 ,*福建农林大学农业部福建甘蔗生物学与遗传育种重点实验室 / 国家甘蔗工程技术研究中心, 福建福州 350002
,*福建农林大学农业部福建甘蔗生物学与遗传育种重点实验室 / 国家甘蔗工程技术研究中心, 福建福州 350002A Sugarcane Phosphatidylinositol Transfer Protein Gene ScSEC14 Responds to Drought and Salt Stresses
MAO Hua-Ying, LIU Feng, SU Wei-Hua, HUANG Ning, LING Hui, ZHANG Xu, WANG Wen-Ju, LI Cong-Na, TANG Han-Chen, SU Ya-Chun, QUE You-Xiong ,*Key Laboratory of Sugarcane Biology and Genetic Breeding (Fujian), Ministry of Agriculture, Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University / Sugarcane Research & Development Center, China Agricultural Technology System, Fuzhou 350002, Fujian, China
,*Key Laboratory of Sugarcane Biology and Genetic Breeding (Fujian), Ministry of Agriculture, Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University / Sugarcane Research & Development Center, China Agricultural Technology System, Fuzhou 350002, Fujian, China通讯作者:
第一联系人:
收稿日期:2017-12-10接受日期:2018-03-15网络出版日期:2018-06-12
| 基金资助: |
Received:2017-12-10Accepted:2018-03-15Online:2018-06-12
| Fund supported: |

