全文HTML
--> --> --> 好氧颗粒污泥是指在有氧环境条件下微生物相互聚集形成的生物聚集体[1]。与传统活性污泥相比,好氧颗粒污泥具有生物量高、结构稳定、沉降性能好、耐冲击负荷强和处理构筑物占地面积小等优点[2]。与厌氧颗粒相比,好氧颗粒具有启动时间短、操作温度低等特点。由于颗粒结构内部存在氧浓度梯度,故能在一定程度上实现多种生物群落共存,以完成同步脱氮除碳。有的研究表明,好氧颗粒污泥不能在自然条件下出现,必须在具有强选择压力的特定条件下培养。以往研究采用特殊操作条件(如调节水力剪切力、好氧饥饿时间、水力停留时间等)来培育,也有的研究通过调整进水负荷(如有机负荷率(OLR)、化学需氧量和氮之比(C/N))来促进颗粒化形成[3-4]。目前,很多产业生产排出高C/N的污水,如氮肥行业、化工行业、制药行业等。活性污泥处理高C/N污水存在系统不稳定、污泥容易膨胀、处理效果不理想等问题[5-6]。好氧颗粒污泥因结构致密,有胞外聚合物(extracellular polymeric substances,EPS)保护,颗粒内部可截留多种功能菌群,是高C/N污水可选择的理想处理工艺,且高C/N也是启动好氧颗粒污泥反应器的一种条件[7-8]。冯殿宝等[9]用高C/N的番茄废水成功培养好氧颗粒污泥,COD和
1.1. 实验装置及运行
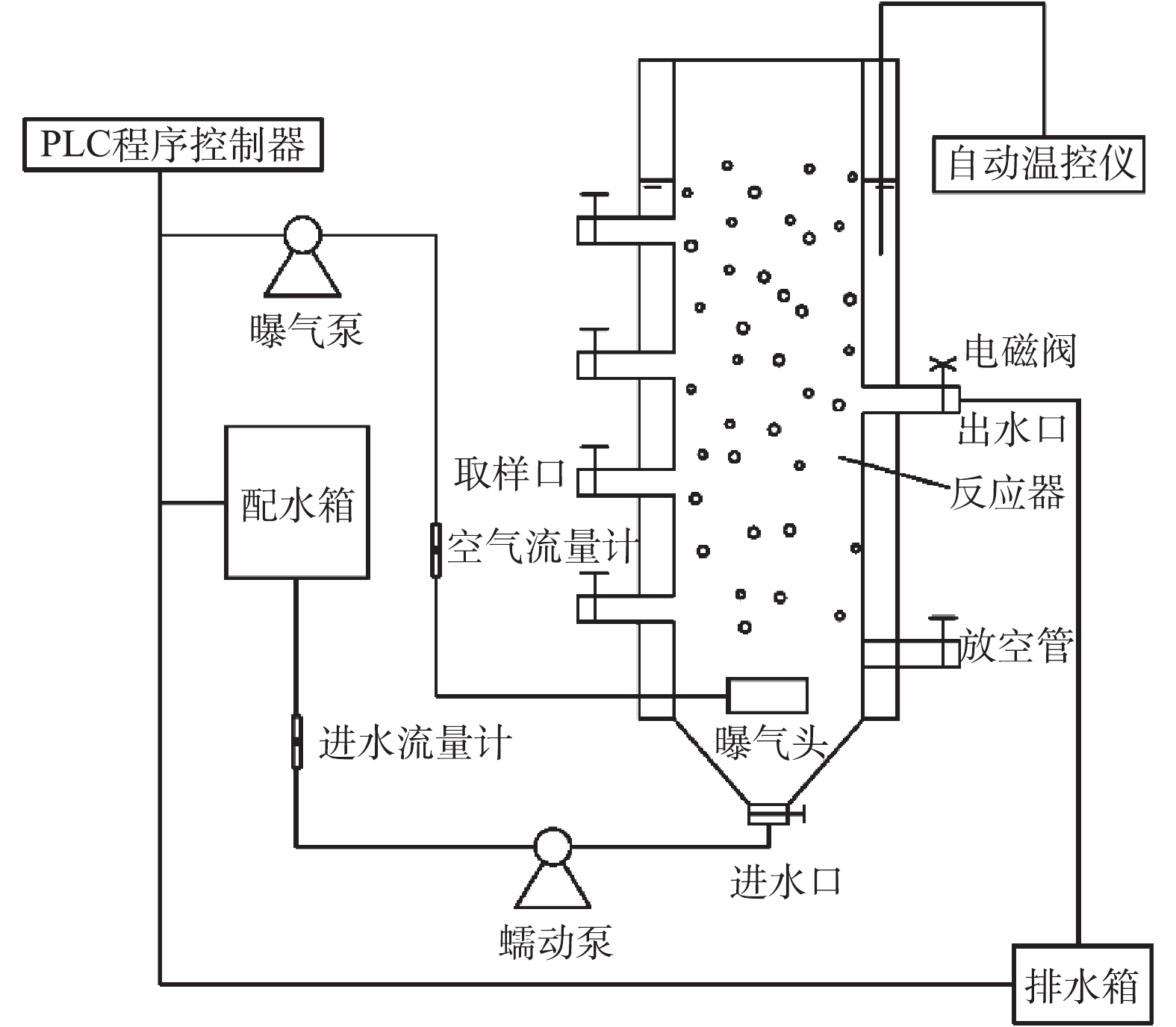
本实验采用SBR实验装置(图1)研究好氧颗粒污泥对高负荷污水的处理性能。SBR材质为有机玻璃,装置内径60 mm,柱高径比H/D为16.7∶1,有效容积3 L,有效水深1 m。水浴套管通过电加热棒维持环境温度25~30 ℃。反应器通过蠕动泵(杰恒BT-300EA)从底部进水,出水由常闭型电磁阀控制,出水口距离反应器底部500 mm。进水中COD和
1.2. 实验进水及接种污泥
