全文HTML
--> --> --> 农村污水的分质收集处理是农村污水资源化的重要方式。农村生活污水按照其污水来源和水质特征的不同,可以大致分为灰水和黑水2大类。其中,灰水是指不包括冲厕污水(黑水)在内的生活杂排水,主要包括餐厨污水、洗涤污水和洗浴污水等[1-2]。灰水由于基本不含肠道病原微生物、污染物浓度较低且易于自然生物处理的特点,具有很高的直接回用价值[1]。为缓解水资源压力,灰水单独采用管道收集并直接用于灌溉的回用方式已经得到了一定的应用[3]。而农村污水治理工程设施投资中的管道敷设成本占所有建设投资的70%以上,管道敷设成本过高直接限制了农村地区污水收集治理工作的有效开展[4-5]。小管径重力流排水系统具有管道成本低、施工开挖土方量少、建设迅速等诸多优点,非常适用于经济条件相对落后的农村地区[6-7]。基于此,小管径重力流灰水管道系统具有明显的经济优势和生态环境效益,具有较大的推广潜力和应用前景。排水管道生物膜具有一定的污水预处理功能,并且可能产生CH4、H2S等具有环境和健康风险的气体,对于市政排水管道生物膜的微生物群落特征已经有了相对广泛的研究[8-10]。然而,农村污水特征与市政排水相比,其水质水量具有明显的随时间变化规律,即每天在用餐时段污水水量较大,而夜间基本没有污水排放[11]。具体到管道容量较小的小管径系统中,在早中晚时段,污水排放高峰期,管道经常临近满管流状态;而在夜间,基本处于断流状态。不同的流态决定了不能直接套用市政污水管道生物膜数据来解析农村污水管道生物膜,当前对于农村污水管道生物膜的认识仍处于起步阶段,更是罕有针对农村灰水管道生物膜的研究。
本研究采用实验室规模的小管径重力流灰水管道系统,研究了小管径重力流灰水管道生物膜的细菌群落、氮硫循环管道功能菌特征以及氮循环功能基因分布情况,重点探讨了管道敷设坡度对于小管径重力流灰水管道生物膜细菌群落的影响。本研究丰富了排水管道生物膜认知体系,为小管径重力流灰水管道的优化设计和应用提供了参考。
1.1. 实验装置
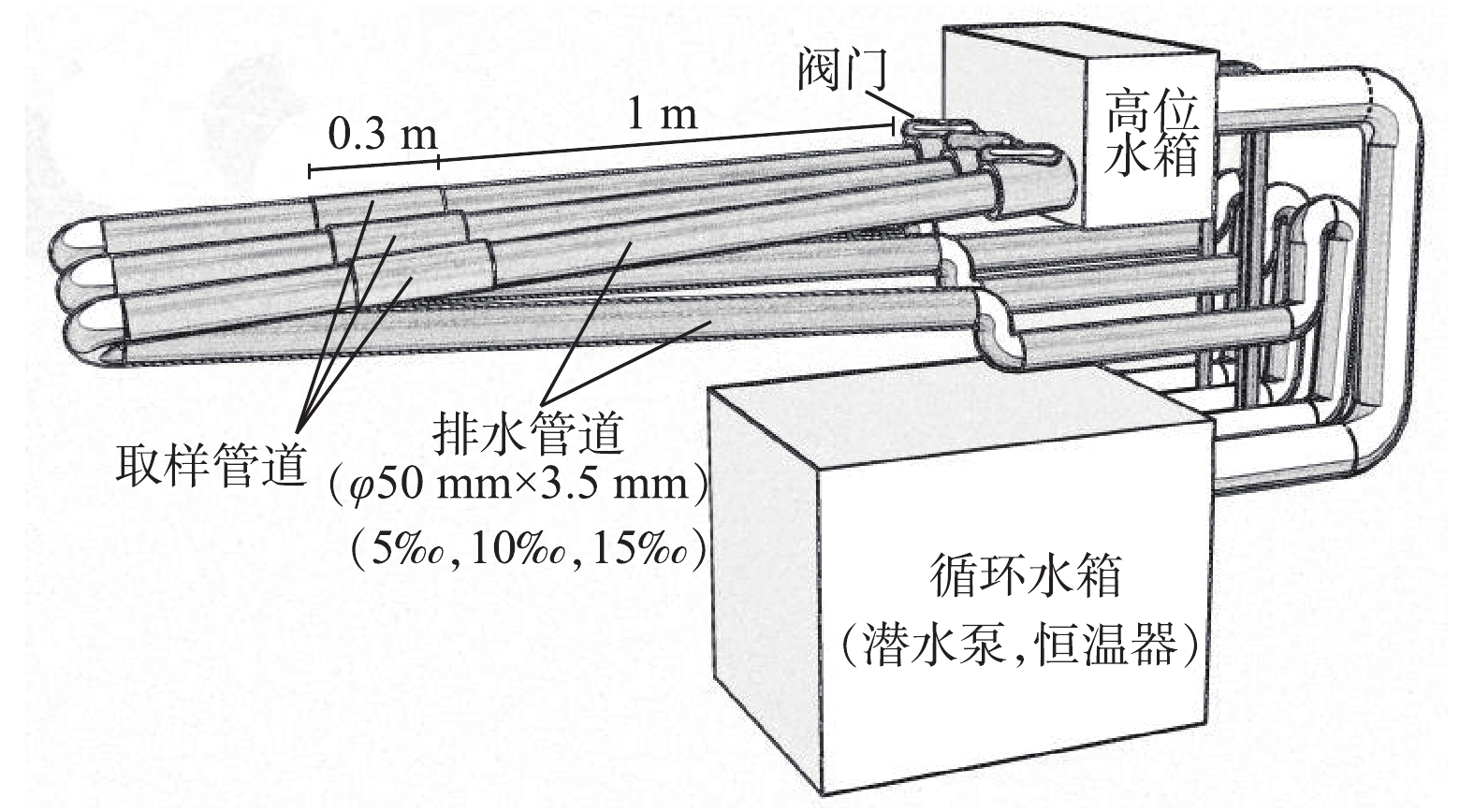
