全文HTML
--> --> --> 随着城市点源污染得到基本控制,由暴雨径流引起的非点源污染逐渐成为城市水体主要污染来源[1]。在城市分流制排水系统中,暴雨径流携带的部分颗粒物在重力作用下沉积在雨水管道底部,形成管道沉积物。这些沉积物在后续管道径流的冲刷作用下,部分又将重新进入管流并随之排入城市水体,成为水体污染重要的源和汇[2-4]。李海燕等[5-6]对北京市某区域分流制雨水管道进行了调查,结果表明,约80%以上管道存在不同程度的沉积现象,管道沉积物中TN对径流污染负荷的贡献率约为23%,TP贡献率约为30%。管道沉积物对径流污染负荷的贡献可能与沉积物-水界面污染物交换特性有关。影响沉积物-水界面污染物交换的因素有沉积物的理化性质、环境因子和扰动(包括物理扰动和生物扰动)等[7]。近年来一些****在管道沉积物污染分布[8-9]、冲刷沉积规律[10]、吸附解吸[11]及溶出特性[12]等方面开展了研究。陈红等[13]对合流制入河管道沉淀物中氮转化规律进行了探究,结果表明,氨氮是其主要释放形态。李明怡[14]利用北京市雨水管道沉积物进行了研究,发现上覆水体pH和流速是影响沉积物中磷和重金属释放的主要因素,并利用连续函数法计算出:当流速为1.1 m·s?1时,沉积物和水之间磷的平均交换速率为4.09 mg·(m2·min)?1。目前,有关分流制雨水管道沉积物-水界面的研究很少,关于微生物对沉积物-水界面之间污染物交换特性的影响尚未见有报道。