摘要
关键词:
Abstract
Keywords:
PDF (7592KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
本文引用格式
毛花英, 刘峰, 苏炜华, 黄宁, 凌辉, 张旭, 王文举, 李聪娜, 汤翰臣, 苏亚春, 阙友雄. 甘蔗磷脂酰肌醇转运蛋白基因ScSEC14响应干旱和盐胁迫[J]. 作物学报, 2018, 44(6): 824-835. doi:10.3724/SP.J.1006.2018.00824
MAO Hua-Ying, LIU Feng, SU Wei-Hua, HUANG Ning, LING Hui, ZHANG Xu, WANG Wen-Ju, LI Cong-Na, TANG Han-Chen, SU Ya-Chun, QUE You-Xiong.
磷酸肌醇是磷脂酰肌醇及其磷酸衍生物的总称, 是一类由磷脂酸与肌醇结合的脂质。磷酸肌醇由一分子的甘油和一分子磷酸结合而成, 并可以通过磷酸化或去磷酸化获得到多种不同衍生物[1,2]。目前, 植物中发现的磷酸肌醇主要包括磷脂酰肌醇-3-磷酸(phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate, PtdIns3P)、磷脂酰肌醇-4-磷酸(phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate, PtdIns4P)、磷脂酰肌醇-5-磷酸(phosphatidylinositol- 5-phosphate, PtdIns5P)、磷脂酰肌醇-3,5-二磷酸(phosphatidylinositol-3,5-bisphosphate, PtdIns (3,5) P2)和磷脂酰肌醇-4,5-二磷酸(phosphatidylinositol-4,5- bisphosphate, PtdIns (4,5) P2)[1]。这些植物磷酸肌醇在细胞内特定位置合成, 并被转运到特定的位置发挥功能, 其功能包括: 维持细胞结构、控制膜流动、调节膜物质的转运及调控离子通道和细胞信号转导等[3]。
磷脂酰肌醇转运蛋白(phosphatidylinositol transfer protein, PITP)是真核生物中普遍存在的一种脂质转运蛋白[4]。根据物种来源, 磷脂酰肌醇转运蛋白可被分为哺乳动物和昆虫等多细胞动物的PITP及植物和真菌的PITP两大类[5]。其中植物与真菌PITP的序列同源性高, 但除PITP结构域外, C端还包含其他的结构域, 如GOLD-domain和Nodulin- domain[1]。根据C端结构域的不同, 植物PITP又可以分为三类, 一是只含有磷脂转移功能域的PITP, 如大豆中发现的Ssh1p和Ssh2p, 该类蛋白主要参与渗透调节[6]; 二是C端具有GOLD-domain的PITP, 该类蛋白主要参与细胞分裂和囊泡运输, 如拟南芥AtPATL蛋白[7]和意大利青瓜CpPATL1蛋白[8]; 三是C端具有Nodulin-domain的PITP, 该类蛋白主要与细胞的极性生长有关, 如拟南芥AtSFH蛋白[9]。前人研究显示, 在真核生物细胞内, 该蛋白能够发挥调节真核生物细胞内膜系统间磷脂的转运、调节磷脂信号的传递、调节植物生长发育和响应植物逆境胁迫等功能[5,10]。该基因在不同作物中响应盐胁迫、干旱、低温等均有相关报道。Kiba等[11,12]在本氏烟中鉴定了一个NbSEC14, 该基因在脂质介导的信号途径中参与植物的免疫应答, 随后又发现烟草SEC14磷脂转运蛋白可以通过茉莉酸依赖的防御信号途径来调控植物对假单胞菌的抗性。Kielbowicz- Matuk等[13]报道了抗旱大麦中一个HvSec14p基因, 在种子形成与萌发的特定发育阶段以及不同渗透胁迫下, 其转录水平与蛋白水平均上调表达。苏世超等[14]在普通小麦中克隆了一个TaSEC14p-5基因, 该基因在小麦孕穗期的不同组织中组成型表达, 并受盐、脱落酸、干旱及低温胁迫的诱导。王晓宇等[15]在玉米中分离鉴定了一个ZmSEC14p基因, 该基因在4℃、盐胁迫、ABA处理时上调表达, 稳定表达该基因则能提高转基因拟南芥植株对冷胁迫的耐受性。Kearns等[6]和Monks等[16]报道了2个大豆磷脂酰肌醇转运蛋白Ssh1p和Ssh2p参与渗透胁迫下植物的应答, 随后又报道了细胞高渗压力下Ssh1p蛋白通过激活蛋白激酶SPK1和SPK2使其快速磷酸化。
甘蔗(Saccharum spp.)是一种重要的糖料作物, 蔗糖占全世界食糖的60%以上, 占我国的90%以上[17]。我国甘蔗主要种植在盐碱地和旱地[18]。研究表明, 在甘蔗生长发育过程中, 干旱胁迫和高盐环境对其萌芽、分蘖、伸长生长、叶片扩展和成熟等进程具有重要的影响, 最终造成蔗茎产量的减少和蔗糖分的降低[19,20]。近年来, 从甘蔗克隆出一些与逆境胁迫有关的基因。例如, 郭晋隆等[21]报道了甘蔗ScDir基因, 其参与了甘蔗对干旱、盐和氧化应激反应; 苏亚春等[22,23]报道了2种应激相关基因, 即ScGluA1和ScGluD1, 以及从甘蔗中分离的新型应激诱导基因Scdr1, 含有该基因的转基因烟草植株对干旱、盐和氧化胁迫具有较高的耐受性; 陈云等[24]报道了一个甘蔗非特异性脂质转运蛋白ScNsLTP, 该基因对适应干旱和低温环境发挥重要作用。
从基因工程角度看, 一旦挖掘鉴定到控制某种优良性状的主效基因, 我们就有可能通过遗传转化途径将其用于改良甘蔗品种的目标性状[25]。迄今为止, SEC14基因仅在几种作物中被报道[15,26-27], 国内外均未见在甘蔗中的研究报道。本研究拟以甘蔗受黑穗病胁迫下转录组数据库中SEC14基因序列作为探针, 电子克隆ScSEC14的全长cDNA序列; 利用RT-PCR技术扩增验证ScSEC14基因序列的正确性; 并采用实时荧光定量PCR (reverse transcript-qPCR, RT-qPCR)等方法分析该基因在根、侧芽、蔗皮、蔗髓、叶中表达的特异性及其在不同外源胁迫(salicylic acid、CaCl2、PEG、NaCl、CuCl2和CdCl2)下的表达特性。希望能为进一步深入理解ScSEC14基因在甘蔗中的功能表达和作用机制奠定一定基础, 并为甘蔗抗逆性状的基因工程改良提供具有潜在育种利用价值的基因资源。
1 材料与方法
1.1 植物材料及主要试剂
供试甘蔗材料品种ROC22由福建农林大学农业部福建甘蔗生物学与遗传育种重点实验室提供。试剂主要为PrimeScript RT-PCR Kit反转录试剂盒(TaKaRa, 中国大连)、TRIzol Reagent (Invitrogen, USA)、Gel Extracti on Kit (TIANGEN, 中国北京)、SYBRGreen PCR Master Mix Kit (Roche, USA)。1.2 材料处理和RNA提取
从田间选取生长健壮、长势相似的植株, 砍成单芽茎段, 用流动清水浸泡24 h, 于高温高压灭菌营养土中催芽(16 h/8 h, 光/暗, 28℃), 待4~6叶时取长势一致的蔗苗用于组培苗的诱导, 而后将组培甘蔗幼苗移出并在温室内开放水培一周。设置对照组和试验组, 生物学重复为3次。试验组以5 mmol L-1水杨酸(SA: 3、6和12 h)、50 μmol L-1氯化钙(CaCl2: 3、6和12 h)、25.0% PEG (模拟干旱: 6、12和24 h)、250 mmol L-1氯化钠(NaCl: 6、12和24 h)、500 mmol L-1氯化铜(CuCl2: 12、24和48 h)、500 mmol L-1氯化铬(CdCl2: 12、24和48 h)水溶液培养, 以0 h未处理的蔗苗为对照。以上所有甘蔗材料取样后被立即投入液氮并保存于-80℃冰箱至RNA提取。采用TRIzol法提取所有样品的总RNA, 包括用于甘蔗ScSEC14基因RT-PCR扩增的蔗苗, 用于组织特异性表达分析的甘蔗根、侧芽、蔗皮、蔗髓和叶片组织, 以及用于SA、CaCl2、PEG、NaCl、CuCl2和CdCl2 6种外源胁迫处理材料。Table 1
表1
表1实时荧光定量材料处理
Table 1
| 处理条件 Treatment condition | 取样时间Sampling time (h) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 取样点1 Site 1 | 取样点2 Site 2 | 取样点3 Site 3 | |
| 5 mmol L-1 SA | 3 | 6 | 12 |
| 25.0% PEG模拟干旱 25.0% PEG simulated drought | 6 | 12 | 24 |
| 50 μmol L-1 CaCl2 | 3 | 6 | 12 |
| 250 mmol L-1 NaCl | 6 | 12 | 24 |
| 500 mmol L-1 CuCl2 | 12 | 24 | 48 |
| 500 mmol L-1 CdCl2 | 12 | 24 | 48 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
1.4 甘蔗ScSEC14基因的RT-PCR扩增及序列测定
使用Prime-Script RT Reagent Kit反转录试剂盒合成cDNA作为RT-PCR扩增模板。应用Primer 5.0软件设计甘蔗ScSEC14基因的RT-PCR扩增引物(表2)。PCR扩增体系总体积为25 μL, 含10×Ex Taq buffer 2.5 μL、10 mmol L-1dNTPs 2 μL、20 μmol L-1上下游引物各1.0 μL、Ex Taq酶0.125 μL、cDNA模板1.0 μL、ddH2O 17.375 μL。PCR程序为95℃预变性4 min; 95℃变性30 s, 65℃ (每个循环降0.5℃)退火30 s, 72℃延伸1 min 30 s, 35个循环; 72℃延伸10 min。先将扩增产物纯化回收, 然后将回收产物连接到pMD-19T载体并转化到大肠杆菌DH5α感受态细胞中, 于含有氨苄青霉素的LB平板上进行阳性克隆筛选并挑取单菌落鉴定, 随后送上海铂尚生物工程技术服务有限公司测序, 并通过DNAMAN软件比对测序结果的正确性。Table 2
表2
表2ScSEC14基因克隆与表达所用引物
Table 2
| 引物 Primer | 引物序列 Sequence information (5'-3') | 用途 Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| SEC14 | F: AGGAAGCGCACAAGAACAGA | 基因克隆 Gene cloning |
| R: GGGAGTACAAGTCTCCTTGCATA | ||
| qSEC14 | F: CCACGAGTCACTTCCACACT | 荧光定量Real-time-qPCR |
| R: TGGGACCAAGAGAGTCCTGA | ||
| CUL | F: TGCTGAATGTGTTGAGCAGC | 内参基因 Reference genes |
| R: TTGTCGCGCTCCAAGTAGTC | ||
| CAC | F: ACAACGTCAGGCAAAGCAAA | 内参基因 Reference genes |
| R: AGATCAACTCCACCTCTGCG | ||
| G-SEC14 | F: GGGGACAAGTTTGTACAAAAAAGCAGGCTTCATGGCGGCCACCTCCGGAAGG | 载体构建 Vector construction |
| R: GGGGACCACTTTGTACAAGAAAGCTGGGTCTGGACCTTCGATCTGTATGCTG |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
1.5 甘蔗ScSEC14基因序列的生物信息学分析
利用在线工具ExPASy中的Protparam tool (http://web.expasy.org/compute_pi/)预测ScSEC14基因的理化性质及其编码的蛋白的一级结构、亲疏水性等; 利用Prabi (https://npsa-prabi.ibcp.fr/cgi-bin/ npsa_automat.pl?page=/NPSA/npsa_hnn.html)、ProtFun (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/ProtFun/)、SignalP (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/ services/SignalP/)和TMHMM (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TMHMM/)分别对其二级结构、功能特性、信号肽、和跨膜特性进行预测分析; 用SWISSMODEL (https://swissmodel.expasy.org/interactive)在线预测工具预测分析蛋白三级结构; 通过NCBI中的CDD (conserved domain database)数据库预测蛋白保守结构域; 用Blastp在线工具查找甘蔗ScSEC14同源氨基酸序列, 并使用DNAMAN 7.0软件多重比对同源氨基酸序列, 使用MEGA 6.0软件ML (maximum likelihood,LG+G)法构建系统进化树。1.6 甘蔗ScSEC14基因的亚细胞定位分析
采用双酶切方法将ScSEC14基因构建到亚细胞定位载体pCAMBIA 2300-GFP上, 然后将筛选好的阳性质粒转化农杆菌GV3101菌株。在含50 μg mL-1卡那霉素和35 μg mL-1利福平的LB液体培养基上, 用含200 μmol L-1乙酰丁香酮的MS空白培养基, 将菌液浓度调整至OD600=0.8, 然后选择5~8片叶龄、长势一致的本氏烟进行叶片注射, 对照组为空载pCAMBIA 2300-GFP。注射完在28℃下光照16 h/黑暗8 h培养, 2 d后, 显微镜观察亚细胞定位结果。1.7 甘蔗ScSEC14基因原核表达分析
运用Gateway构载体方法将ScSEC14基因构到原核表达载体pEZY19中得到重组菌ScSEC14- pEZY19, 将阳性重组菌株、空白菌株BL21和空载BL21-pEZY19菌液, 分别加至20 mL LB液体培养基中, 于37℃下200 r min-1振荡培养至OD600约为0.6后, 加入异丙基硫代半乳糖苷(IPTG)至终浓度为1.0 mmol L-1, 在28℃下200 r min-1摇床内进行蛋白诱导, 分别于0、1.5、1、2、4、6、8 h取样。将上述样品在4℃下8000 r min-1离心10 min收集菌体, 去除上清液后, 加入30 μL 2×蛋白上样缓冲液, 混匀后于100℃水浴5 min进行裂解, 各取10 μL上清液用12%十二烷基磺酸钠-聚丙烯酰氨凝胶电泳(SDS-PAGE)检测, 经考马斯亮蓝染色和成像分析。1.8 甘蔗ScSEC14基因表达的RT-qPCR分析
参照Prime-Script RT Reagent Kit操作说明书, 将RNA反转录合成cDNA得到模板。采用NCBI引物在线设计工具Primer designing tool (https://www.ncbi. nlm.nih.gov/tools/primer-blast/index.cgi?LINK_LOC=BlastHome)设计ScSEC14基因和内参基因(CUL和CAC)[28]的定量PCR引物(表2)。RT-qPCR体系(20 μL)含SYBRGreen Primix Ex Taq (2×) 10 μL、10 μmol L-1上下游引物各1 μL、cDNA 1.0 μL、ddH2O 7 μL。扩增程序为50℃ 2 min; 95℃ 10 min; 95℃ 15 s, 60℃ 1 min, 45个循环; 增加熔解曲线; 反应时设置3次技术重复。在ABI PRISM7500 Real-time PCR System进行实时荧光定量PCR分析, 实验结束后导出Microsoft Excel工作表, 采用2-ΔΔCt算法[29]分析RT-qPCR试验结果, 计算3次重复数据的标准误后绘图。2 结果与分析
2.1 甘蔗ScSEC14基因序列的获得
应用电子克隆技术获得甘蔗磷脂酰肌醇转运蛋白基因ScSEC14的cDNA全长序列, 并根据该序列设计特异性引物, 经过RT-PCR扩增、胶回收、连接转化、菌液PCR鉴定和测序获得约1008 bp的单一条带(图1)。序列比对表明, 测序序列与电子克隆序列同源性高达99.40%, 验证了RT-PCR扩增产物的正确性, 将该基因命名为ScSEC14, 其GenBank登录号为MG571103。ScSEC14基因的核酸序列及其推导的氨基酸序列如图2。图1
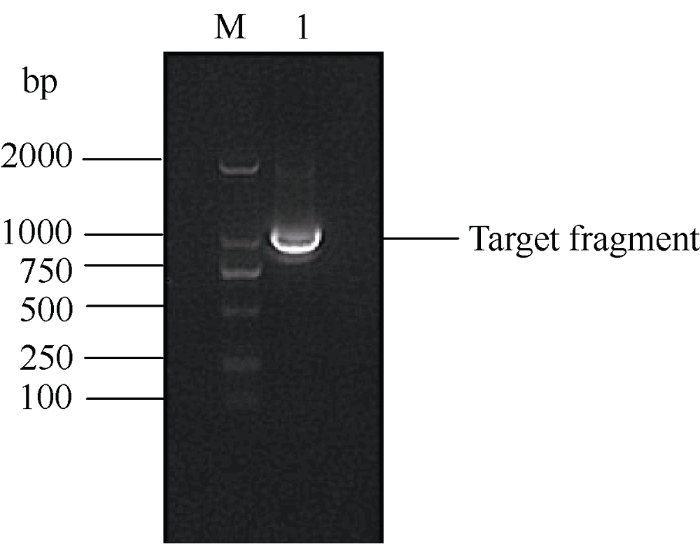 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图1甘蔗ScSEC14基因的RT-PCR扩增
M: DNA marker, D2000 bp; 1:目的条带。
Fig. 1RT-PCR amplification of ScSEC14 gene in sugarcane
M: DNA marker, D2000 bp; 1: Target fragment.
图2
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图2甘蔗ScSEC14基因的cDNA序列及其推导的氨基酸序列(*终止密码子)
方框部分为特异性引物在基因序列中的位置。
Fig. 2Nucleotide sequence and deduced amino acid sequence of sugarcane ScSEC14 gene (* stop codon)
The sequence fragment complementary to primer is highlighted in the box.
2.2 甘蔗ScSEC14基因的生物信息学分析
