全文HTML
--> --> --> 颗粒物是环境污染与控制相关研究的重要对象[1]。尽管给水处理工艺通常能够保证出厂水的水质达标,但出厂水经过管网到达用户端的输配过程中难以避免发生水质变化[2]。其中,管网疏松沉积物再悬浮引发自来水变色(如“黄水”)是全世界自来水投诉中最常见的问题[3]。然而,管网疏松沉积物的结构特征及其潜在健康危害目前尚不明确。管网疏松沉积物来源复杂,包括出厂水中的残余物质和管道的腐蚀产物等。由于给水管网中广泛使用铁质管材和管件,管网铁腐蚀产物释放是导致用户龙头“黄水”的主要原因[4-7]。ZHUANG等[8]利用合成的铁颗粒物实验首次提出,铁颗粒物导致的“黄水”不仅是感官性状问题,且铁颗粒物可通过2种机制产生潜在毒性:1)铁颗粒物(主要是针铁矿)与微量有机污染物通过特定的共价键结合方式强化电子转移,产生活性氧物种(reactive oxygen species,ROS)而增强细胞损伤[8-9];2)微量有机污染物能够显著提升铁颗粒物的比表面积,从而增强其对水中污染物的富集能力[10]。实际管网条件下生成的疏松沉积物组成往往非常复杂,以往对于“黄水”带来的风险都是基于管网的水质和水力条件进行评价和预测[11],然而“黄水”可能引发的毒性风险至今尚无评价标准[12-13]。水质的评价不能仅以饮用水标准限值为判据, 更为重要的是以水质安全风险的综合控制为依据[14]。因此,“黄水”中沉积物颗粒的风险亟需受到重视。
