 ,1,*, 唐雪明
,1,*, 唐雪明 ,1,*
,1,*A Qualitative and Quantitative PCR Detection Method for Disease-resistant Genetically Modified Rice M12 and Its Derivates
LI Peng1,2, ZHANG Lin3, YE Ji-Ni4, HE Shi-Yao4, JIA Jun-Wei1, PAN Ai-Hu ,1,*, TANG Xue-Ming
,1,*, TANG Xue-Ming ,1,*
,1,*通讯作者:
收稿日期:2017-12-3接受日期:2018-03-26网络出版日期:2018-04-16
| 基金资助: |
Received:2017-12-3Accepted:2018-03-26Online:2018-04-16
| Fund supported: |

摘要
关键词:
Abstract
Keywords:
PDF (661KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
本文引用格式
李鹏, 张琳, 叶吉妮, 贺诗瑶, 贾军伟, 潘爱虎, 唐雪明. 抗病转基因水稻M12及其产品成分的定性、定量PCR检测方法[J]. 作物学报, 2018, 44(7): 949-955. doi:10.3724/SP.J.1006.2018.00949
LI Peng, ZHANG Lin, YE Ji-Ni, HE Shi-Yao, JIA Jun-Wei, PAN Ai-Hu, TANG Xue-Ming.
安徽省农业科学院和中国农业科学院通过基因枪转基因方法将包含Xa21基因的质粒pC822和潮霉素抗性基因hpt的质粒pHX4转入优良恢复系明恢63, 得到转基因品系M12。M12对中国所有白叶枯病小种都表现出高度抗性, 通过多代回交和分子标记辅助选择, 以M12为亲本, 培育得到多个抗白叶枯病水稻组合品系皖21B、皖21A和抗优97 (皖21A×R-18)等[1]。农业部发布了转基因水稻M12及其衍生品种的定性PCR检测方法[2], 但目前M12事件特异性的定量PCR检测方法尚未建立。为了便于对转基因水稻M12进行定量检测和分析, 需要建立准确、特异的转基因水稻M12事件特异性检测方法。
目前, 用于转基因植物及其加工产品检测的方法主要有两种, 一种基于核酸的检测, 一种基于蛋白质的免疫学检测。在转基因植物及其加工产品的检测过程中, 以DNA检测为基础的核酸检测已经成为最主要、最适用的方法。基于DNA的转基因检测技术除了传统的定性PCR和定量PCR检测技术之外, 等温扩增技术[3]、基因芯片技术[4]、数字PCR技术[5]和生物传感器检测技术[6,7]获得快速发展和应用, 但这些新技术同时也存在一些问题和不足。等温扩增技术具有快速、特异、敏感等特点, 但其扩增产物易污染, 引物间非连续配对的假阳性问题亟待解决[8]。基因芯片技术和数字PCR技术具有高通量、高灵敏度、高特异性的优点, 但是仪器设备昂贵, 操作复杂, 需要特殊的消耗品, 增加了使用成本。生物传感器检测技术能够实时显示采集数据, 无需放射性或荧光物质标记, 可以对相互作用的反应动力学、结合亲和力和样品浓度进行分析, 但其应用受到稳定性、重现性和使用寿命的限制, 再加上转基因生物成分的复杂性, 使商业化的生物传感器数量受到制约[9]。而定性、定量PCR检测技术具有低成本、灵敏度高、特异性强、操作相对简单等特点, 成为国家标准、农业部公告及出入境检验检疫行业标准等推荐的主要的转基因检测技术被广泛采用[10]。目前基于DNA的转基因产品检测方法经历了4个发展阶段, 即筛选特异性检测、基因特异性检测、构建特异性检测和品系(转化事件)特异性检测[11]。其中事件特异性检测方法是针对特定转化事件的, 具有高度特异性, 已成为国际上转基因产品检测方法的发展趋势。本研究旨在建立抗病转基因水稻M12及其加工品的品系特异性定性、定量PCR检测方法, 为抗病转基因水稻M12的进口检测、国内监管及环境安全评价提供依据。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料
转基因水稻华恢1号和旱恢3T, 非转基因水稻旱优3号由上海市农业基因中心提供; 转基因水稻M12和非转基因水稻花优14由本实验室提供。1.2 DNA的提取与纯化
参照Li等[12]方法提取和纯化试验材料DNA。采用微量紫外可见分光光度计Nano Drop ND1000 (Thermo Fisher Scientific Co., Ltd., Madison)测定DNA浓度和纯度。1.3 转基因水稻M12质粒分子的构建
将水稻内源基因蔗糖磷酸合酶基因(sucrose phosphate synthase, sps)检测序列(277 bp)和外源基因旁邻序列(380 bp)进行PCR扩增, 连接到pMD18-T, 得到质粒分子pM12。具体构建方法及步骤如下: (1)使用引物sps-F/R[13]和M12-SF/SR[2]扩增M12水稻基因组DNA, 采用胶回收试剂盒AP-GX-250 (爱思进生物技术(杭州)有限公司)纯化回收扩增片段, 采用Zhang等[14]方法将2个片段基因融合, 用限制性内切酶BamH I和Hind III酶切回收产物, 连接到载体pMD18-T, 得到质粒, 命名为pM12。(2) pM12转化大肠杆菌 DH5α 感受态细胞, 进行增殖和后续试验。(3)委托生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司对pM12测序确认。分别采用引物sps-F/R和M12-F/R进行PCR扩增, 验证其作为转基因水稻M12定量分析的标准分子。(4)采用胶回收试剂盒AP-GX-250凝胶回收pM12, 用分光光度计测量质粒 DNA 质量数。根据质粒分子大小, 将质粒质量数换算成拷贝数。将pM12梯度稀释, 用于标准曲线建立和方法重复性评估。1.4 事件特异性引物设计
