 )
) 天津师范大学管理学院, 天津 300387
收稿日期:2018-09-20出版日期:2019-10-31发布日期:2019-09-23通讯作者:杜伟强E-mail:weiqiangdu@163.com基金资助:* 国家自然科学基金项目(71502128, 71472136);天津市哲学社会科学规划项目(TJGL15-043)Disgust and consumer behavior
DU Weiqiang( )
) Management School, Tianjin Normal University, Tianjin 300387, China
Received:2018-09-20Online:2019-10-31Published:2019-09-23Contact:DU Weiqiang E-mail:weiqiangdu@163.com摘要/Abstract
摘要: 厌恶与其他消极情绪存在差异, 不同类型的厌恶也不完全相同。可以采用不同的方法来诱发消费者的不同类型的厌恶。产品与服务、宣传、组织行为等均可能导致消费者产生不同类型的厌恶。不同类型的厌恶又会影响消费者行为, 如产品评价、购买意向、支付意愿、延迟决策、口碑、产品消费等。未来可以对厌恶与其他消极情绪对消费者行为影响的差异、不同类型的厌恶对消费者行为影响的差异、厌恶的前因变量与结果变量进行更深入的探索。
图/表 1
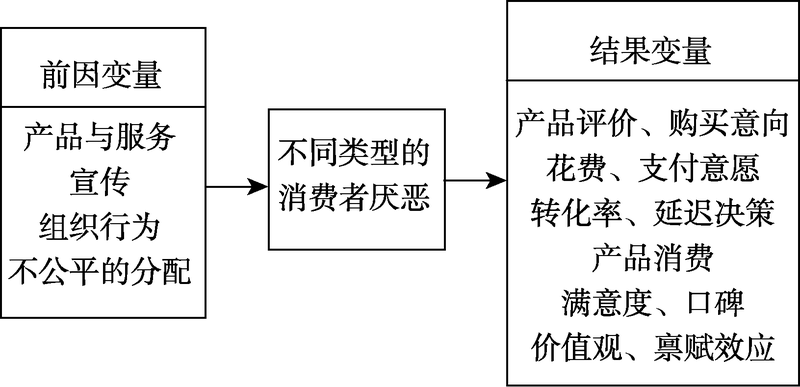
图1消费者行为中厌恶的前因变量与结果变量
 图1消费者行为中厌恶的前因变量与结果变量
图1消费者行为中厌恶的前因变量与结果变量参考文献 70
| 1 | 金熠, 张丹丹, 柳昀哲, 罗跃嘉 . ( 2014). 厌恶情绪加工特点的事件相关电位研究. 心理学报, 46( 11), 1682-1690. |
| 2 | 彭明, 张雷 . ( 2016). 厌恶情绪影响道德判断的发展研究. 心理科学, 39( 5), 1110-1115. |
| 3 | Amar M., Ariely D., Carmon Z., & Yang H . ( 2018). How counterfeits infect genuine products: The role of moral disgust. Journal of Consumer Psychology, 28( 2), 329-343. |
| 4 | Antonetti, P. . ( 2016). Consumer anger: A label in search of meaning. European Journal of Marketing, 50( 9/10), 1602-1628. |
| 5 | Argo J. J., Dahl D. W., & Morales A. C . ( 2006). Consumer contamination: How consumers react to products touched by others. Journal of Marketing, 70( 2), 81-94. |
| 6 | Barnes S. J., Mattsson J., & S?rensen F . ( 2016). Remembered experiences and revisit intentions: A longitudinal study of safari park visitors. Tourism Management,57, 286-294. |
| 7 | B?ckler A., Sharifi M., Kanske P., Dziobek I., & Singer T . ( 2017). Social decision making in narcissism: Reduced generosity and increased retaliation are driven by alterations in perspective-taking and anger. Personality and Individual Differences, 104, 1-7. |
| 8 | Boudens,C. J . ( 2005). The story of work: A narrative analysis of workplace emotion. Organization Studies, 26( 9), 1285-1306. |
| 9 | Breaban, A., &Noussair,C. N . ( 2017). Emotional state and market behavior. Review of Finance, 22( 1), 279-309. |
| 10 | Bri?ol P., Petty R. E., Stavraki M., Lamprinakos G., Wagner B., & Díaz D . ( 2018). Affective and cognitive validation of thoughts: An appraisal perspective on anger, disgust, surprise, and awe. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 114( 5), 693-718. |
| 11 | Chan C., van Boven L., Andrade E. B., & Ariely D . ( 2014). Moral violations reduce oral consumption. Journal of Consumer Psychology, 24( 3), 381-386. doi: 10.1016/j.jcps.2013.12.003 |
| 12 | Chapman,H. A., &Anderson,A. K . ( 2013). Things rank and gross in nature: A review and synthesis of moral disgust. Psychological bulletin, 139( 2), 300-327. doi: 10.1037/a0030964 |
| 13 | Chapman,H. A., &Anderson,A. K . ( 2014). Trait physical disgust is related to moral judgments outside of the purity domain. Emotion, 14( 2), 341-348. doi: 10.1037/a0035120 |
| 14 | Chapman H. A., Kim D. A., Susskind J. M., & Anderson A. K . ( 2009). In bad taste: Evidence for the oral origins of moral disgust. Science, 323( 5918), 1222-1226. |
| 15 | Chowdhry N., Winterich K. P., Mittal V., & Morales A. C . ( 2015). Not all negative emotions lead to concrete construal. International Journal of Research in Marketing, 32( 4), 428-430. |
