 ), 叶秀敏, 马慧姣
), 叶秀敏, 马慧姣 福建师范大学心理学院, 福州 350117
收稿日期:2019-03-25出版日期:2020-02-25发布日期:2019-12-24通讯作者:孟迎芳E-mail:175695016@qq.com基金资助:* 国家自然科学基金青年项目(31800906);2018 年福建省自然基金面上项目(2018J01719)Comparing the attentional boost effect between classified learning and mixed learning
MENG Yingfang( ), YE Xiumin, MA Huijiao
), YE Xiumin, MA Huijiao School of Psychology, Fujian Normal University, Fuzhou 350117, China
Received:2019-03-25Online:2020-02-25Published:2019-12-24Contact:MENG Yingfang E-mail:175695016@qq.com摘要/Abstract
摘要: 注意促进效应(ABE)是指目标探测性质的干扰会促进与之同时进行的背景刺激的记忆编码, 产生比分心拒绝下更优的记忆成绩。Spataro等人(2017)对此提出项目特异性解释, 认为目标探测主要促进的是对项目的特异性信息而非关系性信息加工。本研究采用混合学习和分类学习的方式形成对背景刺激的特异性信息和关系性信息加工。结果表明, 与混合学习相比, 分类学习下的ABE有所减少(实验2), 甚至消失(实验1), 表明当编码过程中对背景刺激的加工主要依赖于关系性信息时, 目标探测所产生的促进效应会被削弱, 从而为ABE的项目特异性解释提供更为直接的证据。
图/表 5
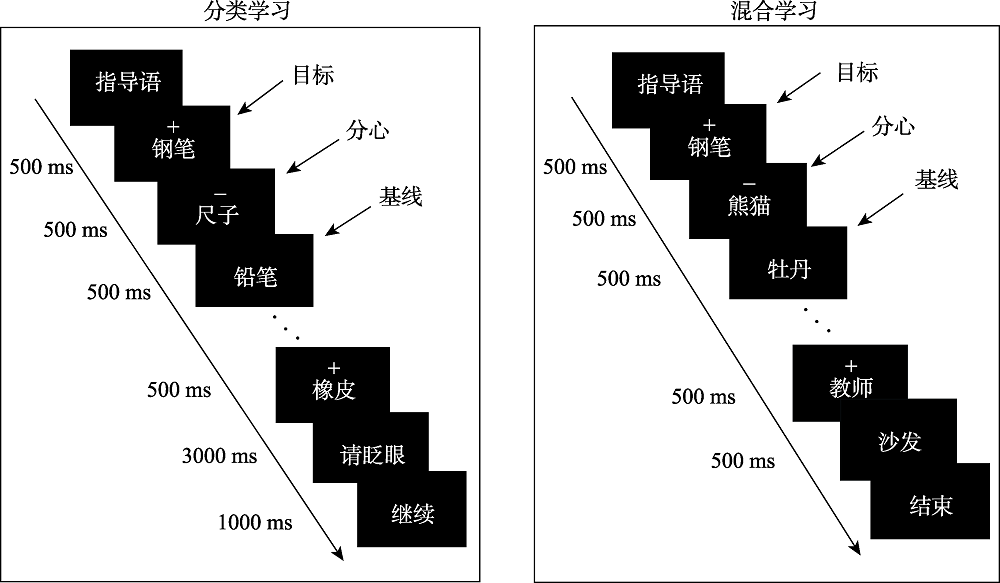
图1学习阶段的实验流程图
 图1学习阶段的实验流程图
图1学习阶段的实验流程图表1分类学习和混合学习下两类新词的虚报率(%)
| 学习方式 | 范畴新词(N) | 无关新词(P) |
|---|---|---|
| 分类学习 | 30.7 (12.7) | 17.7 (12.1) |
| 混合学习 | 24.8 (14.2) | 21.4 (13.0) |
表1分类学习和混合学习下两类新词的虚报率(%)
| 学习方式 | 范畴新词(N) | 无关新词(P) |
|---|---|---|
| 分类学习 | 30.7 (12.7) | 17.7 (12.1) |
| 混合学习 | 24.8 (14.2) | 21.4 (13.0) |
表2分类学习和混合学习下三类旧词的再认正确率(%)
| 再认正确率 | 分类学习 | 混合学习 |
|---|---|---|
| 目标词 | 56.33 (12.2) | 54.78 (13.1) |
| 分心词 | 56.89 (12.0) | 47.89 (13.4) |
| 空白词 | 54.22 (13.3) | 52.78 (15.1) |
表2分类学习和混合学习下三类旧词的再认正确率(%)
| 再认正确率 | 分类学习 | 混合学习 |
|---|---|---|
| 目标词 | 56.33 (12.2) | 54.78 (13.1) |
| 分心词 | 56.89 (12.0) | 47.89 (13.4) |
| 空白词 | 54.22 (13.3) | 52.78 (15.1) |
表3分类学习和混合学习下两类新图的虚报率(%)
| 学习方式 | 范畴新图(N) | 无关新图(P) |
|---|---|---|
| 分类学习 | 26.49 (12.21) | 12.22 (9.78) |
| 混合学习 | 19.38 (11.81) | 15.36 (12.72) |
表3分类学习和混合学习下两类新图的虚报率(%)
| 学习方式 | 范畴新图(N) | 无关新图(P) |
|---|---|---|
| 分类学习 | 26.49 (12.21) | 12.22 (9.78) |
| 混合学习 | 19.38 (11.81) | 15.36 (12.72) |
表4分类学习和混合学习下三类旧图的再认正确率(%)
| 再认正确率 | 分类学习 | 混合学习 |
|---|---|---|
| 目标图 | 62.6 (12.5) | 60.8 (17.3) |
| 分心图 | 52.4 (15.4) | 45.1 (15.4) |
| 空白图 | 56.9 (14.4) | 49.1 (17.3) |
表4分类学习和混合学习下三类旧图的再认正确率(%)
| 再认正确率 | 分类学习 | 混合学习 |
|---|---|---|
| 目标图 | 62.6 (12.5) | 60.8 (17.3) |
| 分心图 | 52.4 (15.4) | 45.1 (15.4) |
| 空白图 | 56.9 (14.4) | 49.1 (17.3) |
参考文献 42
| [1] | Carvalho P. F., & Goldstone R. L . (2017). Carnegie mellon university the sequence of study changes what information is attended to, encoded, and remembered during category learning. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning Memory & Cognition, 43(11), 1-21. |
| [2] | Cohen J . (1992). Statistical power analysis. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 1(3), 98-101. |
| [3] | Dong C. F . (2004). Effect of category variables on false recognition (Master's thesis). South China Normal University. |