根据转基因水稻M12插入载体与旁邻序列信息[2], 应用软件Primer Express Software Version 3.0 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Co., Ltd.)设计事件特异性PCR引物M12-F/R (表1), 采用蔗糖磷酸合酶基因(sucrose phosphate synthase, sps)[13]作为水稻内标准基因(表1)。引物均由生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司合成。扩增靶标序列及引物如图1。Table 1
表1
表1定性、定量PCR反应所用引物
Table 1
| 引物 Primer | 引物序列 Primer sequence (5°-3°) |
|---|---|
| sps-F | TTGCGCCTGAACGGATAT [13] |
| sps-R | CGGTTGATCTTTTCGGGATG [13] |
| M12-SF | GTTGGAGATTTTGGGCTTG [2] |
| M12-SR | ATAGCCTCTCCACCCAAGCG [2] |
| M12-F | GTTGGAGATTTTGGGCTTGC |
| M12-R | CGGCAAGAAACCATCCAGTT |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
图1
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图1抗病水稻M12特异性序列
箭头代表引物的位置和方向。
Fig. 1Specific sequence of genetically modified rice M12
The arrows show the location and orientation of primers.
1.5 定性PCR检测
定性PCR反应体系包含10×PCR buffer (宝生物工程(大连)有限公司) 3 μL, 2 mmol L-1 dNTP 3 μL, 正、反向引物M12-F/R (10 μmol L-1)各2 μL, 5 U μL-1Taq DNA polymerase 0.3 μL, 模板DNA 2 μL, 加蒸馏水补充至30 μL。定性PCR反应程序为94℃预变性, 5 min; 94℃变性30 s, 56℃退火30 s, 72℃延伸30 s, 35个循环; 72℃延伸7 min。1.6 定量PCR检测
定量PCR反应体系含2×SYBR Premix Ex Taq II 5 μL (宝生物工程(大连)有限公司), 50×Rox Reference dye 0.2 μL, 正、反向引物M12-F/R (10 μmol L-1)各0.4 μL, 模板DNA 4 μL。定量PCR反应程序为94℃预变性, 5 min; 94℃变性30 s, 60℃退火30 s, 72℃延伸30 s (收集荧光信号), 40个循环。1.7 标准曲线的制作
提取质粒DNA用Easy Dilution缓冲液(宝生物工程(大连)有限公司), 依次稀释至10 000 000、1 000 000、100 000、10 000、1000、100、10、5拷贝, 以此为标准品分别扩增内标基因sps和M12品系特异性基因, 设置每个梯度3个平行重复, 绘制标准曲线。在PCR扩增的指数期设定阈值, 使任何2个样品间的相对Ct值(ΔCt)保持不变, 计算不同样本间基因表达的倍数变化, 并依标准曲线定量分析。本研究中, 内标基因sps和M12品系特异性基因的标准曲线阈值分别为6.8023和0.4097。
1.8 数据处理与统计分析
采用SPSS 18.0统计软件(IBM Group, Inc)处理定量检测体系重复性的数据, 分析其Ct值的平均值(mean)和标准差(standard deviation, SD)。2 结果与分析
2.1 抗病转基因水稻M12质粒分子的构建
将转基因水稻M12的旁侧序列和内标准基因sps检测序列插入质粒pMD18-T, 得到3349 bp质粒分子pM12。对质粒pM12分别进行旁邻序列和内标准基因PCR扩增, 电泳结果如图2, 得到2个条带258 bp和277 bp。对pM12测序, 得到的序列与预期一致, 证明该质粒为构建正确的pM12质粒。提取和纯化质粒pM12的DNA, 根据标准分子基因组DNA的大小和平均DNA质量分数, 计算出1 g质粒分子DNA的拷贝数为2.77×109。图2
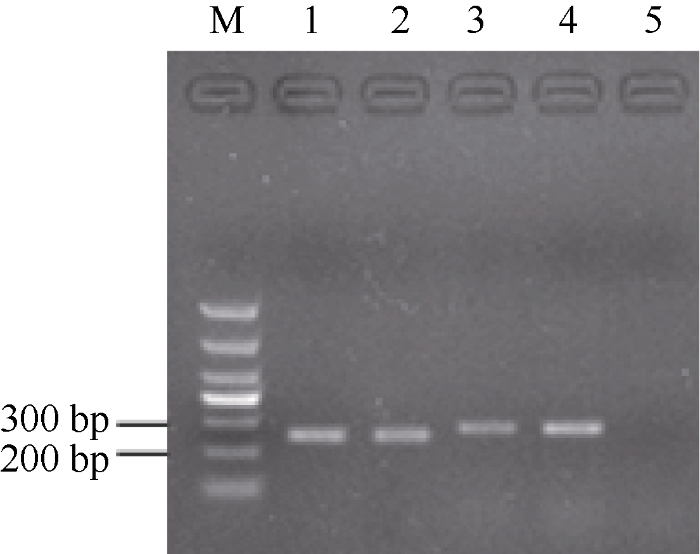 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图2pM12质粒的PCR鉴定
M: DNA marker (DL1000); 1~2: 引物M12-F/R; 3~4: 引物sps-F/R; 5: 阴性对照。
Fig. 2PCR result of pM12
M: DNA marker (DL1000); 1-2: primer: M12-F/R; 3-4: primer: sps-F/R; 5: negative control.