| 16 | Clifford, S., &Piston S. 2017). Explaining public support for counterproductive homelessness policy: The role of disgust. Political Behavior, 39( 2), 503-525. |
| 17 | Clifford, S., &Wendell,D. G . ( 2016). How disgust influences health purity attitudes. Political Behavior, 38( 1), 155-178. |
| 18 | Coleman,N. V., &Williams P. 2013). Feeling like my self: Emotion profiles and social identity. Journal of Consumer Research, 40( 2), 203-222. doi: 10.1086/669483 |
| 19 | Coleman N. V., Williams P., Morales A. C., & White A. E . ( 2017). Attention, attitudes, and action: When and why incidental fear increases consumer choice. Journal of Consumer Research, 44( 2), 283-312. |
| 20 | Collymore,N. N., &Mcdermott,M. R . ( 2015). Evaluating the effects of six alcohol-related message frames on emotions and intentions: The neglected role of disgust. Journal of Health Psychology, 21( 9), 1907-1917. |
| 21 | Condon, P., &Barrett L. 2013). Conceptualizing and experiencing compassion. Emotion, 13( 5), 817-821. doi: 10.1037/a0033747 |
| 22 | Dion, D., &Borraz S. 2017). Managing status: How luxury brands shape class subjectivities in the service encounter. Journal of Marketing, 81( 5), 67-85. |
| 23 | Dolan P., Hallsworth M., Halpern D., King D., Metcalfe R., & Vlaev I . ( 2012). Influencing behaviour: The mindspace way. Journal of Economic Psychology, 33( 1), 264-277. |
| 24 | Faraji-Rad, A., &Pham,M. T . ( 2017). Uncertainty increases the reliance on affect in decisions. Journal of Consumer Research, 44( 1), 1-21. |
| 25 | Gable P. A., Poole B. D., & Harmon-Jones E . ( 2015). Anger perceptually and conceptually narrows cognitive scope. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 109( 1), 163-174. |
| 26 | Galoni, C., &Noseworthy,T. J . ( 2015). Does dirty money influence product valuations?. Journal of Consumer Psychology, 25( 2), 304-310. |
| 27 | Gatrell,C. J . ( 2013). Maternal body work: How women managers and professionals negotiate pregnancy and new motherhood at work. Human Relations, 66( 5), 621-644. doi: 10.1177/0018726712467380 |
| 28 | Goerdeler K. J., Wegge J., Schrod N., Bilinska P., & Rudolf M . ( 2015). “Yuck, that’s disgusting!”—“No, not to me!”: Antecedents of disgust in geriatric care and its relation to emotional exhaustion and intention to leave. Motivation and Emotion, 39( 2), 247-259. |
| 29 | Gopaldas, A. . ( 2014). Marketplace sentiments. Journal of Consumer Research, 41( 4), 995-1014. doi: 10.1086/678034 |
| 30 | Grappi S., Romani S., & Bagozzi R. P . ( 2013). Consumer response to corporate irresponsible behavior: Moral emotions and virtues. Journal of Business Research, 66( 10), 1814-1821. doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2013.02.002 |
| 31 | Griskevicius V., Tybur J. M., &van den Bergh, B. . ( 2010). Going green to be seen: Status, reputation, and conspicuous conservation. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 98( 3), 392-404. |
| 32 | Hackel L. M., Coppin G., Wohl M. J., &van Bavel, J. J. . ( 2018). From groups to grits: Social identity shapes evaluations of food pleasantness. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 74, 270-280. |