本研究采用的实验装置为实验室规模的小管径重力流管道模拟系统。整个系统由3套不同敷设坡度(5‰,10‰,15‰)的透明UPVC排水管道系统(φ50 mm×3.5 mm,单组管道总长5 m,溢彩,中国)、PVC阀门(百盛,中国)、高位水箱(PVC板自制)、循环水箱(PVC板自制)、潜水泵(HQB-5000,森森,中国)、恒温器(300 W,YEE,中国)等组成(图1)。灰水由潜水泵经循环水箱提升至高位水箱,沿排水管道依靠重力作用流下,最终回到循环水箱。灰水在整套系统中循环流动,模拟小管径重力流灰水管道的生物膜生境,同时保证了3套管道中的灰水水质相同,有效避免了水质差异造成的生物膜群落结构差异。为进行生物膜取样,在距直管道起点1 m处设置30 cm长的取样管道,两侧采用50 mm PVC活接头(联塑,中国)连接,确保取样管道的轴线与直管道重合。1.2. 水质特征及分析测试方法
为模拟实际农村灰水在小管径重力流管道中的真实流态,本研究利用调节潜水泵功率和阀门开闭的方式保持管道内的充满度随时间有规律的变化,管道实际充满度和平均灰水流速如图2所示。整个实验设备的运行水温维持在20 ℃并保持避光运行,以模拟真实的灰水管道运行状态。本研究进水采用人工配制的灰水,配制方法见表1。每2 d换水一次,运行水质条件见表2。整套设备连续运行60 d,形成成熟的管道生物膜。相关研究[12-13]表明,经过60 d的连续运行,排水管道生物膜可以发育成熟。连续运行后,在第60天拆卸取样管道,用经过灭菌处理的药匙刮下少量位于管道内表面底部的生物膜样品,置于无菌离心管中,迅速置于4 ℃冰箱中保存,用于生物膜样品的形貌观测。另取3份平行样品,迅速置于4 ℃便携式恒温箱(FYL-12MC-B4,福意联,中国)中临时暂存,在0.5 h内,转移至?80 ℃冰箱中保存,用于生物膜细菌的群落分析,取3份平行样品群落分析结果的算术平均值。
将生物膜样品浸没于2.5%的戊二醛溶液中,4 ℃避光静置24 h。然后依次利用25%、50%、75%、95%和100%的乙醇溶液进行梯度脱水,最后于?50 ℃中冷冻干燥,制得扫描电镜样品。将样品喷碳后,置于JSM-5610LV型扫描电镜(JEOL,日本)下,分析生物膜样品的形貌特征。
