticular joint. Posttreatment with Ac 2-26 decreased neutrophil accumulation, IL-10205, and hypernociception, and improved the articular histopathological score. Importantly, the therapeutic effects of Ac 2-26 were associated with increased neutrophils apoptosis and shortened resolution intervals. In conclusion, AnxA1 plays a crucial role in the context of acute gouty inflammation by promoting timely resolution of inflammation. 0008 2016 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
DOI:10.3390/ijms18040863URLPMID:5412444 [本文引用: 2]

Annexins are an evolutionary conserved superfamily of proteins able to bind membrane phospholipids in a calcium-dependent manner. Their physiological roles are still being intensively examined and it seems that, despite their general structural similarity, individual proteins are specialized toward specific functions. However, due to their general ability to coordinate membranes in a calcium-sensitive fashion they are thought to participate in membrane flow. In this review, we present a summary of the current understanding of cellular transport in plant cells and consider the possible roles of annexins in different stages of vesicular transport.
DOI:10.12659/MSM.905372URLPMID:29306955 [本文引用: 2]

Gastric cancer (GC) is one of the most common malignant tumors in the world and in China the incidence and mortality rates of gastric cancer are the second highest among all forms of cancer. Annexin A11 (ANXA11) is a member of the annexins family. Previous studies have shown that ANXA11 participates in many cellular functions and has significant influence on ovarian, breast, liver, and colorectal cancer. However, the expression and biological functions of ANXA11 in GC are still unknown. A total of 63 paired gastric cancer tissues and matched adjacent mucosa were used to measure the ANXA11 levels and its correlation with clinical characteristics. We carried out the biological functions and underlying mechanism study using SGC-7901and AGS cell lines. The expression of ANXA11 in cancer tissues was higher than in adjacent mucosa at mRNA and protein levels. In clinicopathological analysis, we found that increased expression of ANXA11 was significantly associated with tumor size, tumor infiltration, local lymph node metastasis, TNM staging, and vascular invasion. Small interfering RNA (siRNA) silencing of ANXA11 inhibits cell proliferation, colony formation, migration, and invasion through the AKT/GSK-3 pathway. ANXA11 plays a critical role in regulating GC proliferation, migration, and invasion via the AKT/GSK-3 pathway, and can potentially be used as a prognostic factor and therapeutic target for gastric cancer patients.
DOI:10.1016/j.nano.2016.11.015URLPMID:27890659 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract A novel modified nucleic acid nanoparticle harboring an annexin A2 aptamer for ovarian cancer cell targeting and a GC rich sequence for doxorubicin loading is designed and constructed. The system utilizes a highly stable three-way junction (3WJ) motif from phi29 packaging RNA as a core structure. A phosphorothioate-modified DNA aptamer targeting annexin A2, Endo28, was conjugated to one arm of the 3WJ. The pRNA-3WJ motif retains correct folding of attached aptamer, keeping its functions intact. It is of significant utility for aptamer-mediated targeted delivery. The DNA/RNA hybrid nanoparticles remained intact after systemic injection in mice and strongly bound to tumors with little accumulation in healthy organs 6 h post-injection. The Endo28-3WJ-Sph1/Dox intercalates selectively enhanced toxicity to annexin A2 positive ovarian cancer cells in vitro. The constructed RNA/DNA hybrid nanoparticles can potentially enhance the therapeutic efficiency of doxorubicin at low doses for ovarian cancer treatment through annexin A2 targeted drug delivery. Copyright 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
URLPMID:29393380 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract Annexin0002A9 (ANXA9), a member of annexin family, has been reported be associated with colorectal cancer (CRC) carcinogenesis. However, the clinical significance of ANXA9 in CRC, particularly its correlation to invasion and metastasis remains ambiguous. The aim of the present study was to investigate the significance of ANXA9 in CRC and understand the molecular mechanism of ANXA9 in CRC invasion and metastasis. Expression levels of the ANXA9 protein in CRC tissues were detected using immunohistochemistry (IHC), and the clinical and prognostic value of ANXA9 was investigated. ANXA9090007siRNA was utilized to investigate the effect and molecular mechanism of ANXA9 in HCT116 cells. The IHC result demonstrated that the positivity rate of the ANXA9 protein in CRC tissue was significantly higher than that in adjacent mucosa (P<0.05), which was consistent with the western blot results. ANXA9 protein expression levels are associated with invasion depth and lymphatic metastasis. Furthermore, patients with ANXA9090007positive expression demonstrated a poor prognosis and ANXA9 was an independent risk factor for survival (P<0.05). After inhibiting ANXA9 in HCT116 cells, the activity and metastatic and invasion capacity of cells decreased significantly, and expression levels of ADAM metallopeptidase domain000217 and matrix metallopeptidase 9 were significantly downregulated, while the expression levels of tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases0900071 and E090007cadherin were upregulated (P<0.05). Thus, positive ANXA9 expression may present as a novel marker for predicting poor prognosis in CRC patients, and ANXA9 may promote the invasion and metastasis of CRC by regulating invasion and metastasis090007associated genes.
URL [本文引用: 1]

乳腺癌是女性最常见的恶性肿瘤,发病率和死亡率都处于较高水平,严重威胁女性健康。虽然近年来随着研究的不断深入,乳腺癌的诊断和治疗手段都取得了极大地进步,但是仍经常观察到部分乳腺癌对现有治疗手段(放疗,化疗,激素治疗)存在耐受或响应差的现象,这样的现实迫使我们不断寻找新的治疗方法和更有效的靶点。肿瘤干细胞是近年来提出的理论,该理论认为肿瘤干细胞是肿瘤内一群具有自我更新能力和分化潜能的细胞,在癌症形成和生长中发挥着决定性作用,而且由于其对传统治疗的有较强的耐受性,因而也是导致癌症复发转移的根源。因此,研究肿瘤干细胞的调控机制的研究是解决癌症治疗难题必不可少的前提。乳腺癌患者来源异种移植瘤模型(Patient-derived tumor xenograft, PDX)是使用病人来源的乳腺肿瘤组织建立的小鼠原位荷瘤模型,能够很大程度反映病人的信息,从而有较高的应用价值。本课题主要研究了乳腺肿瘤干细胞的调控机制及其临床应用,同时进行了部分工作对PDX模型的建立方法进行了优化了。研究内容主要分为以下两个部分:1、我们发现膜联蛋白A3 (AnnexinA3,ANXA3)在乳腺肿瘤组织中高表达,并与病人的预后呈现负相关。在进一步的功能实验中我们发现在乳腺肿瘤细胞中使用shRNA干扰ANXA3的表达后虽然抑制了细胞侵袭但促进了细胞的增殖能力。进一步的研究中我们发现敲低ANXA3是通过抑制间充质样乳腺肿瘤干细胞的同时富集上皮样乳腺肿瘤干细胞实现的。我们还发现干扰ANXA3后可以通过上调IκBα抑制NF-κB通路,这与敲低ANXA3所诱导的MET过程相关。最后我们发现干扰ANXA3后能够促进化疗药物在肿瘤细胞内的蓄积从而提高化疗药物的疗效,小鼠治疗实验显示敲低ANXA3表达的同时施加化疗药物处理,能够同时抑制乳腺肿瘤的转移和生长。2、我们对已有的乳腺癌PDX模型构建方法进行了优化,改进了组织处理和植瘤操作,提高了模型构建的成功率,成功建立了十二例不同亚型的中国乳腺癌患者来源异种移植瘤模型。使用小鼠对移植瘤模型进行传代,免疫组化染色结果显示,各代间组织形态与分子表型均与原代组织保持一致,证明所构建模型均可稳定传代,且很大程度能够维持病人原有病理信息,可用于新药开发与新疗法探究。
URL [本文引用: 1]