2.2 抗病转基因水稻M12的定性PCR检测
根据确定的外源基因插入位点旁邻序列, 设计扩增片段大小不同的引物对。经过筛选, 得到特异性引物对M12-F/R。同时以M12质粒分子和水稻品种M12、花优14、华恢1号、旱优3号和旱恢3T DNA为模板进行定性PCR扩增。结果显示, 只有M12质粒分子和水稻M12扩增得到258 bp条带, 而其他品种和对照均没有扩增到目的条带(图3), 说明这对引物特异性好, 可用于M12品系特异性定性PCR检测。利用M12-F/R引物, 使用10倍连续稀释的M12质粒DNA (10 000、1000、100、10、5拷贝)为模板进行定性PCR扩增(图4)。显示, M12-F/R这对引物的PCR扩增灵敏度较高, 100拷贝的M12质粒DNA能够扩增到比较清晰、特异的258 bp条带, 且随着模板DNA浓度的增加, 扩增条带亮度增加。
图3
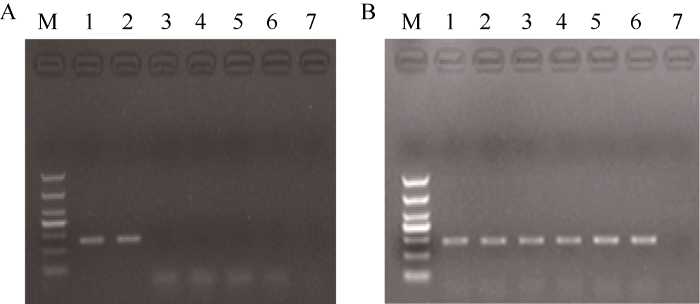 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图3M12事件特异性定性PCR的特异性检测
M12品系特异性扩增(A)和水稻内标准基因sps扩增(B)。M: DNA marker (DL1000); 1: M12质粒pM12; 2: M12; 3: 花优14; 4: 华恢1号; 5: 旱优3号; 6: 旱恢3T; 7: 阴性对照。
Fig. 3Event-specific detection of qualitative PCR for M12: The qualitative PCR of event-specific M12 (A) and rice endogenous gene sps (B).
M: DNA marker (DL1000); 1: pM12; 2: rice variety M12; 3: rice variety Huayou 14; 4: rice variety Huahui 1; 5: rice variety Hanyou 3; 6: rice variety Hanhui 3T; 7: negative control.
图4
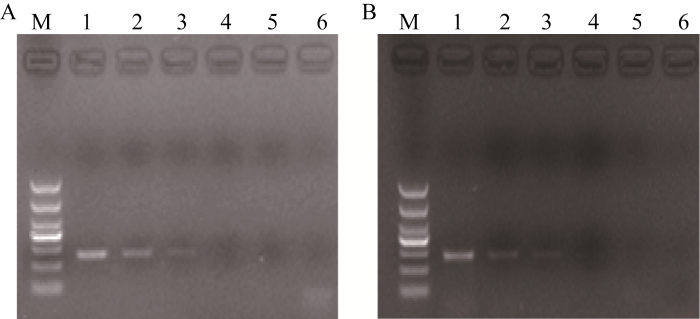 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图4M12事件特异性定性PCR的灵敏度分析
M12品系特异性扩增(A)和水稻内标准基因sps扩增(B)。M: DNA marker (DL1000); 1~5: 10 000、1000、100、10、5个拷贝单倍体水稻基因组; 6: 阴性对照。
Fig. 4Sensitivity detection of qualitative PCR for M12 The qualitative PCR of event-specific M12 (A) and rice endogenous gene sps (B).
M: DNA marker (DL1000); 1-5: 10 000, 1000, 100, 10, 5 copies of haploid rice genomic DNA; 6: negative control.
