 )
) 1 华东师范大学心理与认知科学学院, 上海 200062
2 香港中文大学(深圳)人文社会科学学院, 深圳 518172
收稿日期:2019-09-29出版日期:2020-05-25发布日期:2020-03-26通讯作者:刘永芳E-mail:yfliu@psy.ecnu.edu.cn基金资助:* 国家社会科学基金重大项目资助(15ZDB121)Effects of others’ reference points and psychological distance on self-other welfare tradeoff in gain and loss situations
GAO Juan1, WANG Peng1, Xiao Tian WANG2, SUN Qian1, LIU Yongfang1( )
) 1 School of Psychology and Cognitive Science, East China Normal University, Shanghai 200062, China
2 School of Humanities and Social Science, Chinese University of Hong Kong, Shenzhen 518172, China
Received:2019-09-29Online:2020-05-25Published:2020-03-26Contact:LIU Yongfang E-mail:yfliu@psy.ecnu.edu.cn摘要/Abstract
摘要: 以福利权衡率(WTR)为利他程度的指标, 通过3个实验逐步深入地考察了得失情境下他人参照点及心理距离对自我-他人利益权衡的影响。实验1的结果表明, 得失情境并未改变被试的WTR。实验2引入他人底线、现状和目标三个参照点变量, 发现被试获益情境下的WTR高于损失情境, 且WTR从高到低依次为他人临近底线、目标和现状; 他人临近底线时, 被试在获益情境下的WTR高于损失情境, 而他人临近现状和目标时, 个体在得失情境下的WTR无显著差异。实验3进一步引入心理距离变量, 发现心理距离较近他人的WTR高于较远他人, 且与得失情境和参照点发生了复杂的交互效应, 得失情境的主效应消失了, 但总体上并未改变实验2发现的参照点效应。这些结果对于更深入地理解得失不对称效应、三参照点理论及社会折扣和自我-他人决策差异研究的相关发现具有一定的启示意义。
图/表 5

图1三个参照点和四个结果功能区(Wang & Johnson, 2012; 王晓田, 王鹏, 2013)
 图1三个参照点和四个结果功能区(Wang & Johnson, 2012; 王晓田, 王鹏, 2013)
图1三个参照点和四个结果功能区(Wang & Johnson, 2012; 王晓田, 王鹏, 2013)表1得失情境下每道题目的设置及其WTR
| 题号 | 选项 | 自我加分 (减分) | 他人加分 (减分) | 自我-他人 利益比 | WTR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | A | 15 | 0 | 1.50 | 1.60 |
| B | 0 | 10 | |||
| 2 | A | 12 | 0 | 1.20 | 1.35 |
| B | 0 | 10 | |||
| 3 | A | 10 | 0 | 1.00 | 1.10 |
| B | 0 | 10 | |||
| 4 | A | 8 | 0 | 0.80 | 0.90 |
| B | 0 | 10 | |||
| 5 | A | 6 | 0 | 0.60 | 0.70 |
| B | 0 | 10 | |||
| 6 | A | 4 | 0 | 0.40 | 0.50 |
| B | 0 | 10 | |||
| 7 | A | 2 | 0 | 0.20 | 0.30 |
| B | 0 | 10 | |||
| 8 | A | 1 | 0 | 0.10 | 0.15 |
| B | 0 | 10 | |||
| 9 | A | -1 | 0 | -0.10 | 00 |
| B | 0 | 10 | |||
| 10 | A | -3 | 0 | -0.30 | -0.20 |
| B | 0 | 10 |
表1得失情境下每道题目的设置及其WTR
| 题号 | 选项 | 自我加分 (减分) | 他人加分 (减分) | 自我-他人 利益比 | WTR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | A | 15 | 0 | 1.50 | 1.60 |
| B | 0 | 10 | |||
| 2 | A | 12 | 0 | 1.20 | 1.35 |
| B | 0 | 10 | |||
| 3 | A | 10 | 0 | 1.00 | 1.10 |
| B | 0 | 10 | |||
| 4 | A | 8 | 0 | 0.80 | 0.90 |
| B | 0 | 10 | |||
| 5 | A | 6 | 0 | 0.60 | 0.70 |
| B | 0 | 10 | |||
| 6 | A | 4 | 0 | 0.40 | 0.50 |
| B | 0 | 10 | |||
| 7 | A | 2 | 0 | 0.20 | 0.30 |
| B | 0 | 10 | |||
| 8 | A | 1 | 0 | 0.10 | 0.15 |
| B | 0 | 10 | |||
