 ), 王志伟, 胡竞元
), 王志伟, 胡竞元 东北师范大学心理学院, 长春 130024
收稿日期:2019-12-04出版日期:2020-10-25发布日期:2020-08-24通讯作者:姜英杰E-mail:jiangyj993@nenu.edu.cn基金资助:* 国家社会科学基金项目(19BSH113)Influence of encoding strength on the font size effect
ZHAO Wenbo, JIANG Yingjie( ), WANG Zhiwei, HU Jingyuan
), WANG Zhiwei, HU Jingyuan School of Psychology, Northeast Normal University, Changchun 130024, China
Received:2019-12-04Online:2020-10-25Published:2020-08-24Contact:JIANG Yingjie E-mail:jiangyj993@nenu.edu.cn摘要/Abstract
摘要: 本研究采用3个实验考察编码强度对字体大小效应的影响, 探讨由于知觉特征而引发的元认知错觉的内在产生机制(实验1)与有效的矫正措施(实验2和实验3)。结果发现:(1)大字体词语的知觉流畅性显著优于小字体, 并且贝叶斯多层中介分析结果表明, 知觉流畅性对字体大小效应起部分中介作用(实验1); (2)随着编码强度的增加, 由字体大小引起的学习判断错觉逐渐消失(实验2和实验3)。以上结果表明, 刺激的知觉特征(字体大小)对个体学习判断的影响, 随编码强度激活线索的增加而逐渐减弱。这一结果为真实教学情境中提高学习者的编码强度, 进而削弱学习判断对知觉特征线索的依赖, 并准确地监测自身的学习进程提供了科学依据。
图/表 8
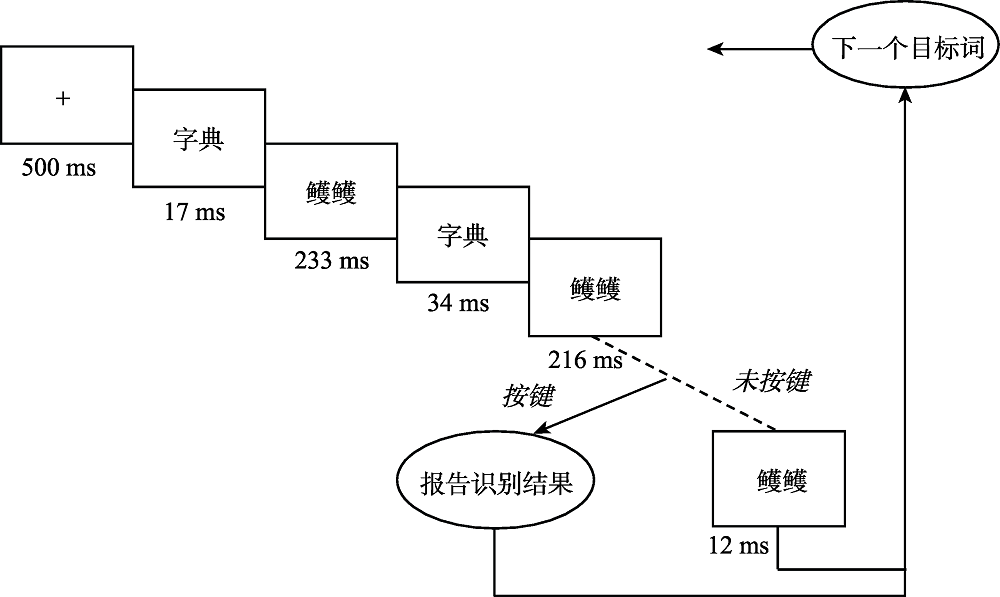
图1CID任务流程图
 图1CID任务流程图
图1CID任务流程图表1不同字体大小词语的自由回忆正确率、学习判断值和识别反应时(M ± SD)
| 字体大小 | 自由回忆正确率 | 学习判断值 | 识别反应时(ms) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 小字体 | 0.26 ± 0.07 | 48.63 ± 12.69 | 1864.77 ± 310.97 |
| 大字体 | 0.27 ± 0.07 | 61.68 ± 13.01 | 1519.95 ± 342.17 |
表1不同字体大小词语的自由回忆正确率、学习判断值和识别反应时(M ± SD)
| 字体大小 | 自由回忆正确率 | 学习判断值 | 识别反应时(ms) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 小字体 | 0.26 ± 0.07 | 48.63 ± 12.69 | 1864.77 ± 310.97 |
| 大字体 | 0.27 ± 0.07 | 61.68 ± 13.01 | 1519.95 ± 342.17 |

图2大字体和小字体词语的学习判断值和自由回忆正确率
 图2大字体和小字体词语的学习判断值和自由回忆正确率
图2大字体和小字体词语的学习判断值和自由回忆正确率表2知觉流畅性在字体大小与学习判断值间中介分析结果
| 字体大小 - 识别反应时 - 学习判断值 | 回归系数(β) | 标准误(SE) | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|
| 字体大小对识别反应时的 效应(a) | -0.34 | 0.04 | [-0.41, -0.27] |
| 识别反应时对学习判断值 的效应(b) | -2.32 | 1.03 | [-4.32, -0.31] |
| 字体大小对学习判断值的 总效应(c) | 13.05 | 2.63 | [7.89, 18.23] |
| 字体大小对学习判断值的 直接效应(c′) | 12.27 | 2.63 | [7.12, 17.43] |
| 识别反应时在字体大小效应中的中介效应(me) | 0.79 | 0.37 | [0.07, 1.55] |
| 中介效应百分比(pme) | 6% | 4% | [1%, 14%] |
表2知觉流畅性在字体大小与学习判断值间中介分析结果
| 字体大小 - 识别反应时 - 学习判断值 | 回归系数(β) | 标准误(SE) | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|
| 字体大小对识别反应时的 效应(a) | -0.34 | 0.04 | [-0.41, -0.27] |
| 识别反应时对学习判断值 的效应(b) | -2.32 | 1.03 | [-4.32, -0.31] |
| 字体大小对学习判断值的 总效应(c) | 13.05 | 2.63 | [7.89, 18.23] |
| 字体大小对学习判断值的 直接效应(c′) | 12.27 | 2.63 | [7.12, 17.43] |
| 识别反应时在字体大小效应中的中介效应(me) | 0.79 | 0.37 | [0.07, 1.55] |
| 中介效应百分比(pme) | 6% | 4% | [1%, 14%] |
表3三种学习时间条件下不同字体大小词语的回忆成绩和学习判断值(M ± SD)
| 学习 时间 | 自由回忆正确率 | 学习判断值 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 小字体 | 大字体 | 小字体 | 大字体 | |
| 2 s | 0.16 ± 0.06 | 0.15 ± 0.05 | 50.83 ± 11.93 | 64.91 ± 13.53 |