实验进水采用人工配水,主要成分见表1。在第Ⅰ阶段,采用无水乙酸钠(50%)和蔗糖(50%)混合碳源;在第Ⅱ阶段,采用无水乙酸钠(45%)、蔗糖(45%)和蛋白胨(10%)混合碳源。2个阶段均采用氯化铵作为氮源,第Ⅰ、Ⅱ阶段的C/N分别为20、40。配水中加入3 mL·L?1微量元素溶液,配方为:3 g·L?1 MgSO4·7H2O,3.36 g·L?1 MnSO4·H2O,3 g·L?1 ZnSO4·7H2O,1.12 g·L?1 H3BO3,0.3 g·L?1 FeSO4·7H2O和0.6 g·L?1 CaCl2,实验药品均采用化学纯。接种污泥来自重庆市鸡冠石污水厂二沉池。活性污泥颜色呈深褐色,形状无规则,呈絮体,初始SV30为35%,SV5为28%,SVI为44 mg·L?1,混合液挥发性悬浮固体浓度/混合液悬浮固体浓度(MLVSS/MLSS)为0.63。取回的污泥静止后,去掉上清液,取少量浓缩的活性污泥在显微镜下观察。同时将1 L浓缩污泥投入反应器中,闷曝24 h,调节污泥MLSS为6.4 g·L?1左右,正常进水。
1.3. 分析方法
在实验中,EPS的提取采取离心与阳离子树脂相结合的方法。多糖(polysaccharide,PS)含量采用硫酸-蒽酮法测定,蛋白质(proteins, PN)含量采用Lowry试剂盒方法(Solarbio,日本)测定。取反应器中的颗粒污泥样品1 mL,使用土壤DNA分离试剂盒(GenElute? Soil DNA Isolation Kit)抽提群落DNA,样品需要前处理,以去除腐殖质等的干扰且保证群落DNA纯度。MisSeq高通量测序及数据整理由上海美吉公司开发的I-Sanger云平台完成。
2.1. 颗粒污泥的形成