株洲市位于湖南省东部,湘江中下游,其中白石港是湘江在株洲最大的支流,沿河两岸雨水及溢流污水均直接排入白石港。港道水体氨氮等指标超标明显,水质较差[15]。基于此,本研究选取株洲市某分流制雨水管道沉积物作为研究对象,通过模拟实验考察了溶解氧、温度、水力扰动强度及微生物种群对污染物在沉积物-水界面之间交换的影响,剖析上覆水中污染物转化途径与规律,为雨水管道沉积物污染控制提供参考。
1.1. 区域概况
研究区域位于株洲市白石港流域职教城片区,汇水面积约为0.29 km2。该区域为新建城区,毗邻长株高速,以教育用地为主,下垫面主要由沥青道路、建筑屋面及绿地组成。区域内颗粒物污染来源主要为大气沉降、土壤以及道路磨损等,未见垃圾填埋场、工厂等大型污染源。研究区域排水体制为雨污分流制,雨水管道管径为1 000~1 500 mm,降雨时管道径流直接排入白石港主河道。2020年7—9月调研期间,受强降雨条件下管道径流冲刷的影响,该区域雨水管道沉积物主要分布在拐弯及交汇处的管段末端,平均沉积厚度为10 cm。取样点处管道直径为1 200 mm,旱季无流量,沉积物呈黑色,有轻微气味。采样点位置见图1。
1.2. 样品采集与分析
样品采集日前期的干旱天数为12 d。采样时,利用铲子铲取采样点表层沉积物,置于黑色聚乙烯袋中,采样后立即送回实验室。利用真空冷冻干燥机对部分沉积物进行干燥处理,其余沉积物去除树叶、石块等杂物后采用四分法进行均化,所有样品置于?20 ℃条件下冷冻保存。