| [ 董昌锋 . (2004). 范畴变量对虚假再认的影响 (硕士学位论文). 华南师范大学.] | |
| [4] | Einstein G. O., & Hunt R. R . (1980). Levels of processing and organization: Additive effects of individual-item and relational processing. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Learning & Memory, 6(5), 588-598. |
| [5] | Engelkamp J . (1995). Visual imagery and enactment of actions in memory. British Journal of Psychology, 86(2), 227-240. |
| [6] | Fang Y. H., Zhang J. J . (2009). Asymmetry in naming and categorizing of Chinese words and pictures: Role of semantic radicals. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 41(2), 114-126. |
| [ 方燕红, 张积家 . (2009). 汉字词和图片命名与分类的比较. 心理学报, 41(2), 114-126.] | |
| [7] | Faul F., Erdfelder E., Lang A. G., & Buchner A . (2007). G*power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behavior Research Methods, 39(2), 175-191. |
| [8] | Gollin E. S., & Sharps M. J . (1988). Facilitation of free recall by categorical blocking depends on stimulus type. Memory & Cognition, 16(6), 539-544. |
| [9] | Huff M. J., & Bodner G. E . (2014). All varieties of encoding variability are not created equal: Separating variable processing from variable tasks. Journal of Memory and Language, 73, 43-58. |
| [10] | Humphreys G. W., Lamote C., & Lloydjones T. J . (1995). An interactive activation approach to object processing: Effects of structural similarity, name frequency, and task in normality and pathology. Memory, 3(3-4), 535-586. |
| [11] | Hunt R. R . (1981). Relational and item-specific information in memory. Journal of Verbal Learning & Verbal Behavior, 20(5), 497-514. |
| [12] | Hunt R. R., & McDaniel M. A . (1993). The enigma of organization and distinctiveness. Journal of Memory and Language, 32(4), 421-445. |
| [13] | Hunt R. R., & Seta C. E . (1984). Category size effects in recall: The roles of relational and individual item information. Journal of Experimental Psychology Learning Memory & Cognition, 10(3), 454-464. |
| [14] | Johnston W. A., & Dark V. J . (1986). Selective attention. Annual Review of Psychology, 37(1), 43-75. |
| [15] | Li G. Z., Li M., Lin W. Y., & Wang L. J . (2016). The Encoding Mechanism of SPT Effect: Item-Specific and Item-Relational Information. Journal of Psychological Science, 41(2), 292-297. |
| [ 李广政, 李梅, 林文毅, 王丽娟 . (2016). SPT效应的编码机制: 项目特异性与项目关联性信息. 心理科学, 41(2), 292-297.] | |
| [16] | Lin J. Y., Pype A. D., Murray S. O., & Boynton G. M . (2010). Enhanced memory for scenes presented at behaviorally relevant points in time. PloS Biology, 8(3), e1000337. |
| [17] | Liu X. P., & Li Y. M . (2007). The effects of gist representations and verbatim representations on false recognition. Journal of Psychological Science, 30(5), 1091-1094. |
