 )
) 华南师范大学心理应用研究中心, 心理学院, 广东省心理健康与认知科学重点实验室, 广州 510631
收稿日期:2018-05-07出版日期:2019-03-25发布日期:2019-01-22通讯作者:梅磊磊E-mail:mll830925@126.com基金资助:* 国家自然科学基金项目(31771199);广东省普通高校创新团队项目(人文社科)(2017WCXTD002);广东省普通高校哲学社会科学重点实验室项目资助(2015WSYS009)Impacts of chunking strategy on memorising similar words
ZHANG Lei, LU Chengrou, LIN Junfeng, MEI Leilei( )
) Center for Studies of Psychological Application, School of Psychology, Guangdong Key Laboratory of Mental Health and Cognitive Science, South China Normal University, Guangzhou 510631, China
Received:2018-05-07Online:2019-03-25Published:2019-01-22Contact:MEI Leilei E-mail:mll830925@126.com摘要/Abstract
摘要: 已有关于材料相似性影响短时记忆的研究提示, 不相似材料组块相比于相似材料组块可能促进记忆。为验证该假设, 该研究采用学习-测查范式, 通过4个实验考察了学习材料组块方式对相似词长时记忆的影响及机制。结果发现:1)与相似词组块相比, 不相似词组块促进了相似词记忆; 2)不相似词组块的促进效应是通过增强相似词表共同词根的记忆而实现的; 3)不相似词组块的促进效应可能依赖于语音相似性。该结果说明不相似词组块可能是促进相似词汇记忆的有效途径之一。
图/表 8
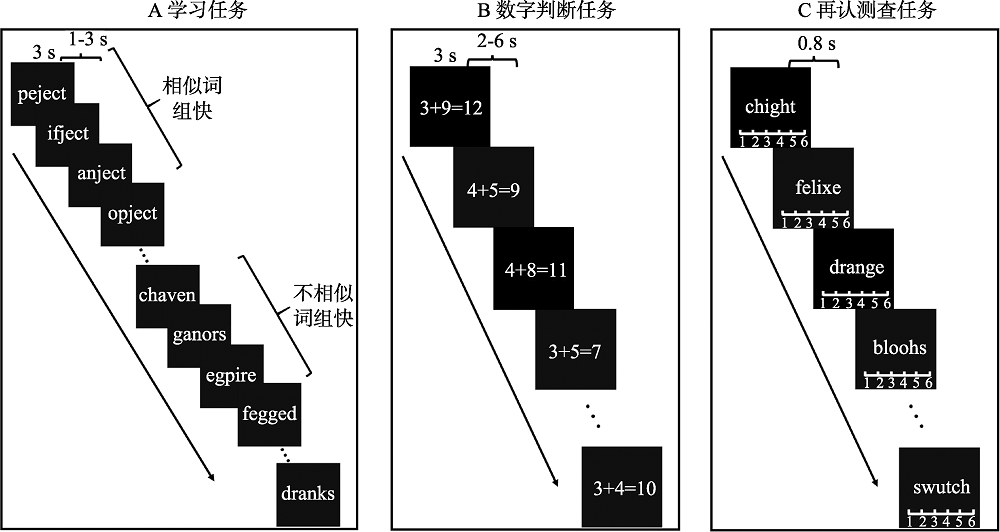
图1实验流程示意图:学习任务(A), 数字判断任务(B)和再认测查任务(C)。
 图1实验流程示意图:学习任务(A), 数字判断任务(B)和再认测查任务(C)。
图1实验流程示意图:学习任务(A), 数字判断任务(B)和再认测查任务(C)。表1再认记忆测查的平均正确率(标准差)及t检验结果
| 实验编号 | 正确率 | t | d |
|---|---|---|---|
| 实验1A | 0.82 (0.09) | 17.01*** | 3.63 |
| 实验1B | 0.70 (0.09) | 9.87*** | 2.10 |
| 实验2 | 0.71 (0.08) | 11.71*** | 2.49 |
| 实验3 | 0.67 (0.08) | 10.17*** | 1.99 |
表1再认记忆测查的平均正确率(标准差)及t检验结果
| 实验编号 | 正确率 | t | d |
|---|---|---|---|
| 实验1A | 0.82 (0.09) | 17.01*** | 3.63 |
| 实验1B | 0.70 (0.09) | 9.87*** | 2.10 |
| 实验2 | 0.71 (0.08) | 11.71*** | 2.49 |
| 实验3 | 0.67 (0.08) | 10.17*** | 1.99 |
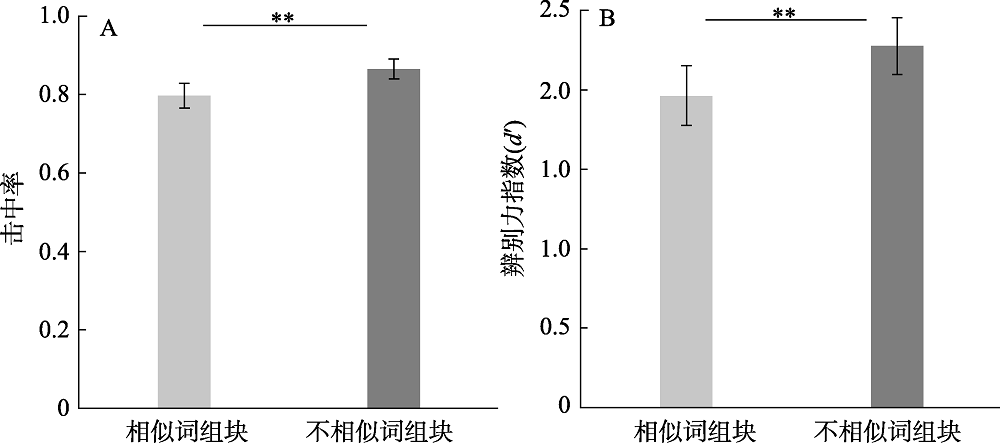
图2实验1A中两种组块条件的击中率(A)和辨别力指数(B)。
 图2实验1A中两种组块条件的击中率(A)和辨别力指数(B)。
图2实验1A中两种组块条件的击中率(A)和辨别力指数(B)。表2再认记忆测查中两种组块条件的平均反应时(标准差)及t检验结果
| 实验编号 | 相似词组块 | 不相似词组块 | t | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 实验1A | 2020.76 (757.13) | 1908.26 (735.72) | 1.55 | 0.136 |
| 实验1B | 2151.65 (781.03) | 2128.97 (727.22) | 0.33 | 0.747 |
| 实验2 | 2386.15 (986.30) | 2336.87 (925.58) | 0.62 | 0.545 |
| 实验3 | 2286.98 (803.35) | 2441.74 (1200.42) | -0.84 | 0.409 |
表2再认记忆测查中两种组块条件的平均反应时(标准差)及t检验结果
| 实验编号 | 相似词组块 | 不相似词组块 | t | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 实验1A | 2020.76 (757.13) | 1908.26 (735.72) | 1.55 | 0.136 |
| 实验1B | 2151.65 (781.03) | 2128.97 (727.22) | 0.33 | 0.747 |
| 实验2 | 2386.15 (986.30) | 2336.87 (925.58) | 0.62 | 0.545 |
| 实验3 | 2286.98 (803.35) | 2441.74 (1200.42) | -0.84 | 0.409 |
表3再认记忆测查中两种组块条件的高、低自信击中率(标准差)及t检验结果
| 实验编号 | 低自信 | 高自信 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 相似词组块 | 不相似词组块 | t | p | 相似词组块 | 不相似词组块 | t | p | |
