 ,1,*, 李丽霞1, 王丽2, 李元铭1, 张俊莲
,1,*, 李丽霞1, 王丽2, 李元铭1, 张俊莲 ,1,*
,1,*Cloning and Functional Analysis of R2R3 MYB Genes Involved in Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Potato Tuber
TAN Huan1, LIU Yu-Hui ,1,*, LI Li-Xia1, WANG Li2, LI Yuan-Ming1, ZHANG Jun-Lian
,1,*, LI Li-Xia1, WANG Li2, LI Yuan-Ming1, ZHANG Jun-Lian ,1,*
,1,*通讯作者:
第一联系人:
收稿日期:2017-10-27接受日期:2018-03-26网络出版日期:2018-04-09
| 基金资助: |
Received:2017-10-27Accepted:2018-03-26Online:2018-04-09
| Fund supported: |

摘要
关键词:
Abstract
Keywords:
PDF (1822KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
本文引用格式
谈欢, 刘玉汇, 李丽霞, 王丽, 李元铭, 张俊莲. 马铃薯块茎花色素苷合成相关R2R3 MYB蛋白基因的克隆和功能
分析 [J]. 作物学报, 2018, 44(7): 1021-1031. doi:10.3724/SP.J.1006.2018.01021
TAN Huan, LIU Yu-Hui, LI Li-Xia, WANG Li, LI Yuan-Ming, ZHANG Jun-Lian.
花色素苷是一类以花色基元为基本结构的水溶性色素, 主要分为飞燕草色素、芍药色素和天竺葵色素等[1]。它们不仅可以使植物呈现出不同的色彩, 还有助于昆虫的传粉、植物生长素的运输以及保护叶片免受紫外线损伤, 同时具有抑制病虫害等重要的作用。此外, 它还具有抗癌、抗氧化等保健作用和药用价值[2], 因此近年来备受人们的关注。
花色素苷是类黄酮类次生代谢物质, 合成前体为苯丙氨酸。苯丙氨酸经苯丙氨酸裂解酶(PAL)、查尔酮合成酶(CHS)、查尔酮异构酶(CHI)、黄烷酮-3-羟基化酶(F3H)、黄烷酮-3'-羟基化酶(F3'H)、二氢黄酮醇还原酶(DFR)、花色素苷合成酶(ANS)或无色花色素双加氧酶(LDOX)形成不稳定的花色素苷, 再经类黄酮3-0-葡萄糖基转移酶(UFGT)催化生成稳定的花色素苷[3,4]。研究证实, 参与花色素苷合成的调控因子包括R2R3 MYB蛋白、bHLH蛋白和WD40蛋白三大类转录因子, 其中R2R3 MYB为最重要的转录因子, 其调控花色素苷合成已在苹果和葡萄上证实[5,6]。R2R3 MYB中R2和R3基序能够特异性识别DNA序列, R3 C端的螺旋结构能特异结合目标基因启动子区顺式作用元件中的核心序列[7]。植物bHLH转录因子能调控花器官发育和激素应答等[8,9], 其最重要的功能是调节类黄酮和花色素苷的合成。
R2R3 MYB蛋白调控植物花色素苷的合成已在果树[10]、小麦[11]、拟南芥[12]、甘蔗[13]等植物中报道, 例如, 苹果R2R3 MYB蛋白中的MdMYB10使DFR基因表达量上调[14], MdMYBA使ANS的转录水平提高[15], MdMYB1激活结构基因UFGT和DFR, 从而提高了苹果花色素苷的含量[16]; 油桃中分离的MYB10能够正向调控DFR基因的表达, 促进花青素在果实中大量积累[17]; 拟南芥AtMYB75转录因子调控花色素苷的生物合成, 其异位表达促进类黄酮类物质生物合成相关基因的表达, 导致植物的大多数器官呈现紫色[18,19,20]。
马铃薯中有117个MYB类转录因子, 其中R2R3型MYB数量最多, 它参与植物次生代谢调控、激素刺激和环境胁迫应答等过程[21], R2R3 MYB转录因子能够调控马铃薯薯皮和叶片中花色素苷合成途径结构基因的表达, 从而促进花色素苷的积累[22,23]。生物或非生物因素均能影响花色素苷的生物合成, 光照强度与StCHS、StDFR和StR2R3-MYB的表达正相关; 环境温度与StPAL、StDFR和StR2R3-MYB的表达负相关[24,25,26,27,28]。本试验以彩色四倍体马铃薯为研究对象, 分离了3个马铃薯R2R3 MYB基因, 并以烟草为受体进行稳定遗传转化, 利用qPCR进行转基因烟草叶片中与花色素苷合成相关基因和转录因子的相对表达分析, 并分析3个同源基因的功能。本研究为进一步探究马铃薯块茎花色素苷合成的调控机制以及人工调控马铃薯块茎花色素苷合成提供理论和方法。
1 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料和试剂
马铃薯品种 “新大坪”(XD: 白皮白肉)、“黑美人”(HM: 紫皮紫肉)、“甘农薯5号”(GN: 红皮白肉)和“青薯9号”(QS: 红皮白肉, 红色的维管束), 均在甘肃农业大学温室内种植。其中GN由甘肃农业大学培育, HM和XD是甘肃省当地栽培品种, QS由青海省农林科学院培育。分别在块茎收获期采集4个品种薯皮和薯肉, 立即放入液氮速冻, 于-80℃冰箱保存备用。野生型烟草由甘肃省作物遗传改良与种质创新重点实验室提供。大肠杆菌DH5α感受态细胞和pGEM-T Easy Vector载体(抗性标记为氨苄青霉素)购自Promega公司; 限制性内切酶、T4 DNA连接酶和Taq DNA聚合酶购自TaKaRa公司; PureLink Plant RNA Reagent Kit购自Invitrogen公司; QuantiTect Reverse Transcription Kit购自Qiagen公司; DNA凝胶回收试剂盒购自北京天根公司; 其他生化试剂均为国产分析纯。
1.2 3个StAN1基因编码序列的克隆
将已报道的马铃薯StAN1的基因序列(AY841129)作为参考序列[29], 利用Oligo6设计引物StAN1-F (5°-ATGAGTACTCCTATGATGTGTA- 3°)和StAN1-R (5°-CTAATTAAGTAGATTCCATATATC-3°), 克隆4个品种StAN1基因的编码序列。用PureLink Plant RNA Reagent Kit试剂盒分别抽提4种马铃薯薯皮薯肉的总RNA。用Nanodrop ND-1000分光光度计(Thermofisher公司, 美国)测定RNA纯度和浓度, 并用1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳鉴定其完整性。利用QuantiTect Reverse Transcription Kit试剂盒进行反转录, 其中以Oligo(dT)20为引物, 在M-MLV反转录酶作用下合成cDNA第1链, 并在-20℃下保存。PCR反应体系是由cDNA模板2 μL、10×buffer 2.5 μL、10 mmol L-1的上下游引物各1 μL、Taq DNA聚合酶0.5 μL、ddH2O 18 μL组成。反应程序为94℃预变性5 min; 94℃变性50 s, 57℃退火50 s, 72℃延伸1 min, 35个循环; 72℃延伸10 min。用1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测扩增产物。
将扩增得到的目的片段用琼脂糖凝胶试剂盒回收纯化, 并分别与pGEM-T Easy Vector载体连接, 转化大肠杆菌DH5α感受态细胞, 对所获得的白斑通过滞后质粒、PCR扩增、EcoR I酶切鉴定后, 于-80℃下保存, 并将阳性克隆送到生工生物工程(上海)有限公司进行DNA测序验证。
1.3 马铃薯StAN1转录因子家族成员的生物信息学分析
用在线软件Expasy (以StAN1-R0为参比序列, 通过NCBI在线比对(
1.4 农杆菌介导叶盘法共转化烟草及表达分析
利用EcoR I酶切位点将StAN1 3个同源基因的全长片段重组到植物表达载体pSAK277中, 再将构建体转入农杆菌。使用农杆菌介导叶盘法[30]将StAN1-R0、StAN1-R1和StAN1-R3基因转化到野生型烟草中, 通过Kan抗性筛选和颜色判定初步筛选阳性抗性苗。根据特异性引物(F1: 5°-GGCCACATATC AAGAGAGGTGACTTTG-3°, R1: 3°-TCACATCGTT AGCTGTCCTTCCTGG-5°)对所对应的目的基因进行PCR扩增鉴定, 分别用1.5%琼脂糖电泳检测扩增产物, 根据鉴定结果最终获得转StAN1-R0、StAN1-R1和StAN1-R3基因的烟草株系分别为6、9和7株。1.5 利用qPCR分析转基因烟草中MYB基因的相对表达
分别提取转StAN1-R0、 StAN1-R1和StAN1-R3基因烟草叶片的总RNA, 反转录获得的cDNA作为qPCR扩增模板, 根据特异性设计qPCR引物(表1)。以NtEF-1α基因(序列号为D63396)为内参, 在Mx3005p型实时荧光定量PCR仪中进行定量分析。反应体系包含浓度为50 ng μL-1的cDNA 2.0 μL、上下游引物0.4 μL、Nuclease-Free Water 7.2 μL和Go Taq qPCR Master Mix 10 μL。反应程序为95℃预变性5 min; 95℃变性5 s, 60℃退火5 s, 72℃延伸10 s, 循环40次。每个样品重复3次, 反应结束后采用2-ΔΔCT [31]法分析数据。Table 1
表1
表1定量PCR分析的引物序列
Table 1
| 基因 Gene | 登录号 Accession number | 上游引物 Forward primer (5'-3') | 下游引物 Reverse primer (5'-3') |
|---|---|---|---|
| StAN1 | AY841129.1 | GGCCACATATCAAGAGAGGTGACTTTG | TCACATCGTTAGCTGTCCTTCCTGG |
| NtCHS | AF311783.1 | TTGTTCGAGCTTGTCTCTGC | AGCCCAGGAACATCTTTGAG |
| NtCHI | AB213651.1 | GTCAGGCCATTGAAAAGCTC | CTAATCGTCAATGCCCCAAC |
| NtF3H | AB289450.1 | CAAGGCATGTGTGGATATGG | TGTGTCGTTTCAGTCCAAGG |
| NtF3'H | AB289449.1 | AGGCTCAACACTTCTCGT | CATCAACTTTGGGCTTCT |
| NtDFR | EF421429.1 | AACCAACAGTCAGGGGAATG | TTGGACATCGACAGTTCCAG |
| NtANS | AB289447.1 | TGGCGTTGAAGCTCATACTG | GGAATTAGGCACACACTTTGC |
| NtUFGT | FG627024.1 | GAGTGCATTGGATGCCTTTT | CCAGCTCCATTAGGTCCTTG |
| NtbHLH | HQ589208.1/HQ589209.1 | ATGKGCGCAAACGAGGTTGATAGC | TRGCTGAGGTTGTTGTTGCTCA |
| NtEF-1α | D63396.1 | TGAACCATCCAKGACAGATTGG | TGGGCTCCTTCTCAATCTCCTT |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
1.6 转基因烟草中花色素苷平均含量的分析
将不同转基因烟草叶片样品在液氮中充分研磨, 取0.5 g转至5 mL的离心管, 加入酸性甲醇提取液至满管, 混匀, 4℃下黑暗放置24 h, 离心, 上清液转入25 mL的容量瓶, 残渣中加入酸性甲醇提取液, 悬浮混匀, 4℃下黑暗放置12 h, 离心取上清液。重复以上步骤1次, 最后将浸提液定容至25 mL。在400~800 nm可见光的波长范围内进行紫外-可见光吸收光谱的扫描, 确定其在可见光区的最大吸收波长。取1 mL花色苷提取液, 分别加入pH 1.0氯化钾缓冲液和pH 4.5醋酸钠缓冲液9 mL, 室温平衡1 h, 蒸馏水做空白对照, 分别在λmax和λ700下测定吸光值, 代入公式计算花色素苷总含量[32,33], 最后求其花色素苷含量平均值。2 结果与分析
2.1 StAN1基因序列的克隆和分析
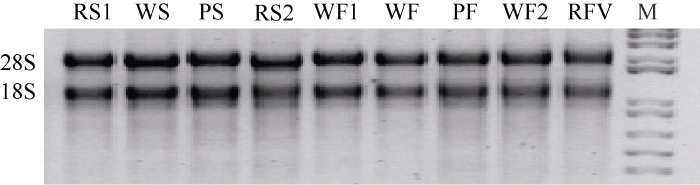
从图1可以看出, 总RNA的28S和18S条带完整、清晰, 表明RNA的完整性良好。图1
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图1总RNA的电泳图
RS1:“甘农薯5号”红色薯皮; WS:“新大坪”白色薯皮; PS:“黑美人”紫色薯皮; RS2:“青薯9号”红色薯皮; WF1:“甘农薯5号”白色薯肉; WF:“新大坪”白色薯肉; PF:“黑美人”紫色薯肉; WF2:“青薯9号”白色薯肉; RFV:“青薯9号”红色维管束; M: DNA marker。
Fig. 1Electrophoresis of the total RNA
RS1: GN, red skin; WS: XD, white skin; PS: HM, purple skin; RS2: QS, red skin; WF1: GN, white flesh; WF: XD, white flesh; PF: HM, purple flesh; WF2: QS, white flesh; RFV: QS, red vascular bundle; M: DNA marker.
以cDNA为模板, 通过PCR扩增, 从4个马铃薯品种的薯皮和薯肉中分别获得了长度为735、777和837 bp的完整片段(图2)。根据C端10个氨基酸序列组成的重复结构(R: TIAPQPQEGI)数目的不同(图3), 分别命名为StAN1-R0、StAN1-R1和StAN1-R3 (GenBank登录号依次为AKA95391、AKA95392和AKA95392)。其中在WS中含有StAN1-R0, WF中含有StAN1-R1; PS和PF只含有StAN1-R1; RS1、RS2、WF1、WF2和WFV中含有StAN1-R3。序列比对分析发现这3个序列间的同源性达到88.85%。StAN1-R0、StAN1-R1、StAN1-R3与参考序列(AY841129)的同源性分别为87.98%、94.57%和90.29%; StAN1-R0与StAN1-R1、StAN1-R3的同源性分别为89.15%和82.37%; StAN1-R1与StAN1-R3的同源性为89.57%, 二者同源性最高。
图2
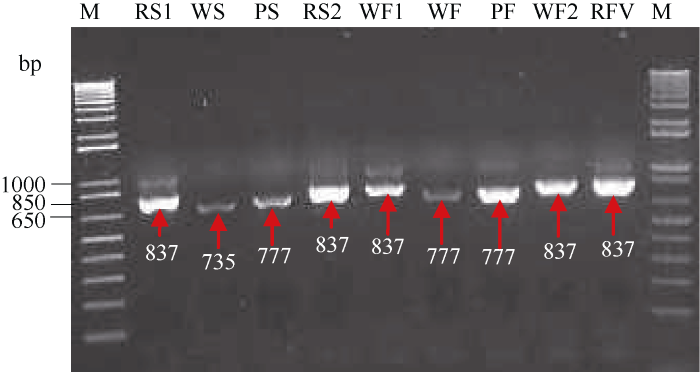 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图2基因克隆过程的PCR产物电泳图
RS1:“甘农薯5号”红色薯皮; WS:“新大坪”白色薯皮; PS:“黑美人”紫色薯皮; RS2:“青薯9号”红色薯皮; WF1:“甘农薯5号”白色薯肉; WF:“新大坪”白色薯肉; PF:“黑美人”紫色薯肉; WF2:“青薯9号”白色薯肉; RFV:“青薯9号”红色维管束; M: DNA marker。
Fig. 2PCR map of gene cloning
RS1: GN, red skin; WS: XD, white skin; PS: HM, purple skin; RS2: QS, red skin; WF1: GN, white flesh; WF: XD, white flesh; PF: HM, purple flesh; WF2: QS, white flesh; RFV: QS, red vascular bundle; M: DNA marker.
图3
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图3序列比对图 R表示重复结构TIAPQPQEGI。
Fig. 3Sequence comparison chart R indicates the repeat structure for TIAPQPQEGI.
2.2 马铃薯StAN1基因的生物信息学分析