| 9 | A | -1 | 0 | -0.10 | 00 |
| B | 0 | 10 | |||
| 10 | A | -3 | 0 | -0.30 | -0.20 |
| B | 0 | 10 |
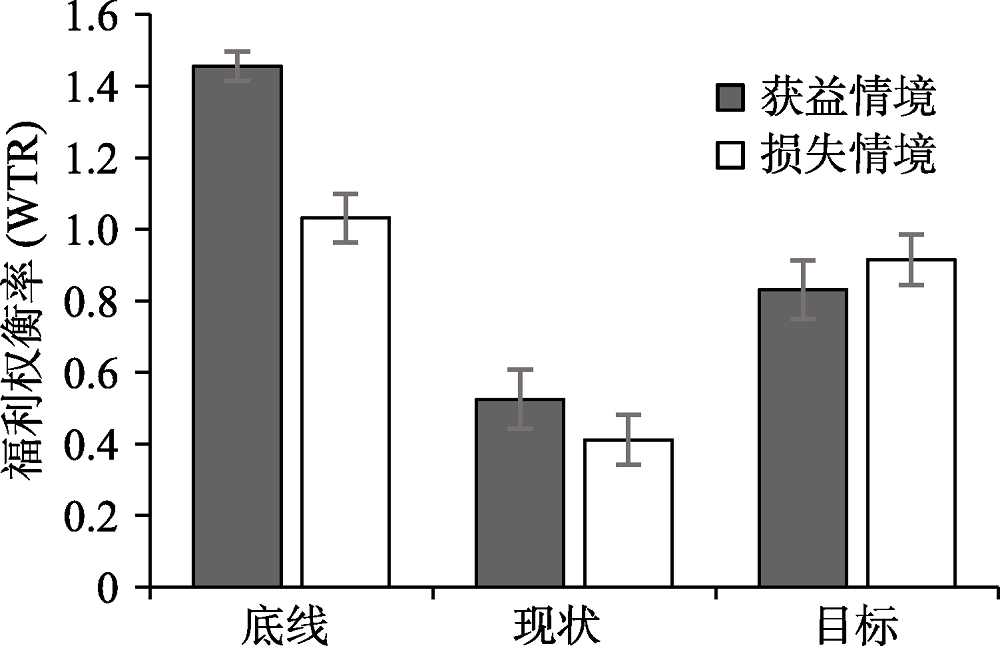
图2得失情境和他人参照点对WTR的影响 注:误差线为标准误(SE)
 图2得失情境和他人参照点对WTR的影响 注:误差线为标准误(SE)
图2得失情境和他人参照点对WTR的影响 注:误差线为标准误(SE) 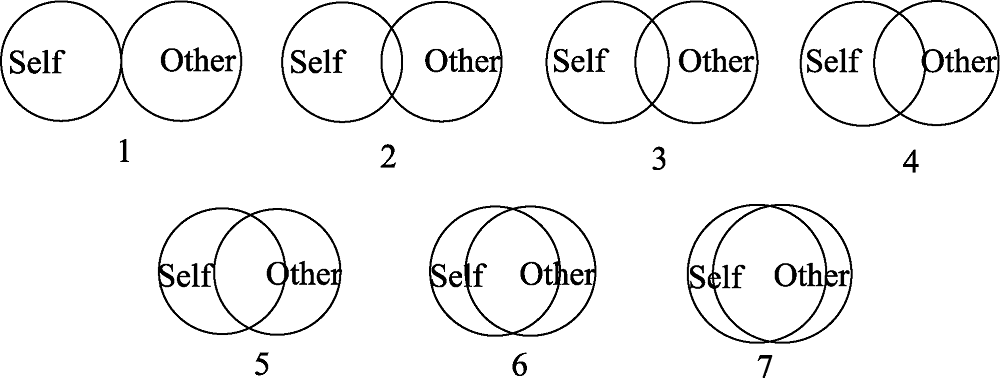
图3我中包含多少他量表(IOS) (Aron et al, 1992)
 图3我中包含多少他量表(IOS) (Aron et al, 1992)
图3我中包含多少他量表(IOS) (Aron et al, 1992) 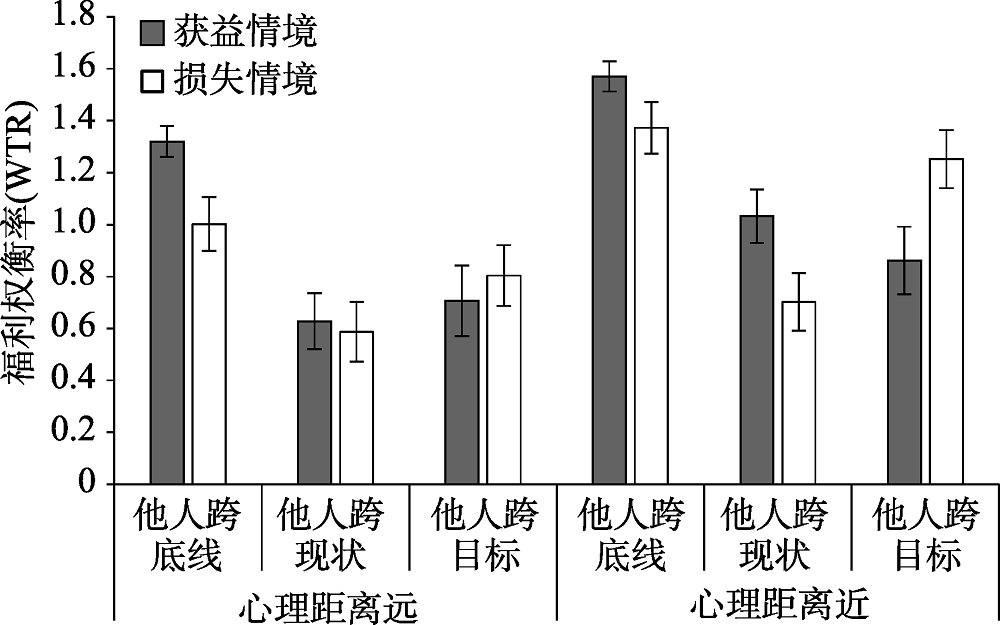
图4得失情境下他人参照点和心理距离对WTR的影响 注:误差线为标准误(SE)
 图4得失情境下他人参照点和心理距离对WTR的影响 注:误差线为标准误(SE)
图4得失情境下他人参照点和心理距离对WTR的影响 注:误差线为标准误(SE) 参考文献 54
| [1] | Aquino K., Steisel V., & Kay A . (1992). The effects of resource distribution, voice, and decision framing on the provision of public goods. Journal of Conflict Resolution, 36(4), 665-687. |
| [2] | Aron A., Aron E. N., & Smollan D . (1992). Inclusion of other in the self scale and the structure of interpersonal closeness. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 63(4), 596-612. |
| [3] | Beisswanger A. H., Stone E. R., Hupp J. M., & Allgaier L . (2003). Risk taking in relationships: Differences in deciding for oneself versus for a friend. Basic and Applied Social Psychology, 25(2), 121-135. |
| [4] | Brewer M. B., & Kramer R. M . (1986). Choice behavior in social dilemmas: Effects of social identity, group size, and decision framing. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 50(3), 543-549. |
| [5] | Burnstein E., Crandall C., & Kitayama S . (1994). Some neo- Darwinian decision rules for altruism: Weighing cues for inclusive fitness as a function of the biological importance of the decision. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 67(5), 773-789. |
| [6] | Carlo G., Mestre M. V., Samper P., Tur A., & Armenta B. E . (2011). The longitudinal relations among dimensions of parenting styles, sympathy, prosocial moral reasoning, and prosocial behaviors. International Journal of Behavioral Development, 35(2), 116-124. |
| [7] | Delton A. W . (2010). A psychological calculus for welfare tradeoffs (Unpublished doctorial dissertation). Santa Barbara: University of California. |
| [8] | Delton A. W., & Robertson T. E . (2016). How the mind makes welfare tradeoffs: Evolution, computation, and emotion. Current Opinion in Psychology, 7, 12-16. doi: 10.1016/j.copsyc.2015.06.006URL |