本研究在北方某城市频繁发生“黄水”的区域采集了管网疏松沉积物,对样品的表面形貌、元素组成、表面电位和粒径等结构特征进行了表征,利用人体健康肝脏细胞对样品的细胞毒性进行了测试,并开展了疏松沉积物的细胞毒性与其结构特征之间的相关性分析,初步明确了给水管网疏松沉积物的风险因素。
1.1. 采样方法
对中国北方某城市频繁发生“黄水”的小区进行了实地调研,截取了7个小区的入楼管管道,管材为镀锌钢管,管径均为DN40,管龄约为(15±5) a。利用软毛刷刷取管道表层疏松沉积物,将获得的疏松沉积物冷冻干燥,再通过90目(160 μm)筛网进行筛分,样品编号1#~7#。1.2. 样品表征
管网疏松沉积物样品的表面形貌和元素组成利用场发射扫描电子显微镜(SEM,H-7500)获得,微观结构照片利用显微镜(Leica MGD41)拍摄;表面电位和粒径使用zeta电位分析仪(Malvern,Zetasizer2000)测定;样品晶体结构利用X射线衍射光谱仪(XRD, Rigaku,D/Max-2200)测试;样品粗糙度(Ra)利用原子力显微镜(AFM,Nanosurf C3000, Switzerland)测定。以DMPO作为捕获剂添加浓度为10 mmol·L?1的H2O2,利用电子顺磁共振谱仪(ESR,Bruker A300-10/12)在无光照条件下对样品产生自由基的能力进行测定。1.3. 毒性实验
以体外细胞毒性实验(MTT法)进行了疏松沉积物样品的毒性检测。实验所用的LO2人体健康肝脏细胞购买自赛柏慷生物有限公司。