 )
) 1. 教育部人文社会科学重点研究基地天津师范大学心理与行为研究院, 天津 30074
2. 天津师范大学心理学部, 天津 30387
3. 国民心理健康评估与促进协同创新中心, 天津 30074
4. 北京大学心理与认知科学学院, 北京 100080
收稿日期:2018-10-08出版日期:2019-11-25发布日期:2019-09-24通讯作者:李量E-mail:liangli@pku.edu.cn基金资助:*全国教育科学规划教育部重点课题“创伤后应激障碍中学生注意偏向的心理机制研究”(DBA150235)The role of masking stimulation in target recognition processing: Evidence from fNIRS
YANG Haibo1,2,3, LIU Hejun2, ZHANG Peng2, LI Liang4( )
) 1. Key Research Base of Humanities and Social Sciences of the Ministry of Education, Academy of Psychology and Behavior, Tianjin Normal University, Tianjin 300074, China
2. Faculty of Psychology, Tianjin Normal University, Tianjin 300387, China
3. Center of Collaborative Innovation for Assessment and Promotion of Mental Health, Tianjin 300074, China
4. School of Psychological and Cognitive Sciences, Peking University, Beijing 100080, China
Received:2018-10-08Online:2019-11-25Published:2019-09-24Contact:LI Liang E-mail:liangli@pku.edu.cn摘要/Abstract
摘要: 信息掩蔽刺激(如随机字母群)对字母视觉搜索的干扰大于能量掩蔽刺激(如将字母群像素随机化后的散点), 但相应的中枢机理还不清楚。本研究采用记录脑代谢激活模式的功能性近红外光学脑成像技术(fNIRS), 考察年轻成年被试分别在字母掩蔽、字母碎片掩蔽、像素掩蔽条件下判断上、下、左、右四个目标字母是否相同时的大脑皮层氧合血红蛋白浓度的变化。结果显示, 依字母、字母碎片、随机散点掩蔽条件顺序, 被试的搜索任务成绩显著递增, 而顶-枕皮层的激活范围与程度显著递减, 表明信息掩蔽较匹配的能量掩蔽对视觉搜索有更大的干扰作用, 并在初级和联合视觉皮层引发更大的激活。在字母碎片掩蔽条件下, 视觉初级皮层部分区域的激活水平与搜索行为绩效的相关显著, 而在字母掩蔽条件下, 视觉联合皮层部分区域的激活水平与搜索行为绩效的相关显著。这进一步说明信息掩蔽中的字母掩蔽和字母碎片掩蔽的掩蔽作用在大脑皮层上所造成的加工负载存在差异。
图/表 12

图1无掩蔽噪音的刺激样例(仅有目标刺激)
 图1无掩蔽噪音的刺激样例(仅有目标刺激)
图1无掩蔽噪音的刺激样例(仅有目标刺激)
图2不同类型掩蔽刺激样例
 图2不同类型掩蔽刺激样例
图2不同类型掩蔽刺激样例
图3不同类型掩蔽刺激的视觉物理特征分析
 图3不同类型掩蔽刺激的视觉物理特征分析
图3不同类型掩蔽刺激的视觉物理特征分析
图4一个试次的呈现过程
 图4一个试次的呈现过程
图4一个试次的呈现过程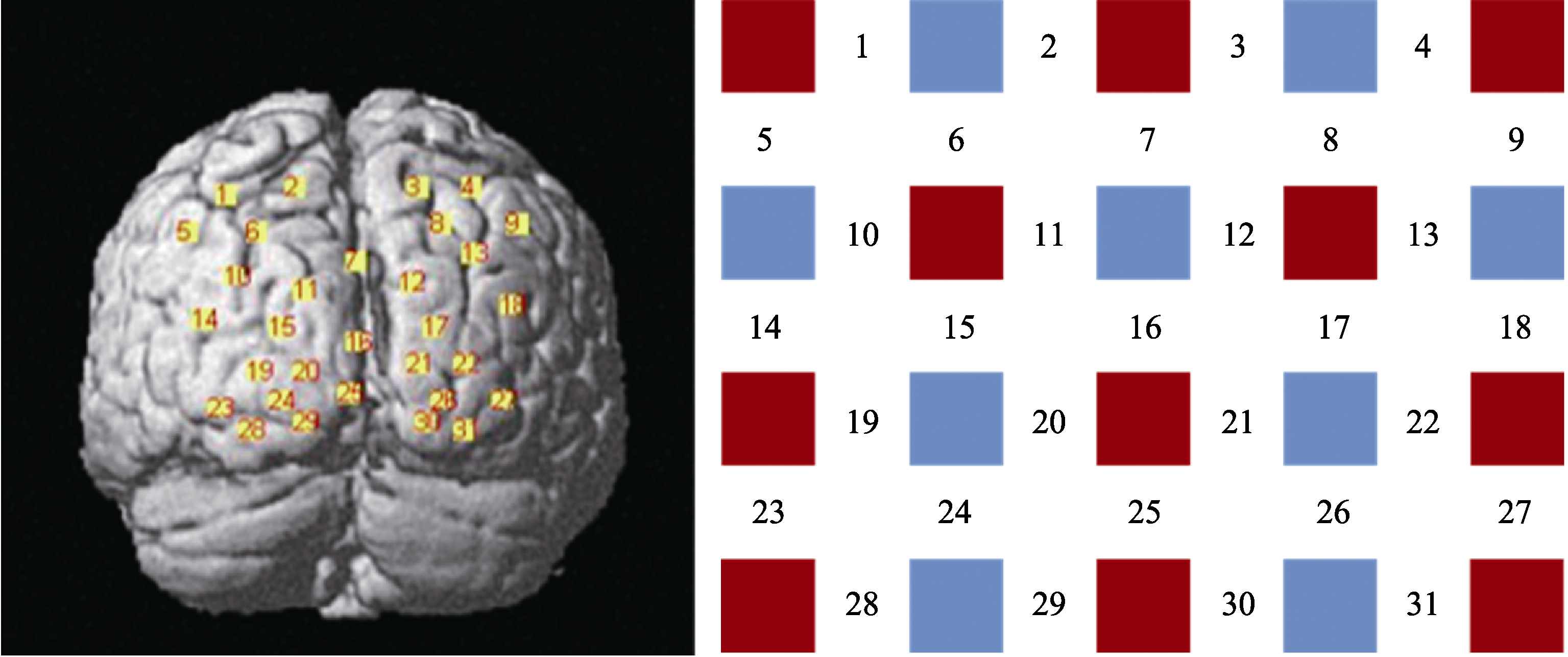
图5fNIRS通道布局
 图5fNIRS通道布局
图5fNIRS通道布局表1通道布局与布鲁德曼分区的对应关系
| 布鲁德曼分区 | 对应通道 |
|---|---|
| 视觉初级皮层 | ch15, ch17, ch19, ch20, ch21, ch22, ch24, ch25, ch26 |
| 视觉联合皮层 | ch6, ch7, ch8, ch10, ch11, ch12, ch13, ch14, ch16, ch18, ch23, ch27, ch28, ch29, ch30, ch31 |
| 躯体感觉联合皮层 | ch1, ch2, ch3, ch4 |
| 角回 | ch5, ch9 |
表1通道布局与布鲁德曼分区的对应关系
| 布鲁德曼分区 | 对应通道 |
|---|---|
| 视觉初级皮层 | ch15, ch17, ch19, ch20, ch21, ch22, ch24, ch25, ch26 |
| 视觉联合皮层 | ch6, ch7, ch8, ch10, ch11, ch12, ch13, ch14, ch16, ch18, ch23, ch27, ch28, ch29, ch30, ch31 |
| 躯体感觉联合皮层 | ch1, ch2, ch3, ch4 |
| 角回 | ch5, ch9 |
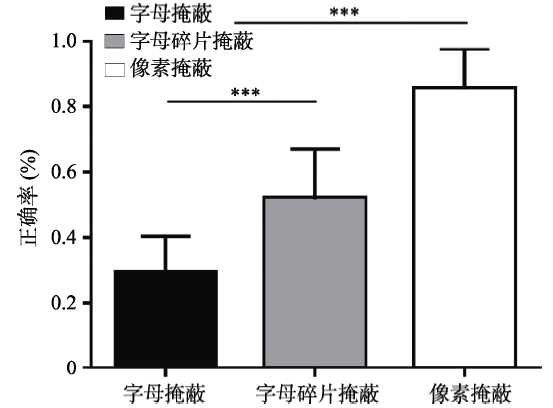
