 )
) 中国人民大学心理学系, 北京 100872
收稿日期:2019-05-24出版日期:2019-12-15发布日期:2019-10-21通讯作者:张清芳E-mail:qingfang.zhang@ruc.edu.cn基金资助:* 北京市社科基金重点项目(16YYA006);中国人民大学科学研究基金项目(中央高校基本科研业务费专项)项目(18XNLG28);国家自然科学基金面上项目资助(31471074);中国人民大学中央高校建设世界一流大学(学科)和特色发展引导专项资金支持Cognition or metacognition: The psychological mechanism of tip-of-the-tongue in spoken production
OUYANG Mingkun, CAI Xiao, ZHANG Qingfang( )
) Department of Psychology, Renmin University of China, Beijing 100872, China
Received:2019-05-24Online:2019-12-15Published:2019-10-21Contact:ZHANG Qingfang E-mail:qingfang.zhang@ruc.edu.cn摘要/Abstract
摘要: 舌尖效应(Tip-of-the-tongue, TOT)在口语产生领域存在认知和元认知两种研究视角。认知视角主要针对口语产生的词汇通达过程, 认为信息激活或提取不充分是TOT发生的主要原因。元认知视角则主要关注口语产生的元认知过程, 认为个体对目标词提取状态的监测引发了TOT。TOT的元认知过程不仅可以监测目标词的提取状态及词汇通达过程中相关信息的提取, 而且可以控制词汇通达过程, 使目标词在TOT发生后成功地提取出来。两种研究视角在TOT发生的认知机制、影响因素以及生理基础方面均存在分离。未来研究应该探讨TOT监测和控制口语产生的作用机制和生理基础, 关注汉语背景下TOT发生规律及其对口语产生年老化的积极影响。
图/表 3

图1TOT的传递缺陷假说
 图1TOT的传递缺陷假说
图1TOT的传递缺陷假说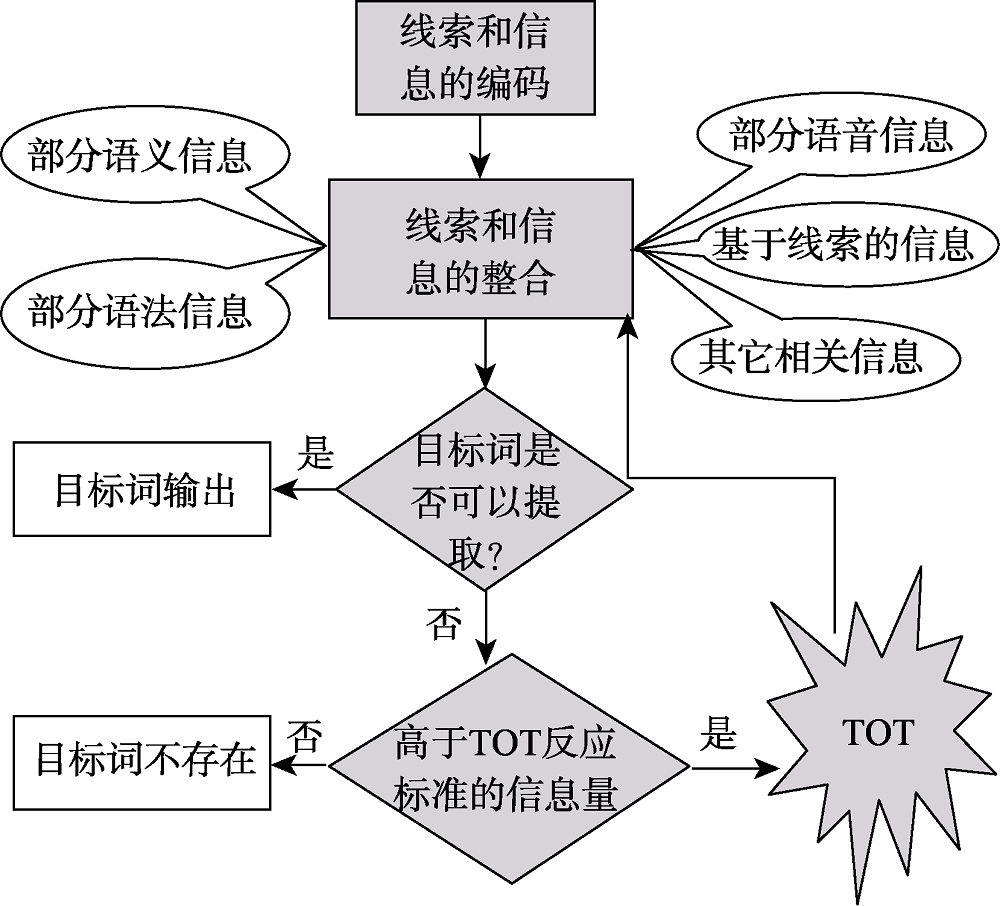
图2TOT的启发式元认知模型(引自Schwartz & Metcalfe, 2011)
 图2TOT的启发式元认知模型(引自Schwartz & Metcalfe, 2011)
图2TOT的启发式元认知模型(引自Schwartz & Metcalfe, 2011)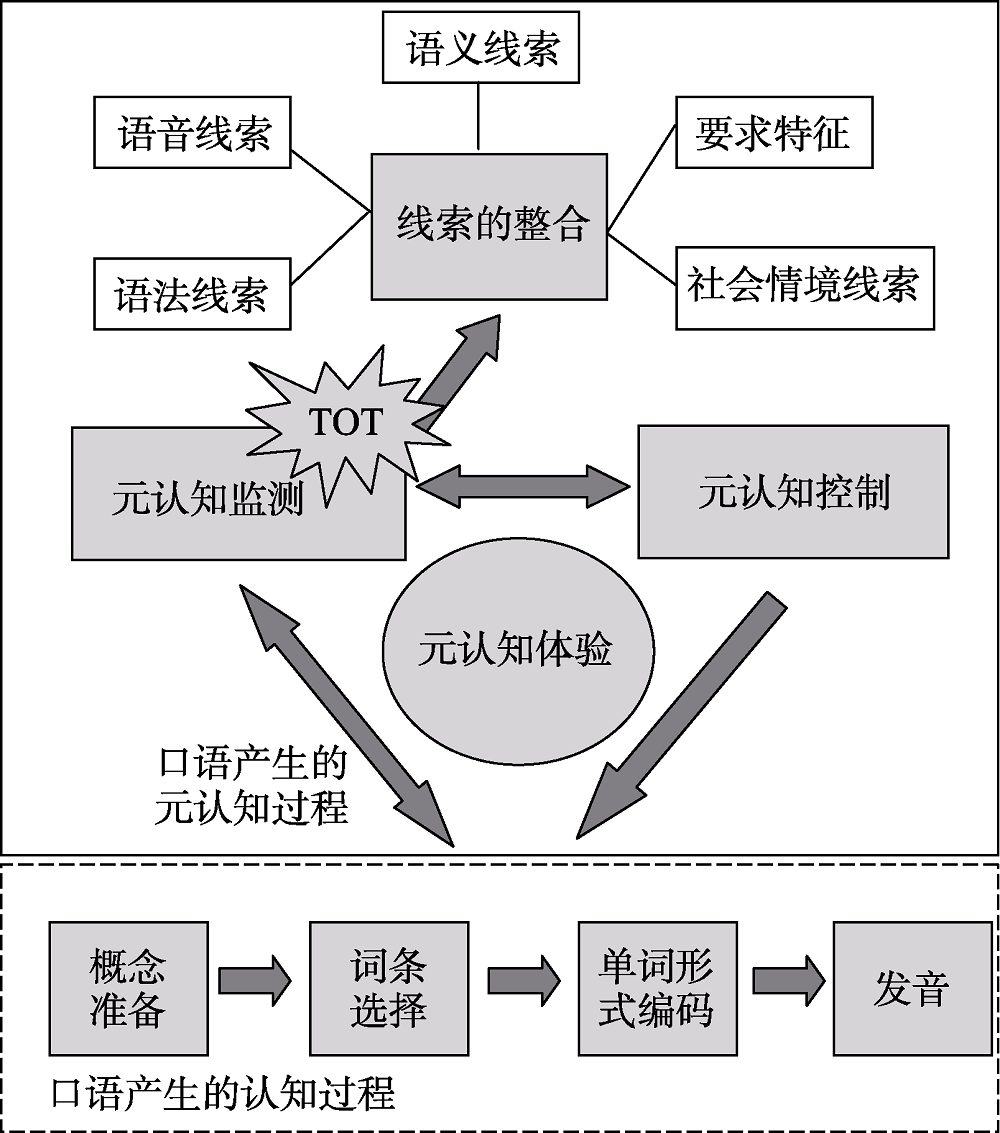
图3认知和元认知视角下TOT发生机制的联系
 图3认知和元认知视角下TOT发生机制的联系
图3认知和元认知视角下TOT发生机制的联系参考文献 92
| [1] | 陈芳艳, 李锋盈, 李伟健 . ( 2016). 知觉线索对元记忆监控的影响. 心理科学进展, 24( 4), 494-500. |
| [2] | 何文广 . ( 2017). 语言认知老化机制及其神经基础. 心理科学进展, 25( 9), 1479-1491. |
| [3] | 黄立鹤 . ( 2015). 近十年老年人语言衰老现象研究: 回顾与前瞻. 北京第二外国语学院学报, 37( 10), 17-24. |
| [4] | 彭华茂, 毛晓飞 . ( 2018). 抑制对老年人舌尖现象的影响. 心理学报, 50( 10), 1142-1150. |
| [5] | 孙彦, 李纾, 殷晓莉 . ( 2007). 决策与推理的双系统——启发式系统和分析系统. 心理科学进展, 15( 5), 721-726. |
| [6] | 汪玲, 郭德俊 . ( 2000). 元认知的本质与要素. 心理学报, 32( 4), 458-463. |
| [7] | 杨群, 张清芳 . ( 2015). 口语产生中的认知年老化及其神经机制. 心理科学进展, 23( 12), 2072-2084. |
| [8] | 赵瑞瑛, 娄昊, 欧阳明昆, 张清芳 . ( 2019). 自然情境下舌尖效应的认知年老化——日记研究. 心理学报, 51( 5), 598-611. |
| [9] | Abrams, L., & Davis, D. K . ( 2017). Competitors or teammates: How proper names influence each other. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 26( 1), 87-93. |
| [10] | Abrams, L., & Rodriguez, E. (2005). Syntactic class influences phonological priming of tip-of-the-tongue resolution. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 12( 6), 1018-1023. |
| [11] | Abrams, L., Trunk, D. L., & Merrill, L. A . ( 2007). Why a superman cannot help a tsunami: Activation of grammatical class influences resolution of young and older adults’ tip- of-the-tongue states. Psychology and Aging, 22( 4), 835-845. |
| [12] | Allan, K., Wolf, H. A., Rosenthal, C. R., & Rugg, M. D . ( 2001). The effect of retrieval cues on post-retrieval monitoring in episodic memory: An electrophysiological study. Cognitive Brain Research, 12( 2), 289-299. |
