全文HTML
--> --> --> 挥发性有机化合物(volatile organic compounds,VOCs)来源广泛且难降解,对全球气候变暖起着推动作用[1-3],芳香族和脂肪族有机化合物是VOCs的重要组分[2-4],有研究[5]表明,苯系物占目前大气中排放的挥发性有机污染物总量的50%以上。氯苯类(chlorobenzenes,CBs)物质在农药、染料和其他化学品制造中作为溶剂和反应物被广泛使用,在环境中广泛存在[6-7]。间二氯苯作为氯代苯系物的一种,具有刺激性气味,能够引发头晕、恶心等症状[8],具有生物毒性,可以导致生物体内内分泌紊乱、各项机能失调、神经行为和发育紊乱,甚至存在致癌的风险[9],被美国环境保护署归为优先污染物[10]。生物净化氯苯因其无二次污染、操作简单、处理效果好等优点,越来越受到人们的关注[11-13]。生物法处理氯苯,就是将废气中氯苯与载体上的生物膜充分接触,通过微生物的代谢将废气中有害的氯苯转化为无害的物质(CO2、水等)[14]。生物净化法在水溶性较好或者恶臭气体的工程应用方面效果显著,欧洲约有8 000座废气生物净化装置投入运行,对VOCs的去除率可以达到90%以上[15-16]。目前,生物净化苯系物的目标物主要是易于生物降解且毒性较低的物质,包括苯、甲苯、乙苯和二甲苯等,对于CBs的生物净化处理研究[17-21]还不够深入。针对不同种类的VOCs,筛选和分离纯化出具有特殊效果的菌株尤为关键。许多国内外****在获得和选育VOCs高效降解菌方面做了大量的研究工作,已报道的菌株主要分为霉菌和真菌2种:霉菌包括青霉属[22]、外瓶霉属[23];真菌包括假单胞菌属[24]、肠杆菌属[25]、克雷伯氏菌[26]等。本研究从芦苇根系土壤中筛选出1株能够以间二氯苯为唯一碳源和能源的优势降解菌(Brevibacillus agri),考察其在生物滴滤器中降解间二氯苯的性能,研究空床停留时间、进气浓度和进气负荷等因素对生物滴滤器降解性能的影响,确定优势菌株在生物滴滤器微生物群落结构中的占比,为工业化处理间二氯苯提供参考。