图6不同掩蔽条件下被试的目标识别正确率 注:*** p < 0.001。
 图6不同掩蔽条件下被试的目标识别正确率 注:*** p < 0.001。
图6不同掩蔽条件下被试的目标识别正确率 注:*** p < 0.001。
图7不同掩蔽条件下大脑皮层各通道激活t值热量图
 图7不同掩蔽条件下大脑皮层各通道激活t值热量图
图7不同掩蔽条件下大脑皮层各通道激活t值热量图表2不同掩蔽类型条件下重复测量方差分析检验结果
| 通道 | MNI坐标 | 布鲁德曼分区 | 覆盖率(%) | F | η2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11 | -12 | -99 | 28 | V2(BA18) | 74 | 3.93* | 0.17 |
| 15 | -17 | -104 | 17 | V1(BA17) | 84 | 5.02* | 0.21 |
| 17 | 23 | -102 | 18 | V1(BA17) | 66 | 3.80* | 0.17 |
| 20 | -11 | -108 | 6 | V1(BA17) | 99 | 3.63* | 0.16 |
| 22 | 29 | -101 | 7 | V1(BA17) | 73 | 5.56* | 0.23 |
| 25 | 1 | -102 | -1 | V1(BA17) | 99 | 6.75* | 0.26 |
| 27 | 39 | -95 | -2 | V2(BA18) | 92 | 3.31* | 0.15 |
| 31 | 31 | -100 | -9 | V2(BA18) | 81 | 8.13** | 0.30 |
表2不同掩蔽类型条件下重复测量方差分析检验结果
| 通道 | MNI坐标 | 布鲁德曼分区 | 覆盖率(%) | F | η2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11 | -12 | -99 | 28 | V2(BA18) | 74 | 3.93* | 0.17 |
| 15 | -17 | -104 | 17 | V1(BA17) | 84 | 5.02* | 0.21 |
| 17 | 23 | -102 | 18 | V1(BA17) | 66 | 3.80* | 0.17 |
| 20 | -11 | -108 | 6 | V1(BA17) | 99 | 3.63* | 0.16 |
| 22 | 29 | -101 | 7 | V1(BA17) | 73 | 5.56* | 0.23 |
| 25 | 1 | -102 | -1 | V1(BA17) | 99 | 6.75* | 0.26 |
| 27 | 39 | -95 | -2 | V2(BA18) | 92 | 3.31* | 0.15 |
| 31 | 31 | -100 | -9 | V2(BA18) | 81 | 8.13** | 0.30 |

图8掩蔽类型对视觉搜索影响的主效应热量图
 图8掩蔽类型对视觉搜索影响的主效应热量图
图8掩蔽类型对视觉搜索影响的主效应热量图
图9视觉搜索任务下不同类型掩蔽刺激的两两对比热量图
 图9视觉搜索任务下不同类型掩蔽刺激的两两对比热量图
图9视觉搜索任务下不同类型掩蔽刺激的两两对比热量图表3被试识别正确率与fNIRS数据的相关(n = 20)
| 皮层 | 通道 | 布鲁德曼分区 | 皮尔逊相关系数r | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 像素掩蔽 | 字母碎片掩蔽 | 字母掩蔽 | |||
| 视觉皮层 | 15 | V1 (BA17) | -0.114 | -0.023 | -0.261 |
| 17 | V1 (BA17) | -0.074 | 0.101 | 0.090 | |
| 20 | V1 (BA17) | -0.028 | -0.068 | 0.007 | |
| 22 | V1 (BA17) | 0.082 | 0.473* | -0.085 | |
| 视觉联合皮层 | 25 | V1 (BA17) | 0.035 | 0.122 | -0.062 |
| 11 | V2 (BA18) | 0.001 | 0.245 | -0.011 | |
| 27 | V2 (BA18) | 0.011 | 0.021 | -0.222 | |
| 31 | V2 (BA18) | -0.081 | 0.124 | -0.478* | |
表3被试识别正确率与fNIRS数据的相关(n = 20)
| 皮层 | 通道 | 布鲁德曼分区 | 皮尔逊相关系数r | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 像素掩蔽 | 字母碎片掩蔽 | 字母掩蔽 | |||
| 视觉皮层 | 15 | V1 (BA17) | -0.114 | -0.023 | -0.261 |
| 17 | V1 (BA17) | -0.074 | 0.101 | 0.090 | |
| 20 | V1 (BA17) | -0.028 | -0.068 | 0.007 | |
