 ), 温恒福1(
), 温恒福1( ), 程淑华2, 张淳淦2, 李欣3
), 程淑华2, 张淳淦2, 李欣3 1哈尔滨师范大学教育科学学院, 哈尔滨 150025
2齐齐哈尔大学教师教育学院, 齐齐哈尔 161006
3哈尔滨剑桥学院大学生心理健康教育中心, 哈尔滨 150040
收稿日期:2020-03-23出版日期:2020-11-25发布日期:2020-09-22通讯作者:韩毅初,温恒福E-mail:hanyichu@126.com;wenhengfu@126.comRelationship between perceived discrimination and mental health of migrant children: A meta-analysis of Chinese students
HAN Yichu1( ), WEN Hengfu1(
), WEN Hengfu1( ), CHENG Shuhua2, ZHANG Chungan2, LI Xin3
), CHENG Shuhua2, ZHANG Chungan2, LI Xin3 1College of Educational Science, Harbin Normal University, Harbin 150025, China
2College of Teachers Education, Qiqihar Medical University, Qiqihar 161006, China
3Education Center for Mental Health, Harbin Cambridge College, Harbin 150040, China
Received:2020-03-23Online:2020-11-25Published:2020-09-22Contact:HAN Yichu,WEN Hengfu E-mail:hanyichu@126.com;wenhengfu@126.com摘要/Abstract
摘要: 本研究基于心理健康双因素模型,通过运用元分析技术探讨流动儿童歧视知觉与各项心理健康指标的关系,以及调节变量对二者关系的影响,以期为提升流动儿童心理健康提供有效借鉴。经过文献检索和筛选,共纳入原始文献3篇,含49个独立样本,被试总数达到40351名。根据同质性检验结果,选择随机效应模型分析发现,流动儿童歧视知觉与积极心理健康指标存在中等程度的负相关(r=-0.323,95%CI为[-0.378,-0.266]),与消极心理健康指标存在中等程度的正相关(r = 0.41, 95%CI为[0.36,0.458])。流动儿童歧视知觉测量工具、学龄段对流动儿童歧视知觉与积极心理健康的关系存在显著的调节效应,而对流动儿童歧视知觉与消极心理健康的关系不存在显著的调节效应。同时,元回归分析结果发现,性别对二者的关系不存在显著的调节效应。后续研究应该进一步探索流动儿童歧视知觉与心理健康间的调节变量,结合中国流动儿童心理发展特点, 探索提升流动儿童心理健康水平的新路径。
图/表 11

图1元分析文献筛选流程
 图1元分析文献筛选流程
图1元分析文献筛选流程表1纳入元分析的原始研究的基本资料
| 第一作者 | 发表 年份 | 被试 数量 | 相关 系数 | 发表 类型 | 学龄段 | 歧视知觉测量工具 | 因变量效价 | 因变量指标 | 文献 语种 | 男性比 | 文献 质量 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 郑久波a | 2012 | 767 | -0.624 | 学位论文 | 初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 自尊 | 中文 | 0.334 | 4 |
| 刘霞a | 2010 | 1350 | -0.38 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 自尊 | 中文 | 0.535 | 7 |
| 蔺秀云a | 2009 | 1164 | -0.39 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 自尊 | 中文 | 0.544 | 8 |
| 郝振a | 2014 | 437 | -0.13 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 自尊 | 中文 | 0.449 | 7 |
| 范兴华a | 2016 | 507 | -0.27 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | F-PDS | 积极指标 | 自尊 | 中文 | 0.531 | 8 |
| 邓小晴a | 2013 | 503 | -0.44 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 自尊 | 中文 | 0.531 | 8 |
| 肖倩怡 | 2017 | 345 | -0.33 | 学位论文 | 初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 幸福感 | 中文 | 0.470 | 6 |
| 师保国 | 2013 | 559 | -0.28 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 幸福感 | 中文 | 0.565 | 7 |
| Liu X. | 2016 | 798 | -0.36 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 幸福感 | 英文 | 0.521 | 8 |
| 郑久波b | 2012 | 767 | 0.478 | 学位论文 | 初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 心理弹性 | 中文 | 0.334 | 4 |
| 王盈 | 2017 | 555 | -0.143 | 学位论文 | 初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 心理弹性 | 中文 | 0.575 | 5 |
| 牛品超 | 2019 | 606 | -0.124 | 学位论文 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 心理弹性 | 中文 | 0.581 | 6 |
| 张岩a | 2019 | 614 | -0.15 | 期刊 | 小学 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 其他 | 中文 | 0.538 | 8 |
| 张晓玲 | 2018 | 525 | -0.14 | 学位论文 | 初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 其他 | 中文 | 0.441 | 5 |
| 卢璇b | 2012 | 557 | -0.675 | 学位论文 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 生活满意度 | 中文 | 0.544 | 6 |
| 刘霞e | 2013 | 1350 | -0.33 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 生活满意度 | 中文 | 0.534 | 7 |
| 刘霞d | 2013 | 1551 | -0.33 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 生活满意度 | 中文 | 0.562 | 8 |
| 林良章 | 2015 | 313 | -0.304 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 生活满意度 | 中文 | 0.502 | 4 |
| 郝振b | 2014 | 437 | -0.25 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 生活满意度 | 中文 | 0.449 | 7 |
| 白佳蕊 | 2019 | 892 | -0.34 | 学位论文 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 生活满意度 | 中文 | 0.511 | 6 |
| 张岩c | 2017 | 1131 | -0.16 | 期刊 | 小学 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 社会支持 | 中文 | 0.554 | 7 |
| 张岩b | 2017 | 1101 | -0.16 | 期刊 | 小学 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 社会支持 | 中文 | 0.553 | 7 |
| 倪士光 | 2014 | 1307 | -0.29 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | F-PDS | 积极指标 | 社会支持 | 中文 | 0.541 | 7 |
| 卢璇c | 2012 | 557 | -0.745 | 学位论文 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 社会支持 | 中文 | 0.544 | 6 |
| 李越b | 2018 | 504 | -0.31 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 社会支持 | 中文 | 0.452 | 7 |
| 侯舒艨b | 2011 | 680 | -0.23 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 社会支持 | 中文 | 0.541 | 8 |
| 侯舒艨a | 2011 | 1132 | -0.07 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 社会支持 | 中文 | 0.559 | 7 |
