全文HTML
--> --> --> 水稻是全球也是我国主要粮食作物之一[1-2],我国有超过65%的人口以稻米为主食[3]。近年来,我国农作物重金属污染日益严重,以大米镉(Cd)超标问题最为突出[4-6]。广泛存在的Cd超标大米现象对我国稻米生产造成了巨大负面影响[7]。有报道指出,稻米Cd已经成为我国以稻米为主食人群的主要Cd暴露源[5, 8-9]。控制和降低稻米Cd累积是保障稻米质量安全的关键,也是当前我国粮食重金属污染研究的主要方向[10]。在稻米Cd污染防控措施中,石灰作为有效且经济的重金属污染土壤修复材料已被广泛应用,但其大田应用效果存在较强的不确定性[11-13]。WANG等[14]通过小区实验发现,施用石灰后,稻米Cd含量下降、不变和上升的比例分别为50.0%、18.8%和31.2%。YANG等[15]通过大田示范发现,稻米Cd含量随着石灰添加量的升高,出现先降低再升高的现象。当前,对于石灰田间施用降低稻米Cd含量的具体效果和潜在风险仍不明确;而且,将大田施用和田间实验相结合的研究较少。
攸县为我国湖南省稻米主产区,近年来的“镉大米”事件引发了社会的广泛关注,为当地经济发展和农产品安全带来挑战[16]。石灰是降低土壤Cd活性和抑制农作物Cd累积的有效途径,但其大田应用效果具有一定不确定性[15],针对其长期施用的可持续性亟待研究。本研究以攸县为研究区,结合区域调查和田间实验,探究石灰施用对于土壤-水稻系统Cd污染的控制效果及施用风险,以期为当前镉米控制措施的安全应用和调整提供参考。
1.1. 实验区域和供试材料
田间实验在攸县大同桥镇进行,实验点为攸县稻米主要生产乡镇。供试土壤类型为典型的潴育型水稻土,土壤质地为粘土,成土母质为以红色泥页岩土为主,土壤基本理化性质见表1。田间实验所用石灰为CaCO3,与当地大田施用石灰来源一致。供试水稻为低积累品种“JU59”和高积累品种“VU8”[5, 12]。1.2. 实验设计
田间实验分为3个处理,分别为对照、石灰播撒1.20 t·hm?2和石灰播撒2.25 t·hm?2。每个处理设置4个重复,2个品种共布设24个小区,每个小区面积为30 m2;小区采用二因素随机区组实验设计,播种前15 d将石灰混匀处理播撒,按照当地种植习惯进行管理。在水稻成熟期,针对当地农业部门施用石灰处理(1.20 t·hm?2)的62个田块和未处理的62个对照田块进行全县尺度的采样调查[15]。1.3. 采样与分析
水稻成熟期在每个调查地块或小区内随机选取5穴整株水稻样品。水稻样品经自来水冲洗后按照根系、秸秆、稻壳和米粒分离。再用去离子水清洗后于105 ℃下杀青30 min,60 ℃烘至恒重,应用HNO3-HClO4法[5]消解稻米样品。在每个水稻采样点采集土壤样品1份(5点混合采样法,采样深度0~10 cm)。所有样品密封后带回实验室于阴凉处室温风干。土壤样品经研磨后过100目尼龙筛,密封保存用于测定土壤pH,有机质含量等基本物理性质,分析方法参见文献[17]。应用四酸法(HCl-HNO3-HF-HClO4)法[5]消解土壤样品。土壤有效态Cd通过0.01 mol·L?1 CaCl2溶液(1∶2.5,质量与体积比)提取[15]。