1.1. 菌株来源
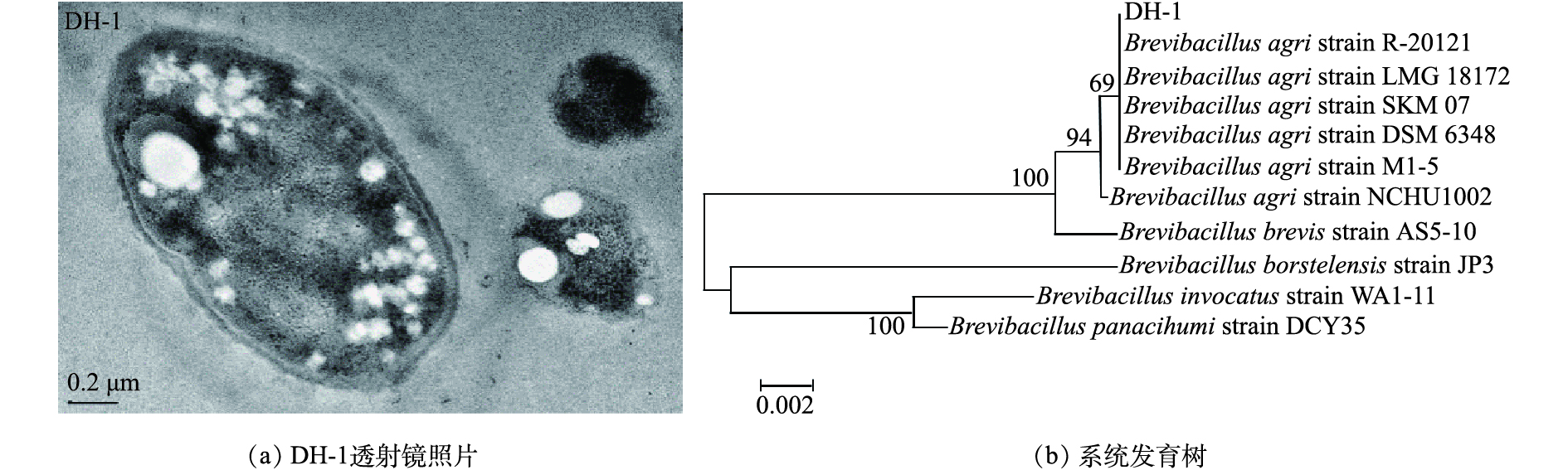
本菌株取自盐城工学院盆栽1年芦苇根际土壤,经初筛、复筛、富集培养驯化而得,整个培养过程均在超净工作环境下进行。按照研究中的方法[27-28],对筛选出的间二氯苯优势菌进行形态观察和生理生化实验分析。筛选即将分离自土壤中的菌株,用6 mm无菌滤纸片吸收培养液后,贴于选择培养基上,在37 ℃培养2 d后,滴加AgNO3溶液,根据滤纸片周围生长圈和显色圈大小,判断菌株的降解能力。挑取降解能力较大的一些菌株降解间二氯苯,使用气相色谱仪,测试间二氯苯的剩余浓度,得到降解能力较好的菌株,标号为DH-1。菌株单体面积为0.96~1.5 μm2,有荚膜,有芽孢,有鞭毛;菌落呈现圆形,乳白色黏稠状,边缘光滑,表面平滑,培养基不变色。如图1所示,用透射电镜观察菌株,呈杆状,有芽孢,形态饱满。菌株的生理生化实验鉴定结果都为淀粉水解阳性、革兰氏阴性、明胶水解阳性、甲基红阴性以及伏-普实验阴性。以DH-1的基因序列构造系统发育树,通过分析可知,菌株DH-1属于土壤短芽孢杆菌(Brevibacillus agri)。1.2. 培养基和化学试剂
筛选鉴定所需培养基:富集培养基(蛋白胨10.0 g·L?1,酵母膏5.0 g·L?1,NaCl 10.0 g·L?1)、无机盐培养基(K2HPO4·3H2O 13.75 g·L?1,KH2PO4 1.8 g·L?1,(NH4)2SO4 1 g·L?1)、LB固体培养基(琼脂15.0 g·L?1,蛋白胨10.0 g·L?1,酵母膏5.0 g·L?1,NaCl 10.0 g·L?1)。生理生化实验所需试剂:卢戈氏碘液、结晶紫染液、乙醇、番红复红液、甲基红试剂、KOH、α-萘酚溶液(5%)。
