 )
) 1首都师范大学心理学院, 北京市“学习与认知”重点实验室, 北京 100048
2新乡医学院心理学院, 河南 新乡 453003
收稿日期:2020-06-24出版日期:2021-03-25发布日期:2021-01-27通讯作者:丁锦红E-mail:dingjh@cnu.edu.cn基金资助:* 国家自然科学基金(61572076);北京自然科学基金(4202011);首都师范大学交叉学院引导研发基金资助(jckxyj2019018)Neural mechanism underlying the effects of object color on episodic memory
ZHOU Wenjie1,2, DENG Liqun1, DING Jinhong1( )
) 1Department of Psychology, Learning and Cognitive Key Laboratory, Capital Normal University, Beijing 100048, China
2Department of Psychology, Xinxiang Medical University, Xinxiang 453003, China
Received:2020-06-24Online:2021-03-25Published:2021-01-27Contact:DING Jinhong E-mail:dingjh@cnu.edu.cn摘要/Abstract
摘要: 本研究采用ERP技术和学习-再认范式考察视觉输入的颜色和记忆中的物体颜色知识一致性对情景记忆编码和提取的影响。结果显示, 在对物体图片进行编码时颜色不一致图片诱发更大N400, 而提取阶段则对颜色一致图片有更多熟悉性加工(实验1); 物体名称能够更快激活典型颜色知识, 对颜色一致名称有更多细节回想(LPC更正) (实验2)。实验结果表明, 颜色一致促进知觉水平的记忆编码, 而阻碍语义水平编码。同时, 颜色一致促进物体图片提取(知觉水平)中的熟悉性和回想过程; 而对物体名称提取(概念水平)的促进作用仅表现在回想上。此外, 颜色与物体名称有着密切联系, 同样影响物体的语义表征, 支持激活-扩散模型理论。本研究从知觉和概念水平上为揭示物体颜色在联结记忆中的作用提供了证据。
图/表 9
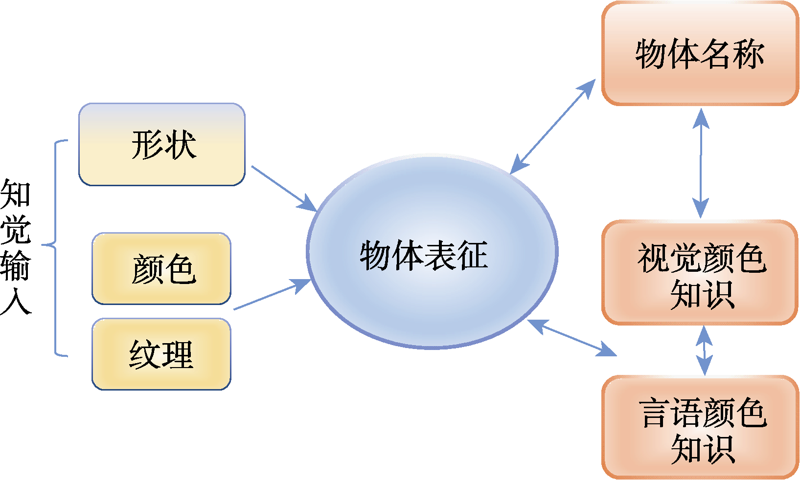
图1“形状+表面”识别模型(修改自Tanaka, Weiskopf, & Williams, 2001)
 图1“形状+表面”识别模型(修改自Tanaka, Weiskopf, & Williams, 2001)
图1“形状+表面”识别模型(修改自Tanaka, Weiskopf, & Williams, 2001)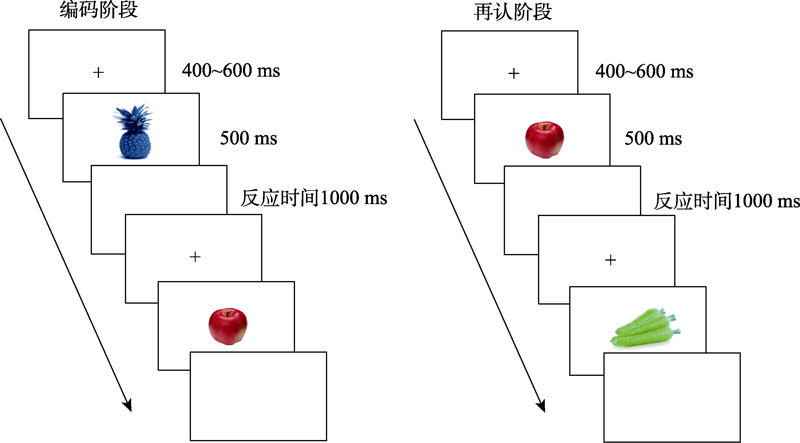
图2实验1流程图
 图2实验1流程图
图2实验1流程图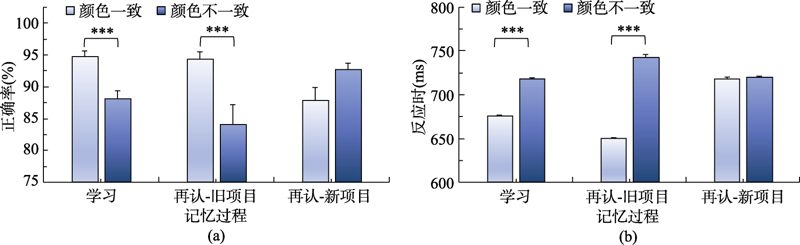
图3不同条件下物体图片的学习与再认成绩(注:***表示p < 0.001)
 图3不同条件下物体图片的学习与再认成绩(注:***表示p < 0.001)
图3不同条件下物体图片的学习与再认成绩(注:***表示p < 0.001)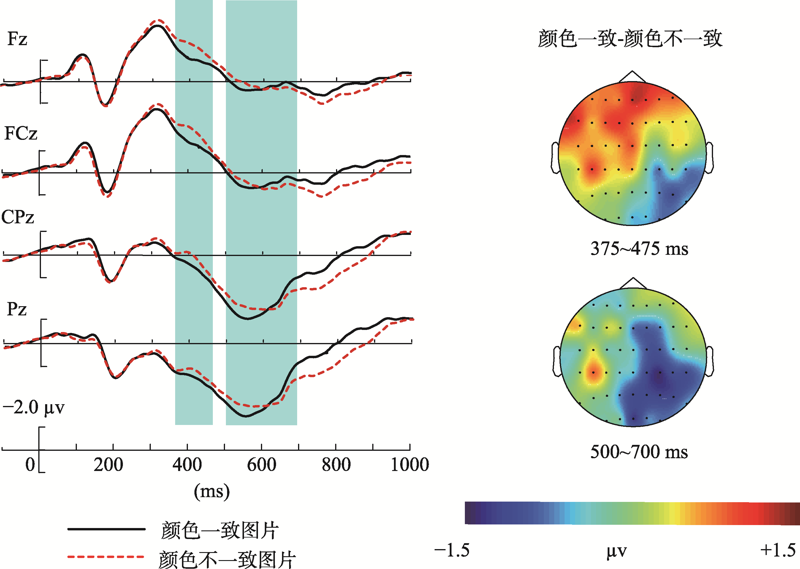
图4学习阶段颜色一致与颜色不一致图片的ERP波形和差异波(颜色一致-颜色不一致)地形图分布
 图4学习阶段颜色一致与颜色不一致图片的ERP波形和差异波(颜色一致-颜色不一致)地形图分布
图4学习阶段颜色一致与颜色不一致图片的ERP波形和差异波(颜色一致-颜色不一致)地形图分布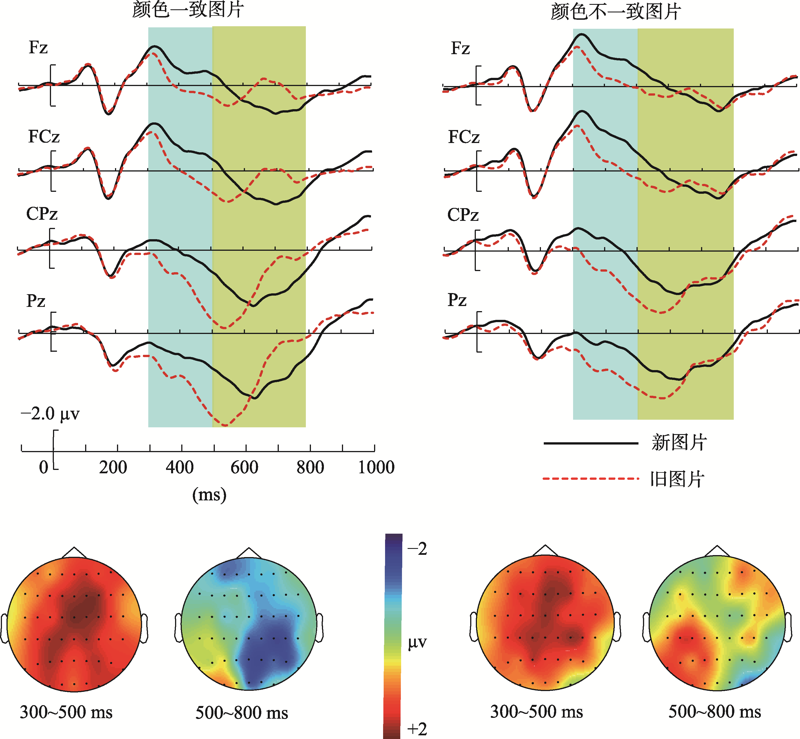
图5再认阶段不同颜色一致性条件下的新旧效应及新旧效应(旧-新)地形图分布
 图5再认阶段不同颜色一致性条件下的新旧效应及新旧效应(旧-新)地形图分布
图5再认阶段不同颜色一致性条件下的新旧效应及新旧效应(旧-新)地形图分布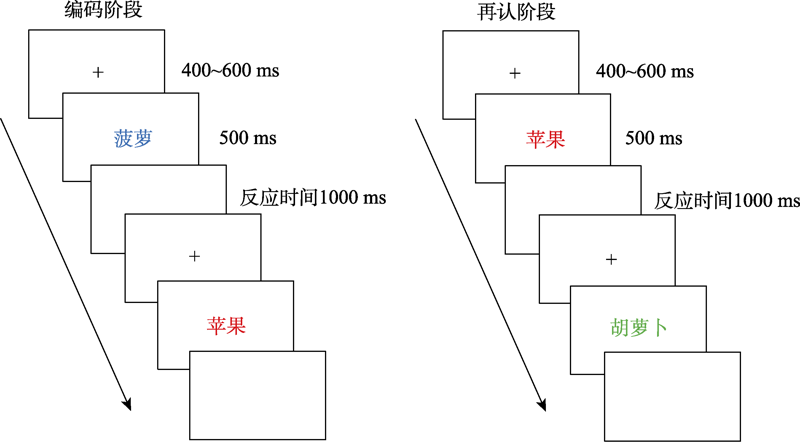
图6实验2流程图 注:彩图见电子版
 图6实验2流程图 注:彩图见电子版
图6实验2流程图 注:彩图见电子版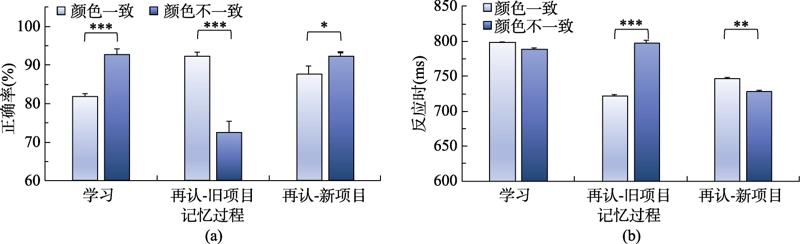
图7不同条件下物体名称的学习与再认成绩(注:*表示p < 0.05, **表示p < 0.01, ***表示p < 0.001)
 图7不同条件下物体名称的学习与再认成绩(注:*表示p < 0.05, **表示p < 0.01, ***表示p < 0.001)
图7不同条件下物体名称的学习与再认成绩(注:*表示p < 0.05, **表示p < 0.01, ***表示p < 0.001)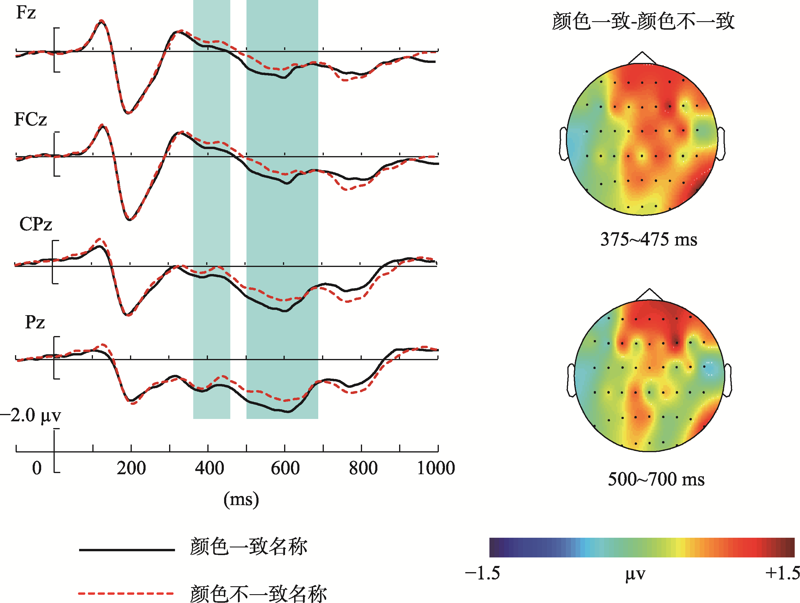
图8学习阶段颜色一致与颜色不一致名称的ERP波形和差异波(颜色一致-颜色不一致)地形图分布
 图8学习阶段颜色一致与颜色不一致名称的ERP波形和差异波(颜色一致-颜色不一致)地形图分布
图8学习阶段颜色一致与颜色不一致名称的ERP波形和差异波(颜色一致-颜色不一致)地形图分布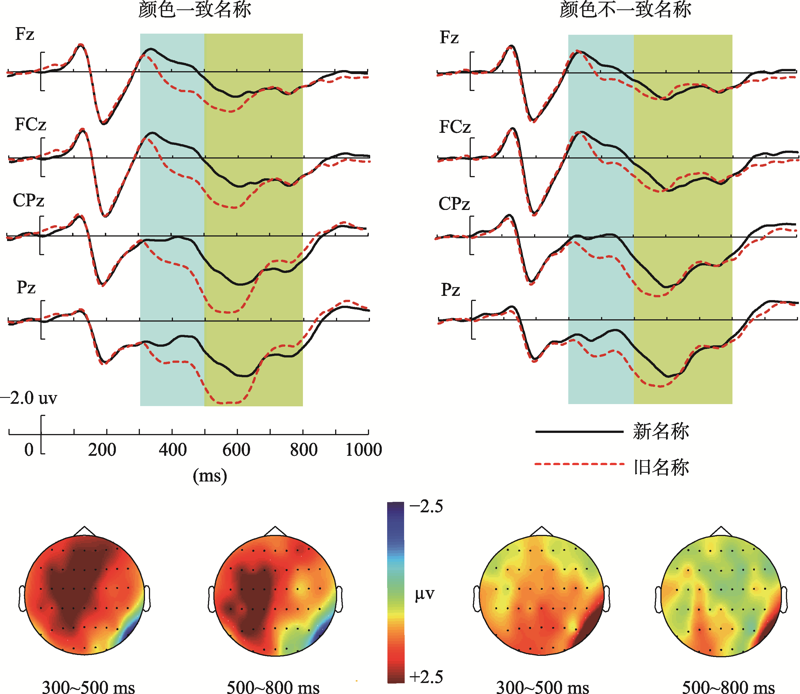
图9再认阶段不同颜色一致性条件下的新旧效应及新旧效应(旧-新)地形图分布
 图9再认阶段不同颜色一致性条件下的新旧效应及新旧效应(旧-新)地形图分布
图9再认阶段不同颜色一致性条件下的新旧效应及新旧效应(旧-新)地形图分布参考文献 71