2.2.1 马铃薯StAN1基因编码蛋白质的一级结构预测 通过在线工具ExPASy中的ProtParam预测马铃薯StAN1基因编码蛋白质的一级结构, 蛋白质分子式分别为C1227H1936N362O365S14、C1284H2019N377 O390S15和C1371H2164N402O423S15, 分子量分别为28 047.91、29 458.35和31 527.60 Da。等电点(pI)分别为8.39、6.90和6.14, 等电点的差异表明, 3个同源基因与其他植物的MYB基因在编码蛋白质稳定性、功能或者调控方式上有所差异[34]。3个蛋白质分别有负电荷残基(Asp+Glu) 30、32和34个, 正电荷残基(Arg+Lys) 33、32和32个。蛋白质三维结构不稳定系数(II)分别为46.97、48.64和50.76, 平均疏水性(GRAVY)分别为-0.693、-0.720和-0.712, 脂肪系数分别为(AI)为79.14、74.88和76.15。蛋白质不稳定系数均大于40, 三者表现为不稳定状态[35](表2)。2.2.2 马铃薯StAN1基因编码蛋白质的疏水性/亲水性的预测和分析 蛋白质的疏水性可根据蛋白质的平均疏水性(GRAVY)值来预测, 当GRAVY大于0时, 为疏水蛋白; 当GRAVY小于0时, 为亲水蛋白[36]。根据ProtScale软件预测, 三者的平均疏水性GRAVY均小于0 (表2), 故推测马铃薯R2R3 MYB蛋白均为亲水蛋白。
Table 2
表2
表2马铃薯StAN1基因编码蛋白质的一级结构预测
Table 2
| 基因 Gene | 蛋白质分子式 Formula | 分子量 Molecular weight (Da) | 等电点 pI | 不稳定系数 Instability index | 平均疏水性 Average of hydropathicity | 脂肪系数 Aliphatic index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| StAN1-R0 | C1227H1936N362O365S14 | 28047.91 | 8.39 | 46.97 | -0.693 | 79.14 |
| StAN1-R1 | C1284H2019N377O390S15 | 29458.35 | 6.90 | 48.64 | -0.720 | 74.88 |
| StAN1-R3 | C1371H2164N402O423S15 | 31527.60 | 6.14 | 50.76 | -0.712 | 76.15 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
2.2.3 马铃薯StAN1基因编码蛋白质的二级结构的预测和分析 根据SOPMA软件预测, 3种马铃薯StAN1基因编码的蛋白质均由α-螺旋、β-螺旋、无规则卷曲和延伸链组成。3个蛋白均为无规则卷曲>α-螺旋>延伸链>β-螺旋(表3)。
Table 3
表3
表3StAN1基因编码蛋白质的二级结构分析
Table 3
| 基因 Gene | α-螺旋 Alpha helix | β-螺旋 Beta turn | 无规则卷曲 Random coil | 延伸链 Extended strand |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| StAN1-R0 | 34.84 | 9.84 | 40.57 | 14.75 |
| StAN1-R1 | 35.27 | 8.91 | 42.25 | 13.57 |
| StAN1-R3 | 28.06 | 7.55 | 47.84 | 16.55 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
2.2.4 马铃薯StANI-R0、StANI-R1和StANI-R3氨基酸同源性分析 多重序列比对结果显示, 这3个同源基因的编码区均含高度保守的R2和R3 MYB结构域, 分别由48个和46个氨基酸组成, 该结构域与来自茄科植物和其他科属植物MYB转录因子的保守结构域具有很高的同源性(图4)。系统进化分析表明, 与StAN1-R0智利番茄和多毛番茄同源基因相似性最高, 同源性为53.0%; 与单子叶植物玉米和水稻同源基因相似性较低, 分别为33.2%和29.3% (图5)。
图4
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图4一些茄科植物与其他科属植物的R2R3 MYB氨基酸序列多重比对
StAN1-R0_PSAK277, StAN1-R1_PSAK277, StAN1-R3_PSAK277: 马铃薯; AAF66727: 矮牵牛; AAA33482.1: 玉米; AAG42001.1-AAG42002.1: 拟南芥; ABB84753.1: 苹果; ABD72956.1: 葡萄; ABO26065.1: 智利番茄; ABX71488.1: 沙梨; ACI195261.1: 多毛番茄; ACN79541.1: 蒺藜苜蓿; ACO52470.1: 烟草; ADW94950.1: 矮牵牛; AFD31843.1: 马铃薯; AIP93873.1: 茄子; AMK01804.1: 茄子; BAF45114.1: 甘薯; NP_001311547.1: 辣椒; ABX71493.1: 甜樱桃; sp_O23892.1: 水稻。
Fig. 4Multiple alignment of amino acid sequence of R2R3 MYB in some solanaceae plants and other subfamily
StAN1-R0_PSAK277, StAN1-R1_PSAK277, StAN1-R3_PSAK277: Solanum tuberosum; AAF66727.1: Petunia×hybrida; AAA33482.1: Zea mays; AAG42001.1-AAG42002.1: Arabidopsis thaliana; ABB84753.1: Malus pumila; ABD72956.1: Vitis vinifera; ABO26065.1: Solanum chilense; ABX71488.1: Pyrus pyrifolia; ACI195261.1: Solanum habrochites; ACN79541.1: Medicago truncatula; ACO52470.1: Nicotiana tabacum; ADW94950.1: Petunia×hybrida; AFD31843.1: Solanum tuberosum; AIP93873.1: Solanum melongena; AMK01804.1: Solanum melongena; BAF45114.1: Ipomoes batats; NP_001311547.1: Capsicum annuum; ABX71493.1: Cerasus avium; sp_O23892.1: Oryza sativa.
图5
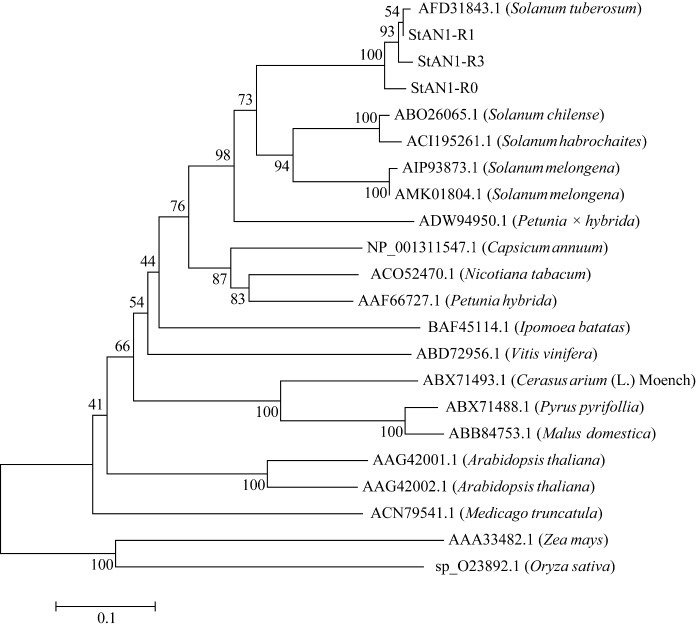 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图5StAN1基因与一些茄科和其他植物R2R3 MYB转录因子家族氨基酸序列的系统进化树分析
Fig. 5Phylogenetic tree analysis of the amino acid sequence of StAN1 genes and some R2R3 MYB transcription factor families in solanaceae and other plants
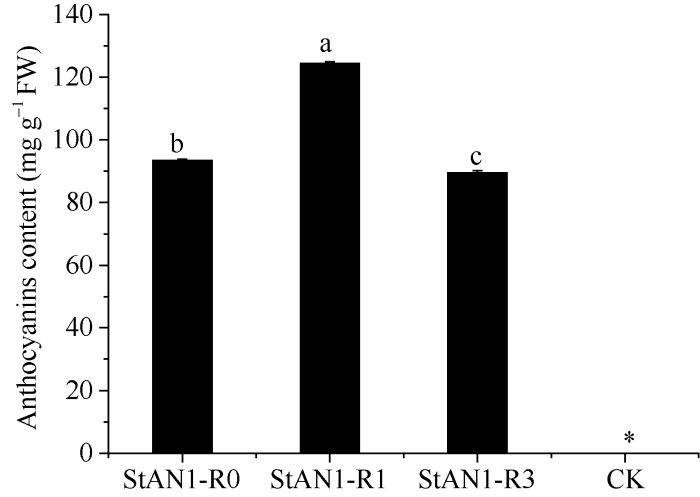
2.2.5 转StAN1基因烟草的鉴定及其花色素苷平均含量的分析 转目的基因StAN1的烟草叶片颜色呈现红色, 而CK的叶片为绿色, 转基因烟草的叶片和叶脉颜色深度分别为StAN1-R1>StAN1-R0>StAN1- R3 (图6-a, b)。对转基因烟草植株进行目的基因的PCR鉴定, 结果进一步证实3个目的基因已成功转入野生型烟草中(图7)。分别取转StAN1基因烟草和CK各3个株系的叶片测定花色素苷的含量发现, 转基因烟草叶片的花色素苷含量均明显高于CK, 且3个转基因烟草之间的花色素苷含量差异显著(图8), 转StAN1-R1烟草叶片中花色素苷平均含量最高, 为124.46 mg g-1 FW, StAN1-R3中平均含量最低, 为89.51 mg g-1 FW, 与表型相一致。
图6
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图6转StAN1基因烟草的表型分析
a: 转StAN1基因烟草的整株; b: 转StAN1基因烟草的叶片。
Fig. 6Phenotypic analysis of StAN1 transgenic tobacco
a: whole plant of StAN1 transgenic tobacco; b: leaves of StAN1 transgenic tobacco.
图7
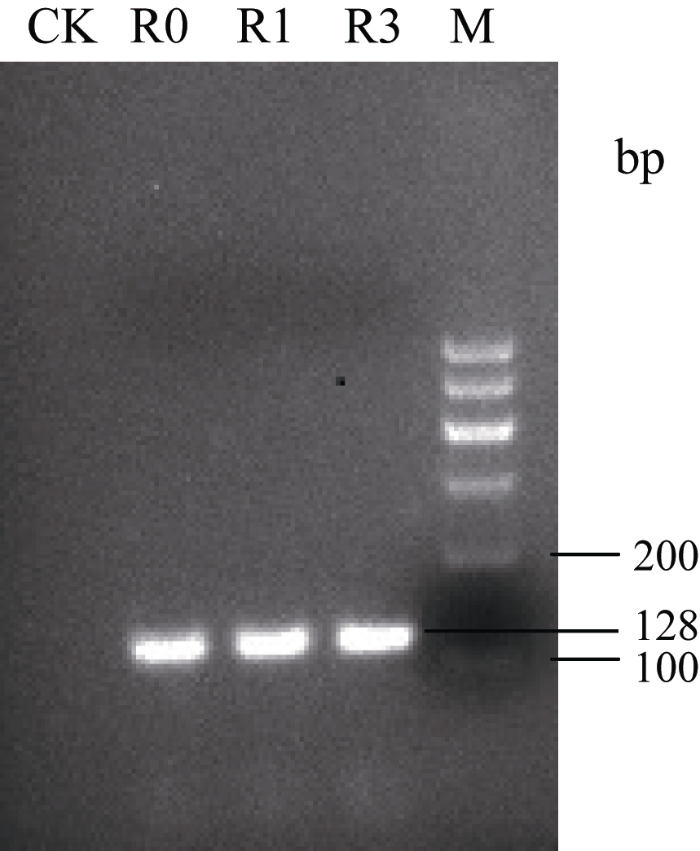 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图7转StAN1基因烟草的PCR鉴定
M: DNA marker; CK: 未转基因烟草; R0、R1、R3分别为转StAN1-R0、StAN1-R1、StAN1-R3基因烟草。
Fig. 7PCR identification of StAN1 transgenic tobacco
M: DNA marker; CK: non-genetically modified tobacco; R0, R1, R3: the transgenic tobacco of StAN1-R0, StAN1-R1, StAN1-R3, respectively.
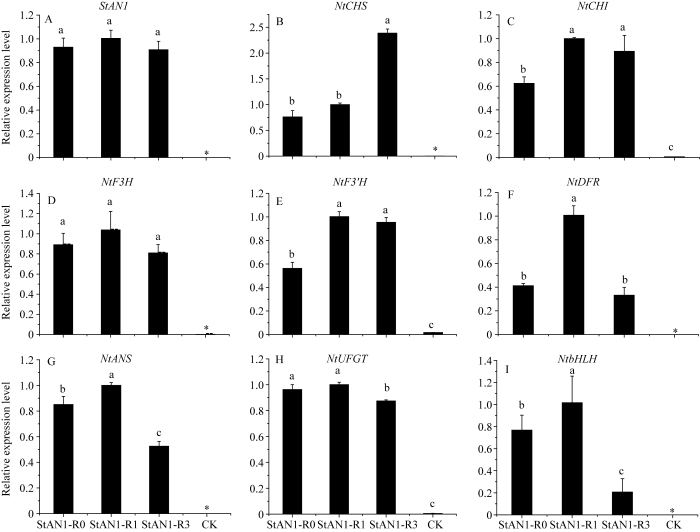
2.2.6 转基因烟草中花色素苷合成关键基因的表达分析 从图9-A可以看出, 外源基因StAN1在转基因烟草中显著上调表达, 且3个基因的表达量之间无显著差异, 而在对照烟草中检测不到StAN1, 进一步说明外源基因StAN1已导入到烟草中。与CK相比, 转StAN1-R0、StAN1-R1和StAN1-R3基因烟草中参与花色素苷合成的相关基因表达量大幅上调, 包括合成途径中的早期表达基因NtCHS、NtCHI、NtF3H、NtF3’H和晚期表达基因NtDFR、NtANS、NtUFGT。其中NtDFR和NtANS在转StAN1-R1烟草中的表达量显著高于转StAN1-R0和StAN1-R3烟草中的。此外, 与CK相比, 转StAN1-R0, StAN1-R1和StAN1-R3烟草叶片中内源NtbHLH转录因子(NtAN1a和NtAN1b)的相对表达量均大幅度上调(图9-B~I), 说明3个目的基因的转入显著增强了NtbHLH基因的表达, 其中StAN1-R1对其调控能力最强, StAN1-R3的调控能力最弱, StAN1-R0的调控能力介于两者之间。
图8
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图8转StAN1基因烟草与对照的花色素苷平均含量
采用Duncan’s多重比较方法分析(P < 0.05, n = 3)。
Fig. 8Average content of anthocyanin in StAN1 transgenic tobacco and control
Duncan’s multiple comparisons were used to analyze (P < 0.05,n = 3).
图9
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图9转基因烟草中与花色素苷合成相关基因相对表达量
采用Duncan’s多重比较方法分析(P < 0.05, n = 3)。
Fig. 9Gene expression relative to anthocyanin biosynthesis in transgenic tobacco
Duncan’s multiple comparisons were used to analyze (P < 0.05, n = 3).
3 讨论
四倍体马铃薯的栽培种遗传背景复杂, 不同品种的彩色马铃薯所合成花色素苷的种类和数量也不同。MYB是参与调控植物花色素苷合成中涉及最广泛的转录因子, 研究者已在多种植物中克隆分离出大量的与花色素苷合成积累有关的MYB转录因子, 且对其研究较为深入[37]。植物MYB蛋白的结构域高度保守, 该结构域通常包括1~4个重复的氨基酸R基序, 根据R基序的数量分为R1 MYB蛋白、R2R3 MYB蛋白、R1R2R3 MYB蛋白和4R MYB蛋白[10], 其中R2R3 MYB在参与调控不同植物以及同种植物不同组织器官中的花色素苷合成与积累中尤为重要[38]。研究发现, 在马铃薯红色薯皮和紫色薯皮中表达的基因D是二倍体马铃薯薯皮花色素苷合成的转录调控基因, 其编码R2R3 MYB-StAN1转录因子[25]。StAN1不仅调控薯皮颜色, 而且与StJAF13转录因子协同调控马铃薯红叶品种“Magenta Love”的叶片颜色; 在另一个红叶品种‘Double Fun’中, StbHLH1转录因子与StAN1和StJAF13共同调控叶片颜色[23]。本实验从不同颜色的四倍体马铃薯块茎中克隆分离了StAN1的3个同源基因, 通过序列比对分析发现其区别在于C末端3个重复序列数目(R)不同, 根据R数目分别命名为StAN1-R0、StAN1-R1和StAN1-R3。通过进一步转化烟草分析发现, StAN1-R0、StAN1-R1以及StAN1-R3均显著调控烟草叶片花色素苷合成相关的结构基因, 使烟草叶片明显积累花色素苷从而呈现红色, 其中含有一个重复序列R的StAN1-R1调控能力最强, 烟草叶片呈现深红色, 花色素苷含量积累最多, StAN1-R3调控能力最弱, 说明R在StAN1调控花色素苷能力方面具有重要功能。
另有研究表明, MYB转录因子需要与其他转录因子结合协同调控花色素苷的合成[39,40]。本研究发现转StAN1-R0、StAN1-R1和StAN1-R3烟草叶片中NtbHLH基因显著上调表达, 说明外源基因StAN1导入烟草后可以激活烟草内源转录因子NtbHLH的表达, 其表达量在转StAN1-R1烟草中最高, 在转StAN1-R3烟草中最低, 与烟草叶片中花色素苷含量相一致, 因此推测NtbHLH也是调控花色素苷合成的重要转录因子, StAN1与NtbHLH协同调控烟草叶片花色素苷的合成。
综上所述, StAN1转录因子调控花色素苷合成有两个重要机制, 一是C末端结构不同的3个StAN1同源蛋白调控花色素苷合成的能力不同, 其中含一个重复序列R的StAN1-R1调控能力最强, 说明R具有重要功能; 二是StAN1显著调控内源bHLH转录因子的表达, 推测其与bHLH转录因子协同调控花色素苷生物合成相关结构基因的表达, 从而促进花色素苷的合成与积累。
4 结论
本试验克隆了马铃薯R2R3 MYB家族的3个同源基因StAN1-R0、StAN1-R1和StAN1-R3。StAN1-R0的分子量最小, StAN1-R3分子量最大。3个同源基因编码的蛋白质均为不稳定状态, 二级结构均由α-螺旋、β-螺旋、无规则卷曲和延伸链组成, 均含有2个高度保守结构域R2和R3。与StAN1基因同源性最高的为智利番茄和多毛番茄, 同源性最低的为玉米和水稻。叶色深度为StAN1-R1>StAN1-R0>StAN1- R3>CK。花色素苷含量为StAN1-R1>StAN1-R0> StAN1-R3>CK。StAN1的异源表达激活了烟草叶片内花色素苷合成的早期生物基因(NtCHS、NtCHI、NtF3H和NtF3’H)和晚期生物基因(NtDFR、NtANS和NtUFGT)的表达, 同时也显著增强了内源NtbHLH转录因子的表达, 其中, 含有一个R基序的StAN1-R1调控能力最强。本研究为更深入了解R2R3 MYB转录因子参与调控马铃薯块茎花色素苷合成提供了理论基础。参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03447.xURLPMID:18476875 [本文引用: 1]