1.3. 分析方法
在无机盐培养基(50 mL)中,添加土壤短芽孢杆菌均匀菌液和间二氯苯(经丙酮助溶),按照不同实验条件恒温培养,直至适当时间终止培养。在波长为600 nm下,使用紫外分光光度计测量吸光度,测得值即为菌液浓度OD600值。采用顶空法,在气相色谱仪(Clarus580,PerkinElmer,美国)上记录间二氯苯峰面积,外标法得出间二氯苯的剩余浓度值[29]。气相色谱工作条件如下:色谱柱为石英毛细管色谱柱(30 m×0.32 mm×0.5 μm),柱温采用程序升温方式,初温40 ℃保持4 min,经过40 ℃·min?1,达到终温220 ℃;1 μL汽化室温度为300 ℃,检测器温度为300 ℃,载气流速为1.0 mL·min?1,分流比为60∶1[30]。所有实验均重复3次。
使用傅里叶红外光谱仪(fourier transform infrared spectroscopy,FTIR)和X射线光电子能谱仪(X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy,XPS)对细菌表面官能团进行表征分析。菌体经冷冻干燥后,磨成粉末,得到生物样品,送至盐城工学院分析测试中心进行检测。
菌株的16S rRNA基因序列的同源性分析鉴定一般分为2步:第1步提取DNA;第2步将DNA进行PCR扩增,得到16S rRNA基因序列,最后对序列进行分析鉴定。产物进行电泳检测,整个菌种测序工作由上海生工生物工程技术服务有限公司完成。
1.4. 废气处理装置和流程