采用PowerSoil? DNA Isolation Kit (MoBio,美国)试剂盒提取生物膜样品的DNA,并利用细菌16S rRNA通用引物338F和806R进行PCR扩增。总PCR反应体系的体积为20 μL,包括超纯水13.25 μL,10×PCR ExTaq Buffer 2.0 μL,DNA模板(100 ng·mL?1)0.5 μL,引物338F和806R (10 mmol·L?1)各1.0 μL,dNTP 2.0 μL, ExTaq (5 U·mL?1) 0.25 μL;在95 ℃中维持5 min,继而进行30个扩增循环,每个循环包括95 ℃孵育30 s,58 ℃孵育20 s,72 ℃孵育6 s;最后在72 ℃维持7 min,得到扩增产物。扩增产物经纯化定量回收后,采用Illumina HiSeq 2500 (Illumina,美国)高通量测序平台进行测序分析。细菌高通量测序结果以97%的相似度划分为分类操作单元(OTU),获得的OTU与细菌Silva分类学数据库比对,得到细菌群落组成信息。DNA提取和高通量测序工作由北京百迈客生物科技有限公司完成,高通量测序数据通过百迈客云计算平台进行处理和分析(
将细菌16S rRNA测序结果与Greengenes分类学数据库比对后形成的OTU文件(97%相似度)上传至PICRUSt在线分析网站(
2.1. 灰水管道内胶状生物膜的形貌结构
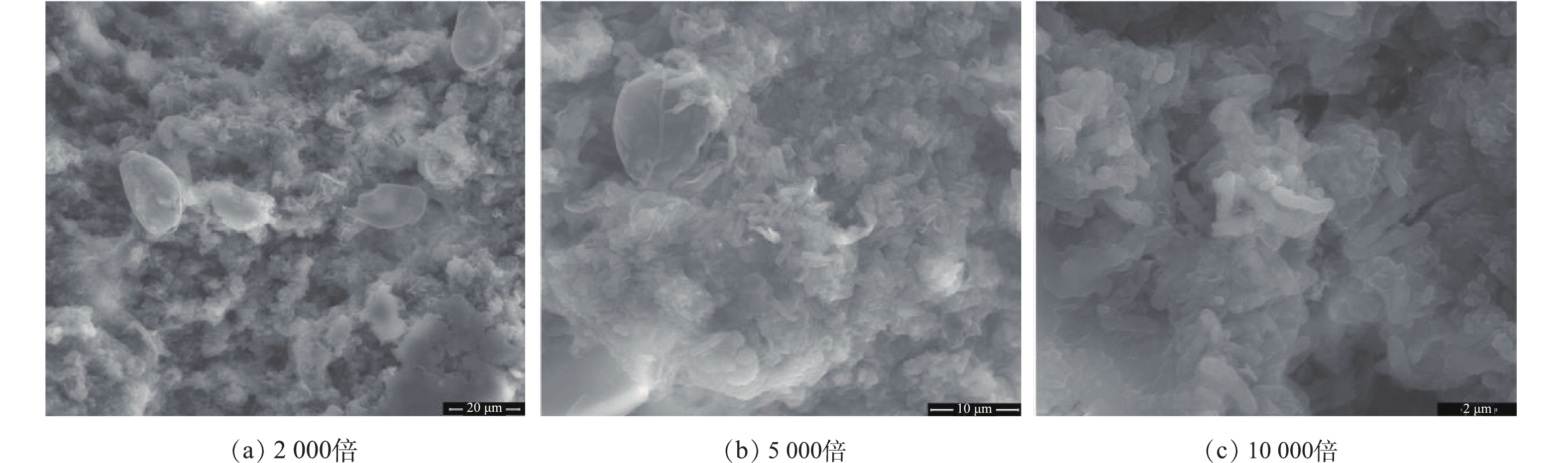
经过60 d的连续运行,小管径重力流灰水管道内壁形成了厚度相对均匀的淡黄色的胶状生物膜。生物膜的扫描电镜结果如图3所示。可以看出,脱水后的灰水管道生物膜呈粗糙的表面结构,生物膜中分布着大量的不同种类的细菌、真菌、原生动物和胞外聚合物(EPS),灰水管道生物膜中的微生物以细菌为主,细菌种类多样,杆菌球菌密布,覆盖了整个生物膜表面。真菌数量相对较少,但仍广泛分布在灰水管道生物膜中。观察到的原生动物体表有六边形鳞片构成的外壳,从形貌特征上分析可能为网足属原生动物。原生动物的大量出现表明经过60 d的连续运行,灰水管道生物膜已经形成了复杂的微型生态系统,确认了此时生物膜已经成熟。2.2. 灰水管道胶状生物膜的细菌群落结构