| [9] | Dreber A., Ellingsen T., Johannesson M., & Rand D. G . (2013). Do people care about social context? Framing effects in dictator games. Experimental Economics, 16(3), 349-371. doi: 10.1007/s10683-012-9341-9URL |
| [10] | Duan J., Liu Y. F., & He Q . (2012). The effects of decision makers' roles and related variables on risk preferences. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 44(3), 369-376. |
| [ 段婧, 刘永芳, 何琪 . (2012). 决策者角色及相关变量对风险偏好的影响. 心理学报, 44(3), 369-376.] | |
| [11] | Fehr E., Bernhard H., & Rockenbach B . (2008). Egalitarianism in young children. Nature, 454(28), 1079-1083. |
| [12] | Fehr E., & Schmidt K. M . (1999). A theory of fairness, competition and cooperation. Quarterly Journal of Economics, 114(3), 817-868. |
| [13] | Goerg S. J., Rand D. G., & Walkowitz G . (2017). Framing effects in the prisoner's dilemma but not in the dictator game. Retrieved Feb 8, 2017 from https://ssrn.com/abstract=2912982 |
| [14] | Handgraaf M. J. J., van Dijk E., Vermunt R. C., Wilke H. A. M., & de Dreu C. K. W . (2008). Less power or powerless? Egocentric empathy gaps and the irony of having little versus no power in social decision making. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 95(5), 1136-1149. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.95.5.1136URLpmid: 18954198 |
| [15] | He G. B., & Jiang D . (2013). The effect of task frames and altruism on social discounting. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 45(10), 1131-1146. |
| [ 何贵兵, 蒋多 . (2013). 任务框架及利他人格对社会折扣的影响. 心理学报, 45(10), 1131-1146.] | |
| [16] | He G. B., Yang X. W., & Jiang D . (2017). The effect of altruism on social discounting of environmental gain and loss. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 49(10), 1334-1343. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2017.01334URL |
| [ 何贵兵, 杨鑫蔚, 蒋多 . (2017). 环境损益的社会折扣: 利他人格的影响. 心理学报, 49(10), 1334-1343.] | |
| [17] | Hu H. G . (1999). Consistency of ideological system: Discussion on "Adam Smith Problem". Economic Science, 21(4), 121-128. |
| [ 胡怀国 . (1999). 斯密思想体系的一致性: “斯密问题”略论. 经济科学, 21(4), 121-128.] | |
| [18] | Jones B. A., & Rachlin H . (2006). Social discounting. Psychological Science, 17(4), 283-286. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9280.2006.01699.xURLpmid: 16623683 |
| [19] | Jones B. A., & Rachlin H . (2009). Delay, probability, and social discounting in a public goods game. Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 91(1), 61-73. doi: 10.1901/jeab.2009.91-61URLpmid: 19230512 |