2.3 转基因水稻M12的定量PCR检测
2.3.1 定量PCR检测体系的检测极限和定量极限在定量分析中, 检测极限(limit of detection, LOD)和定量极限(limit of quantification, LOQ)指的是定量分析过程的最低检测极限和最低有效定量极限, 即被检测的样品在95%的精确度水平上能被检测出和可被定量的最低含量或质量。LOD和LOQ是评价定量方法有效检测范围和准确定量范围的重要参数, 可通过低浓度样品多次重复数值的再现性来确定。利用优化好的M12水稻事件特异性定量PCR反应体系, 分别以不同浓度的转基因水稻M12质粒分子10 000 000、1 000 000、100 000、10 000、1000、100、10拷贝)为标准DNA样品进行PCR扩增, 作为标准样品测试建立的定量PCR方法的LOD和LOQ如表2所示, 根据9次重复试验结果, M12基因定量PCR方法的LOD和LOQ分别是10和100拷贝单倍体水稻基因组, 说明本研究中检测M12定量PCR方法具有高度的灵敏度。
2.3.2 标准曲线的构建 以梯度稀释的M12质粒DNA (10 000 000、1 000 000、100 000、10 000、1000、100拷贝)为模板, 采用SYBR Green I染料法得到的M12和内标准基因sps扩增曲线和标准曲线(图5和图6)。M12事件特异性扩增标准曲线Ct值与起始模板线性方程为: Y= -3.441X+39.88, 相关系数R2=0.998; 扩增效率为95.3%; sps基因标准曲线Ct值与起始模板量线性方程为: Y= -3.136X+33.356, 相关系数R2=0.997, 扩增效率为108.4%, 所得参数可信度较高, 结果比较可信。
2.3.3 重复性分析 定量检测体系的重复性(repeatability), 是指在不同时间段重复实验之间的差异, 用标准偏差(SD)来表示。本试验的重复性通过对试验体系的3次重复来计算(表3)。根据不同浓度的标准质粒分子3次平行测定的Ct值计算标准偏差(SD), 结果如表3所示, SD变化范围为0.043~0.276。说明本研究建立的定量检测方法重复性较好, 结果比较可信。
Table 2
表2
表2M12定量PCR检测方法的检测极限和定量极限分析
Table 2
| 拷贝数 Copy | 出现次数/检测次数 Signal rate (positive signals) | 循环数平均值 Ct mean | 标准差 SD |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10000000 | 9/9 | 6.54 | 0.256 |
| 1000000 | 9/9 | 9.72 | 0.324 |
| 100000 | 9/9 | 13.15 | 0.236 |
| 10000 | 9/9 | 17.53 | 0.103 |
| 1000 | 9/9 | 20.82 | 0.265 |
| 100 | 9/9 | 24.12 | 0.231 |
| 10 | 2/9 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
图5
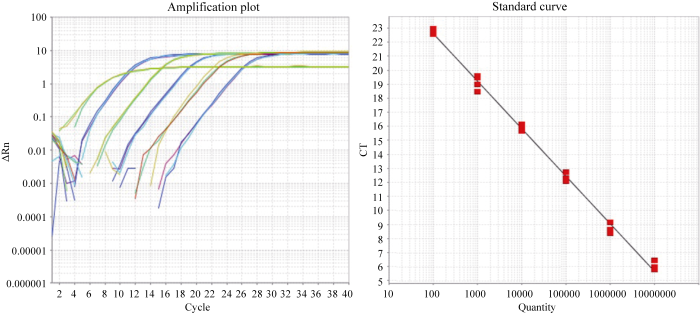 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图5M12事件特异性扩增曲线及标准曲线
质粒DNA拷贝数分别为10 000 000、1 000 000、100 000、10 000、1000、100拷贝。
Fig. 5Amplification plots and standard curves of M12
10 000 000, 1 000 000, 100 000, 10 000, 1000, and 100 copies of plasmid DNA respectively
图6
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图6内标基因sps扩增曲线及标准曲线
质粒DNA拷贝数分别为10 000 000、1 000 000、100 000、10 000、1000、100拷贝。
Fig. 6Amplification plots and standard curves of sps gene
10 000 000, 1 000 000, 100 000, 10 000, 1000, and 100 copies of plasmid DNA, respectively.