在采样结束后的雨天,采集该处降雨中期管道径流样,置于聚乙烯塑料瓶中,带回实验室于4 ℃条件下冷藏保存,以供模拟实验用。沉积物样品主要由粒径在380~830 μm和75~150 μm内的颗粒物组成。沉积物初始pH为7.89,含水率为23.44%,有机质含量为4.22%,SCOD、氨氮、硝酸盐氮、TP质量分数分别为2 154.99、20.41、11.05、1 200.86 mg·kg?1,无机磷(IP)占总磷含量的68.9%,Fe/Al-P占IP的70.2%,可见,该区域沉积物中的磷活性较高,沉积物释磷潜力较大[16]。管道径流初始水样pH为7.6,氨氮、硝酸盐氮和亚硝酸盐氮质量浓度分别为0.467、1.283和0.106 mg·L?1,SCOD、DTP和DIP质量浓度分别为41.77、0.025和0.014 mg·L?1。
1.3. 实验设计
分别考察溶解氧、温度和扰动强度3种环境因素对污染物转化的影响。具体实验条件设置如下:为模拟管道中不同溶解氧含量的环境,采取滴加亚硫酸钠和人工曝气的方式控制上覆水溶解氧质量浓度,使其分别保持在≤1、3和5 mg·L?1,此时环境温度均为25 ℃,不进行扰动;为模拟不同季节下管道环境温度,采用恒温培养箱实现对环境温度的控制,使其分别保持在15、25和35 ℃,此时上覆水溶解氧质量浓度为3 mg·L?1,不进行扰动;为模拟管道中不同水流流速情景,通过调节搅拌器的转速实现对扰动强度的控制,分别设置转速为0、150和300 r·min?1,此时环境温度为25 ℃,实验过程中监测各组上覆水pH及DO值。