1) 污泥形态变化。采用光学显微镜对污泥生物相和颗粒形态进行观察,结果如图2所示。从二沉池取出的接种污泥在显微镜下为絮状,轮廓和边缘不清晰,整体松散,有大量菌胶团且混有活性良好的原生动物和后生动物(如钟虫、轮虫等),为成熟的活性污泥。在SBR启动20 d后(阶段Ⅰ),可观察到小颗粒污泥出现,颜色由棕褐色转变成黄色,颗粒形态整体为椭球状,缠绕有固着型微生物(累枝虫等),颗粒有较清晰的边缘轮廓且粒径较小,有少量的污泥絮体未被洗脱存留在视野内。当反应器运行到46 d时(阶段Ⅱ),反应器中整体污泥颗粒化程度高,大小均匀。取46 d时反应器中的典型颗粒,在SEM下进一步观察,颗粒呈轮廓清晰的椭球体,结构紧实,表面倾斜分布着排列紧密的短杆细菌,几乎不存在丝状菌。同时颗粒表面也存在一些扩散开的网状物质。这与LIU等[11]和TAY等[12]的观察结果类似,推测应该是细菌分泌的EPS。2) 粒径分布、比好氧速率及含水率变化。SBR运行到46 d时,采用标准筛法测量污泥粒径的分布,结果见表2。此时反应器中的好氧颗粒污泥粒径大于0.38 mm的污泥占总体积的91.6%。根据研究[2],当粒径超过0.36 mm的颗粒污泥的比例超过总污泥体积的50%时,可以认定好氧颗粒污泥颗粒化完成,在本研究中,46 d反应器内的颗粒污泥已经成熟。
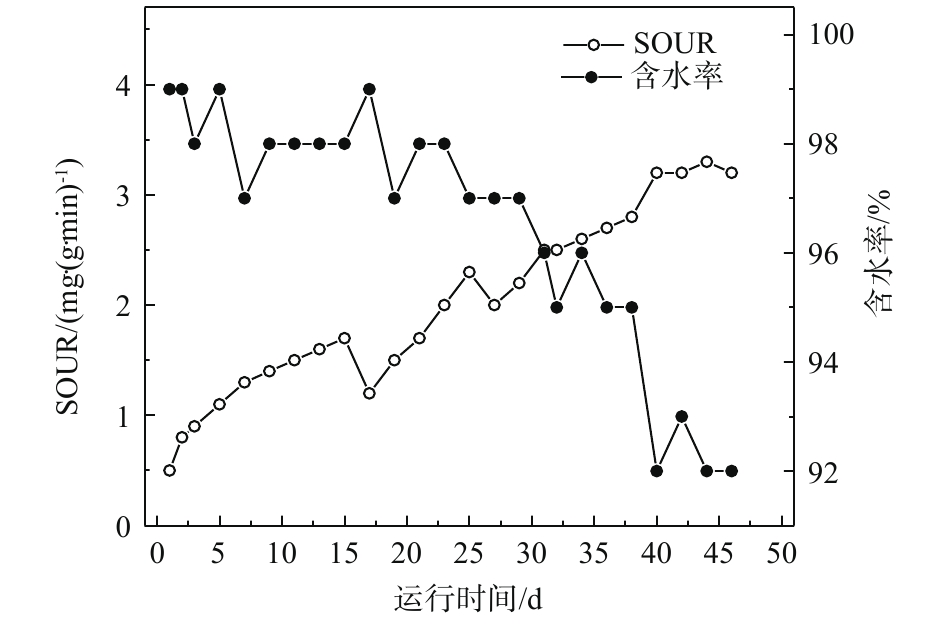
颗粒污泥的比耗氧速率(specific oxygen uptake rate,SOUR)及含水率变化如图3所示。由于闷曝处理活性降低,初始投加污泥的SOUR为0.5 mg·(g·min)?1(以VSS计),随着培养过程中污泥颗粒化的形成,SOUR有所提升,最终稳定在3.2 mg·(g·min)?1左右。SOUR逐步提高,说明培养过程中污泥的微生物活性提升,高负荷污水的处理效果得到有效改善。污水厂的曝气池污泥为絮状活性污泥,其含水率为99%,颗粒形成后,含水率降低至92%。好氧颗粒污泥与活性污泥相比,结构更加密实,其含水率也会降低。一般污泥机械脱水后含水率为97%,而颗粒污泥较低的含水率可以减少污泥浓缩工序,降低污水处理厂的经济成本,这在污水处理中是一种经济有效的方式。