样品Mn、Al、Fe、Zn、K和Na等微量元素含量应用电感耦合等离子体光谱仪(ICP-OES,PerkinElmer Optima 8300,USA)测定,样品Cd含量应用电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(ICP-MS,Agilent 7500a,USA)测定[18]。测定过程中采用国家标准物质GSS-5和GSB-5进行对土壤和稻米的质量控制,测得各元素标准回收率在83.7%~116.8%。
1.4. 数据分析
应用LSD进行显著性差异检验,应用reml混合线性模型对不平衡数据进行检验[19]。区组实验设计、数据统计和方差分析应用Genstat 18.0进行。典型相关分析(CCA)应用Canoco 4.5进行。2.1. 石灰对土壤pH和Cd植物有效性的影响
相关报道指出,在土壤酸化严重区域生产的稻米富Cd现象比较严重[5, 9]。在本研究区域的调查中发现,当土壤pH低于5.5时,稻米Cd超标率高达80.0%;而当土壤pH在6.0以上时,稻米Cd超标率降至46.5%。经石灰处理后,土壤pH平均值为5.61,较对照组有显著提升(图1(a))。田间实验结果表明,经石灰施用后,土壤pH有一定提高;当施用石灰量达到1.20 t·hm?2时,土壤pH较对照组上升了0.3个单位,但无显著性差异;而当施用石灰量达到2.25 t·hm?2时,土壤pH的平均水平为6.56,显著高于对照组(图1(a))。由此可知,石灰量的增加有助于改良土壤酸化趋势。区域调查结果显示,攸县土壤Cd平均含量为0.33 mg·kg?1,高达湖南省土壤背景值的2.6倍,相应超标率高达98.4%(122/124),为国家土壤环境质量标准[20](0.3 mg·kg?1,pH≤5.5)的1.1倍,相应超标率为58.1%(72/124)。考虑到实验所用肥料中Cd含量均未检出,而该地周围没有大型工厂和采矿基地[16],可推测该地区存在一定的外来Cd源,灌溉水和大气沉降可能为主要的Cd输入途径。研究区土壤Cd活性较高,土壤Cd有效态含量占到总Cd含量的57.6%。经石灰处理后,土壤Cd有效态含量(0.15 mg·kg?1)较对照组(0.19 mg·kg?1)有一定下降(图1(b)),降低了21.1%,但无显著性差异。田间实验石灰处理组的土壤Cd有效态含量为0.17 mg·kg?1(图1(b)),与对照组土壤Cd有效态含量(0.18 mg·kg?1)相比无明显差别。由此可知,石灰可在一定程度上降低土壤Cd有效态含量,但存在一定不确定性。
2.2. 石灰对水稻生长和稻米Cd富集的影响
本研究区域调查(图2(a))结果显示,攸县稻米Cd富集显著,平均含量为0.47 mg·kg?1,约为国家大米安全标准[21](GB 2762-2005,0.2 mg·kg?1)值的2.4倍,超标率高达72.6%(90/124)。经石灰处理后,稻米Cd超标率为67.7%(42/62),与对照组(77.4%,48/62)相比,石灰处理能降低9.7%的稻米Cd超标率。在稻米Cd含量较高的3个乡镇WL、XS和TS均出现了石灰处理后稻米Cd含量高于对照组的样点,可见石灰的大田应用效果差异较大。