| [1] | Allen, R. J., Hitch, G. J., Mate, J., & Baddeley, A. D. (2012). Feature binding and attention in working memory: A resolution of previous contradictory findings. The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 65(12), 2369-2383. doi: 10.1080/17470218.2012.687384URLpmid: 22670689 |
| [2] | Baddeley, A. D. (2002). Fractionating the central executive. Brain and Cognition, 47(1-2), 6-6. |
| [3] | Balass, M., Nelson, J. R., & Perfetti, C. A. (2010). Word learning: An ERP investigation of word experience effects on recognition and word processing. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 35(2), 126-140. doi: 10.1016/j.cedpsych.2010.04.001URLpmid: 22399833 |
| [4] | Boldini, A., Algarabel, S., Iba?ez, A., & Bajo, M. T. (2008). Perceptual and semantic familiarity in recognition memory: An event-related potential study . NeuroReport, 19(3), 305-308. URLpmid: 18303571 |
| [5] | Brady, T. F., Konkle, T., Alvarez, G. A., & Oliva, A. (2013). Real-world objects are not represented as bound units: Independent forgetting of different object details from visual memory. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 142(3), 791-808. |
| [6] | Brady, T. F., St?rmer, V. S., & Alvarez, G. A. (2016). Working memory is not fixed-capacity: More active storage capacity for real-world objects than for simple stimuli. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 113(27), 7459-7464. |
| [7] | Brainerd, C. J., Reyna, V. F., & Kneer, R. (1995). False- recognition reversal: When similarity is distinctive. Journal of Memory & Language, 34(2), 157-185. |
| [8] | Bram?o, I., Faísca, L., Forkstam, C., Inácio, F., Araújo, S., Petersson, K. M., & Reis, A. (2011). The interaction between surface color and color knowledge: Behavioral and electrophysiological evidence. Brain and Cognition, 78(1), 28-37. URLpmid: 22070924 |
| [9] | Bram?o, I., Faísca, L., Petersson, K. M., & Reis, A. (2010). The influence of surface color information and color knowledge information in object recognition. The American Journal of Psychology, 123(4), 437-446. URLpmid: 21291160 |
| [10] | Bram?o, I., Francisco, A., Inácio, F., Faísca, L., Reis, A., & Petersson, K. M. (2012). Electrophysiological evidence for colour effects on the naming of colour diagnostic and noncolour diagnostic objects. Visual Cognition, 20(10), 1164-1185. |
| [11] | Bram?o, I., Reis, A., Petersson, K. M., & Faísca, L. (2011). The role of color information on object recognition: A review and meta-analysis. Acta Psychologica, 138(1), 244-253. doi: 10.1016/j.actpsy.2011.06.010URLpmid: 21803315 |