3) 好氧颗粒污泥沉降性能变化。污泥的SV5、SV5/SV30、SVI、MLSS和MLVSS变化情况如图4所示。初始污泥的SV5为35 mL·g?1,培养20 d后降低50%,这表明污泥团聚成小颗粒的过程使污泥的沉降性逐步提高。在28~39 d,反应器内发生污泥轻微膨胀现象,沉降性随之降低。这是由于进水负荷从800 mg·L?1 (COD)提高到2 400 mg·L?1 (COD)后,对已形成的颗粒污泥有一定的冲击作用。但随着颗粒适应进水环境,颗粒污泥沉降性持续升高,46 d时SV5降低至12 mL·g?1,SV30降低至11 mL·g?1。好氧颗粒污泥形成过程中,SV5/SV30的变化幅度很小,基本维持在1.1左右,说明SV30与SV5的变化趋势基本一致,颗粒污泥沉降性良好。LIU等[11]发现,SV30与SV5的差异小于10%时,有利于好氧颗粒污泥的形成。污泥容积指数SVI从43.6 mL·g?1降低到了17.8 mL·g?1,除了适应进水变化时期发生轻微的污泥膨胀,整体趋势均随着颗粒粒径的增长,沉降性变好。SBR内生物量的变化有一定的波动性,但在进水COD提高至2 400 mg·L?1 时,MLSS和MLVSS持续上升,表明高负荷可以刺激微生物的增长。
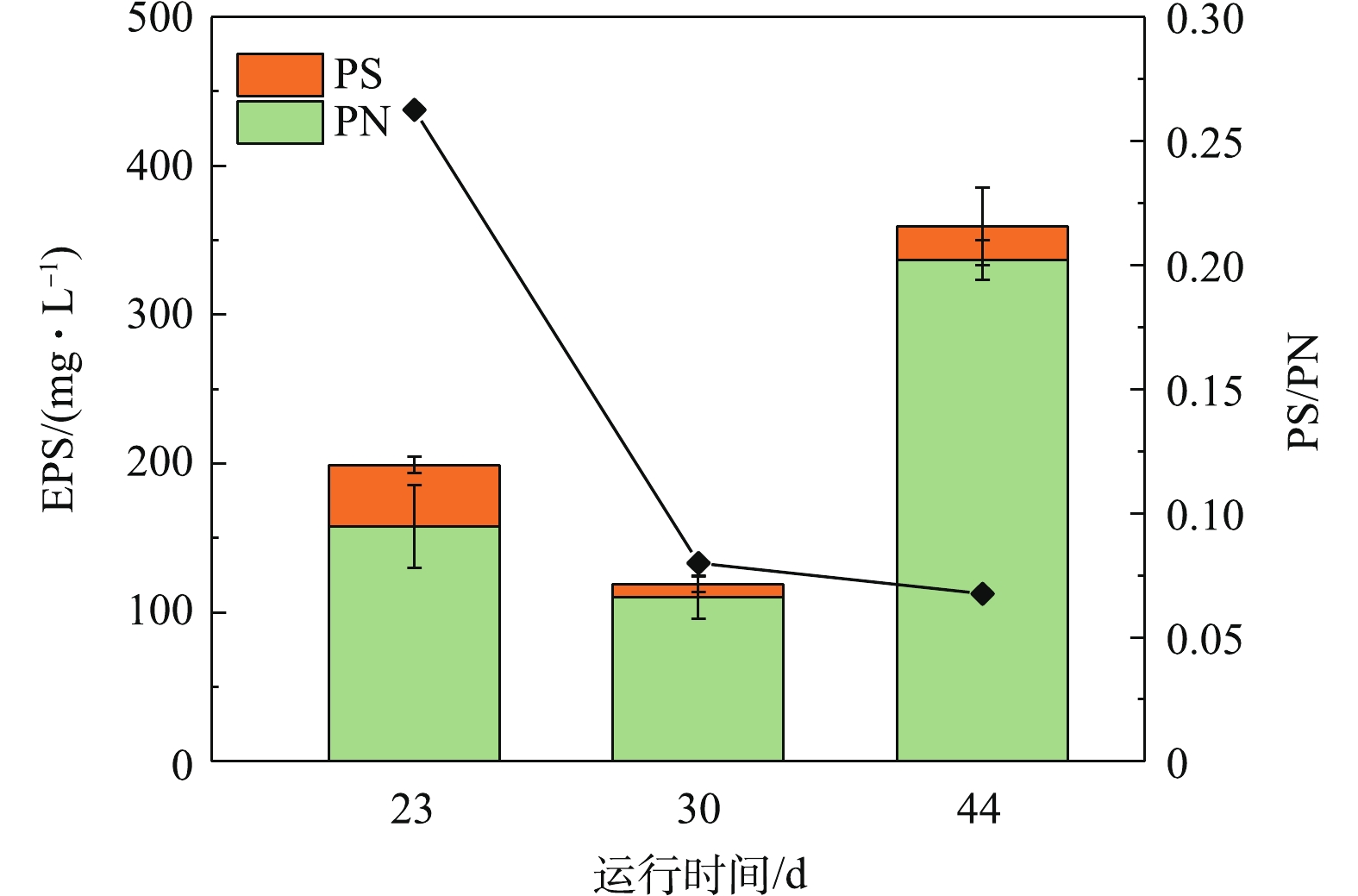
4) 好氧颗粒污泥胞外聚合物变化。通常认为,EPS对于好氧颗粒污泥的形成有促进作用[13-14]。好氧颗粒污泥形成过程中的EPS含量如图5所示。在23 d时,污泥的EPS总量为199 mg·L?1,其中蛋白质的含量为157 mg·L?1,多糖的含量为41.4 mg·L?1,PS/PN为0.3左右。而在30 d时,EPS总量下降为119 mg·L?1,其中蛋白质的含量为110 mg·L?1,多糖的含量为8.8 mg·L?1,PS/PN为0.08。