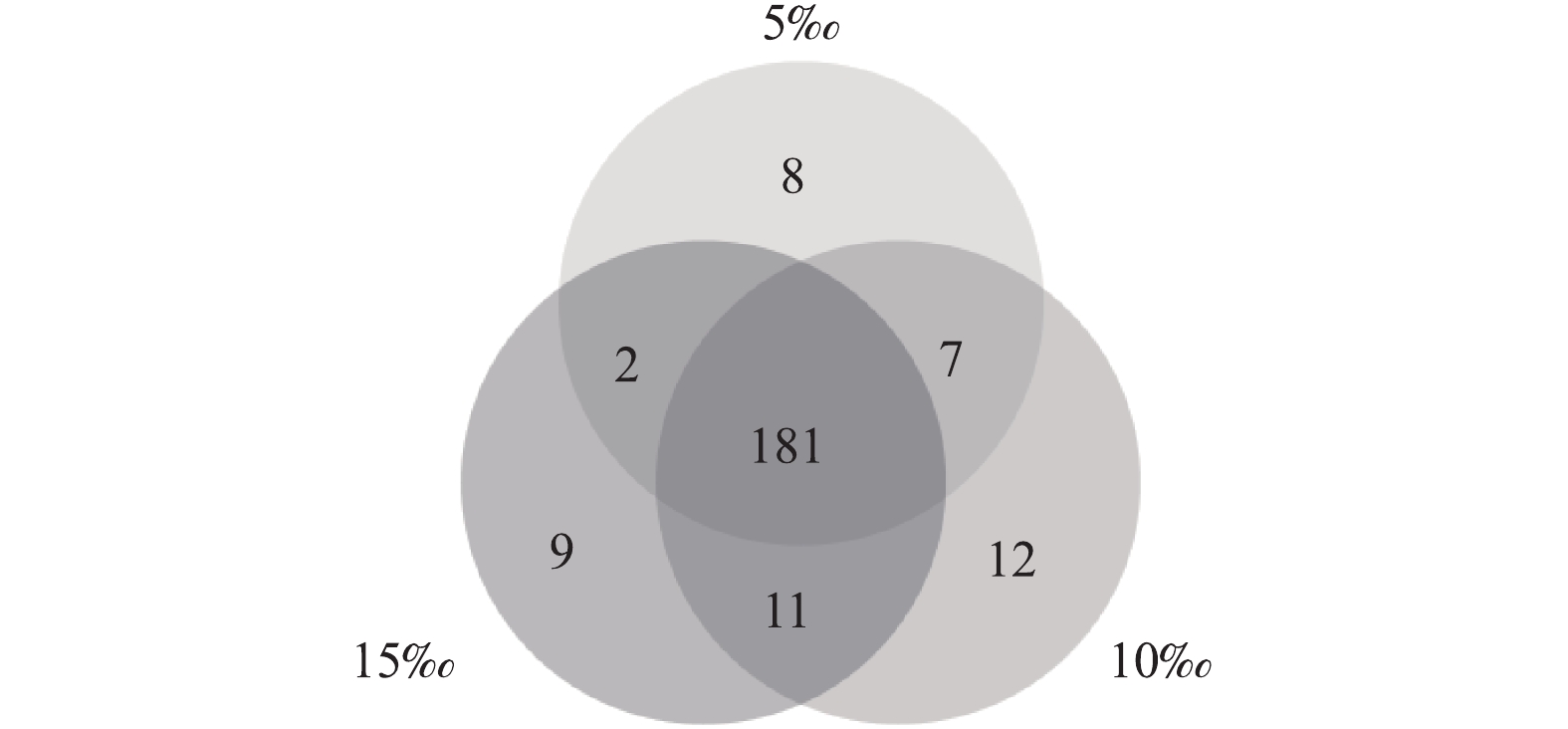
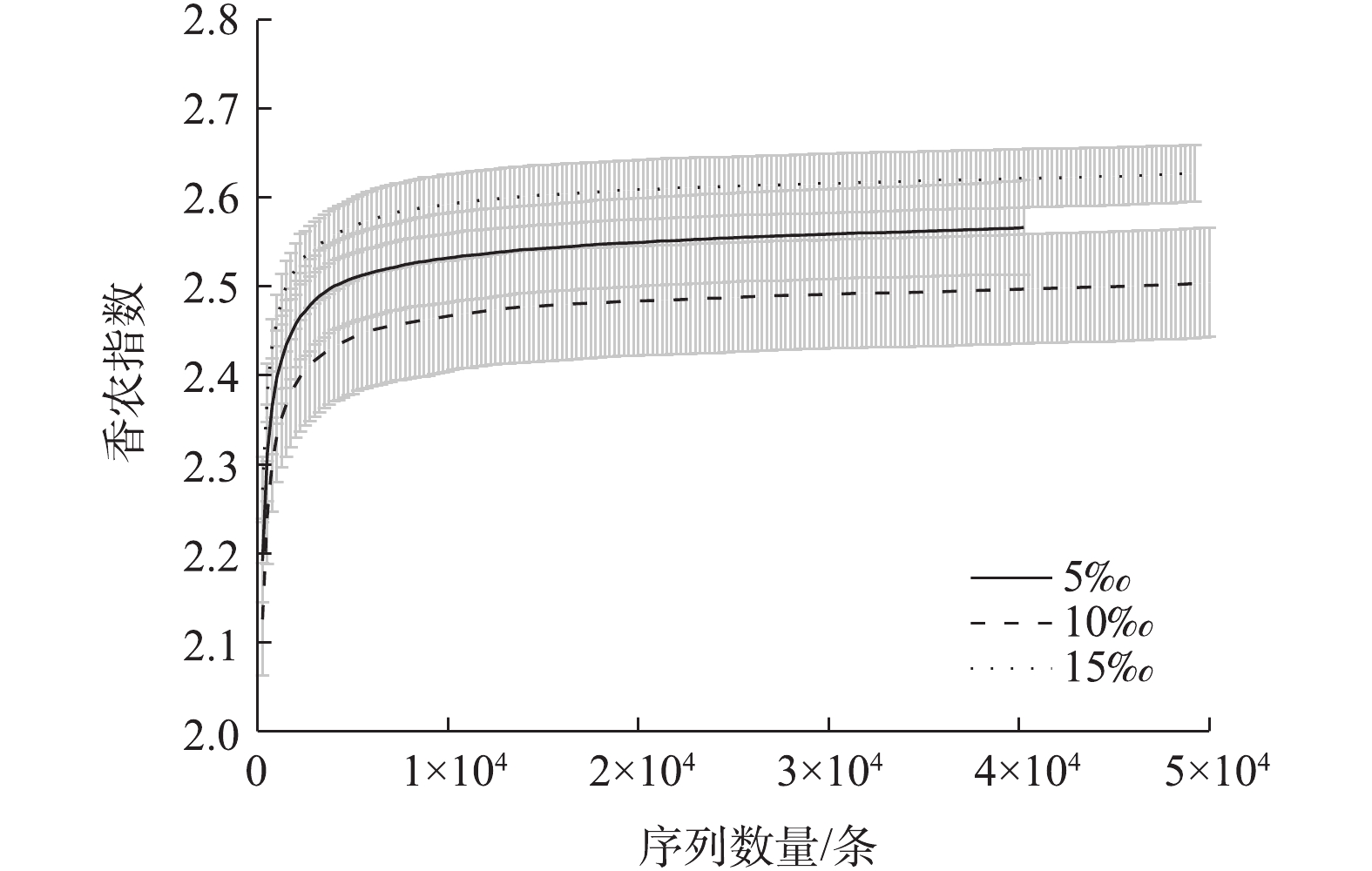
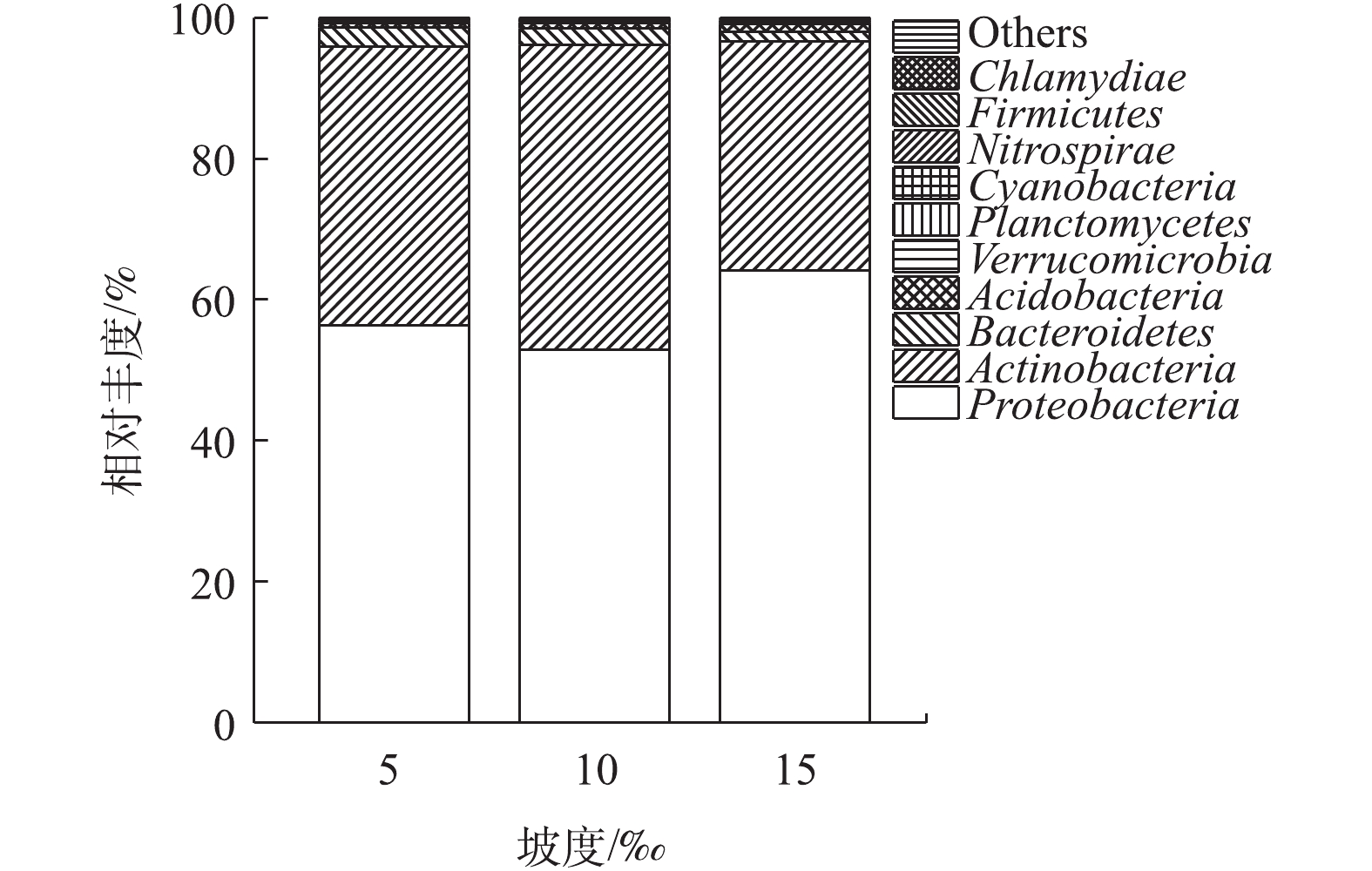
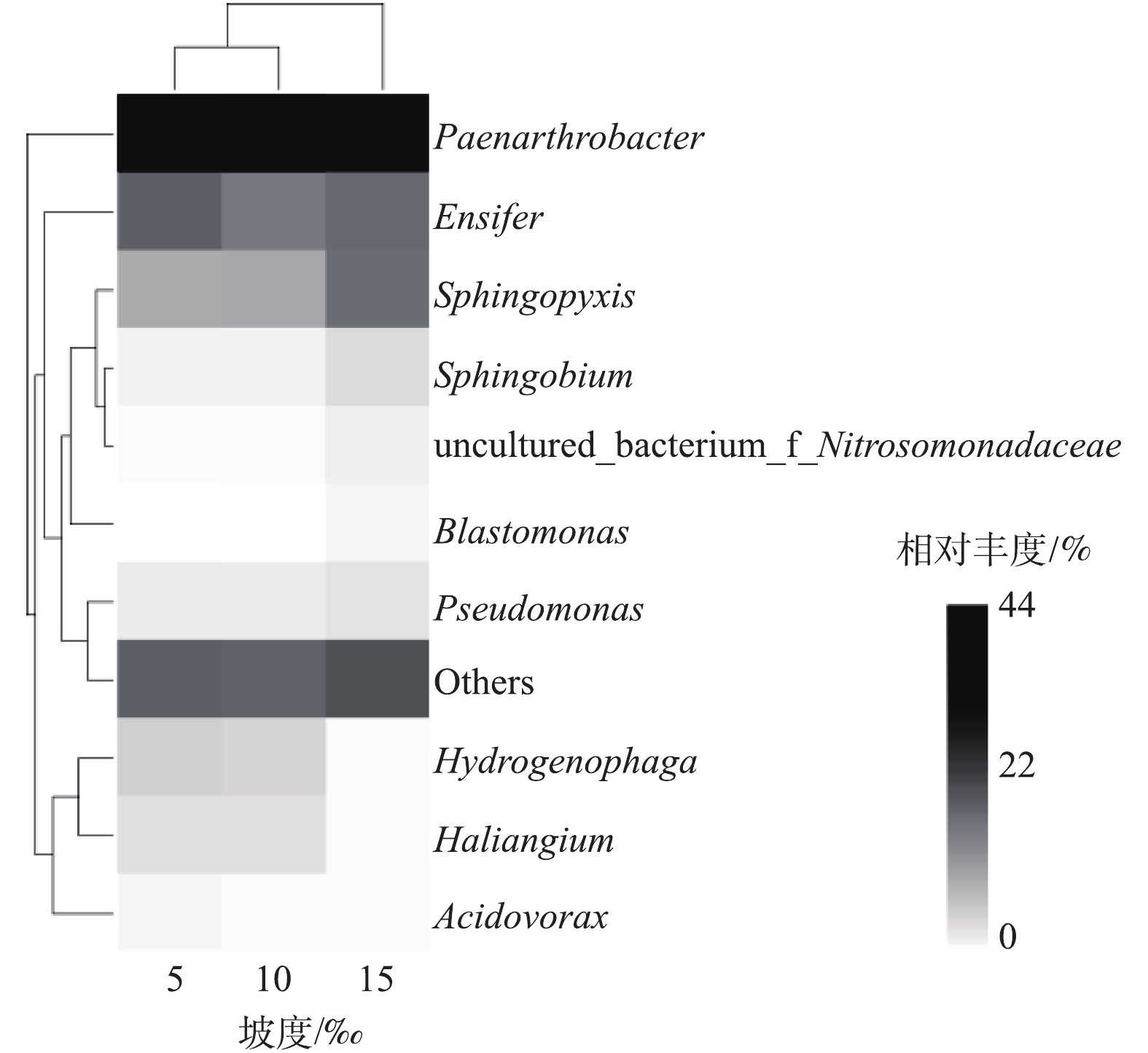
通过对9个样品(每组管道各3个平行样品)的高通量测序,共获得443 338条有效序列,共划分为230个OTU。其中181个OTU为3个坡度共有(图4),说明不同坡度下小管径重力流灰水管道生物膜细菌中绝大部分物种是共有的,坡度变化对于灰水管道生物膜中主要的细菌种类影响不大。根据香农指数曲线(图5)所示,随着取样序列数的增加,3个坡度下的平均Shannon指数逐渐趋于平缓,这说明本研究中的高通量测序深度满足进一步分析的要求,测序结果能够充分反映细菌的群落结构。小管径重力流灰水管道生物膜的细菌群落结构如图6和图7所示。细菌主要以Proteobacteria (变形菌门) (57.76%±5.76%)、Actinobacteria (放线菌门) (38.46%±5.50%)、Bacteroidetes (拟杆菌门) (2.18%±0.73%)和Acidobacteria (酸杆菌门) (0.79%±0.25%)为主,其中以变形菌门和放线菌门为优势菌门。在15‰的坡度下,放线菌门的丰度显著减小,高流速条件下不利于生物膜上放线菌的生存。另外,生物膜中存在一定丰度的Nitrospirae (硝化螺旋菌门) (0.12%±0.01%),这证明生物膜中存在硝化过程。Paenarthrobacte (38.35%±5.50%)、Ensifer (剑菌属) (17.11%±1.50%)和Spingopyxis (11.73%±4.32%)是生物膜中的优势细菌属。