| [13] | Bjork, R. A., Dunlosky, J., & Kornell, N . ( 2013). Self-regulated learning: Beliefs, techniques, and illusions. Annual Review of Psychology, 64, 417-444. |
| [14] | Borodkin, K., Maliniak, O., & Faust, M . ( 2017). Exploring the nature of phonological weakness in low-proficiency second language learners. Learning and Individual Differences, 57, 133-140. |
| [15] | Brown, A. S. ( 2012). The tip of the tongue state. Hove, United Kingdom: Psychology Press. |
| [16] | Brown, R., & McNeill, D. (1966). The “tip of the tongue” phenomenon. Journal of Verbal Learning and Behavior, 5( 4), 325-337. |
| [17] | Buján, A., Galdo-álvarez, S., Lindín, M., & Díaz, F . ( 2012). An event-related potentials study of face naming: Evidence of phonological retrieval deficit in the tip-of- the-tongue state. Psychophysiology, 49( 7), 980-990. |
| [18] | Burke, D. M. & Graham, E. R. ,( 2012). The neural basis for aging effects on language. In ). E. Faust (Ed. ), The handbook of the neuropsychology of language (pp. 778-800). Oxford, UK: Blackwell Publishing Ltd. |
| [19] | Burke, D. M., MacKay, D. G., Worthley, J. S., & Wade, E . ( 1991). On the tip of the tongue: What causes word finding failures in young and older adults? Journal of Memory and Language, 30( 5), 542-579. |
| [20] | Calabi, C. (2016). “Ancona?” Aha! that’s her name! Tip-of-the- tongue experiences. Analysis, 76( 4), 409-418. |
| [21] | Cleary, A. M., & Claxton, A. B . ( 2015). The tip-of-the-tongue heuristic: How tip-of-the-tongue states confer perceptibility on inaccessible words. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 41( 5), 1533-1539. |
| [22] | Cleary, A. M., Staley, S. R., & Klein, K. R. ( 2014). The effect of tip-of-the-tongue states on other cognitive judgments. In B. L. Schwartz, & A. S. Brown (Eds.), Tip-of-the-tongue states and related phenomena (pp. 75-94). New York, NY: Cambridge University Press. |
| [23] | D’Angelo, M. C., & Humphreys, K. R . ( 2012). Emotional cues do not increase the likelihood of tip-of-the-tongue states. Memory & Cognition, 40( 8), 1331-1338. |
| [24] | Dell, G. S . ( 1986). A spreading-activation theory of retrieval in sentence production. Psychological Review, 93( 3), 283-321. |
| [25] | Díaz, F., Lindín, M., Galdo-Alvarez, S., Facal, D., & Juncos-Rabadán, O . ( 2007). An event-related potentials study of face identification and naming: The tip-of-the tongue state. Psychophysiology, 44( 1), 50-68. |
| [26] | Facal, D., Juncos-Rabadán, O., Rodríguez, M. S., & Pereiro, A. X . ( 2012). Tip-of-the-tongue in aging: Influence of vocabulary, working memory and processing speed. Aging Clinical and Experimental Research, 24( 6), 647-656. |
| [27] | Farrell, M. T . ( 2012). What's in a name? Predictors of proper name retrieval deficits in older age (Unpublished doctorial dissertation). University of Florida. |