| 范兴华f | 2012 | 558 | -0.221 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | F-PDS | 积极指标 | 社会支持 | 中文 | 0.522 | 7 |
| 范兴华d | 2012 | 1164 | -0.18 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | F-PDS | 积极指标 | 社会支持 | 中文 | 0.544 | 7 |
| 邓小晴b | 2013 | 503 | -0.5 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 社会支持 | 中文 | 0.531 | 8 |
| 邓欢 | 2012 | 386 | -0.25 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 社会支持 | 中文 | 0.575 | 6 |
| 刘霞g | 2013 | 1551 | -0.34 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 其他 | 中文 | 0.562 | 8 |
| 刘霞 | 2013 | 1350 | -0.34 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 其他 | 中文 | 0.534 | 7 |
| 卢璇a | 2012 | 557 | 0.66 | 学位论文 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 消极指标 | 抑郁 | 中文 | 0.544 | 6 |
| 蔺秀云b | 2009 | 1164 | 0.37 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 消极指标 | 抑郁 | 中文 | 0.544 | 8 |
| 李越a | 2018 | 504 | 0.39 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 消极指标 | 抑郁 | 中文 | 0.452 | 7 |
| 范兴华c | 2016 | 507 | 0.42 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | F-PDS | 消极指标 | 抑郁 | 中文 | 0.531 | 8 |
| 范兴华b | 2012 | 558 | 0.463 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | F-PDS | 消极指标 | 抑郁 | 中文 | 0.522 | 7 |
| 刘霞c | 2013 | 1350 | 0.39 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 消极指标 | 其他情绪问题 | 中文 | 0.534 | 7 |
| 刘霞b | 2013 | 1551 | 0.39 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 消极指标 | 其他情绪问题 | 中文 | 0.562 | 8 |
| 朱倩 | 2015 | 577 | 0.42 | 期刊 | 小学 | L-PDS | 消极指标 | 行为问题 | 中文 | 0.574 | 7 |
| 蔺秀云c | 2009 | 1164 | 0.38 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 消极指标 | 其他情绪问题 | 中文 | 0.544 | 8 |
| 蔺秀云d | 2009 | 1164 | 0.5 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 消极指标 | 孤独感 | 中文 | 0.544 | 8 |
| 李越c | 2018 | 504 | 0.35 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 消极指标 | 孤独感 | 中文 | 0.452 | 7 |
| 侯舒艨c | 2011 | 680 | 0.42 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 消极指标 | 孤独感 | 中文 | 0.541 | 8 |
| 侯舒艨d | 2011 | 1132 | 0.4 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 消极指标 | 孤独感 | 中文 | 0.559 | 7 |
| 方晓义 | 2008 | 1164 | 0.18 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 消极指标 | 孤独感 | 中文 | 0.544 | 7 |
| Liu D. | 2014 | 357 | 0.47 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | F-PDS | 消极指标 | 孤独感 | 英文 | 0.541 | 8 |
| Jia X. | 2017 | 897 | 0.3 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 消极指标 | 行为问题 | 英文 | 0.512 | 8 |
表1纳入元分析的原始研究的基本资料
| 第一作者 | 发表 年份 | 被试 数量 | 相关 系数 | 发表 类型 | 学龄段 | 歧视知觉测量工具 | 因变量效价 | 因变量指标 | 文献 语种 | 男性比 | 文献 质量 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 郑久波a | 2012 | 767 | -0.624 | 学位论文 | 初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 自尊 | 中文 | 0.334 | 4 |
| 刘霞a | 2010 | 1350 | -0.38 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 自尊 | 中文 | 0.535 | 7 |
| 蔺秀云a | 2009 | 1164 | -0.39 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 自尊 | 中文 | 0.544 | 8 |
| 郝振a | 2014 | 437 | -0.13 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 自尊 | 中文 | 0.449 | 7 |
| 范兴华a | 2016 | 507 | -0.27 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | F-PDS | 积极指标 | 自尊 | 中文 | 0.531 | 8 |
| 邓小晴a | 2013 | 503 | -0.44 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 自尊 | 中文 | 0.531 | 8 |
| 肖倩怡 | 2017 | 345 | -0.33 | 学位论文 | 初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 幸福感 | 中文 | 0.470 | 6 |
| 师保国 | 2013 | 559 | -0.28 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 幸福感 | 中文 | 0.565 | 7 |
| Liu X. | 2016 | 798 | -0.36 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 幸福感 | 英文 | 0.521 | 8 |
| 郑久波b | 2012 | 767 | 0.478 | 学位论文 | 初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 心理弹性 | 中文 | 0.334 | 4 |
| 王盈 | 2017 | 555 | -0.143 | 学位论文 | 初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 心理弹性 | 中文 | 0.575 | 5 |
| 牛品超 | 2019 | 606 | -0.124 | 学位论文 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 心理弹性 | 中文 | 0.581 | 6 |
| 张岩a | 2019 | 614 | -0.15 | 期刊 | 小学 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 其他 | 中文 | 0.538 | 8 |
| 张晓玲 | 2018 | 525 | -0.14 | 学位论文 | 初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 其他 | 中文 | 0.441 | 5 |
| 卢璇b | 2012 | 557 | -0.675 | 学位论文 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 生活满意度 | 中文 | 0.544 | 6 |
| 刘霞e | 2013 | 1350 | -0.33 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 生活满意度 | 中文 | 0.534 | 7 |
| 刘霞d | 2013 | 1551 | -0.33 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 生活满意度 | 中文 | 0.562 | 8 |
| 林良章 | 2015 | 313 | -0.304 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 生活满意度 | 中文 | 0.502 | 4 |