Paenarthrobacte是一种好氧生长的球形放线菌,可以利用多种碳源,并且可以水解淀粉类物质[15]。剑菌属是一种好氧生长的杆状变形菌,能够利用包括葡萄糖、半乳糖在内的多种碳源,不能水解淀粉,具有硝酸盐和亚硝酸盐还原能力,能够附着在其他细菌表面并使其裂解,是一种非专性捕食性细菌[16]。Spingopyxis是一种好氧生长的呈黄色外观的杆状变形菌,可以利用多种碳源,没有发酵功能,不能水解淀粉,部分种有硝酸盐还原能力[17],它的存在解释了灰水管道生物膜淡黄色外观的成因。优势细菌属都能利用多种碳源,说明小管径重力流灰水管道生物膜对于多种有机物都有一定的生物降解能力。坡度对细菌优势属的相对丰度有显著的影响:5‰和10‰坡度下细菌丰度差异不明显,而15‰坡度下的细菌丰度与前2个坡度有显著差异。主要表现在15‰坡度下,Paenarthrobacte、Hydrogenophaga(噬氢菌属)和Haliangium丰度降低,而Ensifer (剑菌属)、Spingopyxis、Sphingobium (鞘脂菌属)和Pseudomonas (假单胞菌属) 丰度升高。
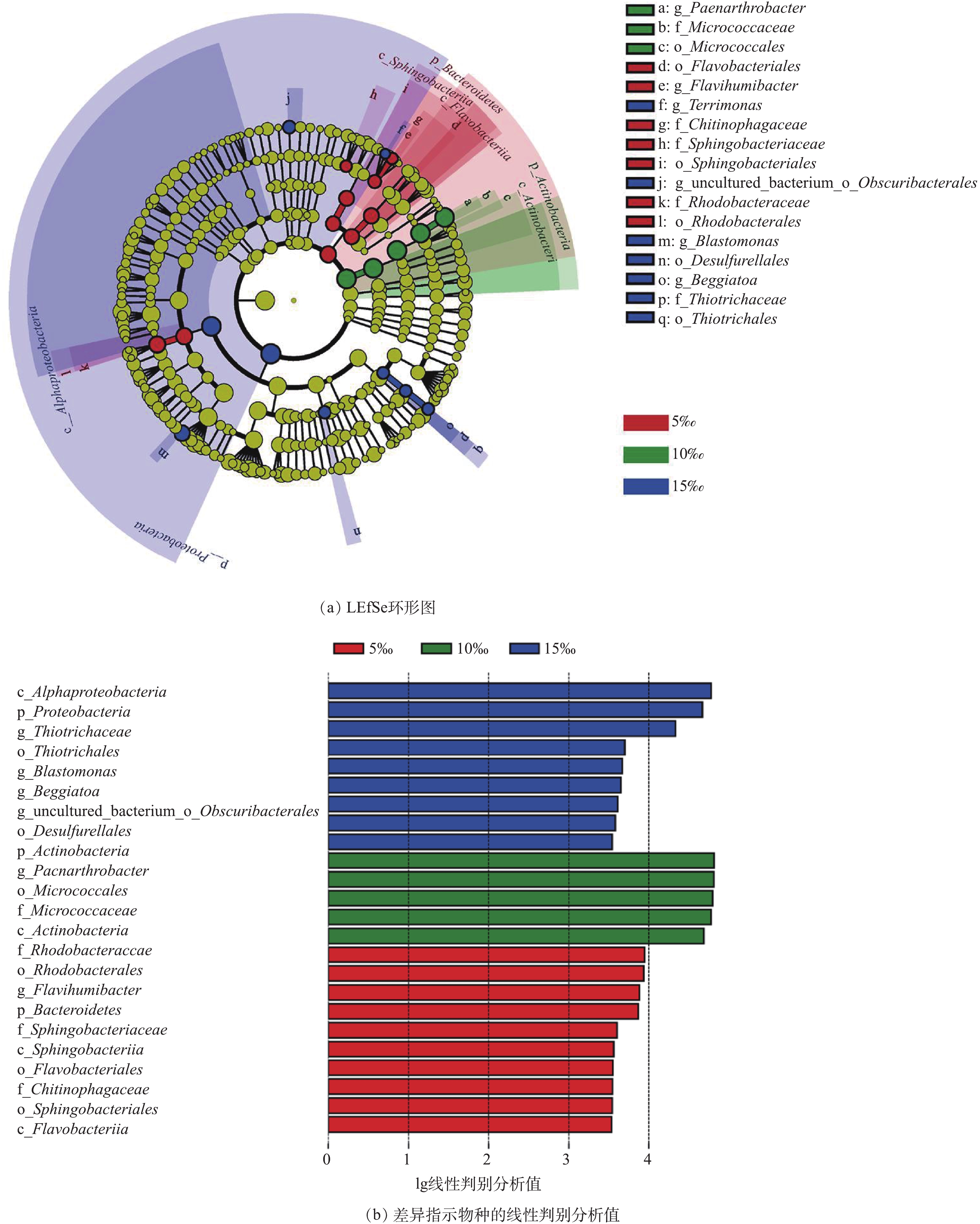
为深入分析管道坡度对细菌群落结构的影响,在属水平下进行LEfSe分析(图8)。图8只显示满足线性判别分析LDA值大于3.5的差异指示物种。LEfSe分析表明,在本研究中的3个管道坡度下,管道生物膜的细菌中共有24个差异指示物种,其中5‰坡度下含有10个,10‰坡度下含有5个,15‰坡度下含有9个,差异指示物种的丰度在相应的坡度下的丰度显著高于另外2个坡度的丰度。5‰坡度下的差异指示物种包括Rhodobacteraceae (红杆菌科)、Rhodobacterales (红杆菌目)、Flavihumibacter、Bacteroidetes (拟杆菌门)、Sphingobacteriaceae (鞘脂杆菌科)、Sphingobacteriia (鞘脂杆菌纲)、Flavobacteriales、Chitinophagaceae、Sphingobacteriales (鞘脂杆菌目)、Flavobacteriia。