| [28] | Farrell, M. T., & Abrams, L. (2011). Tip-of-the-tongue states reveal age differences in the syllable frequency effect. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 37( 1), 277-285. |
| [29] | Fieder, N., Nickels, L., & Biedermann, B . ( 2014). Representation and processing of mass and count nouns: A review. Frontiers in Psychology, 5, 589. |
| [30] | Funnel, M., Metcalfe, J., & Tsapkini, K . ( 1996). In the mind but not on the tongue: Feeling of knowing in an anomic patient. In L. M. Reder (Ed.), Implicit memory and metacognition(pp. 171-194). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum. |
| [31] | Ganushchak, L. Y., & Schiller, N. O . ( 2006). Effects of time pressure on verbal self-monitoring: An ERP study. Brain Research, 1125( 1), 104-115. |
| [32] | Geva, S., Jones, P. S., Crinion, J. T., Price, C. J., Baron, J. C., & Warburton, E. A . ( 2012). The effect of aging on the neural correlates of phonological word retrieval. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 24( 11), 2135-2146. |
| [33] | Gianico-Relyea, J. L., & Altarriba, J. (2012). Word concreteness as a moderator of the tip-of-the-tongue effect. The Psychological Record, 62( 4), 763-776. |
| [34] | Gollan, T. H., & Brown, A. S . ( 2006). From tip-of-the-tongue (TOT) data to theoretical implications in two steps: When more TOTs means better retrieval. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 135( 3), 462-483. |
| [35] | Gollan, T. H., Ferreira, V. S., Cera, C., & Flett, S . ( 2014). Translation-priming effects on tip-of-the-tongue states. Language, Cognition and Neuroscience, 29( 3), 274-288. |
| [36] | Gordon, J. K., & Kurczek, J. C . ( 2014). The ageing neighbourhood: Phonological density in naming. Language, Cognition and Neuroscience, 29( 3), 326-344. |
| [37] | Hayashi, T., Ko, J. H., Strafella, A. P., & Dagher, A . ( 2013). Dorsolateral prefrontal and orbitofrontal cortex interactions during self-control of cigarette craving. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 110( 11), 4422-4427. |
| [38] | Heine, M. K., Ober, B. A., & Shenaut, G. K . ( 1999). Naturally occurring and experimentally induced tip-of-the-tongue experiences in three adult age groups. Psychology and Aging, 14( 3), 445-457. |
| [39] | Huijbers, W., Papp, K. V., LaPoint, M., Wigman, S. E., Dagley, A., Hedden, T., .. Sperling, R. A . ( 2016). Age-related increases in tip-of-the-tongue are distinct from decreases in remembering names: A functional MRI study. Cerebral Cortex, 27( 9), 4339-4349. |
| [40] | Indefrey, P., & Levelt, W. J.M . ( 2004). The spatial and temporal signatures of word production components. Cognition, 92( 1-2), 101-144. |