| [12] | Bram?o, I., Reis, A., Petersson, K. M., & Faísca, L. (2016). Knowing that strawberries are red and seeing red strawberries: The interaction between surface colour and colour knowledge information. Journal of Cognitive Psychology, 28(6), 641-657. |
| [13] | Brodeur, M. B., O’Sullivan, M., & Crone, L. (2017). The impact of image format and normative variables on episodic memory. Cogent Psychology, 4(1), 1-22. |
| [14] | Bruett, H., & Leynes, P. A. (2015). Event-related potentials indicate that fluency can be interpreted as familiarity. Neuropsychologia, 78, 41-50. URLpmid: 26432342 |
| [15] | Chai, M. T., Amin, H. U., Izhar, L. I., Saad, M. N. M., Rahman, M. A., Malik, A. S., & Tang, T. B. (2019). Exploring EEG effective connectivity network in estimating influence of color on emotion and memory. Frontiers in Neuroinformatics, 13, 66. doi: 10.3389/fninf.2019.00066URLpmid: 31649522 |
| [16] | Cohen, N. J.& Eichenbaum, H.(1993) Memory, amnesia, and the hippocampal system. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press. |
| [17] | Collins, A. M., & Loftus, E. F. (1975). A spreading-activation theory of semantic processing. Psychological Review, 82(6), 407-428. |
| [18] | Cui, X., Gao, C., Zhou, J., & Guo, C. (2016). Can color changes alter the neural correlates of recognition memory? Manipulation of processing affects an electrophysiological indicator of conceptual implicit memory. NeuroReport, 27(14), 1037-1045. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0000000000000652URLpmid: 27489100 |
| [19] | Curran, T.(2000). Brain potentials of recollection and familiarity. Memory & Cognition, 28(6), 923-938. doi: 10.3758/bf03209340URLpmid: 11105518 |
| [20] | Cycowicz, Y. M., Nessler, D., Horton, C., & Friedman, D. (2008). Retrieving object color: The influence of color congruity and test format. NeuroReport, 19(14), 1387-1390. URLpmid: 18766017 |
| [21] | Diana, R. A., van den Boom, W., Yonelinas, A. P., & Ranganath, C. (2011). ERP correlates of source memory: Unitized source information increases familiarity-based retrieval. Brain Research, 1367, 278-286. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.10.030URLpmid: 20965154 |
| [22] | Ding, J. H., & Lin, Z. X. (2000). Research on representation features of color, shape and texture of pictures. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 32(3), 253-257. |
| [ 丁锦红, 林仲贤. (2000). 图形颜色、形状及质地表征特性的研究. 心理学报, 32(3), 253-257.] | |