2.2.1 甘蔗ScSEC14蛋白信号肽、疏水性/亲水性的预测和分析 甘蔗ScSEC14蛋白氨基酸残基的加权平均值较小, 为0.101 (<0.5), 推测该蛋白不存在信号肽。即甘蔗ScSEC14蛋白为非分泌蛋白, 在细胞质中合成后不能被转运。从图3可以看出, 第93位具有最高分值, 为1.633, 疏水性最强; 第215位具有最低分值, 为-2.544, 亲水性最强。分值大于0的氨基酸数为112个, 分值小于0的氨基酸数为223个, 推测甘蔗ScSEC14蛋白是一种亲水蛋白。图3
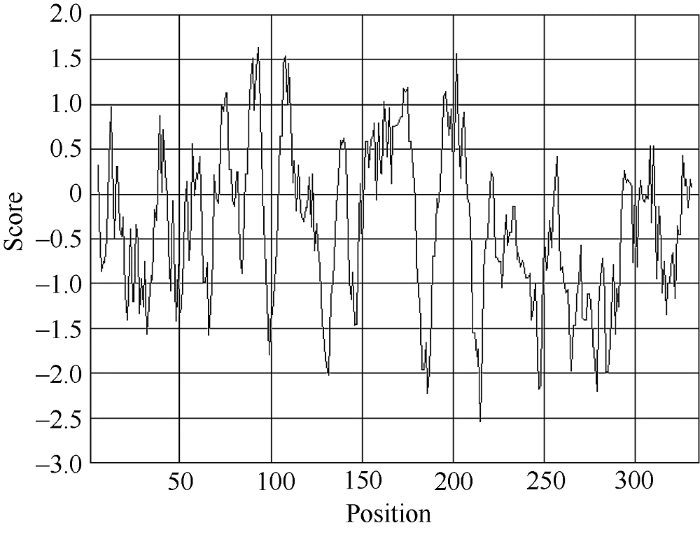 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图3甘蔗ScSEC14蛋白氨基酸疏水性/亲水性预测
Fig. 3Predicted hydrophobicity of the amino acid sequence of sugarcane ScSEC14 protein
2.2.2 甘蔗ScSEC14基因编码蛋白的一级和二级结构预测 甘蔗ScSEC14基因编码蛋白的一级结构预测显示, 该蛋白分子式为C1698H2684N460O500S17, 分子量为38 087.79, 编码了335个氨基酸, 其等电点(pI)为8.6, 不稳定系数为42.31, 数值大于40表明该蛋白不稳定, 推测为不稳定的碱性蛋白质。二级结构预测显示, 甘蔗ScSEC14蛋白中α-螺旋所占的比例最高, 为43.28%, 延伸链所占比例最低, 为15.52%, 无规则卷曲结构占41.19% (表3)。
Table 3
表3
表3甘蔗ScSEC14蛋白二级结构预测分析
Table 3
| 二级结构类型 Secondary structure type | 氨基酸残基数目 Amino acid residue number | 百分比 Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|
| α-螺旋Alpha-helix | 145 | 43.28 |
| 延伸链Extended strand | 52 | 15.52 |
| 无规则卷曲Random coil | 138 | 41.19 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
2.2.3 甘蔗ScSEC14蛋白三级结构预测 用SWISSMODEL软件预测甘蔗ScSEC14的三级结构(图4), 由图4中可以看出, 其结构主要以螺旋和无规则卷曲为主。比较甘蔗、高粱、玉米、小米和水稻的SEC14蛋白的三级结构图, 结果如图4所示: 甘蔗ScSEC14蛋白与高粱、玉米、小米和水稻的SEC14蛋白相似度较高, 其中甘蔗与高粱的SEC14蛋白的相似度最高。
图4
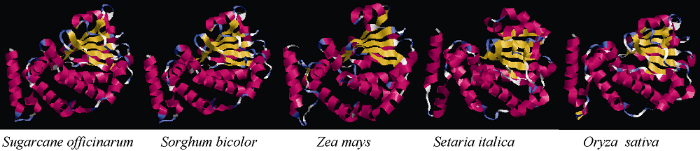 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图4甘蔗、高粱、玉米、粟和水稻SEC14蛋白三级结构预测
Fig. 4Predicted tertiary structure of SEC14 protein in Sugarcane officinarum, Sorghum bicolor, Zea mays, Setaria italic, and Oryza sativa
2.2.4 甘蔗ScSEC14蛋白的功能预测和保守结构域分析 Profun 2.2 Server网站预测分析显示, 甘蔗ScSEC14蛋白的主要功能与氨基酸生物合成(优势比Odd: 5.878)和辅酶因子生物合成(优势比Odd: 2.893)相关, 其次也可能是翻译(优势比Odd: 2.818)。保守结构域分析显示, 甘蔗ScSEC14蛋白隶属的家族为SEC14 superfamily, N端包含一个CRAL_ TRIO_N结构域(图5)。
图5
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图5甘蔗ScSEC14蛋白的保守结构域分析
Fig. 5Conserved domain prediction of sugarcane ScSEC14 protein
2.2.5 甘蔗ScSEC14蛋白的氨基酸序列同源性分析和系统进化树分析 通过NCBI中的Blastp程序对甘蔗及其他物种SEC14蛋白的氨基酸序列进行同源性分析。结果显示, ScSEC14蛋白与高粱(Sorghum bicolor |XP_002459926.1|)、玉米(Zea mays |NP_ 001136689.1|)、粟(Setaria italica |XP_004956364.1|)、水稻(Oryza brachyantha |XP_006660469.1|)、二穗短柄草(Brachypodium distachyon |XP_003576972.1|)、粗山羊草亚种(Aegilops tauschii subsp. tauschii |XP_ 020197696.1|)、大麦(Hordeum vulgare subsp. vulgare |BAK00848.1|)、油棕(Elaeis quineensis |XP_010942585.1|)和海枣(Phoenix dactylifera |XP_008797755.1|)中SEC14蛋白的氨基酸序列相似性分别为95%、93%、90%、84%、81%、81%、80%、71%和69% (图6-A)。本研究中克隆得到的ScSEC14基因编码蛋白与其他物种的SEC14蛋白具有较高的同源性。将甘蔗ScSEC14与拟南芥、大豆等植物的PITP基因[11]进行系统进化树分析(图6-B), 可知植物Sec14-like蛋白主要分为4组: SSH (soybean Sec14 homolog group)、UCSH (uncharacterized SEC14p homolog group)、SFH (Sec14 homolog group)和PATL (patellin group), 其中甘蔗ScSEC14属于Sec14-like蛋白家族的SSH亚家族, 其结构域中只包含1个N端SEC14结构域(图6-C)。
图6
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图6ScSEC14 蛋白的氨基酸序列同源性分析和系统进化树分析
A: ScSEC14 蛋白与其他物种的SEC14 蛋白的氨基酸序列比对; B: ScSEC14 蛋白与其他物种SEC14 蛋白的系统进化树分析; C: ScSEC14 蛋白与其他物种SEC14 蛋白的结构域分析。
Fig. 6Deduced amino acid sequence and the phylogenic tree of ScSEC14 protein
A: Amino acid sequence alignment of the ScSEC14 protein with SEC14 proteins of other species; B: Phylogenetic tree analysis of ScSEC14 protein and SEC14 protein from other species; C: Domain analysis of ScSEC14 protein and SEC14 proteins of other species.
2.3 甘蔗ScSEC14蛋白的亚细胞定位
运用DAPI核染色的方法, 采用明场、绿色荧光、蓝色荧光及绿色荧光和蓝色荧光叠加这4个视野拍摄ScSEC14蛋白的亚细胞定位图片。从图7中可以看出, 对照组在细胞膜、细胞核、细胞质中均有定位, ScSEC14蛋白在细胞膜和细胞核中均有定位, 但在细胞核中的表达较弱, 因此ScSEC14蛋白主要定位于细胞膜。图7
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图7甘蔗ScSEC14蛋白在烟草叶片中的亚细胞定位
红色箭头代表细胞核; 白色箭头代表细胞膜; 蓝色箭头代表细胞质。
Fig. 7Subcellular localization of ScSEC14 in Nicotiana benthamiana leaves
Red arrow represents nucleus; white arrow represents plasma membrane; blue arrow represents cytoplasm.
2.4 甘蔗ScSEC14基因的原核表达实验
在获得ScSEC14基因全长cDNA的基础上, 将其克隆至原核表达载体pEZY19中, 构建了重组表达载体pEZY19-ScSEC14, 表达产物经SDS-PAGE验证, 获得与预期相符的38 kDa左右的重组蛋白, 表明目的蛋白在大肠杆菌表达菌株BL21 (DE3)中得到成功表达(图8)。图8
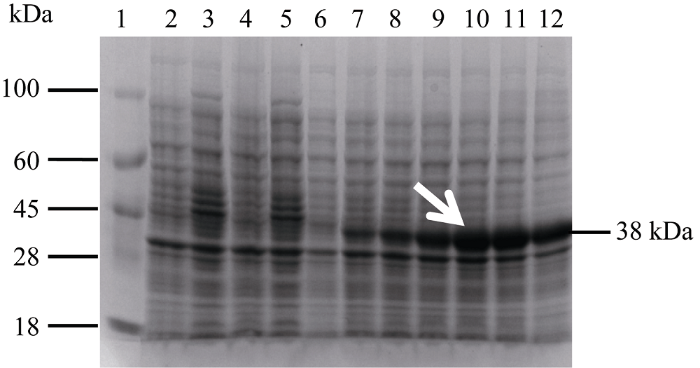 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图8pEZY19-ScSEC14和pEZY19(+)表达产物的SDS-PAGE分析
1: marker; 2: 空菌诱导0 h; 3: 空菌诱导8 h; 4: 空载诱导0 h; 5: 空载诱导8 h; 6~12: 重组菌诱导0、1.5、1、2、4、6、8 h; 白色箭头代表被诱导的目标蛋白。
Fig. 8SDS-PAGE analysis of the expression of pEZY19-ScSEC14 and pEZY19(+)
1: marker; 2: empty bacteria induced for 0 h; 3: empty bacteria induced for 8 h; 4: empty vector induced for 0 h; 5: empty vector induced for 8 h; 6-12: recombinant bacteria induced for 0, 1.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8 h; white arrow represents the target protein induced.
2.5 甘蔗ScSEC14基因的组织特异性表达分析
组织特异性表达的分析结果显示, 甘蔗ScSEC14基因在ROC22中组成型表达, 即在植株的根、侧芽、蔗皮、蔗髓、叶中均有表达。其中在叶中的表达量最高, 约为蔗皮的4.9倍, 其次是在根中的表达量, 约为蔗皮的2.0倍, 在蔗皮中的表达量则最低(图9), 推测该基因的表达可能与叶片的水分运输、蒸腾作用相关[36]。图9
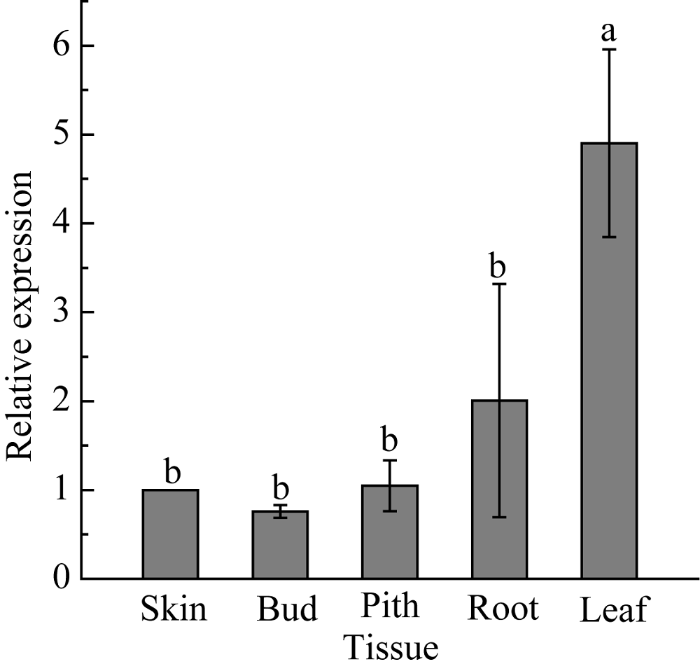 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图9甘蔗ScSEC14基因在不同组织中的表达
误差线为每组处理的标准误差(N = 3)。
Fig. 9Relative expression of ScSEC14 gene in different tissues of sugarcane
Error bars represent the standard error of each treating group (N = 3).
2.4 甘蔗ScSEC14基因在不同外源胁迫下的表达特性分析
ScSEC14基因在NaCl、SA、PEG、CaCl2胁迫下表达量均上调, 其中在NaCl胁迫下12 h的表达量最高, 约为对照的4.7倍, 同样在PEG胁迫下12 h的表达量最高, 约为对照的5.5倍(图10-A); SA胁迫下6 h达到最高, 约为对照的2.4倍, 在CaCl2胁迫下12 h达到最高, 约为对照的2.3倍(图10-B); 在CuCl2和CdCl2胁迫下的表达量先上调后下调, 且都在12 h处理时的表达量最高, CuCl2约为对照的1.6倍, CdCl2约为对照的1.1倍(图10-C)。图10
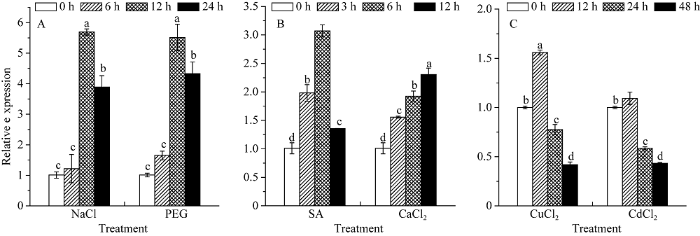 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图10甘蔗ScSEC14基因在不同外源胁迫下的表达特性
误差线为每组处理的标准误差(N = 3)。
Fig. 10Relative expression of ScSEC14 in sugarcane under different exogenous stresses
Error bars represent the standard error of each treating group (N = 3).
3 讨论
磷酸肌醇在细胞中发挥着重要的作用[1]。前人研究表明, Sec14-like磷脂酰肌醇转运蛋白是一个信号集成器(signal integrators), 在时间和空间上连接了脂质代谢和磷酸肌醇信号, 并参与细胞内肌醇磷酸代谢、膜运输、极性生长、信号转导、逆境胁迫等多种重要的生命过程[1,4]。本研究以课题组前期甘蔗受黑穗病胁迫下转录组数据库中SEC14作为探针, 结合电子克隆和RT-PCR扩增验证获得一条具有完整开放读码框的甘蔗ScSEC14基因cDNA全长序列。ScSEC14蛋白与高粱、玉米的同源性较高, 分别为95%和93%, 说明ScSEC14基因编码的蛋白在不同物种间具有较高的保守性。ScSEC14属于Sec14-like蛋白家族的SSH (soybean Sec14 homolog group)亚家族, 其功能主要与渗透调节相关[1,11]。生物信息学分析显示, 甘蔗ScSEC14蛋白为不稳定的亲水性蛋白, 这与罗明武等[30]对巴西橡胶树磷脂酰肌醇转移蛋白基因R291的分析的结果相同。此外, 该蛋白的二级结构主要为α-螺旋, 这与苏世超等[14]获得的小麦SEC14和Kie?bowiczmatuk等[13]获得的大麦SEC14蛋白的二级结构特征相符。三级结构预测分析结果显示, 甘蔗ScSEC14与高粱SEC14蛋白的差异较小, 而与玉米、水稻、小米的SEC14蛋白差异较大, 其原因可能是甘蔗与高粱的亲缘关系较近而与其他物种的亲缘关系较远。保守结构域分析显示, 甘蔗ScSEC14 蛋白的N端具有一个高等植物特有的CRAL_ TRIO_N结构域和一个典型的SEC14结构域。CRAL_TRIO_N结构域通常存在于植物中, 被称为脂质结合结构域, SEC14结构域则在细胞内脂质代谢、膜运输等方面发挥重要作用[26,31], 这2个结构域的存在对预测甘蔗ScSEC14蛋白的功能具有一定的参考价值。
磷脂酰肌醇转运蛋白最核心的基础功能是转运在内质网膜(ER)上合成的磷脂酰肌醇或磷脂酰肌醇衍生物[32]。亚细胞定位实验结果显示, ScSEC14在细胞核与细胞膜均有定位, 但主要定位于细胞膜, 这与其在质膜间转运物质的功能相符[32]。目前, 与ScSEC14属于同一亚家族的拟南芥Atsec14-1、Atsec14-5和大豆Ssh1p, 尚无亚细胞定位的文献报道。但是, 莫萍丽[33]在研究2个拟南芥花中特异表达的Sec14-like磷脂酰肌醇转移蛋白AtSFH3和AtSFH12 (与ScSEC14亲缘关系较近的另一亚家族)时发现, AtSFH3定位在细胞膜, AtSFH12则定位于细胞核与细胞膜上。
干旱、高盐等逆境在不同程度上影响植物体内的水分状况, 从而严重影响作物产量及品质[34], 是植物面临的主要非生物胁迫。苏世超等[14]在研究普通小麦TaSEC14p-5基因时发现, 该基因在高盐胁迫下的响应程度较明显, 可能参与盐依赖抗逆信号转导途径。本研究中甘蔗ScSEC14基因的RT-qPCR表达分析结果显示, 在NaCl和PEG下, 该基因的表达量均上调, 且上调幅度较大, 推测该基因在植物抗逆过程中积极响应干旱和盐胁迫。近来研究表明, 水杨酸不仅在植物对多种病原体的胁迫响应中发挥作用, 还在非生物胁迫诱导的信号传导中起重要作用[35]。本研究中, ScSEC14在水杨酸(SA)胁迫处理下的表达量上调, 推测该基因参与了水杨酸(SA)介导的抗逆信号途径。有研究报道, 在磷酸肌醇代谢PITP-PLC途径中, 磷脂酰肌醇转运蛋白通过结合磷脂酰肌醇将其转运到质膜, 该过程会产生第二信使IP3和DAG, 其中IP3释放到细胞质中与胞内Ca2+结合, 激活多种依赖Ca2+的生理生化反应[2,36]。本研究中ScSEC14基因在CaCl2胁迫下的表达量上调, 一定程度上说明该基因参与了甘蔗细胞内Ca2+信号途径。当重金属含量超过某一临界值时, 会破坏植物生物膜系统, 对植物产生一定的毒害作用, 轻则使植物体内的代谢过程紊乱, 重则导致植物死亡[37]。本研究中甘蔗ScSEC14基因在CuCl2、CdCl2处理下的表达量在12 h上调, 24 h和48 h下调, 说明在Cu2+和Cd2+胁迫初期, 细胞内Cu2+和Cd2+浓度的增加促使磷脂酰肌醇转运蛋白将磷脂酰肌醇从内质网转运到质膜以降低细胞内离子浓度, 维持细胞稳态[38], 但随着胁迫时间的延长, 植物体受到毒害作用, 磷脂酰肌醇转运蛋白功能受阻, ScSEC14基因表达量也随之下降。
4 结论
从甘蔗中克隆到一个典型的Sec14-like磷脂酰肌醇转运蛋白基因ScSEC14 (GenBank登录号为MG571103), 其全长1617 bp, 包含一个1008 bp的完整开放阅读框, 编码335个氨基酸。ScSEC14蛋白隶属于Sec14-like 蛋白家族的SSH (soybean Sec14 homolog group)亚家族。ScSEC14蛋白主要定位于细胞膜。在NaCl、PEG、SA、CaCl2以及重金属Cu2+和Cd2+胁迫诱导下, ScSEC14基因的表达均有不同程度的响应, 特别是在干旱和高盐胁迫下响应程度较明显, 因此推测该基因积极响应干旱和盐胁迫。该基因在蔗皮中的表达量最少, 在叶中的表达量最高, 其功能可能与叶片的水分运输和蒸腾作用相关。参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
DOI:10.1002/biof.180URLPMID:21915936 [本文引用: 6]