Table 3
表3
表3M12和sps基因定量PCR检测体系的重复性分析
Table 3
| 质粒分子DNA拷贝数 Copies of plasmid DNA | sps | M12 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 循环数平均值 Ct mean | 循环数标准差 Ct SD | 循环数平均值 Ct mean | 循环数标准差 Ct SD | ||
| 1000000 | 12.15 | 0.087 | 6.52 | 0.276 | |
| 100000 | 15.30 | 0.076 | 9.72 | 0.154 | |
| 10000 | 18.62 | 0.067 | 13.13 | 0.186 | |
| 10000 | 21.91 | 0.043 | 17.52 | 0.133 | |
| 1000 | 24.32 | 0.123 | 20.71 | 0.165 | |
| 100 | 27.60 | 0.124 | 24.05 | 0.134 | |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
2.3.4 转基因水稻M12混合样品定量检测 利用建立的M12事件特异性定量PCR检测方法, 使用sps基因做内源参照基因, 分别对2个已知转基因含量的转基因水稻M12样品(转基因成分含量分别为1.0%、0)定量分析, 总共100 ng DNA用于每个扩增反应。如表4所示, 2个混合样品的真实值和检测值检测定量偏差在8.0%, SD值为0.04。说明建立的M12水稻品系特异性定量PCR检测方法可实际用于转基因M12样品的定量检测分析。
Table 4
表4
表4转基因水稻M12定量PCR检测的混合样品分析
Table 4
| 混合样本 Mixed samples (%) | 平均值1 Mean 1 | 平均值2 Mean 2 | 平均值3 Mean 3 | 平均值 Mean (%) | 标准差 SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.88 | 0.92 | 0.04 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | — |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
3 讨论
欧盟于1997年首先实施转基因产品标识制度, 之后全球四十多个国家和地区相继颁布了转基因产品标识制度。我国于2015年10月1日正式开始执行的《食品安全法》第六十九条就转基因标示问题明确提出: “生产经营转基因食品应当按照规定显著标示”, 这表明我国对转基因技术的重视, 也体现了对消费者知情权的尊重。建立转基因成分灵敏、准确的定量标识是实施转基因安全标识管理的一个关键步骤。目前, 针对转基因产品成分的检测, 国家标准、农业行业标准和出入境检验检疫行业标准中, 主要应用以DNA为检测对象的核酸扩增检测技术, 特别是定性、定量PCR检测技术。定量PCR检测包括SYBR Green I染料法和TaqMan探针法等。染料法经济实惠, 不需要特别定制不同的特异性探针, 通用性较好, 可以通过溶解曲线分析扩增产物的特异性。本研究根据对GC含量、发卡结构、二级结构、Tm值、扩增片段大小等参数分析, 研发了最佳的引物序列(M12-F/R), 但未发现最佳探针序列。本研究建立的基于SYBR Green I染料法的M12定性、定量PCR检测方法, 均采用引物(M12-F/R), PCR扩增序列横跨水稻自身基因和外源基因, 在对含有多组分加工产品检测时, 可以确定所检出的基因片段来自M12, 从而达到品种或品系鉴定的目的。在定性PCR检测方法中, 检测的特异性较好, 灵敏度达到100拷贝单倍体水稻基因组; 在定量PCR检测方法中, LOD和LOQ分别是10和100拷贝单倍体水稻基因组, 重复性较好, 可对混合样本进行准确定量检测分析。由于本试验转基因水稻M12质量较少, 我们构建了M12的质粒分子。质粒分子的优点主要体现在可以通过微生物大量培养, DNA易于纯化, 质量高, 已开始作为标准物质应用于转基因检测[15], 同时也被认为是解决转基因作物检测标准物质严重缺乏的有效途径之一[16,17]。本研究结果表明基于M12质粒分子的定性、定量PCR方法, 最低检测下限和定量下限均可达100拷贝DNA, 相当于100 ng水稻基因组DNA中含有0.05%转基因成分, 可满足世界各国和地区标识制度管理需要。因此, 本研究构建的M12质粒分子可用于相应转基因水稻M12及其衍生品种事件特异性定性、定量检测。但是本研究建立的M12质粒分子和定性、定量PCR检测方法的适用性、稳定性、定量的准确性等都需要通过多个实验室参与的协同试验验证, M12质粒分子才可能被认证为标准物质, 检测方法才能得到更为广泛和普遍的应用, 进而申报国家或农业行业标准, 这也是我们接下来要做的工作。
4 结论
建立了抗病水稻M12及其加工产品转基因成分定性、定量检测体系, 有助于相关行政主管部门加强对转基因水稻及其产品的监管, 为规范转基因产品标识制度提供有力的技术支持。致谢: 上海交通大学生命科学技术学院杨立桃教授对试验材料的研究背景及分析方法进行指导, 特此致谢。
参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-416X.2006.02.005URL [本文引用: 1]

通过基因枪转基因方法和双质粒共转化体系将Xa21基因转入优良恢复系明恢63,得到转基因 系M12和M22,并进一步做田间试验、新品种选育和食用安全性评价。结果显示:M12和M22对中国的所有白叶枯病小种都表现出高度抗性,但与原受体品 种明恢63相比,农艺性状上有许多变异,主要表现在:结实率、千粒重等农艺性状变差,与珍汕97A的配合力显著降低;但与温敏不育系(X07S、 056S)配组的F1有较好的田间表现。通过多代回交和分子标记辅助选择,成功地将Xa21基因从M12株系转到保持系80-4B和不育系80-4A中, 得到抗白叶枯病的皖21B和皖21A。并利用皖21A不育系选育出优良杂交组合抗优97(皖21Ax R-18),该组合在两年区域试验和一年生产试验中产量表现突出,米质优良。对不同世代和不同遗传背景的转基因品系进行白叶枯病鉴定和Southern分 析表明:Xa21基因都能稳定遗传和正常表达,连续16代的种植并没使其白叶枯病的抗性减弱或丧失,而且不论Xa21基因是纯合的还是杂合的都有相同的抗 性表现。对大鼠和小鼠的饲喂试验表明:转基因大米实质上等同于非转基因大米,是安全无害的。
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-416X.2006.02.005URL [本文引用: 1]

通过基因枪转基因方法和双质粒共转化体系将Xa21基因转入优良恢复系明恢63,得到转基因 系M12和M22,并进一步做田间试验、新品种选育和食用安全性评价。结果显示:M12和M22对中国的所有白叶枯病小种都表现出高度抗性,但与原受体品 种明恢63相比,农艺性状上有许多变异,主要表现在:结实率、千粒重等农艺性状变差,与珍汕97A的配合力显著降低;但与温敏不育系(X07S、 056S)配组的F1有较好的田间表现。通过多代回交和分子标记辅助选择,成功地将Xa21基因从M12株系转到保持系80-4B和不育系80-4A中, 得到抗白叶枯病的皖21B和皖21A。并利用皖21A不育系选育出优良杂交组合抗优97(皖21Ax R-18),该组合在两年区域试验和一年生产试验中产量表现突出,米质优良。对不同世代和不同遗传背景的转基因品系进行白叶枯病鉴定和Southern分 析表明:Xa21基因都能稳定遗传和正常表达,连续16代的种植并没使其白叶枯病的抗性减弱或丧失,而且不论Xa21基因是纯合的还是杂合的都有相同的抗 性表现。对大鼠和小鼠的饲喂试验表明:转基因大米实质上等同于非转基因大米,是安全无害的。
[本文引用: 5]
[本文引用: 5]