蛋白质和多糖含量的降低可能是由于提高负荷后,颗粒污泥沉降性降低导致微生物流失引起的。在44 d,颗粒污泥逐渐成熟后,EPS总量上升为345.2 mg·L?1,其中蛋白质的含量为336.5 mg·L?1,多糖的含量为8.7 mg·L?1,PS/PN约为0.03。可以看出,好氧颗粒污泥的成熟过程伴随着EPS含量的增多和PS/PN的下降。PS/PN的持续降低是由于蛋白质的增长量相比多糖更为显著造成的,这说明在好氧颗粒污泥的形成过程中,蛋白质可能比多糖作用更大[15]。
2.2. 反应器同步脱氮除碳性能
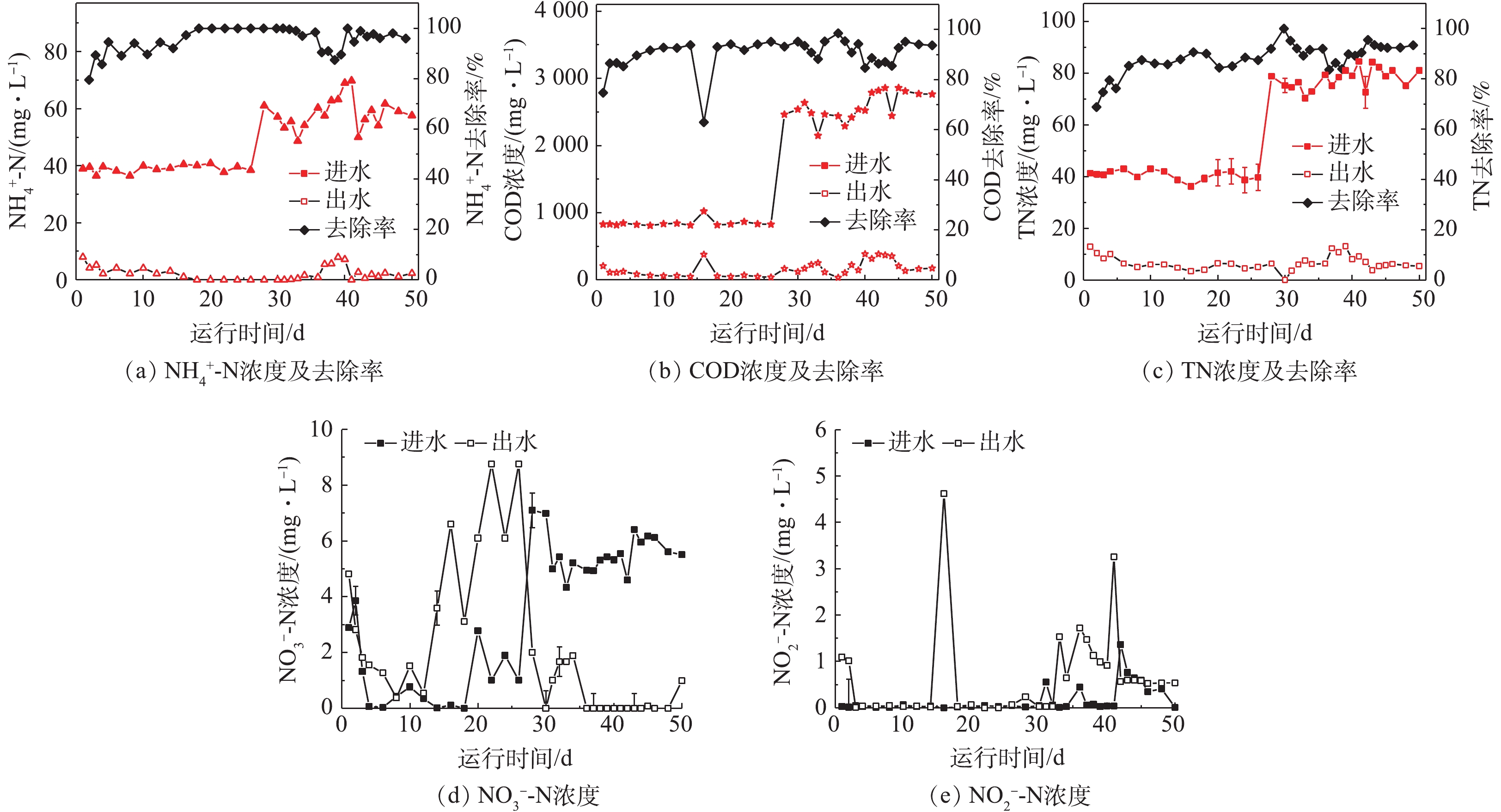
如图6所示,第Ⅰ阶段,SBR在进水COD为800 mg·L?1和2.3. 好氧颗粒污泥微生物群落结构分析
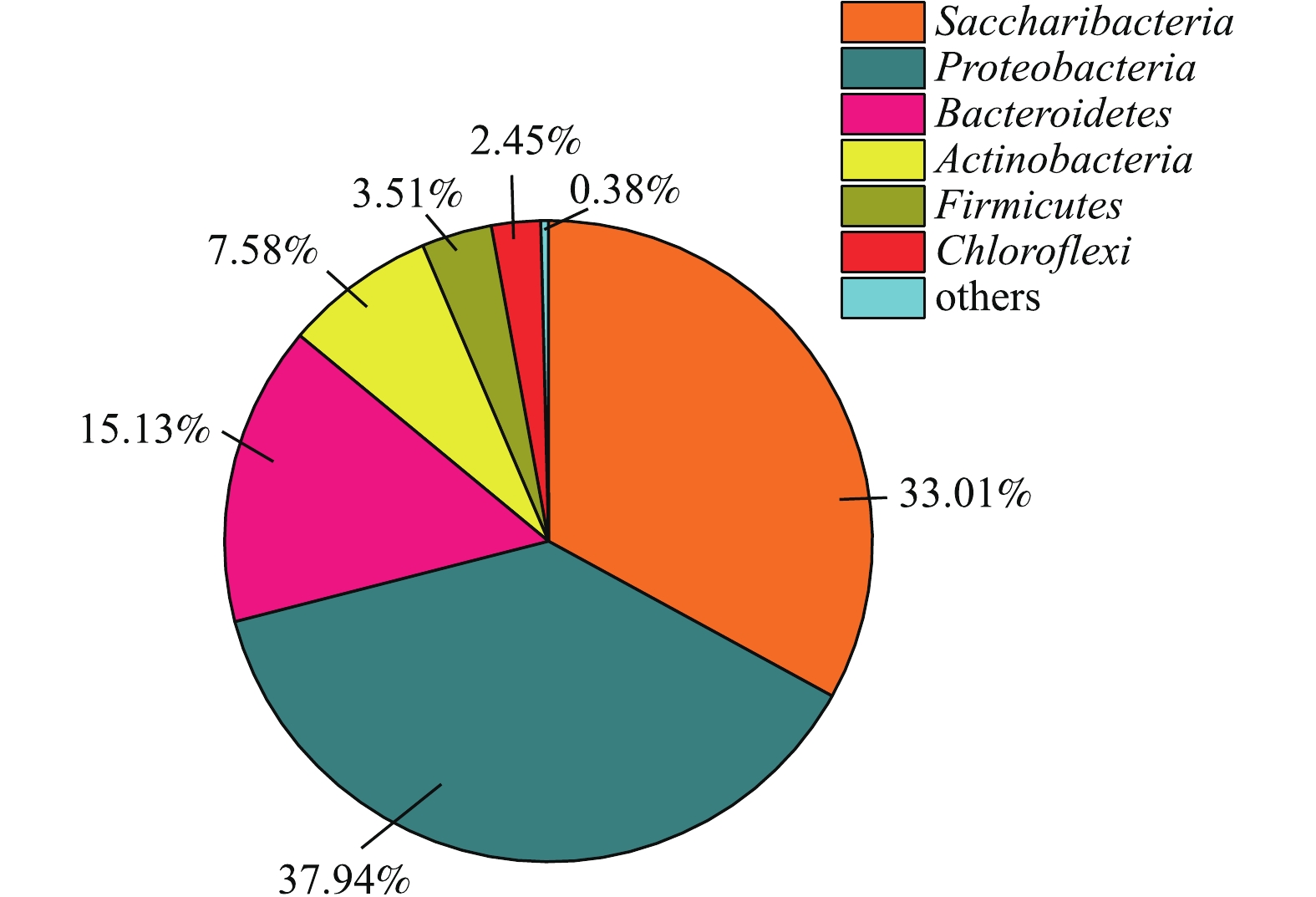
对培养46 d的好氧颗粒污泥进行高通量测序分析,按照可生物学分类的最小水平分类获得总样本数69 341条,采用Usearch软件(vsesion 7.0在门水平上(图7),颗粒污泥中的优势菌群主要为Saccharibacteria、Proteobacteria(变形菌门)、Bacteroidetes(拟杆菌门)、Actinobacteria(放线菌门)、Firmicutes(厚壁菌门)、Chloroflexi(绿弯菌门),上述菌群在总微生物中的相对丰度分别为38.01%、37.94%、15.13%、7.58%、3.51%和2.45%。杨冰[16]在SBR好氧颗粒污泥的菌群结构中发现有Saccharibacteria的存在。SEVIOUR等[17]发现,好氧污泥颗粒形成过程中Proteobacteria相对丰度增加,推测Proteobacteria在颗粒污泥中起到重要作用。刘风华等[18]通过克隆测序得到Bacteroidetes是厌氧出水培养的好氧颗粒污泥中的优势菌。