 ), 罗天瑞2, 赛李阳1
), 罗天瑞2, 赛李阳1 1 杭州师范大学心理科学研究院, 杭州 311121
2 香港中文大学心理学系, 香港
收稿日期:2018-09-18出版日期:2019-07-15发布日期:2019-05-22通讯作者:田蜜E-mail:tianmi@link.cuhk.edu.hk基金资助:* 香港研究资助局RGC资助项目(CUHK14611718);国家自然科学基金青年项目(31600875);杭州市哲学社会科学规划课题(2018RCZX17)Transfer-of-learning effect based on response selection: From individual to social situations
XU Sheng1, TIAN Mi2( ), LUO Tianrui2, SAI Liyang1
), LUO Tianrui2, SAI Liyang1 1 Institutes of Psychological Sciences, Hangzhou Normal University, Hangzhou 311121, China
2 Department of Psychology, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China
Received:2018-09-18Online:2019-07-15Published:2019-05-22Contact:TIAN Mi E-mail:tianmi@link.cuhk.edu.hk摘要/Abstract
摘要: 先前习得的空间不相容联结可以减少、消除甚至反转Simon效应, 这种现象被称为学习迁移效应。研究者已经在个人情境和社会情境中发现一些影响学习迁移效应的因素, 并提出短时记忆联结解释、自下而上的启动机制和反应对立策略等相关解释。未来研究需要澄清刺激-反应迁移的双向性以及学习迁移效应的认知神经机制和发展路径。
图/表 2
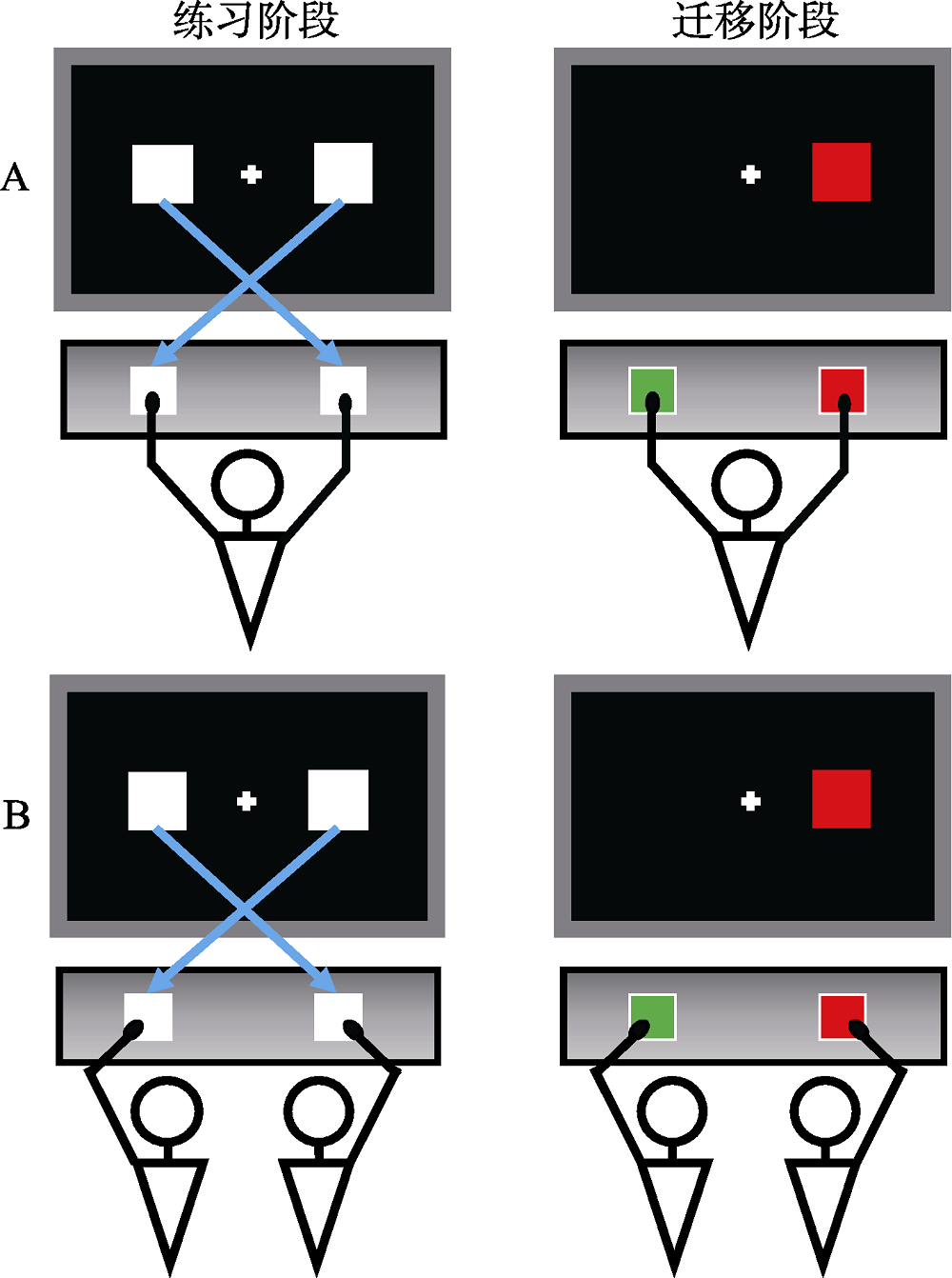
图1学习迁移(ToL)范式示意图 注:A.个人情境下的ToL范式; B.社会情境下的ToL范式。彩图见电子版
 图1学习迁移(ToL)范式示意图 注:A.个人情境下的ToL范式; B.社会情境下的ToL范式。彩图见电子版
图1学习迁移(ToL)范式示意图 注:A.个人情境下的ToL范式; B.社会情境下的ToL范式。彩图见电子版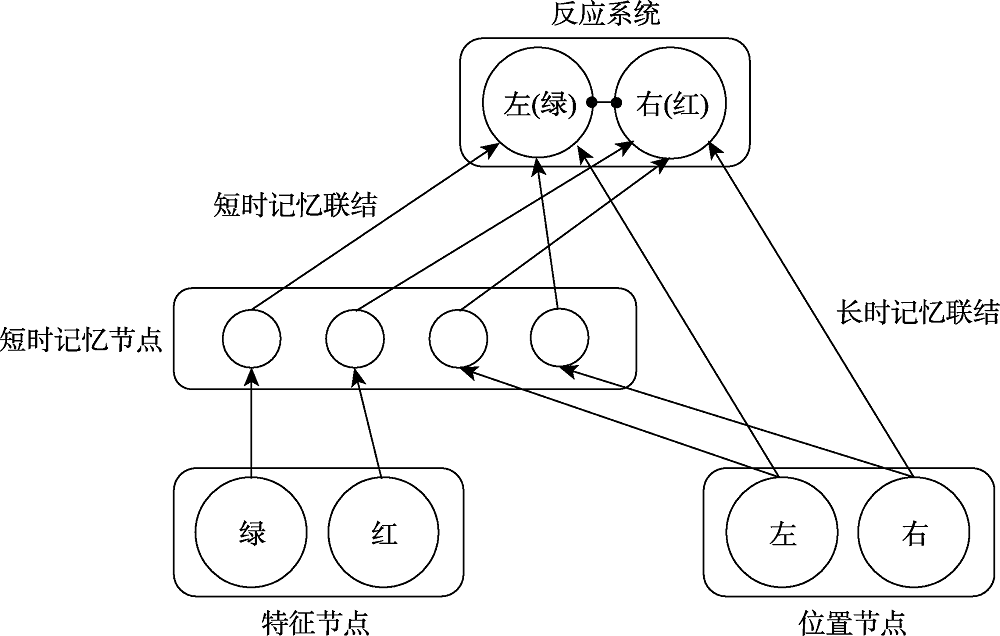
图2短时记忆联结解释模型
 图2短时记忆联结解释模型
图2短时记忆联结解释模型参考文献 44
| [1] | 宋晓蕾, 李洋洋, 杨倩, 游旭群 . (2018). 反应手的不同状态对联合任务中观察学习的影响. 心理学报, 50(9), 975-984. |
| [2] | 王力, 陈安涛 . (2012). 习得性空间联结的迁移依赖于语义工作记忆. 心理学报, 44(5), 605-613. |
| [3] | 徐胜, 宋晓蕾 . (2016). 联合Simon效应: 现状、影响因素与理论解释. 心理科学进展, 24(3), 367-378. |
| [4] | Bae G. Y., Cho Y. S., & Proctor R. W . (2009). Transfer of orthogonal stimulus-response mappings to an orthogonal Simon task. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 62(4), 746-765. doi: 10.1080/17470210802303883URL |
| [5] | Barber P. J., & O'Leary M. J . (1997). The relevance of salience: Towards an account of irrelevant stimulus- response compatibility effects. In B. Hommel & W. Prinz (Eds.), Theoretical issues in stimulus-response compatibility(pp. 135-172). Amsterdam: North-Holland. |
| [6] | Conde E. F. Q., Fraga-Filho R. S., Lameira A. P., Mograbi D. C., Riggio L., & Gawryszewski L. G . (2015). Influence of short incompatible practice on the Simon effect: Transfer along the vertical dimension and across vertical and horizontal dimensions. Experimental Brain Research, 233(11), 3313-3321. doi: 10.1007/s00221-015-4399-1URL |