| 4 s | 0.26 ± 0.05 | 0.27 ± 0.07 | 45.12 ± 13.02 | 57.80 ± 17.60 |
| 8 s | 0.34 ± 0.17 | 0.34 ± 0.18 | 50.97 ± 18.97 | 54.61 ± 17.89 |
表3三种学习时间条件下不同字体大小词语的回忆成绩和学习判断值(M ± SD)
| 学习 时间 | 自由回忆正确率 | 学习判断值 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 小字体 | 大字体 | 小字体 | 大字体 | |
| 2 s | 0.16 ± 0.06 | 0.15 ± 0.05 | 50.83 ± 11.93 | 64.91 ± 13.53 |
| 4 s | 0.26 ± 0.05 | 0.27 ± 0.07 | 45.12 ± 13.02 | 57.80 ± 17.60 |
| 8 s | 0.34 ± 0.17 | 0.34 ± 0.18 | 50.97 ± 18.97 | 54.61 ± 17.89 |
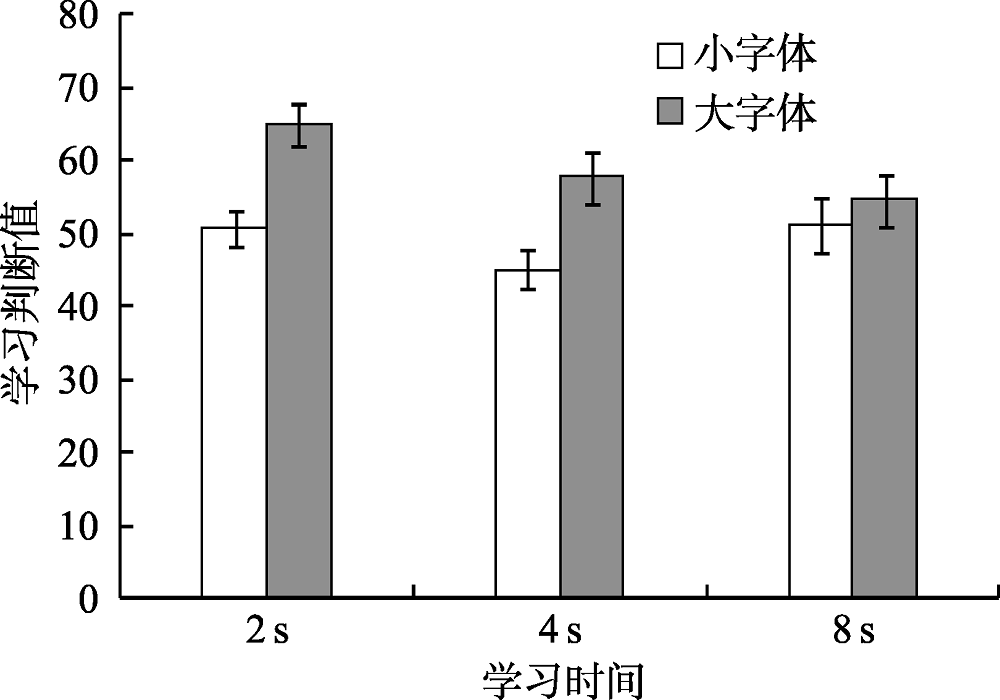
图3不同学习时间和字体大小词语的学习判断值
 图3不同学习时间和字体大小词语的学习判断值
图3不同学习时间和字体大小词语的学习判断值表4两种加工深度条件下不同字体大小词语的回忆成绩和学习判断值(M ± SD)
| 加工深度 | 自由回忆正确率 | 学习判断值 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 小字体 | 大字体 | 小字体 | 大字体 | |
| 深层加工 | 0.42 ± 0.09 | 0.42 ± 0.14 | 56.42 ± 14.53 | 56.96 ± 15.16 |
| 浅层加工 | 0.19 ± 0.08 | 0.20 ± 0.08 | 45.77 ± 15.18 | 60.16 ± 15.08 |
表4两种加工深度条件下不同字体大小词语的回忆成绩和学习判断值(M ± SD)
| 加工深度 | 自由回忆正确率 | 学习判断值 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 小字体 | 大字体 | 小字体 | 大字体 | |
| 深层加工 | 0.42 ± 0.09 | 0.42 ± 0.14 | 56.42 ± 14.53 | 56.96 ± 15.16 |
| 浅层加工 | 0.19 ± 0.08 | 0.20 ± 0.08 | 45.77 ± 15.18 | 60.16 ± 15.08 |
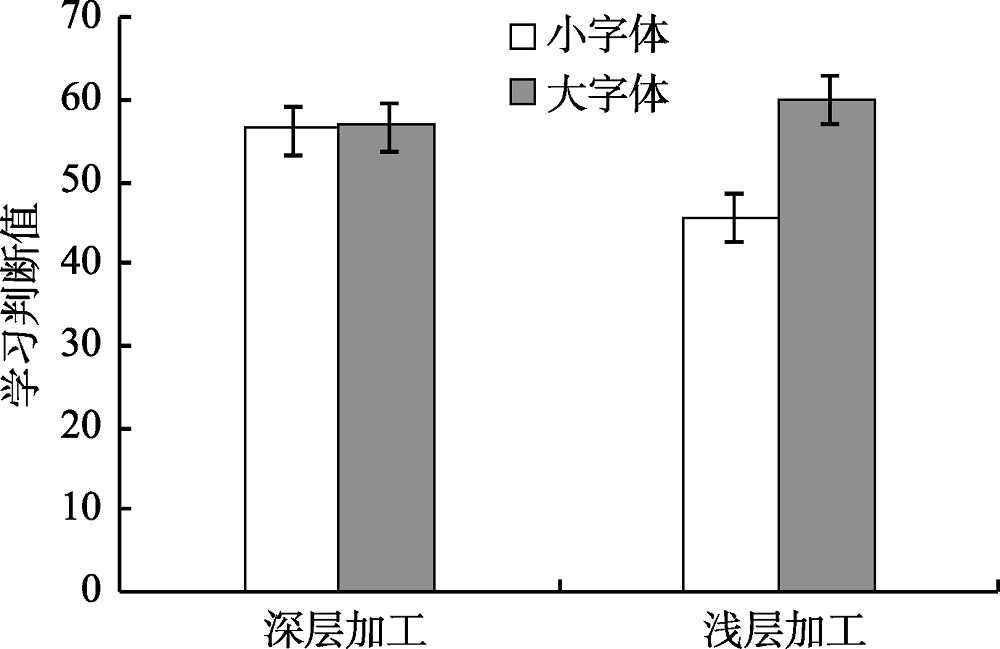
图4不同加工深度和字体大小词语的学习判断值
 图4不同加工深度和字体大小词语的学习判断值
图4不同加工深度和字体大小词语的学习判断值参考文献 45
| [1] | Ball, B. H., Klein, K. N., & Brewer, G. A. (2014). Processing fluency mediates the influence of perceptual information on monitoring learning of educationally relevant materials. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Applied, 20(4), 336-348. URLpmid: 25347408 |
| [2] | Belmore, S. M. (1981). Imagery and semantic elaboration in hypermnesia for words. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Learning & Memory, 7(3), 191-203. doi: 10.1037/0278-7393.7.3.191URL |
| [3] | Benjamin, A. S., Bjork, R. A., & Schwartz, B. L. (1998). The mismeasure of memory: When retrieval fluency is misleading as a metamnemonic index. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 127(1), 55-68. doi: 10.1037/0096-3445.127.1.55URL |
| [4] | Besken, M., & Mulligan, N. W. (2014). Perceptual fluency, auditory generation, and metamemory: Analyzing the perceptual fluency hypothesis in the auditory modality. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 40(2), 429-440. doi: 10.1037/a0034407URLpmid: 24016138 |
| [5] | Bjork, R. A., Dunlosky, J., & Kornell, N. (2013). Self-regulated learning: Beliefs, techniques, and illusions. Annual Review of Psychology, 64(1), 417-444. doi: 10.1146/annurev-psych-113011-143823URL |