| [20] | Kahneman D., Knetsch J. L., & Thaler R. H . (1990). Experimental tests of the endowment effect and the Coase theorem. Journal of Political Economy, 158, 1325-1348. |
| [21] | Kahneman D., & Tversky A . (1979). Prospect theory: An analysis of decision under risk. Econometrica, 47(2), 263-291. |
| [22] | Kahneman D., & Tversky A . (1984). Choices, values, and frames. American Psychologist, 39(4), 341-350. |
| [23] | Kennedy D., & Norman C . (2005). What don't we know? Science, 309(5731), 75-75. doi: 10.1126/science.309.5731.75URLpmid: 15994521 |
| [24] | Kirkpatrick M., Delton A. W., Robertson T. E., & de Wit H . (2015). Prosocial effects of MDMA: A measure of generosity. Journal of Psychopharmacology, 29(6), 661-668. doi: 10.1177/0269881115573806URLpmid: 25735993 |
| [25] | Klimecki O. M., Mayer S. V., Jusyte A., Scheeff J., & Schönenberg M . (2016). Empathy promotes altruistic behavior in economic interactions. Scientific Reports, 6(3), 19-61. doi: 10.1038/srep31961URLpmid: 27578563 |
| [26] | Krupka E. L., & Weber R. A . (2013). Identifying social norms using coordination games: Why does dictator game sharing vary? Journal of the European Economic Association, 11(3), 495-524. doi: 10.1111/jeea.12006URL |
| [27] | Levitt S. D., & List J. A . (2008). Homo economicus evolves. Science, 319(5865), 909-910. doi: 10.1126/science.1153640URLpmid: 18276876 |
| [28] | Liu Y. F., Bi Y. F., & Wang H. Y . (2010). The effects of emotions and task frames on risk preferences in self decision making and anticipating others’ decisions. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 42(3), 317-324. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2010.00317URL |
| [ 刘永芳, 毕玉芳, 王怀勇 . (2010). 情绪和任务框架对自我和预期他人决策时风险偏好的影响. 心理学报, 42(3), 317-324.] | |
| [29] | Liu Y. F., Fan W. J., & Hou R. X . (2019). From theory, research, to applications: Richard H. Thaler and his contributions. Advances in Psychological Science, 27(3), 381-393. |
| [ 刘永芳, 范雯健, 侯日霞 . (2019). 从理论到研究, 再到应用: 塞勒及其贡献. 心理科学进展, 27(3), 381-393.] | |
| [30] | McCullough M. E., Kurzban R., & Tabak B. A . (2013). Cognitive systems for revenge and forgiveness. Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 36(1), 1-15. doi: 10.1017/S0140525X11002160URLpmid: 23211191 |