实验所用小试规模的生物滴滤器(biotrickling filter, BTF)结构如图2所示。包括有机玻璃柱(高度1 000 mm,外径200 mm,壁厚2.5 mm)、填料(2层圆柱形聚氨酯海绵结构,高度 300 mm)、矩形槽(营养池,长度400 mm,宽度300 mm,高度 200 mm)。将生物填料连续喷洒10 L·h?1的再循环水相从营养池中喷出,下方的多孔承载板(孔径10 mm)既保护填料避免脱落,也保证气体和营养液轻易通过。为了确保工艺条件,循环营养液由液压泵提升至喷淋口,间二氯苯经挥发槽鼓泡混合清洁空气而形成模拟气体,通过调节流量计来控制模拟气体间二氯苯的质量浓度。2.1. 优势菌最佳生长条件的确定
在50 mL的无机盐培养基中添加130 mg·L?1的间二氯苯,控制降解时间、菌液接种量、pH和温度4个变量,确保OD600值在0.2~0.8,测定不同条件下的菌液浓度OD600值和间二氯苯剩余浓度。结果显示,OD600值和间二氯苯去除率曲线趋势一致,在菌液浓度达到最高的同时,间二氯苯的去除率也能达到峰值,此时对应的横坐标变量值即为最佳条件下的变量条件。在48 h,控制其他3个变量不变,在不同降解时间、菌液接种量、pH和温度条件下,OD600值可达0.51、0.44、0.42和0.39,间二氯苯去除率可达85.46%、84.28%、81.05%和83.51%。实验结果表明,菌株DH-1降解间二氯苯的最佳条件为:降解时间48 h,菌液接种量10%,pH=7,温度25 ℃(图3)。2.2. 生物滴滤器的启动
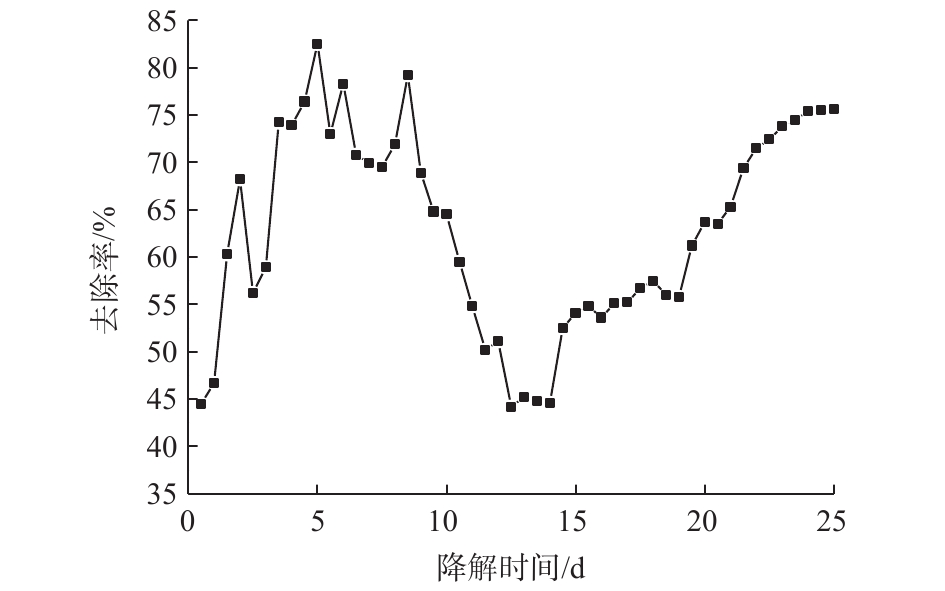
在2.1节的最佳生长条件下,考察生物滴滤器在启动阶段的性能。运行前期,BTF性能不稳定,间二氯苯的去除率呈现很大的波动性。在图4中,随着进气浓度的逐渐升高,菌株对有机废气的耐受能力时强时弱,导致在0~8 d过程中间二氯苯的去除率时高时低。在9~14 d过程中,高浓度间二氯苯废气使菌株受到了毒副作用,BTF去除率大幅衰减。