3.江苏理工学院化学与环境工程学院,常州 213001
1.School of Resources and Environmental Science, Hunan Normal University, Changsha 410006, China
2.Key Laboratory for Agro-Ecological Processes in Subtropical Region, Institute of Subtropical Agriculture, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changsha 410125, China
3.School of Chemical and Environmental Engineering, Jiangsu University of Technology, Changzhou 213001, China
养殖废水浓度过高,直接排入生态湿地容易造成植物死亡。因此,在养殖废水进入生态湿地之前,须进行前处理,降低其养分浓度,以确保生态湿地对养殖废水的处理效果。通过野外控制实验,研究了添加不同作物秸秆对养殖废水的处理效果,并考察了作物秸秆材料对氮的转化特征。结果表明:通过设置麦秸、玉米秆、稻草和对照4个实验组,在经过6个月的连续处理后,总氮出水浓度为359.8~614.0 mg·L
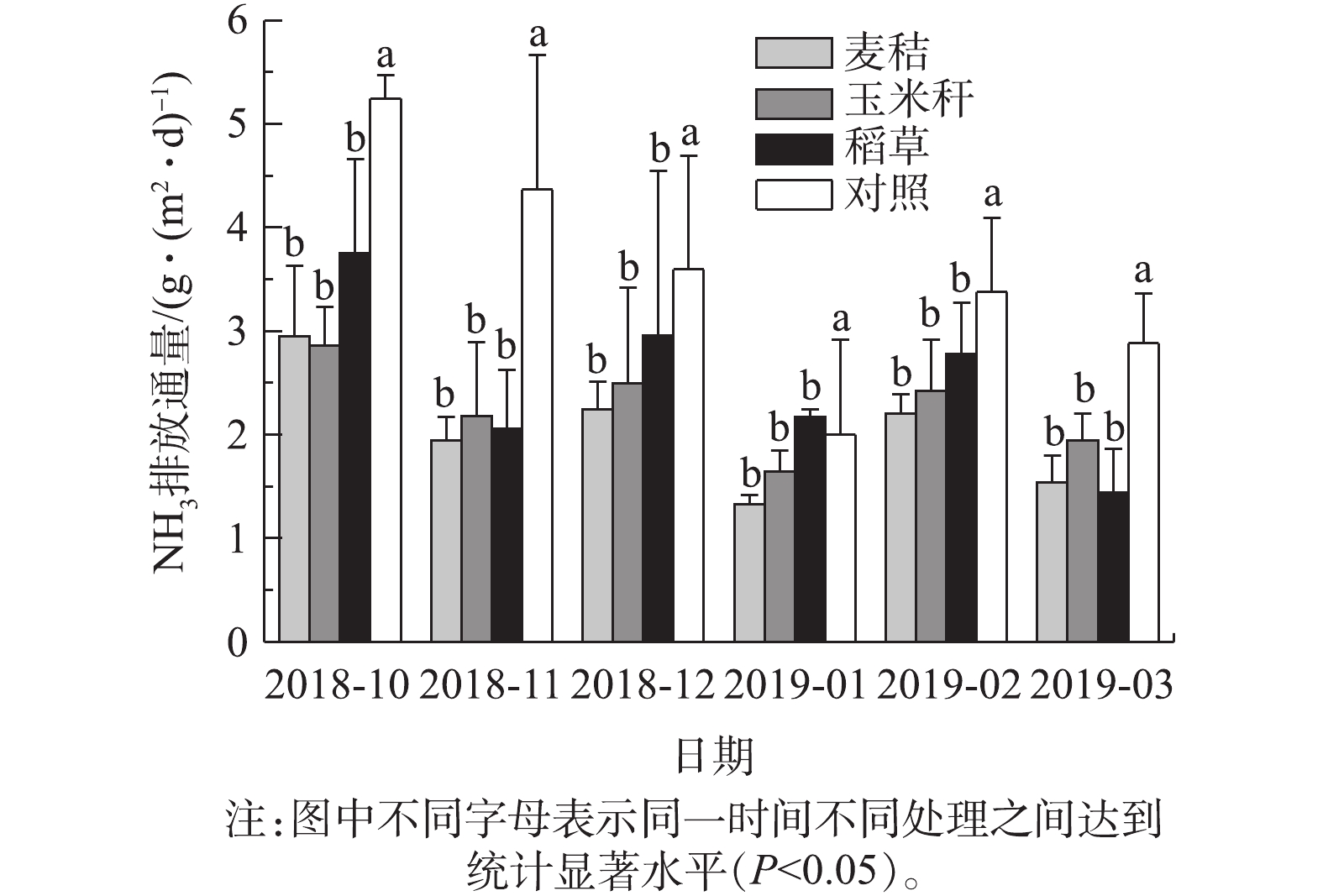
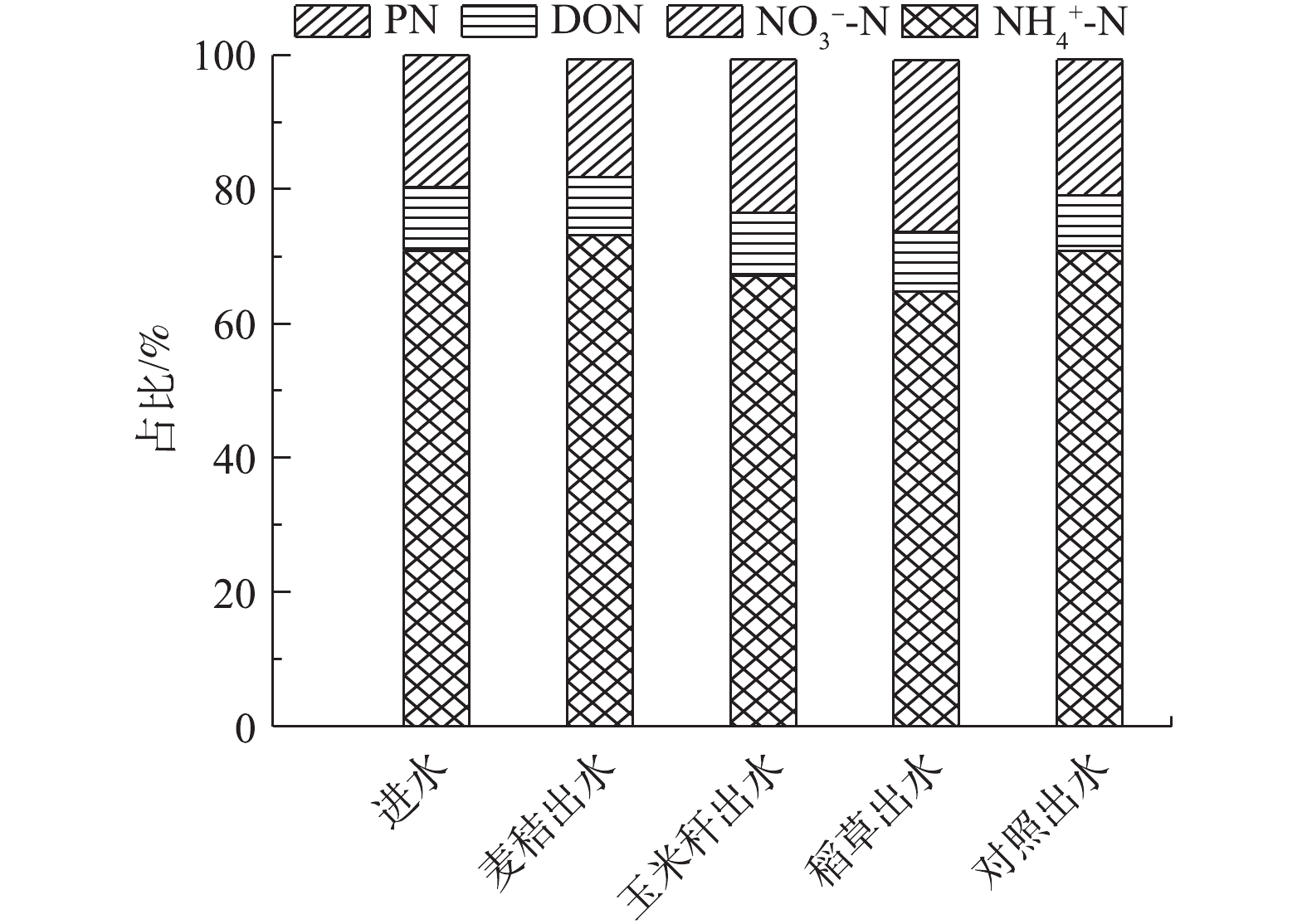
)人工湿地要求的植物耐受限度内;不同形态氮浓度在基质系统处理前后的占比变化不大,主要以氨氮为主(平均为68.3%),其次为颗粒态氮(平均为22.0%),硝态氮占比极低(<1%);添加作物秸秆能降低养殖废水的氨挥发,生物基质消纳系统中以氨挥发形式损失的氮约占TN去除量的10%,明显低于自然条件下的损失率(60%)。以上研究结果对优化生态湿地处理高负荷畜禽养殖废水工艺具有参考价值和指导意义。
Swine wastewater has pollutants with too high concentrations, its directly discharging into constructed wetlands (CWs) can cause plant death. Therefore, the concentration of nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) in