| [23] | Ding, J. H., & Lin, Z. X. (2001). The retrieval of different features of pictures from memory. Journal of Psychological Science, 24(3), 273-381. |
| [ 丁锦红, 林仲贤. (2001). 记忆系统中图形不同特征的提取. 心理科学, 24(3), 273-381.] | |
| [24] | Ding, J. H., Wang, L. Y., & Guo, C. Y. (2004). Temporal- Spatial in integration during picture identification. Journal of Psychological Science, 27(2), 477-479. |
| [ 丁锦红, 王丽燕, 郭春彦. (2004). 时-空整合影响图形识别的眼动研究. 心理科学, 27(2), 477-479.] | |
| [25] | Dzulkifli, M. A., & Mustafar, M. F. (2013). The Influence of colour on memory performance: A review. Malaysian Journal of Medical Sciences, 20(2), 3-9. |
| [26] | Ecker, U. K. H., Zimmer, H. D., & Groh-Bordin, C. (2007). Color and context: An ERP study on intrinsic and extrinsic feature binding in episodic memory. Memory & Cognition, 35(6), 1483-1501. doi: 10.3758/bf03193618URLpmid: 18035643 |
| [27] | Evans, L. H., & Wilding, E. L. (2012). Recollection and familiarity make independent contributions to memory judgments. Journal of Neuroscience, 32(21), 7253-7257. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6396-11.2012URLpmid: 22623670 |
| [28] | Fu, Y. Q. (2019). An event-related potentials study of maintenance of binding spatial object in working memory. Psychological Exploration, 39(2), 127-132. |
| [ 傅亚强. (2019). 双特征空间客体捆绑关系的存储机制——来自ERP的证据. 心理学探新, 39(2), 127-132.] | |
| [29] | Ganis, G., & Kutas, M. (2003). An electrophysiological study of scene effects on object identification. Cognitive Brain Research, 16(2), 123-144. doi: 10.1016/S0926-6410(02)00244-6URL |
| [30] | Guillaume, F., Baier, S., & Etienne, Y. (2020). An ERP investigation of item-scene incongruity at encoding on subsequent recognition. Psychophysiology, 57(5), 1-15. |
| [31] | Hintzman, D. L., & Curran, T. (1994). Retrieval dynamics of recognition and frequency judgments: Evidence for separate processes of familiarity and recall. Journal of Memory & Language, 33(1), 1-18. |
| [32] | Huettig, F., & Altmann, G. T. M. (2011). Looking at anything that is green when hearing “frog”: How object surface colour and stored object colour knowledge influence language-mediated overt attention. The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 64(1), 122-145. doi: 10.1080/17470218.2010.481474URLpmid: 20521211 |
| [33] | Jacoby, L. L. (1991). A process dissociation framework: Separating automatic from intentional uses of memory. Journal of Memory & Language, 30(5), 513-541. |