10‰坡度下的差异指示物种包括Actinobacteria (放线菌门)、Paenarthrobacter、Micrococcales (微球菌目)、Micrococcaceae (微球菌科)、Actinobacteria (放线菌门)。15‰坡度下的差异指示物种包括Alphaproteobacteria (α变形菌纲)、Proteobacteria (变形菌门)、Terrimonas、Thiotrichaceae (硫发菌科)、Thiotrichales (硫发菌目)、Blastomonas (芽单胞菌属)、Beggiatoa (贝日阿托菌属)、Obscuribacterales、Desulfurellales (硫还原菌目)。5‰、10‰、15‰ 3个坡度下差异贡献最大的指示物种分别是Rhodobacteraceae (红杆菌科)、Actinobacteria (放线菌门)和Alphaproteobacteria (α变形菌纲)。管道敷设坡度的变化可显著影响小管径重力流灰水管道生物膜的细菌群落结构。
2.3. 氮循环和硫循环功能细菌分布特征
排水管道生物膜中的功能细菌主要由氮循环细菌和硫循环细菌组成,一般可以将其分为反硝化细菌、亚硝酸细菌、硝酸细菌、硫酸盐还原细菌和硫氧化细菌5类[18-20]。本研究利用基于通用引物的高通量测序技术,研究了小管径重力流灰水管道生物膜中功能细菌(属水平)的分布特征(表3)。在本研究中,灰水管道生物膜中存在大量的以Pseudomonas (假单胞菌属) (2.78%±0.56%)和Rhodobacter (红杆菌属) (2.05%±0.94%)为主体的含有反硝化细菌的属,其中,假单胞菌属下的部分种属于好氧反硝化细菌[21],含有反硝化细菌的属总丰度随着管道坡度的增大而逐渐降低。Nitrospira (硝化螺菌属) (0.13%±0.01%)是本研究中唯一检出的一种硝酸细菌属,以Acidiphilium (嗜酸菌属) (0.04%±0.02%)为主要代表的硫氧化菌属也有检出。