swine wastewater should be reduced before it was discharged into CWs, which could ensure the N and P treatment effects in swine wastewater by CWs. Through field experiments, the treatment effects of swine wastewater by addition of different crop straws were studied, as well as the N transformation characteristics by crop straws. The results showed that four experimental groups with wheat straw, corn straw, straw and control were conducted for 6-month continuous treatment, total nitrogen (TN) concentration in effluent ranged from 359.8 to 613.99 mg·L
, and the corresponding removal rates were 30% to 40%. Ammonia nitrogen (
. Crop straw showed significant nitrogen removal effect from high-load breeding wastewater. The
in CWs. Slight changes occurred in the proportion of different N forms before and after treatment by biological matrix systems. The main form was
with average the proportion of 68.3%, which was followed by particulate nitrogen (PN) with average the proportion of 22.0%, and nitrate nitrogen (
) presented very low proportion <1%. Adding crop straws into swine wastewater could reduce the ammonia volatilization. Ammonia volatilization in the biological matrix pool accounted for 10% TN removal, which was significantly lower than the loss (60%) in natural conditions of the control group. This provides important theoretical value and guiding significance for optimizing constructed wetland treating high load swine wastewater.
.
Schematic diagram of test area
Collection device of ammonia emission flux
Inlet and outlet TN concentration and its removal rate
-N concentration and its removal rate
Ammonia discharge flux of biological matrix material tank
生物基质材料池进出水不同形态氮素构成的特征
Characteristics of nitrogen composition in the inlet and outlet of biological matrix materials tank
Dynamic characteristics of ammonia emissions proportion in TN removal from biological matrix material tank
| [1] | 陈希, 周脚根, 李希, 等. 洞庭湖生态经济区养猪业污染物排放时空格局分析[J]. 农业现代化研究, 2017, 38(2): 291-297. |
| [2] | 李裕元, 李希, 吴金水, 等. 绿狐尾藻区域适应性与生态竞争力研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2018, 37(10): 2252-2261. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2018-1036 |
