 ), 朱君3
), 朱君3 1. 集美大学师范学院, 厦门 361021
2. 中国人民大学心理学系、国家民委民族语言文化心理重点研究基地、教育部民族教育发展中心民族心理与教育重点研究基地, 北京 100872
3. 广东省轻工业高级技工学校, 广州 510310
收稿日期:2019-03-19出版日期:2019-11-25发布日期:2019-09-24通讯作者:张积家E-mail:Zhangjj1955@163.com基金资助:* 福建省社会科学规划项目(FJ2016B286);中国人民大学科学研究基金(中央高校科研业务费专项资金资助项目)(17XNL002);国家留学基金(留金发[2018]3058号)Categorical perception of color is significant both in the right visual field and the left: Evidence from Naxi speakers and Mandarin speakers
XIE Shushu1, ZHANG Jijia2( ), ZHU Jun3
), ZHU Jun3 1. Teachers College, Jimei University, Xiamen 361021, China
2. Department of Psychology, Renmin University of China; The State Ethnic Affairs Commission Key Research, Center for Language, Cultural, and Psychology; Key Research Center for National Psychology and Education, the National Education Development Center of the Ministry of Education, Beijing 100872, China
3. Guangdong Province Technician Institute of Light Industry, Guangzhou 510310, China
Received:2019-03-19Online:2019-11-25Published:2019-09-24Contact:ZHANG Jijia E-mail:Zhangjj1955@163.com摘要/Abstract
摘要: 采用色环搜索单任务和双任务范式, 考察语言中区分蓝、绿的汉族和语言中蓝、绿混用的纳西族对蓝色和绿色的辨别是否存在颜色范畴知觉效应(Categorical perception, 以下简称为CP效应)。结果发现:(1)纳西族对蓝色和绿色的区分比汉族困难, 体现了语言的作用; (2)语言中蓝、绿混用的纳西族与语言中区分蓝、绿的汉族都出现显著的蓝绿CP效应; (3)两个民族被试的左视野的CP效应受到图形记忆次任务的显著干扰, 说明左视野的CP效应与右脑激活有关。整个研究表明, 颜色CP效应既存在普遍的知觉机制, 也存在语言驱动机制, 语言的作用存在直接效应。研究结果支持颜色词与颜色认知的相互作用理论。
图/表 15

图1蓝绿搜索任务使用的颜色块
 图1蓝绿搜索任务使用的颜色块
图1蓝绿搜索任务使用的颜色块
图2蓝绿色环搜索任务的刺激样例
 图2蓝绿色环搜索任务的刺激样例
图2蓝绿色环搜索任务的刺激样例表1被试搜索不同视野目标色块的平均反应时(ms)和错误率(%)
| 民族 | 反应 | 左视野 | 右视野 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 范畴间 | 范畴内 | 范畴间 | 范畴内 | ||
| 汉族 | 反应时 | 374 (90) | 402 (101) | 373 (87) | 394 (90) |
| 错误率 | 9.38 (10.49) | 20.31 (15.20) | 3.13 (6.72) | 10.94 (7.89) | |
| 纳西族 | 反应时 | 431 (132) | 535 (128) | 458 (185) | 511 (123) |
| 错误率 | 12.50 (11.39) | 27.69 (18.21) | 10.42 (13.44) | 19.27 (13.85) | |
表1被试搜索不同视野目标色块的平均反应时(ms)和错误率(%)
| 民族 | 反应 | 左视野 | 右视野 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 范畴间 | 范畴内 | 范畴间 | 范畴内 | ||
| 汉族 | 反应时 | 374 (90) | 402 (101) | 373 (87) | 394 (90) |
| 错误率 | 9.38 (10.49) | 20.31 (15.20) | 3.13 (6.72) | 10.94 (7.89) | |
| 纳西族 | 反应时 | 431 (132) | 535 (128) | 458 (185) | 511 (123) |
| 错误率 | 12.50 (11.39) | 27.69 (18.21) | 10.42 (13.44) | 19.27 (13.85) | |
表2被试在左、右视野的反应时(ms)和错误率(%)CP效应量的平均值
| 民族 | 反应 | 左视野CP效应量 | 右视野CP效应量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 汉族 | 反应时 | 28 (56) | 21 (62) |
| 错误率 | 10.93 (20.35) | 7.81 (10.31) | |
| 纳西族 | 反应时 | 104 (82) | 53 (161) |
| 错误率 | 15.19 (14.93) | 8.85 (15.05) |
表2被试在左、右视野的反应时(ms)和错误率(%)CP效应量的平均值
| 民族 | 反应 | 左视野CP效应量 | 右视野CP效应量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 汉族 | 反应时 | 28 (56) | 21 (62) |
| 错误率 | 10.93 (20.35) | 7.81 (10.31) | |
| 纳西族 | 反应时 | 104 (82) | 53 (161) |
| 错误率 | 15.19 (14.93) | 8.85 (15.05) |

图3红紫范畴判断任务使用的色块
 图3红紫范畴判断任务使用的色块
图3红紫范畴判断任务使用的色块表3被试判断不同颜色范畴色块的平均反应时(ms)和错误率(%)
| 民族 | 反应 | 蓝-绿范畴判断 | 红-紫范畴判断 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 汉族 | 反应时 | 366 (86) | 409 (121) |
| 错误率 | 9.13 (6.55) | 14.13 (10.70) | |
| 纳西族 | 反应时 | 431 (78) | 377 (82) |
| 错误率 | 29.03 (21.71) | 18.33 (10.25) |