Phosphoinositides represent only a small percentage of the total cellular lipid pool. Yet, these molecules play crucial roles in diverse intracellular processes such as signal transduction at membrane-cytosol interface, regulation of membrane trafficking, cytoskeleton organization, nuclear events, and the permeability and transport functions of the membrane. A central principle in such lipid-mediated signaling is the appropriate coordination of these events. Such an intricate coordination demands fine spatial and temporal control of lipid metabolism and organization, and consistent mechanisms for specifically coupling these parameters to dedicated physiological processes. In that regard, recent studies have identified Sec14-like phosphatidylcholine transfer protein (PITPs) as 090008coincidence detectors,090009 which spatially and temporally link the diverse aspects of the cellular lipid metabolome with phosphoinositide signaling. The integral role of PITPs in eukaryotic signal transduction design is amply demonstrated by the mammalian diseases associated with the derangements in the function of these proteins, to stress response and developmental regulation in plants, to fungal dimorphism and pathogenicity, to membrane trafficking in yeast, and higher eukaryotes. This review updates the recent advances made in the understanding of how these proteins, specifically PITPs of the Sec14-protein superfamily, operate at the molecular level and further describes how this knowledge has advanced our perception on the diverse biological functions of PITPs.
DOI:10.1104/pp.004770URL [本文引用: 2]
DOI:10.1152/physrev.00028.2012URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1080/10409230500519573URL [本文引用: 2]
DOI:10.1016/0005-2728(90)90016-WURLPMID:2407740 [本文引用: 2]