| [3] | 李远航, 刘洋, 刘铭羽, 等. 稻草-绿狐尾藻复合人工湿地技术处理养猪废水综合效益分析[J]. 农业现代化研究, 2018, 39(2): 325-334. |
| [4] | 岳彩德, 董红敏, 张万钦, 等. 陶瓷膜净化猪场沼液的效果试验[J]. 农业工程学报, 2018, 34(5): 212-218. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.05.028 |
| [5] | 郑晓英, 乔露露, 王慰, 等. 碳源对反硝化生物滤池运行及微生物种群的影响[J]. 环境工程学报, 2018, 12(5): 1434-1442. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201710046 |
| [6] | SHEN Q, ZHOU Y X, WANG J L. Comparison of denitrification performance and microbial diversity using starch/polylactic acid blends and ethanol as electron donor for nitrate removal[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2013, 131: 33-39. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2012.12.169 |
| [7] | 唐婧, 刘昱迪, 孙凤海, 等. 以玉米芯为外加碳源的SBBR脱氮特性[J]. 环境工程学报, 2016, 10(6): 2775-2780. |
| [8] | 宋爱红, 沈志强, 周岳溪, 等. 以稻秆为固体碳源处理分散养猪冲洗水的试验研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 2015, 35(7): 2052-2058. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2015.07.022 |
| [9] | 马斌, 许鑫鑫, 高茂鸿, 等. 基于短程反硝化厌氧氨氧化的低碳源城市污水深度脱氮特性[J/OL]. [2019-11-13]. https://doi.org/10.13227/j.hjkx.201907135. |
| [10] | 周卿伟, 祝惠, 阎百兴, 等. 添加填料的人工湿地反硝化过程研究[J]. 湿地科学, 2017, 15(4): 588-594. |