乳腺癌是女性最常见的恶性肿瘤,发病率和死亡率都处于较高水平,严重威胁女性健康。虽然近年来随着研究的不断深入,乳腺癌的诊断和治疗手段都取得了极大地进步,但是仍经常观察到部分乳腺癌对现有治疗手段(放疗,化疗,激素治疗)存在耐受或响应差的现象,这样的现实迫使我们不断寻找新的治疗方法和更有效的靶点。肿瘤干细胞是近年来提出的理论,该理论认为肿瘤干细胞是肿瘤内一群具有自我更新能力和分化潜能的细胞,在癌症形成和生长中发挥着决定性作用,而且由于其对传统治疗的有较强的耐受性,因而也是导致癌症复发转移的根源。因此,研究肿瘤干细胞的调控机制的研究是解决癌症治疗难题必不可少的前提。乳腺癌患者来源异种移植瘤模型(Patient-derived tumor xenograft, PDX)是使用病人来源的乳腺肿瘤组织建立的小鼠原位荷瘤模型,能够很大程度反映病人的信息,从而有较高的应用价值。本课题主要研究了乳腺肿瘤干细胞的调控机制及其临床应用,同时进行了部分工作对PDX模型的建立方法进行了优化了。研究内容主要分为以下两个部分:1、我们发现膜联蛋白A3 (AnnexinA3,ANXA3)在乳腺肿瘤组织中高表达,并与病人的预后呈现负相关。在进一步的功能实验中我们发现在乳腺肿瘤细胞中使用shRNA干扰ANXA3的表达后虽然抑制了细胞侵袭但促进了细胞的增殖能力。进一步的研究中我们发现敲低ANXA3是通过抑制间充质样乳腺肿瘤干细胞的同时富集上皮样乳腺肿瘤干细胞实现的。我们还发现干扰ANXA3后可以通过上调IκBα抑制NF-κB通路,这与敲低ANXA3所诱导的MET过程相关。最后我们发现干扰ANXA3后能够促进化疗药物在肿瘤细胞内的蓄积从而提高化疗药物的疗效,小鼠治疗实验显示敲低ANXA3表达的同时施加化疗药物处理,能够同时抑制乳腺肿瘤的转移和生长。2、我们对已有的乳腺癌PDX模型构建方法进行了优化,改进了组织处理和植瘤操作,提高了模型构建的成功率,成功建立了十二例不同亚型的中国乳腺癌患者来源异种移植瘤模型。使用小鼠对移植瘤模型进行传代,免疫组化染色结果显示,各代间组织形态与分子表型均与原代组织保持一致,证明所构建模型均可稳定传代,且很大程度能够维持病人原有病理信息,可用于新药开发与新疗法探究。
.
URL [本文引用: 1]

统计数据显示在美国女性中因肿瘤所致死亡病因中卵巢癌排名第五位,同时也是死亡率最高的妇科恶性肿瘤。预计在2017年美国新发卵巢癌病例数量为22,440例,死亡数量为14,080例。卵巢癌致死率高的主要的原因在于70%的患者在患病最初就发生了腹腔转移。在过去的20年,以紫杉醇、铂类为基础的化疗,腹腔灌注化疗、靶向药物新型单抗如贝伐单抗等的应用提高了早期患者的总生存率。但是卵巢
URL [本文引用: 1]

统计数据显示在美国女性中因肿瘤所致死亡病因中卵巢癌排名第五位,同时也是死亡率最高的妇科恶性肿瘤。预计在2017年美国新发卵巢癌病例数量为22,440例,死亡数量为14,080例。卵巢癌致死率高的主要的原因在于70%的患者在患病最初就发生了腹腔转移。在过去的20年,以紫杉醇、铂类为基础的化疗,腹腔灌注化疗、靶向药物新型单抗如贝伐单抗等的应用提高了早期患者的总生存率。但是卵巢
DOI:10.1186/s12864-016-2750-yURLPMID:4884362 [本文引用: 1]

Annexins are an evolutionarily conserved multigene family of calcium-dependent phospholipid binding proteins that play important roles in stress resistance and plant development. They have been relatively well characterized in model plants Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) and rice (Oryza sativa), but nothing has been reported in hexaploid bread wheat (Triticum aestivum) and barely (Hordeum vulgare), which are the two most economically important plants. Based on available genomic and transcriptomic data, 25 and 11 putative annexin genes were found throughin silicoanalysis in wheat and barley, respectively. Additionally, eight and 11 annexin genes were identified from the draft genome sequences ofTriticum urartuandAegilops tauschii, progenitor for the A and D genome of wheat, respectively. By phylogenetic analysis, annexins in these four species together with other monocots and eudicots were classified into six different orthologous groups. Pi values of each ofAnn1 12genes amongT. aestivum,T. urartu,A. tauschiiandH. vulgarespecies was very low, with the exception ofAnn2andAnn5genes.Ann2gene has been under positive selection, butAnn6andAnn7have been under purifying selection among the four species in their evolutionary histories. The nucleotide diversities ofAnn1 12genes in the four species were 0.52065, 0.59239, 0.60691 and 0.53421, respectively. No selective pressure was operated on annexin genes in the same species. Gene expression patterns obtained by real-time PCR and re-analyzing the public microarray data revealed differential temporal and spatial regulation of annexin genes in wheat under different abiotic stress conditions such as salinity, drought, cold and abscisic acid. Among those genes,TaAnn10is specifically expressed in the anther but fails to be induced by low temperature in thermosensitive genic male sterile lines, suggesting that specific down-regulation ofTaAnn10is associated with conditional male sterility in wheat. This study analyzed the size and composition of the annexin gene family in wheat and barley, and investigated differential tissue-specific and stress responsive expression profiles of the gene family in wheat. These results provided significant information for understanding the diverse roles of plant annexins and opened a new avenue for functional studies of cold induced male sterility in wheat. The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s12864-016-2750-y) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
DOI:10.1104/pp.16.00597URL [本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]