| [41] | James, L. E., Schmank, C. J., & Castro, N . ( 2013, August). Word retrieval is harmed by stressful conditions. Poster presented at the 121st annual convention of the American Psychological Association, Honolulu, HI. |
| [42] | James, L. E., Schmank, C. J., Castro, N., & Buchanan, T. W . ( 2018). Tip of the tongue states increase under evaluative observation. Journal of Psycholinguistic Research, 47( 1), 169-178. |
| [43] | Jersakova, R., Souchay, C., & Allen, R. J . ( 2015). Negative affect does not impact semantic retrieval failure monitoring. Canadian Journal of Experimental Psychology/Revue canadienne de psychologie expérimentale, 69( 4), 314-326. |
| [44] | Jones, G. V . ( 1989). Back to woodworth: Role of interlopers in the tip of the tongue phenomenon. Memory & Cognition, 17( 1), 69-76. |
| [45] | Juncos-Rabadán, O., Facal, D., Lojo-Seoane, C., & Pereiro, A. X . ( 2013). Tip-of-the-tongue for proper names in non-amnestic mild cognitive impairment. Journal of Neurolinguistics, 26( 3), 409-420. |
| [46] | Kavanaugh, S. P . ( 2015). Effects of phonologically related words on tip-of-the-tongue (TOT)(Unpublished bachelor’s thesis). University of Montana, Missoula. |
| [47] | Kikyo, H., Ohki, K., & Sekihara, K . ( 2001). Temporal characterization of memory retrieval processes: An fMRI study of the ‘tip of the tongue’ phenomenon. European Journal of Neuroscience, 14( 5), 887-892. |
| [48] | Kljajevic, V., & Erramuzpe, A. (2018). Proper name retrieval and structural integrity of cerebral cortex in midlife: A cross-sectional study. Brain and Cognition, 120, 26-33. |
| [49] | Koriat, A., & Lieblich, I. (1977). A study of memory pointers. Acta Psychologica, 41( 2-3), 151-164. |
| [50] | Kostic, B., Booth, S. E., & Cleary, A. M . ( 2015). The role of analogy in reports of presque vu: Does reporting the presque vu state signal the near retrieval of a source analogy? Journal of Cognitive Psychology, 27( 6), 739-754. |
| [51] | Kuipers, S. C . ( 2013). Effect of incubation on the resolution of tip-of-the-tongue states and the relation with attention and concentration (Unpublished bachelor’s thesis). University of Twente,Enschede. |
| [52] | Levelt, W. J. M., Roelofs, A., & Meyer, A. S . ( 1999). A theory of lexical access in speech production. Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 22( 1), 1-38. |
| [53] | Lindín, M., & Díaz, F. (2010). Event-related potentials in face naming and tip-of-the-tongue state: Further results. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 77( 1), 53-58. |
| [54] | Lindín, M., Díaz, F., Capilla, A., Ortiz, T., & Maestú, F . ( 2010). On the characterization of the spatiotemporal profiles of brain activity associated with face naming and the tip-of-the-tongue state: A magnetoencephalographic (MEG) study. Neuropsychologia, 48( 6), 1757-1766. |