| [11] | 张伟明, 陈温福, 孟军, 等. 东北地区秸秆生物炭利用潜力、产业模式及发展战略研究[J]. 中国农业科学, 2019, 52(14): 2406-2424. doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2019.14.003 |
| [12] | 李斌, 郝瑞霞. 固体纤维素类废物作为反硝化碳源滤料的比选[J]. 环境科学, 2013, 34(4): 1428-1434. |
| [13] | 李裕元, 刘锋, 吴金水, 等. 一种利用稻草处理养猪场废水的方法: ZL201310314561.4[P]. 2015-03-04. |
| [14] | 刘铭羽, 夏梦华, 李远航, 等. 3种基质材料对高浓度养殖废水处理效果及降解过程[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(8): 3650-3659. |
| [15] | 美英, 魏坤昊, 崔钠淇, 等. 集约化奶牛养殖场不同粪尿处理阶段氮素分布及氨排放特征[J]. 农业工程学报, 2018, 34(18): 261-267. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.18.032 |
| [16] | KOERKAMP P W G G, BLEILEIJENBERG R. Effect of type of aviary, manure and litter handling on the emission kinetics of ammonia from layer houses[J]. British Poultry Science, 1998, 39(3): 379-392. doi: 10.1080/00071669888935 |
| [17] | 申南竹. 氨气增强了二氧化硫对林木的伤害[J]. 环境科学, 1991, 12(5): 95. |
| [18] | 王岩, 娄新乾, 王文亮, 等. 水分调节材料对牛粪堆肥氨气挥发的影响[J]. 农村生态环境, 2003, 19(4): 56-58. |
| [19] | 谢海林. 垂直潜流人工湿地脱氮机理及效果改善研究[D]. 上海: 同济大学, 2007. |