| 33 | Haidt J., Mccauley C., & Rozin P . ( 1994). Individual differences in sensitivity to disgust: A scale sampling seven domains of disgust elicitors. Personality and Individual Differences, 16( 5), 701-713. |
| 34 | Harmon-Jones E., Harmon-Jones C., & Summerell E . ( 2017). On the importance of both dimensional and discrete models of emotion. Behavioral Sciences, 7( 4), 66-71. |
| 35 | Hodson G., Choma B. L., Boisvert J., Hafer C. L., Macinnis C. C., & Costello K . ( 2013). The role of intergroup disgust in predicting negative outgroup evaluations. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 49( 2), 195-205. |
| 36 | Hubbard, P., &Colosi R. 2015). Respectability, morality and disgust in the night-time economy: Exploring reactions to ‘lap dance’clubs in England and Wales. The Sociological Review, 63( 4), 782-800. |
| 37 | Kecinski M., Keisner D. K., Messer K. D., & Schulze W. D . ( 2016). Stigma mitigation and the importance of redundant treatments. Journal of Economic Psychology, 54, 44-52. |
| 38 | Koopmann-Holm, B., &Tsai,J. L . ( 2014). Focusing on the negative: Cultural differences in expressions of sympathy. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 107( 6), 1092-1115. doi: 10.1037/a0037684 |
| 39 | Lee S. M., Heflick N. A., Park J. W., Kim H., Koo J., & Chun S . ( 2017). When sex doesn’t sell to men: Mortality salience, disgust and the appeal of products and advertisements featuring sexualized women. Motivation and emotion, 41( 4), 478-491. |
| 40 | Lerner J. S., Small D. A., & Loewenstein G . ( 2004). Heart strings and purse strings: carryover effects of emotions on economic decisions. Psychological Science, 15( 5), 337-341. |
| 41 | Ludwig S., de Ruyter K., Friedman M., Brüggen E. C., Wetzels M., & Pfann G . ( 2013). More than words: The influence of affective content and linguistic style matches in online reviews on conversion rates. Journal of Marketing, 77( 1), 87-103. |
| 42 | McColl-Kennedy J. R., Patterson P. G., Smith A. K., & Brady M. K . ( 2009). Customer rage episodes: Emotions, expressions and behaviors. Journal of Retailing, 85( 2), 222-237. doi: 10.1016/j.jretai.2009.04.002 |
| 43 | Meier,L. L., &Spector,P. E . ( 2013). Reciprocal effects of work stressors and counterproductive work behavior: A five-wave longitudinal study. Journal of Applied Psychology, 98( 3), 529-539. doi: 10.1037/a0031732 |
| 44 | Mishra A. K., Mishra K. E., & Spreitzer G. M . ( 2009). Downsizing the company without downsizing morale. MIT Sloan Management Review, 50( 3), 39-44. |
| 45 | Morales,A. C., &Fitzsimons,G. J . ( 2007). Product contagion: Changing consumer evaluations through physical contact with "disgusting" products. Journal of Marketing Research, 44( 2), 272-283. |
| 46 | Morales A. C., Wu E. C., & Fitzsimons G. J . ( 2012). How disgust enhances the effectiveness of fear appeals. Journal of Marketing Research, 49( 3), 383-393. |
| 47 | Muro,F. D., &Noseworthy,T. J . ( 2013). Money isn’t everything, but it helps if it doesn’t look used: How the physical appearance of money influences spending. Journal of Consumer Research, 39( 6), 1330-1342. doi: 10.1086/668406 |