Summary Plant compounds that are perceived by humans to have color are generally referred to as igments. Their varied structures and colors have long fascinated chemists and biologists, who have examined their chemical and physical properties, their mode of synthesis, and their physiological and ecological roles. Plant pigments also have a long history of use by humans. The major classes of plant pigments, with the exception of the chlorophylls, are reviewed here. Anthocyanins, a class of flavonoids derived ultimately from phenylalanine, are water-soluble, synthesized in the cytosol, and localized in vacuoles. They provide a wide range of colors ranging from orange/red to violet/blue. In addition to various modifications to their structures, their specific color also depends on co-pigments, metal ions and pH. They are widely distributed in the plant kingdom. The lipid-soluble, yellow-to-red carotenoids, a subclass of terpenoids, are also distributed ubiquitously in plants. They are synthesized in chloroplasts and are essential to the integrity of the photosynthetic apparatus. Betalains, also conferring yellow-to-red colors, are nitrogen-containing water-soluble compounds derived from tyrosine that are found only in a limited number of plant lineages. In contrast to anthocyanins and carotenoids, the biosynthetic pathway of betalains is only partially understood. All three classes of pigments act as visible signals to attract insects, birds and animals for pollination and seed dispersal. They also protect plants from damage caused by UV and visible light.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1104/pp.112.206771URLPMID:23096157 [本文引用: 1]