| [6] | Bradley, M. M., & Lang, P. J. (2015). Memory, emotion, and pupil diameter: Repetition of natural scenes. Psychophysiology, 52(9), 1186-1193. doi: 10.1111/psyp.12442URLpmid: 25943211 |
| [7] | Carpenter, S. K., Mickes, L., Rahman, S., & Fernandez, C. (2016). The effect of instructor fluency on students’ perceptions of instructors, confidence in learning, and actual learning. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Applied, 22(2), 161-172. doi: 10.1037/xap0000077URLpmid: 26844368 |
| [8] | Carpenter, S. K., Wilford, M. M., Kornell, N., & Mullaney, K. M. (2013). Appearances can be deceiving: Instructor fluency increases perceptions of learning without increasing actual learning. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 20(6), 1350-1356. URLpmid: 23645413 |
| [9] | Castel, A. D. (2008). Metacognition and learning about primacy and recency effects in free recall: The utilization of intrinsic and extrinsic cues when making judgments of learning. Memory & Cognition, 36(2), 429-437. doi: 10.3758/mc.36.2.429URLpmid: 18426071 |
| [10] | Chen, G. X., & Fu, X. L. (2004). Judgment of learning and its accuracy. Advances in Psychological Science, 12(2), 176-184. |
| [ 陈功香, 傅小兰. (2004). 学习判断及其准确性. 心理科学进展, 12(2), 176-184.] | |
| [11] | Chumbley, J. I., & Balota, D. A. (1984). A word’s meaning affects the decision in lexical decision. Memory & Cognition, 12(6), 590-606. doi: 10.3758/bf03213348URLpmid: 6533428 |
| [12] | Cooper, E. H., & Pantle, A. J. (1967). The total time hypothesis in verbal learning. Psychological Bulletin, 68(4), 221-234. URLpmid: 4865090 |
| [13] | Flavell, J. H. (1979). Metacognition and cognitive monitoring: A new area of cognitive-developmental inquiry. American Psychologist, 34(10), 906-911. doi: 10.1037/0003-066X.34.10.906URL |
| [14] | Hertzog, C., Dunlosky, J., & Sinclair, S. M. (2010). Episodic feeling-of-knowing resolution derives from the quality of original encoding. Memory & Cognition, 38(6), 771-784. doi: 10.3758/MC.38.6.771URLpmid: 20852240 |
| [15] | Hertzog, C., Fulton, E. K., Sinclair, S. M., & Dunlosky, J. (2014). Recalled aspects of original encoding strategies influence episodic feelings of knowing. Memory & Cognition, 42(1), 126-140. doi: 10.3758/s13421-013-0348-zURLpmid: 23835601 |
| [16] | Hu, X., Li, T., Zheng, J., Su, N., Liu, Z., & Luo, L. (2015). How much do metamemory beliefs contribute to the font- size effect in judgments of learning?. PloS One, 10(11), e0142351. URLpmid: 26556478 |