取250 g经均化处理的沉积物置于1 L烧杯底部,沿杯壁缓慢加入经0.45 μm滤膜过滤后的管道径流,稍没过底泥后进行搅拌使泥水充分混合,于25 ℃恒温培养箱中静置24 h,之后再加入剩余上覆水至水土比为1.5∶1。实验周期为7 d,装置全程避光置于恒温培养箱中,每隔12 h用注射器抽取50 mL水样,经0.45 μm滤膜过滤后,测定相关污染物质量浓度。取样后向烧杯中补充同体积的原上覆水,补充过程中尽量避免对沉积物造成扰动。在25 ℃条件下,每隔24 h取5~10 g(DO=3 mg·L?1)的沉积物,用以测定沉积物中微生物群落。实验结束后测定各组沉积物中污染物质量浓度。
1.4. 分析方法
本实验主要检测分析沉积物和上覆水中氨氮、硝酸盐氮、淋溶态化学需氧量(SCOD)、溶解态总磷(DTP)及溶解态正磷酸盐(DIP)等指标。沉积物中SCOD和无机氮含量测定采用浸提法[17];沉积物磷形态分析采用SMT磷分级分离方法[18];各步骤提取液以及上覆水中SCOD、DTP、DIP、氨氮、硝态氮、亚硝态氮的测定方法均参照国标法[19]。样品做2次平行样测定,结果取平均值,利用Excel和SPSS分析数据,Origin2018作图。委托上海美吉生物利用细菌/古菌通用引物对(GTGYCAGCMGCCGCGGTAA/GGACTACNVGGGTWTCTAAT)进行16S rRNA基因扩增,并通过Illumina Miseq平台进行高通量测序[20],将结果与Silva数据库比对进行物种注释,得出微生物群落结构组成。