表3被试判断不同颜色范畴色块的平均反应时(ms)和错误率(%)
| 民族 | 反应 | 蓝-绿范畴判断 | 红-紫范畴判断 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 汉族 | 反应时 | 366 (86) | 409 (121) |
| 错误率 | 9.13 (6.55) | 14.13 (10.70) | |
| 纳西族 | 反应时 | 431 (78) | 377 (82) |
| 错误率 | 29.03 (21.71) | 18.33 (10.25) |

图4图形干扰任务的材料范例
 图4图形干扰任务的材料范例
图4图形干扰任务的材料范例
图5言语干扰任务材料范例
 图5言语干扰任务材料范例
图5言语干扰任务材料范例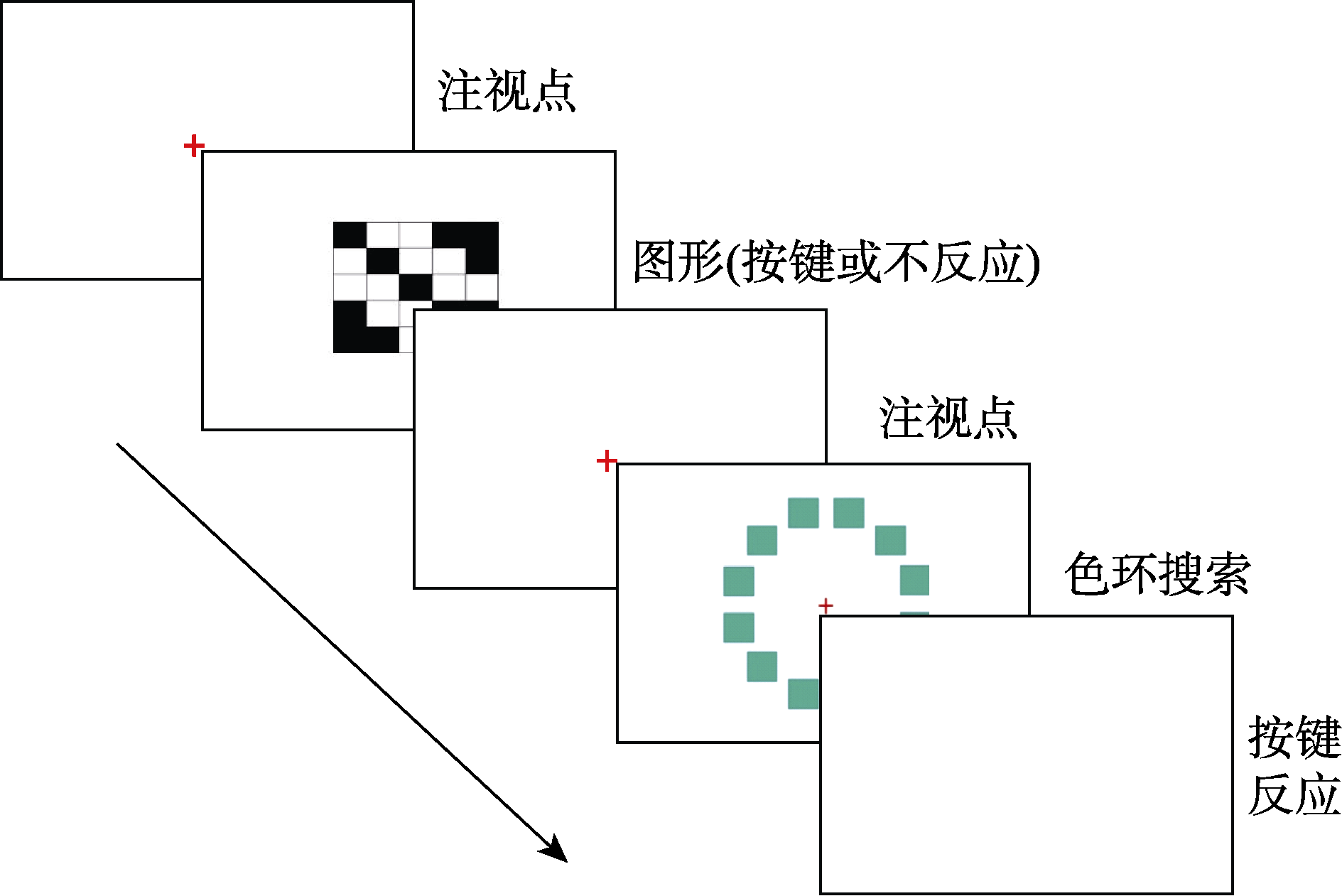
图6色环搜索+图形记忆双任务流程图
 图6色环搜索+图形记忆双任务流程图
图6色环搜索+图形记忆双任务流程图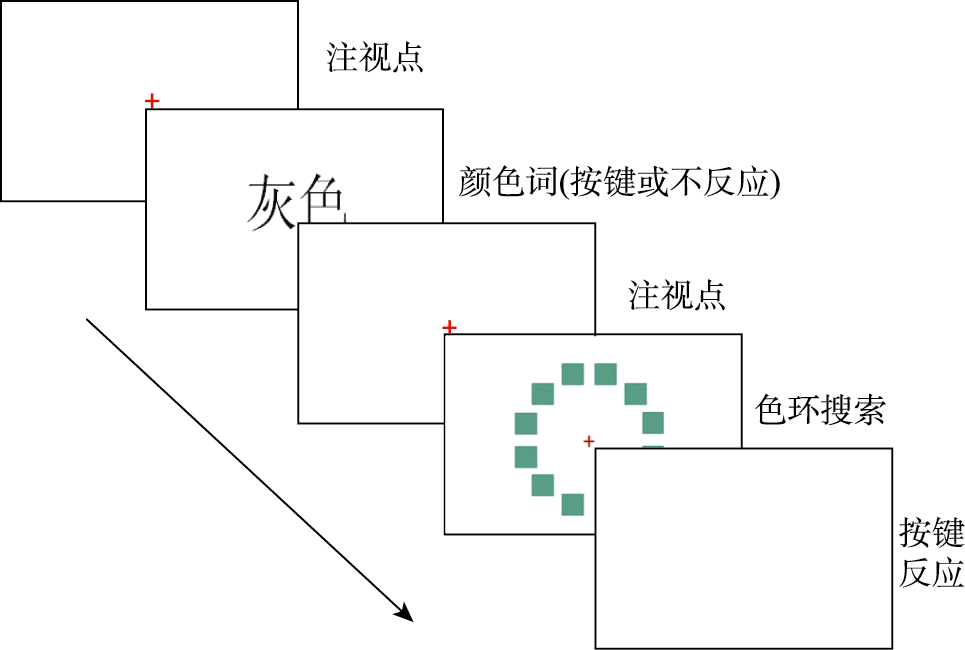
图7色环搜索+颜色词记忆双任务流程图
 图7色环搜索+颜色词记忆双任务流程图
图7色环搜索+颜色词记忆双任务流程图表4图形干扰任务下被试搜索不同视野目标色块的平均反应时(ms)和错误率(%)
| 民族 | 反应 | 左视野 | 右视野 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 范畴间 | 范畴内 | 范畴间 | 范畴内 | ||
| 汉族 | 反应时 | 482 (102) | 520 (100) | 418 (77) | 485 (83) |
| 错误率 | 9.16 (13.76) | 20.83 (13.92) | 3.33 (6.84) | 11.25 (11.24) | |
| 纳西族 | 反应时 | 528 (166) | 543 (129) | 431 (97) | 478 (132) |
| 错误率 | 21.88 (25.62) | 34.37 (17.97) | 11.46 (15.77) | 13.54 (11.74) | |
表4图形干扰任务下被试搜索不同视野目标色块的平均反应时(ms)和错误率(%)
| 民族 | 反应 | 左视野 | 右视野 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 范畴间 | 范畴内 | 范畴间 | 范畴内 | ||
| 汉族 | 反应时 | 482 (102) | 520 (100) | 418 (77) | 485 (83) |
| 错误率 | 9.16 (13.76) | 20.83 (13.92) | 3.33 (6.84) | 11.25 (11.24) | |
| 纳西族 | 反应时 | 528 (166) | 543 (129) | 431 (97) | 478 (132) |
| 错误率 | 21.88 (25.62) | 34.37 (17.97) | 11.46 (15.77) | 13.54 (11.74) | |
表5被试在色环搜索-图形双任务中左、右视野的反应时(ms)和错误率(%)CP效应量的平均值
| 民族 | 反应 | 左视野CP效应量 | 右视野CP效应量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 汉族 | 反应时 | 38 (64) | 67 (47) |
| 错误率 | 11.67 (18.26) | 7.92 (14.14) | |
| 纳西族 | 反应时 | 15 (102) | 47 (55) |
| 错误率 | 12.49 (16.49) | 2.08 (14.04) |
表5被试在色环搜索-图形双任务中左、右视野的反应时(ms)和错误率(%)CP效应量的平均值
| 民族 | 反应 | 左视野CP效应量 | 右视野CP效应量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 汉族 | 反应时 | 38 (64) | 67 (47) |
| 错误率 | 11.67 (18.26) | 7.92 (14.14) | |
| 纳西族 | 反应时 | 15 (102) | 47 (55) |
| 错误率 | 12.49 (16.49) | 2.08 (14.04) |
表6言语任务干扰下被试搜索不同视野目标色块的平均反应时(ms)和错误率(%)
| 民族 | 反应 | 左视野 | 右视野 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 范畴间 | 范畴内 | 范畴间 | 范畴内 | ||
| 汉族 | 反应时 | 466 (105) | 486 (108) | 436 (123) | 428 (105) |
| 错误率 | 14.82 (16.06) | 20.83 (12.54) | 12.03 (18.79) | 12.96 (14.36) | |
| 纳西族 | 反应时 | 538 (181) | 544 (136) | 464 (120) | 490 (86) |
| 错误率 | 24.60 (20.15) | 28.97 (20) | 14.29 (19.92) | 17.86 (17.73) | |
表6言语任务干扰下被试搜索不同视野目标色块的平均反应时(ms)和错误率(%)
| 民族 | 反应 | 左视野 | 右视野 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 范畴间 | 范畴内 | 范畴间 | 范畴内 | ||
| 汉族 | 反应时 | 466 (105) | 486 (108) | 436 (123) | 428 (105) |
| 错误率 | 14.82 (16.06) | 20.83 (12.54) | 12.03 (18.79) | 12.96 (14.36) | |
| 纳西族 | 反应时 | 538 (181) | 544 (136) | 464 (120) | 490 (86) |
| 错误率 | 24.60 (20.15) | 28.97 (20) | 14.29 (19.92) | 17.86 (17.73) | |
表7被试在色环搜索-言语双任务中左、右视野的反应时(ms)和错误率(%)CP效应量的平均值
| 民族 | 反应 | 左视野CP效应量 | 右视野CP效应量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 汉族 | 反应时 | 20 (58) | -8 (86) |
| 错误率 | 6.01 (12.72) | 0.93 (4.53) | |
| 纳西族 | 反应时 | 6 (142) | 26 (98) |
| 错误率 | 4.37 (18.23) | 3.57 (8.24) |
表7被试在色环搜索-言语双任务中左、右视野的反应时(ms)和错误率(%)CP效应量的平均值
| 民族 | 反应 | 左视野CP效应量 | 右视野CP效应量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 汉族 | 反应时 | 20 (58) | -8 (86) |