高景峰等[19]在监测颗粒化过程中微生物群落动态变化时发现,相对于活性污泥,Bacteroidetes在成熟好氧颗粒污泥中整个培养时间段内的比例很高,相同的结果出现于已报道的研究[20]中。侯爱月等[21]研究发现,不同颗粒化方法培育出的好氧颗粒污泥共同的优势菌群为Proteobacteria和Bacteroidetes。杨春等[22]发现,折流板厌氧反应器(ABR)中的颗粒污泥优势菌群主要分布在Proteobacteria、Bacteroidetes、Chloroflexi。邢雅娟[23]采用高效厌氧反应器培育的颗粒污泥菌群组成中,有很高比例的Firmicutes。Actinobacteria是丝状菌,在促进污泥絮凝方面有良好的效果[24]。
在属水平上,Saccharibacteria下没有得到进一步的分类信息(unclassified)。在Proteobacteria门下,单一菌属相对丰度大于0.5%的依次为Paracoccus(副球菌属,5%)、Brevundimonas(短波单胞菌属,3.2%)、Rhodobacter(红细菌属,2.1%)、Aquimonas(水单胞菌属,1.7%)、Shinella(申氏杆菌属,1.7%)、Acidovorax(食酸菌属,0.9%)、Bdellovibrio(蛭弧菌属,0.5%)、Hydrogenophaga(氢噬胞菌属,0.5%)。远野[25]在废水碳、氮、硫污染物共脱系统中驯化的反硝化优势菌群包含Paracoccus。在膜生物反应器中,Paracoccus作为好氧反硝化菌占比最高[26]。聂毅磊等[27]从环境样品中筛选出了具有良好脱氮效果的好氧反硝化菌,属于Brevundimonas。杨浩等[28]利用16S rRNA高通量测序在雨窖水中发现了异养硝化-好氧反硝化优势菌Rhodobacter。SAHA等[29]分离出了自养硝化菌Aquimonas。潘丹等[30]从养猪场污水中筛选鉴定Shinella是异养反硝化细菌,并考察了其脱氮特性。