沉积物与上覆水中营养盐交换通量[21]参照式(1)进行计算。
式中:M为平均交换通量,mg?(m2?h)?1;V为上覆水总体积,L;





2.1. 沉积物微生物种群结构分析
微生物种群结构如图2所示。由图2(b)可见,方格颜色代表样品中某一物种的种群数量,颜色越深表明种群数量越大。沉积物中共有25个门水平的物种丰度大于0.2%,其中与氮磷转化相关的变形菌门、绿弯菌门、厚壁菌门[22]等7个物种的总丰度达80%以上,表明在沉积物中进行着大量与氮磷转化相关的生物过程。泉古菌门是一类具有氨氧化功能的古菌,能在有氧条件下将氨氧化为亚硝酸盐,是硝化过程的关键限制反应[23],其相对丰度为0.2%~1.05%。硝化螺旋菌门和硝化刺菌门可将亚硝酸盐氧化为硝酸盐,在样品中的相对丰度为0.56%~0.58%。1个实验周期内所取的7个样品中,优势种群均为与氨化、反硝化及聚磷作用相关的菌属,主要包括变形菌门的不动杆菌属(Acinetobacter)、食酸菌属(Acidovorax)、热单胞菌属(Thermomonas)、假单胞菌属(Pseudomonas),厚壁菌门的微小杆菌属(Exiguobacterium)以及绿弯菌门的厌氧绳菌属(Anaerolinea)[22]。2.2. 环境因素对污染物交换特性的影响