| 错误率 | 6.01 (12.72) | 0.93 (4.53) | |
| 纳西族 | 反应时 | 6 (142) | 26 (98) |
| 错误率 | 4.37 (18.23) | 3.57 (8.24) |
表8被试在三种任务条件下左、右视野的范畴知觉效应量
| 民族 | 反应 | 左视野 | 右视野 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 单任务 | 图形干扰 双任务 | 言语干扰 双任务 | 单任务 | 图形干扰 双任务 | 言语干扰 双任务 | ||
| 汉族 | 反应时(ms) | 28 | 38 | 20 | 21 | 67 | -8 |
| 错误率(%) | 10.93 | 11.67 | 6.01 | 7.81 | 7.92 | 0.93 | |
| 纳西族 | 反应时(ms) | 104 | 15 | 6 | 53 | 47 | 26 |
| 错误率(%) | 15.19 | 12.49 | 4.37 | 8.85 | 2.08 | 3.57 | |
表8被试在三种任务条件下左、右视野的范畴知觉效应量
| 民族 | 反应 | 左视野 | 右视野 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 单任务 | 图形干扰 双任务 | 言语干扰 双任务 | 单任务 | 图形干扰 双任务 | 言语干扰 双任务 | ||
| 汉族 | 反应时(ms) | 28 | 38 | 20 | 21 | 67 | -8 |
| 错误率(%) | 10.93 | 11.67 | 6.01 | 7.81 | 7.92 | 0.93 | |
| 纳西族 | 反应时(ms) | 104 | 15 | 6 | 53 | 47 | 26 |
| 错误率(%) | 15.19 | 12.49 | 4.37 | 8.85 | 2.08 | 3.57 | |
参考文献 95
| [1] | Bai, G. S. (2001). Color and Naxi culture. Social Science Literature Press of China. |
| [2] | [ 白庚胜 . (2001). 色彩与纳西族民俗. 北京: 社会科学文献出版社.] |
| [3] | Bao, S. W . (2015). Perceptual learning in the developing auditory cortex. European Journal of Neuroscience, 41(5), 718-724. |
| [4] | Berlin, B., & Kay, P.. (1991) Basic color terms: Their universality and evolution Berkeley: University of California Press Their universality and evolution . Berkeley: University of California Press. |
| [5] | Bird, C. M., Berens, S. C., Horner, A. J., & Franklin, A . (2014). Categorical encoding of color in the brain. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 111(12), 4590-4595. |
| [6] | Bornstein, M. H., & Korda, N. O . (1984). Discrimination and matching within and between hues measured by reaction times: Some implications for categorical perception and levels of information processing. Psychological Research, 46(3), 207-222. |
| [7] | Boynton, R. M., & Olson, C. X . (1990). Salience of chromatic basic color terms confirmed by three measures. Vision Research, 30(9), 1311-1317. |
| [8] | Brouwer, G., J., & Heeger, D. J . (2013). Categorical clustering of the neural representation of color. The Journal of Neuroscience, 33(39), 15454-15465. |
| [9] | Brown, A. M., Lindsey, D. T., & Guckes, K. M . (2011). Color names, color categories, and color-cued visual search: Sometimes, color perception is not categorical. Journal of Vision, 11(12), 1-21. |
| [10] | Cibelli, E., Xu, Y., Austerweil, J. L., Griffiths, T. L., & Regier, T . (2016). The Sapir-Whorf hypothesis and probabilistic inference: Evidence from the domain of color. PLoS One, 11(8), e0161521. |
| [11] | Clifford, A., Franklin, A., Davies, I. R. L., & Holmes, A . (2009). Electrophysiological markers of categorical perception of color in 7-month old infants. Brain and Cognition, 71(2), 165-172. |
| [12] | Clifford, A., Holmes, A., Davies, I. R. L., & Franklin, A . (2010). Color categories affect pre-attentive color perception. Biological Psychology, 85(2), 275-282. |
| [13] | Constable, M. D., & Becker, S. I . (2017). Right away: A late, right-lateralized category effect complements an early, left- lateralized category effect in visual search. Psychonomic bulletin & Review, 24(5), 1611-1619. |