| [ 刘希平, 李永梅 . (2007). 要点表征与字词表征在错误再认中的作用. 心理科学, 30(5), 1091-1094.] | |
| [18] | Makovski T., Swallow K. M., & Jiang Y. V . (2011). Attending to unrelated targets boosts short-term memory for color arrays. Neuropsychologia, 49(6), 1498-1505. |
| [19] | Meng Y. F., & Lin H. R . (2018). Attentional boost effect: New insights on relationship between attention and memory. Advances in Psychological Science, 26(2), 221-228. |
| [ 孟迎芳, 林惠茹 . (2018). 注意促进效应: 注意与记忆关系的新见解. 心理科学进展, 26(2), 221-228.] | |
| [20] | Meng Y. F., Lin G. Y., & Lin H. R . (2019). The role of distractor inhibition in the attentional boost effect: Evidence from the R/K paradigm. Memory, 27(6), 750-757. |
| [21] | Meng Y. F., Zheng S. Q., Wang D. P., & Nie A. Q . (2018). Limits to the attentional boost effect: The moderating influence of negative emotion. Journal of Psychological Science, 41(2), 298-304. |
| [ 孟迎芳, 郑思琦, 王大鹏, 聂爱情 . (2018). 负性情绪对注意促进效应的调节. 心理科学, 41(2), 298-304.] | |
| [22] | Mulligan N. W . (1999). The effects of perceptual interference at encoding on organization and order: Investigating the roles of item-specific and relational information. Journal of Experimental Psychology. Learning, Memory & Cognition, 25(1), 54-69. |
| [23] | Mulligan N. W . (2008). Attention and memory. In H. L. Roediger (Ed.), Learning and memory: A comprehensive reference (pp. 7-22). Oxford, England: Elsevier. |
| [24] | Mulligan N. W., Smith S. A., & Spataro P . (2015). The attentional boost effect and context memory. Journal of Experimental Psychology Learning Memory & Cognition, 42(4), 598-607. |
| [25] | Mulligan N. W., Spataro P., & Picklesimer M . (2014). The attentional boost effect with verbal materials. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning Memory & Cognition, 40(4), 1049-1063. |
| [26] | Olofsson U . (1996). The effect of enactment on memory for order. Psychological Research, 59(1), 75-79. |
| [27] | Paivio A . (1991). Dual coding theory: Retrospect and current status. Canadian Journal of Psychology Revue Canadienne De Psychologie, 45(3), 255-287. |
| [28] | Parks C. M . (2013). Transfer-appropriate processing in recognition memory: Perceptual and conceptual effects on recognition memory depend on task demands. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning Memory & Cognition, 39(4), 1280-1286. |
| [29] | Pashler H . (1994). Dual-task interference in simple tasks: Data and theory. Psychological Bulletin, 116(2), 220-244. |
| [30] | Ren J .(2010). The visual processing of words and object shapes: An FMRI study (Unpublished master’s thesis), Guangzhou University. |
| [ 任静 . (2010). 文字和物体图形视觉加工脑成像研究(硕士学位论文). 广州大学.] | |