| 实验1A | 0.24 (0.16) | 0.25 (0.12) | -0.68 | 0.506 | 0.55 (0.23) | 0.61 (0.19) | -2.66 | 0.015 |
| 实验1B | 0.44 (0.18) | 0.45 (0.18) | -0.98 | 0.338 | 0.24 (0.20) | 0.27 (0.21) | -2.31 | 0.031 |
| 实验2 | 0.39 (0.17) | 0.39 (0.17) | 0.03 | 0.972 | 0.25 (0.19) | 0.32 (0.20) | -5.03 | < 0.001 |
| 实验3 | 0.29 (0.15) | 0.32 (0.18) | -1.69 | 0.103 | 0.49 (0.24) | 0.48 (0.26) | 0.24 | 0.815 |
表3再认记忆测查中两种组块条件的高、低自信击中率(标准差)及t检验结果
| 实验编号 | 低自信 | 高自信 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 相似词组块 | 不相似词组块 | t | p | 相似词组块 | 不相似词组块 | t | p | |
| 实验1A | 0.24 (0.16) | 0.25 (0.12) | -0.68 | 0.506 | 0.55 (0.23) | 0.61 (0.19) | -2.66 | 0.015 |
| 实验1B | 0.44 (0.18) | 0.45 (0.18) | -0.98 | 0.338 | 0.24 (0.20) | 0.27 (0.21) | -2.31 | 0.031 |
| 实验2 | 0.39 (0.17) | 0.39 (0.17) | 0.03 | 0.972 | 0.25 (0.19) | 0.32 (0.20) | -5.03 | < 0.001 |
| 实验3 | 0.29 (0.15) | 0.32 (0.18) | -1.69 | 0.103 | 0.49 (0.24) | 0.48 (0.26) | 0.24 | 0.815 |
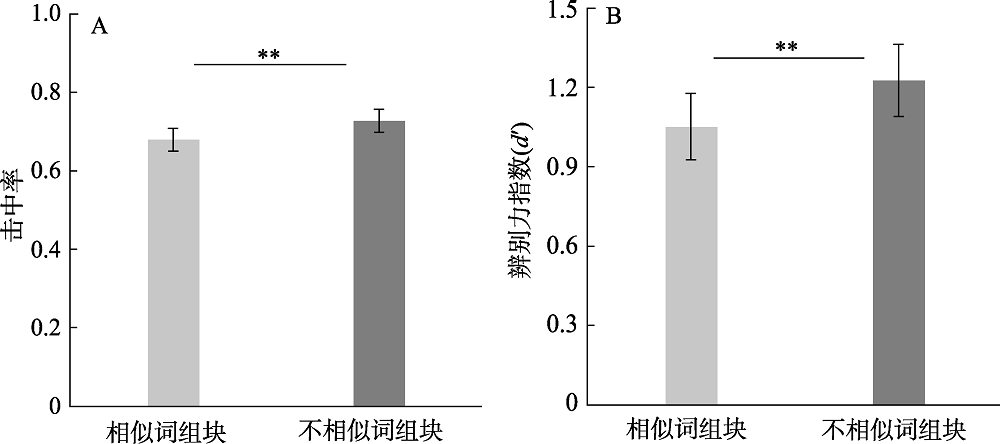
图3实验1B中两种组块条件在学习一周后的击中率(A)和辨别力指数(B)。
 图3实验1B中两种组块条件在学习一周后的击中率(A)和辨别力指数(B)。
图3实验1B中两种组块条件在学习一周后的击中率(A)和辨别力指数(B)。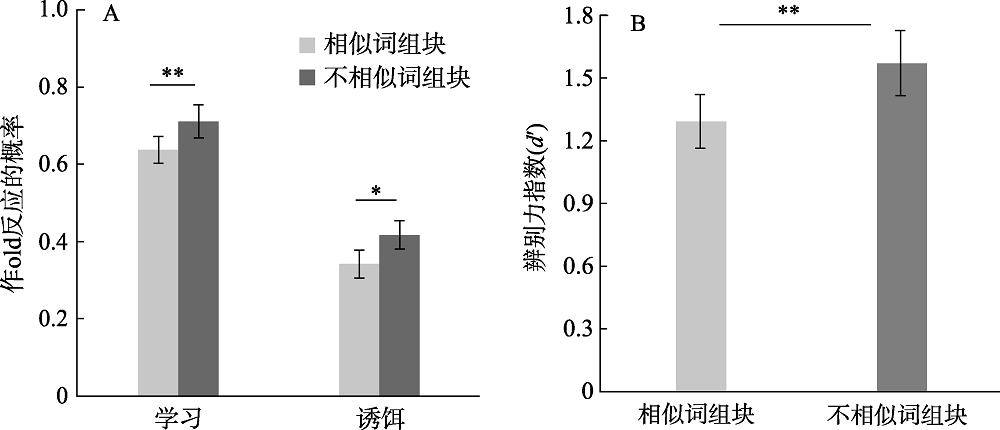
图4实验2两种学习条件的击中率、错误记忆率(A)和辨别力指数(B)。
 图4实验2两种学习条件的击中率、错误记忆率(A)和辨别力指数(B)。
图4实验2两种学习条件的击中率、错误记忆率(A)和辨别力指数(B)。
图5实验3两种学习条件的击中率(A)和辨别力指数(B)。
 图5实验3两种学习条件的击中率(A)和辨别力指数(B)。
图5实验3两种学习条件的击中率(A)和辨别力指数(B)。参考文献 33
| [1] | Avons , S.E . ( 1999). Effects of visual similarity on serial report and item recognition. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 52( 1), 217-240. doi: 10.1080/713755809URL |
| [2] | Balota D. A., Yap M. J., Hutchison K. A., Cortese M. J., Kessler B., Loftis B., … Treiman R . ( 2007). The English lexicon project. Behavior Research Methods, 39( 3), 445-459. doi: 10.3758/BF03193014URL |
| [3] | Chen ,J.Y . ( 2007). Formulas and the definition of “word” in the Chinese language. Foreign Language Research,( 5), 1-7. |
| [ 陈嘉映 . ( 2007). 约定用法和“词”的定义. 外语学刊, ( 5), 1-7.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0100.2007.05.001URL | |
| [4] | Cohen J. ( 1988). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. 2nd ed. L. Erlbaum Associates. |
| [5] | DeAnda S., Poulin-Dubois D., Zesiger P., &Friend M . ( 2016). Lexical processing and organization in bilingual first language acquisition: Guiding future research. Psychological Bulletin, 142( 6), 655-667. doi: 10.1037/bul0000042 doi: 10.1037/bul0000042URLpmid: 26866430 |