| [14] | Cowey, A., Heywood, C.A., & Irving-Bell, L . (2001). The regional cortical basis of achromatopsia: A study on macaque monkeys and an achromatopsic patient. European Journal of Neuroscience, 14(9), 1555-1566. |
| [15] | Daoutis, C. A., Pilling, M& Davies, I. R. L. (2006). Categorical effects in visual search for colour. Visual Cognition, 14(2), 217-240. |
| [16] | Davidoff, J . (2001). Language and perceptual categorization. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 5(9), 382-387. |
| [17] | Davidoff, J., Davies, I., & Roberson, D . (1999). Color categories in a stone-age tribe. Nature, 398(6724), 203-204. |
| [18] | Davies, I. R. L., Corbett, G. G., Laws, G., McGurk, H., Moss, A. E. S. G., & Smith, M. W . (1991). Linguistic basicness and colour information processing. International Journal of Psychology, 26(3), 311-327. |
| [19] | Drivonikou, G. V., Kay, P., Regier, T., Ivry, R. B., Gilbert, A. L., Franklin, A& Davies, I. R. L. (2007). Further evidence that Whorfian effects are stronger in the right visual field than the left. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 104(3), 1097-1102. |
| [20] | Edwards, D. J . (2017). Unsupervised categorization with a child sample: Category cohesion development. European Journal of Developmental Psychology, 14(1), 75-86. |
| [21] | Fagot, J., Goldstein, J., Davidoff, J., & Pickering, A . (2006). Cross-species differences in color categorization. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 13(2), 275-280. |
| [22] | Folstein, J. R., Palmeri, T. J., van Gulick, A. E., & Gauthier, I . (2015). Category learning stretches neural representations in visual cortex. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 24(1), 17-23. |
| [23] | Fonteneau, E., & Davidoff, J. (2007). Neural correlates of colour categories. Neuroreport, 18(13), 1323-1327. |
| [24] | Franklin, A., Clifford, A., Williamson, E., & Davies, I . (2005). Color term knowledge does not affect categorical perception of color in toddlers. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 90(2), 114-141. |
| [25] | Franklin, A., & Davies, I. R. L . (2004). New evidence for infant color categories. British Journal of Development Psychology, 22(3), 349-377. |
| [26] | Franklin, A., Pilling, M., & Davies, I . (2005). The nature of infant color categorization: evidence from eye movements on a target detection task. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 91(3), 227-248. |
| [27] | Franklin, A., Wright, O., & Davies, I. R. L. .(2009). What can we learn from toddlers about categorical perception of color? Comments on Goldstein, Davidoff, and Roberson. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 102(2), 239-245. |
| [28] | Gilbert, A.L., Regier, T., Kay, P., & Ivry, R. B . (2006). Whorf hypothesis is supported in the right visual field but not the left. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 103(2), 489-494. |
| [29] | Gilbert, A. L., Regier, T., Kay, P., & Ivry, R. B . (2008). Support for lateralization of the Whorf effect beyond the realm of color discrimination. Brain and Language, 105(2), 91-98. |