| 22 | V1 (BA17) | 0.082 | 0.473* | -0.085 | |
| 视觉联合皮层 | 25 | V1 (BA17) | 0.035 | 0.122 | -0.062 |
| 11 | V2 (BA18) | 0.001 | 0.245 | -0.011 | |
| 27 | V2 (BA18) | 0.011 | 0.021 | -0.222 | |
| 31 | V2 (BA18) | -0.081 | 0.124 | -0.478* | |
参考文献 41
| [1] | Breitmeyer, B. G . (2008). Visual masking: Past accomplishments, present status, future developments. Advances in Cognitive Psychology, 3(1-2), 9-20. doi: 10. 2478/v10053-008-0010-7 |
| [2] | Brigadoi, S., Ceccherini, L., Cutini, S., Scarpa, F., Scatturin, P., Selb, J., … Cooper, R. J . (2014). Motion artifacts in functional near-infrared spectroscopy: A comparison of motion correction techniques applied to real cognitive data. Neuroimage, 85(1), 181-191. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.04.082 |
| [3] | Bonner, M. F., Vesely, L., Price, C., Anderson, C., Richmond, L., Farag, C., .. Grossman, M . (2009). Reversal of the concreteness effect in semantic dementia. Cognitive Neuropsychology, 26(6), 568-579. doi: 10.1080/02643290903512305 |
| [4] | Cai, T. T., Zhu, H. L., Xu, J., Wu, S. J., Li, X. G., & He, S. L . (2017). Human cortical neural correlates of visual fatigue during binocular depth perception: An fNIRS study. PLoS One, 12(2), 1-16. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0172426 |
| [5] | Calvert, G. A., & Thesen, T. (2004). Multisensory integration: methodological approaches and emerging principles in the human brain. Journal of Physiology-Paris, 98(1-3), 191-205. doi: 10.1016/j.jphysparis.2004.03.018 |
| [6] | Chen, M. L . (2012). Disparity-based binocular unmasking effect in complex visual scenes (Unpublished master's thesis). Peking University. |
| [7] | [ 陈明立 . (2012). 复杂环境下基于立体视觉的双眼去掩蔽效应 (硕士学位论文). 北京大学.] |
| [8] | Chen, M. L., Zhang, C. X., Yang, S. J., Mao, L. H., Tian, Y. H., Huang, T. J., … Li, L . (2012). Stereopsis-based binocular unmasking. Advances in Psychological Science, 20(9), 1355-1363. |
| [9] | [ 陈明立, 张畅芯, 杨少娟, 毛利华, 田永鸿, 黄铁军, …李量 . (2012). 基于双眼视差的立体视觉去掩蔽效应. 心理科学进展, 20(9), 1355-1363.] |
| [10] | Chubb, C., Olzak, L., & Derrington, A . (2001). Second-order processes in vision: Introduction. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 18(9), 2175-2178. doi: 10.1364/josaa. 18.002175 |