在0.01%的检出限下,没有检出属水平的亚硝酸细菌和硫酸盐还原细菌。在排水系统中,亚硝酸细菌的丰度比硝酸细菌的丰度大约低一个数量级[22],而本研究中灰水管道生物膜的硝酸细菌丰度仅为0.1%左右,因此,亚硝酸细菌在基于通用引物的高通量测序中难以检出。在本研究中,基于通用引物未能检出硫酸盐还原菌,说明硫酸盐还原菌在管道生物膜内丰度很低,这可能是由于2个原因:其一,灰水中不含人类粪便,生活污水中的硫酸盐还原菌主要源自人类粪便[23],本研究采用的灰水引入的硫酸盐还原菌数量较少;其二,在硫酸盐还原菌适宜生长在厌氧环境中,而本研究是好氧管道系统,环境条件不利于硫酸盐还原菌的生长。小管径重力流灰水管道生物膜中存在大量的反硝化菌和一定量的硝化细菌,而在生物膜中的硫酸盐还原菌没有达到检出水平,表明小管径重力流灰水管道具有一定的生物脱氮功能并且H2S积累的风险很低。输送生活污水的小管径重力流管道普遍存在的H2S积累问题,在小管径重力流灰水管道中可以忽略,这一现象有利于小管径灰水管道的安全应用和大范围推广。
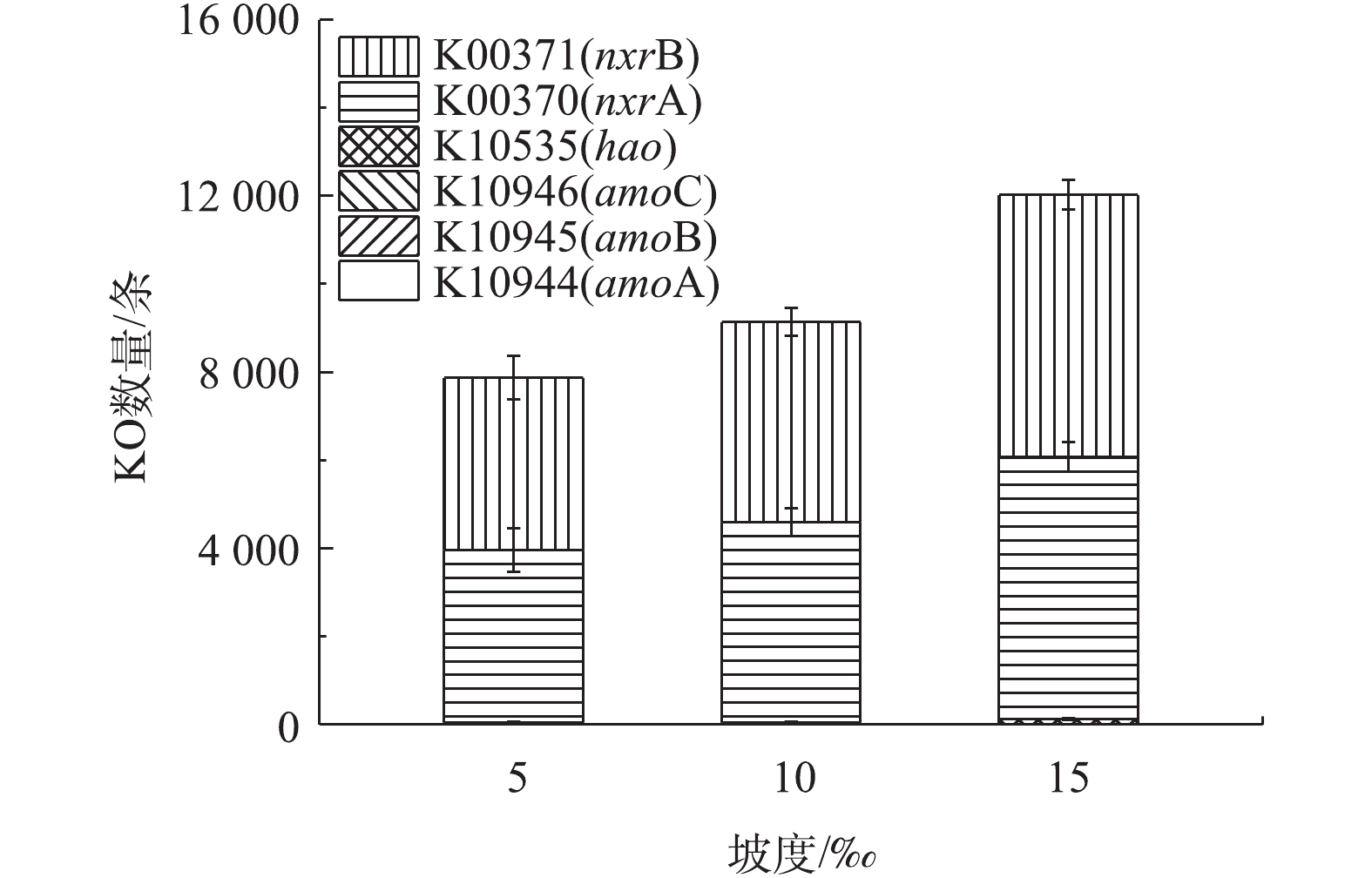
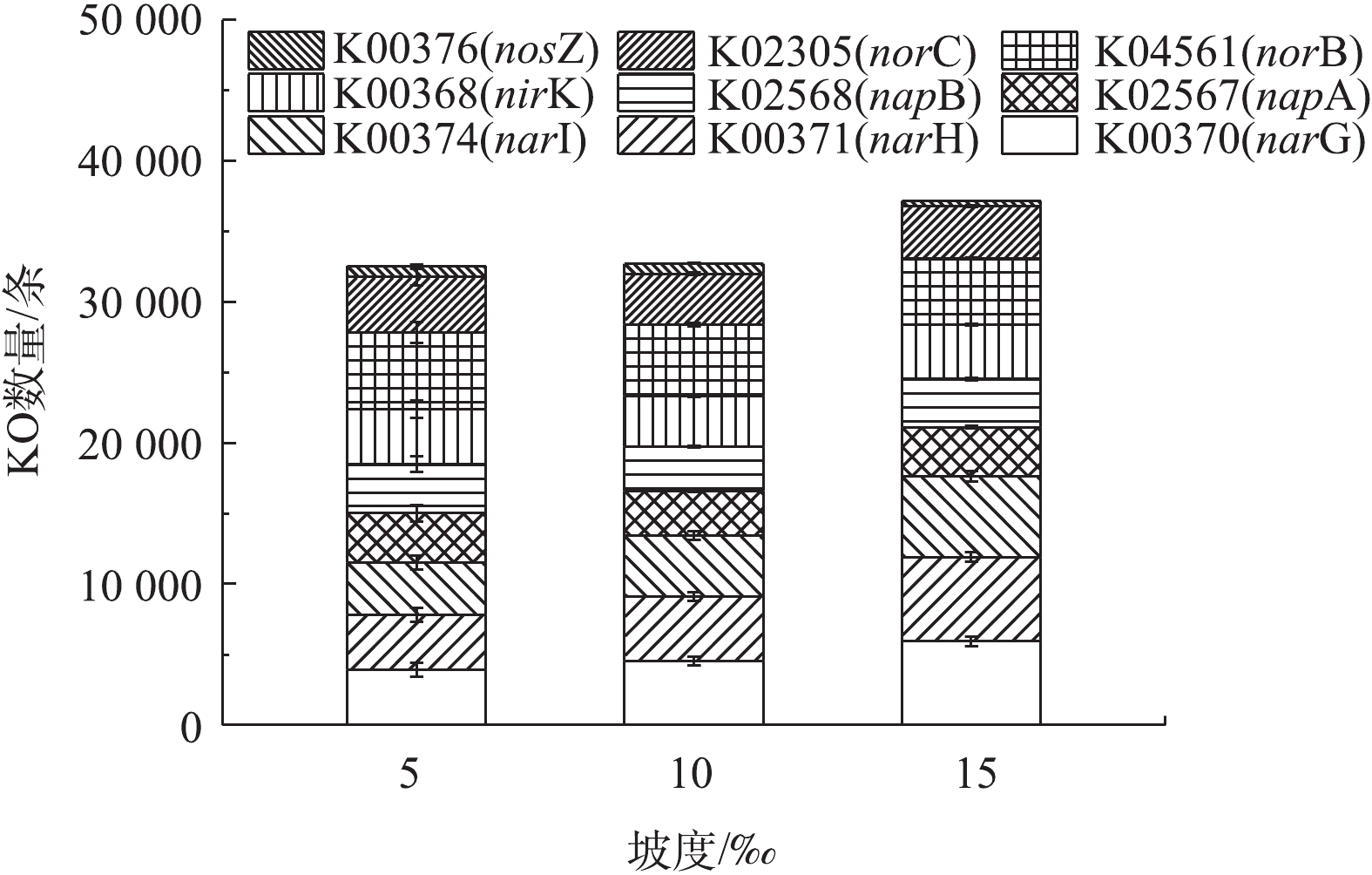
2.4. 氮循环功能基因分布特征
基于2.3节中功能细菌的分析结果,小管径重力流灰水管道生物膜中S循环过程(特别是H2S产生过程)基本可以忽略,而反硝化菌广泛存在于自然界中,其属水平的分类尚不完全,并且已确认的反硝化菌属中并非所有的菌种都具备反硝化功能[24],须从功能基因的角度进行深入分析,因此,本章节探讨氮循环功能基因在不同坡度管道下的分布特征。硝化功能基因的PICRUSt预测丰度如图9所示。由于灰水管道生物膜中基本不含亚硝化细菌,因此,氨单加氧酶基因amoABC以及羟胺氧化酶基因hao基本没有预测丰度,而灰水管道生物膜中一定丰度的硝化细菌携带的亚硝酸盐氧化酶基因nxrA和nxrB预测丰度很高,这明确了灰水管道生物膜中硝化作用的存在。