| [30] | Goldstein, J., Davidoff, J., & Roberson, D . (2009). Knowing color terms enhances recognition: Further evidence from English and Himba. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 102(2), 219-238. |
| [31] | Hanazawa, A., Komatsu, H., & Murakami, I . (2000). Neural selectivity for hue and saturation of color in the primary visual cortex of the monkey. European Journal of Neuroscience, 12(5), 1753-1763. |
| [32] | Harnad, S. (1987). Categorical perception: the groundwork of cognition. New York: Cambridge University Press. |
| [33] | Holmes, K. J., & Wolff, P. (2012). Does categorical perception in the left hemisphere depend on language? Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 141(3), 439-443. |
| [34] | Hu, Z. H., Hanley, J. R., Zhang, R., Liu, Q., & Roberson, D . (2014). A conflict-based model of color categorical perception: Evidence from a priming study. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 21(5), 1214-1223. |
| [35] | Jameson, K. A . (2005). Culture and cognition: What is universal about the representation of color experience? Journal of Cognition and Culture, 5(3-4), 293-347. |
| [36] | Kay, P.. (2002). Color categories are not arbitrary. Journal of Vision, 2(10), 1-21. |
| [37] | Kay, P., & Kempton W. (1984). What is the Sapir-Whorf hypothesis? American Anthropologist, 86(1), 65-79. |
| [38] | Kay, P., & Regier, T. (2003). Resolving the question of color naming universals. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 100(15), 9085-9089. |
| [39] | Kay, P., & Regier, T. (2006). Language, thought and color: Recent developments. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 10(2), 51-54. |
| [40] | Koida, K., &, Komatsu , H. (2007). Effects of task demands on the responses of color-selective neurons in the inferior temporal cortex. Nature Neuroscience, 10(1), 108-116. |
| [41] | Kwok, V., Niu, Z. D., Kay, P., Zhou, K., Mo, L., Jin, Z., … Tan, L. H . (2011). Learning new color names produces rapid increase in gray matter in the intact adult human cortex. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science, 108(16), 6686-6688. |
| [42] | Levinson, S., C . (2000). Yél? Dnye and the theory of basic color terms. Journal of Linguistic Anthropology, 10(1), 3-55. |
| [43] | Li, J., He, H., Wu, B. Z., Hou, Y., Cao, K., & A, R . (2018). Behavioral and ERP study of color categorical perception in proficient and nonproficient bilinguals. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 50(11), 1259-1268. |
| [44] | [ 李杰, 何虎, 吴柏周, 侯友, 曹亢, 阿如罕 . (2018). 不同熟练度双语者的颜色范畴知觉效应:来自行为和ERP的证据. 心理学报, 50(11), 1259-1268.] |
| [45] | Lillo, J., González-Perilli, F., Prado-León, L., Melnikova, A., álvaro, L., Collado, J. A., & Moreira, H . (2018). Basic color terms (BCTs) and categories (BCCs) in three dialects of the Spanish language: Interaction between cultural and universal factors. Frontiers in Psychology, 9,1-19. |
| [46] | Liu, Q., Li, H., Campos, J. L., Teeter, C., Tao, W. D., Zhan, Q. L., & Sun, H. J . (2010). Language suppression effects on the categorical perception of colour as evidenced through ERPs. Biological Psychology, 85(1), 45-52. |