| [34] | Kelter, S., Gr?tzbach, H., Freiheit, R., H?hle, B., Wutzig, S., & Diesch, E. (1984). Object identification: The mental representation of physical and conceptual attributes. Memory & Cognition, 12(2), 123-133. URLpmid: 6727634 |
| [35] | Konkel, A., & Cohen, N. J. (2009). Relational memory and the hippocampus: Representations and methods. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 3(2), 166-174. |
| [36] | Kuhbandner, C., Spitzer, B., Lichtenfeld, S., & Pekrun, R. (2015). Differential binding of colors to objects in memory: Red and yellow stick better than blue and green. Frontiers in Psychology, 6, 231. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2015.00231URLpmid: 25784892 |
| [37] | Küper, K., & Zimmer, H. D. (2018). The impact of perceptual changes to studied items on ERP correlates of familiarity and recollection is subject to hemispheric asymmetries. Brain and Cognition, 122, 17-25. doi: 10.1016/j.bandc.2018.01.006URLpmid: 29396208 |
| [38] | Kutas, M., & Hillyard, S. A. (1980). Reading between the lines: Event-related brain potentials during natural sentence processing. Brain and Language, 11(2), 354-373. doi: 10.1016/0093-934x(80)90133-9URLpmid: 7470854 |
| [39] | Lee, J., Leonard, C. J., Luck, S. J., & Geng, J. J. (2018). Dynamics of feature-based attentional selection during color-shape conjunction search. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 30(12), 1773-1787. doi: 10.1162/jocn_a_01318URLpmid: 30063176 |
| [40] | Lewis, D. E., Pearson, J., & Khuu, S. K. (2013). The color “fruit”: Object memories defined by color. PLoS One, 8(5), e64960. URLpmid: 23717677 |
| [41] | Leynes, P. A., & Crawford, C. J. (2018). Event-related potential (ERP) evidence that encoding focus alters recollected Features. Brain and Cognition, 127, 42-50. doi: 10.1016/j.bandc.2018.09.005URLpmid: 30253265 |
| [42] | Li, Y., & Shang, L. L. (2017). An ERPs study on the mental simulation of implied object color information during chinese sentence comprehension. Journal of Psychological Science, 40(1), 29-36. |
| [ 李莹, 商玲玲. (2017). 汉语句子理解中物体隐含颜色心理模拟的ERPs研究. 心理科学, 40(1), 29-36.] | |
| [43] | Liang, J. Q., & Guo, C. Y. (2012). Dissociating the neural correlates of item retrieval and relational retrieval in between-domain inter-item associative memory: An event-related potentials study. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 44(5), 625-633. |
| [ 梁九清, 郭春彦. (2012). 跨领域项目间联结记忆中项目提取和关系提取的分离: 一项事件相关电位研究. 心理学报, 44(5), 625-633.] | |