BTF的去除率在运行22 d后,达到70%以上,并趋于稳定,这是因为菌株耐受能力增强后大量繁殖导致的。第20天时,当进气浓度达到1 000 mg·m?3时,BTF的去除率为63.7%;运行25 d后,BTF的去除率达到75.6%,且趋于稳定,说明此时BTF挂膜成功,启动阶段完成。2.3. 生物滴滤器的稳定运行
生物滴滤器处理间二氯苯废气实验运行了125 d,包括启动运行阶段和稳定运行阶段。启动25 d后,反应器进入稳定运行阶段,总计运行100 d。1)空床停留时间对间二氯苯去除率的影响。空床停留时间(empty bed residence time, EBRT)为生物滴滤塔容积与进气流量的比,进气流量决定了EBRT,是影响传质的重要因素[31]。在相同进气负荷(intake load rate, ILR)条件下,即当生物滴滤器中ILR为4.55~122.57 g·(m3·h)?1时,研究不同EBRT对去除率的影响。由图5可见,降低空床停留时间,BTF的去除率会显著下降。当EBRT为90 s时,BTF的去除率可以维持在80%以上,这是由于停留时间较长,微生物能够捕捉更多废气中的间二氯苯分子。随着EBRT的减少,微生物较少地甚至来不及捕捉间二氯苯分子,因此去除效果变差。在EBRT为30、60和90 s时,数据表明在相同ILR、较长的EBRT下可以获得较高的去除率。
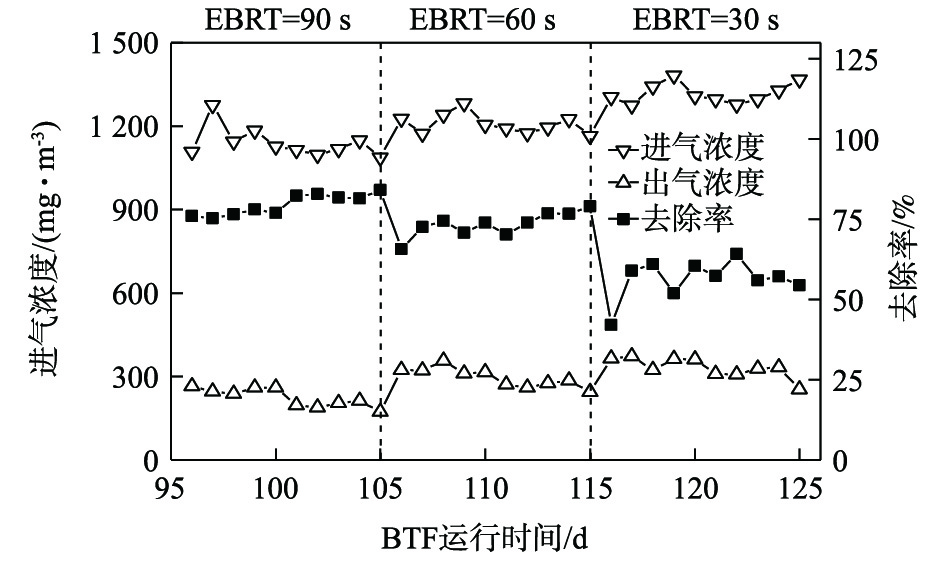
2)进气浓度对间二氯苯去除率的影响。当进气浓度过低时,当微生物得不到充足的碳源,生长迟缓;当进气浓度过高时,微生物被严重毒害,生物膜提前老化。适宜的进气浓度范围是考察BTF性能的关键因素。当进气浓度从1 107.7 mg·m?3增加至1 383.28 mg·m?3时,出气浓度从173.18 mg·m?3上升到371.89 mg·m?3(图6)。