| [47] | Maier, M., Glage, P., Hohlfeld, A., & Rahman, R. A . (2014). Does the semantic content of verbal categories influence categorical perception? An ERP study. Brain and Cognition, 91,1-10. |
| [48] | Mo, L., Xu, G. P., Kay, P., & Tan, L. H . (2011). Electrophysiological evidence for the left-lateralized effect of language on preattentive categorical perception of color. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 108(34), 14026-14030. |
| [49] | Okajima, K., Robertson, A. R., & Fielder, G. H . (2002). A quantitative network model for color categorization. Color Research & Application, 27(4), 225-232. |
| [50] | Ozgen, E., & Davies, I. R. L . (2002). Acquisition of categorical color perception: A perceptual learning approach to the linguistic relativity hypothesis. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 131(4), 477-493. |
| [51] | Pilling, D. M., & Davies, I. R. L . (2004). Linguistic relativism and colour cognition. British Journal of Psychology, 95(4), 429-455. |
| [52] | Pilling, M., Wiggett, A., ?zgen, E., & Davies, I. R. L. (2003). Is color “categorical perception” really perceptual? Memory & Cognition, 31(4), 538-551. |
| [53] | Pitchford, N. J., & Mullen, K. T . (2002). Is the acquisition of basic-color terms in young children constrained? Perception, 31(11), 1349-1370. |
| [54] | Regier, T., & Kay, P. (2009). Language, thought, and color: Whorf was half right. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 13(10), 439-446. |
| [55] | Regier, T., Kay, P., & Cook, R. S . (2005). Focal colors are universal after all. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 102(23), 8386-8391. |
| [56] | Regier, T., Kay, P., & Khetarpal, N . (2007). Color naming reflects optimal partitions of color space. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 104(4), 1436-1441. |
| [57] | Regier, T., & Xu, Y .(2017). The Sapir-Whorf hypothesis and inference under uncertainty. WIREs Cognitive Science, 8(6), e1440. |
| [58] | Roberson, D., & Davidoff, J. (2000). The categorical perception of colors and facial expressions: The effect of verbal interference. Memory and Cognition, 28(6), 977-986. |
| [59] | Roberson, D., Pak, H., & Hanley, J. R . (2008). Categorical perception of colour in the left and right visual field is verbally mediated: Evidence from Korean. Cognition, 107(2), 752-762. |
| [60] | Siok, W. T., Kay, P., Wang, W. S. Y., Chan, A. H. D., Chen, L., Luke, K. K., & Tan, L. H . (2009). Language regions of brain are operative in color perception. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 106(20), 8140-8145. |
| [61] | Siok, W. T., Perfetti, C. A., Jin, Z., & Tan, L. H . (2004). Biological abnormality of impaired reading is constrained by culture. Nature, 431,71-76. |
| [62] | Tan, L. H., Chan, A. H. D., Kay, P., Khong, P. L., Yip, L. K. C., & Luke, K. K . (2008). Language affects patterns of brain activation associated with perceptual decision. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 105(10), 4004-4009. |