| 郝振b | 2014 | 437 | -0.25 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 生活满意度 | 中文 | 0.449 | 7 |
| 白佳蕊 | 2019 | 892 | -0.34 | 学位论文 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 生活满意度 | 中文 | 0.511 | 6 |
| 张岩c | 2017 | 1131 | -0.16 | 期刊 | 小学 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 社会支持 | 中文 | 0.554 | 7 |
| 张岩b | 2017 | 1101 | -0.16 | 期刊 | 小学 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 社会支持 | 中文 | 0.553 | 7 |
| 倪士光 | 2014 | 1307 | -0.29 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | F-PDS | 积极指标 | 社会支持 | 中文 | 0.541 | 7 |
| 卢璇c | 2012 | 557 | -0.745 | 学位论文 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 社会支持 | 中文 | 0.544 | 6 |
| 李越b | 2018 | 504 | -0.31 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 社会支持 | 中文 | 0.452 | 7 |
| 侯舒艨b | 2011 | 680 | -0.23 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 社会支持 | 中文 | 0.541 | 8 |
| 侯舒艨a | 2011 | 1132 | -0.07 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 社会支持 | 中文 | 0.559 | 7 |
| 范兴华f | 2012 | 558 | -0.221 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | F-PDS | 积极指标 | 社会支持 | 中文 | 0.522 | 7 |
| 范兴华d | 2012 | 1164 | -0.18 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | F-PDS | 积极指标 | 社会支持 | 中文 | 0.544 | 7 |
| 邓小晴b | 2013 | 503 | -0.5 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 社会支持 | 中文 | 0.531 | 8 |
| 邓欢 | 2012 | 386 | -0.25 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 社会支持 | 中文 | 0.575 | 6 |
| 刘霞g | 2013 | 1551 | -0.34 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 其他 | 中文 | 0.562 | 8 |
| 刘霞 | 2013 | 1350 | -0.34 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 积极指标 | 其他 | 中文 | 0.534 | 7 |
| 卢璇a | 2012 | 557 | 0.66 | 学位论文 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 消极指标 | 抑郁 | 中文 | 0.544 | 6 |
| 蔺秀云b | 2009 | 1164 | 0.37 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 消极指标 | 抑郁 | 中文 | 0.544 | 8 |
| 李越a | 2018 | 504 | 0.39 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 消极指标 | 抑郁 | 中文 | 0.452 | 7 |
| 范兴华c | 2016 | 507 | 0.42 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | F-PDS | 消极指标 | 抑郁 | 中文 | 0.531 | 8 |
| 范兴华b | 2012 | 558 | 0.463 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | F-PDS | 消极指标 | 抑郁 | 中文 | 0.522 | 7 |
| 刘霞c | 2013 | 1350 | 0.39 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 消极指标 | 其他情绪问题 | 中文 | 0.534 | 7 |
| 刘霞b | 2013 | 1551 | 0.39 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 消极指标 | 其他情绪问题 | 中文 | 0.562 | 8 |
| 朱倩 | 2015 | 577 | 0.42 | 期刊 | 小学 | L-PDS | 消极指标 | 行为问题 | 中文 | 0.574 | 7 |
| 蔺秀云c | 2009 | 1164 | 0.38 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 消极指标 | 其他情绪问题 | 中文 | 0.544 | 8 |
| 蔺秀云d | 2009 | 1164 | 0.5 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 消极指标 | 孤独感 | 中文 | 0.544 | 8 |
| 李越c | 2018 | 504 | 0.35 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 消极指标 | 孤独感 | 中文 | 0.452 | 7 |
| 侯舒艨c | 2011 | 680 | 0.42 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 消极指标 | 孤独感 | 中文 | 0.541 | 8 |
| 侯舒艨d | 2011 | 1132 | 0.4 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 消极指标 | 孤独感 | 中文 | 0.559 | 7 |
| 方晓义 | 2008 | 1164 | 0.18 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 消极指标 | 孤独感 | 中文 | 0.544 | 7 |
| Liu D. | 2014 | 357 | 0.47 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | F-PDS | 消极指标 | 孤独感 | 英文 | 0.541 | 8 |
| Jia X. | 2017 | 897 | 0.3 | 期刊 | 小学初中 | L-PDS | 消极指标 | 行为问题 | 英文 | 0.512 | 8 |
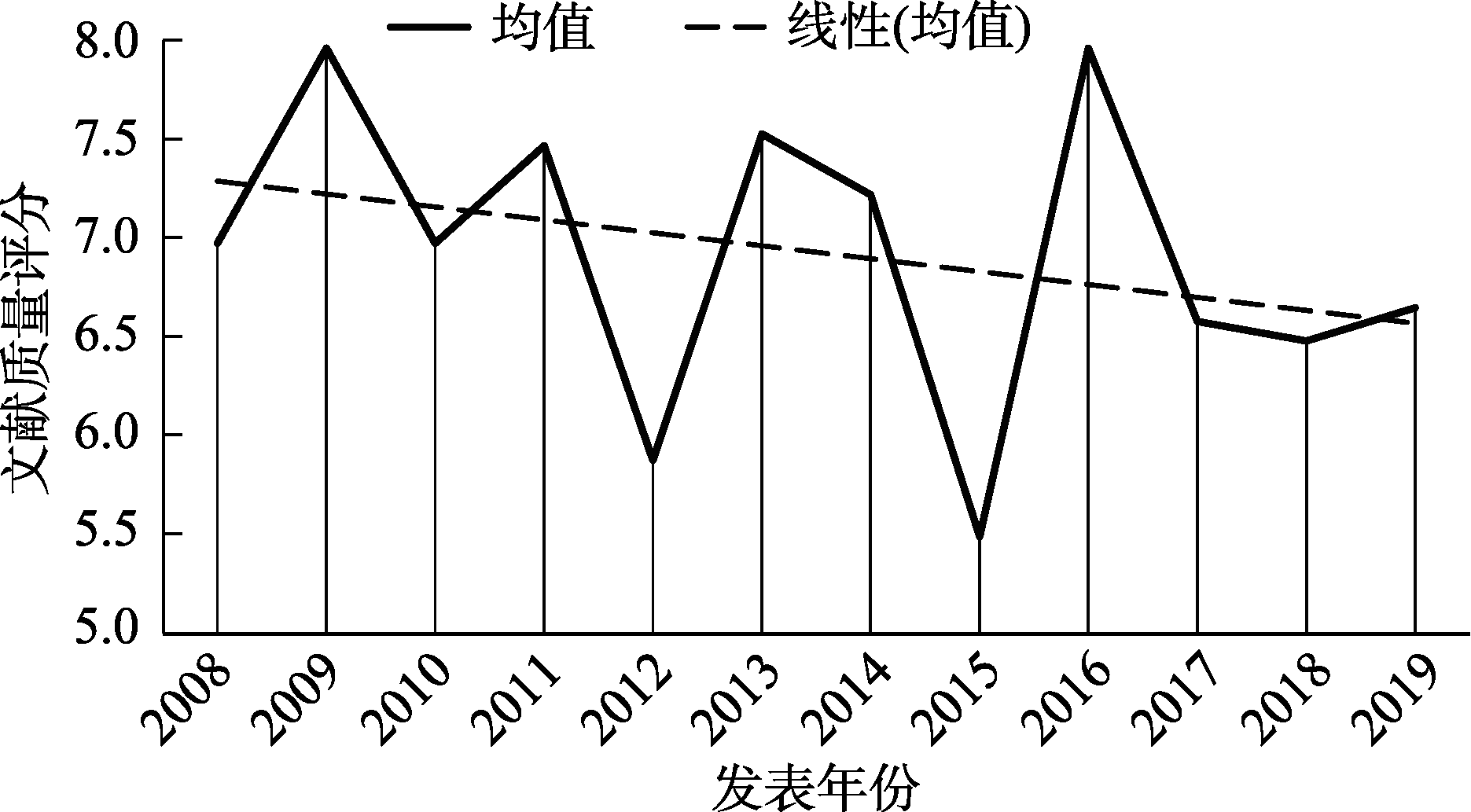
图2研究质量变化趋势
 图2研究质量变化趋势
图2研究质量变化趋势表2歧视知觉与心理健康的效应值同质性检验结果(Q统计)
| 指标 | 模型 | 研究数 | 同质性 | Tau-squared | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q值 | df (Q) | P-value | I-squared | Tau Squared | SE | Variance | Tau | |||
| 积极心理健康 | 随机模型 | 33 | 843.499 | 32.000 | 0.000 | 96.206 | 0.032 | 0.009 | 0.000 | 0.179 |
| 消极心理健康 | 随机模型 | 16 | 184.321 | 15.000 | 0.000 | 91.862 | 0.013 | 0.006 | 0.000 | 0.115 |
表2歧视知觉与心理健康的效应值同质性检验结果(Q统计)
| 指标 | 模型 | 研究数 | 同质性 | Tau-squared | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q值 | df (Q) | P-value | I-squared | Tau Squared | SE | Variance | Tau | |||
| 积极心理健康 | 随机模型 | 33 | 843.499 | 32.000 | 0.000 | 96.206 | 0.032 | 0.009 | 0.000 | 0.179 |
| 消极心理健康 | 随机模型 | 16 | 184.321 | 15.000 | 0.000 | 91.862 | 0.013 | 0.006 | 0.000 | 0.115 |
表3歧视知觉与心理健康关系随机模型分析
| 指标 | 模型 | 研究数 | 效应值及95%的置信区间 | 双尾检验 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 点估计 | 下限 | 上限 | Z值 | p | |||
| 积极心理健康 | 随机模型 | 33 | -0.323 | -0.378 | -0.266 | -10.537 | 0.000 |
| 消极心理健康 | 随机模型 | 16 | 0.410 | 0.360 | 0.458 | 14.406 | 0.000 |
表3歧视知觉与心理健康关系随机模型分析