| [31] | Novemsky N., & Kahneman D . (2005). The boundaries of loss aversion. Journal of Marketing Research, 42(2), 119-128. doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2013.11.010URLpmid: 24334107 |
| [32] | Polman E . (2010). Information distortion in self-other decision making. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 46(2), 432-435. |
| [33] | Polman E . (2012). Self-other decision making and loss aversion. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 119(2), 141-150. |
| [34] | Polman E., & Emich K. J . (2011). Decisions for others are more creative than decisions for the self. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 37(4), 492-501. doi: 10.1177/0146167211398362URLpmid: 21317316 |
| [35] | Rilling J. K., & Sanfey A. G . (2011). The neuroscience of social decision-making. Annual Review of Psychology, 62(1), 23-48. |
| [36] | Smith A . (2015). An inquiry into the nature and causes of the wealth of nations. (Guo, D. L, & Wang, Y. N, Trans.). Beijing: The Commercial Press. (Original work published in 1880) |
| [ 亚当·斯密 . (2015). 国富论. 郭大力, 王亚南译. 商务印书馆. (原著出版于1880年)] | |
| [37] | Smith A . (2015). The theory of moral sentiments. (Jiang, Z. Q, Qin, B. Y, Zhu, Z. L, & Shen, K. Z, Trans.) Beijing: The Commercial Press. (Original work published 1833) |
| [ 亚当·斯密 . (2015). 道德情操论. 蒋自强, 钦北愚, 朱钟棣, 沈凯璋译. 商务印书馆. (原著出版于1833年)] | |
| [38] | Smith A., Pedersen E. J., Forster D. E., McCullough M. E., & Lieberman D . (2017). Cooperation: The roles of interpersonal value and gratitude. Evolution and Human Behavior, 38(6), 695-703. |
| [39] | Sonnemans J., Schram A., & Offerman T . (1998). Public good provision and public bad prevention: The effect of framing. Journal of Economic Behavior & Organization, 34(1), 143-161. |
| [40] | Stone E. R., & Allgaier L . (2008). A social values analysis of self-other differences in decision making involving risk. Basic and Applied Social Psychology, 30(2), 114-129. |
| [41] | Su Y. J., Zhang H., Zhang K . (2012). Social decision-making: The equilibrium between self interest and the interests of others. Journal of Psychological Science, 35(6), 1423-1428. |
| [ 苏彦捷, 张慧, 张康 . (2012). 社会决策: 自我利益与他人利益的权衡. 心理科学, 35(6), 1423-1428.] | |
| [42] | Sze J. A., Gyurak A., Goodkind M. S., & Levenson R. W . (2012). Greater emotional empathy and prosocial behavior in late life. Emotion, 12(5), 1129-1140. doi: 10.1037/a0025011URLpmid: 21859198 |