| [63] | Tan, L. H., Laird, A. R., Li, K., & Fox, P. T . (2005). Neuroanatomical correlates of phonological processing of Chinese characters and alphabetic words: A meta-analysis. Human Brain Mapping, 25(1), 83-91. |
| [64] | Tan, L. H., Liu, H. L., Perfetti, C. A., Spinks, J. A., Fox, P. T., & Gao, J. H . (2001). The neural system underlying Chinese logograph reading. NeuroImage, 13(5), 836-846. |
| [65] | Thériault, C., Pérez-Gay, F., Rivas, D., & Harnad, S . (2018). Learning-induced categorical perception in a neural network model. Topics in Cognitive Science, (3), 1-11. |
| [66] | Thierry, G., Athanasopoulos, P., Wiggett, A., Dering, B., & Kuipers, J. R . (2009). Unconscious effects of language- specific terminology on preattentive color perception. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 106(11), 4567-4570. |
| [67] | Wang, J., & Zhang, J. J . (2012). Color terms and color cognition: based on the perspective of national psychology. Advances in Psychological Science, 20(8), 1159-1168. |
| [68] | [ 王娟, 张积家 .(2012). 颜色词与颜色认知的关系——基于民族心理学的研究视角. 心理科学进展, 20(8), 1159-1168.] |
| [69] | Wang, J., Zhang, J. J., & Lin, N . (2010). Nari people's concept structure on color terms - Compared with Naxi people's concept structure on color terms. Journal of Minzu University of China (Philosophy and Social Sciences Edition), 37(2), 87-93. |
| [70] | [ 王娟, 张积家, 林娜 . (2010). 纳日人颜色词的概念结构——兼与纳西族人颜色词概念结构比较. 中央民族大学学报(哲学社会科学版), 37(2), 87-93.] |
| [71] | Winawer, J. A., Witthoft, N., Wu, L. S., & Boroditsky, L . (2003). Effects of language on color discriminability. Journal of Vision, 3(9), 711. |
| [72] | Witzel, C., & Gegenfurtner, K. R . (2013). Categorical sensitivity to color differences. Journal of Vision, 13(7). |
| [73] | Wu, B. Z., Li, J., He, H., Hou, Y., Jia, Y. Q., & Feng, S. X . (2019). Categorical perception of color can be instantly influenced by color vision fatigue and semantic satiation. Acta Psychological Sinica, 51(2), 196-206. |
| [74] | Xie, S. S., & Zhang, J. J . (2008). A research summary and new perspective of the study of the nature of Naxi Dongba script. Journal of South China Normal University (Social Science Edition), (3), 107-114. |
| [75] | [ 谢书书, 张积家 . (2008). 纳西东巴文字性质研究进展和新视角. 华南师范大学学报(社会科学版), (3), 107-114.] |
| [76] | Xie, S. S., & Zhang, J. J . (2012). The contribution of Naxi Dongba characters to language cognition researches. Advances in Psychological Science, 20(8), 1212-1221. |
| [77] | [ 谢书书, 张积家 . (2012). 东巴文认知研究对心理语言学的贡献及展望. 心理科学进展, 20(8), 1212-1221.] |
| [78] | Xie, S. S., & Zhang, J. J . (2019). The mechanism of color category perception: Effects of language. Advances in Psychological Science, 27(8), 1384-1393. |
| [79] | [ 谢书书, 张积家 . (2019). 颜色类别知觉效应的机制:语言的作用. 心理科学进展, 27(8), 1384-1393.] |
| [80] | Xie, S. S., Zhang, J. J., He, X. M., Lin, N., & Xiao, E. P . (2008). Culture’s effects on ‘black’ and ‘white’ color cognition of undergraduates from Yi Nation, Bai Nation, Naxi Nation and Han Nation. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 40(8), 890-901. |
| [81] | [ 谢书书, 张积家, 和秀梅, 林娜, 肖二平 . (2008). 文化差异影响彝、白、纳西和汉族大学生对黑白的认知. 心理学报, 40(8), 890-901.] |