高温是影响植物生长和繁殖的最重要的环境压力之一。由于其固着生长的特性,植物更容易受到温度变动的影响。为应对高温对其产生的威胁,植物进化出了一系列的适应机制。膜联蛋白是一类多功能的蛋白,该蛋白家族的特点在于它们能结合钙离子和带负电荷的脂类。越来越多的证据表明植物膜联蛋白可能具有过氧化物酶的活性,暗示其与植物逆境应答相关,然而,植物膜联蛋白在高温逆境中的作用还未见报道。 目前关于植物高温耐性的分子生物学研究已有不少,但极少是以种子为材料进行的,尽管植物种子是具有重要价值的基因材料。曾有研究指出莲种子具有耐受极端高温的能力,为寻找种子适应机制中的新基因/蛋白提供了宝贵的材料。本研究采用比较蛋白质组学的方法以寻找高温胁迫信号通路中的新蛋白,由此在莲种子中鉴定到膜联蛋白,将其命名为NnANN1,并研究了该蛋白在高温逆境以及种子活力中的功能。本研究的主要结果如下: 1.为研究莲种子的基础耐热性,用高温处理成熟莲种子,结果约50%种子在90°C处理24h后仍能萌发。为鉴定莲种子中的高温响应蛋白,从未处理的对照种子和90°C处理24h的种子的胚中提取蛋白经双向电泳分离用于比较蛋白质组学研究。10个高温处理后含量上调2倍以上的蛋白得到鉴定,其中大部分为能量代谢相关或逆境相关蛋白。在这些热响应蛋白中,选取被鉴定为膜联蛋白的蛋白点2作进一步研究。 2.实时定量PCR(qRT-PCR)和蛋白质印记(western blot)的结果显示,与未经处理的莲种子相比,经高温处理的种子中NnANN1的表达在mRNA水平和蛋白水平都有大幅提高,证实与上述蛋白质组学的结果一致,NnANN1是热响应蛋白。亚细胞定位分析发现NnANN1表现出典型的细胞质定位模式,qRT-PCR分析发现NnANN1主要在种子发育和萌发过程中大量表达,暗示该蛋白可能在种子发育和萌发中发挥作用。 3.为证实NnANN1在体内的保护作用,在大肠杆菌细胞和植物种子中进行了功能研究。结果表明,与对照相比,在高温逆境下,NnANN1转化的大肠杆菌细胞和拟南芥的种子耐热性提高。此外,加速老化实验表明NnANN1的表达提高了转基因拟南芥种子的活力。相反,与野生型种子相比,拟南芥同源基因AtANN1、AtANN2的T-DNA插入突变株的种子对于高温逆境和加速老化处理表现得更为敏感。NnANN1转基因种子中观察到过氧化物酶活性提高,并伴随活性氧(ROS)释放水平的降低,这可能帮助阐释NnANN1在体内的保护功能。综上所述,本研究实验结果表明NnANN1在耐热性和种子活力中发挥着重要功能,支持NnANN1在清除ROS中的作用,为研究植物高温应答的分子机制,提高作物耐热性和种子活力开拓了新的可能性。
URL [本文引用: 1]

高温是影响植物生长和繁殖的最重要的环境压力之一。由于其固着生长的特性,植物更容易受到温度变动的影响。为应对高温对其产生的威胁,植物进化出了一系列的适应机制。膜联蛋白是一类多功能的蛋白,该蛋白家族的特点在于它们能结合钙离子和带负电荷的脂类。越来越多的证据表明植物膜联蛋白可能具有过氧化物酶的活性,暗示其与植物逆境应答相关,然而,植物膜联蛋白在高温逆境中的作用还未见报道。 目前关于植物高温耐性的分子生物学研究已有不少,但极少是以种子为材料进行的,尽管植物种子是具有重要价值的基因材料。曾有研究指出莲种子具有耐受极端高温的能力,为寻找种子适应机制中的新基因/蛋白提供了宝贵的材料。本研究采用比较蛋白质组学的方法以寻找高温胁迫信号通路中的新蛋白,由此在莲种子中鉴定到膜联蛋白,将其命名为NnANN1,并研究了该蛋白在高温逆境以及种子活力中的功能。本研究的主要结果如下: 1.为研究莲种子的基础耐热性,用高温处理成熟莲种子,结果约50%种子在90°C处理24h后仍能萌发。为鉴定莲种子中的高温响应蛋白,从未处理的对照种子和90°C处理24h的种子的胚中提取蛋白经双向电泳分离用于比较蛋白质组学研究。10个高温处理后含量上调2倍以上的蛋白得到鉴定,其中大部分为能量代谢相关或逆境相关蛋白。在这些热响应蛋白中,选取被鉴定为膜联蛋白的蛋白点2作进一步研究。 2.实时定量PCR(qRT-PCR)和蛋白质印记(western blot)的结果显示,与未经处理的莲种子相比,经高温处理的种子中NnANN1的表达在mRNA水平和蛋白水平都有大幅提高,证实与上述蛋白质组学的结果一致,NnANN1是热响应蛋白。亚细胞定位分析发现NnANN1表现出典型的细胞质定位模式,qRT-PCR分析发现NnANN1主要在种子发育和萌发过程中大量表达,暗示该蛋白可能在种子发育和萌发中发挥作用。 3.为证实NnANN1在体内的保护作用,在大肠杆菌细胞和植物种子中进行了功能研究。结果表明,与对照相比,在高温逆境下,NnANN1转化的大肠杆菌细胞和拟南芥的种子耐热性提高。此外,加速老化实验表明NnANN1的表达提高了转基因拟南芥种子的活力。相反,与野生型种子相比,拟南芥同源基因AtANN1、AtANN2的T-DNA插入突变株的种子对于高温逆境和加速老化处理表现得更为敏感。NnANN1转基因种子中观察到过氧化物酶活性提高,并伴随活性氧(ROS)释放水平的降低,这可能帮助阐释NnANN1在体内的保护功能。综上所述,本研究实验结果表明NnANN1在耐热性和种子活力中发挥着重要功能,支持NnANN1在清除ROS中的作用,为研究植物高温应答的分子机制,提高作物耐热性和种子活力开拓了新的可能性。
DOI:10.7666/d.y2116641URL [本文引用: 2]

钙离子作为重要的细胞内信使,参与的信号转导过程在植物生长发育过程中中起到重要的调节作用。真核细胞中含有多种钙离子效应蛋白,通过改变细胞内钙离子水平调节细胞的生理活动。膜联蛋白(Annexin)属于其中一类钙离子效应蛋白,它们以钙离子依赖方式结合某些细胞膜磷脂,介导钙离子信号与膜之间的信号转导。已知Annexin参与动物的多种细胞过程,如膜转运,离子运输,有丝分裂,细胞骨架重排及DNA折叠等。Annexin在植物中广泛存在,但对其确切功能了解较少。 本研究对拟南芥Annexin家族成员的基因表达、蛋白的亚细胞定位和AnnAt3的功能等进行了初步分...
DOI:10.7666/d.y2116641URL [本文引用: 2]