| [6] | Gallo ,D.A . ( 2010). False memories and fantastic beliefs: 15 years of the DRM illusion. Memory & Cognition, 38( 7), 833-848. doi: 10.3758/MC.38.7.833 doi: 10.3758/MC.38.7.833URLpmid: 20921097 |
| [7] | Gilbert A. C., Boucher V. J., &Jemel B . ( 2014). Perceptual chunking and its effect on memory in speech processing: ERP and behavioral evidence. Frontiers in Psychology, 5, 220. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2014.00220 doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2014.00220URLpmid: 24678304 |
| [8] | Glezer L. S., Jiang X., &Riesenhuber M . ( 2009). Evidence for highly selective neuronal tuning to whole words in the "visual word form area". Neuron, 62( 2), 199-204. doi: 10. 1016/j.neuron.2009.03.017 doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.03.017URLpmid: 2706007 |
| [9] | Glezer L. S., Kim J., Rule J., Jiang X., &Riesenhuber M . ( 2015). Adding words to the brain's visual dictionary: Novel word learning selectively sharpens orthographic representations in the VWFA. Journal of Neuroscience, 35( 12), 4965-4972. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4031-14.2015 doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4031-14.2015URLpmid: 25810526 |
| [10] | Li M. ( 2015). A new exploration on the definition of modern Chinese word. Overseas English, 208-210. |
| [ 李敏 . ( 2015). 关于现代汉语词的定义新探. 海外英语, 208-210.] | |
| [11] | Li , X. &Liu ,S.Y . ( 2012). The effects of phonological similarity and visual similarity in immediate serial recall of Chinese characters. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 44 ( 12), 1571-1582. doi: 10.3724/sp.j.1041.2012.01571 |
| [ 李轩, 刘思耘 . ( 2012). 汉语短时序列回忆中的语音相似性和视觉相似性效应. 心理学报, 44 ( 12), 1571-1582.] doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2012.01571URL | |
| [12] | Lin Y. C., Chen H. Y., Lai Y. C., &Wu D. H . ( 2015). Phonological similarity and orthographic similarity affect probed serial recall of Chinese characters. Memory & Cognition, 43( 3), 538-554. doi: 10.3758/s13421-014-0495-x doi: 10.3758/s13421-014-0495-xURLpmid: 25537954 |
| [13] | Logie R. H., Della Sala S., Wynn V., &Baddeley A. D . ( 2000). Visual similarity effects in immediate verbal serial recall. The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 53( 3), 626-646. doi: 10.1080/713755916URLpmid: 10994221 |
| [14] | Logie R. H., Saito S., Morita A., Varma S., &Norris D . ( 2016). Recalling visual serial order for verbal sequences. Memory & Cognition, 44( 4), 590-607. doi: 10.3758/s13421- 015-0580-9 doi: 10.3758/s13421-015-0580-9URLpmid: 4835526 |