| [55] | MacDonald, A.W., Cohen, J. D., Stenger, V. A., & Carter, C. S . ( 2000). Dissociating the role of the dorsolateral prefrontal and anterior cingulate cortex in cognitive control. Science, 288( 5472), 1835-1838. |
| [56] | Maril, A., Simons, J. S., Weaver, J. J., & Schacter, D. L . ( 2005). Graded recall success: An event-related fMRI comparison of tip of the tongue and feeling of knowing. Neuroimage, 24( 4), 1130-1138. |
| [57] | Maril, A., Wagner, A. D., & Schacter, D. L . ( 2001). On the tip of the tongue: An event-related fMRI study of semantic retrieval failure and cognitive conflict. Neuron, 31( 4), 653-660. |
| [58] | Masselink, J. (2012). The effect of incubation on the resolution of tip-of-the-tongue states and the relation between resolution, incidence and cognitive ability (Unpublished bachelor’s thesis). , University of Twente Enschede. |
| [59] | Metcalfe, J., Schwartz, B. L., & Joaquim, S. G . ( 1993). The cue familiarity heuristic in metacognition. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 19( 4), 851-861. |
| [60] | Navarrete, E., Pastore, M., Valentini, R., & Peressotti, F . ( 2015). First learned words are not forgotten: Age-of-acquisition effects in the tip-of-the-tongue experience. Memory & Cognition, 43( 7), 1085-1103. |
| [61] | Oberle, S., & James, L. E . ( 2013). Semantically- and phonologically-related primes improve name retrieval in young and older adults. Language and Cognitive Processes, 28( 9), 1378-1393 |
| [62] | Oh-Lee, J. D., Szymkowicz, S. M., Smith, S. L., & Otani, H . ( 2012). Metacognitive performance, the tip-of-tongue experience, is not disrupted in parkinsonian patients. Parkinson’s Disease, 1-12. |
| [63] | O’Seaghdha, P. G., Chen, J.-Y., & Chen, T.-M . ( 2010). Proximate units in word production: Phonological encoding begins with syllables in Mandarin Chinese but with segments in English. Cognition, 115( 2), 282-302. |
| [64] | Payne, B. R . ( 2014). The effects of verbal working memory training on language comprehension in older adulthood (Unpublished doctorial dissertation). Urbana, Illinois: University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. |
| [65] | Pureza, R., Soares, A. P., & Comesaña, M . ( 2013). Syllabic pseudohomophone priming in tip-of-the-tongue states resolution: The role of syllabic position and number of syllables. The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 66( 5), 910-926. |
| [66] | Pureza, R., Soares, A. P., & Comesaña, M . ( 2016). Cognate status, syllable position and word length on bilingual tip-of-the-tongue states induction and resolution. Bilingualism: Language and Cognition, 19( 3), 533-549. |