| 指标 | 模型 | 研究数 | 效应值及95%的置信区间 | 双尾检验 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 点估计 | 下限 | 上限 | Z值 | p | |||
| 积极心理健康 | 随机模型 | 33 | -0.323 | -0.378 | -0.266 | -10.537 | 0.000 |
| 消极心理健康 | 随机模型 | 16 | 0.410 | 0.360 | 0.458 | 14.406 | 0.000 |
表4相关因素对歧视知觉与积极心理健康指标关系的调节效应检验
| 调节变量 | 异质性检验 | 类别 | K | 95% CI | 双尾检验 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QB | df | p | 点估计 | 下限 | 上限 | Z值 | p | |||
| 歧视知觉测量工具 | 4.785 | 1 | 0.029 | F-PDS | 4 | -0.240 | -0.296 | -0.183 | -8.043 | 0.000 |
| L-PDS | 29 | -0.334 | -0.395 | -0.271 | -9.732 | 0.000 | ||||
| 学龄段 | 25.503 | 2 | 0.000 | 初中 | 5 | -0.360 | -0.546 | -0.140 | -3.136 | 0.002 |
| 小学 | 3 | -0.158 | -0.194 | -0.122 | -8.478 | 0.000 | ||||
| 小学初中 | 25 | -0.335 | -0.393 | -0.274 | -10.168 | 0.000 | ||||
表4相关因素对歧视知觉与积极心理健康指标关系的调节效应检验
| 调节变量 | 异质性检验 | 类别 | K | 95% CI | 双尾检验 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QB | df | p | 点估计 | 下限 | 上限 | Z值 | p | |||
| 歧视知觉测量工具 | 4.785 | 1 | 0.029 | F-PDS | 4 | -0.240 | -0.296 | -0.183 | -8.043 | 0.000 |
| L-PDS | 29 | -0.334 | -0.395 | -0.271 | -9.732 | 0.000 | ||||
| 学龄段 | 25.503 | 2 | 0.000 | 初中 | 5 | -0.360 | -0.546 | -0.140 | -3.136 | 0.002 |
| 小学 | 3 | -0.158 | -0.194 | -0.122 | -8.478 | 0.000 | ||||
| 小学初中 | 25 | -0.335 | -0.393 | -0.274 | -10.168 | 0.000 | ||||
表5相关因素对歧视知觉与消极心理健康指标关系的调节效应检验
| 调节变量 | 异质性检验 | 类别 | K | 95% CI | 双尾检验 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QB | df | p | 点估计 | 下限 | 上限 | Z值 | p | |||
| 歧视知觉测量工具 | 0.589 | 1 | 0.443 | F-PDS | 3 | 0.451 | 0.332 | 0.556 | 6.741 | 0.000 |
| L-PDS | 13 | 0.401 | 0.345 | 0.455 | 12.679 | 0.000 | ||||
| 学龄段 | 0.058 | 1.000 | 0.810 | 小学 | 1 | 0.420 | 0.350 | 0.485 | 10.726 | 0.000 |
| 小学初中 | 15 | 0.410 | 0.356 | 0.460 | 13.619 | 0.000 | ||||
表5相关因素对歧视知觉与消极心理健康指标关系的调节效应检验
| 调节变量 | 异质性检验 | 类别 | K | 95% CI | 双尾检验 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QB | df | p | 点估计 | 下限 | 上限 | Z值 | p | |||
| 歧视知觉测量工具 | 0.589 | 1 | 0.443 | F-PDS | 3 | 0.451 | 0.332 | 0.556 | 6.741 | 0.000 |
| L-PDS | 13 | 0.401 | 0.345 | 0.455 | 12.679 | 0.000 | ||||
| 学龄段 | 0.058 | 1.000 | 0.810 | 小学 | 1 | 0.420 | 0.350 | 0.485 | 10.726 | 0.000 |
| 小学初中 | 15 | 0.410 | 0.356 | 0.460 | 13.619 | 0.000 | ||||
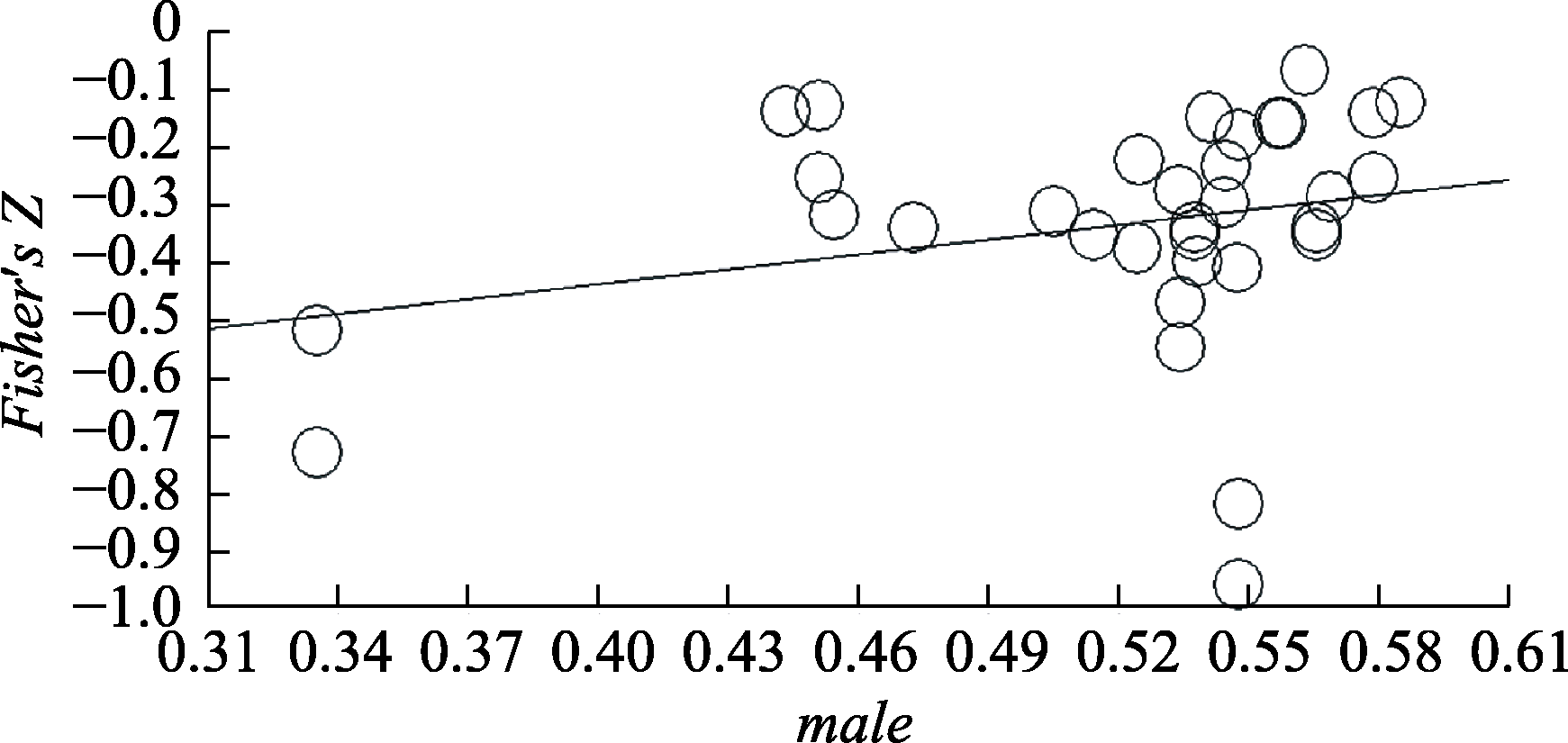
图3性别对歧视知觉与积极心理健康关系的回归分析
 图3性别对歧视知觉与积极心理健康关系的回归分析
图3性别对歧视知觉与积极心理健康关系的回归分析表6性别对歧视知觉与积极心理健康关系的回归的贝叶斯分析
| Models | P (M) | P (M|data) | BFM | BF10 | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Null model | 0.500 | 0.534 | 1.145 | 1.000 | 0 |
| gender | 0.500 | 0.466 | 0.873 | 0.873 | 0.076 |
表6性别对歧视知觉与积极心理健康关系的回归的贝叶斯分析
| Models | P (M) | P (M|data) | BFM | BF10 | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Null model | 0.500 | 0.534 | 1.145 | 1.000 | 0 |
| gender | 0.500 | 0.466 | 0.873 | 0.873 | 0.076 |
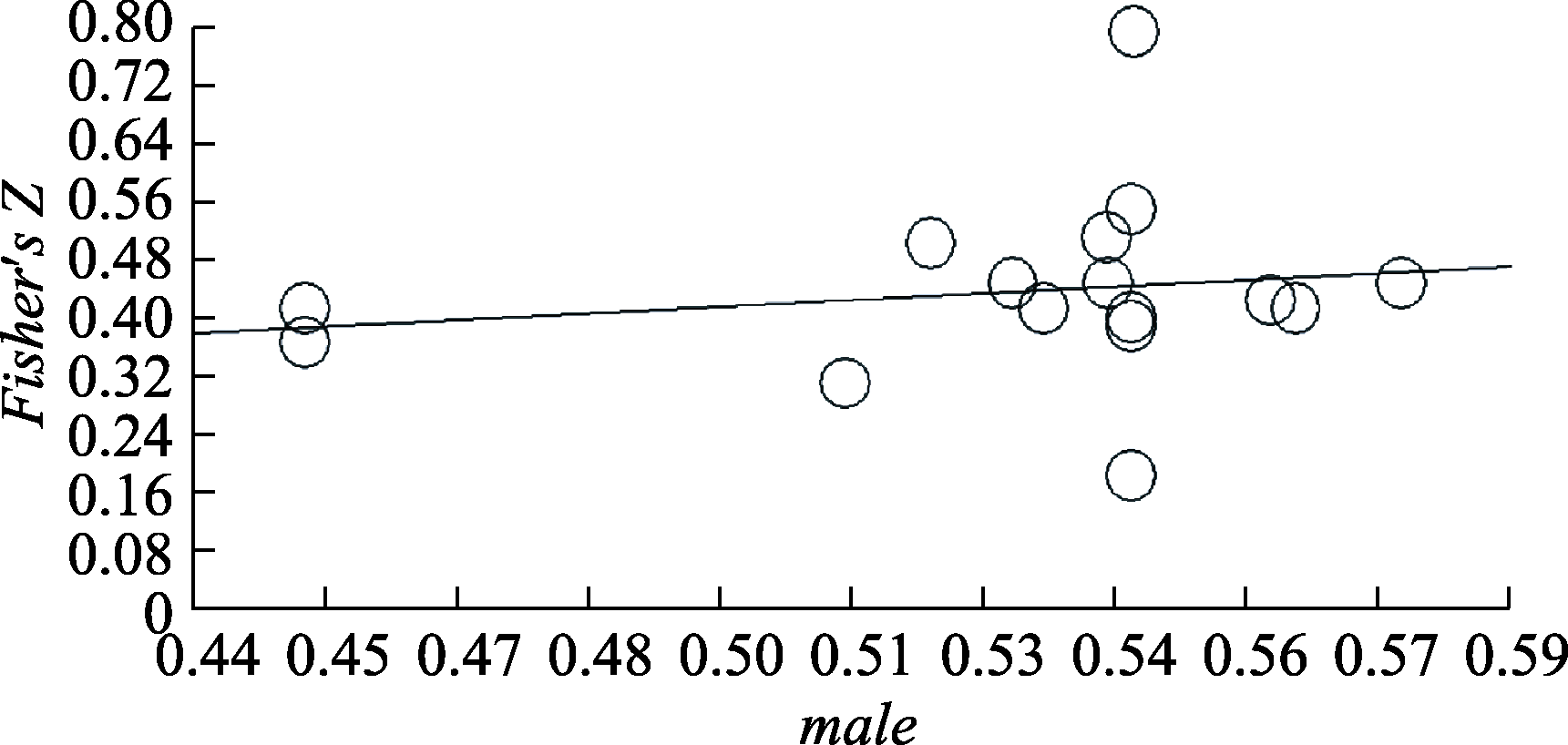
图4性别对歧视知觉与消极心理健康关系的回归分析
 图4性别对歧视知觉与消极心理健康关系的回归分析
图4性别对歧视知觉与消极心理健康关系的回归分析表7性别对歧视知觉与消极心理健康关系的回归的贝叶斯分析
| Models | P (M) | P (M|data) | BFM | BF10 | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Null model | 0.500 | 0.671 | 2.037 | 1.000 | 0 |
| gender | 0.500 | 0.329 | 0.491 | 0.491 | 0.028 |
表7性别对歧视知觉与消极心理健康关系的回归的贝叶斯分析
| Models | P (M) | P (M|data) | BFM | BF10 | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Null model | 0.500 | 0.671 | 2.037 | 1.000 | 0 |
| gender | 0.500 | 0.329 | 0.491 | 0.491 | 0.028 |
参考文献 67
| *元分析用到的参考文献 | |
| [1] | Antaramian, S. P., Huebner, E. S., Hills, K. J., & Valois, R. F.(2010). A dual-factor model of mental health: Toward a more comprehensive understanding of youth functioning. American Journal of Orthopsychiatry, 80(4), 462-472. doi: 10.1111/j.1939-0025.2010.01049.xURLpmid: 20950287 |
| [2] | *Bai, J. R.(2019). Relationships between perceived discrimination and life satisfaction in migrant children: A moderated mediation model (Unpublished master's thesis). Tianjin Normal University, China. |
| [ 白佳蕊.(2019). 流动儿童歧视知觉与生活满意度的关系:有调节的中介模型 (硕士论文). 天津师范大学.] | |
| [3] | Beiser, M., Dion, R., Gotowiec, A., Hyman, I ., & Vu, N.(1995). Immigrant and refugee children in Canada. The Canadian Journal of Psychiatry, 40(2), 67-72. URLpmid: 7788620 |
| [4] | Borenstein, M., Hedges, L. V., Higgins, J. P. T., & Rothstein, H. R.(2009). Effect sizes based on means. In M.Borenstein, L. V. Hedges, J. P. T. Higgins, & H. R. Rothstein (Eds.), Introduction to meta-analysis(pp. 21-32). United Kingdom: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. |
| [5] | Branscombe, N. R., Schmit, M. T., & Harvey, R. D.(1999). Perceiving pervasive discrimination among African Americans: Implications for group identification and well-being. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 77(1), 135-149. |