Anthocyanin accumulation is coordinated in plants by a number of conserved transcription factors. In apple (Malus 3 domestica), an R2R3 MYB transcription factor has been shown to control fruit flesh and foliage anthocyanin pigmentation (MYB10) and fruit skin color (MYB1). However, the pattern of expression and allelic variation at these loci does not explain all anthocyanin-related apple phenotypes. One such example is an open-pollinated seedling of cv Sangrado that has green foliage and develops red flesh in the fruit cortex late in maturity. We used methods that combine plant breeding, molecular biology, and genomics to identify duplicated MYB transcription factors that could control this phenotype. We then demonstrated that the red-flesh cortex phenotype is associated with enhanced expression of MYB110a, a paralog of MYB10. Functional characterization of MYB110a showed that it was able to up-regulate anthocyanin biosynthesis in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum). The chromosomal location of MYB110a is consistent with a whole-genome duplication event that occurred during the evolution of apple within the Maloideae. Both MYB10 and MYB110a have conserved function in some cultivars, but they differ in their expression pattern and response to fruit maturity.
DOI:10.1104/pp.108.118919URL [本文引用: 1]

Among the dramatic changes occurring during grape berry (Vitis vinifera) development, those affecting the flavonoid pathway have provoked a number of investigations in the last 10 years. In addition to producing several compounds involved in the protection of the berry and the dissemination of the seeds, final products of this pathway also play a critical role in berry and wine quality. In this article, we describe the cloning and functional characterization of VvMYB5b, a cDNA isolated from a grape berry (V. vinifera 'Cabernet Sauvignon') library. VvMYB5b encodes a protein belonging to the R2R3-MYB family of transcription factors and displays significant similarity with VvMYB5a, another MYB factor recently shown to regulate flavonoid synthesis in grapevine. The ability of VvMYB5a and VvMYB5b to activate the grapevine promoters of several structural genes of the flavonoid pathway was confirmed by transient expression of the corresponding cDNAs in grape cells. Overexpression of VvMYB5b in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) leads to an up-regulation of genes encoding enzymes of the flavonoid pathway and results in the accumulation of anthocyanin- and proanthocyanidin-derived compounds. The ability of VvMYB5b to regulate particularly the anthocyanin and the proanthocyanidin pathways is discussed in relation to other recently characterized MYB transcription factors in grapevine. Taken together, data presented in this article give insight into the transcriptional mechanisms associated with the regulation of the flavonoid pathway throughout grape berry development.
DOI:10.1046/j.1365-2923.2001.00865.xURLPMID:7796266 [本文引用: 1]