| [43] | Tooby J., Cosmides L., Sell A., Lieberman D., & Sznycer D . (2008). Internal regulatory variables and the design of human motivation: A computational and evolutionary approach. In A. J. Elliot (ed.), Handbook of approach and avoidance motivation (pp. 251-271). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates. |
| [44] | Trope Y., & Liberman N . (2010). Construal-level theory of psychological distance. Psychological Review, 117(2), 440-463. doi: 10.1037/a0018963URLpmid: 20438233 |
| [45] | Wallach M. A., & Wing C. W . (1968). Is risk a value? Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 9(1), 101-106. doi: 10.1037/h0025719URLpmid: 5667432 |
| [46] | Wang X. T., & Johnson G. J . (2012). A tri-reference point theory of decision making under risk. Journal of Experimental Psychology General, 141(4), 743-756. doi: 10.1037/a0027415URLpmid: 22390265 |
| [47] | Wang X. T., & Wang P . (2013). Tri-reference point theory of decision making: From principles to applications. Advances in Psychological Science, 21(8), 1331-1346. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2013.01331URL |
| [ 王晓田, 王鹏 . (2013). 决策的三参照点理论: 从原理到应用. 心理科学进展, 21(8), 1331-1346.] | |
| [48] | Xie X. F., & Wang X. T . (2002). Achievement motive and opportunity-threat perception. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 34(2), 192-199. |
| [ 谢晓非, 王晓田 . (2002). 成就动机与机会–威胁认知. 心理学报, 34(2), 192-199] | |
| [49] | Xu F. M., Jiang D., Zhang H., Li O., Kong, S X., & Shi, Y W . (2016). The effect of psychological distance on the base-rate neglect. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 48(10), 1292-1301. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2016.01292URL |
| [ 徐富明, 蒋多, 张慧, 李欧, 孔诗晓, 史燕伟 . (2016). 心理距离对基线比例忽略的影响. 心理学报, 48(10), 1292-1301.] | |
| [50] | Zhang X. Y., Chen X. Y., Gao Y., Liu Y. J. & Liu Y. F . (2018). Self-promotion hypothesis: The impact of self-esteem on self-other discrepancies in decision making under risk. Personality and Individual Differences, 127, 26-30. |
| [51] | Zhang W., Liu Y. F., Sun Q. Z., Hu Q. X., & Liu Y . (2014). Risk preference in making romantic relationship decisions for others with different psychological distance. Acta Psychologica Sinica. 46(10), 1580-1590. |
| [ 张葳, 刘永芳, 孙庆洲, 胡启旭, 刘毅 . (2014). 异性交友决策任务上为不同心理距离他人决策的风险偏好. 心理学报, 46(10), 1580-1590.] | |