Abstract Phosphatidylinositol transfer proteins (PI-TPs) catalyze the transfer of phosphatidylinositol and phosphatidylcholine between membranes in vitro. However, the in vivo function of these proteins is unknown. In this paper, we use a combined biochemical and genetic approach to determine the importance of PI-TP in vivo. An oligonucleotide based on the amino-terminal sequence of the PI-TP from Saccharomyces cerevisiae was used to screen a yeast genomic library for the gene encoding PI-TP (PIT1 gene). Positive clones showed overproduction of transfer activities and transfer protein in the 100,000 x g supernatants. The 5' terminus of the PIT1 gene correlates with the predicted codons for residues 3-30 of the determined protein sequence. A putative intron is located between the codons for residues 2 and 3 of the protein sequence. The codons for the first two amino acids of the protein and the presumptive initiation methionine precede the intron. Tetrad analysis of a heterozygous diploid (PIT1/pit1::LEU2) revealed that the PIT1 gene is essential for cell growth. Nonviable spores could be rescued by transformation of the above diploid prior to sporulation, with a plasmid-borne copy of the wild type gene.
DOI:10.1093/emboj/17.14.4004URLPMID:9670016 [本文引用: 2]

Phosphatidylinositol transfer proteins (PITPs) have been shown to play important roles in regulating a number of signal transduction pathways that couple to vesicle trafficking reactions, phosphoinositide-driven receptor-mediated signaling cascades, and development. While yeast and metazoan PITPs have been analyzed in some detail, plant PITPs remain entirely uncharacterized. We report the identification and characterization of two soybean proteins, Ssh1p and Ssh2p, whose structural genes were recovered on the basis of their abilities to rescue the viability of PITP-deficient Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains. We demonstrate that, while both Ssh1p and Ssh2p share 芒聢录25% primary sequence identity with yeast PITP, these proteins exhibit biochemical properties that diverge from those of the known PITPs. Ssh1p and Ssh2p represent high-affinity phosphoinositide binding proteins that are distinguished from each other both on the basis of their phospholipid binding specificities and by their substantially non-overlapping patterns of expression in the soybean plant. Finally, we show that Ssh1p is phosphorylated in response to various environmental stress conditions, including hyperosmotic stress. We suggest that Ssh1p may function as one component of a stress response pathway that serves to protect the adult plant from osmotic insult.
DOI:10.1104/pp.104.045369URLPMID:15466235 [本文引用: 1]

Membrane trafficking is central to construction of the cell plate during plant cytokinesis. Consequently, a detailed understanding of the process depends on the characterization of molecules that function in the formation, transport, targeting, and fusion of membrane vesicles to the developing plate, as well as those that participate in its consolidation and maturation into a fully functional partition. Here we report the initial biochemical and functional characterization of patellin1 (PATL1), a novel cell-plate-associated protein that is related in sequence to proteins involved in membrane trafficking in other eukaryotes. Analysis of the Arabidopsis genome indicated that PATL1 is one of a small family of Arabidopsis proteins, characterized by a variable N-terminal domain followed by two domains found in other membrane-trafficking proteins (Sec14 and Golgi dynamics domains). Results from immunolocalization and biochemical fractionation studies suggested that PATL1 is recruited from the cytoplasm to the expanding and maturing cell plate. In vesicle-binding assays, PATL1 bound to specific phosphoinositides, important regulators of membrane trafficking, with a preference for phosphatidylinositol(5)P,$\text{phosphatidylinositol}(4,5)\text{P}_{2}$, and phosphatidylinositol(3)P. Taken together, these findings suggest a role for PATL1 in membrane-trafficking events associated with cell-plate expansion or maturation and point to the involvement of phosphoinositides in cell-plate biogenesis.
DOI:10.1016/j.jplph.2006.01.009URLPMID:16542754 [本文引用: 1]

A full-length patellin1 (PATL1) cDNA was cloned and characterized from zucchini ( Cucurbita pepo). PATL1, originally discovered in the higher plant Arabidopsis thaliana, is a plant Sec14-related protein that localizes to the cell plate during the late stages of cytokinesis. PATL1 is related in sequence to other eukaryotic proteins involved in membrane trafficking and is thought to participate in vesicle trafficking events associated with cell plate maturation. The zucchini PATL1 (CpPATL1) cDNA predicts a 605 amino acid protein which consists of an acidic N-terminal domain (pI=4.2) followed by a Sec14 lipid-binding domain and a C-terminal Golgi dynamics domain (GOLD). The predicted CpPATL1 protein sequence shows a high degree of similarity to Arabidopsis PATL1, especially in the Sec14 (84%) and GOLD domains (87%). A phylogenetic analysis of all available full-length PATL sequences revealed that the PATLs belong to four distinct clades; CpPATL1 is a member of the PATL1/2 clade. RT-PCR analysis showed that the CpPATL1 gene is highly expressed throughout the plant. The domain structure, as well as biochemical fractionation studies, which demonstrated that CpPATL1 is a peripheral membrane protein, support a role in membrane trafficking events.
DOI:10.1083/jcb.200412074URLPMID:2171805 [本文引用: 1]