钙离子作为重要的细胞内信使,参与的信号转导过程在植物生长发育过程中中起到重要的调节作用。真核细胞中含有多种钙离子效应蛋白,通过改变细胞内钙离子水平调节细胞的生理活动。膜联蛋白(Annexin)属于其中一类钙离子效应蛋白,它们以钙离子依赖方式结合某些细胞膜磷脂,介导钙离子信号与膜之间的信号转导。已知Annexin参与动物的多种细胞过程,如膜转运,离子运输,有丝分裂,细胞骨架重排及DNA折叠等。Annexin在植物中广泛存在,但对其确切功能了解较少。 本研究对拟南芥Annexin家族成员的基因表达、蛋白的亚细胞定位和AnnAt3的功能等进行了初步分...
URL [本文引用: 3]

Annexins are homologous,soluble and multifunctional proteins capable of Ca-dependent and Ca-independent binding to or insert into the membranes.Annexins exist in some prokaryotes and all eukaryotic phyla and always represent in high organisms as multiple gene family.The structure of plant annexins has only 1 or 2 repeats which are highly conserved (usually the first and the fourth).Functionally,plant annexins have the abilities of binding to cytoskeleton,hydrolysing ATP and GTP,acting as peroxidases or cation channels in response to abiotic stresses such as salinity,drought,high and low temperature,metal stress and wounding and biotic stresses such as fungi and pests.Annexins are expressed in a majority of plant organs and throughout the whole life cycle and varied with the body growth,development and environment change and play an important role in resistance to stress.In this paper,the known structure and function of plant annexins,especially the relationship between annexins and plant stress response were systematically summarized so as to offer an oriented suggestion for researches in plant annexins and stress resistance.
URL [本文引用: 3]

Annexins are homologous,soluble and multifunctional proteins capable of Ca-dependent and Ca-independent binding to or insert into the membranes.Annexins exist in some prokaryotes and all eukaryotic phyla and always represent in high organisms as multiple gene family.The structure of plant annexins has only 1 or 2 repeats which are highly conserved (usually the first and the fourth).Functionally,plant annexins have the abilities of binding to cytoskeleton,hydrolysing ATP and GTP,acting as peroxidases or cation channels in response to abiotic stresses such as salinity,drought,high and low temperature,metal stress and wounding and biotic stresses such as fungi and pests.Annexins are expressed in a majority of plant organs and throughout the whole life cycle and varied with the body growth,development and environment change and play an important role in resistance to stress.In this paper,the known structure and function of plant annexins,especially the relationship between annexins and plant stress response were systematically summarized so as to offer an oriented suggestion for researches in plant annexins and stress resistance.
URL [本文引用: 3]

膜联蛋白(annexin)是一类依赖钙离子的多功能磷脂结合蛋白家族,在进化上高度保守,但不同的膜联蛋白基因的表达模式和蛋白质的亚细胞定位具有特异性。拟南芥中已经鉴定出8个编码膜联蛋白的基因,在生长发育和对逆境胁迫响应过程中起作用。已知拟南芥膜联蛋白2参与根的分泌活动和生长素介导的根的向地性反应,但作用机制不清楚。蛋白质的亚细胞定位能为研究其功能和作用机制提供重要参考信息。将编码膜联蛋白2的序列克隆到植物双元表达载体p CAMBIA1300-m Cherry上,在拟南芥中表达Ann At2-m Cherry。利用荧光蛋白技术、m Cherry与绿色荧光蛋白标记的细胞器标记物共定位技术以及细胞器特异性荧光染料染色技术,作者研究了膜联蛋白2的亚细胞定位。结果显示,膜联蛋白2定位于细胞质、细胞核、高尔基体和内质网中,表明该蛋白质可能具有非常重要的功能和复杂的蛋白质翻译与转运调控机制。更多结果发现,转基因拟南芥中膜联蛋白2与绿色荧光蛋白标记的微丝骨架存在共定位现象,推测该蛋白可能通过微丝骨架调节及微丝骨架介导的囊泡运输参与细胞分泌活动。该文为进一步研究膜联蛋白2蛋白质的翻译与转运调控以及作用机制提供了实验依据。
URL [本文引用: 3]

膜联蛋白(annexin)是一类依赖钙离子的多功能磷脂结合蛋白家族,在进化上高度保守,但不同的膜联蛋白基因的表达模式和蛋白质的亚细胞定位具有特异性。拟南芥中已经鉴定出8个编码膜联蛋白的基因,在生长发育和对逆境胁迫响应过程中起作用。已知拟南芥膜联蛋白2参与根的分泌活动和生长素介导的根的向地性反应,但作用机制不清楚。蛋白质的亚细胞定位能为研究其功能和作用机制提供重要参考信息。将编码膜联蛋白2的序列克隆到植物双元表达载体p CAMBIA1300-m Cherry上,在拟南芥中表达Ann At2-m Cherry。利用荧光蛋白技术、m Cherry与绿色荧光蛋白标记的细胞器标记物共定位技术以及细胞器特异性荧光染料染色技术,作者研究了膜联蛋白2的亚细胞定位。结果显示,膜联蛋白2定位于细胞质、细胞核、高尔基体和内质网中,表明该蛋白质可能具有非常重要的功能和复杂的蛋白质翻译与转运调控机制。更多结果发现,转基因拟南芥中膜联蛋白2与绿色荧光蛋白标记的微丝骨架存在共定位现象,推测该蛋白可能通过微丝骨架调节及微丝骨架介导的囊泡运输参与细胞分泌活动。该文为进一步研究膜联蛋白2蛋白质的翻译与转运调控以及作用机制提供了实验依据。
DOI:10.1007/BF00201617URLPMID:11538119 [本文引用: 1]

As part of a study to identify potential targets of calcium action in plant cells, a 35-kDa, annexin-like protein was purified from pea (Pisum sativum L.) plumules by a method used to purify animal annexins. This protein, called p35, binds to a phosphatidylserine affinity column in a calcium-dependent manner and binds 45Ca2+ in a dot-blot assay. Preliminary sequence data confirm a relationship for p35 with the annexin family of proteins. Polyclonal antibodies have been raised which recognize p35 in Western and dot blots. Immunofluorescence and immunogold techniques were used to study the distribution and subcellular localization of p35 in pea plumules and roots. The highest levels of immunostain were found in young developing vascular cells producing wall thickenings and in peripheral root-cap cells releasing slime. This localization in cells which are actively involved in secretion is of interest because one function suggested for the animal annexins is involvement in the mediation of exocytosis.
DOI:10.1016/S0981-9428(98)80010-7URLPMID:11542469 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract Immunofluorescent localization of annexins using an anti-pea annexin polyclonal antibody (anti-p35) in pea (Pisum sativum) leaf and stem epidermal peels showed staining of the nuclei and the cell periphery. Nuclear staining was also seen in cell teases prepared from pea plumules. The amount of nuclear stain was reduced both by fixation time and by dehydration and organic solvent treatment. Observation with confocal microscopy demonstrated that the anti-p35 stain was diffusely distributed throughout the nuclear structure. Immunoblots of purified nuclei, nuclear envelope matrix, nucleolar, and chromatin fractions showed a cross-reactive protein band of 35 kDa. These data are the first to show annexins localized in plant cell nuclei where they may play a role in nuclear function.
DOI:10.1104/pp.106.4.1403URL [本文引用: 2]