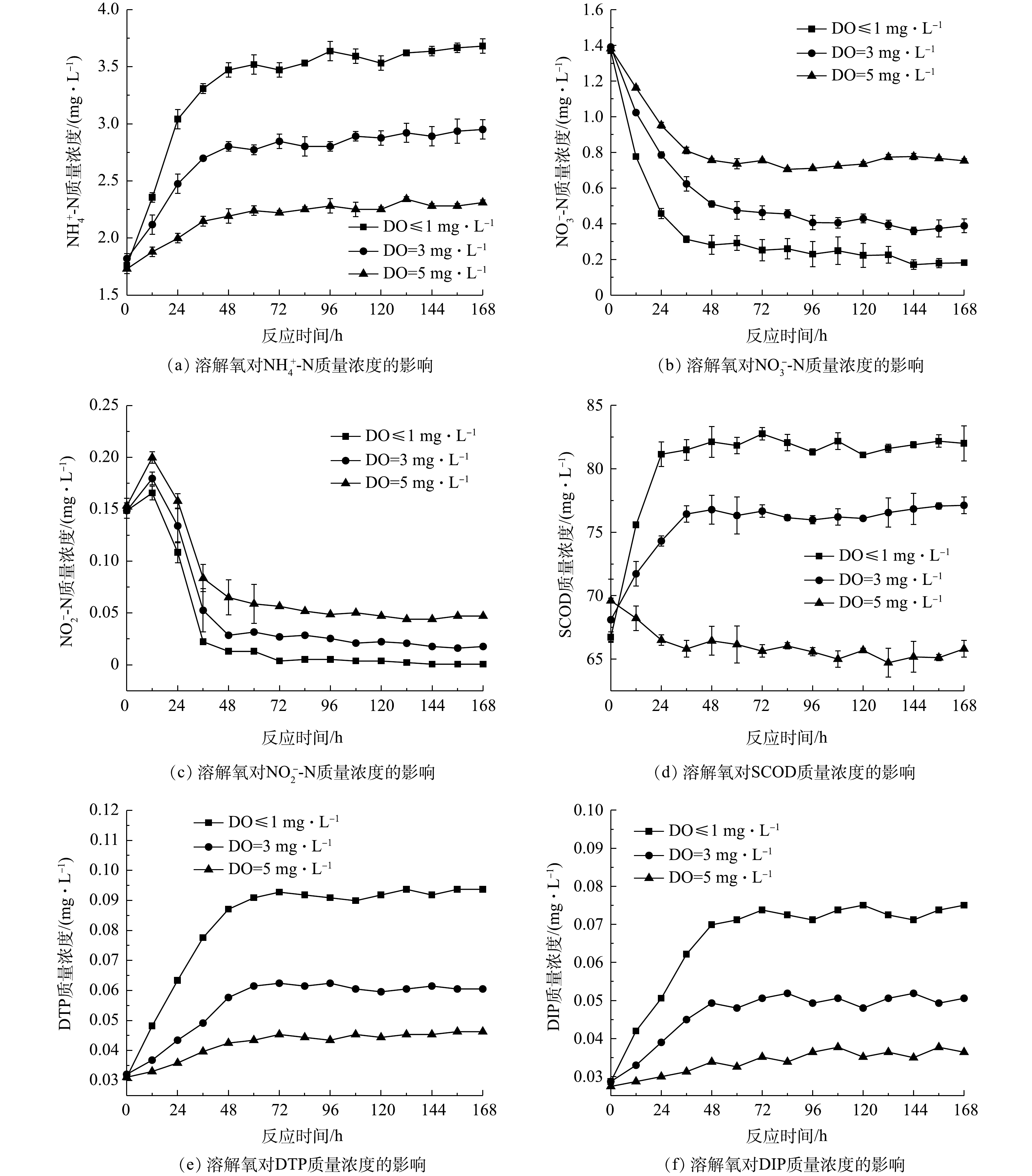
1)不同溶解氧水平下污染物交换特性。各实验组污染物平均交换通量见表1,上覆水污染物浓度随时间变化见图3。由图3(a)~(c)可知,






实验初期,大量










由图3(d)可见,缺氧条件下SCOD质量浓度随反应时间逐渐升高,好氧条件下SCOD质量浓度逐渐降低。这可能是由于溶解氧较低时体系中还原态物质逐渐增多,并在浓度差的作用下向上覆水中释放;而好氧条件下微生物活性较强,对有机物的降解相对较快。
由图3(e)~(f)可见:磷质量浓度随反应时间逐渐升高,DTP峰值浓度为初始浓度的1.49~3.01倍,DIP峰值质量浓度为初始浓度的1.33~2.61倍。其中,上覆水DIP含量占DTP的78.2%~83.6%,说明上覆水中溶解态磷主要以无机磷为主。好氧条件下磷的释放强度低于缺氧条件,一是由于好氧环境中Pseudomonas、Arthrobacter、Anaerolinea等聚磷菌属[28]释磷过程受抑制,磷的生物释放强度减弱;二是由于此时表层沉积物中Fe2+被氧化为Fe3+,部分磷被Fe(OH)3胶体吸附发生沉积[29];三可能是由于好氧条件下,上覆水中较高浓度的

由表1可见,




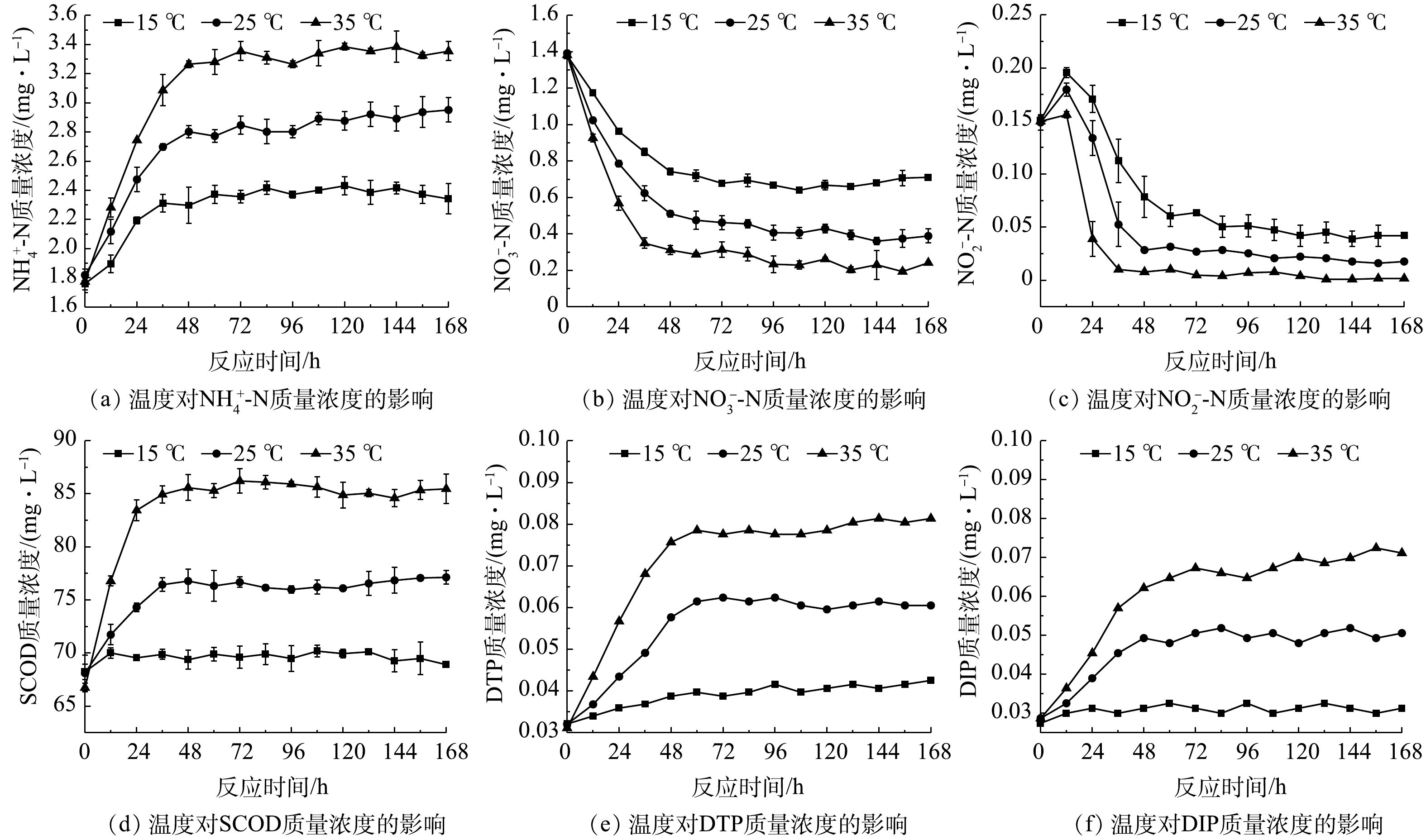