Phosphatidylinositol (PtdIns) transfer proteins (PITPs) regulate signaling interfaces between lipid metabolism and membrane trafficking. Herein, we demonstrate that AtSfh1p, a member of a large and uncharacterized Arabidopsis thaliana Sec14p-nodulin domain family, is a PITP that regulates a specific stage in root hair development. AtSfh1p localizes along the root hair plasma membrane and is enriched in discrete plasma membrane domains and in the root hair tip cytoplasm. This localization pattern recapitulates that visualized for PtdIns(4,5)P2 in developing root hairs. Gene ablation experiments show AtSfh1p nullizygosity compromises polarized root hair expansion in a manner that coincides with loss of tip-directed PtdIns(4,5)P2, dispersal of secretory vesicles from the tip cytoplasm, loss of the tip f-actin network, and manifest disorganization of the root hair microtubule cytoskeleton. Derangement of tip-directed Ca2+ gradients is also apparent and results from isotropic influx of Ca2+ from the extracellular milieu. We propose AtSfh1p regulates intracellular and plasma membrane phosphoinositide polarity landmarks that focus membrane trafficking, Ca2+ signaling, and cytoskeleton functions to the growing root hair apex. We further suggest that Sec14p-nodulin domain proteins represent a family of regulators of polarized membrane growth in plants.
DOI:10.1139/o03-089URLPMID:15052341 [本文引用: 1]

Phosphatidylinositol/phosphatidylcholine transfer proteins (PITPs) are ubiquitous and highly conserved proteins that are believed to regulate lipid-mediated signaling events. Their ubiquity and conservation notwithstanding, PITPs remain remarkably uninvestigated. Little is known about the coupling of specific PITPs to explicit cellular functions or the mechanisms by which PITPs interface with appropriate cellular functions. The available information indicates a role for these proteins in regulating the interface between lipid metabolism and membrane trafficking in yeast, signaling in plant development, the trafficking of specialized luminal cargo in mammalian enterocytes, and neurological function in mammals. Herein, we review recent advances in PITP biology and discuss as yet unresolved issues in this field.
[本文引用: 3]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.plantsci.2016.02.014URLPMID:26993240 [本文引用: 2]

Abstract Phosphatidylinositol transfer proteins (PITPs) include a large group of proteins implicated in the non-vesicular traffic of phosphatidylinositol (PI) between membranes. In yeast, the structure and function of the PITP Sec14-p protein have been well characterized. In contrast, the knowledge on plant PITP proteins is very scarce. In this work, we characterized a novel type of PITP protein in barley named HvSec14p and related to the yeast Sec14-p protein. Our data reveal that HvSec14p consists of only the Sec14p-domain structurally homologous to the yeast phosphoinositide binding domain. We show that HvSec14p expression is up-regulated at both transcript and protein levels at specific stages of development during seed formation and germination, and in leaves of a drought-tolerant barley genotype under osmotic constraints. Modeling analyses of the protein three-dimensional structure revealed its capacity to dock the phosphoinositides, PtdIns(3)P, PtdIns(4)P, PtdIns(5)P and PtdIns(3,5)P2. Consistently, the recombinant HvSec14p protein is able to bind in vitro most PIP types, the highest affinity being observed with PtdIns(3,5)P2. Based on the high gene expression at specific developmental stages and in drought-tolerant barley genotypes, we propose that HvSec14p plays essential roles in the biogenesis of membranes in expanding cells and in their preservation under osmotic stress conditions. Copyright 脗漏 2016 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
URL [本文引用: 3]

具有TPR基序的蛋白质被认为能够介导蛋白质间的相互作用,并且参与多种生物学过程,如细胞周期调控、转录调控、过氧化物酶等蛋白质的运输、信号传导和蛋白质折叠等。为了在小麦分子育种研究中获得更多有价值的候选基因,本研究采用电子克隆和RT PCR方法从小麦中克隆得到1个TPR类基因,命名为 。该基因ORF 长度972 bp,推测编码包含323个氨基酸残基的蛋白,相对分子质量34.9 kD,理论等电点为5.89。氨基酸序列分析表明,该蛋白在142~207区和207~274区分别含有TPR类基因家族特有的保守结构域(TPR_16和TPR_11)。进化和聚类分析表明,小麦 基因与粗山羊草 基因、乌拉尔图小麦 基因的亲缘关系较近,蛋白相似度分别为91.28%和91.55%。Real time PCR表达特性分析显示,该基因为组成型表达,在根、茎、叶中均表达;幼苗期茎中表达量较高,随幼苗的生长,茎中表达量上调显著;该基因表达受高盐的强烈诱导,也受水分、低温和外源ABA胁迫诱导。
URL [本文引用: 3]

具有TPR基序的蛋白质被认为能够介导蛋白质间的相互作用,并且参与多种生物学过程,如细胞周期调控、转录调控、过氧化物酶等蛋白质的运输、信号传导和蛋白质折叠等。为了在小麦分子育种研究中获得更多有价值的候选基因,本研究采用电子克隆和RT PCR方法从小麦中克隆得到1个TPR类基因,命名为 。该基因ORF 长度972 bp,推测编码包含323个氨基酸残基的蛋白,相对分子质量34.9 kD,理论等电点为5.89。氨基酸序列分析表明,该蛋白在142~207区和207~274区分别含有TPR类基因家族特有的保守结构域(TPR_16和TPR_11)。进化和聚类分析表明,小麦 基因与粗山羊草 基因、乌拉尔图小麦 基因的亲缘关系较近,蛋白相似度分别为91.28%和91.55%。Real time PCR表达特性分析显示,该基因为组成型表达,在根、茎、叶中均表达;幼苗期茎中表达量较高,随幼苗的生长,茎中表达量上调显著;该基因表达受高盐的强烈诱导,也受水分、低温和外源ABA胁迫诱导。
.
DOI:10.1007/s00299-016-1980-4URLPMID:27061906 [本文引用: 2]

Abstract KEY MESSAGE: A Sec14-like protein, ZmSEC14p , from maize was structurally analyzed and functionally tested. Overexpression of ZmSEC14p in transgenic Arabidopsis conferred tolerance to cold stress. Sec14-like proteins are involved in essential biological processes, such as phospholipid metabolism, signal transduction, membrane trafficking, and stress response. Here, we reported a phosphatidylinositol transfer-associated protein, ZmSEC14p (accession no. KT932998), isolated from a cold-tolerant maize inbred line using the cDNA-AFLP approach and RACE-PCR method. Full-length cDNA that consisted of a single open reading frame (ORF) encoded a putative polypeptide of 295 amino acids. The ZmSEC14p protein was mainly localized in the nucleus, and its transcript was induced by cold, salt stresses, and abscisic acid (ABA) treatment in maize leaves and roots. Overexpression of ZmSEC14p in transgenic Arabidopsis conferred tolerance to cold stress. This tolerance was primarily displayed by the increased germination rate, root length, plant survival rate, accumulation of proline, activities of antioxidant enzymes, and the reduction of oxidative damage by reactive oxygen species (ROS). ZmSEC14p overexpression regulated the expression of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C, which cleaves phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) and generates second messengers (inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and 1,2-diacylglycerol) in the phosphoinositide signal transduction pathways. Moreover, up-regulation of some stress-responsive genes such as CBF3, COR6.6, and RD29B in transgenic plants under cold stress could be a possible mechanism for enhancing cold tolerance. Taken together, this study strongly suggests that ZmSEC14p plays an important role in plant tolerance to cold stress.
DOI:10.1105/tpc.13.5.1205URL [本文引用: 1]
.
DOI:10.7666/d.y774985URL [本文引用: 1]

甘蔗是我国乃至世界最重要的糖料作物。我国蔗糖产量占食糖总产量 的90%以上,世界蔗糖产量占食糖总产量的65%。随着人口增多,生态环境条件恶化如土壤沙漠化等,导致粮食安全问题日益突出。甘蔗种植区由原先水肥条件 充足的地区逐渐移到了比较贫瘠甚至缺水的旱坡地,迫使甘蔗育种向着培育抗旱、耐瘠以及宿根性强的品种方向发展。 本研究针对甘蔗抗旱育种中存在的遗传基础狭窄、品种抗旱性较差等问题,联合福建农林大学农业部甘蔗生理生态与遗传改良重点实验室(福州)与福建省农科 院甘蔗研究所(漳州)共同筛选甘蔗抗旱种质资源,以期为甘蔗抗旱育种提供新的...
DOI:10.7666/d.y774985URL [本文引用: 1]

甘蔗是我国乃至世界最重要的糖料作物。我国蔗糖产量占食糖总产量 的90%以上,世界蔗糖产量占食糖总产量的65%。随着人口增多,生态环境条件恶化如土壤沙漠化等,导致粮食安全问题日益突出。甘蔗种植区由原先水肥条件 充足的地区逐渐移到了比较贫瘠甚至缺水的旱坡地,迫使甘蔗育种向着培育抗旱、耐瘠以及宿根性强的品种方向发展。 本研究针对甘蔗抗旱育种中存在的遗传基础狭窄、品种抗旱性较差等问题,联合福建农林大学农业部甘蔗生理生态与遗传改良重点实验室(福州)与福建省农科 院甘蔗研究所(漳州)共同筛选甘蔗抗旱种质资源,以期为甘蔗抗旱育种提供新的...
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1006.2015.00499URL [本文引用: 1]