| [15] | Mei L., Qu J., &Li H. L . ( 2017). The cognitive neural mechanism of second language learning. Journal of South China Normal University (Society Science Edition),( 6), 63-73. |
| [ 梅磊磊, 屈婧, 李会玲 . ( 2017). 第二语言学习的认知神经机制. 华南师范大学学报(社会科学版), ( 6), 63-73.] | |
| [16] | Mei L., Xue G., Chen C. S., Xue F., Zhang M. X., &Dong Q . ( 2010). The "visual word form area" is involved in successful memory encoding of both words and faces. NeuroImage, 52( 1), 371-378. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010. 03.067 doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.03.067URLpmid: 2883627 |
| [17] | Nairne ,J.S . ( 1990). A feature model of immediate memory. Memory & Cognition, 18( 3), 251-269. doi: 10.3758/BF03213879URLpmid: 2192233 |
| [18] | Piguet O., Connally E., Krendl A. C., Huot J. R., &Corkin S . ( 2008). False memory in aging: Effects of emotional valence on word recognition accuracy. Psychology and Aging, 23( 2), 307-314. doi: 10.1037/0882-7974.23.2.307 doi: 10.1037/0882-7974.23.2.307URLpmid: 18573005 |
| [19] | Poirer M., Saint-Aubin J., Musselwhite K., Mohanadas T., &Mahammed G . ( 2007). Visual similarity effects on short-term memory for order: The case of verbally labeled pictorial stimuli. Memory & Cognition, 35( 4), 711-723. doi: 10.3758/BF03193309URLpmid: 17848029 |
| [20] | Qu ,Z. &Ding ,Y.L . ( 2010). The effect of Chinese phonological association on false memory. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 42 ( 2), 193-199. |
| [ 曲折, 丁玉珑 . ( 2010). 汉字语音关联对错误记忆的影响. 心理学报, 42 ( 2), 193-199.] doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2010.00193URL | |
| [21] | Qu Z., Liu Y., &Bi Y. H . ( 2010). The effect of Chinese orthographic association on false memory. Chinese Journal of Applied Psychology, 16 ( 2), 146-153. |
| [ 曲折, 刘优, 毕耀华 . ( 2010). 汉字字形关联对错误记忆的影响. 应用心理学, 16 ( 2), 146-153.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6020.2010.02.007URL | |
| [22] | Reyna ,V. F. &Brainerd ,C.J . ( 1995). Fuzzy-trace theory: An interim synthesis. Learning and Individual Differences, 7( 1), 1-75. doi: 10.1016/1041-6080(95)90031-4URL |
| [23] | Roediger ,H. L. &Mcdermott ,K.B . ( 1995). Creating false memories: Remembering words not presented in lists. Journal of Experimental Psychology Learning Memory & Cognition, 21( 4), 803-814. doi: 10.1037/0278-7393.21.4.803URL |