| [44] | Lloyd-Jones, T. J., & Nakabayashi, K. (2009). Independent effects of colour on object identification and memory. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 62(2), 310-322. |
| [45] | Lu, A., Xu, G., Jin, H., Mo, L., Zhang, J., & Zhang, J. X. (2010). Electrophysiological evidence for effects of color knowledge in object recognition. Neuroscience Letters, 469(3), 405-410. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2009.12.039URLpmid: 20026380 |
| [46] | Ludaji?, T., & Zdravkovi?, S. (2016). The role of shape and colour in recognition and classification of familiar visual objects. Primenjena Psihologija, 9(3), 333-352. |
| [47] | Lupyan, G.(2015). Object knowledge changes visual appearance: Semantic effects on color afterimages. Acta Psychologica, 161, 117-130. doi: 10.1016/j.actpsy.2015.08.006URLpmid: 26386775 |
| [48] | Mandler, G.(1980). Recognizing: The judgment of previous occurrence. Psychological Review, 87(3), 252-271. doi: 10.1037/0033-295X.87.3.252URL |
| [49] | Mayes, A., Montaldi, D., & Migo, E. (2007). Associative memory and the medial temporal lobes. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 11(3), 126-135. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2006.12.003URL |
| [50] | Nagai, J., & Yokosawa, K. (2003). What regulates the surface color effect in object recognition: Color diagnosticity or category? Technical Report on Attention & Cognition, 28, 1-4. |
| [51] | Naor-Raz, G., Tarr, M. J., & Kersten, D. (2003). Is color an intrinsic property of object representation? Perception, 32(6), 667-680. URLpmid: 12892428 |
| [52] | Nyhus, E., & Curran, T. (2009). Semantic and perceptual effects on recognition memory: Evidence from ERP . Brain Research, 1283, 102-114. URLpmid: 19505439 |
| [53] | Oakes, L. M., Baumgartner, H. A., Kanjlia, S., & Luck, S. J. (2017). An eye tracking investigation of color-location binding in infants' visual short-term memory. Infancy, 22(5), 584-607. doi: 10.1111/infa.12184URLpmid: 28966559 |
| [54] | Read, C. A., Rogers, J. M., & Wilson, P. H. (2016). Working memory binding of visual object features in older adults. Aging, Neuropsychology, and Cognition, 23(3), 263-281. |
| [55] | Rugg, M. D., & Curran, T. (2007). Event-related potentials and recognition memory. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 11(6), 251-257. URLpmid: 17481940 |
| [56] | Schacter, D. L., Cooper, L. A., & Valdiserri, M. (1992). Implicit and explicit memory for novel visual objects in older and younger adults. Psychology and Aging, 7(2), 299-308. doi: 10.1037//0882-7974.7.2.299URLpmid: 1610519 |