CIPK (calcineurin B-like-interacting protein kinase)是植物特有一类的丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶,该蛋白在植物响应逆境胁迫中发挥着重要的作用,尤其与非生物逆境胁迫(干旱、高盐、ABA等)的信号传导密切相关。根据玉米CIPK15基因(EU957447.1,2247 bp)核酸序列保守区域设计1对同源克隆PCR引物,以甘蔗品种崖城05-179的cDNA为模板,通过RT-PCR扩增得到甘蔗CIPK基因的一条全长cDNA序列(GenBank登录号为 KM114052)。序列分析结果表明,甘蔗ScCIPK基因全长1782 bp,具有完整的开放阅读框(ORF,91~1631 bp),编码513个氨基酸,该基因具有CIPK基因的2个特征结构域(Kc-like superfamily和AMPKA-C-like superfamily)。生物信息学分析显示该基因编码的蛋白定位于内质网,为可溶性蛋白,不存在信号肽,二级结构元件多为α-螺旋,含有多个保守功能域,主要参与中间代谢。实时定量PCR表达分析表明,该基因表达具有组织特异性,虽在甘蔗各组织中均有表达,但在芽中的表达量最高。该基因在PEG、NaCl、ABA、SA和MeJA的胁迫诱导过程中,受ABA胁迫后表达量最高,约为对照的5.3倍,推测该基因的表达与甘蔗抗干旱和抗渗透胁迫有关。
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1006.2015.00499URL [本文引用: 1]

CIPK (calcineurin B-like-interacting protein kinase)是植物特有一类的丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶,该蛋白在植物响应逆境胁迫中发挥着重要的作用,尤其与非生物逆境胁迫(干旱、高盐、ABA等)的信号传导密切相关。根据玉米CIPK15基因(EU957447.1,2247 bp)核酸序列保守区域设计1对同源克隆PCR引物,以甘蔗品种崖城05-179的cDNA为模板,通过RT-PCR扩增得到甘蔗CIPK基因的一条全长cDNA序列(GenBank登录号为 KM114052)。序列分析结果表明,甘蔗ScCIPK基因全长1782 bp,具有完整的开放阅读框(ORF,91~1631 bp),编码513个氨基酸,该基因具有CIPK基因的2个特征结构域(Kc-like superfamily和AMPKA-C-like superfamily)。生物信息学分析显示该基因编码的蛋白定位于内质网,为可溶性蛋白,不存在信号肽,二级结构元件多为α-螺旋,含有多个保守功能域,主要参与中间代谢。实时定量PCR表达分析表明,该基因表达具有组织特异性,虽在甘蔗各组织中均有表达,但在芽中的表达量最高。该基因在PEG、NaCl、ABA、SA和MeJA的胁迫诱导过程中,受ABA胁迫后表达量最高,约为对照的5.3倍,推测该基因的表达与甘蔗抗干旱和抗渗透胁迫有关。
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.2134/agronj1982.00021962007400050018xURL [本文引用: 1]

Though drip irrigation is used on more than half of the irrigated sugarcane (Saccharum spp. hybrid) in Hawaii, the effects of drought stress on the growth and yield of drip-irrigated sugarcane has not been investigated extensively. This study reports the effects of a single period of drought stress on the growth and metabolism of cultivar H62-4671 during vegetative growth in drip-irrigated fields during the 1st year of a normal 2-year crop in five fields at Kekaha Sugar Company, Kauai, Hawaii. The plants ranged from 5.4 to 9.8 months of age at the beginning of the experiment.
DOI:10.1007/s00299-012-1293-1URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0044697URLPMID:3439409 [本文引用: 1]

Drought is a major abiotic stress that affects crop productivity worldwide. Sugarcane can withstand periods of water scarcity during the final stage of culm maturation, during which sucrose accumulation occurs. Meanwhile, prolonged periods of drought can cause severe plant losses. In a previous study, we evaluated the transcriptome of drought-stressed plants to better understand sugarcane responses to drought. Among the up-regulated genes was Scdr1 (sugarcane drought-responsive 1). The aim of the research reported here was to characterize this gene. Scdr1 encodes a putative protein containing 248 amino acids with a large number of proline (19%) and cysteine (13%) residues. Phylogenetic analysis showed that ScDR1is in a clade with homologs from other monocotyledonous plants, separate from those of dicotyledonous plants. The expression of Scdr1 in different varieties of sugarcane plants has not shown a clear association with drought tolerance. The overexpression of Scdr1 in transgenic tobacco plants increased their tolerance to drought, salinity and oxidative stress, as demonstrated by increased photosynthesis, water content, biomass, germination rate, chlorophyll content and reduced accumulation of ROS. Physiological parameters, such as transpiration rate (E), net photosynthesis (A), stomatal conductance (gs) and internal leaf CO(2) concentration, were less affected by abiotic stresses in transgenic Scdr1 plants compared with wild-type plants. Overall, our results indicated that Scdr1 conferred tolerance to multiple abiotic stresses, highlighting the potential of this gene for biotechnological applications.
DOI:10.1007/s12355-016-0431-4URL [本文引用: 1]

Non-specific lipid transfer proteins (NsLTPs) are soluble, small, basic proteins in plant, which have been reported to be involved in plant physiological functions such as the catalyzing transfer of p
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1006.2016.01074URL [本文引用: 1]

CAX(Ca^2+/H^+antiporter)是植物细胞膜Ca^2+主动运输体系的一个大类。本研究以高粱的CAX1基因(GenBank登录号为XM_002441593)为探针,利用电子克隆并结合RT-PCR技术,获得甘蔗CAX1基因的1条cDNA序列,命名为Sc CAX1(GenBank登录号为KT799799)。生物信息学分析显示,ScCAX1基因全长784 bp,包含1个645 bp的开放阅读框,编码1个214个氨基酸的蛋白质。ScCAX1蛋白被定位于叶绿体类囊体膜,为稳定的疏水性蛋白,不存在信号肽。蛋白二级结构元件多为α-螺旋,具有1个Na_Ca_ex superfamily。实时荧光定量PCR分析表明,甘蔗ScCAX1基因的表达具有组织特异性,在各组织中均表达,但在茎中表达量最低,叶中的表达量最高。在PEG、NaCl、SA、ABA和Me JA胁迫过程中,ScCAX1基因的表达均受到调控。其中ABA、SA和PEG胁迫下表达量上调,均在胁迫24 h达到最大值。SA胁迫24 h的表达量为对照的5.47倍,而ABA胁迫24 h的表达量为对照的3.5倍。NaCl胁迫6 h的表达量达最大值,为对照的2.14倍。推测ScCAX1基因能够响应逆境胁迫,其表达可能与甘蔗的抗盐、抗渗透胁迫性状有关。
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1006.2016.01074URL [本文引用: 1]

CAX(Ca^2+/H^+antiporter)是植物细胞膜Ca^2+主动运输体系的一个大类。本研究以高粱的CAX1基因(GenBank登录号为XM_002441593)为探针,利用电子克隆并结合RT-PCR技术,获得甘蔗CAX1基因的1条cDNA序列,命名为Sc CAX1(GenBank登录号为KT799799)。生物信息学分析显示,ScCAX1基因全长784 bp,包含1个645 bp的开放阅读框,编码1个214个氨基酸的蛋白质。ScCAX1蛋白被定位于叶绿体类囊体膜,为稳定的疏水性蛋白,不存在信号肽。蛋白二级结构元件多为α-螺旋,具有1个Na_Ca_ex superfamily。实时荧光定量PCR分析表明,甘蔗ScCAX1基因的表达具有组织特异性,在各组织中均表达,但在茎中表达量最低,叶中的表达量最高。在PEG、NaCl、SA、ABA和Me JA胁迫过程中,ScCAX1基因的表达均受到调控。其中ABA、SA和PEG胁迫下表达量上调,均在胁迫24 h达到最大值。SA胁迫24 h的表达量为对照的5.47倍,而ABA胁迫24 h的表达量为对照的3.5倍。NaCl胁迫6 h的表达量达最大值,为对照的2.14倍。推测ScCAX1基因能够响应逆境胁迫,其表达可能与甘蔗的抗盐、抗渗透胁迫性状有关。
DOI:10.1007/s11103-013-0033-4URLPMID:23456248 [本文引用: 2]

Rice is cultivated in water-logged paddy lands. Thus, rice root hairs on the epidermal layers are exposed to a different redox status of nitrogen species, organic acids, and metal ions than root...
DOI:10.1016/j.plantsci.2016.02.014URLPMID:26993240 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract Phosphatidylinositol transfer proteins (PITPs) include a large group of proteins implicated in the non-vesicular traffic of phosphatidylinositol (PI) between membranes. In yeast, the structure and function of the PITP Sec14-p protein have been well characterized. In contrast, the knowledge on plant PITP proteins is very scarce. In this work, we characterized a novel type of PITP protein in barley named HvSec14p and related to the yeast Sec14-p protein. Our data reveal that HvSec14p consists of only the Sec14p-domain structurally homologous to the yeast phosphoinositide binding domain. We show that HvSec14p expression is up-regulated at both transcript and protein levels at specific stages of development during seed formation and germination, and in leaves of a drought-tolerant barley genotype under osmotic constraints. Modeling analyses of the protein three-dimensional structure revealed its capacity to dock the phosphoinositides, PtdIns(3)P, PtdIns(4)P, PtdIns(5)P and PtdIns(3,5)P2. Consistently, the recombinant HvSec14p protein is able to bind in vitro most PIP types, the highest affinity being observed with PtdIns(3,5)P2. Based on the high gene expression at specific developmental stages and in drought-tolerant barley genotypes, we propose that HvSec14p plays essential roles in the biogenesis of membranes in expanding cells and in their preservation under osmotic stress conditions. Copyright 脗漏 2016 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1006/meth.2001.1262URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.3969/gab.029.000164URL [本文引用: 1]