主要步骤为:在5% CO2、37 ℃条件下,加入疏松沉积物分散液(100 mg·L?1)和细胞共培养24 h;然后吸走原有培养基,加入PBS轻微地清洗2次,再加入200 μL含0.5 mg·mL?1 MTT的培养基,继续培养4 h后,吸走原有培养基,最后加入150 μL DMSO,振荡5 min,利用全波长酶标仪(EPOCH2, Biotek)在570 nm进行检测。实验结果以细胞存活率表示(见式(1))。2.1. 管网中疏松沉积物的结构特征
2.1.1. 形貌和元素组成
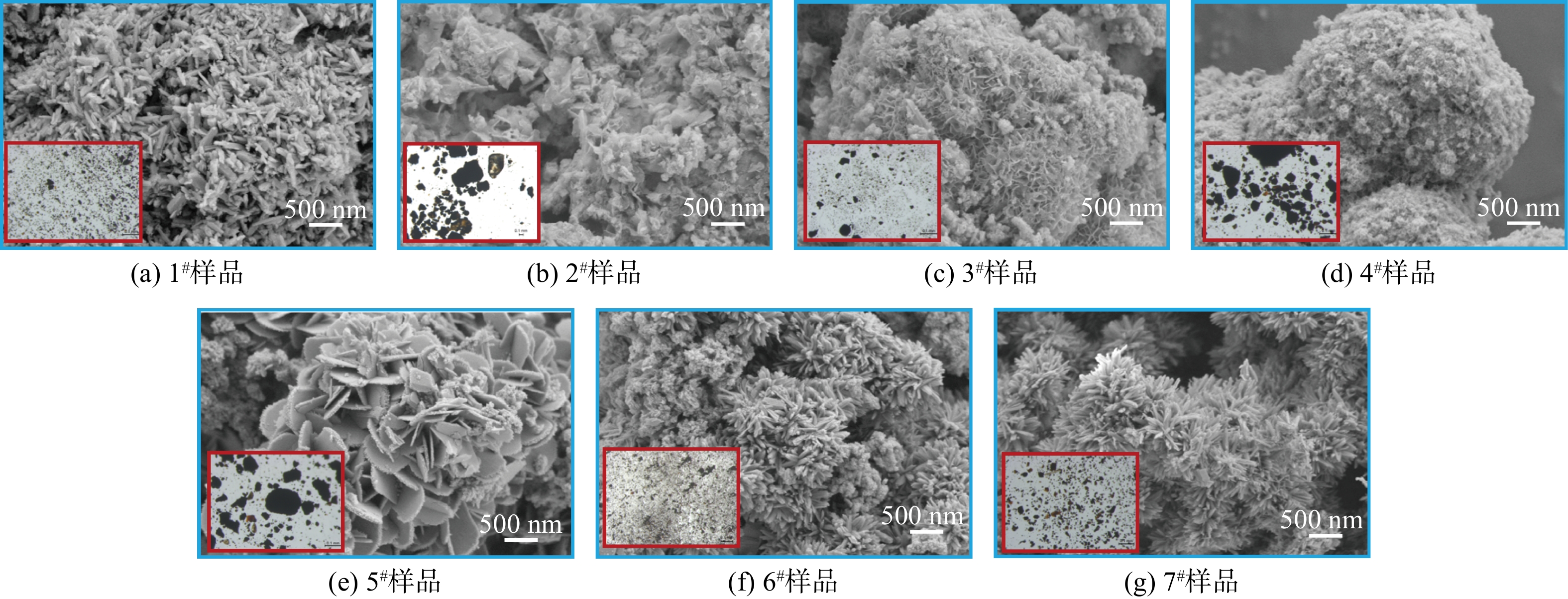
管网疏松沉积物样品1#~7#的SEM照片如图1所示。样品微观形貌中大多存在锋利的针刺状结构,这种结构可能来自于亚单元纳米颗粒取向聚集生长[15]。在所有样品SEM照片中,样品6#的表面针刺最密集且最为锋利,其在显微镜照片(图1内嵌图)中的结构也更加分散和细密,这可能是由于细密锋利的微观结构有助于抑制颗粒之间的团聚作用[16],而具有松散结构的沉积物更易于再悬浮到水中,导致“黄水”的风险更高。在所有样品的元素组成中(见表1),占比最大的均为铁元素,质量占比为55%~80%,这与以往研究中镀锌钢管管垢中含量最高为铁元素一致[17]。除铁元素以外,样品中还检测到一定量的锰、铜、铝、铅、砷等金属元素。对样品6#进行进一步的元素面扫(见图2)发现,铁元素和氧元素分布均匀,故可推测,样品的主要成分为铁氧化物。此外,样品中的针刺状结构可能源于铁氧化物的取向聚集生长。
2.1.2. 粒径和晶体组成
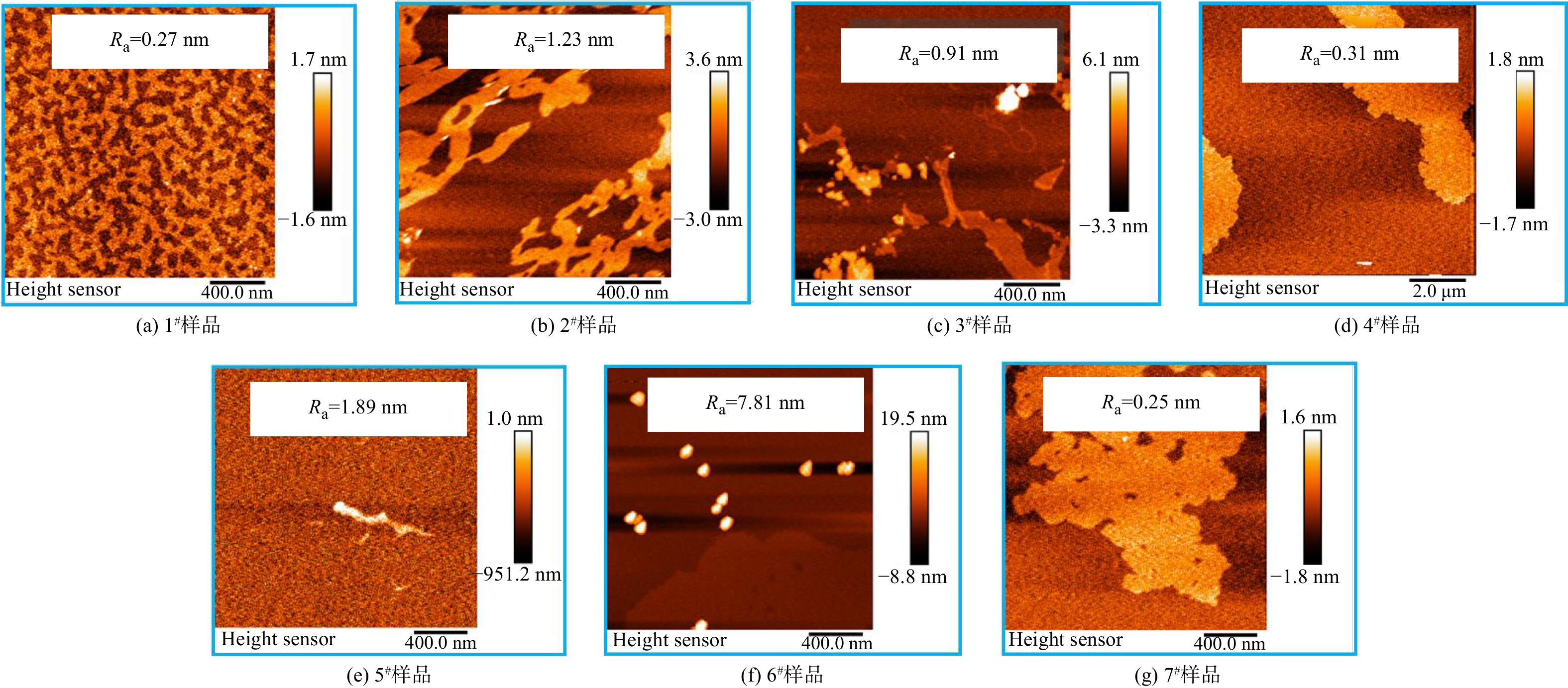