| [20] | 韩增, 王美慧, 周脚根, 等. 亚热带丘陵小流域氮平衡及调控对策[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2017, 36(4): 743-752. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2016-1346 |
| [21] | 王朝辉, 刘学军, 巨晓棠, 等. 北方冬小麦/夏玉米轮作体系土壤氨挥发的原位测定[J]. 生态学报, 2002, 22(3): 359-365. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2002.03.011 |
| [22] | 邬刚, 袁嫚嫚, 曹哲伟, 等. 不同水氮管理条件下稻田氨挥发损失特征[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2019, 35(5): 651-658. |
| [23] | 山楠, 毕晓庆, 杜连凤, 等. 基施氮肥对麦田冬前氨挥发损失的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2013(6): 51-55. |
| [24] | 邓欧平, 姜丽娜, 陈丁江, 等. 大量沼液施灌稻田的氨挥发特征[J]. 水土保持学报, 2011, 25(6): 233-236. |
| [25] | 徐珊珊, 侯朋福, 范立慧, 等. 生活污水灌溉对麦秸还田稻田氨挥发排放的影响[J]. 环境科学, 2016, 37(10): 3963-3970. |
| [26] | LI X, ZHANG M M, LIU F, et al. Seasonality distribution of the abundance and activity of nitrification and denitrification microorganisms in sediments of surface flow constructed wetlands planted with Myriophyllum elatinoides during swine wastewater treatment[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 248: 89-97. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2017.06.102 |