DOI:10.1097/RLU.0b013e3181f49ac7URLPMID:102748 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract We have developed a novel method, termed loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP), that amplifies DNA with high specificity, efficiency and rapidity under isothermal conditions. This method employs a DNA polymerase and a set of four specially designed primers that recognize a total of six distinct sequences on the target DNA. An inner primer containing sequences of the sense and antisense strands of the target DNA initiates LAMP. The following strand displacement DNA synthesis primed by an outer primer releases a single-stranded DNA. This serves as template for DNA synthesis primed by the second inner and outer primers that hybridize to the other end of the target, which produces a stem-loop DNA structure. In subsequent LAMP cycling one inner primer hybridizes to the loop on the product and initiates displacement DNA synthesis, yielding the original stem-loop DNA and a new stem-loop DNA with a stem twice as long. The cycling reaction continues with accumulation of 10(9) copies of target in less than an hour. The final products are stem-loop DNAs with several inverted repeats of the target and cauliflower-like structures with multiple loops formed by annealing between alternately inverted repeats of the target in the same strand. Because LAMP recognizes the target by six distinct sequences initially and by four distinct sequences afterwards, it is expected to amplify the target sequence with high selectivity.
DOI:10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.08.030URLPMID:26471572 [本文引用: 1]

Detection of GMO material in crop and food samples is the primary step in GMO monitoring and regulation, with the increasing number of GM events in the world market requiring detection solutions with high multiplexing capacity. In this study, we test the suitability of a high-density oligonucleotide microarray platform for direct, quantitative detection of GMOs found in the Turkish feed market. We tested 1830 different 60/nt probes designed to cover the GM cassettes from 12 different GM cultivars (3 soya, 9 maize), as well as plant species-specific and contamination controls, and developed a data analysis method aiming to provide maximum throughput and sensitivity. The system was able specifically to identify each cultivar, and in 10/12 cases was sensitive enough to detect GMO DNA at concentrations of 猢1%. These GMOs could also be quantified using the microarray, as their fluorescence signals increased linearly with GMO concentration.
DOI:10.1073/pnas.96.16.9236URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1021/jf0341013URLPMID:14705890 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) based biosensors have been described for the identification of genetically modified organisms (GMO) by biospecific interaction analysis (BIA). This paper describes the design and testing of an SPR-based BIA protocol for quantitative determinations of GMOs. Biotinylated multiplex Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) products from nontransgenic maize as well as maize powders containing 0.5 and 2% genetically modified Bt-176 sequences were immobilized on different flow cells of a sensor chip. After immobilization, different oligonucleotide probes recognizing maize zein and Bt-176 sequences were injected. The results obtained were compared with Southern blot analysis and with quantitative real-time PCR assays. It was demonstrated that sequential injections of Bt-176 and zein probes to sensor chip flow cells containing multiplex PCR products allow discrimination between PCR performed using maize genomic DNA containing 0.5% Bt-176 sequences and that performed using maize genomic DNA containing 2% Bt-176 sequences. The efficiency of SPR-based BIA in discriminating material containing different amounts of Bt-176 maize is comparable to real-time quantitative PCR and much more reliable than Southern blotting, which in the past has been used for semiquantitative purposes. Furthermore, the approach allows the BIA assay to be repeated several times on the same multiplex PCR product immobilized on the sensor chip, after washing and regeneration of the flow cell. Finally, it is emphasized that the presented strategy to quantify GMOs could be proposed for all of the SPR-based, commercially available biosensors. Some of these optical SPR-based biosensors use, instead of flow-based sensor chips, stirred microcuvettes, reducing the costs of the experimentation.