在EBRT为90 s时,进气浓度维持在1 100 mg·m?3左右,出气浓度曲线逐渐走低,去除率在运行后期达到75%以上。在EBRT为30 s时,进气浓度渐渐升高至1 383.28 mg·m?3,出气浓度也不断升高,去除效果变差,去除率低于60%;生物菌受到高浓度间二氯苯气体的毒害作用,失去活性甚至衰弱死亡,BTF去除率过低,表明该范围浓度不适合BTF的稳定运行。每次改变EBRT,去除率都会发生明显的改变,这是由生物降解体系有一定的滞后性引起的,EBRT越短,滞后性越明显[32]。当EBRT较短时,进气浓度升高,BTF的去除效果降低,耿凤华等[33]也得出了类似结论。
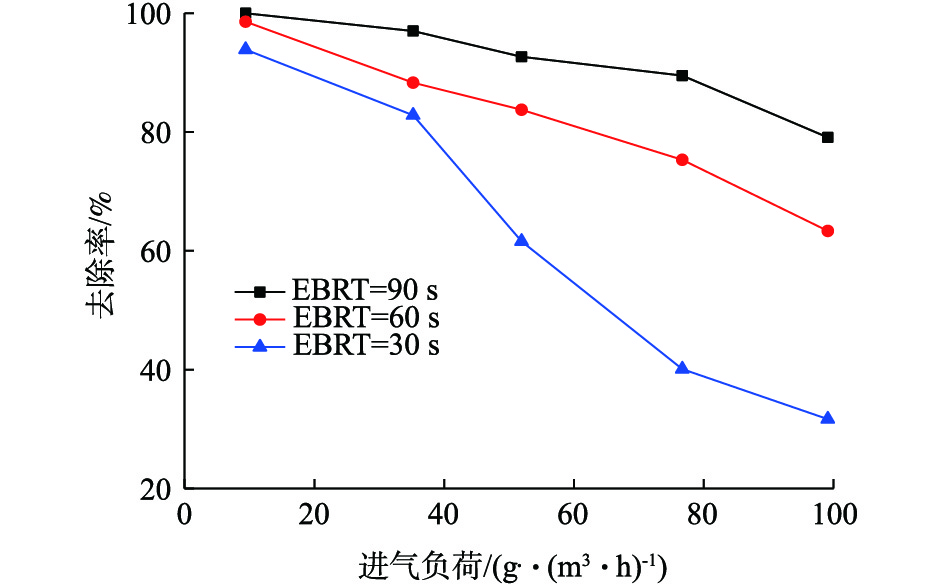
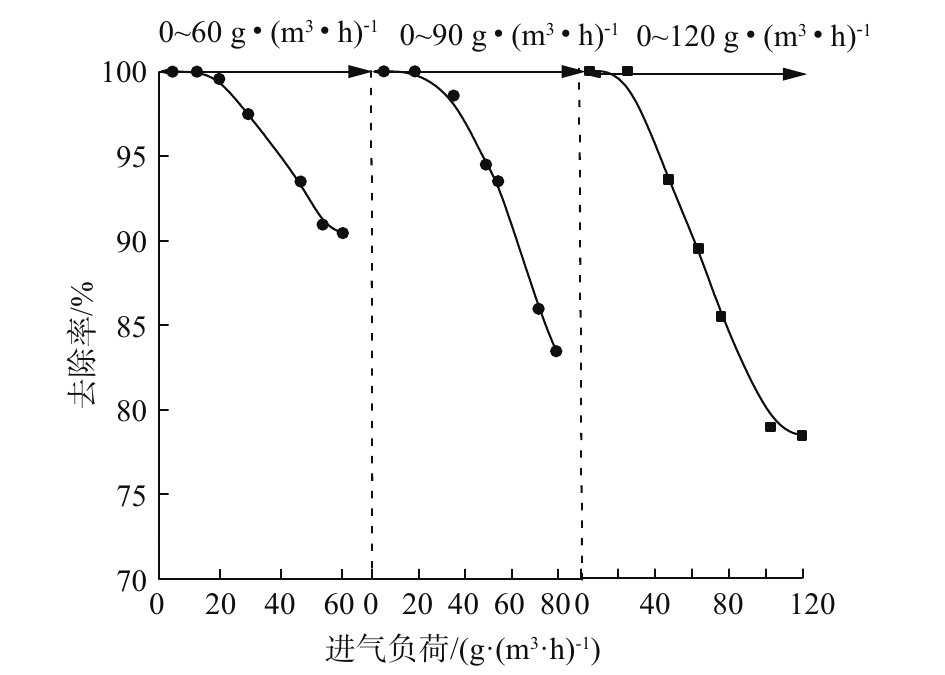
3)进气负荷对间二氯苯去除率的影响。在EBRT为90 s时,研究不同进气负荷(ILR)对去除率的影响,确定微生物降解的最佳进气负荷范围(如图7所示)。当BTF中进气负荷(ILR)为4.55~60.32 g·(m3·h)?1、4.95~79.23 g·(m3·h)?1、4.75~119.78 g·(m3·h)?1时,在EBRT为90 s时,间二氯苯的去除率降幅明显。在低浓度进气负荷范围内,去除率数据点比较集中,在90%以上,这是由于微生物充分利用了低浓度间二氯苯提供的碳源,提高了间二氯苯的去除率。在高浓度进气负荷范围内,去除率曲线迅速下降,相比低浓度范围的ILR,ILR为4.75~119.78 g·(m3·h)?1,去除率降速明显,这是由于高负荷的间二氯苯废气对微生物产生了抑制作用。研究结果表明,在相同EBRT下,ILR的增加不利于间二氯苯在BTF中的去除,最佳进气负荷为4.55~60.32 g·(m3·h)?1。