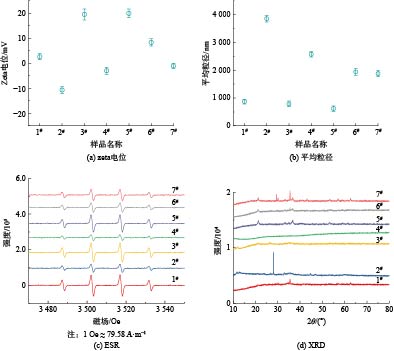
AFM测试结果(见图3)表明,样品粗糙度(Ra)为0.25~7.81 nm,具有最为细密锋利微观形貌的样品6#粗糙度最大,其表面粗糙度明显高于其他样品可能是由于细密锋利的针刺结构导致。样品的zeta电位分布在?15~20 mV,可见,管网疏松沉积物的表面电位既有可能呈正电性也有可能呈负电性。样品平均粒径范围为500~4 000 nm,表明其中包含具有较高毒性风险的纳米尺寸细颗粒。有研究表明,水中颗粒物粒径越大时水体色度变化越明显[18],可见,2#样品的致色风险最高。由于氧化应激是纳米颗粒损伤细胞的重要机制[19],故对样品产生羟基自由基的能力进行了测试(见图4),发现所有样品均能够与双氧水反应产生羟基自由基,其反应位点可能是沉积物中丰富的铁基组分[20]。通过XRD对管网疏松沉积物的晶体成分进行分析,结果如图4和表2所示,表明样品中主要晶体成分是多种铁氧化物,包括Fe2O3(α-Fe2O3、γ-Fe2O3)、FeOOH(α-FeOOH、β-FeOOH、γ-FeOOH、δ-FeOOH)、Fe3O4等,也含有少量SiO2和CaCO3晶体。大多样品中的铁氧化物晶体以γ-Fe2O3为主,但样品6#中晶体占比最高的是γ-FeOOH,故推测样品6#细密锋利的针刺状结构可能与γ-FeOOH晶体生长有关。2.2. 疏松沉积物的细胞毒性
2.2.1. MTT细胞毒性
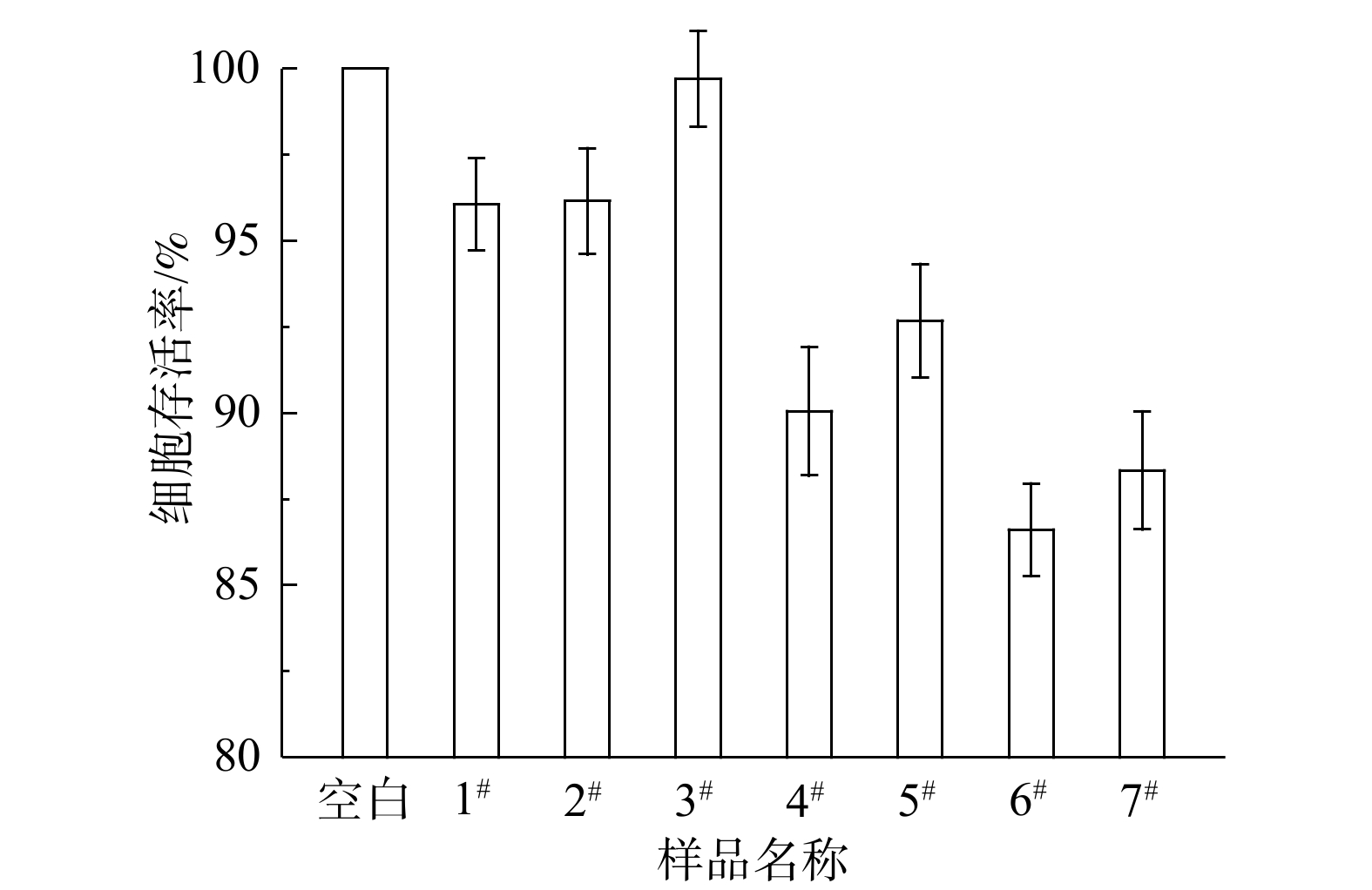