Acidovorax是一种利用氢作为电子供体进行反硝化脱氮的异养反硝化菌[31]。Bdellovibrio作为优势菌,存在于厌氧氨氧化反应器并起到脱氮作用[32]。Hydrogenophaga等反硝化细菌实现利用固体碳源对生化池尾水进行反硝化脱氮的作用[33]。陈小军等[34]发现,在反硝化滤池生物/化学协同处理系统中,脱氮主要功能菌属包括Hydrogenophag。
在Bacteroidetes中,Flavobacterium(黄杆菌属)相对丰度高达11%。Flavobacterium是一种被广泛报道能够表征颗粒污泥成熟与否的菌属[35-36]。同时?WIATCZAK等[37]发现,Flavobacterium属细菌具有异养硝化特性,说明其对反应器的脱氮能力也有促进作用。其他相对丰度大于0.5%的菌属为Leadbetterella(里德拜特氏菌属,0.7%)和Ferruginibacter(0.6%)。Ferruginibacter被发现于潜流人工湿地中,是一种不常见的反硝化功能菌[38]。
在Actinobacteria门下,单一菌属相对丰度大于0.5%的依次为Micropruina(微白霜菌属,5.7%)和Propioniciclava(丙酸棒状体菌属,0.8%)。李建婷等[39]报道了Micropruina存在于好氧颗粒污泥中且具有很好的COD和氨氮去除能力。
在Firmicutes门下,单一菌属相对丰度大于0.5%的依次为Clostridium(梭菌属,0.9%)、Proteocatella(0.7%)、Sedimentibacter(0.5%)和Acetoanaerobium(厌氧醋菌属,0.5%)。Clostridium是低溶解氧下好氧颗粒污泥SBR内的优势菌群,与除磷过程[40]相关。Acetoanaerobium是一种能将H2和CO2转化为醋酸的厌氧菌,常出现于微生物燃料电池中。LI等[41]首次报道,Acetoanaerobium产生醋酸的过程可以为异养反硝化提供电子和碳源,从而参与到反硝化过程中。