| [6] | Bronstein, I., & Montgomery, P.(2011). Psychological distress in refugee children: A systematic review. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 14(1), 44-56. doi: 10.1007/s10567-010-0081-0URLpmid: 21181268 |
| [7] | Caravita, S. C. S., Strohmeier, D., Salmivalli, C., & Blasio, P. D.(2019). Bullying immigrant versus non-immigrant peers: Moral disengagement and participant roles. Journal of School Psychology, 75, 119-133. URLpmid: 31474278 |
| [8] | Chang, C. D.(2019). Social determinants of health and health disparities among immigrants and their children. Current Problems in Pediatric and Adolescent Health Care, 49(1), 23-30. URLpmid: 30595524 |
| [9] | Cheng, S. H., Li, X., & Han, Y. C.(2017). The relation of intergroup contact and out-group trust: Mediator role of in-group identification. Psychological Exploration, 37(1), 54-58. |
| [ 程淑华, 李欣, 韩毅初.(2017). 群际接触对外群体信任的影响: 内群体认同的中介效应. 心理学探新, 37(1), 54-58.] | |
| [10] | *Deng, H., Ma, J., Ji, T. T., & Jiang, Q.(2012). Relationship between social support and perception of discrimination in mobile children: The moderating role of role identity. Journal of Inner Mongolia Normal University (Educational Science), 25 (2), 39-42. |
| [ 邓欢, 马静, 纪婷婷, 江琦.(2012). 流动儿童社会支持与歧视知觉关系: 角色认同的调节作用. 内蒙古师范大学学报(教育科学版), 25(2), 39-42.] | |
| [11] | *Deng, X. Q., & Shi, B. G.(2013). Migrant children's perceived discrimination and self-esteem: The effect of social support and migration duration. Chinese Journal of Special Education, 158(8), 48-54. |
| [ 邓小晴, 师保国.(2013). 流动儿童歧视知觉与自尊: 社会支持与流动时间的作用. 中国特殊教育, 158(8), 48-54.] | |
| [12] | Dimitrova, R., Chasiotis, A., & van de Vijver F.(2016). Adjustment outcomes of immigrant children and youth in Europe: A meta-analysis. European Psychologist,21, 150-162. |
| [13] | *Fan, X. H., & Chen, F. J.(2012). Perceived discrimination and depression: Moderating of coping, and social support in migrant children. Chinese Journal of Clinical Psychology, 20(4), 539-542. |
| [ 范兴华, 陈锋菊.(2012). 流动儿童歧视知觉与抑郁: 应对方式与社会支持的调节. 中国临床心理学杂志, 20(4), 539-542.] | |
| [14] | *Fan, X. H., Chen, F. J., Tang W. P., Huang Y. S., & Yuan, S. Y.(2016). The dynamic relationship between perceived discrimination, self-esteem and depression in migrant children. Chinese Journal of Clinical Psychology, 24(1), 51-54. |
| [ 范兴华, 陈锋菊, 唐文萍, 黄月胜, 袁宋云.(2016). 流动儿童歧视知觉、自尊与抑郁的动态关系: 模型检验. 中国临床心理学杂志, 24(1),51-54.] | |
| [15] | *Fan, X. H., Fang, X. Y., Liu, Y., Ling, X. Y., & Yuan, X. J.(2012). The effect of social support and social identity on the relationship between perceived discrimination and socio-cultural adjustment among Chinese migrant children. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 44(5), 647-663. |
| [ 范兴华, 方晓义, 刘杨, 蔺秀云, 袁晓娇. (2012). 流动儿童歧视知觉与社会文化适应: 社会支持和社会认同的作用. 心理学报, 44(5), 647-663.] | |
| [16] | *Fang, X. Y., Fan X. H., & Liu, Y.(2008). Perceived discrimination and loneliness: Moderating effects of coping style among migrant children. Psychological Development and Education, 24(4), 93-99. |
| [ 方晓义, 范兴华, 刘杨.(2008). 应对方式在流动儿童歧视知觉与孤独情绪关系上的调节作用. 心理发展与教育, 24(4), 93-99.] | |
| [17] | Goffman, E.(1963). Stigma: Notes on the management of spoiled identity. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall. |
| [18] | Guerra, R., Rodrigues, R. B., Aguiar, C., Carmona, M., Alexandre, J., & Lopes, R. C.(2019). School achievement and well-being of immigrant children: The role of acculturation orientations and perceived discrimination. Journal of school psychology, 75, 104-118. URLpmid: 31474277 |
| [19] | *Hao, Z., & Cui, L. J.(2014). The impact of perceived discrimination on Chinese migrant children's social integration: Mediator mechanisms and moderator effect of self-esteem. Psychological Development and Education, 30(2), 137-144. |
| [ 郝振, 崔丽娟.(2014). 受歧视知觉对流动儿童社会融入的影响: 中介机制及自尊的调节作用. 心理发展与教育, 30(2), 137-144.] | |
| [20] | *Hou, S. M., Yuan X. J., Liu, Y., Ling, X. Y, &Fang, X. Y.(2011). The effect of social support and perceived discrimination on loneliness among migrant children: A longitudinal study. Psychological Development and Education, 27(4), 401-412. |
| [ 侯舒艨, 袁晓娇, 刘杨, 蔺秀云, 方晓义.(2011). 社会支持和歧视知觉对流动儿童孤独感的影响: 一项追踪研究. 心理发展与教育, 27(4), 401-412.] | |
| [21] | Hu, C. P., Kong, X. Z., Wagenmakers, E-J., Ly, A., & Peng K. P.(2018). The bayes factor and its implementation in JASP: A practical primer. Advances in Psychological Science,26(6), 951-965. |
| [ 胡传鹏 孔祥祯 Wagenmakers, E-J., Ly, A., 彭凯平.(2018). 贝叶斯因子及其在JASP中的实现. 心理科学进展, 26(6), 951-965.] | |