| [17] | Koriat, A. (1997). Monitoring one's own knowledge during study: A cue-utilization approach to judgments of learning. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 126(4), 349-370. doi: 10.1037/0096-3445.126.4.349URL |
| [18] | Luo, J., & Lin, Z. X. (2000). Monitoring of multiple memory systems: The influence of LOP and metamemory training. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 32(1), 25-29. |
| [ 罗劲, 林仲贤. (2000). 加工深度和元记忆训练对多重记忆系统监测的影响. 心理学报, 32(1), 25-29.] | |
| [19] | Lupker, S. J., Harbluk, J. L., & Patrick, A. S. (1991). Memory for things forgotten. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 17(5), 897-907. doi: 10.1037//0278-7393.17.5.897URLpmid: 1834771 |
| [20] | Magreehan, D. A., Serra, M. J., Schwartz, N. H., & Narciss, S. (2016). Further boundary conditions for the effects of perceptual disfluency on judgments of learning. Metacognition and Learning, 11(1), 35-56. doi: 10.1007/s11409-015-9147-1URL |
| [21] | McCabe, D. P., & Soderstrom, N. C. (2011). Recollection- based prospective metamemory judgments are more accurate than those based on confidence: Judgments of remembering and knowing (JORKs). Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 140(4), 605-621. doi: 10.1037/a0024014URL |
| [22] | Mueller, M. L., Dunlosky, J., Tauber, S. K., & Rhodes, M. G. (2014). The font size effect on judgments of learning: Does it exemplify fluency effects or reflect people’s beliefs about memory?. Journal of Memory and Language, 70, 1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.jm1.2013.09.007URL |
| [23] | Mulligan, N. W., Buchin, Z. L., & West, J. T. (2019). Assessing why the testing effect is moderated by experimental design. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition. Advance online publication. doi: 10.1037/xlm0000942URLpmid: 32730055 |
| [24] | Nelson, T. O., Dunlosky, J., Graf, A., & Narens, L. (1994). Utilization of metacognitive judgments in the allocation of study during multitrial learning. Psychological Science, 5(4), 207-213. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9280.1994.tb00502.xURL |
| [25] | Rawson, K. A., O'Neil, R., & Dunlosky, J. (2011). Accurate monitoring leads to effective control and greater learning of patient education materials. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Applied, 17(3), 288-302. doi: 10.1037/a0024749URLpmid: 21942317 |