| [67] | Rodd, J. M., Vitello, S., Woollams, A. M., & Adank, P . ( 2015). Localising semantic and syntactic processing in spoken and written language comprehension: An activation likelihood estimation meta-analysis. Brain and Language, 141( 1), 89-102. |
| [68] | Sadat, J., Martin, C. D., Costa, A., & Alario, F.-X . ( 2014). Reconciling phonological neighborhood effects in speech production through single trial analysis. Cognitive Psychology, 68, 33-58. |
| [69] | Salthouse, T. A., & Mandell, A. R . ( 2013). Do age-related increases in tip-of-the-tongue experiences signify episodic memory impairments? Psychological Science, 24( 12), 2489-2497. |
| [70] | Schwartz, B. L . ( 2001). The relation of tip-of-the-tongue states and retrieval time. Memory & Cognition, 29( 1), 117-126. |
| [71] | Schwartz, B. L . ( 2002). Tip-of-the-tongue states: Phenomenology, mechanism, and lexical retrieval. Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum. |
| [72] | Schwartz, B. L . ( 2008). Working memory load differentially affects tip-of-the-tongue states and feeling-of-knowing judgment. Memory & Cognition, 36( 1), 9-19. |
| [73] | Schwartz, B. L . ( 2010). The effects of emotion on tip-of- the-tongue states. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 17( 1), 82-87. |
| [74] | Schwartz, B. L . ( 2011). The effect of being in a tip-of-the- tongue state on subsequent items. Memory & Cognition, 39( 2), 245-250. |
| [75] | Schwartz, B. L & Brown, A. S. ,(Eds.).( 2014) . Tip-of-the- tongue states and related phenomena. Cambridge, United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press. |
| [76] | Schwartz, B. L. & Cleary, A. M. ( 2016) . Tip-of-the-tongue states, déjà vu and other metacognitive oddities. In J. Dunlosky & S. Tauber (Eds.), Oxford handbook of metamemory (pp. 95-108). New York: Oxford University Press. |
| [77] | Schwartz, B. L., & Metcalfe, J. (2011). Tip-of-the-tongue (TOT) states: Retrieval, behavior, and experience. Memory & Cognition, 39( 5), 737-749. |
| [78] | Schwartz, B. L., & Metcalfe, J. ( 2014). Tip-of-the-tongue (TOT) states: Mechanisms and metacognitive control. In B. L. Schwartz, & A. S. Brown (Eds.), Tip-of-the-tongue states and related phenomena (pp. 15-31). New York, NY: Cambridge University Press. |
| [79] | Schwartz, B. L., &Smith, S. M . ( 1997). The retrieval of related information influences tip-of-the-tongue states. Journal of Memory and Language, 36( 1), 68-86. |
| [80] | Schwartz, B. L., Travis, D. M., Castro, A. M., & Smith, S. M . ( 2000). The phenomenology of real and illusory tip-of-the-tongue states. Memory & Cognition, 28( 1), 18-27. |