| [22] | *Jia, X., & Liu, X.(2017). Perceived discrimination and antisocial behaviour among Chinese rural‐to‐urban migrant adolescents: Mediating effects of social support. International Journal of Psychology, 52(4), 327-335. URLpmid: 27168094 |
| [23] | Jiang, N., Zhang, G. Z., Liang, Z. B., & Yang, X. L.(2014). Perception of discrimination and problematic behaviour in migrant children: The role of social support and gender regulation. Abstract of the 17th National Conference on Psychology, China. |
| [ 姜宁, 张光珍, 梁宗保, 杨雪莉.(2014). 流动儿童歧视知觉与问题行为:社会支持与性别的调节作用. 第十七届全国心理学学术会议论文摘要集.] | |
| [24] | *Jin, C. C., Qu, Z. Y., & Wang, X. H.(2010). On the current situation of internet addiction of left-at-home children and migrant children, their mental health and interpersonal relationships. Chinese Journal of Special Education, (7), 59-64. |
| [ 金灿灿, 屈智勇, 王晓华.(2010). 留守与流动儿童的网络成瘾现状及其心理健康与人际关系. 中国特殊教育, (7), 59-64.] | |
| [25] | Keyes, C. L. M., & Lopez, S. J.(2002) Toward a science of mental health: Positive directions in diagnosis and interventions. In C. R. Snyder & S. J. Lopez (Eds.), Handbook of positive psychology(pp.45-59). New York: Oxford University Press. |
| [26] | Leonardelli, G. J., & Tormala, Z. L.(2003). The negative impact of perceiving discrimination on collective well- being: The mediating role of perceived ingroup status. European Journal of Social Psychology, 33(4), 507-514. |
| [27] | *Li, Y., Ma, Z. Q., & Zhang, L.(2018). Mediating role of social support and loneliness between perceived discrimination and depression symptoms among migrant children. Modern Preventive Medicine, 45(5), 70-72, 76. |
| [ 李越, 马智群, 张澜.(2018). 流动儿童受歧视知觉对抑郁症状的影响: 社会支持和孤独感的中介作用. 现代预防医学, 45(5), 70-72, 76.] | |
| [28] | *Lin, L. Z., Chen, X. Y., Lin, L. H., Kang, Y. L., & Huang, T. T.(2015). On effects of discrimination against migrant children on subjective well-being: Intermediary role of self- concealing. Journal of Shenyang Institute of Engineering (Social Science), 11(1), 26-30, 49. |
| [ 林良章, 陈雪英, 林丽红, 康亚丽, 黄婷婷.(2015). 流动儿童歧视知觉对主观幸福感的影响:自我隐瞒的中介作用. 沈阳工程学院学报(社会科学版), 11(1), 26-30, 49.] | |
| [29] | *Lin, X. Y., Fang, X. Y., Liu, Y., & Lan, J.(2009). The effect mechanism of stigma perception on mental health among migrant children in Beijing. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 41(10), 967-979. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2009.00967URL |
| [ 蔺秀云, 方晓义, 刘杨, 兰菁.(2009). 流动儿童歧视知觉与心理健康水平的关系及其心理机制. 心理学报, 41(10), 967-979.] | |
| [30] | Linton, J. M., Griffin, M., Shapiro, A. J., & Council on Community Pediatrics.(2017). Detention of immigrant children. Pediatrics, 139(5), e20170483. URLpmid: 28289140 |
| [31] | Lipsey, M. W., & Wilson, D. B.(Eds). (2001). Practical meta analysis. Califrnia: SAGE Publications. |
| [32] | *Liu, D., Yu, X., Wang, Y., Zhang, H., & Ren, G. (2014). The impact of perception of discrimination and sense of belonging on the loneliness of the children of Chinese migrant workers: A structural equation modeling analysis. International Journal of Mental Health Systems, 8(1), 1-6. doi: 10.1186/1752-4458-8-1URLpmid: 24393301 |
| [33] | *Liu X.(2013). Influences of perceived personal and group discrimination on the subjective well-being among Chinese migrant children. Journal of Psychological Science, 36(1), 116-121. |
| [ 刘霞.(2013). 个体和群体歧视知觉对流动儿童主观幸福感的影响. 心理科学, 36(1), 116-121.] | |
| [34] | *Liu, X., & Shen, J. L.(2010). Chinese migrant children's perceived discrimination and its relation self-esteem. Journal of Psychological Science, 33(3), 695-697. |
| [ 刘霞, 申继亮.(2010). 流动儿童的歧视知觉及与自尊的关系. 心理科学, 33(03), 695-697.] | |
| [35] | *Liu, X., & Zhao, J.(2016). Chinese migrant adolescents' perceived discrimination and psychological well-being: The moderating roles of group identity and the type of school. PloS one, 11(1), e0146559. URLpmid: 26731529 |
| [36] | *Liu, X., Zhao, J. X., & Shen, J. L.(2013). Perceived discrimination and subjective well-being among urban migrant children: The effect of mediator and moderator. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 45(5), 568-584. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2013.00568URL |
| [ 刘霞, 赵景欣, 申继亮.(2013). 歧视知觉对城市流动儿童幸福感的影响: 中介机制及归属需要的调节作用. 心理学报, 45(5), 568-584.] | |
| [37] | *Lu, X.(2012). Perceived discrimination and psychological adjustment among migrant children: The effects of social support (Unpublished master's thesis). Hunan University of Science and Technology, China. |
| [ 卢璇.(2012). 流动儿童歧视知觉与心理适应:社会支持的作用 (硕士论文). 湖南科技大学.] | |