A 42-kD, calcium-dependent, membrane-binding protein (VCaB42) was associated with partially purified vacuole membranes. Membrane-dissociation assays indicated that VCaB42 binding to vacuole membranes was selective for calcium over other cations and that 50% of VCaB42 remained membrane bound at 61 卤 11 nM free calcium. A 13-amino acid sequence obtained from VCaB42 showed 85% similarity with the endonexin fold, a sequence found in the annexin family of proteins that is thought to be essential for calcium and lipid binding. The greatest similarity in amino acid sequence was observed with annexin VIII (VAC- ). The calcium-binding properties and sequence similarities suggest that VCaB42 is a member of the annexin family of calcium-dependent, membrane-binding proteins. Functional assays for VCaB42 on vacuole membrane transport processes indicated that it did not significantly affect the initial rate of calcium uptake into vacuole membrane vesicles. Because VCaB42 is vacuole localized (likely on the cytosolic surface of the vacuole) and is 50% dissociated within the physiological range of cytosolic free calcium, we hypothesize that this protein is a sensor that monitors cytosolic calcium levels and transmits that information to the vacuole.
DOI:10.1093/molehr/gam026URLPMID:9232879 [本文引用: 1]

Mechanical stimulation exerted by rubbing a young internode of Bryonia dioica plants inhibits its growth. Previous cellular and biochemical studies showed that this growth inhibition is associated with Ca2+redistribution and profound modifications of plasma membrane characteristics. We extracted and purified Ca2+-dependent phospholipid-binding proteins from B. dioica internodes. Two main proteins, p33 and p35, and other minor bands were isolated and identified as annexin-like proteins because of their biochemical properties and their cross-reactions with antibodies against maize (Zea mays L.) annexins. Rabbit antiserum was obtained by injection of B. dioica p35. This antiserum was used for the immunocytolocalization of annexin-like proteins in internode parenchyma cells. It appeared that the distribution of annexin-like proteins was different before and 30 min after the mechanical stimulation. Western analysis of proteins in membrane fractions after separation by free-flow electrophoresis showed that p35 was present in most fractions, whereas p33 appeared mainly in plasmalemma-enriched fractions after the mechanical stimulation. It is hypothesized that a subcellular redistribution of these proteins might be involved in growth inhibition by mechanical stress.
URL [本文引用: 1]

花生是主要的油料和经济作物,由于其重要的经济价值,因此深入研究花生基因组结构进化与演变,具有重要的科研价值和经济意义。花生两个二倍体祖先野生种(A.duranensis和A.ipaensis)的基因测序工作完成,为花生重复基因间基因置换研究提供了基因组数据材料。课题研究以重要豆科模式植物苜蓿为外类群,对花生的两个祖先物种进行了系统的全基因组比较分析,基于同源染色体片段的基因同源共线性,统计推断了花生基因组内由多倍化事件所产生重复基因的规模,其中苜蓿12.2%(7286),花生A14.4%(5167),花生B 12.5%(5202);同时研究中对基因组间的同源关系进行了细致的相似性结构分析,构建了以苜蓿为参考,与多倍化相关的多次级基因比对列表。研究发现,加倍后物种基因内重复基因丢失是一个随机的过程,近似服从几何分布。突出地,课题研究中结合系统发育和非参数bootstrap方法建立了推断重复基因置换算法,并利用Perl、Bioperl语言集成Clustalw和PAML,实现了物种全基因组重复基因间的基因置换推断。推断结果显示,花生A基因组中有2.8%(135个),花生B基因组中有2.6%(147个)重复基因在进化过程中发生了基因置换。统计分析发现,靠近染色体端粒位置的重复基因对间更容易发生基因置换;基因置换可能更偏向于某些功能基因。课题中所建立的方法和流程能够使用于对其它物种基因组多倍化过程,及同源染色体片段间的遗传重组的探索研究,具有良好的推广性;研究产生的结果对花生基因组相关领域研究具有理论支撑作用。
URL [本文引用: 1]

花生是主要的油料和经济作物,由于其重要的经济价值,因此深入研究花生基因组结构进化与演变,具有重要的科研价值和经济意义。花生两个二倍体祖先野生种(A.duranensis和A.ipaensis)的基因测序工作完成,为花生重复基因间基因置换研究提供了基因组数据材料。课题研究以重要豆科模式植物苜蓿为外类群,对花生的两个祖先物种进行了系统的全基因组比较分析,基于同源染色体片段的基因同源共线性,统计推断了花生基因组内由多倍化事件所产生重复基因的规模,其中苜蓿12.2%(7286),花生A14.4%(5167),花生B 12.5%(5202);同时研究中对基因组间的同源关系进行了细致的相似性结构分析,构建了以苜蓿为参考,与多倍化相关的多次级基因比对列表。研究发现,加倍后物种基因内重复基因丢失是一个随机的过程,近似服从几何分布。突出地,课题研究中结合系统发育和非参数bootstrap方法建立了推断重复基因置换算法,并利用Perl、Bioperl语言集成Clustalw和PAML,实现了物种全基因组重复基因间的基因置换推断。推断结果显示,花生A基因组中有2.8%(135个),花生B基因组中有2.6%(147个)重复基因在进化过程中发生了基因置换。统计分析发现,靠近染色体端粒位置的重复基因对间更容易发生基因置换;基因置换可能更偏向于某些功能基因。课题中所建立的方法和流程能够使用于对其它物种基因组多倍化过程,及同源染色体片段间的遗传重组的探索研究,具有良好的推广性;研究产生的结果对花生基因组相关领域研究具有理论支撑作用。
.
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
URL [本文引用: 1]

生物及非生物胁迫是影响植物生长发育的重要因素。揭示逆境胁迫下植物体内的基因表达调控机制对于阐明植物的应答反应及培育抗逆品种具有重要的理论和现实意义。膜联蛋白(Annexin)是一类多功能蛋白,存在于部分原核生物以及全部的真核生物中。在大多数高等生物中以多基因家族形式存在。Annexin基因在植物体各组织器官及生育期的各个阶段均有表达,参与植物体的胞外分泌、细胞伸长、细胞壁生成、根瘤形成、果实成熟以及胁迫响应等生理过程。本研究通过同源克隆及RACE技术,从花生品种"冀花2"中克隆获得6个annexin基因(AnnAhs)cDNA全长和2个AnnAhs cDNA部分序列,分别命名为AnnAh1,AnnAh2,AnnAh3,AnnAh5,AnnAh6,AnnAh7,AnnAh4和AnnAh8
URL [本文引用: 1]