| [26] | Rhodes, M. G., & Castel, A. D. (2008). Memory predictions are influenced by perceptual information: Evidence for metacognitive illusions. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 137(4), 615-625. doi: 10.1037/a0013684URL |
| [27] | Rhodes, M. G., & Castel, A. D. (2009). Metacognitive illusions for auditory information: Effects on monitoring and control. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 16(3), 550-554. doi: 10.3758/PBR.16.3.550URLpmid: 19451383 |
| [28] | Rummer, R., Schweppe, J., & Schwede, A. (2016). Fortune is fickle: Null-effects of disfluency on learning outcomes. Metacognition and Learning, 11(1), 57-70. doi: 10.1007/s11409-015-9151-5URL |
| [29] | Seli, P., Risko, E. F., Smilek, D., & Schacter, D. L. (2016). Mind-wandering with and without intention. Trends in cognitive sciences, 20(8), 605-617. URLpmid: 27318437 |
| [30] | Soderstrom, N. C., & Rhodes, M. G. (2014). Metacognitive illusions can be reduced by monitoring recollection during study. Journal of Cognitive Psychology, 26(1), 118-126. doi: 10.1080/20445911.2013.834906URL |
| [31] | Strukelj, A., Scheiter, K., Nystr?m, M., & Holmqvist, K. (2016). Exploring the lack of a disfluency effect: Evidence from eye movements. Metacognition and Learning, 11(1), 71-88. doi: 10.1007/s11409-015-9146-2URL |
| [32] | Susser, J. A., Mulligan, N. W., & Besken, M. (2013). The effects of list composition and perceptual fluency on judgments of learning (jols). Memory & Cognition, 41(7), 1000-1011. URLpmid: 23661189 |
| [33] | Tauber, S., & Dunlosky, J. (2016). A brief history of metamemory research and handbook overview. In S. Tauber & J. Dunlosky (Eds.), The Oxford handbook of metamemory (pp. 7-22). New York: Oxford University Press. |
| [34] | Toftness, A. R., Carpenter, S. K., Geller, J., Lauber, S., Johnson, M., & Armstrong, P. I. (2018). Instructor fluency leads to higher confidence in learning, but not better learning. Metacognition and Learning, 13(1), 1-14. doi: 10.1007/s11409-017-9175-0URL |
| [35] | Undorf, M., & Br?der, A. (2019). Cue integration in metamemory judgements is strategic. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 73(4), 629-642. doi: 10.1177/1747021819882308URL |
| [36] | Undorf, M., S?llner, A., & Br?der, A. (2018). Simultaneous utilization of multiple cues in judgments of learning. Memory & Cognition, 46(4), 507-519. doi: 10.3758/s13421-017-0780-6URLpmid: 29327336 |
| [37] | Undorf, M., Zimdahl, M. F., & Bernstein, D. M. (2017). Perceptual fluency contributes to effects of stimulus size on judgments of learning. Journal of Memory and Language, 92, 293-304. doi: 10.1016/j.jml.2016.07.003URL |