| [11] | Durantin, G., Gagnon, J. -F., Tremblay, S., & Dehais, F . (2014). Using near infrared spectroscopy and heart rate variability to detect mental overload. Behavioural Brain Research, 259, 16-23. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2013.10.042 |
| [12] | Durantin, G., Scannella, S., Gateau, T., Delorme, A., & Dehais, F . (2016). Processing functional near infrared spectroscopy signal with a Kalman filter to assess working memory during simulated flight. Frontiers in human neuroscience, 9, 707. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2015.00707 |
| [13] | Fahrenfort, J. J., Scholte, H. S., & Lamme, V.. A. F .(2007). Masking disrupts reentrant processing in human visual cortex. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 19(9), 1488-1497. doi: 10.1162/jocn.2007.19.9.1488 |
| [14] | Gao, Y. Y., Schneider, B., & Li, L . (2017). The effects of the binocular disparity differences between targets and maskers on visual search. Attention, Perception, & Psychophysics, 79(2), 459-472. doi: 10.3758/s13414-016-1252-y |
| [15] | Herrmann, M. J., Neueder, D., Troeller, A. K., & Schulz, S. M . (2016). Simultaneous recording of EEG and fNIRS during visuo-spatial and facial expression processing in a dual task paradigm. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 109, 21-28. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2016.09.013 |
| [16] | Hoshi, Y., Kobayashi, N., & Tamura, M . (2001). Interpretation of near-infrared spectroscopy signals: A study with a newly developed perfused rat brain model. Journal of Applied Physiology, 90(5), 1657-1662. doi: 10.1152/jappl.2001. 90.5.1657 |
| [17] | Jang, K. E., Tak, S., Jung, J., Jang, J., Yong, J., & Ye, J. C . (2009). Wavelet minimum description length detrending for near-infrared spectroscopy. Journal of Biomedical Optics, 14(3), 1-13. doi: 10.1117/1.3127204 |
| [18] | Kok, P., & de, Lange, Floris, P . (2014). Shape perception simultaneously up- and downregulates neural activity in the primary visual cortex. Current Biology, 24(13), 1531-1535. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2014.05.042 |