生物及非生物胁迫是影响植物生长发育的重要因素。揭示逆境胁迫下植物体内的基因表达调控机制对于阐明植物的应答反应及培育抗逆品种具有重要的理论和现实意义。膜联蛋白(Annexin)是一类多功能蛋白,存在于部分原核生物以及全部的真核生物中。在大多数高等生物中以多基因家族形式存在。Annexin基因在植物体各组织器官及生育期的各个阶段均有表达,参与植物体的胞外分泌、细胞伸长、细胞壁生成、根瘤形成、果实成熟以及胁迫响应等生理过程。本研究通过同源克隆及RACE技术,从花生品种"冀花2"中克隆获得6个annexin基因(AnnAhs)cDNA全长和2个AnnAhs cDNA部分序列,分别命名为AnnAh1,AnnAh2,AnnAh3,AnnAh5,AnnAh6,AnnAh7,AnnAh4和AnnAh8
DOI:10.1038/nbt.1621URLPMID:20436464 [本文引用: 1]

High-throughput mRNA sequencing (RNA-Seq) promises simultaneous transcript discovery and abundance estimation. However, this would require algorithms that are not restricted by prior gene annotations and that account for alternative transcription and splicing. Here we introduce such algorithms in an open-source software program called Cufflinks. To test Cufflinks, we sequenced and analyzed >430 million paired 75-bp RNA-Seq reads from a mouse myoblast cell line over a differentiation time series. We detected 13,692 known transcripts and 3,724 previously unannotated ones, 62% of which are supported by independent expression data or by homologous genes in other species. Over the time series, 330 genes showed complete switches in the dominant transcription start site (TSS) or splice isoform, and we observed more subtle shifts in 1,304 other genes. These results suggest that Cufflinks can illuminate the substantial regulatory flexibility and complexity in even this well-studied model of muscle development and that it can improve transcriptome-based genome annotation.
DOI:10.12688/f1000research.2-188.v1URLPMID:3892928 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract Alternative splicing is widely recognized for its roles in regulating genes and creating gene diversity. However, despite many efforts, the repertoire of gene splicing variation is still incompletely characterized, even in humans. Here we describe a new computational system, ASprofile, and its application to RNA-seq data from Illumina's Human Body Map project (>2.5 billion reads). Using the system, we identified putative alternative splicing events in 16 different human tissues, which provide a dynamic picture of splicing variation across the tissues. We detected 26,989 potential exon skipping events representing differences in splicing patterns among the tissues. A large proportion of the events (>60%) were novel, involving new exons (~3000), new introns (~16000), or both. When tracing these events across the sixteen tissues, only a small number (4-7%) appeared to be differentially expressed ('switched') between two tissues, while 30-45% showed little variation, and the remaining 50-65% were not present in one or both tissues compared. Novel exon skipping events appeared to be slightly less variable than known events, but were more tissue-specific. Our study represents the first effort to build a comprehensive catalog of alternative splicing in normal human tissues from RNA-seq data, while providing insights into the role of alternative splicing in shaping tissue transcriptome differences. The catalog of events and the ASprofile software are freely available from the Zenodo repository ( http://zenodo.org/record/7068; doi: 10.5281/zenodo.7068) and from our web site http://ccb.jhu.edu/software/ASprofile.
DOI:10.1016/0273-1177(94)90421-9URLPMID:11537937 [本文引用: 1]

Although calcium has been proposed to be an important regulatory element in plant gravitropic growth, as yet no specific function of Ca 2+ in growth regulation has been discovered. Our recent studies on a Ca 2+ -binding protein in pea seedlings called p35 indicate that it is a member of the annexin family of proteins and may play a key role in growth regulation through its function in delivering polysaccharides needed for wall construction. We previously reported the isolation of p35 from pea plumules and the production of polyclonal antibodies to it. Immunolocalization analyses of p35 in pea tissues revealed high levels of staining in secretory cell types such as developing vascular cells and outer root cap cells. To test how general was the occurrence and distribution of this annexin-like protein in plant cells we initiated an analysis of annexins in the monocot corn using immunological techniques. Our results indicate the immunochemical properties and localization of corn annexins are very similar to those reported for pea. They are consistent with the postulate that annexins may play a general role in the regulation of the secretion of wall polysaccharides needed for growth, and thus could be an important target of calcium action during gravitropic growth.
DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0047801URLPMID:23133603 [本文引用: 4]

Most annexins are calcium-dependent, phospholipid-binding proteins with suggested functions in response to environmental stresses and signaling during plant growth and development. They have previously been identified and characterized in Arabidopsis and rice, and constitute a multigene family in plants. In this study, we performed a comparative analysis of annexin gene families in the sequenced genomes of Viridiplantae ranging from unicellular green algae to multicellular plants, and identified 149 genes. Phylogenetic studies of these deduced annexins classified them into nine different arbitrary groups. The occurrence and distribution of bona fide type II calcium binding sites within the four annexin domains were found to be different in each of these groups. Analysis of chromosomal distribution of annexin genes in rice, Arabidopsis and poplar revealed their localization on various chromosomes with some members also found on duplicated chromosomal segments leading to gene family expansion. Analysis of gene structure suggests sequential or differential loss of introns during the evolution of land plant annexin genes. Intron positions and phases are well conserved in annexin genes from representative genomes ranging from Physcomitrella to higher plants. The occurrence of alternative motifs such as K/R/HGD was found to be overlapping or at the mutated regions of the type II calcium binding sites indicating potential functional divergence in certain plant annexins. This study provides a basis for further functional analysis and characterization of annexin multigene families in the plant lineage.
URL [本文引用: 2]

膜联蛋白属于依赖Ca2+的磷脂结合蛋白,组成了一个多功能、多基因的蛋白家族。膜联蛋白家族成员之间序列保守性高,功能结构域相似,一般具有四个保守的内膜联序列区域。植物膜联蛋白参与植物细胞的多个代谢过程,包括参与植物分泌型细胞极性发育、影响植物细胞中关键酶的活性、属于蛋白质磷酸化的底物、参与植物非生物逆境反应、植物细胞中作用位点的多样化。阐明膜联蛋白基因在植物细胞中介导的信号转导机制和调控植物逆境反应机制,为非生物逆境多抗作物品种的培育提供重要的基因资源。
URL [本文引用: 2]