| [57] | Schendan, H. E., & Kutas, M. (2002). Neurophysiological evidence for two processing times for visual object identification. Neuropsychologia, 40(7), 931-945. URLpmid: 11900745 |
| [58] | Schendan, Schendan, H. E. & Kutas, M. (2003). Time course of processes and representations supporting visual object identification and memory. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 15(1), 111-135. |
| [59] | Song, C., Liu, W. Y., Lu, X. Q., & Gu, Q. (2016). Building blocks of visual working memory: Objects, features, or hybrid? Chinese Journal of Applied Psychology, 22(2), 112-126. |
| [ 宋超, 刘婉祎, 鲁溪芊, 顾全. (2016). 表征在视觉工作记忆中的存储单位: 特征、客体或二者并存? 应用心理学, 22(2), 112-126.] | |
| [60] | Spachtholz, P., & Kuhbandner, C. (2017). Visual long-term memory is not unitary: Flexible storage of visual information as features or objects as a function of affect. Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience, 17(6), 1141-1150. |
| [61] | Spence, I., Wong, P., Rusan, M., & Rastegar, N. (2006). How color enhances visual memory for natural scenes. Psychological Science, 17(1), 1-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9280.2005.01656.xURLpmid: 16371136 |
| [62] | Stró?ak, P., Bird, C. W., Corby, K., Frishkoff, G., & Curran, T. (2016). FN400 and LPC memory effects for concrete and abstract words: FN400 and LPC for concrete and abstract words. Psychophysiology, 53(11), 1669-1678. doi: 10.1111/psyp.12730URLpmid: 27463978 |
| [63] | Tanaka, J., Weiskopf, D., & Williams, P. (2001). The role of color in high-level vision. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 5(5), 211-215. doi: 10.1016/s1364-6613(00)01626-0URLpmid: 11323266 |
| [64] | Tanaka, J. W., & Presnell, L. M. (1999). Color diagnosticity in object recognition. Perception & Psychophysics, 61(6), 1140-1153. doi: 10.3758/bf03207619URLpmid: 10497433 |
| [65] | Teichmann, L., Quek, G. L., Robinson, A. K., Grootswagers, T., Carlson, T. A., & Rich, A. N. (2020). The influence of object-color knowledge on emerging object representations in the brain. The Journal of Neuroscience, 40(35), 6779-6789. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0158-20.2020URLpmid: 32703903 |
| [66] | Vernon, D., & Lloyd-Jones, T. J. (2003). The role of colour in implicit and explicit memory performance. The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology Section A, 56(5), 779-802. |