| [38] | Lustig, S. L., Kia-Keating, M., Knight, W. G., Geltman, P., Ellis, H., Kinzie, J. D., … Saxe, G. N.(2004). Review of child and adolescent refugee mental health. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 43(1), 24-36. |
| [39] | Major, B., Quinton, W. J., & McCoy, S. K.(2002). Antecedents and consequences of attributions to discrimination: Theoretical and empirical advances. Advances in Experimental Social Psychology, 34, 251-330. |
| [40] | Mummendey, A., Kessler, T., Klink, A., & Mielke, R. (1999). Strategies to cope with negative social identity: Predictions by social identity theory and relative deprivation theory. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 76(2), 229-245. |
| [41] | Neitzel, C., Drennan, K., & Fouts, H. N.(2019). Immigrant and nonimmigrant children's social interactions and peer responses in mainstream preschool classrooms. The Journal of Educational Research, 112(1), 46-60. |
| [42] | *Ni, S. G., & Li, H.(2014). The effect of coping and social support on the relationship between perceived discrimination and identity integration among Chinese migrant children. Psychological Development and Education, 30(1), 31-38. |
| [ 倪士光, 李虹.(2014). 流动儿童认同整合与歧视知觉的关系:社会支持和应对方式的作用. 心理发展与教育, 30(1), 31-38.] | |
| [43] | *Niu, P. C.(2019). Research on the influence of urban migrant children's discrimination perception on their social adaptation (Unpublished master's thesis). Lanzhou University, China. |
| [ 牛品超.(2019). 城市流动儿童歧视知觉对其社会适应的影响研究 (硕士论文). 兰州大学.] | |
| [44] | Orwin, R. G.(1994). Evaluating coding decisions. In H. Cooper & L. V. Hedges (Eds). The handbook of research synthesis. New York (NY): Russell Sage Foundation. |
| [45] | Pascoe, E. A., & Richman, L. S.(2009). Perceived discrimination and health: A meta-analytic review. Psychological Bulletin, 135(4), 531-554. URLpmid: 19586161 |
| [46] | Ponnet, K.(2014). Financial stress, parent functioning and adolescent problem behavior: An actor-partner interdependence approach to family stress processes in low-, middle-, and high-income families. Journal of Youth & Adolescence, 43, 1752-1769. doi: 10.1007/s10964-014-0159-yURLpmid: 25053382 |
| [47] | Schmitt, M. T., Branscombe, N. R., Postmes, T., & Garcia, A. (2014). The consequences of perceived discrimination for psychological well-being: A meta-analytic review. Psychological Bulletin, 140(4), 921-948. doi: 10.1037/a0035754URLpmid: 24547896 |
| [48] | *Shi, B. G., Deng, X. Q., & Liu, X.(2013). Well-being, perception of discrimination and relationships among migrant children in public schools. Journal of Capital Normal University (Social Sciences Edition), (3), 143-149. |
| [ 师保国, 邓小晴, 刘霞.(2013). 公立学校流动儿童的幸福感、歧视知觉及其关系. 首都师范大学学报(社会科学版), (3), 143-149.] | |
| [49] | Sun, X. H., & Han, B. X.(2018). A study on mental health status of mobile children and adolescents at home and abroad: visual analysis based on CiteSpace. China Youth Study, (12), 67-73. |
| [ 孙晓红, 韩布新.(2018). 国内外流动儿童青少年心理健康状况研究: 基于CiteSpace的可视化分析. 中国青年研究, (12), 67-73.] | |
| [50] | Verkuyten, M.(1998). Perceived discrimination and self- esteem among ethnic minority adolescents. Journal of Social Psychology, 138(4), 479-493. |
| [51] | Wagenmakers, E. J., Love, J., Marsman, M., Jamil, T., Ly, A., Verhagen, J., … Morey, R. D.(2017). Bayesian inference for psychology. Part II: Example applications with JASP. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 25(1), 1-19. |
| [52] | Wang, P.(2019). Prosperity and evolution of positive psychology - return of Yin and Yang dialectical philosophy. Psychological Exploration, 39(5), 406-410. |
| [ 王萍.(2019). 积极心理学的繁荣与演变——阴阳辩证哲理的回归. 心理学探新, 39(5), 406-410.] | |
| [53] | Wang, X., & Zhang, D.(2012). The criticism and amendment for the dual-factor model of mental health: From Chinese psychological suzhi research perspectives. International Journal of Clinical Medicine, 3(5), 319-327 |
| [54] | *Wang, Y.(2017). The research of the relationship among perception of discrimination, resilience and school adjustment of floating children (Unpublished master's thesis). Liaocheng University, China. |
| [ 王盈.(2017). 流动儿童歧视知觉、心理弹性与学校适应的关系研究 (硕士论文). 聊城大学.] | |
| [55] | Wirth, J. H., & Williams, K. D.(2009). "They don't like our kind": Consequences of being ostracized while possessing a group membership. Group Processes & Intergroup Relations, 12(1), 111-127. |
| [56] | Wong, P. T. P.(2011). Positive psychology 2.0: Towards a balanced interactive model of the good life. Canadian Psychology, 52(2), 69-81. |