田间实验结果表明,稻米Cd平均含量为0.14 mg·kg?1,超标率为30%,显著低于区域调查结果(图2(a))。在田间实验中,石灰处理下稻米Cd含量(0.11 mg·kg?1)较对照组(0.26 mg·kg?1)降低近60%,可见石灰对稻米富集Cd有一定控制效果。当石灰施用量增加到2.25 t·hm?2时,稻米Cd含量反而高于施用1.20 t·hm?2石灰时的处理效果(图2(b)),可见增加石灰量并不能持续减少Cd含量,这与RIZWAN等[22]的报道较为类似。
不同品种稻米Cd富集水平不一。由图2(b)可见,高积累品种(VU8)稻米Cd含量高于低积累品种(JU59)。石灰施用对2个品种的Cd累积趋势有一定的控制作用。VU8在石灰处理后,Cd含量降为0.12 mg·kg?1,显著低于对照组;JU59的Cd含量在石灰处理后,降为0.11 mg·kg?1,但效果并不显著。石灰施用量从1.20 t·hm?2提高到2.25 t·hm?2时,VU8和JU59的Cd含量均有一定上升,其中VU8的变化程度最大。可见,石灰降Cd效果对于不同水稻品种也不稳定,高积累品种对于石灰施用量变化较为敏感。
2.3. 石灰对PUF及主要微量元素影响
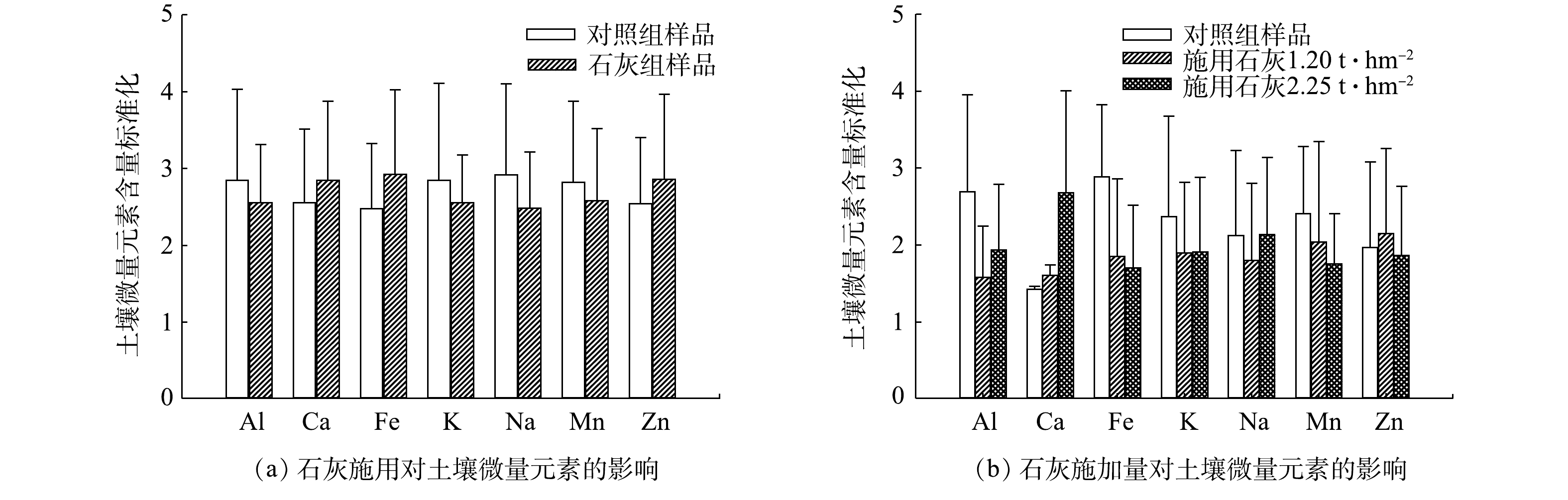
本研究的区域调查结果表明,研究区稻米Cd富集因子(PUF)平均值为1.86,PUF大于1.0和2.0的比例分别为62.9%(78/124)和41.9%(52/124),可见攸县土壤-稻米系统Cd富集显著现象广泛存在且较为严重(图3(a))。经石灰处理后,PUF略有下降(降幅6.3%),但无显著性差异。田间实验中,PUF平均值为0.47,显著低于区域调查结果。与对照相比,施用石灰后不同品种的PUF均出现显著下降的现象,而不同水稻品种的PUF在同一石灰施用量下差异较大(图3(b))。可见,石灰施用可在一定程度上减少Cd在土壤-水稻系统中的富集,但存在一定不确定性。URAGUCHI等[11]和SEBASTIAN等[23]的研究指出,土壤微量元素会影响植物体膜转运蛋白的表达,进而影响水稻对Cd的吸收和转运。本研究的区域调查结果显示,在石灰处理条件下,土壤Zn、Fe、Ca含量较对照组均有一定程度增加,而土壤K、Na、Mn和Al均有下降(图4(a)),可见石灰施用对土壤养分库元素平衡造成了一定影响。田间实验结果显示,与对照组相比,土壤Ca含量显著增加,土壤Fe、Mn、Al含量下降显著(图4(b))。相关分析结果表明,田间实验中土壤Mn与稻米Cd含量显著相关(r2=0.25,p<0.01);而石灰处理下,土壤Mn含量较对照下降8.3%,当石灰施用量增加时,土壤Mn含量较对照下降11.9%(图4(b))。YANG等[15]也发现,石灰施用会促进水稻土Mn的流失。这可能是增加石灰施用量反而造成稻米Cd含量上升的主要原因。PITTMAN[24]和YANG等[25]的报道指出,土壤Mn能够在水稻抽穗期抑制Cd从水稻根部到稻米的转运,本研究区土壤Mn平均水平为215 mg·kg?1,仅为湖南省土壤Mn背景值(459 mg·kg?1)[26]的46.8%。土壤Mn活性与田间氧化还原状态密切相关,区域土壤酸化及水稻田排水是造成稻田土壤Mn流失的主要原因[7],石灰的施用会进一步加速了土壤Mn的流失,进而降低了Mn对Cd在土壤-稻米系统中转移的抑制作用。这可能是石灰施用下,大田效果不明显的主要原因之一。