The DNA-binding domain of c-Myb consists of three imperfect tandem repeats (R1, R2 and R3). The three repeats have similar overall architectures. each containing a helix-turn-helix variation motif. The three conserved tryptophans in each repeat participate in forming a hydrophobic core. Comparison of the three repeat structures indicated that cavities are found in the hydrophobic core of R2, which is thermally unstable. On complexation with DNA, the orientations of R2 and R3 are fixed by tight binding and their conformations;ire slightly changed. No significant changes occur in the chemical shifts of R1 consistent with its loose interaction with DNA. [References: 50]
DOI:10.1007/s004290100164URLPMID:11245574 [本文引用: 1]

Studies involving mutants of the gene SPATULA indicate that it promotes the growth of carpel margins and of pollen tract tissues derived from them. We show that it encodes a new member of the basic-helix-loop-helix family of transcription factors. SPATULA is expressed in marginal and pollen tract tissues throughout their development confirming its role in regulating their growth. It is also expressed in many other tissues where it may act redundantly to control growth, including the peripheral zone of the shoot apical meristem, and specific tissues within leaves, petals, stamens and roots. Expression in the stomium, funiculus and valve dehiscence zone indicates an additional role in abscission. SPATULA expression does not require the function of the other carpel development genes CRABS CLAW and AGAMOUS, although its expression is repressed in first whorl organs by the A function gene APETALA2. Further, we have shown that disruptions to gynoecial pattern formation seen in ettin mutants can largely be attributed to ectopic SPATULA action. ETTIN's role seems to be to negatively regulate SPATULA expression in abaxial regions of the developing gynoecium. SPATULA is the first basic-helix-loop-helix gene in plants known to play a role in floral organogenesis.
DOI:10.4161/psb.3.7.5599URLPMID:19704482 [本文引用: 1]

PHYTOCHROME RAPIDLY REGULATED1 (PAR1) and PAR2 are two negative regulators of shade avoidance syndrome (SAS) responses in Arabidopsis. PAR1 and PAR2 belong to the bHLH family of transcription factors and act as direct transcriptional repressors of auxin- and brassinosteroid-responsive genes. These observations led us to propose that PAR1 and PAR2 might integrate shade and hormone signals. After plant proximity perception by the phytochrome photoreceptors, the expression of PAR1, PAR2 and dozens of additional PAR genes is affected, initiating a complex web of transcriptional events instrumental for the establishment of the SAS responses. Studying the organization of this complex transcriptional network, that is, the interactions amongst the different PAR factors involved and how they are connected with the endogenous hormone-regulated transcriptional networks, seems therefore fundamental to understand how SAS is modulated.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1005.2014.0985URL [本文引用: 1]

拟南芥R2R3-MYB转录因子在拟南芥生长发育、代谢及响应生物和非生物胁迫的调控网络中具有重要作用。根据保守的氨基酸序列,R2R3-MYB转录因子被分为25个亚族,其中第22亚族包含AtMYB44、AtMYB77、AtMYB73和AtMYB70 4个基因,主要响应生物和非生物胁迫。文章从基因功能的相似性、基因表达的一致性和基因结构的保守性3方面综述了第22亚族的4个基因,并综合讨论了其在结构与功能上的冗余性和多样性。
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1005.2014.0985URL [本文引用: 1]

拟南芥R2R3-MYB转录因子在拟南芥生长发育、代谢及响应生物和非生物胁迫的调控网络中具有重要作用。根据保守的氨基酸序列,R2R3-MYB转录因子被分为25个亚族,其中第22亚族包含AtMYB44、AtMYB77、AtMYB73和AtMYB70 4个基因,主要响应生物和非生物胁迫。文章从基因功能的相似性、基因表达的一致性和基因结构的保守性3方面综述了第22亚族的4个基因,并综合讨论了其在结构与功能上的冗余性和多样性。
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-7968.2012.09.004URL [本文引用: 1]

R2R3-MYB是MYB转录因子基因家族的主要成员,已被证明在次生代谢和非生物逆境胁迫应答中起重要作用。为获得甘蔗(Saccharumcomplex)R2R3-MYB转录因子基因序列信息及其在不同非生物因子胁迫下的表达情况,本研究通过对甘蔗EST数据的分析,运用电子克隆获得一个甘蔗R2R3.MYB类似基因序列,进而采用PCR方法从甘蔗中克隆了该基因的基因组DNA和cDNA序列,基因命名为Sc2RMybl(GenBank序列号:JQ823165)。Sc2RMybl的基因组DNA全长1807bp,由3个外显子和2个内含子构成,编码区长度为1284bp,编码427个氨基酸。构建含有Sc2RMybl基因的原核表达载体并转入大肠杆菌(Escherichiacoli),经IPTG诱导产生的重组蛋白相对分子量约为52kD。在NaCl胁迫的LB培养基上,重组菌生长明显优于对照菌。实时荧光定量PCR分析表明,甘蔗中Sc2RMybl基因的表达受H2O2和NaCl抑制而下调,推测该基因作为负调节因子参与了NaCl胁迫应答相关基因的调控过程。本研究结果为后续该类转录因子基因在甘蔗抗逆相关机理研究和抗逆育种中的应用提供了基础资料。
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-7968.2012.09.004URL [本文引用: 1]

R2R3-MYB是MYB转录因子基因家族的主要成员,已被证明在次生代谢和非生物逆境胁迫应答中起重要作用。为获得甘蔗(Saccharumcomplex)R2R3-MYB转录因子基因序列信息及其在不同非生物因子胁迫下的表达情况,本研究通过对甘蔗EST数据的分析,运用电子克隆获得一个甘蔗R2R3.MYB类似基因序列,进而采用PCR方法从甘蔗中克隆了该基因的基因组DNA和cDNA序列,基因命名为Sc2RMybl(GenBank序列号:JQ823165)。Sc2RMybl的基因组DNA全长1807bp,由3个外显子和2个内含子构成,编码区长度为1284bp,编码427个氨基酸。构建含有Sc2RMybl基因的原核表达载体并转入大肠杆菌(Escherichiacoli),经IPTG诱导产生的重组蛋白相对分子量约为52kD。在NaCl胁迫的LB培养基上,重组菌生长明显优于对照菌。实时荧光定量PCR分析表明,甘蔗中Sc2RMybl基因的表达受H2O2和NaCl抑制而下调,推测该基因作为负调节因子参与了NaCl胁迫应答相关基因的调控过程。本研究结果为后续该类转录因子基因在甘蔗抗逆相关机理研究和抗逆育种中的应用提供了基础资料。
DOI:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02964.xURLPMID:1865000 [本文引用: 1]

Anthocyanin concentration is an important determinant of the colour of many fruits. In apple (Malus x domestica), centuries of breeding have produced numerous varieties in which levels of anthocyanin pigment vary widely and change in response to environmental and developmental stimuli. The apple fruit cortex is usually colourless, although germplasm does exist where the cortex is highly pigmented due to the accumulation of either anthocyanins or carotenoids. From studies in a diverse array of plant species, it is apparent that anthocyanin biosynthesis is controlled at the level of transcription. Here we report the transcript levels of the anthocyanin biosynthetic genes in a red-fleshed apple compared with a white-fleshed cultivar. We also describe an apple MYB transcription factor, MdMYB10, that is similar in sequence to known anthocyanin regulators in other species. We further show that this transcription factor can induce anthocyanin accumulation in both heterologous and homologous systems, generating pigmented patches in transient assays in tobacco leaves and highly pigmented apple plants following stable transformation with constitutively expressed MdMYB10. Efficient induction of anthocyanin biosynthesis in transient assays by MdMYB10 was dependent on the co-expression of two distinct bHLH proteins from apple, MdbHLH3 and MdbHLH33. The strong correlation between the expression of MdMYB10 and apple anthocyanin levels during fruit development suggests that this transcription factor is responsible for controlling anthocyanin biosynthesis in apple fruit; in the red-fleshed cultivar and in the skin of other varieties, there is an induction of MdMYB10 expression concurrent with colour formation during development. Characterization of MdMYB10 has implications for the development of new varieties through classical breeding or a biotechnological approach.
DOI:10.1093/pcp/pcm066URLPMID:17526919 [本文引用: 1]

Red coloration of apple (Malus x domestica) skin is an important determinant of consumer preference and marketability. Anthocyanins are responsible for this coloration, and their accumulation is positively correlated with the expression level of anthocyanin biosynthetic genes. Regulation of expression of these genes is believed to be controlled by MYB transcription factors, and the MYB transcription factors involved in the activation of anthocyanin biosynthetic genes have been isolated in various plants. In the present study, we isolated and characterized a MYB transcription factor gene (MdMYBA) from apple skin. Characterization of MdMYBA demonstrated that (i) MdMYBA expression was specifically regulated depending on the tissue and cultivar/species; (ii) its expression level was much higher in a deep-red cultivar ('Jonathan') than in a pale-red cultivar ('Tsugaru'); (iii) when cauliflower mosaic virus 35S::MdMYBA was introduced into the cotyledons of apple seedlings by means of a transient assay, reddish-purple spots were induced, and MdMYBA also induced anthocyanin accumulation in reproductive tissues of transgenic tobacco; (iv) the expression of MdMYBA was induced by UV-B irradiation and low-temperature treatment, both of which are known to be important in the promotion of anthocyanin accumulation in apple skin; (v) MdMYBA bound specifically to an anthocyanidin synthase (MdANS) promoter region in a gel-shift assay; and (vi) MdMYBA was mapped to the near region of the BC226-STS (a1) marker for the red skin color locus (R(f)). These results suggest that MdMYBA is a key regulatory gene in anthocyanin biosynthesis in apple skin.
DOI:10.1104/pp.106.088104URLPMID:17012405 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract Anthocyanins are secondary metabolites found in higher plants that contribute to the colors of flowers and fruits. In apples (Malus domestica Borkh.), several steps of the anthocyanin pathway are coordinately regulated, suggesting control by common transcription factors. A gene encoding an R2R3 MYB transcription factor was isolated from apple (cv Cripps' Pink) and designated MdMYB1. Analysis of the deduced amino acid sequence suggests that this gene encodes an ortholog of anthocyanin regulators in other plants. The expression of MdMYB1 in both Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) plants and cultured grape cells induced the ectopic synthesis of anthocyanin. In the grape (Vitis vinifera) cells MdMYB1 stimulated transcription from the promoters of two apple genes encoding anthocyanin biosynthetic enzymes. In ripening apple fruit the transcription of MdMYB1 was correlated with anthocyanin synthesis in red skin sectors of fruit. When dark-grown fruit were exposed to sunlight, MdMYB1 transcript levels increased over several days, correlating with anthocyanin synthesis in the skin. MdMYB1 gene transcripts were more abundant in red skin apple cultivars compared to non-red skin cultivars. Several polymorphisms were identified in the promoter of MdMYB1. A derived cleaved amplified polymorphic sequence marker designed to one of these polymorphisms segregated with the inheritance of skin color in progeny from a cross of an unnamed red skin selection (a sibling of Cripps' Pink) and the non-red skin cultivar Golden Delicious. We conclude that MdMYB1 coordinately regulates genes in the anthocyanin pathway and the expression level of this regulator is the genetic basis for apple skin color.
DOI:10.1186/1471-2229-13-68URLPMID:3648406 [本文引用: 1]