现有对饮用水毒性风险的研究大多聚焦于饮用水中的消毒副产物[21-22]和持久性有机污染物(POPs)[23-24]等有机污染物,以及重金属[25]等无机污染物。饮用水中颗粒物的毒性风险尚未引起重视。通常情况下,当滞留水放出后“黄水”会逐渐消失[26],但由于管网疏松沉积物含有细颗粒,即使是在龙头水放水放至无色时,疏松沉积物颗粒仍会不可避免地存在于水中,用户在使用龙头水时很有可能发生颗粒物的暴露。利用人体健康肝脏细胞测试了管网疏松沉积物样品分散液的MTT细胞毒性。利用样品配置分散液时,在100 mg·L?1下肉眼可见明显颜色,故在此浓度下研究了样品的细胞毒性。当样品分散液的质量浓度为100 mg·L?1时,人体健康肝脏细胞的存活率为86.61%~99.71%(如图5所示),可见疏松沉积物的毒性风险不可忽视。具有最为细密锋利结构的样品6#的细胞存活率最低,故推测疏松沉积物样品的形貌对于毒性具有重要影响。2.2.2. 因素分析
主成分分析法旨在保证原始数据信息丢失最小的情况下对原始的高维变量进行降维处理,以少数的综合变量代替原有的多维变量,简化评价工作[27]。虽然粒径是影响颗粒物毒性的最常见因素[28],但在管网疏松沉积物样品的铁含量、zeta电位、粗糙度和平均粒径中(见表3),与毒性相关性最显著的是粗糙度,样品的粗糙度与细胞存活率呈现负相关,Pearson相关系数为?0.507。即粗糙度越大的疏松沉积物,毒性越高,表明形貌对样品毒性的影响比粒径更大。