2.4. 石灰对土壤-稻米系统Cd富集的影响
对区域调查和田间实验观测数据进行了典型相关排序分析(CCA)[2],Monte Carlo检验表明,CCA排序轴典范系数对回归关系的解释达到显著性水平(p<0.05)[6]。前3个排序轴可解释Cd在土壤-稻米系统富集变异程度的96.1%。其中,第1排序轴解释量占到43.5%,土壤Zn(r2=0.56,p<0.001)、土壤pH(r2=0.42,p<0.001)和土壤Mn(r2=0.37,p<0.001)为第1排序轴的3个主要因子。根据CCA排序关系,各环境因子可分为3组(图5(a)),各微量元素主要分布在第1象限,土壤有机质(Som)分布在第3象限,土壤Zn和土壤pH分布在第4象限。环境因子矢量长度(图5(a))显示土壤Mn、土壤pH和土壤Zn是影响Cd在土壤-水稻系统富集变异程度的3个主要因子。根据土壤Cd、稻米Cd和稻米Cd吸收因子(PUF)之间的位置关系可见,PUF与稻米Cd的关系更为密切(图5(a))。而由解释变量在各环境变量上的投影关系可知,土壤pH(r2=0.46,p<0.001)和土壤Zn(r2=0.71,p<0.001)与土壤Cd呈显著正相关,是影响土壤Cd的2个主要因子;稻米Cd含量受微量元素影响较大,其中土壤Mn(r2=?0.47,p<0.001)与稻米Cd呈显著负相关,是微量元素中影响稻米Cd累积的主要因子。
由观测样方与解释变量的CCA排序图(图5(b))可见,田间实验观测结果变异程度显著小于区域调查。随着石灰施用量的增加,田间实验观测值由第2象限向第3象限逐步过度,Cd在土壤-稻米系统富集程度与土壤微量元素关系更为密切。区域调查中发现,经石灰处理后,土壤-稻米系统Cd含量变异程度高于对照组,且该变异程度与土壤pH和微量元素呈显著相关。
综合以上结果可知,石灰对于降低稻米Cd含量和改善土壤酸化程度具有一定作用,但并不稳定。而石灰的过量施用会造成土壤矿质元素流失,特别是对抑制稻米富Cd有一定效果的土壤Mn的缺失,具有一定的施用风险。YANG等[15]指出,石灰的过量施用会造成水稻减产。另一方面,由于石灰的强碱性,过量施用也会造成土壤板结,肥效降低,出现烧苗现象,从而影响水稻产量[27]。因此,因地制宜地调整石灰施用量,增施Mn肥是解决当地水稻Cd污染的科学途径。本研究中,区域观测与田间实验差异较大,但反映趋势相同,两者的结合研究有助于更全面的了解Cd在土壤-稻米系统的富集特征及石灰施用的具体效果和潜在风险,对其他土壤改良剂的效果评估也有一定的借鉴。
2)石灰施用后,会造成土壤微量元素变化,特别是土壤Mn的流失是造成石灰控制Cd米效果不稳定的主要原因之一。
3)低用量石灰施用在田间实验中可有效降低稻米Cd含量,但施用量的增加会带来土壤Mn的进一步流失,进而造成稻米Cd含量不降反升。
参考文献


 下载:
下载: 


 点击查看大图
点击查看大图