| 48 | Nummenmaa L., Glerean E., Hari R., & Hietanen J. K . ( 2014). Bodily maps of emotions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 111( 2), 646-651. |
| 49 | Olatunji B. O., Williams N. L., Tolin D. F., Abramowitz J. S., Sawchuk C. N., Lohr J. M., & Elwood L. S . ( 2007). The disgust scale: Item analysis, factor structure, and suggestions for refinement. Psychological Assessment, 19( 3), 281-297. |
| 50 | Polman, E., &Kim,S. H . ( 2013). Effects of anger, disgust, and sadness on sharing with others. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 39( 12), 1683-1692. |
| 51 | Reynolds L. M., Lin Y. S., Zhou E., & Consedine N. S . ( 2015). Does a brief state mindfulness induction moderate disgust-driven social avoidance and decision-making? An experimental investigation. Journal of behavioral medicine, 38( 1), 98-109. |
| 52 | Romani S., Grappi S., & Bagozzi R. P . ( 2013). My anger is your gain, my contempt your loss: Explaining consumer responses to corporate wrongdoing. Psychology and Marketing, 30( 12), 1029-1042. |
| 53 | Rozin P., Haidt J. ,& McCauley, C. R. ( 2016). Disgust.In L. F. Barrett, M. Lewis, & J. M. Haviland-Jones (Eds.), Handbook of Emotions (4th ed., pp. 815-834). New York: Guilford Press. |
| 54 | Schnall, S. . ( 2016). Disgust as embodied loss aversion. European Review of Social Psychology, 28( 1), 50-94. |
| 55 | Scott S. E., Inbar Y., & Rozin P . ( 2016). Evidence for absolute moral opposition to genetically modified food in the United States. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 11( 3), 315-324. |
| 56 | Shimp,T. A., &Stuart,E. W . ( 2004). The role of disgust as an emotional mediator of advertising effects. Journal of Advertising, 33( 1), 43-53. |
| 57 | Shook N. J., Ford C. G., & Boggs S. T . ( 2017). Dangerous worldview: A mediator of the relation between disgust sensitivity and social conservatism. Personality and Individual Differences, 119, 252-261. |
| 58 | Sintov N., Geislar S., & White L. V . ( 2017). Cognitive accessibility as a new factor in proenvironmental spillover: Results from a field study of household food waste management. Environment and Behavior, 51( 1), 50-80. |
| 59 | Skarlicki D. P., Hoegg J. A., Aquino K., & Nadisic T . ( 2013). Does injustice affect your sense of taste and smell? the mediating role of moral disgust. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 49( 5), 852-859. doi: 10.1016/j.jesp.2013.03.011 |
| 60 | Smith,C. A., &Ellsworth,P. C . ( 1985). Patterns of cognitive appraisal in emotion. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 48( 4), 813-838. |
| 61 | Swencionis,J. K., &Fiske,S. T . ( 2016). Promote up, ingratiate down: Status comparisons drive warmth- competence tradeoffs in impression management. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 64, 27-34. |
| 62 | Tugrul,T. O . ( 2015). The impacts of fear and disgust on the perceived effectiveness of smoking warning labels: A study on Turkish university students. Asia Pacific Journal of Public Health, 27( 2), 506-512. |
| 63 | Tybur J. M., Lieberman D., & Griskevicius V .( 2009). Microbes, mating, and morality: Individual differences in three functional domains of disgust. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 97( 1), 103-122. |