| [57] | *Xiao, Q. Y.(2017). The relationship between discriminationand subjective well-being of migrant children: The mediating role of belief in a just world (Unpublished master's thesis). Hunan University of Science and Technology, China. |
| [ 肖倩怡.(2017). 流动儿童歧视知觉与主观幸福感的关系:公正世界信念的中介作用 (硕士论文). 湖南科技大学.] | |
| [58] | Xiong, M., & Ye, Y. D.(2011). Mental health for the children of farmers who worked in city in China. Advances in Psychological Science, 19(12), 1798-1813. |
| [ 熊猛, 叶一舵.(2011). 中国城市农民工子女心理健康研究述评. 心理科学进展, 19 (12), 1798-1813.] | |
| [59] | Yang, H. S., & Huang, X. T.(2007). Group-reference effect in Chinese. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 39(2), 235-241. |
| [ 杨红升, 黄希庭.(2007). 中国人的群体参照记忆效应. 心理学报, 39(2), 235-241.] | |
| [60] | Zhang, M.(2013). A 10-year review and prospect of the mental health of migrant children in China. Academic Forum, 36(7), 207-214. |
| [ 张敏.(2013). 我国流动儿童心理健康研究10年回顾与展望. 学术论坛, 36(07), 207-214.] | |
| [61] | *Zhang, X. L.(2018). A study on the relationship between perceived discrimination, hope and learning burnout among migrant children. (Unpublished master's thesis). Hunan University of Science and Technology, China. |
| [ 张晓玲.(2018). 流动儿童歧视知觉、希望感和学习倦怠感的关系研究 (硕士论文). 湖南科技大学.] | |
| [62] | *Zhang, Y., Du, A. Z., Tang, D. L., Lei, T. T., & Zhou, Y. G.(2017). Perceived discrimination and social alienation among Chinese migrant children: A moderated mediation model. Psychological Development and Education, 33(6), 719-726. |
| [ 张岩, 杜岸政, 谭顶良, 雷婷婷, 周炎根. (2017). 歧视知觉与流动儿童社会疏离感的关系: 一个有调节的中介模型. 心理发展与教育, 33(6), 719-726.] | |
| [63] | *Zhang, Y., Du, A. Z., & Zhou, Y. G.(2017). The relationship between perceived discrimination and city adaptation in migrant children: The multiple mediator effects of social support and identity integration. Chinese Journal of Special Education,(8), 55-60. |
| [ 张岩, 杜岸政, 周炎根.(2017). 流动儿童歧视知觉和城市适应的关系:社会支持和认同整合的多重中介效应. 中国特殊教育, (8), 55-60.] | |
| [64] | *Zhang, Y., & Tan, D. L.(2019). The relationship between perceived discrimination and school adaptation in migrant children: Hope as a moderator. Chinese Journal of Special Education, 227(5), 59-64. |
| [ 张岩, 谭顶良.(2019). 歧视知觉与流动儿童学校适应的关系: 希望的调节作用——以江苏省为例. 中国特殊教育, 227(5), 59-64.] | |
| [65] | Zhang, Y. L., Li, S., & Yu, G. L.(2019). The relationship between self-esteem and social anxiety: A meta-analysis with Chinese students. Advances in Psychological Science, 27(6), 1005-1018. |
| [ 张亚利, 李森, 俞国良.(2019). 自尊与社交焦虑的关系:基于中国学生群体的元分析. 心理科学进展, 27(6), 1005-1018.] | |
| [66] | *Zheng, J. B.(2013). Correlation study on resilience, self-esteem and individual stigma perception of migrant children in junior middle school (Unpublished master's thesis). Fujian Normal University, China. |
| 郑久波.(2013). 初中流动儿童心理弹性与自尊、个体歧视知觉的关系研究 (硕士论文). 福建师范大学. | |
| [67] | *Zhu, Q., Guo, H. Y., Pan, J., & Lin, D. H.(2015). Perceived discrimination and problem behaviors among rural-to- urban migrant children: The moderating role of resilience. Chinese Journal of Clinical Psychology, 23(3), 529-533. |
| [ 朱倩, 郭海英, 潘瑾, 林丹华.(2015). 流动儿童歧视知觉与问题行为——心理弹性的调节作用. 中国临床心理学杂志, 23(3), 529-533.] |
相关文章 15
| [1] | 任志洪,赵春晓,田凡,闫玉朋,李丹阳,赵子仪,谭梦鸰,江光荣. 中国人心理健康素养干预效果的元分析[J]. 心理学报, 2020, 52(4): 497-512. |
| [2] | 柳武妹, 马增光, 卫旭华. 拥挤影响消费者情绪和购物反应的元分析[J]. 心理学报, 2020, 52(10): 1237-1252. |
| [3] | 任志洪,赵春晓,卞诚,朱文臻,江光荣,祝卓宏. 接纳承诺疗法的作用机制——基于元分析结构方程模型[J]. 心理学报, 2019, 51(6): 662-676. |
| [4] | 任志洪, 张雅文, 江光荣. 正念冥想对焦虑症状的干预: 效果及其影响因素元分析[J]. 心理学报, 2018, 50(3): 283-305. |
| [5] | 杨睿娟, 游旭群. 对付出−回报失衡理论的推进——基于经济报酬对教师心理健康的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2017, 49(9): 1184-1194. |
| [6] | 赵梦雪;冯正直;王毅超;赖薇;胡丰;刘可愚;夏凡;蒋娟;王佳;夏蕾. 1993~2013年常驻高海拔地区军人心理健康状态的横断历史研究[J]. 心理学报, 2017, 49(5): 653-662. |
| [7] | 郭海英;陈丽华; 叶枝;潘瑾;林丹华. 流动儿童同伴侵害的特点及与内化问题的循环作用关系:一项追踪研究[J]. 心理学报, 2017, 49(3): 336-348. |
| [8] | 任志洪, 阮怡君, 赵庆柏, 张微, 赖丽足, 江光荣. 抑郁障碍和焦虑障碍治疗的神经心理机制 ——脑成像研究的ALE元分析[J]. 心理学报, 2017, 49(10): 1302-1321. |
| [9] | 于增艳;赵阿勐;刘爱书. 儿童期受虐经历与抑郁的元分析[J]. 心理学报, 2017, 49(1): 40-49. |
| [10] | 谢和平;王福兴;周宗奎;吴鹏. 多媒体学习中线索效应的元分析[J]. 心理学报, 2016, 48(5): 540-555. |
| [11] | 张淑华;刘兆延. 组织认同与离职意向关系的元分析[J]. 心理学报, 2016, 48(12): 1561-1573. |
| [12] | 李燕芳; 刘丽君;吕莹; 骆方; 王耘. 人际关系状况与学龄前流动儿童的问题行为[J]. 心理学报, 2015, 47(7): 914-927. |
| [13] | 黄四林;侯佳伟;张梅;辛自强;张红川;孙铃;窦东徽. 中国农民工心理健康水平变迁的横断历史研究:1995~2011[J]. 心理学报, 2015, 47(4): 466-477. |
| [14] | 周文霞;谢宝国;辛迅;白光林:苗仁涛. 人力资本、社会资本和心理资本影响中国员工职业成功的元分析[J]. 心理学报, 2015, 47(2): 251-263. |
| [15] | 任真;杨安博;王登峰;林颖. 中西方文化差异视角下领导?部属关系的结构模型[J]. 心理学报, 2014, 46(9): 1355-1377. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlxb/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=4827