| [24] | Rugg ,M. D. &Yonelinas ,A.P . ( 2003). Human recognition memory: A cognitive neuroscience perspective. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 7( 7), 313-319. doi: 10.1016/s1364- 6613(03)00131-1 doi: 10.1016/S1364-6613(03)00131-1URLpmid: 12860190 |
| [25] | Saito S., Logie R. H., Morita A., &Law A . ( 2008). Visual and phonological similarity effects in verbal immediate serial recall: A test with kanji materials. Journal of Memory and Language, 59( 1), 1-17. doi: 10.1016/j.jml.2008.01.004 doi: 10.1016/j.jml.2008.01.004URL |
| [26] | Sanchez ,C. A. &Naylor ,J.S . ( 2018). Disfluent presentations lead to the creation of more false memories. PLoS One, 13( 1), e0191735. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0191735 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0191735URLpmid: 29370255 |
| [27] | Smith C. N., Wixted J. T., &Squire L. R . ( 2011). The hippocampus supports both recollection and familiarity when memories are strong. The Journal of Neuroscience, 31( 44), 15693-15702. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3438-11.2011 doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3438-11.2011URLpmid: 3220416 |
| [28] | Smyth M. M., Hay D. C., Hitch G. J., &Horton N. J . ( 2005). Serial position memory in the visual-spatial domain: Reconstructing sequences of unfamiliar faces. The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 58( 5), 909-930. doi: 10.1080/02724980443000412URLpmid: 16194941 |
| [29] | Squire L. R., Wixted J. T., &Clark R. E . ( 2007). Recognition memory and the medial temporal lobe: A new perspective. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 8( 11), 872-883. doi: 10.1038/nrn2154 doi: 10.1038/nrn2154URLpmid: 2323975 |
| [30] | Wixted ,J. T. &Mickes ,L. ( 2010). A continuous dual-process model of remember/know judgments. Psychological Review, 117( 4), 1025-1054. doi: 10.1037/a0020874 doi: 10.1037/a0020874URLpmid: 20836613 |
| [31] | Xiao H. R., Huang Y. F., Gong X. M., &Wang D. H . ( 2015). Age alters the effects of emotional valence on false memory: Using the simplified conjoint recognition paradigm. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 47 ( 1), 19-28. doi: 10.3724/SP. J.1041.2015.00019 |
| [ 肖红蕊, 黄一帆, 龚先旻, 王大华 . ( 2015). 简化的联合再认范式中情绪对错误记忆影响的年龄差异. 心理学报, 47 ( 1), 19-28.] doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2015.00019URL | |
| [32] | Xue H. L., Mei L., Xue G., Chen C., &Dong Q . ( 2017). The impact of learning method on unfamiliar visual form learning. Journal of Psychological Science, 40 ( 5), 1111-1116. |