| [52] | Zhao H. L., Xu F. J., Guo Y. Y., & Shu S. L . (2018). Difference of prosocial behavior between social classes: Dual perspective of giving and receiving. Chinese Journal of Clinical Psychology, 26(5), 841-846. doi: 10.1002/jclp.22919URLpmid: 31909837 |
| [ 赵华丽, 徐凤娇, 郭永玉, 舒首立 . (2018). 亲社会行为的阶层差异: 施与受的双重视角. 中国临床心理学杂志, 26(5), 841-846.] pmid: 31909837 | |
| [53] | Zhao Q. D., Liu Y. F., Duan J., & Xu S . (2013). The effect of psychological distance and decision makers’ roles on risk decision. Chinese Journal of Applied Psychology, 19( 1) 26-33. |
| [ 赵秋荻, 刘永芳, 段婧, 徐沙 . (2013). 心理距离与决策者角色对风险决策的影响. 应用心理学, 19(1), 26-33.] | |
| [54] | Zhong Y. L., & Liu Y. F . (2013). Risk preferences in monetary auction tasks: The roles of self-esteem levels and genders. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 45(3), 353-362. |
| [ 仲轶璐, 刘永芳 . (2013). 金钱竞拍任务上的风险偏好: 自尊水平和性别的作用. 心理学报, 45(3), 353-362.] |
相关文章 15
| [1] | 陈庆;何泉;陈广耀;郭悦智;张荷婧;何先友. 复杂情境下不同角度及思维方式的决策表现差异:决策视角−心理距离的作用[J]. 心理学报, 2017, 49(3): 383-392. |
| [2] | 何贵兵, 杨鑫蔚, 蒋多. 环境损益的社会折扣:利他人格的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2017, 49(10): 1334-1343. |
| [3] | 费定舟;钱东海;黄旭辰. 利他行为的自我控制过程模型:自我损耗下的道德情绪的正向作用[J]. 心理学报, 2016, 48(9): 1175-1183. |
| [4] | 何宁;朱云莉. 自爱与他爱:自恋、共情与内隐利他的关系[J]. 心理学报, 2016, 48(2): 199-210. |
| [5] | 徐富明;蒋多;张慧;李欧;孔诗晓; 史燕伟. 心理距离对基线比例忽略的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2016, 48(10): 1292-1301. |
| [6] | 肖二平;张积家;王娟. 摩梭走访制下的阿注关系:是亲属还是朋友?[J]. 心理学报, 2015, 47(12): 1486-1498. |
| [7] | 张锋;申之美. 行为表征水平与心理距离间不具自动化联接特性:来自图片-词汇Stroop范式的实验证据[J]. 心理学报, 2014, 46(9): 1317-1330. |
| [8] | 任俊;李瑞雪;詹鋆;刘迪;林曼;彭年强. 好人可能做出坏行为的心理学解释 —— 基于自我控制资源损耗的研究证据[J]. 心理学报, 2014, 46(6): 841-851. |
| [9] | 陈海贤;何贵兵. 心理距离对跨期选择和风险选择的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2014, 46(5): 677-690. |
| [10] | 张葳;刘永芳;孙庆洲;胡启旭;刘毅. 异性交友决策任务上为不同心理距离他人决策的风险偏好[J]. 心理学报, 2014, 46(10): 1580-1590. |
| [11] | 何贵兵;蒋多. 任务框架及利他人格对社会折扣的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2013, 45(10): 1131-1146. |
| [12] | 吴燕,罗跃嘉. 利他惩罚中的结果评价—— ERP研究[J]. 心理学报, 2011, 43(06): 661-673. |
| [13] | 陈海贤,何贵兵. 识解水平对跨期选择和风险选择的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2011, 43(04): 442-452. |
| [14] | 柴俊武,赵广志,何伟. 解释水平对品牌联想和品牌延伸评估的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2011, 43(02): 175-187. |
| [15] | 张雷. 进化心理学的相关概念、理论与历史[J]. 心理学报, 2007, 39(03): 556-570. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlxb/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=4706