| [81] | Shafto, M. A., Stamatakis, E. A., Tam, P. P., & Tyler, L. K . ( 2010). Word retrieval failures in old age: The relationship between structure and function. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 22( 7), 1530-1540. |
| [82] | Shimamura, A. P. ( 2008). A neurocognitive approach to metacognitive monitoring and control. In J. Dunlosky & R. A. Bjork (Eds.), Handbook of metamemory and memory (pp. 373-390). New York, NY, US: Psychology Press. |
| [83] | Souchay, C., & Smith, S. J . ( 2013). Subjective states associated with retrieval failures in Parkinson’s disease. Consciousness and Cognition, 22( 3), 795-805. |
| [84] | Stamatakis, E. A., Shafto, M. A., Williams, G., Tam, P., & Tyler, L. K . ( 2011). White matter changes and word finding failures with increasing age. PloS One, 6( 1), e14496. |
| [85] | Suárez-Coalla, P., Alonso, A. C., & González-Nosti, M . ( 2014). Phonological recovery in Spanish developmental dyslexics through the tip-of-the-tongue paradigm. Psicothema, 25( 4), 476-481. |
| [86] | Vigliocco, G., Vinson, D. P., Martin, R. C., & Garrett, M. F . ( 1999). Is “count” and “mass” information available when the noun is not? An investigation of tip of the tongue states and anomia. Journal of Memory and Language, 40( 4), 534-558. |
| [87] | Warriner, A. B., & Humphreys, K. R . ( 2008). Learning to fail: Reoccurring tip-of-the-tongue states. The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 61( 4), 535-542. |
| [88] | White, K. K., Abrams, L., & Frame, E. A . ( 2013). Semantic category moderates phonological priming of proper name retrieval during tip-of-the-tongue states. Language and Cognitive Processes, 28( 4), 561-576. |
| [89] | Wright, H. H. ( 2016)). Cognition, anguage and aging. Amsterdam and Philadelphia: John Benjamins Publishing Company. |
| [90] | Zhang, Q., Zhu, X., & Damian, M. F . ( 2018). Phonological activation of category coordinates in spoken word production: Evidence for cascaded processing in English but not in Mandarin. Applied Psycholinguistics, 39( 5), 1-26. |
| [91] | Zhu, L., Jenkins, A. C., Set, E., Scabini, D., Knight, R. T., Chiu, P. H., .. Hsu, M . ( 2014). Damage to dorsolateral prefrontal cortex affects tradeoffs between honesty and self-interest. Nature Neuroscience, 17( 10), 1319-1321. |
| [92] | Zhu, X., Damian, M. F., & Zhang, Q . ( 2015). Seriality of semantic and phonological processes during overt speech in Mandarin as revealed by event-related brain potentials. Brain and Language, 144, 16-25. |
相关文章 2
| [1] | Jie Wu , Qiufang Fu . Does Prototype Category Learning Include Declarative Memory?[J]. 心理科学进展, 2017, 25(suppl.): 82-82. |
| [2] | 杨沈龙;郭永玉;李静. 低社会阶层者是否更相信系统公正[J]. 心理科学进展, 2013, 21(12): 2245-2255. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlkxjz/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=4887