2)不同温度水平下污染物交换特性。各实验组上覆水污染物含量随时间变化见图4,平均交换通量见表2。由图4(a)~(c)可知,污染物质量浓度随时间的变化与溶解氧组相似。温度对氮类物质转化的影响主要体现在两方面,一是温度升高,沉积物中微生物活动随之增强,加速体系中氧的消耗,从而促使有机氮氨化及扩散过程加快[21];二是高温为反硝化过程提供了低溶解氧环境与最适温度,体系中反硝化作用增强[27]。由图4(d)可知,高温时SCOD质量浓度升高较明显。这可能是由于高温能促使沉积物中有机物释放,而沉积物中微生物以兼性厌氧型为主,温度的升高对有机物氧化速率的促进作用较弱。由图4(e)~(f)可见,上覆水磷的质量浓度随温度升高而增加。这是因为温度升高促进沉积物中Pseudomonas、Arthrobacter等聚磷菌释磷,以及Fe结合态磷的释放[31];且随着温度升高,磷酸盐的解吸作用增强[32]。
由表2可知,

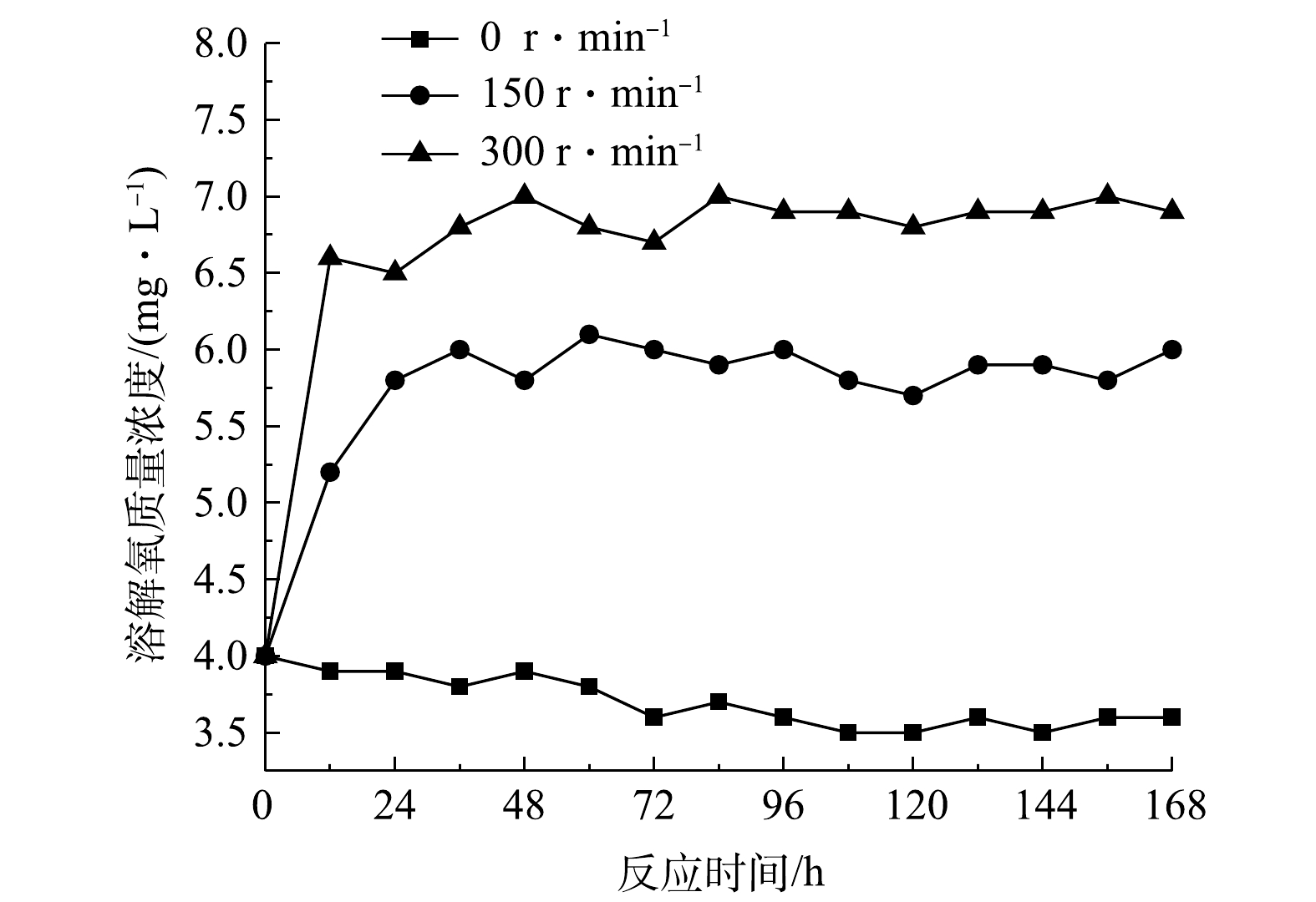
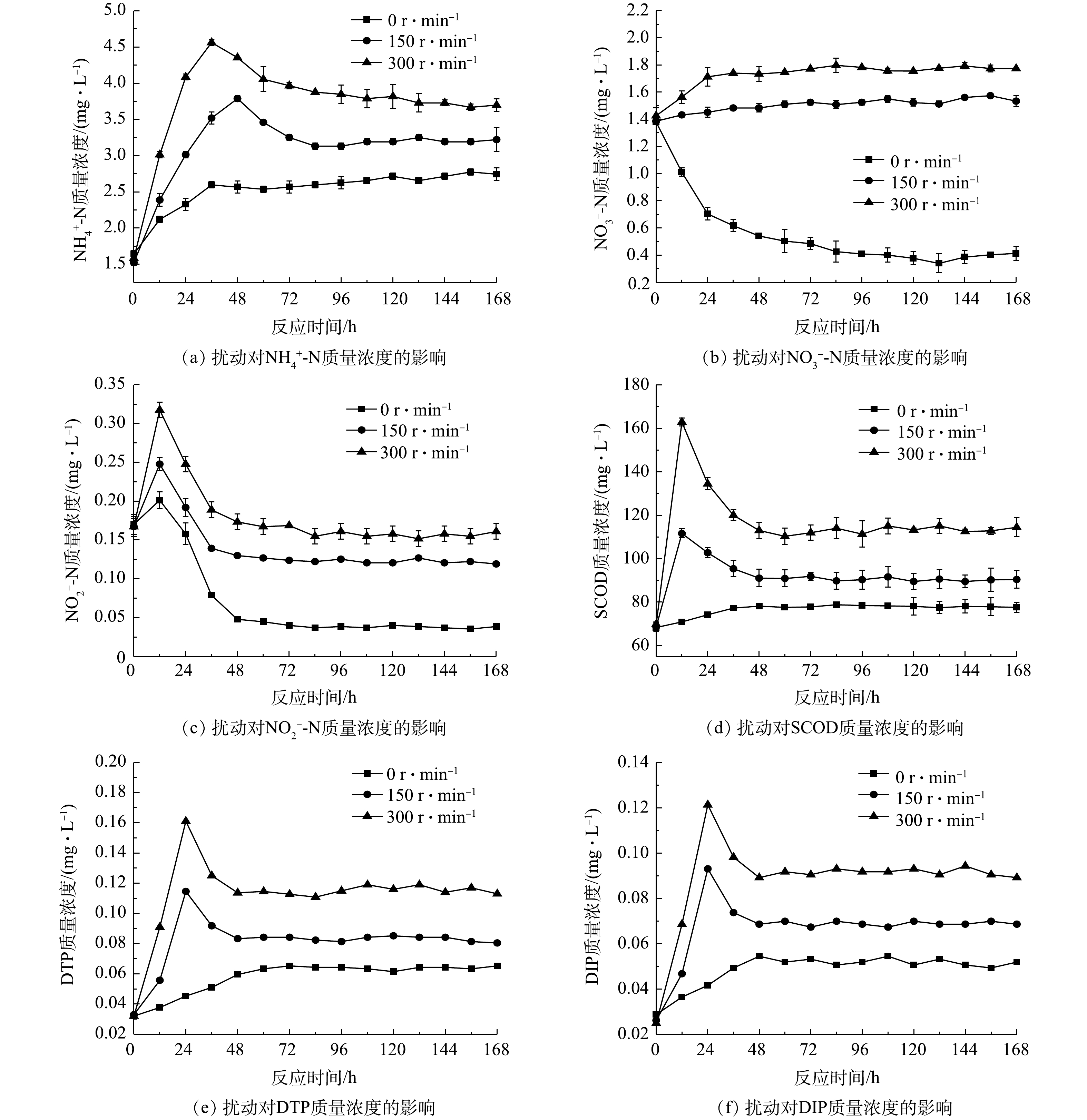
3)不同扰动强度下污染物交换特性。各实验组上覆水溶解氧质量浓度随时间变化见图5,污染物含量随时间变化见图6,平均交换通量见表3。由图5可知,静置组溶解氧质量浓度随反应时间的增加逐渐降低,而扰动组溶解氧始终保持在较高水平,持续的水力扰动增加了泥水混合体系中的氧含量。除图6(b)外,扰动组上覆水污染物质量浓度均呈先升高后降低的趋势。这可能是由于扰动促使沉积物间隙水中高浓度污染物的释放,致使上覆水污染物质量浓度在短时内显著升高[32-33],从而出现明显的初始冲刷现象。