| [27] | LI X, LI Y Y, LI Y, et al. Diversity and distribution of bacteria in a multistage surface flow constructed wetland to treat swine wastewater in sediments[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2018, 102(24): 10755-10765. doi: 10.1007/s00253-018-9426-2 |
| [28] | 刘波, 刘筱, 韩宇捷, 等. 规模化养猪场典型沼气工程各排放节点氨排放特征研究[J]. 农业工程学报, 2018, 34(23): 179-185. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.23.022 |
| [29] | JAMES K M, BLUNDEN J, RUMSEY I C, et al. Characterizing ammonia emissions from a commercial mechanically ventilated swine finishing facility and an anaerobic waste lagoon in North Carolina[J]. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 2012, 3(3): 279-288. doi: 10.5094/APR.2012.031 |
| [30] | 黄丹丹, 罗皓杰, 应洪仓, 等. 沼液贮存中甲烷和氨气排放规律实验[J]. 农业机械学报, 2012, 43(S1): 190-193. |
| [31] | 陈敏, 杨有泉, 邓素芳, 等. 土壤生物过滤去除畜禽养殖臭气[J]. 环境工程学报, 2013, 7(3): 1053-1058. |
| [32] | 盛婧, 徐乔, 朱普平, 等. 基于分级过滤的喷灌用沼液颗粒物组成分析[J]. 农业工程学报, 2016, 32(8): 212-216. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2016.08.030 |
| [33] | 宋思雨. 污水地下渗滤系统氨氮、有机氮的去除机理及影响因素研究[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳师范大学, 2017. |