| [ 薛红莉, 梅磊磊, 薛贵, 陈传升, 董奇 . ( 2017). 学习方法对陌生语言字形学习的影响. 心理科学, 40 ( 5), 1111-1116.] | |
| [33] | Ye Z. F., Zhu B., Zhuang L. P., Lu , Z. L, Chen , C. S., &Xue G . ( 2016). Neural global pattern similarity underlies true and false memories. The Journal of Neuroscience, 36( 25), 6792-6802. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0425-16.2016 doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0425-16.2016URLpmid: 27335409 |
相关文章 15
| [1] | 张瑞, 王振华, 王小娟, 杨剑峰. 汉字识别中亚词汇语音和语义信息在N170上的神经适应[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(8): 807-820. |
| [2] | 李杰, 杨悦, 赵婧. 汉语发展性阅读障碍儿童视觉同时性加工技能子成分的发展及其与阅读的关系[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(8): 821-836. |
| [3] | 陈石, 梁正, 李香兰, 陈嫣然, 赵庆柏, 于全磊, 李松清, 周治金, 刘丽中. 新颖语义联结在顿悟促进记忆效果中的作用[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(8): 837-846. |
| [4] | 程瑞, 卢克龙, 郝宁. 愤怒情绪对恶意创造力的影响及调节策略[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(8): 847-860. |
| [5] | 熊承清, 许佳颖, 马丹阳, 刘永芳. 囚徒困境博弈中对手面部表情对合作行为的影响及其作用机制[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(8): 919-932. |
| [6] | 杨群, 张积家, 范丛慧. 维吾尔族与汉族的大学生在汉语歧义词消解中的语境促进效应及反应抑制效应[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(7): 746-757. |
| [7] | 吴三美, 田良苏, 陈家侨, 陈广耀, 王敬欣. 中文阅读中无关言语效应的认知机制探究:眼动证据[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(7): 729-745. |
| [8] | 田欣然, 侯文霞, 欧玉晓, 易冰, 陈文锋, 尚俊辰. 基于合成平均刺激的平均表征机制——来自平均面孔吸引力的证据[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(7): 714-728. |
| [9] | 车晓玮, 徐慧云, 王凯旋, 张倩, 李寿欣. 工作记忆表征精度加工需求对注意引导的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(7): 694-713. |
| [10] | 张明, 桑汉斌, 鲁柯, 王爱君. 试次历史对跨通道非空间返回抑制的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(7): 681-693. |
| [11] | 袁加锦, 张祎程, 陈圣栋, 罗利, 茹怡珊. 中国情绪调节词语库的初步编制与试用[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(5): 445-455. |
| [12] | 宋锡妍, 程亚华, 谢周秀甜, 龚楠焰, 刘雷. 愤怒情绪对延迟折扣的影响:确定感和控制感的中介作用[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(5): 456-468. |
| [13] | 孟迎芳, 董月晴, 陈荃. 概念内隐记忆中的注意促进效应[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(5): 469-480. |
| [14] | 张环, 王欣, 刘一贝, 曹贤才, 吴捷. 成员关系对协作提取成绩的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(5): 481-493. |
| [15] | 丁锦红, 汪亚珉, 姜扬. 注意促进运动知觉判断的时间进程[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(4): 337-348. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlxb/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=4401