| [82] | Yang, B., Xu, S. T., & Ou, Y. Q . (1989). The functional characteristic of the hemispheres for recognizing Chinese characters and English words in subjects with different native language. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 21(2), 70-74. |
| [83] | [ 羊彪, 许世彤, 区英琦 . (1989). 母语不同者在汉字及英文辨认中大脑两半球的功能特点. 心理学报, 21(2), 70-74.] |
| [84] | Zhang, J. J., Chen, X. Q, You, N., & Wang, B . (2018). On how conceptual connections influence the category perception effect of colors: Another evidence of connections between language and cognition. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 50(4), 390-399. |
| [85] | [ 张积家, 陈栩茜, 尤宁, 王斌 . (2018). 颜色词的语用关系影响颜色认知. 心理学报, 50(4), 390-399.] |
| [86] | Zhang, J. J., Fang, Y. H., & Xie, S. S . (2012). Interactive theory of color cognition and its evidence. Advances in Psychological Science, 20(7), 949-962. |
| [87] | [ 张积家, 方燕红, 谢书书 . (2012). 颜色词与颜色认知的关系: 相互作用理论及其证据. 心理科学进展, 20(7), 949-962.] |
| [88] | Zhang, J. J., Liu, L. H., Chen, X., & He, X. M . (2008). Study on the relationship between the color cognition and Naxi color language. Minority Languages of China, (2), 49-55. |
| [89] | [ 张积家, 刘丽虹, 陈曦, 和秀梅 . (2008). 纳西语颜色认知关系研究. 民族语文, (2), 49-55.] |
| [90] | Zhang, J. J., & Meng, L. (2018). The effect of language and color culture on the colour cognition of undergraduates from Mongol nationality and Han nationality. Journal of South China Normal University (Social Science Edition), (5), 59-69. |
| [91] | [ 张积家, 孟乐 . (2018). 语言和颜色文化对蒙、汉大学生颜色认知的影响. 华南师范大学学报(社会科学版), (5), 59-69.] |
| [92] | Zhang, Q. R., He, X. M., & Zhang, J. J . (2007). A comparative study on the classification of basic color terms by undergraduates from Yi nationality, Bai nationality and Naxi nationality. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 39(1), 18-26. |
| [93] | [ 张启睿, 和秀梅, 张积家 . (2007). 彝族、白族和纳西族大学生的基本颜色词分类. 心理学报, 39(1), 18-26.] |
| [94] | Zhong, W. F., Li, Y., Huang, Y. L., Li, H., & Mo, L . (2018). Is the lateralized categorical perception of color a situational effect of language on color perception? Cognitive Science, 42(1), 350-364. |
| [95] | Zhou, K., Mo, L., Kay, P., Kwok, V. P. Y., Tiffany, N. M. I., & Tan, L. H . (2010). Newly trained lexical categories produce lateralized categorical perception of color. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 107(22), 9974-9978. |
相关文章 8
| [1] | 杨群,张启睿,冯意然,张积家. 语言和文化影响颜色认知:直接语言效应抑或间接语言效应?[J]. 心理学报, 2019, 51(5): 543-556. |
| [2] | 李杰, 何虎, 吴柏周, 侯友, 曹亢, 阿如罕. 不同熟练度双语者的颜色范畴知觉效应:来自行为和ERP的证据[J]. 心理学报, 2018, 50(11): 1259-1268. |
| [3] | 李恒, 曹宇. 时间焦点对前后方向上内隐时空映射的影响——来自汉族和羌族的证据[J]. 心理学报, 2018, 50(10): 1083-1093. |
| [4] | 和秀梅;张夏妮;张积家;肖二平;王 娟. 文化图式影响亲属词语义加工中的空间隐喻 ——来自汉族人和摩梭人的证据[J]. 心理学报, 2015, 47(5): 584-599. |
| [5] | 张积家;王娟;肖二平;和秀梅. 文化和情境影响亲属词的概念结构[J]. 心理学报, 2013, 45(8): 825-839. |
| [6] | 谢书书,张积家,和秀梅,林娜,肖二平. 文化差异影响彝、白、纳西和汉族大学生对黑白的认知[J]. 心理学报, 2008, 40(08): 890-901. |
| [7] | 张启睿,和秀梅,张积家. 彝族、白族和纳西族大学生的基本颜色词分类[J]. 心理学报, 2007, 39(01): 18-26. |
| [8] | 张积家,和秀梅. 纳西族亲属词的概念结构——兼与汉族亲属词概念结构比较[J]. 心理学报, 2004, 36(06): 654-662. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlxb/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=4557