| [34] | 谢龙, 汪德爟, 戴昱. 水平潜流人工湿地氮转化模型研究[J]. 水力发电学报, 2009, 28(6): 151-156. |
| [35] | 薛文涛, 林聪, 孙钦平, 等. 不同发酵原料沼液的氨挥发特性研究[J]. 可再生能源, 2016, 34(5): 780-785. |
| [36] | DUAN Z H, XIAO H L. Effects of soil properties on ammonia volatilization[J]. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2000, 46(4): 845-852. doi: 10.1080/00380768.2000.10409150 |
| [37] | VILLAVERDE S, GARCIA-ENCINA P A, FDZ-POLANCO F. Influence of pH over nitrifying biofilm activity in submerged biofilters[J]. Water Research, 1997, 31(5): 1180-1186. doi: 10.1016/S0043-1354(96)00376-4 |
| [38] | LIU F, ZHANG S, WANG Y, et al. Nitrogen removal and mass balance in newly-formed Myriophyllum aquaticum, mesocosm during a single 28-day incubation with swine wastewater treatment[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2016, 166: 596-604. |
| [39] | 王晓玲, 宋铁红, 殷宝勇, 等. 利用主要缺氧段ORP作为连续流单污泥污水脱氮除磷系统调控参数[J]. 环境科学, 2015, 36(7): 2617-2625. |





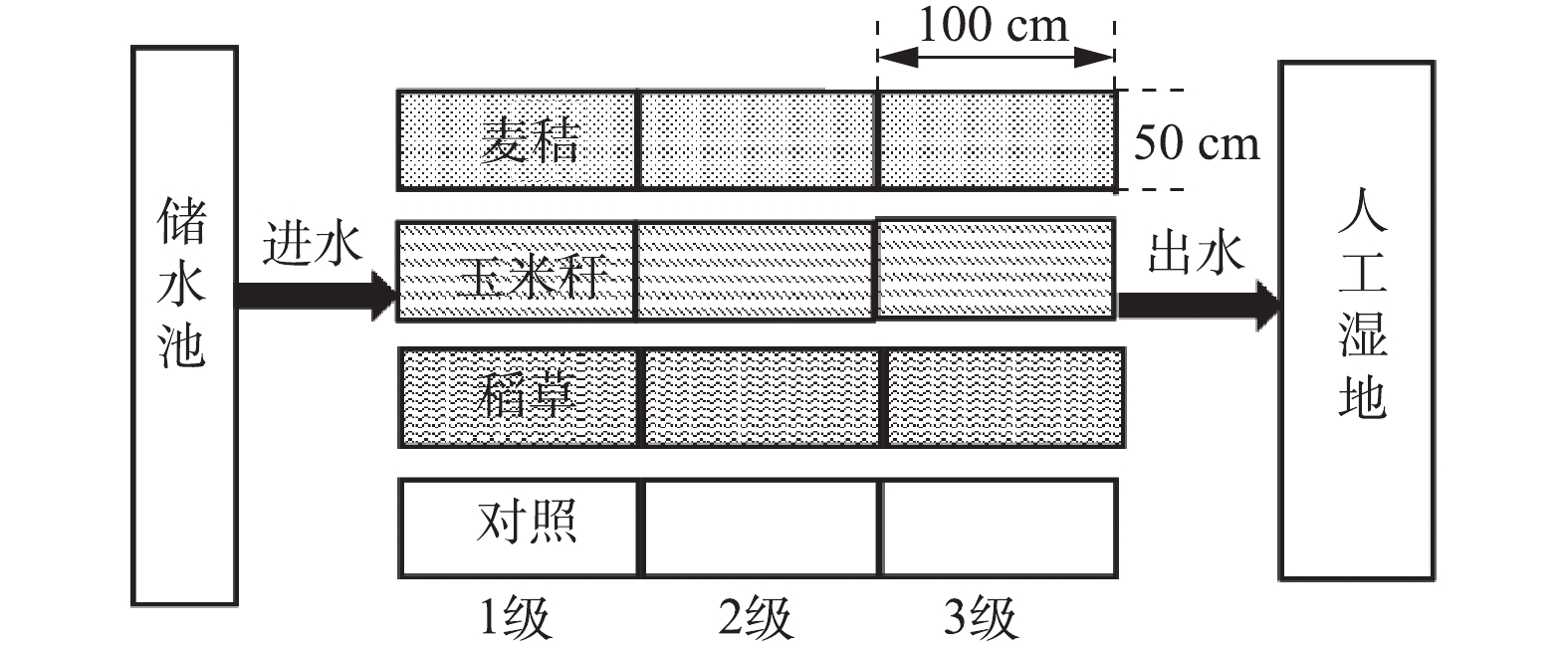
 下载:
下载: 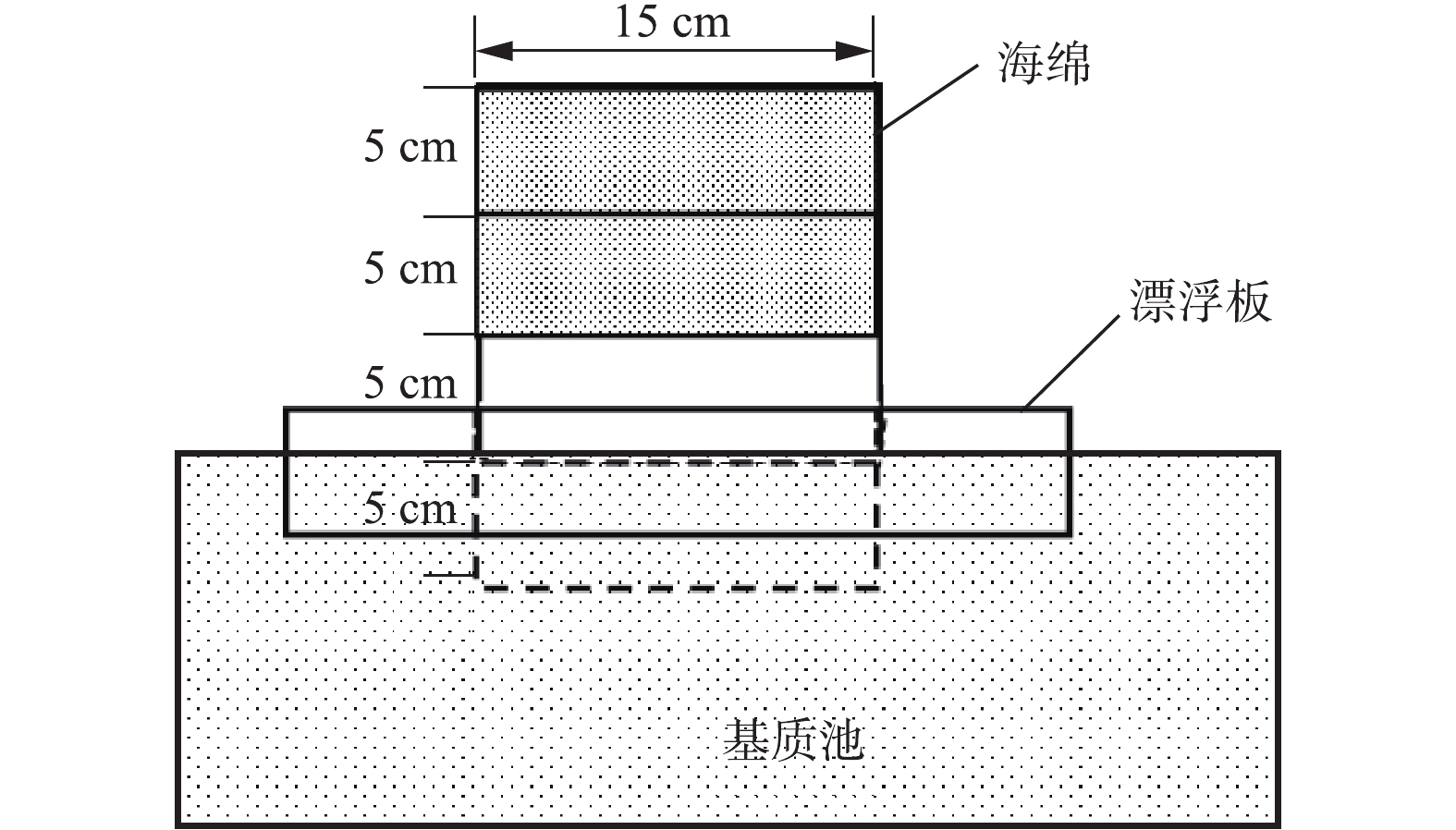
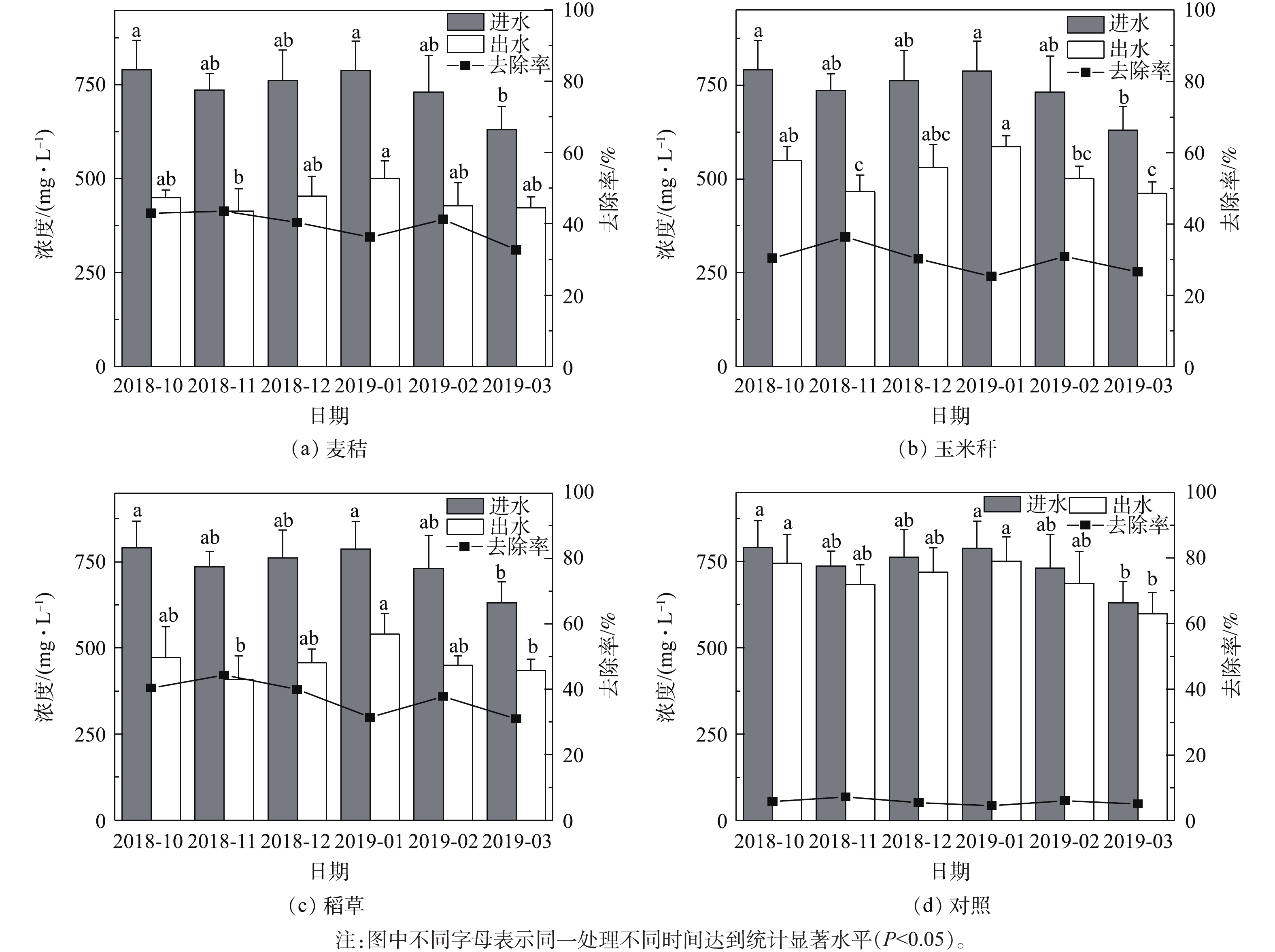
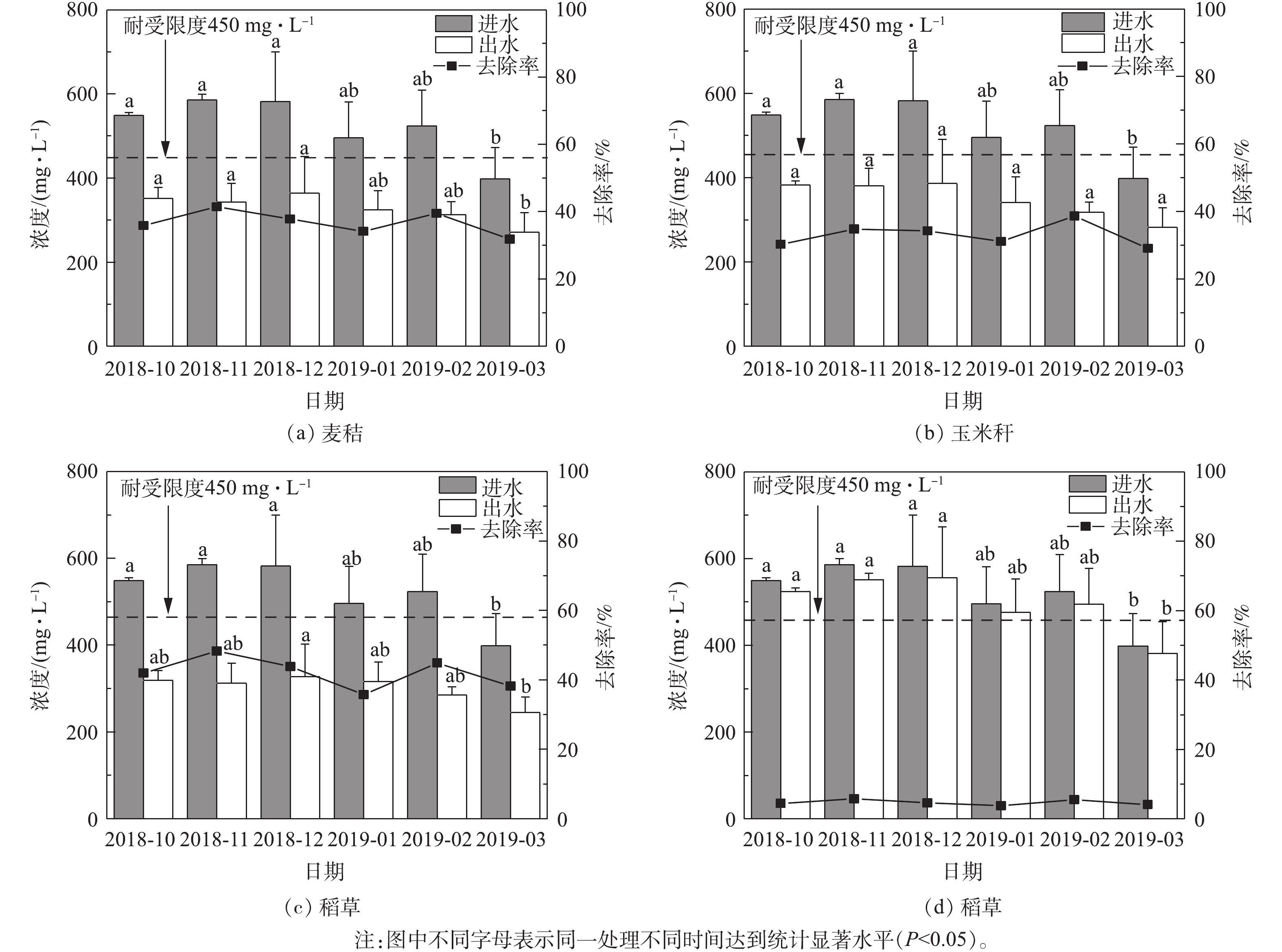












 点击查看大图
点击查看大图