DOI:10.1016/j.bios.2017.01.057URLPMID:28182975 [本文引用: 1]

With the increasing concern of potential health and environmental risk, it is essential to develop reliable methods for transgenic soybean detection. Herein, a simple, sensitive and selective assay was constructed based on homogeneous fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) between CdTe quantum dots (QDs) and multiwalled carbon nanotubes@graphene oxide nanoribbons (MWCNTs@GONRs) to form the fluorescent "on-off-on" switching for simultaneous monitoring dual target DNAs of promoter cauliflower mosaic virus 35s (P35s) and terminator nopaline synthase (TNOS) from transgenic soybean. The capture DNAs were immobilized with corresponding QDs to obtain strong fluorescent signals (turning on). The strong 蟺-蟺 stacking interaction between single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) probes and MWCNTs@GONRs led to minimal background fluorescence due to the FRET process (turning off). The targets of P35s and TNOS were recognized by dual fluorescent probes to form double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) through the specific hybridization between target DNAs and ssDNA probes. And the dsDNA were released from the surface of MWCNTs@GONRs, which leaded the dual fluorescent probes to generate the strong fluorescent emissions (turning on). Therefore, this proposed homogeneous assay can be achieved to detect P35s and TNOS simultaneously by monitoring the relevant fluorescent emissions. Moreover, this assay can distinguish complementary and mismatched nucleic acid sequences with high sensitivity. The constructed approach has the potential to be a tool for daily detection of genetically modified organism with the merits of feasibility and reliability.
URL [本文引用: 1]

环介导等温扩增(LAMP)技术是近年发展起来的新型核酸体外等温扩增技术,具有快速、特异、敏感、简便等特点,使该技术在核酸快速检测领域得到了广泛的应用,但LAMP技术也在不断完善与发展中。本文就LAMP扩增产物的污染,引物间非连续配对的假阳性问题的对策,以及在LAMP技术基础上发展起来的其他相关技术进行综述,为该技术在基层的推广应用提供参考。
URL [本文引用: 1]

环介导等温扩增(LAMP)技术是近年发展起来的新型核酸体外等温扩增技术,具有快速、特异、敏感、简便等特点,使该技术在核酸快速检测领域得到了广泛的应用,但LAMP技术也在不断完善与发展中。本文就LAMP扩增产物的污染,引物间非连续配对的假阳性问题的对策,以及在LAMP技术基础上发展起来的其他相关技术进行综述,为该技术在基层的推广应用提供参考。
DOI:10.15889/j.issn.1002-1302.2017.05.003URL [本文引用: 1]

随着转基因生物在全世界的广泛应用,转基因成分检测技术越来越受到广大消费者、各国政府及相关机构人员的重视.本文从聚合酶链式反应( PCR)检测技术、环介导等温扩增检测技术、近红外光谱检测技术、生物传感器检测技术、生物芯片检测技术和蛋白质检测技术等方面进行综述,并提出今后转基因成分检测技术的发展趋势和研究方向.
DOI:10.15889/j.issn.1002-1302.2017.05.003URL [本文引用: 1]

随着转基因生物在全世界的广泛应用,转基因成分检测技术越来越受到广大消费者、各国政府及相关机构人员的重视.本文从聚合酶链式反应( PCR)检测技术、环介导等温扩增检测技术、近红外光谱检测技术、生物传感器检测技术、生物芯片检测技术和蛋白质检测技术等方面进行综述,并提出今后转基因成分检测技术的发展趋势和研究方向.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-3924.2010.01.029URL [本文引用: 1]

综述了国内外转基因生物(Genetically modified organisms,GMOs)及其产品检测方法的研究进展,并重点介绍了目前广泛应用的一些检测方法。
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-3924.2010.01.029URL [本文引用: 1]

综述了国内外转基因生物(Genetically modified organisms,GMOs)及其产品检测方法的研究进展,并重点介绍了目前广泛应用的一些检测方法。
DOI:10.1007/s12010-013-0254-7URLPMID:23645416 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract Genetically modified carnation (Dianthus caryophyllus L.) Moonshade was approved for planting and commercialization in several countries from 2004. Developing methods for analyzing Moonshade is necessary for implementing genetically modified organism labeling regulations. In this study, the 5'-transgene integration sequence was isolated using thermal asymmetric interlaced (TAIL)-PCR. Based upon the 5'-transgene integration sequence, conventional and TaqMan real-time PCR assays were established. The relative limit of detection for the conventional PCR assay was 0.05 % for Moonshade using 100 ng total carnation genomic DNA, corresponding to approximately 79 copies of the carnation haploid genome, and the limits of detection and quantification of the TaqMan real-time PCR assay were estimated to be 51 and 254 copies of haploid carnation genomic DNA, respectively. These results are useful for identifying and quantifying Moonshade and its derivatives.
DOI:10.1038/423231aURLPMID:19326953 [本文引用: 4]

Abstract One rice ( Oryza sativa ) gene, sucrose phosphate synthase (SPS), has been proven to be a suitable endogenous reference gene for genetically modified (GM) rice detection in a previous study. Herein are the reported results of an international collaborative ring trial for validation of the SPS gene as an endogenous reference gene and its optimized qualitative and quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) systems. A total of 12 genetically modified organism (GMO) detection laboratories from seven countries participated in the ring trial and returned their results. The validated results confirmed the species specificity of the method through testing 10 plant genomic DNAs, low heterogeneity, and a stable single-copy number of the rice SPS gene among 7 indica varieties and 5 japonica varieties. The SPS qualitative PCR assay was validated with a limit of detection (LOD) of 0.1%, which corresponded to about 230 copies of haploid rice genomic DNA, while the limit of quantification (LOQ) for the quantitative PCR system was about 23 copies of haploid rice genomic DNA, with acceptable PCR efficiency and linearity. Furthermore, the bias between the test and true values of eight blind samples ranged from 5.22 to 26.53%. Thus, we believe that the SPS gene is suitable for use as an endogenous reference gene for the identification and quantification of GM rice and its derivates.