随着管道坡度的增大,亚硝酸盐氧化酶基因nxrA和nxrB的丰度均显著增大,管道生物膜的硝化作用增强,说明大坡度的管道有利于灰水氨氮的去除。反硝化功能基因的PICRUSt预测丰度如图10所示。硝酸盐还原酶基因narGHI和napAB、亚硝酸盐还原酶基因nirK、一氧化氮还原酶基因norBC以及氧化亚氮还原酶基因nosZ在生物膜中均能大量预测到,这说明虽然本研究的灰水管道处于好氧运行状态,但其管道生物膜上仍然可以发生完整的反硝化过程。另外,nosZ的丰度显著小于其他反硝化基因,说明在灰水管道生物膜上发生的反硝化过程主要的终产物是N2O,这与好氧反硝化的终产物相吻合,同时结合管道的好氧状态,可以确定小管径灰水管道生物膜主要发生好氧反硝化过程。在15‰坡度下,灰水管道生物膜的反硝化功能基因总数显著高于另外2个坡度,表明大坡度的管道敷设方案可以加强灰水在管道内的反硝化过程,有利于灰水的生物脱氮过程。综合硝化功能基因和反硝化功能基因的预测结果,采用大坡度(15‰)的灰水管道敷设方案有利于促进灰水在管道输送过程中的生物脱氮作用。根据农村地区的污水管网敷设工程经验,15‰的管道敷设坡度在很多农村地区都具有实际应用的可行性,因此,对于小管径重力流灰水管道,在地质条件和经济条件允许的情况下,应尽量采用大坡度(15‰)的管道敷设方案。2)管道功能菌主要以反硝化细菌、硝酸细菌和硫氧化细菌为主。基于通用引物的Illumina HiSeq高通量测序没有检出属水平的亚硝酸细菌和硫酸盐还原细菌。小管径重力流灰水管道具有生物脱氮潜力,H2S积累风险低,有利于其推广应用。
3)灰水管道生物膜中具有完整的反硝化过程功能基因,反硝化过程以好氧过程为主。亚硝化过程功能基因缺失,硝化过程功能基因丰富。大坡度(15‰)的灰水管道敷设方案可以提高氮循环相关功能基因丰度,有利于促进灰水在管道输送过程中的生物脱氮作用,在条件允许的地区,应优先采用大坡度(15‰)的灰水管道设计方案。
参考文献

 下载:
下载: 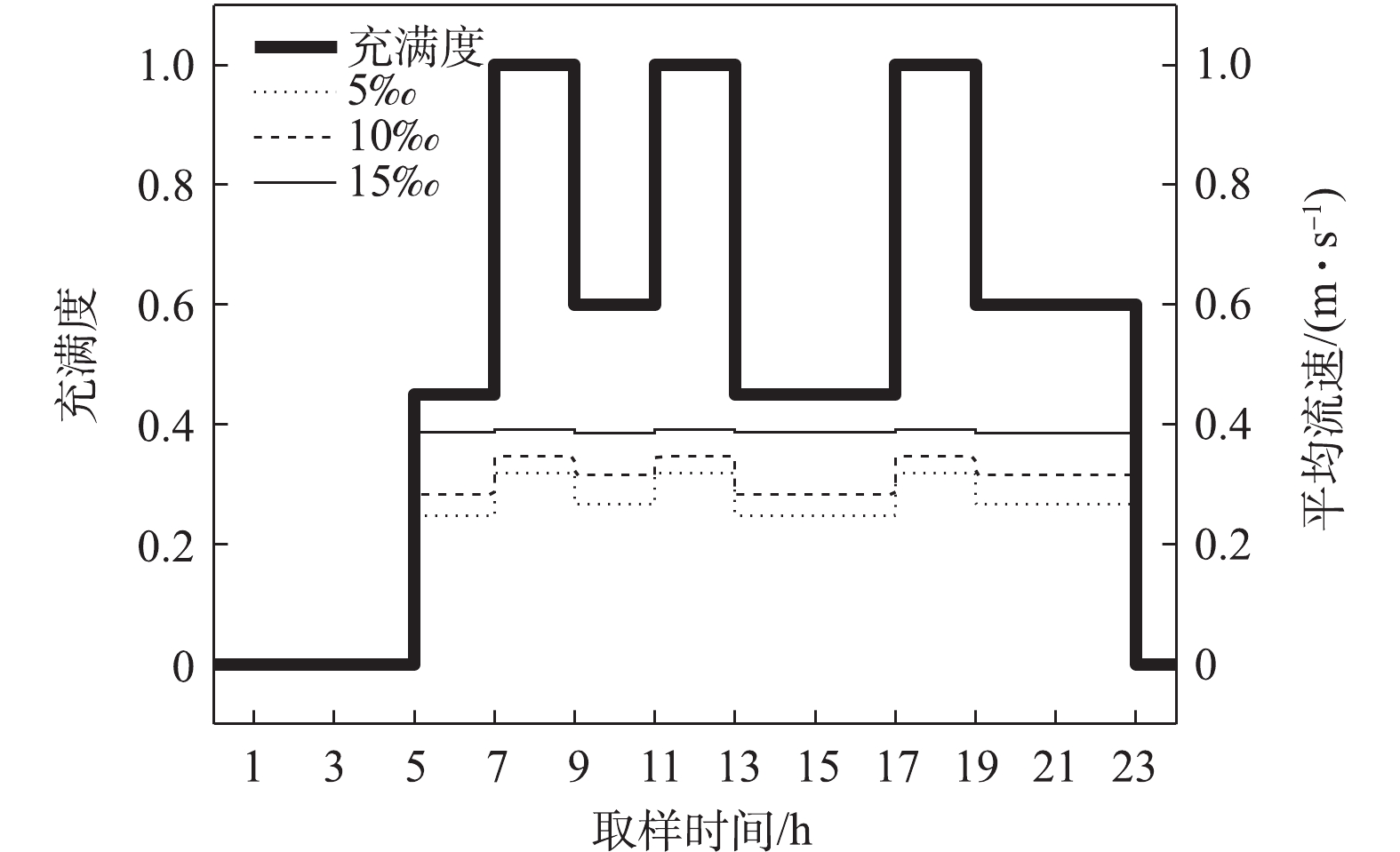






 点击查看大图
点击查看大图