| [19] | Lane, C., Kanjlia, S., Richardson, H., Fulton, A., Omaki, A., & Bedny, M . (2017). Reduced left lateralization of language in congenitally blind individuals. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 29(1), 65-78. doi: 10.1162/jocn_a_01045 |
| [20] | Lavie, N., Hirst, A., de Fockert, J. W., & Viding, E . (2004). Load theory of selective attention and cognitive control. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 133(3), 339-354. doi: 10.1037/0096-3445.133.3.339 |
| [21] | Liu, B. G., Zhou, J., & Li, F. F . (2011). Functional near-infrared spectroscopy: An emerging functional neuroimaging technology. Journal of Psychological Science, 34(4), 943-949. |
| [22] | [ 刘宝根, 周兢, 李菲菲 . (2011). 脑功能成像的新方法——功能性近红外光谱技术(fNIRS). 心理科学, 34(4), 943-949.] |
| [23] | Mattys, S. L., Brooks, J., & Cooke, M . (2009). Recognizing speech under a processing load: Dissociating energetic from informational factors. Cognitive Psychology, 59(3), 203-243. doi: 10.1016/j.cogpsych.2009.04.001 |
| [24] | McIntosh, M. A., Shahani, U., Boulton, R. G., & McCulloch, D. L . (2010). Absolute quantification of oxygenated hemoglobin within the visual cortex with functional near infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS). Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, 51, 4856-4860. doi: 10.1167/iovs.09-4940 |
| [25] | Noble, W. S . (2009). How does multiple testing correction work? Nature Biotechnology, 27, 1135-1137. doi: 10.1038/nbt1209-1135 |
| [26] | Paas, F.,., & Sweller, J. (2012). An evolutionary upgrade of cognitive load theory: Using the human motor system and collaboration to support the learning of complex cognitive tasks. Educational Psychology Review, 24(1), 27-45. doi: 10.1007/s10648-011-9179-2 |
| [27] | Pelli, D. G., Palomares, M., & Majaj, N. J . (2004). Crowding is unlike ordinary masking: Distinguishing feature integration from detection. Journal of Vision, 4(12), 1136-1169. doi: 10.1167/4.12.12 |
| [28] | Rabaglia, C. D., & Schneider, B. A . (2016). Age-related inhibitory deficit, or lack of familiarity benefit? Evidence from letter identification among visual distractors. Attention, Perception, & Psychophysics, 78(2), 542-565. doi: 10.3758/s13414-015-1009-z |