| [38] | van Gog, T., & Scheiter, K. (2010). Eye tracking as a tool to study and enhance multimedia learning. Learning and Instruction, 20(2), 95-99. doi: 10.1016/j.learninstruc.2009.02.009URL |
| [39] | Vuorre, M. (2017). bmlm: Bayesian multilevel mediation. R package version 1.3.4. Retrieved from https://cran.r-project. org/package=bmlm. |
| [40] | Ward, E. V., Berry, C. J., & Shanks, D. R. (2013). An effect of age on implicit memory that is not due to explicit contamination: Implications for single and multiple- systems theories. Psychology and Aging, 28(2), 429-442. doi: 10.1037/a0031888URL |
| [41] | Yan, G. L., Zhang, Q. M., Zhang, L. L., & Bai, X. J. (2013). The effect of masking materials on percetptual span in chinese reading. Journal of Psychological Science, 36(6), 1317-1322. |
| [ 闫国利, 张巧明, 张兰兰, 白学军. (2013). 不同掩蔽材料对阅读知觉广度的影响. 心理科学, 36(6), 1317-1322.] | |
| [42] | Yan, V. X., Bjork, E. L., & Bjork, R. A. (2016). On the difficulty of mending metacognitive illusions: A priori theories, fluency effects, and misattributions of the interleaving benefit. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 145(7), 918-933. doi: 10.1037/xge0000177URL |
| [43] | Yang, C., Huang, T. S. T., & Shanks, D. R. (2018). Perceptual fluency affects judgments of learning: The font size effect. Journal of Memory and Language, 99, 99-110. doi: 10.1016/j.jml.2017.11.005URL |
| [44] | Yap, M. J., Sibley, D. E., Balota, D. A., Ratcliff, R., & Rueckl, J. (2015). Responding to nonwords in the lexical decision task: Insights from the english lexicon project. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 41(3), 597-613. doi: 10.1037/xlm0000064URLpmid: 25329078 |
| [45] | Zhang, X. J. (2010). Effects of perceptual fluency on judgment and decision. Advances in Psychological Science, 18(4), 639-645 |
| [ 张旭锦. (2010). 知觉流畅性对判断和决策的影响. 心理科学进展, 18(4), 639-645.] |
相关文章 5
| [1] | 陈颖,李锋盈,李伟健. 个体关于加工流畅性的信念对字体大小效应的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2019, 51(2): 154-162. |
| [2] | 陈功香, 张承芬,苏雅雯. 延迟学习判断的效应机制[J]. 心理学报, 2010, 42(07): 743-753. |
| [3] | 侯瑞鹤,俞国良. 加工流畅性和提取流畅性与学习不良儿童学习判断的关系[J]. 心理学报, 2008, 40(09): 994-1001. |
| [4] | 张雅明,俞国良. 学习不良儿童元记忆监测与控制的发展[J]. 心理学报, 2007, 39(02): 249-256. |
| [5] | 陈功香,傅小兰. 内外部线索对学习判断的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2003, 35(02): 172-177. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlxb/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=4804