Background Flavonoids such as anthocyanins, flavonols and proanthocyanidins, play a central role in fruit colour, flavour and health attributes. In peach and nectarine ( Prunus persica ) these compounds vary during fruit growth and ripening. Flavonoids are produced by a well studied pathway which is transcriptionally regulated by members of the MYB and bHLH transcription factor families. We have isolated nectarine flavonoid regulating genes and examined their expression patterns, which suggests a critical role in the regulation of flavonoid biosynthesis. Results In nectarine, expression of the genes encoding enzymes of the flavonoid pathway correlated with the concentration of proanthocyanidins, which strongly increases at mid-development. In contrast, the only gene which showed a similar pattern to anthocyanin concentration was UDP-glucose-flavonoid-3-O-glucosyltransferase ( UFGT) , which was high at the beginning and end of fruit growth, remaining low during the other developmental stages. Expression of flavonol synthase ( FLS1) correlated with flavonol levels, both temporally and in a tissue specific manner. The pattern of UFGT gene expression may be explained by the involvement of different transcription factors, which up-regulate flavonoid biosynthesis ( MYB10 , MYB123 , and bHLH3 ), or repress ( MYB111 and MYB16 ) the transcription of the biosynthetic genes. The expression of a potential proanthocyanidin-regulating transcription factor, MYBPA1 , corresponded with proanthocyanidin levels. Functional assays of these transcription factors were used to test the specificity for flavonoid regulation. Conclusions MYB10 positively regulates the promoters of UFGT and dihydroflavonol 4-reductase ( DFR ) but not leucoanthocyanidin reductase ( LAR ). In contrast, MYBPA1 trans-activates the promoters of DFR and LAR , but not UFGT . This suggests exclusive roles of anthocyanin regulation by MYB10 and proanthocyanidin regulation by MYBPA1. Further, these transcription factors appeared to be responsive to both developmental and environmental stimuli.
DOI:10.1104/pp.110.162735URLPMID:20807862 [本文引用: 1]

Deposition of lignified secondary cell walls in plants involves a major commitment of carbon skeletons in both the form of polysaccharides and phenylpropanoid constituents. This process is spatially and temporally regulated by transcription factors, including a number of MYB family transcription factors. MYB75, also called PRODUCTION OF ANTHOCYANIN PIGMENT1, is a known regulator of the anthocyanin branch of the phenylpropanoid pathway in Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana), but how this regulation might impact other aspects of carbon metabolism is unclear. We established that a loss-of-function mutation in MYB75 (myb75-1) results in increased cell wall thickness in xylary and interfascicular fibers within the inflorescence stem. The total lignin content and S/G ratio of the lignin monomers were also affected. Transcript profiles from the myb75-1 inflorescence stem revealed marked up-regulation in the expression of a suite of genes associated with lignin biosynthesis and cellulose deposition, as well as cell wall modifying proteins and genes involved in photosynthesis and carbon assimilation. These patterns suggest that MYB75 acts as a repressor of the lignin branch of the phenylpropanoid pathway. Since MYB75 physically interacts with another secondary cell wall regulator, the KNOX transcription factor KNAT7, these regulatory proteins may form functional complexes that contribute to the regulation of secondary cell wall deposition in the Arabidopsis inflorescence stem and that integrate the metabolic flux through the lignin, flavonoid, and polysaccharide pathways.
DOI:10.1007/s004380000376URLPMID:11254134 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract The chimeric transcriptional activator TGV mediates dexamethasone (dx)-inducible and tetracycline (tc)-repressible transgene expression in tobacco (dx-on/ tc-off system). The expression profiles of four different synthetic target promoters, comprising multiple TGV binding sites upstream of a core promoter, were characterised using the sensitive luciferase assay. Induction factors of over 1,000 were measured in roots and leaves of over 30% of the transgenic plants, irrespective of the promoter used. Promoters PTF and PTax, which carry the -48 to +1 region of the Cauliflower Mosaic Virus 35S promoter, showed higher expression levels in both the uninduced and induced states than PTop10 and PTFM, which harbour several point mutations in this region. Moreover, PTax expressed higher background activities than PTF, indicating that the sequence of the synthetic regulatory region can influence background levels. The usefulness of the dx-on/tc-off system for experiments addressing gene function was demonstrated by using it to control the expression of isopentenyl transferase. This enzyme catalyses the rate-limiting step in cytokinin biosynthesis and causes phenotypic effects even at low expression levels. Only dx-induced transgenic plants displayed phenotypic alterations indicative for increased cytokinin synthesis (e.g. outgrowth of lateral buds). Simultaneous treatment of selected buds with the antiinducer tc suppressed bud growth. This result suggests that cytokinins cannot serve as mobile signals to elicit the release of apical dominance in tissues compromised for enhanced cytokinin synthesis.
DOI:10.1016/j.carres.2003.11.008URL [本文引用: 1]

Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) cv. Micro-Tom plants were transformed with the Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heyhn. MYB75/PAP1 (PRODUCTION OF ANTHOCYANIN PIGMENT 1) gene. This gene encodes for a well known transcription factor, which is involved in anthocyanin production and is modulated by light and sucrose. Transgenic tomato plants expressing AtMYB75 were characterised by a significantly higher anthocyanin production in leaves, stems, roots and flowers under normal growth conditions. Further, they also exhibited anthocyanins in fruits. Anthocyanin accumulation was not widespread but took place in specific groups of cells located in epidermal or cortical regions or in proximity of vascular bundles. In all the organs of the transgenic plants, where AtMYB75 overexpression was determined, a clear increase in the accumulation of DFR (DIHYDROFLAVONOL 4-REDUCTASE) transcript was also detected. The expression of the tomato MYB-gene ANT1 (ANTHOCYANIN1), which had previously been identified as a transcriptional endogenous regulator of anthocyanin biosynthesis, was not altered. The higher basal content of anthocyanins in the leaves of the transgenic plants could be further increased in the presence of high light conditions and contributed to mitigate photobleaching damages under high irradiance.
[本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]

花青素具有抗氧化、抗突变、抗增生等重要的生理功能,紫色马铃薯因其富含花青素而被称为健康食品。花青素 在植物不同组织中积累的模式和程度是受花青素转录激活基因的表达而共同调控的。分离克隆紫色马铃薯花色素合成的转录激活基因(MYC和MYB基因),以进 一步鉴定他们的功能,可为阐明马铃薯花色素生物合成和沉积机制提供理论依据,另外还可为培育高花色素含量的马铃薯新品种提供理论基础。 本文首先采用RT-PCR方法从紫色马铃薯紫皮RNA中扩增了花青素转录激活基因MYC的保守区域片段(Stmyc1),测序后再通过3'-RACE技术 获得马铃薯转录激活基因的cDNA3’末端序列(Stmyc2),拼接获得长为1106bp的Stmyc基因。再对所获得马铃薯Stmyc基因进行阅读编 码框分析及BLASTn和BLASTx分析,并通过ClastalW软件分析Stmyc基因的系统发育树,再对Stmyc基因进行功能预测。 同时采用RT-PCR方法从紫色马铃薯紫皮RNA中扩增了花青素转录激活基因R2R3MYB的保守区域片段(Stmyb280和Stmyb211),对所 获得的片段进行BLASTn、BLASTx、ClastalW和CDDv1.65分析。 结果如下:1)首次从马铃薯紫皮中获得马铃薯Stmyc基因cDNA序列,其长度为1106bp,具有完整的编码阅读框,编码区为10-990bp,共编 码326个氨基酸。经序列比较发现Stmyc基因编码蛋白与紫苏MYC类基因编码蛋白的一致性达94%。蛋白质功能预测具有bHLH结构域,与MYC类蛋 白的保守结构功能域也是基本吻合的,初步认为获得了与马铃薯花色素合成相关的myc基因(Stmyc)。 2)获得马铃薯转录激活基因R2R3MYB基因的保守序列(Stmyb211和Stmyb280)。Stmyb211编码的蛋白与番茄素THM27、葡萄 抗毒素GNF13、拟南芥At4g38620和MYB转录因子的花青素R2R3MYB类蛋白有94%的相似性。Stmyb280编码的蛋白与拟南芥MYB 转录因子At3g61250(AY519601)、玉米R2R3-MYBmyb3蛋白(AF474116)、黑麦R2R3-MYB蛋白 myb4(AY178579)和海棠MYB14(DQ074465)的同源性较低。用蛋白保守结构功能域分析Stmyb211和Stmyb280片段都含 有一个Myb-DNA-binding框。
URL [本文引用: 1]