2.4. 菌株表面官能团分析
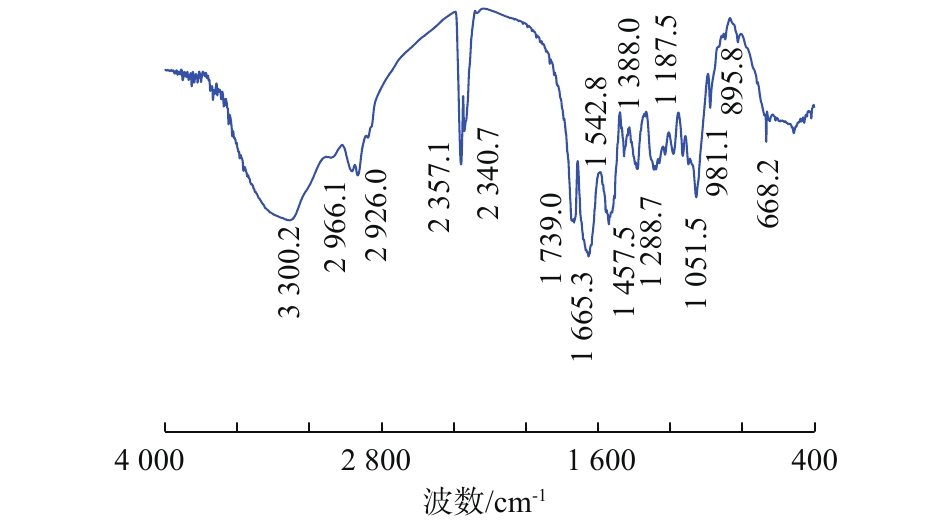
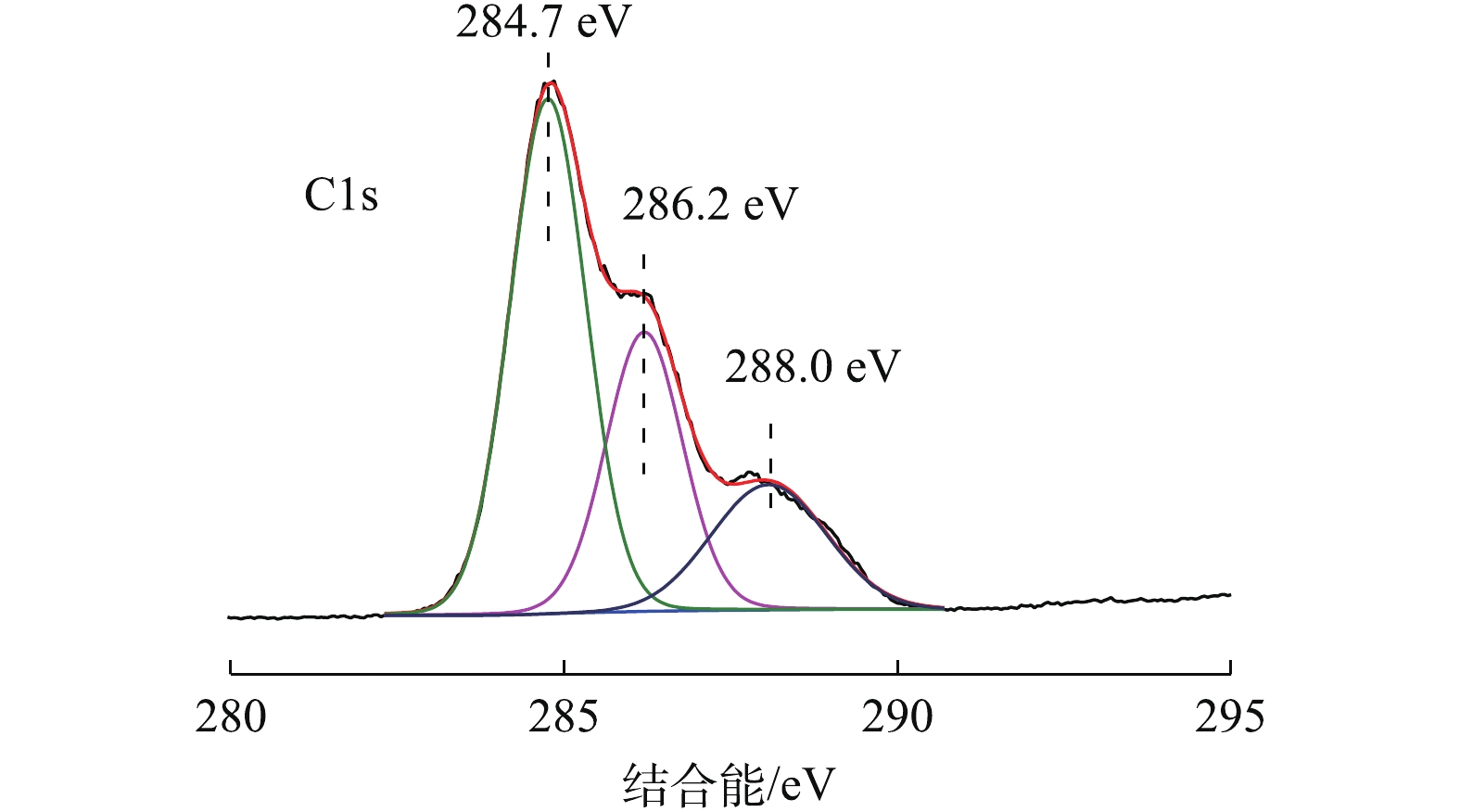
从2.3节已经得知菌株DH-1对间二氯苯的降解能力,可以使用FTIR和XPS,分析间二氯苯在BTF中稳定运行阶段菌株表面的变化情况。采集填料表面菌体按照1.3节中的方法制成生物样品,进行FTIR和XPS表征。从傅里叶红外光谱图(图8)可以看出,在指纹区,波数在900~600 cm?1处,主要是亚甲基的面内摇摆振动和芳环的面内振动,波数895.8 cm?1对应的是间位取代苯环吸收峰,且峰形较弱,说明菌体表面存在间二氯苯分子。在1 300~900 cm?1处,主要存在C—H的面外弯曲振动(981.1 cm?1),游离—OH (1 051.5 cm?1)在官能团区的1 500~1 300 cm?1处,存在甲基的弯曲振动(1 385 cm?1附近)和亚甲基的剪式弯曲振动(1 460 cm?1附近);在2 000~1 500 cm?1和1 542.8 cm?1处,存在来自氨基酸中的C=NH,且峰形较宽;在1 665.3 cm?1处,存在来自羧酸的C=O的伸缩振动,在1 739 cm?1处,存在酸酐;在2 500~2 000 cm?1处,主要出现了1个特征峰,由于峰比较强且尖锐,说明是C=NH或者=NOH;在4 000~2 500、2 966.1和2 926 cm?1处分别是甲基和亚甲基的反对称振动;在3 400~3 200 cm?1处,由于形成氢键导致波数向低频移动,产生了1个很宽的羟基吸收峰。通过官能团区的峰形分析得出,间二氯苯在菌株表面被降解的同时,还与菌株中的蛋白质存在相互键合作用,且逐渐被菌株开环降解。图9为XPS C1s轨道能谱图。