| 64 | Tybur J. M., Lieberman D., Kurzban R., & Descioli P . ( 2013). Disgust: Evolved function and structure. Psychological Review, 120( 1), 65-84. doi: 10.1037/a0030778 |
| 65 | Ullah R., Amblee N., Kim W., & Lee H . ( 2016). From valence to emotions: Exploring the distribution of emotions in online product reviews. Decision Support Systems, 81, 41-53. |
| 66 | Westbrook,R. A . ( 1987). Product/consumption-based affective responses and postpurchase processes. Journal of Marketing Research, 24( 3), 258-270. |
| 67 | Wester J., Timpano K. R., ?ek D., & Broad K . ( 2016). The psychology of recycled water: Factors predicting disgust and willingness to use. Water Resources Research, 52( 4), 3212-3226. |
| 68 | Wong,J. Y., &Wang,C. H . ( 2009). Emotional labor of the tour leaders: An exploratory study. Tourism Management, 30( 2), 249-259. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2008.06.005 |
| 69 | Xie C., Bagozzi R. P., & Gr?nhaug K . ( 2015). The role of moral emotions and individual differences in consumer responses to corporate green and non-green actions. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 43( 3), 333-356. |
| 70 | Yoder A. M., Widen S. C., & Russell J. A . ( 2015). The word disgust may refer to more than one emotion. Emotion, 16( 3), 301-308. |
相关文章 15
| [1] | 张辉华. 社会网络视角的团队情绪智力[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(8): 1381-1395. |
| [2] | 李晓明, 邹是, 高友明. 失望情绪在不作为惯性产生中的作用[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(8): 1396-1401. |
| [3] | 张珊珊, 王婧怡, 李昱汝. 情绪自旋及其心理健康功能[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(8): 1430-1437. |
| [4] | 曾宪卿, 许冰, 孙博, 叶健彤, 傅世敏. EMMN受偏差-标准刺激对类型和情绪类型影响: 来自元分析的证据[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(7): 1163-1178. |
| [5] | 王晓田, 王娜, 何金波. 前瞻性情绪作为社会风险的信息源假说:公共场景下风险决策的情绪及文化机制探讨[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(6): 959-966. |
| [6] | 彭坚, 曹兵兵. 追随者主动工作行为的上行影响:内隐追随视角[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(6): 967-977. |
| [7] | 何蔚祺, 李帅霞, 赵东方. 群体面孔情绪感知的神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(5): 761-772. |
| [8] | 尹俊婷, 王冠, 罗俊龙. 威胁对创造力的影响:认知与情绪双加工路径[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(5): 815-826. |
| [9] | 王学思, 李静雅, 王美芳. 父母婚姻冲突对儿童发展的影响及其机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(5): 875-884. |
| [10] | 丁琳洁, 李旭, 尹述飞. 工作记忆中的积极效应:情绪效价与任务相关性的影响[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(4): 652-664. |
| [11] | 关旭旭, 王红波. 抑制引起的遗忘及其神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(4): 665-676. |
| [12] | 张衍, 王俊秀, 席居哲. 幸灾乐祸的重新审视和互动过程模型的构想[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(3): 505-519. |
| [13] | 赵小红, 童薇, 陈桃林, 吴冬梅, 张蕾, 陈正举, 方晓义, 龚启勇, 唐小蓉. 敬畏的心理模型及其认知神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(3): 520-530. |
| [14] | 霍鹏辉, 冯成志, 陈庭继. 注视者及观察者因素对注视知觉的影响[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(2): 238-251. |
| [15] | 黄挚靖, 李旭. 抑郁症患者工作记忆内情绪刺激加工的特点及其机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(2): 252-267. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlkxjz/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=4864