花青素具有抗氧化、抗突变、抗增生等重要的生理功能,紫色马铃薯因其富含花青素而被称为健康食品。花青素 在植物不同组织中积累的模式和程度是受花青素转录激活基因的表达而共同调控的。分离克隆紫色马铃薯花色素合成的转录激活基因(MYC和MYB基因),以进 一步鉴定他们的功能,可为阐明马铃薯花色素生物合成和沉积机制提供理论依据,另外还可为培育高花色素含量的马铃薯新品种提供理论基础。 本文首先采用RT-PCR方法从紫色马铃薯紫皮RNA中扩增了花青素转录激活基因MYC的保守区域片段(Stmyc1),测序后再通过3'-RACE技术 获得马铃薯转录激活基因的cDNA3’末端序列(Stmyc2),拼接获得长为1106bp的Stmyc基因。再对所获得马铃薯Stmyc基因进行阅读编 码框分析及BLASTn和BLASTx分析,并通过ClastalW软件分析Stmyc基因的系统发育树,再对Stmyc基因进行功能预测。 同时采用RT-PCR方法从紫色马铃薯紫皮RNA中扩增了花青素转录激活基因R2R3MYB的保守区域片段(Stmyb280和Stmyb211),对所 获得的片段进行BLASTn、BLASTx、ClastalW和CDDv1.65分析。 结果如下:1)首次从马铃薯紫皮中获得马铃薯Stmyc基因cDNA序列,其长度为1106bp,具有完整的编码阅读框,编码区为10-990bp,共编 码326个氨基酸。经序列比较发现Stmyc基因编码蛋白与紫苏MYC类基因编码蛋白的一致性达94%。蛋白质功能预测具有bHLH结构域,与MYC类蛋 白的保守结构功能域也是基本吻合的,初步认为获得了与马铃薯花色素合成相关的myc基因(Stmyc)。 2)获得马铃薯转录激活基因R2R3MYB基因的保守序列(Stmyb211和Stmyb280)。Stmyb211编码的蛋白与番茄素THM27、葡萄 抗毒素GNF13、拟南芥At4g38620和MYB转录因子的花青素R2R3MYB类蛋白有94%的相似性。Stmyb280编码的蛋白与拟南芥MYB 转录因子At3g61250(AY519601)、玉米R2R3-MYBmyb3蛋白(AF474116)、黑麦R2R3-MYB蛋白 myb4(AY178579)和海棠MYB14(DQ074465)的同源性较低。用蛋白保守结构功能域分析Stmyb211和Stmyb280片段都含 有一个Myb-DNA-binding框。
DOI:10.1111/tpj.12653URLPMID:25159050 [本文引用: 1]

Summary AN1 is a regulatory gene that promotes anthocyanin biosynthesis in potato tubers and encodes a R2R3 MYB transcription factor. However, no clear evidence implicates AN1 in anthocyanin production in leaves, where these pigments might enhance environmental stress tolerance. In our study we found that AN1 displays intraspecific sequence variability in both coding/non-coding regions and in the promoter, and that its expression is associated with high anthocyanin content in leaves of commercial potatoes. Expression analysis provided evidence that leaf pigmentation is associated to AN1 expression and that StJAF13 acts as putative AN1 co-regulator for anthocyanin gene expression in leaves of the red leaf variety ‘Magenta Love,’ while a concomitant expression of StbHLH1 may contribute to anthocyanin accumulation in leaves of ‘Double Fun.’ Yeast two-hybrid experiments confirmed that AN1 interacts with StbHLH1 and StJAF13 and the latter interaction was verified and localized in the cell nucleus by bimolecular fluorescence complementation assays. In addition, transgenic tobacco ( Nicotiana tabacum ) overexpressing a combination of either AN1 with StJAF13 or AN1 with StbHLH1 showed deeper purple pigmentation with respect to AN1 alone. This further confirmed AN1/StJAF13 and AN1/StbHLH1 interactions. Our findings demonstrate that the classical loci identified for potato leaf anthocyanin accumulation correspond to AN1 and may represent an important step to expand our knowledge on the molecular mechanisms underlying anthocyanin biosynthesis in different plant tissues.
DOI:10.1186/s12864-015-1428-1URLPMID:4404602 [本文引用: 2]

Background The flower colour of agricultural products is very important for their commercial value, which is mainly attributed to the accumulation of anthocyanins. Light is one of the key environmental factors that affect the anthocyanin biosynthesis. However, the deep molecular mechanism remains elusive, and many problems regarding the phenotypic change and the corresponding gene regulation are still unclear. In the present study, Chrysanthemum ?? morifolium ???Purple Reagan???, a light-responding pigmentation cultivar, was selected to investigate the mechanism of light-induced anthocyanin biosynthesis using transcriptomic analyses. Results Only cyanidin derivatives were identified based on the analyses of the pigmentation in ray florets. Shading experiments revealed that the capitulum was the key organ and that its bud stage was the key phase responding to light. These results were used to design five libraries for transcriptomic analyses, including three capitulum developmental stages and two light conditions. RNA sequences were de novo assembled into 103,517 unigenes, of which 60,712 were annotated against four public protein databases. As many as 2,135 unigenes were differentially expressed between the light and dark libraries with 923 up-regulated and 1,212 down-regulated unigenes in response to shading. Next, interactive pathway analysis showed that the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway was the only complete metabolic pathway both modulated in response to light and related to capitulum development. Following the shading treatment, nearly all structural genes involved in the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway were down-regulated. Moreover, three CmMYB genes and one CmbHLH gene were identified as key transcription factors that might participate in the regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis under light conditions based on clustering analysis and validation by RT-qPCR. Finally, a light-induced anthocyanin biosynthesis pathway in chrysanthemums was inferred. Conclusion The pigmentation of the ray florets of chrysanthemum cultivar ???Purple Reagan??? is dependent on light. During the light-induced pigmentation process, the expression of seven structural genes in the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway (regulated by at least four transcription factors in response to light) are the main contributors to the pigmentation of chrysanthemums. This information will further our understanding of the molecular mechanisms governing light-induced anthocyanin biosynthesis in ornamental plants.
URL [本文引用: 1]

【目的】比较2个不同生态区杧果果实着色的差异,并探讨着色差异的内在机理。【方法】试验于2012年比较了‘台农1号’杧果在四川攀枝花和广东雷州2个生态区的果皮颜色、花色苷含量和花色苷合成相关基因表达模式差异。【结果】四川攀枝花地区高海拔、昼夜温差大,较低降雨量,该生态区‘台农1号’杧果果皮花色苷含量显著高于雷州地区,着色较好,果皮色度角显著低于雷州地区。花色苷合成基因Mi PAL、Mi C4H、Mi CHS1、Mi F3H1、Mi DFR和Mi UFGT的相对表达量以攀枝花地区显著高于雷州地区,其中Mi C4H、Mi CHS1、Mi F3H1、Mi DFR和Mi UFGT基因的相对表达量分别为雷州地区的130、228、63、2.7和4.3倍。【结论】四川攀枝花地区海拔高、辐射强和昼夜温差大等生态因子有利于诱导果皮中花色苷合成相关基因尤其是Mi PAL、Mi CHS1、Mi DFR和Mi UFGT的表达,促进‘台农1号’果皮着色。
URL [本文引用: 1]

【目的】比较2个不同生态区杧果果实着色的差异,并探讨着色差异的内在机理。【方法】试验于2012年比较了‘台农1号’杧果在四川攀枝花和广东雷州2个生态区的果皮颜色、花色苷含量和花色苷合成相关基因表达模式差异。【结果】四川攀枝花地区高海拔、昼夜温差大,较低降雨量,该生态区‘台农1号’杧果果皮花色苷含量显著高于雷州地区,着色较好,果皮色度角显著低于雷州地区。花色苷合成基因Mi PAL、Mi C4H、Mi CHS1、Mi F3H1、Mi DFR和Mi UFGT的相对表达量以攀枝花地区显著高于雷州地区,其中Mi C4H、Mi CHS1、Mi F3H1、Mi DFR和Mi UFGT基因的相对表达量分别为雷州地区的130、228、63、2.7和4.3倍。【结论】四川攀枝花地区海拔高、辐射强和昼夜温差大等生态因子有利于诱导果皮中花色苷合成相关基因尤其是Mi PAL、Mi CHS1、Mi DFR和Mi UFGT的表达,促进‘台农1号’果皮着色。
DOI:10.11937/bfyy.201507050URL [本文引用: 2]

苹果果实颜色是影响消费者需求 重要的品质性状,苹果的红色是由花色素苷积累水平决定的,花色素苷是次生代谢产物黄酮类化合物中的一类。文章综述了花色苷合成过程中结构基因、调控基因、 环境因素、管理措施和组织机构对花色苷积累的影响,目的是为实现优质果实品质提供新的方法,包括视觉上的吸引力和营养价值的提升。
DOI:10.11937/bfyy.201507050URL [本文引用: 2]

苹果果实颜色是影响消费者需求 重要的品质性状,苹果的红色是由花色素苷积累水平决定的,花色素苷是次生代谢产物黄酮类化合物中的一类。文章综述了花色苷合成过程中结构基因、调控基因、 环境因素、管理措施和组织机构对花色苷积累的影响,目的是为实现优质果实品质提供新的方法,包括视觉上的吸引力和营养价值的提升。
[本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]