DOI:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2008.07.533URLPMID:18570432 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract To enforce the labeling regulations of genetically modified organisms (GMOs), the application of reference molecules as calibrators is becoming essential for practical quantification of GMOs. However, the reported reference molecules with tandem marker multiple targets have been proved not suitable for duplex PCR analysis. In this study, we developed one unique plasmid molecule based on one pMD-18T vector with three exogenous target DNA fragments of Roundup Ready soybean GTS 40-3-2 (RRS), that is, CaMV35S, NOS, and RRS event fragments, plus one fragment of soybean endogenous Lectin gene. This Lectin gene fragment was separated from the three exogenous target DNA fragments of RRS by inserting one 2.6 kb DNA fragment with no relatedness to RRS detection targets in this resultant plasmid. Then, we proved that this design allows the quantification of RRS using the three duplex real-time PCR assays targeting CaMV35S, NOS, and RRS events employing this reference molecule as the calibrator. In these duplex PCR assays, the limits of detection (LOD) and quantification (LOQ) were 10 and 50 copies, respectively. For the quantitative analysis of practical RRS samples, the results of accuracy and precision were similar to those of simplex PCR assays, for instance, the quantitative results were at the 1% level, the mean bias of the simplex and duplex PCR were 4.0% and 4.6%, respectively, and the statistic analysis ( t-test) showed that the quantitative data from duplex and simplex PCR had no significant discrepancy for each soybean sample. Obviously, duplex PCR analysis has the advantages of saving the costs of PCR reaction and reducing the experimental errors in simplex PCR testing. The strategy reported in the present study will be helpful for the development of new reference molecules suitable for duplex PCR quantitative assays of GMOs.
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2008.07.533URLPMID:18570432 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract To enforce the labeling regulations of genetically modified organisms (GMOs), the application of reference molecules as calibrators is becoming essential for practical quantification of GMOs. However, the reported reference molecules with tandem marker multiple targets have been proved not suitable for duplex PCR analysis. In this study, we developed one unique plasmid molecule based on one pMD-18T vector with three exogenous target DNA fragments of Roundup Ready soybean GTS 40-3-2 (RRS), that is, CaMV35S, NOS, and RRS event fragments, plus one fragment of soybean endogenous Lectin gene. This Lectin gene fragment was separated from the three exogenous target DNA fragments of RRS by inserting one 2.6 kb DNA fragment with no relatedness to RRS detection targets in this resultant plasmid. Then, we proved that this design allows the quantification of RRS using the three duplex real-time PCR assays targeting CaMV35S, NOS, and RRS events employing this reference molecule as the calibrator. In these duplex PCR assays, the limits of detection (LOD) and quantification (LOQ) were 10 and 50 copies, respectively. For the quantitative analysis of practical RRS samples, the results of accuracy and precision were similar to those of simplex PCR assays, for instance, the quantitative results were at the 1% level, the mean bias of the simplex and duplex PCR were 4.0% and 4.6%, respectively, and the statistic analysis ( t-test) showed that the quantitative data from duplex and simplex PCR had no significant discrepancy for each soybean sample. Obviously, duplex PCR analysis has the advantages of saving the costs of PCR reaction and reducing the experimental errors in simplex PCR testing. The strategy reported in the present study will be helpful for the development of new reference molecules suitable for duplex PCR quantitative assays of GMOs.
DOI:10.1021/jf0615754URLPMID:17199308 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract With the development of genetically modified organism (GMO) detection techniques, the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) technique has been the mainstay for GMO detection, and real-time PCR is the most effective and important method for GMO quantification. An event-specific detection strategy based on the unique and specific integration junction sequences between the host plant genome DNA and the integrated gene is being developed for its high specificity. This study establishes the event-specific detection methods for TC1507 and CBH351 maizes. In addition, the event-specific TaqMan real-time PCR detection methods for another seven GM maize events (Bt11, Bt176, GA21, MON810, MON863, NK603, and T25) were systematically optimized and developed. In these PCR assays, the fluorescent quencher, TAMRA, was dyed on the T-base of the probe at the internal position to improve the intensity of the fluorescent signal. To overcome the difficulties in obtaining the certified reference materials of these GM maizes, one novel standard reference molecule containing all nine specific integration junction sequences of these GM maizes and the maize endogenous reference gene, zSSIIb, was constructed and used for quantitative analysis. The limits of detection of these methods were 20 copies for these different GM maizes, the limits of quantitation were about 20 copies, and the dynamic ranges for quantification were from 0.05 to 100% in 100 ng of DNA template. Furthermore, nine groups of the mixed maize samples of these nine GM maize events were quantitatively analyzed to evaluate the accuracy and precision. The accuracy expressed as bias varied from 0.67 to 28.00% for the nine tested groups of GM maize samples, and the precision expressed as relative standard deviations was from 0.83 to 26.20%. All of these indicated that the established event-specific real-time PCR detection systems and the reference molecule in this study are suitable for the identification and quantification of these GM maizes.