本文从巴西橡胶树(Hevea brasiliensis)差减cDNA文库中筛选到一个与磷脂酰肌醇转移蛋白(phos-phatidylinositol transfer protein)同源性较高的基因片段,并根据该基因片段序列信息,设计特异性引物,采用cDNA末端快速扩增技术RACE(rapid amplification of cDNA ends)进行差异片段的5'和3'端的扩增,并获得长度为1081bp的全长cDNA克隆R291(GenBank登陆号:AY589690)。序列分 析表明,该基因包含702bp的开放阅读框,编码234个氨基酸,推测其蛋白质的分子量为26.8kD,等电点为6.51,有一个的跨膜螺旋区(氨基酸位 点为83~103)。R291基因含有一个脂质结合保守区(Sec14p-like lipid-binding domain),具有CRAL-TRIO脂质结合结构域,推测该基因是一个磷脂酰肌醇转移蛋白基因。该基因的克隆将为橡胶树磷脂酰肌醇代谢的研究奠定了基 础,将有助于进一步了解磷脂酰肌醇代谢与胶乳再生之间的关系。
DOI:10.3969/gab.029.000164URL [本文引用: 1]

本文从巴西橡胶树(Hevea brasiliensis)差减cDNA文库中筛选到一个与磷脂酰肌醇转移蛋白(phos-phatidylinositol transfer protein)同源性较高的基因片段,并根据该基因片段序列信息,设计特异性引物,采用cDNA末端快速扩增技术RACE(rapid amplification of cDNA ends)进行差异片段的5'和3'端的扩增,并获得长度为1081bp的全长cDNA克隆R291(GenBank登陆号:AY589690)。序列分 析表明,该基因包含702bp的开放阅读框,编码234个氨基酸,推测其蛋白质的分子量为26.8kD,等电点为6.51,有一个的跨膜螺旋区(氨基酸位 点为83~103)。R291基因含有一个脂质结合保守区(Sec14p-like lipid-binding domain),具有CRAL-TRIO脂质结合结构域,推测该基因是一个磷脂酰肌醇转移蛋白基因。该基因的克隆将为橡胶树磷脂酰肌醇代谢的研究奠定了基 础,将有助于进一步了解磷脂酰肌醇代谢与胶乳再生之间的关系。
DOI:10.1016/S0926-860X(00)00425-7URL [本文引用: 1]

Protein-lipid interactions are important for protein targeting, signal transduction, lipid transport, lipid biosynthesis, lipid metabolism, and the maintenance of cellular compartments and membranes. Specific lipid-binding protein domains, such as PH, FYVE, PX, PHD, C2 and SEC14 homology domains, inediate interactions between proteins and specific phospholipids. Here we review the published literature, plus some of our most recent unpublished findings, regarding the biology of the SEC14 domain, also known as CRAL_TRIO domain. (c) 2007 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
DOI:10.1016/j.bbalip.2016.03.027URL [本文引用: 2]
.
DOI:10.7666/d.y1345372URL [本文引用: 1]

磷脂酰肌醇转移蛋白(PITP)普遍存在于多细胞动物、真菌及高等植物中。PITP能结合及交换一分子的磷脂酰肌醇或磷脂酰胆碱并能促进这两类脂分子在细胞内膜组分间转移。磷脂酰肌醇转移蛋白在哺乳动物细胞分泌囊泡的形成、运输、PLC(磷脂酶C)调节的信号转导以及神经退化中具有重要的作用;PITP调节酵母胞质内膜组分运输和脂类的代谢;在高等植物的发育过程中参与了信号的转导。根据氨基酸序列的保守性,PITP可以分成两大类:一类是以哺乳动物、两栖动物和昆虫为代表的多细胞动物PITP;另一类是以真菌和高等植物为主的PITP。Sec14p是酵母中主要的PITP,对于酵母的...
DOI:10.7666/d.y1345372URL [本文引用: 1]

磷脂酰肌醇转移蛋白(PITP)普遍存在于多细胞动物、真菌及高等植物中。PITP能结合及交换一分子的磷脂酰肌醇或磷脂酰胆碱并能促进这两类脂分子在细胞内膜组分间转移。磷脂酰肌醇转移蛋白在哺乳动物细胞分泌囊泡的形成、运输、PLC(磷脂酶C)调节的信号转导以及神经退化中具有重要的作用;PITP调节酵母胞质内膜组分运输和脂类的代谢;在高等植物的发育过程中参与了信号的转导。根据氨基酸序列的保守性,PITP可以分成两大类:一类是以哺乳动物、两栖动物和昆虫为代表的多细胞动物PITP;另一类是以真菌和高等植物为主的PITP。Sec14p是酵母中主要的PITP,对于酵母的...
URLMagsci [本文引用: 1]

<p>植物抗渗透胁迫基因工程研究进展刘岩1彭学贤2谢友菊1戴景瑞1(中国农业大学植物科技学院北京100094)(中国科学院微生物研究所植物生物技术开放实验室北京100080)2土壤盐渍化是影响农业生产和生态环境的一个重要因素。据统计,全世界的盐土约占陆地面积的三分之一(Epsteinet.1983)。我国大约有一亿亩盐碱地,且有逐年增加的趋势。另外,每年由于干旱将使全球粮食产量降低10-20%。工...</p>
URLMagsci [本文引用: 1]

<p>植物抗渗透胁迫基因工程研究进展刘岩1彭学贤2谢友菊1戴景瑞1(中国农业大学植物科技学院北京100094)(中国科学院微生物研究所植物生物技术开放实验室北京100080)2土壤盐渍化是影响农业生产和生态环境的一个重要因素。据统计,全世界的盐土约占陆地面积的三分之一(Epsteinet.1983)。我国大约有一亿亩盐碱地,且有逐年增加的趋势。另外,每年由于干旱将使全球粮食产量降低10-20%。工...</p>
DOI:10.1007/s11738-014-1603-zURL [本文引用: 1]

Salicylic acid (SA), a key signaling molecule in higher plants, has been found to play a role in the response to a diverse range of phytopathogens and is essential for the establishment of both local and systemic-acquired resistance. Recent studies have indicated that SA also plays an important role in abiotic stress-induced signaling, and studies on SA-modulated abiotic tolerance have mainly focused on the antioxidant capacity of plants by altering the activity of anti-oxidative enzymes. However, little information is available about the molecular mechanisms of SA-induced abiotic stress tolerance. Here, we review recent progress toward characterizing the SA-regulated genes and proteins, the SA signaling pathway, the connections and differences between SA-induced tolerances to biotic and abiotic stresses, and the interaction of SA with other plant hormones under conditions of abiotic stress. The future prospects related to molecular tolerance of SA in response to abiotic stresses are also further summarized.
DOI:10.1038/341197a0URLPMID:2550825 [本文引用: 2]

Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate is a second messenger which regulates intracellular calcium both by mobilizing calcium from internal stores and, perhaps indirectly, by stimulating calcium entry. In these actions it may function with its phosphorylated metabolite, inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate. The subtlety of calcium regulation by inositol phosphates is emphasized by recent studies that have revealed oscillations in calcium concentration which are perhaps part of a frequency-encoded second-messenger system.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1186/gb-2001-2-9-reviews3011URLPMID:138965 [本文引用: 1]

Two families of proteins are able specifically to transfer phosphatidylinositol (PI) and phosphatidylcholine (PC) in eukaryotic cells (Figure 1), namely the PITP and Sec14p families [1]. They share no obvious sequence or structural similarity, but ectopically expressed PITPs can rescue sec14 mutants in yeast. Likewise, in functional studies in mammalian cells, ectopically expressed Sec14p can be used to compensate for the loss of PITPs [2,3]. Whereas Sec14p isoforms are ubiquitous in eukaryotes, members of the PITP family appear to be absent from plants and fungi. It is likely that endogenous Sec14p and PITP family members normally have distinct biological roles, and the two families should not be confused. Accordingly, PITPs define a discrete family, which forms the subject of this review.The first mammalian PITP was identified as a 35 kDa protein with 271 amino acids and no sequence similarity to any known protein [4]. Three subfamilies can now be defined (Figure 2) and all isoforms have an amino-terminal PITP-like domain. Non-systematic nomenclature has arisen as a result of the different methods by which each isoform was identified. All three types occur in humans: the first comprises the small PITP and PITP proteins, which were identified by virtue of their transfer activity in vitro; the second comprises the large rdgB (also called M-RdgB1, Nir2 and PITPnm) and Nir3 (also called M-RdgB2) proteins; and the third type comprises the rdgB尾 protein, which is intermediate in size and was identified by homology to rdgB [5]. The rdgB acronym is derived from a retinal degeneration mutant phenotype (type B) in Drosophila, and the Nir acronym is derived from a reported interaction with the amino-terminal domain of the Pyk2 tyrosine kinase (Pyk2 N-terminal domain-interacting receptor). A third protein, termed Nir1, was also identified, but this lacks a PITP domain [6]. Mammalian rdgB is 39% identical in sequence to Drosophila rdgB, and mammalian Nir3 is 46% identical