膜联蛋白属于依赖Ca2+的磷脂结合蛋白,组成了一个多功能、多基因的蛋白家族。膜联蛋白家族成员之间序列保守性高,功能结构域相似,一般具有四个保守的内膜联序列区域。植物膜联蛋白参与植物细胞的多个代谢过程,包括参与植物分泌型细胞极性发育、影响植物细胞中关键酶的活性、属于蛋白质磷酸化的底物、参与植物非生物逆境反应、植物细胞中作用位点的多样化。阐明膜联蛋白基因在植物细胞中介导的信号转导机制和调控植物逆境反应机制,为非生物逆境多抗作物品种的培育提供重要的基因资源。
DOI:10.1371/journal.pcbi.0020048URLPMID:16733546 [本文引用: 1]

During the course of evolution, new proteins are produced very largely as the result of gene duplication, divergence and, in many cases, combination. This means that proteins or protein domains belong to families or, in cases where their relationships can only be recognised on the basis of structure, superfamilies whose members descended from a common ancestor. The size of superfamilies can vary greatly. Also, during the course of evolution organisms of increasing complexity have arisen. In this paper we determine the identity of those superfamilies whose relative sizes in different organisms are highly correlated to the complexity of the organisms. As a measure of the complexity of 38 uni- and multicellular eukaryotes we took the number of different cell types of which they are composed. Of 1,219 superfamilies, there are 194 whose sizes in the 38 organisms are strongly correlated with the number of cell types in the organisms. We give outline descriptions of these superfamilies. Half are involved in extracellular processes or regulation and smaller proportions in other types of activity. Half of all superfamilies have no significant correlation with complexity. We also determined whether the expansions of large superfamilies correlate with each other. We found three large clusters of correlated expansions: one involves expansions in both vertebrates and plants, one just in vertebrates, and one just in plants. Our work identifies important protein families and provides one explanation of the discrepancy between the total number of genes and the apparent physiological complexity of eukaryotic organisms.
DOI:10.1038/nature08957URL [本文引用: 2]
DOI:10.1105/tpc.107.052621URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1021/jf60171a041URL [本文引用: 1]

react-text: 430 The pathway for the formation of alkylated pyrazine compounds in amino acid-carbohydrate model systems of lowwater content was investigated. Radioisotopic labeling studies indicated that sugars were the principal source of the carbon atoms, while amino acids mostly furnished only nitrogen to the pyrazine molecule. Ammonium ions were not the common intermediate through which nitrogen entered... /react-text react-text: 431 /react-text [Show full abstract]
DOI:10.1104/pp.126.3.1072URL [本文引用: 2]
URL [本文引用: 3]

蛋白质处于特定的亚细胞位置上才能行使其功能,故研究亚细胞定位对了解蛋白质功能非常重要。随着后基因组时代的来临,蛋白质序列信息增长迅速,而利用实验手段分析蛋白亚细胞定位的不易大规模进行。近年来,通过提取蛋白质的各种特征信息,自动预测蛋白质的亚细胞定位的算法得到了较快的发展,本文拟从蛋白质特征信息的提取、预测算法和预测效果检验等方面,介绍蛋白质亚细胞定位预测领域中研究进展。
URL [本文引用: 3]

蛋白质处于特定的亚细胞位置上才能行使其功能,故研究亚细胞定位对了解蛋白质功能非常重要。随着后基因组时代的来临,蛋白质序列信息增长迅速,而利用实验手段分析蛋白亚细胞定位的不易大规模进行。近年来,通过提取蛋白质的各种特征信息,自动预测蛋白质的亚细胞定位的算法得到了较快的发展,本文拟从蛋白质特征信息的提取、预测算法和预测效果检验等方面,介绍蛋白质亚细胞定位预测领域中研究进展。
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2015.10.021URL [本文引用: 1]

Abscisic acid-stress-ripening induced protein(ASR)plays an important role in response to abiotic stresses. In the present study we isolated a first ASR gene designated MeASR from cassava. Sequence analysis showed that the open reading frame of MeASR gene contained 330 bp, encoding 109 amino acids. Multiple sequence alignment and phylogenetic analysis indicated that MeASR protein contained the conserved domains as ASR family had, and had a close genetic relationship with SlASR4 of tomato. Subcellular location assay showed that MeASR protein was localized in nucleus. Real-time quantitative PCR assay revealed that expression of MeASR was induced by osmotic stress and ABA treatments. These results suggested that MeASR might function as a transcription factor to involve in response to drought stress and ABA-signal regulation in cassava.
DOI:10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2015.10.021URL [本文引用: 1]

Abscisic acid-stress-ripening induced protein(ASR)plays an important role in response to abiotic stresses. In the present study we isolated a first ASR gene designated MeASR from cassava. Sequence analysis showed that the open reading frame of MeASR gene contained 330 bp, encoding 109 amino acids. Multiple sequence alignment and phylogenetic analysis indicated that MeASR protein contained the conserved domains as ASR family had, and had a close genetic relationship with SlASR4 of tomato. Subcellular location assay showed that MeASR protein was localized in nucleus. Real-time quantitative PCR assay revealed that expression of MeASR was induced by osmotic stress and ABA treatments. These results suggested that MeASR might function as a transcription factor to involve in response to drought stress and ABA-signal regulation in cassava.
DOI:10.1093/pcp/41.2.177URLPMID:10795312 [本文引用: 1]

Four immunologically related proteins that belong to the annexin family were identified in cold acclimated wheat (Triticum aestivum). Two soluble forms with molecular masses of 34 and 36 kDa were found to bind phospholipid membranes in a calcium-dependent manner. These two forms are similar to the previously reported doublet in several plant species. The other two forms, with molecular masses of 39 and 22.5 kDa, were found associated with the microsomal fraction. Biochemical analysis showed that both forms are intrinsic membrane proteins and their association with the membrane is calcium independent. This is, to our knowledge, the first report of the presence of these annexin forms in plants. Membrane purification by two phase partitioning demonstrated that the p39 form is localized to the plasma membrane. Immunoblot analysis showed that the protein level of both p39 and p22.5 increases gradually reaching a maximum level after one day of low temperature exposure. The protein accumulation was similar in both hardy and less hardy cultivars, suggesting that the accumulation is not correlated with freezing tolerance. The results are discussed with respect to the possible role of these new intrinsic membrane annexins in low temperature signal transduction pathway.
DOI:10.1046/j.1365-313X.2002.01429.xURLPMID:12410812 [本文引用: 1]