由此可以看出,C主要有3种峰,结合能284.7 eV处为芳香碳,286.2 eV处为C—OH,288.0 eV处为C=O且偏移了0.8 eV(文献值为287.3 eV[34])。XPS数据证实了FTIR的结果:间二氯苯在降解过程中,逐渐被羧酸化后开环降解。
2.5. 菌系结构的变化
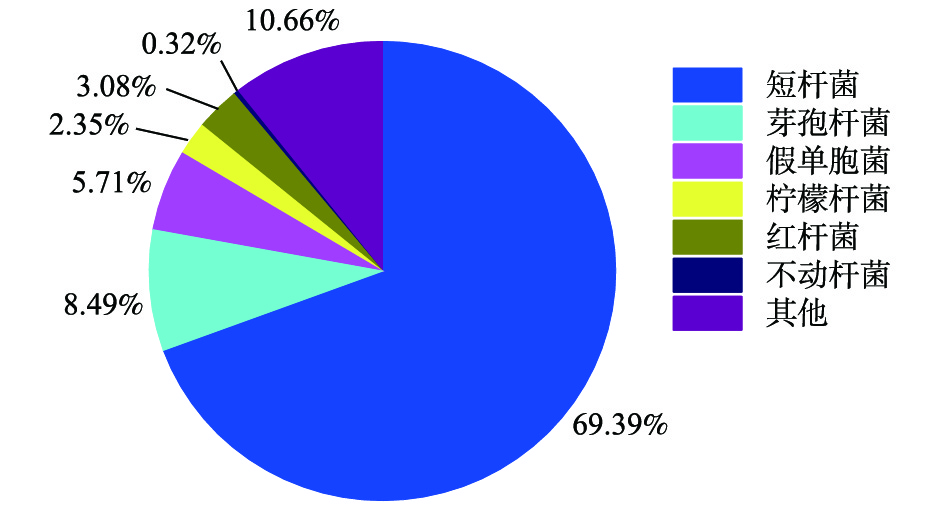
为了研究土壤短芽孢杆菌DH-1在BTF中的含量以及BTF中菌系群落结构的变化,在稳定期间,从BTF中采集填料表面菌体,进行基因序列的同源性分析鉴定[35]。由图10可以看出:短杆菌种类占69.39%,在微生物群落中占优势;在BTF中也存在其他菌株,包括8.49%芽孢杆菌、5.71%假单胞菌、2.35%柠檬酸杆菌、3.08%红杆菌和0.32%不动杆菌等。在稳态操作期间,土壤短芽孢杆菌(Brevibacillus)种群在BTF的细菌群落中占比最大,表明土壤短芽孢杆菌DH-1在BTF中对间二氯苯降解发挥着极大的作用。同时该研究结果也表明,菌株DH-1在未来的工业应用中对间二氯苯废气的连续处理将会是有效的。2)在空床停留时间为90 s、进气浓度为1 000 mg·m?3、进气负荷为60 g·(m3·h)?1条件下,间二氯苯的去除率可以维持在85%以上。说明较长的EBRT、较低的进气浓度和进气负荷下可以获得较高的去除率。
3)在稳定运行期间,菌体表面官能团的变化表明,间二氯苯在降解过程中被加氧羧化后,逐步被生物降解;生物滴滤器中土壤短芽孢杆菌占比达69.39%,在BTF的细菌群落中占主导地位,并可以良好生长。
参考文献


 下载:
下载: 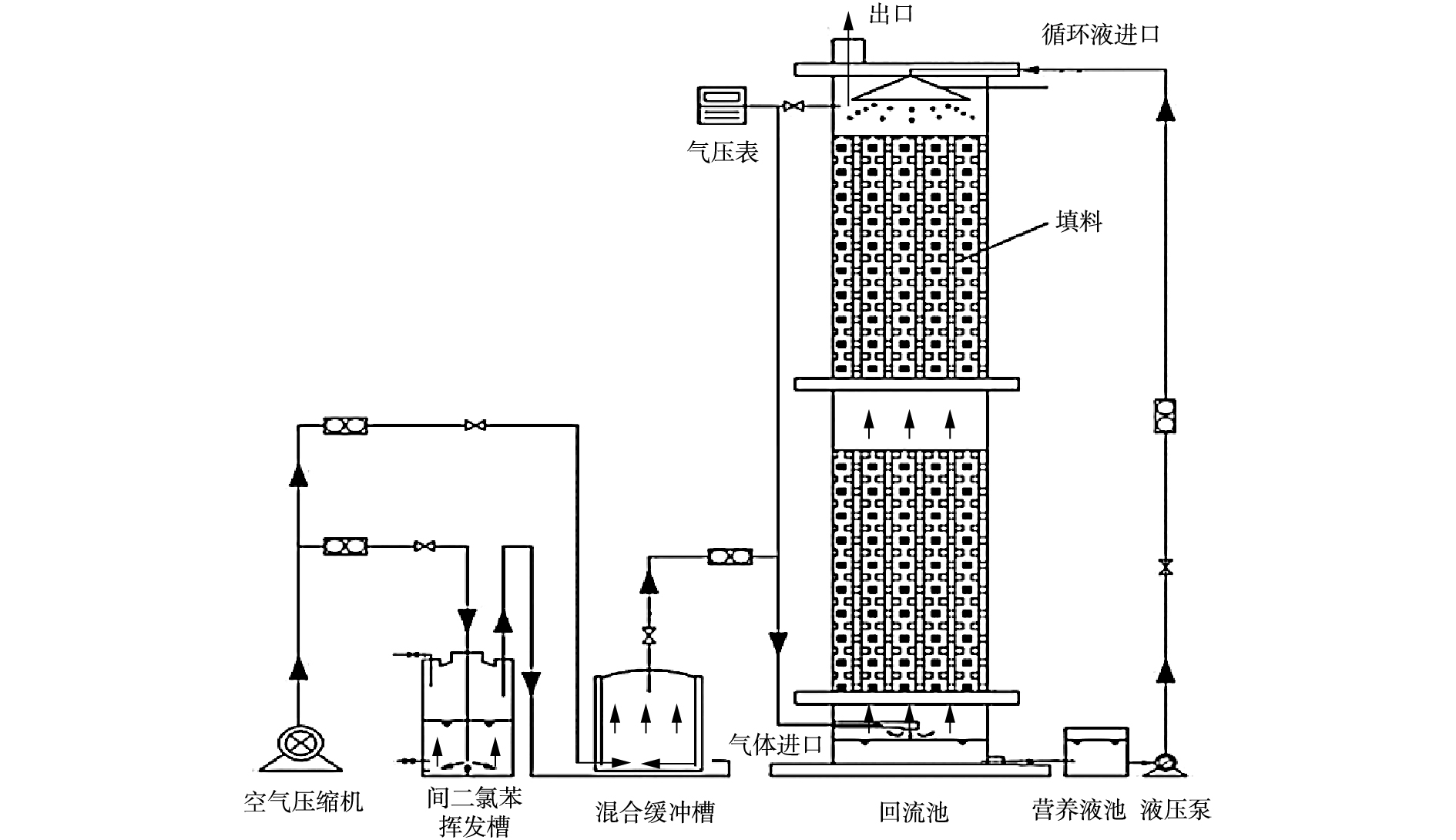

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图