| [31] | Roediger H. L., Watson J. M., Mcdermott K. B., & Gallo D. A . (2001). Factors that determine false recall: A multiple regression analysis. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 8(3), 385-407. |
| [32] | Rossi-Arnaud C., Spataro P., Saraulli D., Mulligan N. W., Sciarretta A., Marques V. R., & Cestari V . (2014). The attentional boost effect in schizophrenia. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 123(3), 588-597. |
| [33] | Spataro P., Mulligan N. W., Bechi G. G., & Rossi-Arnaud C . (2017). Divided attention enhances explicit but not implicit conceptual memory: An item-specific account of the attentional boost effect. Memory, 25(2), 1-6. |
| [34] | Spataro P., Mulligan N. W., & Rossi-Arnaud C . (2013). Divided attention can enhance memory encoding: The attentional boost effect in implicit memory. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 39(4), 1223-1231. |
| [35] | Spataro P., Mulligan N. W., & Rossi-Arnaud C . (2015). Limits to the attentional boost effect: The moderating influence of orthographic distinctiveness. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 22(4), 987-992. |
| [36] | Swallow K. M., & Jiang Y. V . (2010). The attentional boost effect: Transient increases in attention to one task enhance performance in a second task. Cognition, 115(1), 118-132. |
| [37] | Swallow K. M., & Jiang Y. V . (2011). The role of timing in the attentional boost effect. Attention Perception & Psychophysics, 73(2), 389-404. |
| [38] | Swallow K. M., & Jiang Y. V . (2012). Goal-relevant events need not be rare to boost memory for concurrent images. Attention, Perception, and Psychophysics, 74(1), 70-82. |
| [39] | Swallow K. M., & Jiang Y. V . (2014b). The attentional boost effect really is a boost: Evidence from a new baseline. Attention, Perception, & Psychophysics, 76(5), 1298-1307. |
| [40] | Yonelinas A. P . (2002). The nature of recollection and familiarity: A review of 30 years of research . Journal of Memory & Language, 46(3), 441-517. |
| [41] | Yum Y. N., Holcomb P. J., & Grainger J . (2011). Words and pictures: An electrophysiological investigation of domain specific processing in native Chinese and English speakers. Neuropsychologia, 49(7), 1910-1922. |
| [42] | Zhou C . (2007). Strong false memory effect: The impact of presentation duration and presentation mode. Journal of Psychological Science, 30(1), 23-28. |
| [ 周楚 . (2007). 强大的错误记忆效应: 词表呈现时间与呈现方式的影响. 心理科学, 30(1), 23-28.] |
相关文章 1
| [1] | 黄晏清, 孟迎芳. 目标探测对记忆提取的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2020, 52(6): 706-715. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlxb/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=4627