这是由于样品中普遍存在着针刺状结构,所以粗糙度越高的样品具有更丰富更锋利的表面,导致其对细胞的划伤能力更强;此外,样品的平均粒径与zeta电位具有负相关性(Pearson相关系数为?0.851),即粒径越大的样品zeta电位较低,可见表面电荷相同时,带负电的沉积物颗粒比带正电的更难以悬浮进入水中,健康风险较低。如表4所示,在管网疏松沉积物的晶体组成与毒性的相关性中,与样品毒性相关性最显著的是γ-FeOOH,与细胞存活率具有负相关性(Pearson相关系数为=?0.762),即γ-FeOOH含量越高的管网疏松沉积物,毒性越大。结合粗糙度与毒性具有相关性的结果推测,γ-FeOOH可能是通过增加颗粒表面锋利程度进而增大样品毒性。李玉仙等[29]发现给水管网余氯较低时不稳定成分γ-FeOOH含量明显增加;牛璋彬等[30]发现给水管网余氯较低时铁释放现象严重。因此,在余氯不足时,“黄水”具有更高的毒性风险,一方面是由于γ-FeOOH晶体成分增多导致疏松沉积物形成毒性更高的颗粒物结构,另一方面是因为铁释放加剧形成更多的疏松沉积物导致颗粒物浓度增大。
2) 管网疏松沉积物在100 mg·L?1下对应人体健康肝脏细胞的细胞存活率为86.61%~99.71%。粗糙度与疏松沉积物毒性的相关性最显著,表明形貌对疏松沉积物毒性具有显著影响;γ-FeOOH是与管网疏松沉积物毒性相关性最显著的晶体组分,其对毒性的贡献是通过增加样品形貌锋利程度造成的。余氯不足时可能会因铁释放加剧和γ-FeOOH含量增大,造成更高的毒性风险。
参考文献

 下载:
下载: 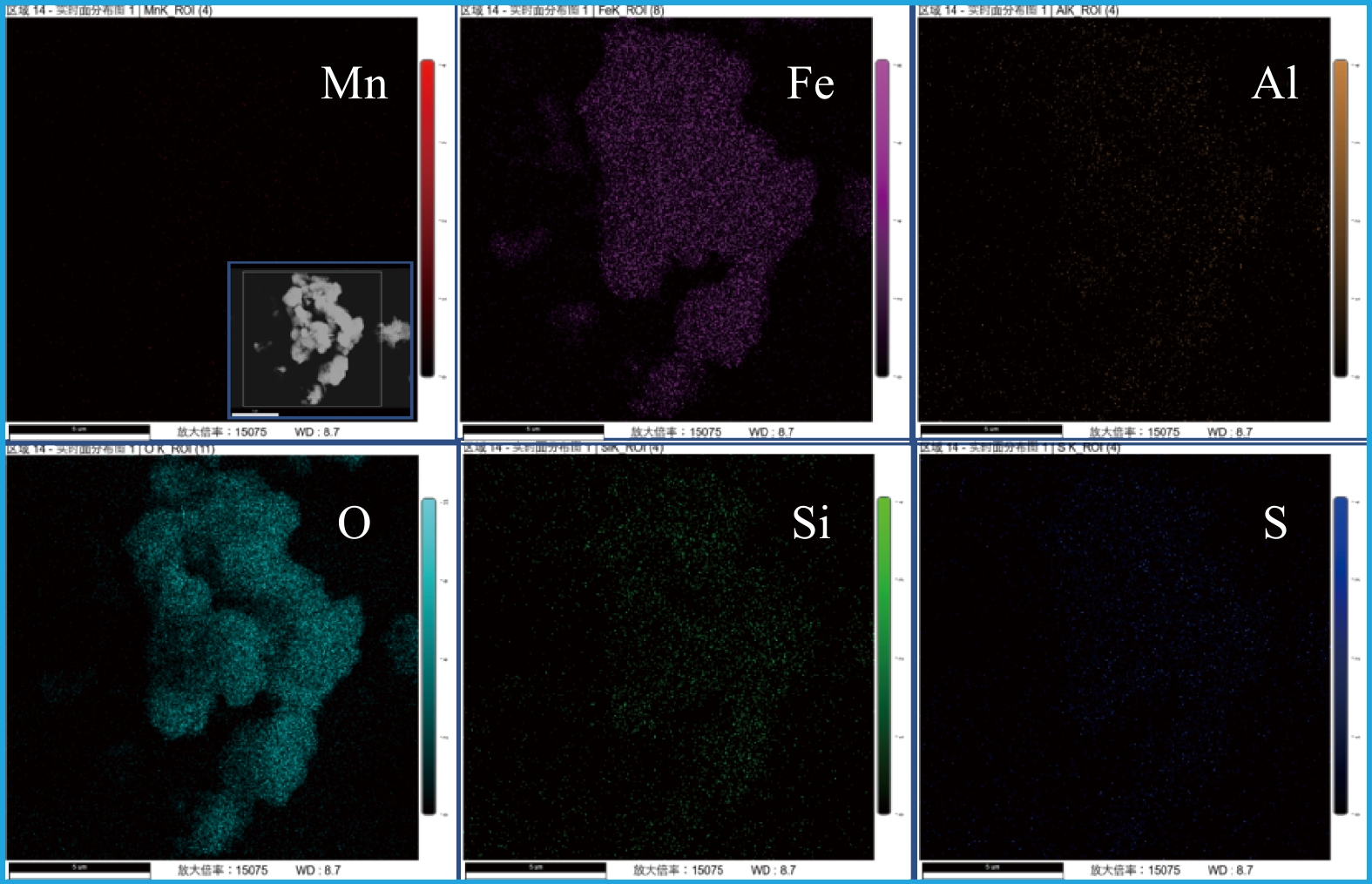
 点击查看大图
点击查看大图