通过群落结构分析可知,对颗粒形成有促进作用的优势菌群包括Saccharibacteria、Proteobacteria、Bacteroidetes和Bacteroidetes菌门下的Flavobacterium、Firmicutes和Chloroflexi,它们都曾作为优势菌群被发现于颗粒污泥反应器中。虽然Actinobacteria未被发现与颗粒污泥形成有直接关联,但以往研究认为,其对污泥絮凝有促进作用,这可能也有利于污泥聚集。在脱氮除碳方面,已发现的优势菌门包含丰富的异养硝化、好氧/缺氧反硝化菌属,如Flavobacterium、Paracoccus、Rhodobacter等;还存在可以降解有机物、提供电子参与反硝化过程的优势菌属,如Acetoanaerobium。这些微生物被高负荷环境筛选出来,在高COD和高C/N条件下,完成了同步脱氮除碳过程,说明它们彼此之间能够协作处理,实现此类污水的处理。同时,在好氧颗粒污泥的群落结构中,自养硝化细菌(如Nitrosomonas(亚硝化单胞菌属))并未成为优势菌属,这也进一步说明异养硝化-好氧/缺氧反硝化可能在好颗粒泥污中起着重要作用。
2)在C/N=20时,SBR中COD、
3)在高负荷下,反应器内促进颗粒化的菌门得到充分增长并成为优势菌群,包括Saccharibacteria、Proteobacteria、Bacteroidetes、Actinobacteria、Firmicutes和Chloroflexi。同时,在颗粒污泥中检测到许多异养硝化、好氧/缺氧反硝化优势菌属,表明异养硝化-好氧/缺氧反硝化脱氮可能存在于好氧颗粒污泥中。
参考文献



 下载:
下载: 

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图