The Medicago truncatula MtAnn1 gene, encoding a putative annexin, is transcriptionally activated in root tissues in response to rhizobial Nod factors. To gain further insight into MtAnn1 function during the early stages of nodulation, we have examined in detail both spatio-temporal gene expression patterns and MtAnn1 activity and localisation in root tissues. Analysis of transgenic Medicago plants expressing a p MtAnn1-GUS fusion has revealed a novel pattern of transcription in both outer and inner cell layers of the root following either Nod factor-treatment or rhizobial inoculation. The highest gene expression levels were observed in the endodermis and outer cortex. These transgenic plants also revealed that MtAnn1 expression is associated with lateral root development and cell differentiation in the root apex independent of nodulation. By purifying recombinant MtAnn1 we were able to demonstrate that this plant annexin indeed possesses the calcium-dependent binding to acidic phospholipids typical of the annexin family. Antisera against recombinant MtAnn1 were then used to show that tissue-specific localisation of the MtAnn1 protein in Medicago roots matches the p MtAnn1-GUS expression pattern. Finally, both immunolabelling and in vivo studies using MtAnn1-GFP reporter fusions have revealed that MtAnn1 is cytosolic and in particular localises to the nuclear periphery in cortical cells activated during the early stages of nodulation. In the light of our findings, we discuss the possible role of this annexin in root tissues responding to symbiotic rhizobial signals.
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-5565.2012.01.13URL [本文引用: 1]

前体mRNA的可变剪接是扩大真核生物蛋白质组多样性的重要基因调控机制。可变剪接的错误调节可以引起多种人类疾病。由于高通量技术的发展,生物信息学成为可变剪接研究的主要手段。本文总结了可变剪接在生物信息学领域的研究方法,同时也分析并预测了可变剪接的发展方向。
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-5565.2012.01.13URL [本文引用: 1]

前体mRNA的可变剪接是扩大真核生物蛋白质组多样性的重要基因调控机制。可变剪接的错误调节可以引起多种人类疾病。由于高通量技术的发展,生物信息学成为可变剪接研究的主要手段。本文总结了可变剪接在生物信息学领域的研究方法,同时也分析并预测了可变剪接的发展方向。
DOI:10.1007/BF00020883URLPMID:7766892 [本文引用: 1]

Fruit ripening is a complex developmental process that involves specific changes in gene expression and cellular metabolism. In climateric fruits these events are coordinated by the gaseous hormone ethylene, which is synthesized autocatalytically in the early stages of ripening. Nonclimacteric fruits do not synthesize or respond to ethylene in this manner, yet undergo many of the same physiological and biochemical changes associated with the production of a ripe fruit. To gain insight into the molecular determinants associated with nonclimacteric fruit ripening, we examined mRNA populations in ripening strawberry fruit using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) differential display. Five mRNAs with ripening-enhanced expression were identified using this approach. Three of the mRNAs appear to be fruit-specific, with little or no expression detected in vegetative tissues. Sequence analysis of cDNA clones revealed positive identities for three of the five mRNAs based on homology to known proteins. These results indicate that the differential display technique can be a useful tool to study fruit ripening and other developmental processes in plants at the RNA level.
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1735.2004.04.023URL [本文引用: 1]

综述了植物膜联蛋白的结构与功能.植物膜联蛋白具有膜联蛋白家族的基本结构,但其三维结构与动物膜联蛋白有所差异.同动物膜联蛋白一样,植物膜联蛋白可能参与植物细胞的分泌作用、胞吐作用、液泡化过程及低温信号转导过程,也可能具有愈伤葡萄糖合成酶、ATPase/GTPase及过氧化物的活性.植物膜联蛋白可能与果实的成熟有关.
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1735.2004.04.023URL [本文引用: 1]

综述了植物膜联蛋白的结构与功能.植物膜联蛋白具有膜联蛋白家族的基本结构,但其三维结构与动物膜联蛋白有所差异.同动物膜联蛋白一样,植物膜联蛋白可能参与植物细胞的分泌作用、胞吐作用、液泡化过程及低温信号转导过程,也可能具有愈伤葡萄糖合成酶、ATPase/GTPase及过氧化物的活性.植物膜联蛋白可能与果实的成熟有关.
.
DOI:10.1093/jxb/err112URLPMID:3134359 [本文引用: 1]

The multifunctionality of plant annexins and their importance for coordinating development and responses to biotic and abiotic environment have been largely reviewed. We recently described a tobacco annexin, named Ntann12, which is mainly localized in the nucleus of root cells when the plant is grown under light conditions. We also found that auxin and polar auxin transport are essential for Ntann12 accumulation in root cells. Under dark condition, Ntann12 is no longer detected in the root system. In the present addendum, light, regulating auxin signaling, is evidenced as an essential determinant for the synchronization of growth and development between the shoot and the root during light/dark cycle. A speculative model for Ntann12 is described and discussed with regards to relevant literature data.
DOI:10.1360/csb2012-57-6-431URL [本文引用: 1]

通过5′RACE扩增了苜蓿膜联蛋白MtAnn3基因cDNA的5′末端序列.典型的膜联蛋白由一个N端结构域和一个C端保守的核心结构域组成,核心结构域一般含有4或8个由70个氨基酸组成的重复单元,而MtAnn3蛋白的核心结构域仅有1个重复单元.在洋葱表皮细胞中瞬时表达MtAnn3蛋白,揭示其具有细胞膜结合的特性.借助农杆菌介导的苜蓿转化实验表明,过表达MtAnn3的根部在不含Ca2+的培养基上生长,改变了根毛的极性,根毛顶端膨大变形,有时出现分叉现象.在农杆菌介导的MtAnn3启动子-GUS实验中,外源植物细胞分裂素可以诱导MtAnn3启动子的增强表达;接种苜蓿中华根瘤菌进行结瘤实验,启动子在根瘤原基和幼嫩根瘤中有较强的活性,而在成熟根瘤中活性较低,在衰老的根瘤中检测不到启动子活性.虽然MtAnn3在根瘤中的表达具有一定的时序性,它却不是瘤特异性的,它在苜蓿的根、茎、叶中都有高水平的转录表达.
DOI:10.1360/csb2012-57-6-431URL [本文引用: 1]

通过5′RACE扩增了苜蓿膜联蛋白MtAnn3基因cDNA的5′末端序列.典型的膜联蛋白由一个N端结构域和一个C端保守的核心结构域组成,核心结构域一般含有4或8个由70个氨基酸组成的重复单元,而MtAnn3蛋白的核心结构域仅有1个重复单元.在洋葱表皮细胞中瞬时表达MtAnn3蛋白,揭示其具有细胞膜结合的特性.借助农杆菌介导的苜蓿转化实验表明,过表达MtAnn3的根部在不含Ca2+的培养基上生长,改变了根毛的极性,根毛顶端膨大变形,有时出现分叉现象.在农杆菌介导的MtAnn3启动子-GUS实验中,外源植物细胞分裂素可以诱导MtAnn3启动子的增强表达;接种苜蓿中华根瘤菌进行结瘤实验,启动子在根瘤原基和幼嫩根瘤中有较强的活性,而在成熟根瘤中活性较低,在衰老的根瘤中检测不到启动子活性.虽然MtAnn3在根瘤中的表达具有一定的时序性,它却不是瘤特异性的,它在苜蓿的根、茎、叶中都有高水平的转录表达.