| [29] | Rowland, S. C., Hartley, D. E. H., & Wiggins, I. M . (2018). Listening in naturalistic scenes: What can functional near-infrared spectroscopy and intersubject correlation analysis tell us about the underlying brain activity? Trends in Hearing, 22 . doi: 10.1177/2331216518804116 |
| [30] | Simons, J. S., Koutstaal, W., Prince, S., Wagner, A. D., & Schacter, D. L . (2003). Neural mechanisms of visual object priming: Evidence for perceptual and semantic distinctions in fusiform cortex. Neuroimage, 19(3), 613-626. doi: 10.1016/s1053-8119(03)00096-x |
| [31] | Tse, P. U., Martinez-Conde, S., Schlegel, A. A., & Macknik, S. L . (2005). Visibility, visual awareness, and visual masking of simple unattended targets are confined to areas in the occipital cortex beyond human V1/V2. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 102(47), 17178-17183. doi: 10.1073/pnas. 0508010102 |
| [32] | Tsubomi, H., Ikeda, T., Hanakawa, T., Hirose, N., Fukuyama, H., & Osaka, N . (2009). Connectivity and signal intensity in the parieto-occipital cortex predicts top-down attentional effect in visual masking: An fMRI study based on individual differences. Neuroimage, 45(2), 587-597. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.11.028 |
| [33] | Ward, L. M., Aitchison, R. T., Tawse, M., Simmers, A. J., & Shahani, U . (2015). Reduced haemodynamic response in the ageing visual cortex measured by absolute fNIRS. PLoS One, 10, 1-16. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125012 |
| [34] | Wardle, S. G., Cass, J., Brooks, K. R., & Alais, D . (2010). Breaking camouflage: Binocular disparity reduces contrast masking in natural images. Journal of Vision, 10(14), 1-12. doi: 10.1167/10.14.38 |
| [35] | Wijeakumar, S., Shahani, U., McCulloch, D. L., & Simpson, W. A . (2012). Neural and vascular responses to fused binocular stimuli: A VEP and fNIRS study. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, 53(9), 5881-5889. doi: 10.1167/iovs.12-10399 |
| [36] | Wijeakumar, S., Shahani, U., Simpson, W. A., & McCulloch, D. L . (2012). Localization of hemodynamic responses to simple visual stimulation: An fNIRS study. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, 53(4), 2266-2273. doi: 10.1167/iovs.11-8680 |
| [37] | Worsley, K. J., Friston, K. J . (1995). Analysis of fMRI time-series revisited - Again. Neuroimage, 2(3), 173-181. doi: 10.1006/nimg.1995.1023 |