[Objective] Expressions of key enzymatic genes involved in phenylpropanoid metabolic pathway in potato and St R2R3-MYB and St TGA transcripters were investigated in the present study. [Method] The primitive cultivar Yan was the materials for replicated trials and total RNA extracted from tissues of seedlings. Real-time florescent quantification PCR, multiple intervals of air temperature, light-illumination and time-duration were factors of treatments in the experiment. Data on gene expressions were obtained and proceed to asses and compare effects based on statistical analysis. [Result] The results showed negative correlations between temperature degrees and expressions of St PAL, St DFR and St R2R3-MYB genes but not St TGA. Positive correlations, however, were derived between those of St CHS,St DFR and St R2R3-MYB and light-intensity. Significant interactive effects between expressions of St PAL and St DFR and treatments, light intensity and temperature degree, along the phenylpropanoid pathway were observed. Transcription regulator of St R2R3-MYB showed significant positive effect on the expression of St CHS of potato. St TGA transcription factor, on the other hand, gave significant negative effects on the expression of St DFR. [Conclusion] Results from present study reveal the role of environmental factors and complicate interactions between such conditions as temperature-light illumination and m RNA function of target genes.
DOI:10.1007/s00122-009-1158-3URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1126/science.227.4691.1229URLPMID:17757866 [本文引用: 1]

Transformed petunia, tobacco, and tomato plants have been produced by means of a novel leaf disk transformation-regeneration method. Surface-sterilized leaf disks were inoculated with an Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain containing a modified tumor-inducing plasmid (in which the phytohormone biosynthetic genes from transferred DNA had been deleted and replaced with a chimeric gene for kanamycin resistance) and cultured for 2 days. The leaf disks were then transferred to selective medium containing kanamycin. Shoot regeneration occurred within 2 to 4 weeks, and transformants were confirmed by their ability to form roots in medium containing kanamycin. This method for producing transformed plants combines gene transfer, plant regeneration, and effective selection for transformants into a single process and should be applicable to plant species that can be infected by Agrobacterium and regenerated from leaf explants.
DOI:10.1006/meth.2001.1262URL [本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]

用酸性溶液浸提法提取三明市野生蕉紫色果皮花青素,pH示差法测定花青素含量。结果表明,以1%盐酸一甲醇为提取液,平衡时间80分钟,测得三明市野生蕉紫色果皮中的花青素含量为矢车菊花青素苷5.43mg/100g。
URL [本文引用: 1]

用酸性溶液浸提法提取三明市野生蕉紫色果皮花青素,pH示差法测定花青素含量。结果表明,以1%盐酸一甲醇为提取液,平衡时间80分钟,测得三明市野生蕉紫色果皮中的花青素含量为矢车菊花青素苷5.43mg/100g。
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1038/nature01853URLPMID:14508488 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract Flooding of soils results in acute oxygen deprivation (anoxia) of plant roots during winter in temperate latitudes, or after irrigation, and is a major problem for agriculture. One early response of plants to anoxia and other environmental stresses is downregulation of water uptake due to inhibition of the water permeability (hydraulic conductivity) of roots (Lp(r)). Root water uptake is mediated largely by water channel proteins (aquaporins) of the plasma membrane intrinsic protein (PIP) subgroup. These aquaporins may mediate stress-induced inhibition of Lp(r) but the mechanisms involved are unknown. Here we delineate the whole-root and cell bases for inhibition of water uptake by anoxia and link them to cytosol acidosis. We also uncover a molecular mechanism for aquaporin gating by cytosolic pH. Because it is conserved in all PIPs, this mechanism provides a basis for explaining the inhibition of Lp(r) by anoxia and possibly other stresses. More generally, our work opens new routes to explore pH-dependent cell signalling processes leading to regulation of water transport in plant tissues or in animal epithelia.
DOI:10.1089/omi.2011.0091URLPMID:3241737 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract The SnRK2 family members are plant-specific serine/threonine kinases involved in plant response to abiotic stresses and abscisic acid (ABA)-dependent plant development. SnRK2s have been classed into three groups; group 1 comprises kinases not activated by ABA, group 2 comprises kinases not activated or activated very weakly by ABA, and group 3 comprises kinases strongly activated by ABA. So far, the ABA-dependent kinases belonging to group 3 have been studied most thoroughly. They are considered major regulators of plant response to ABA. The regulation of the plant response to ABA via SnRK2s pathways occurs by direct phosphorylation of various downstream targets, for example, SLAC1, KAT1, AtRbohF, and transcription factors required for the expression of numerous stress response genes. Members of group 2 share some cellular functions with group 3 kinases; however, their contribution to ABA-related responses is not clear. There are strong indications that they are positive regulators of plant responses to water deficit. Most probably they complement the ABA-dependent kinases in plant defense against environmental stress. So far, data concerning the physiological role of ABA-independent SnRK2s are very limited; it is to be expected they will be studied extensively in the nearest future.
DOI:10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0URLPMID:7108955 [本文引用: 1]

A computer program that progressively evaluates the hydrophilicity and hydrophobicity of a protein along its amino acid sequence has been devised. For this purpose, a hydropathy scale has been composed wherein the hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties of each of the 20 amino acid side-chains is taken into consideration. The scale is based on an amalgam of experimental observations derived from the literature. The program uses a moving-segment approach that continuously determines the average hydropathy within a segment of predetermined length as it advances through the sequence. The consecutive scores are plotted from the amino to the carboxy terminus. At the same time, a midpoint line is printed that corresponds to the grand average of the hydropathy of the amino acid compositions found in most of the sequenced proteins. In the case of soluble, globular proteins there is a remarkable correspondence between the interior portions of their sequence and the regions appearing on the hydrophobic side of the midpoint line, as well as the exterior portions and the regions on the hydrophilic side. The correlation was demonstrated by comparisons between the plotted values and known structures determined by crystallography. In the case of membrane-bound proteins, the portions of their sequences that are located within the lipid bilayer are also clearly delineated by large uninterrupted areas on the hydrophobic side of the midpoint line. As such, the membrane-spanning segments of these proteins can be identified by this procedure. Although the method is not unique and embodies principles that have long been appreciated, its simplicity and its graphic nature make it a very useful tool for the evaluation of protein structures.
URL [本文引用: 1]

类黄酮是一类多酚类次生代谢产物,在植物中广泛存在,具有调节机体免疫力、抗氧化、抗衰老以及抵抗病毒等医疗保健功效。在类黄酮生物合成过程中,MYB转录因子扮演者重要角色,可以调控与类黄酮合成相关的酶基因的表达,从而有效地调控类黄酮物质的生物合成。目前已在很多植物中分离克隆得到了很多调控类黄酮生物合成的MYB转录因子,并对它们的结构功能及表达方式和作用模式进行了深入研究。利用转基因技术将从特定植物中分离得到的MYB转录因子用于植物遗传改良,可有效提高转基因植物中黄酮类物质的含量。因此,MYB转录因子的研究对从分子水平上研究和调节类黄酮的合成具有重要的意义;转录因子的应用是类黄酮生物合成基因工程中的一个新方向。
URL [本文引用: 1]

类黄酮是一类多酚类次生代谢产物,在植物中广泛存在,具有调节机体免疫力、抗氧化、抗衰老以及抵抗病毒等医疗保健功效。在类黄酮生物合成过程中,MYB转录因子扮演者重要角色,可以调控与类黄酮合成相关的酶基因的表达,从而有效地调控类黄酮物质的生物合成。目前已在很多植物中分离克隆得到了很多调控类黄酮生物合成的MYB转录因子,并对它们的结构功能及表达方式和作用模式进行了深入研究。利用转基因技术将从特定植物中分离得到的MYB转录因子用于植物遗传改良,可有效提高转基因植物中黄酮类物质的含量。因此,MYB转录因子的研究对从分子水平上研究和调节类黄酮的合成具有重要的意义;转录因子的应用是类黄酮生物合成基因工程中的一个新方向。
URL [本文引用: 1]

利用徒手切片法、pH差计法及实时荧光定量RT-PCR技术,观察和测定紫心大白菜与同源非紫心大白菜[Brassica campestris L. ssp. pekinensis(Lour)Olsson]花青素在叶片中的分布和总含量变化,比较叶片中花青素合成途径关键酶基因及其转录调控因子的表达特点。结果表明,紫心大白菜花青素不均匀分布于叶片中,尤以叶表皮细胞及临近表皮的叶肉细胞内最为丰富,并且内层球叶含量高于外层球叶。紫心大白菜心叶中花青素含量最高为0.79 mg · g^-1 FW,对照09S17混合样的叶片中花青素总含量为0.01 mg · g^-1 FW。荧光定量PCR分析表明,花青素生物合成途径上游关键酶基因CHS、CHI、F3H、F3′H及下游修饰基因UFGT、转运酶基因GST与转录因子MYB0在紫色大白菜心叶中上调表达,下游关键酶基因DFR、ANS、LDOX与转录因子MYB2、MYB4、MYB12和MYB111的表达在整个紫心大白菜中大幅上调,推测这可能是紫心大白菜花青素积累的重要原因,其中MYB2和MYB4可能起主要作用。
URL [本文引用: 1]

利用徒手切片法、pH差计法及实时荧光定量RT-PCR技术,观察和测定紫心大白菜与同源非紫心大白菜[Brassica campestris L. ssp. pekinensis(Lour)Olsson]花青素在叶片中的分布和总含量变化,比较叶片中花青素合成途径关键酶基因及其转录调控因子的表达特点。结果表明,紫心大白菜花青素不均匀分布于叶片中,尤以叶表皮细胞及临近表皮的叶肉细胞内最为丰富,并且内层球叶含量高于外层球叶。紫心大白菜心叶中花青素含量最高为0.79 mg · g^-1 FW,对照09S17混合样的叶片中花青素总含量为0.01 mg · g^-1 FW。荧光定量PCR分析表明,花青素生物合成途径上游关键酶基因CHS、CHI、F3H、F3′H及下游修饰基因UFGT、转运酶基因GST与转录因子MYB0在紫色大白菜心叶中上调表达,下游关键酶基因DFR、ANS、LDOX与转录因子MYB2、MYB4、MYB12和MYB111的表达在整个紫心大白菜中大幅上调,推测这可能是紫心大白菜花青素积累的重要原因,其中MYB2和MYB4可能起主要作用。
DOI:10.1093/mp/ssp118URLPMID:20118183 [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