| [67] | Vurro, M., Ling, Y., & Hurlbert, A. C. (2013). Memory color of natural familiar objects: Effects of surface texture and 3-D shape. Journal of Vision, 13(7), 20. doi: 10.1167/13.7.20URLpmid: 23814075 |
| [68] | Wichmann, F. A., Sharpe, L. T., & Gegenfurtner, K. R. (2002). The contributions of color to recognition memory for natural scenes. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory and Cognition, 28(3), 509-520. |
| [69] | Yonelinas, A. P. (1994). Receiver-operating characteristics in recognition memory: Evidence for a dual-process model. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, & Cognition, 20(6), 1341-1354. URLpmid: 7983467 |
| [70] | Yonelinas, A. P. (2002). The nature of recollection and familiarity: A review of 30 years of research. Journal of Memory and Language, 46(3), 441-517. |
| [71] | Zokaei, N., Heider, M., & Husain, M. (2014). Attention is required for maintenance of feature binding in visual working memory. The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 67(6), 1191-1213. URLpmid: 24266343 |
相关文章 15
| [1] | 曹敏, 谢和平, 孙丽君, 张冬静, 孔繁昌, 周宗奎. 网络游戏中化身参照的加工优势:来自行为与ERPs的证据[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(6): 639-650. |
| [2] | 张环, 王欣, 刘一贝, 曹贤才, 吴捷. 成员关系对协作提取成绩的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(5): 481-493. |
| [3] | 李琎, 孙宇, 杨子鹿, 钟毅平. 社会价值取向对自我社会奖赏加工的影响——来自ERPs的证据[J]. 心理学报, 2020, 52(6): 786-800. |
| [4] | 章文佩, 沈群伦, 宋锦涛, 周仁来. 基于事件相关电位(ERPs)和机器学习的考试焦虑诊断[J]. 心理学报, 2019, 51(10): 1116-1127. |
| [5] | 刘贵雄,贾永萍,王余娟,买合甫来提·坎吉,郭春彦. 联结再认中双语者第二语言记忆优势效应[J]. 心理学报, 2019, 51(1): 14-23. |
| [6] | 李婷玉, 刘黎, 李宜霖, 朱莉琪. 冲突情境下幼儿的选择性信任和信念修正[J]. 心理学报, 2018, 50(12): 1390-1399. |
| [7] | 赵思敏;吴岩;李天虹;郭庆童. 词汇识别中歧义词素语义加工:ERP研究[J]. 心理学报, 2017, 49(3): 296-306. |
| [8] | 范伟;钟毅平;杨子鹿;李琎;欧阳益; 蔡荣华; 李慧云 ;傅小兰 . 外倾个体的自我参照加工程度效应[J]. 心理学报, 2016, 48(8): 1002-1012. |
| [9] | 吴岩;莫德圆;王海英; 于溢洋;陈烜之;张明. 语义分类任务中部件位置在汉字识别中的作用[J]. 心理学报, 2016, 48(6): 599-606. |
| [10] | 贾永萍;周楚;李林;郭秀艳. 汉字的无线索回忆再认效应:重复学习和重复测验的作用[J]. 心理学报, 2016, 48(2): 111-120. |
| [11] | 王协顺;吴岩;赵思敏;倪超;张明. 形旁和声旁在形声字识别中的作用[J]. 心理学报, 2016, 48(2): 130-140. |
| [12] | 李婧; 陈安涛;陈杰;龙长权. 词语型类别属性归纳中分类与属性推理过程的时间特征[J]. 心理学报, 2016, 48(11): 1410-1422. |
| [13] | 毛新瑞;徐慧芳;郭春彦. 双加工再认提取中的情绪记忆增强效应[J]. 心理学报, 2015, 47(9): 1111-1123. |
| [14] | 叶晓红;陈幼贞;孟迎芳. 回想、熟悉性与启动在编码过程的认知神经机制[J]. 心理学报, 2015, 47(9): 1101-1110. |
| [15] | 岳鹏飞;杜婉婉;白学军;许远理. 情绪标注对情绪的抑制发生在何时:一项ERPs研究[J]. 心理学报, 2015, 47(9): 1124-1132. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlxb/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=4892