| [38] | Yan, G. L., Bai, X. J., Zang, C. L., Bian, Q., Cui, L., Wei, Q., … Liversedge, S. P . (2012). Using stroke removal to investigate Chinese character identification during reading: Evidence from eye movemwnts. Reading and Writing, 25(5), 951-979. doi: 10.1007/s11145-011-9295-x |
| [39] | Yang, Z. G., Zhang, T. T., Song, Y. W., & Li, L . (2014). The subcomponents of informational masking: Evidence from behavioral and neural imaging studies. Advances in Psychological Science, 22(3), 400-408. |
| [40] | [ 杨志刚, 张亭亭, 宋耀武, 李量 . (2014). 听觉信息掩蔽的亚成分:基于行为和脑成像研究的证明. 心理科学进展, 22(3), 400-408.] |
| [41] | Ye, J. C., Tak, S., Jang, K. E., Jung, J., & Jang, J . (2009). NIRS-SPM: Statistical parametric mapping for near-infrared spectroscopy. Neuroimage, 44(2), 428-447. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.08.036 |
相关文章 15
| [1] | 胡晶晶,徐昊骙,曹立人. 感觉记忆中含语义对象的视觉表征[J]. 心理学报, 2019, 51(9): 982-991. |
| [2] | 孙俊才,寻凤娇,刘萍,张文海. 高善良特质在情绪调节行动控制中的内隐优势[J]. 心理学报, 2019, 51(7): 781-794. |
| [3] | 袁小钧, 崔晓霞, 曹正操, 阚红, 王晓, 汪亚珉. 虚拟仿真场景中威胁性视觉刺激搜索的注意偏向效应 *[J]. 心理学报, 2018, 50(6): 622-636. |
| [4] | 李毕琴, 李玲, 王爱君, 张明. 言语工作记忆内容在语义水平的注意捕获[J]. 心理学报, 2018, 50(5): 483-493. |
| [5] | 谭群, 尹月阳, 刘燊, 韩尚锋, 徐强, 张林. 自我积极表情加工优势效应:来自ERPs的证据[J]. 心理学报, 2018, 50(10): 1120-1130. |
| [6] | 李杨卓, 钱浩悦, 朱敏, 高湘萍. 自我相关信息对视觉搜索主动抑制的易化作用[J]. 心理学报, 2018, 50(1): 28-35. |
| [7] | 张豹;胡岑楼;黄赛. 认知控制在工作记忆表征引导注意中的作用:来自眼动的证据[J]. 心理学报, 2016, 48(9): 1105-1118. |
| [8] | 牟兵兵;宛小昂. 视觉搜索中的情绪干扰项预习效应[J]. 心理学报, 2014, 46(11): 1603-1612. |
| [9] | 林欧;王正科;孟祥芝. 汉语发展性阅读障碍儿童的视知觉学习[J]. 心理学报, 2013, 45(7): 762-772. |
| [10] | 张豹;黄赛;祁禄. 工作记忆表征引导视觉注意选择的眼动研究[J]. 心理学报, 2013, 45(2): 139-148. |
| [11] | 李富洪,曹碧华,肖风,李红. 抑制控制在极小概率目标搜索任务中的作用[J]. 心理学报, 2011, 43(05): 509-518. |
| [12] | 李彬寅,许百华,崔翔宇,盛,峰,雷婧宇. 图像记忆对动态搜索的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2010, 42(04): 485-495. |
| [13] | 马艳云. 方位维度视觉搜索的影响因素[J]. 心理学报, 2007, 39(2): 209-214. |
| [14] | 胡凤培,葛列众,徐伟丹. 项目突显方式对视觉搜索策略的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2005, 37(03): 314-319. |
| [15] | 许淑莲,吴志平,吴振云,孙长华. 成年人个性特征与某些认知作业的关系[J]. 心理学报, 2000, 32(3): 276-281. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlxb/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=4553