图6(a)~(c)中,扰动组上覆水中
















对比图3(c)、图4(c)和图6(c)可知,3种条件下






























由表3可知,





2.3. 沉积物中污染物释放情况
实验结束后各组沉积物中污染物释放率见图7。由图7可知,沉积物中各污染物释放率随环境因子变化的规律相似,但相同条件下不同污染物释放率存在一定差异,其中磷的释放率最低,而硝酸盐氮释放率最高。整体来看,SCOD释放率为4.1%~26.3%;




2)研究区域中雨水管道沉积物中优势菌门主要有7种,包括与氮磷转化密切相关的变形菌门、绿弯菌门、放线菌门、厚壁菌门等,优势菌种主要为反硝化菌和聚磷菌。未施加扰动时,沉积物中氮的生物转化以氨化与反硝化过程为主。
3) 研究区域中雨水管道沉积物中磷释放率较低,在管道沉积物中易出现富集现象;有机物释放率次之;氮易于在生物化学作用下发生转化,释放率较高,其中硝酸盐氮释放率最大。沉积物中磷的释放形态以Fe/Al-P为主。
参考文献








 下载:
下载: 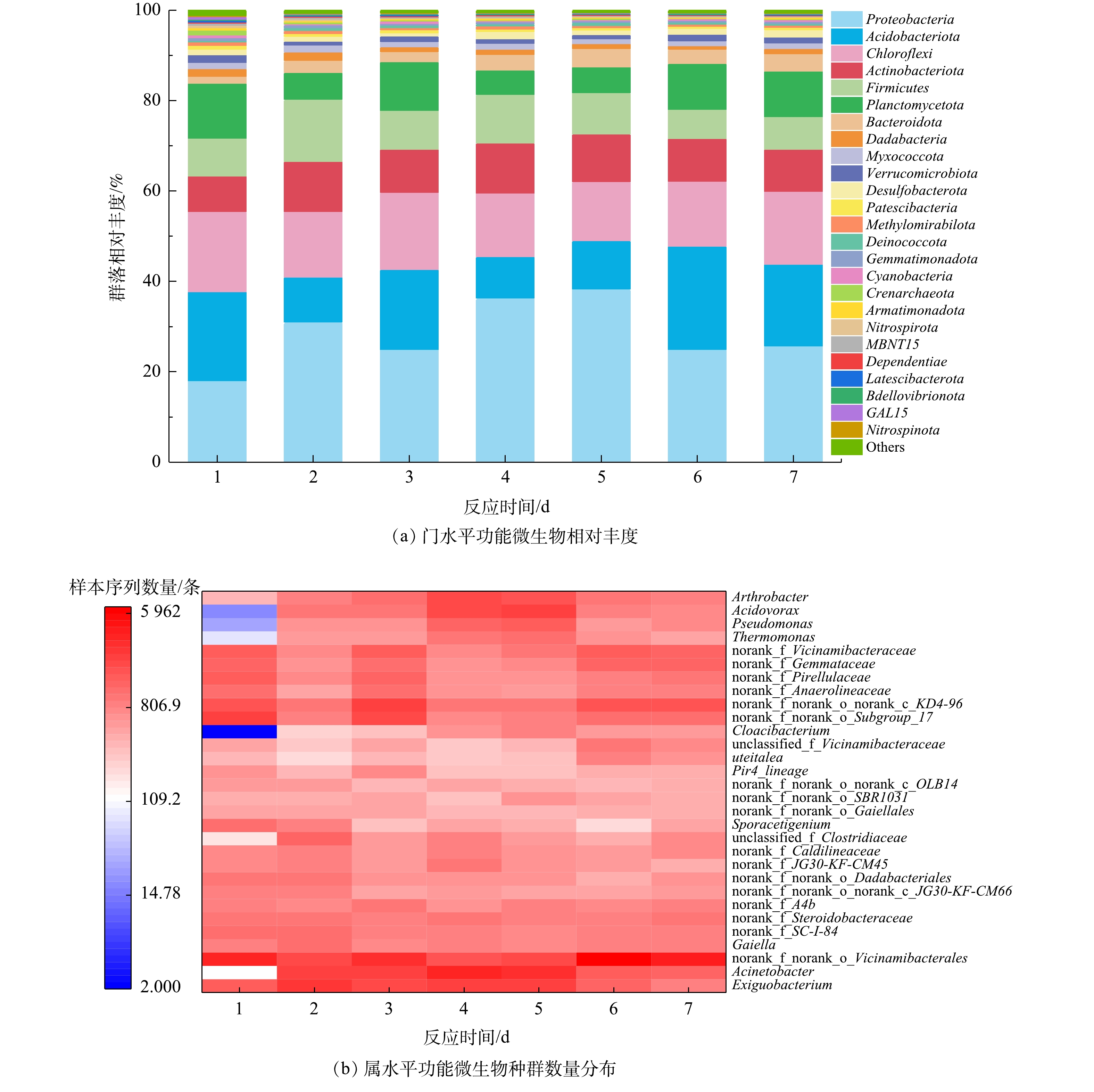

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图