| [7] | Dolk T., Hommel B., Colzato L. S., Schützbosbach S., Prinz W., & Liepelt R . (2014). The joint Simon effect: A review and theoretical integration. Frontiers in Psychology, 5, 974. |
| [8] | Ferraro L., Iani C., Mariani M., Nicoletti R., Gallese V., & Rubichi S . (2012). Look what I am doing: Does observational learning take place in evocative task-sharing situations? PLoS ONE, 7(8), e43311. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043311URL |
| [9] | Finkbeiner M., & Heathcote A. , (2016). Distinguishing the time- and magnitude-difference accounts of the Simon effect: Evidence from the reach-to-touch paradigm. Attention Perception & Psychophysics, 78(3), 848-867. |
| [10] | Hommel B. , (1993). The relationship between stimulus processing and response selection in the Simon task: Evidence for a temporal overlap. Psychological Research, 55(4), 280-290. doi: 10.1007/BF00419688URL |
| [11] | Hommel B. , (2011). The Simon effect as tool and heuristic. Acta Psychologica, 136(2), 189-202. doi: 10.1016/j.actpsy.2010.04.011URL |
| [12] | Housebroke P., van Dantzig S., & Hommel B . (2013). How task goals mediate the interplay between perception and action. Frontiers in Psychology, 4, 247. |
| [13] | Iani C., Milanese N., & Rubichi S . (2014). The influence of prior practice and handedness on the orthogonal Simon effect. Frontiers in Psychology, 5, 39. |
| [14] | Iani C., Rubichi S., Ferraro L., Nicoletti R., & Gallese V . (2013). Observational learning without a model is influenced by the observer's possibility to act: Evidence from the Simon task. Cognition, 128(1), 26-34. doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2013.03.004URL |
| [15] | Iani C., Rubichi S., Gherri E., & Nicoletti R . (2009). Co-occurrence of sequential and practice effects in the Simon task: Evidence for two independent mechanisms affecting response selection. Memory & Cognition, 37(3), 358-367. |
| [16] | Ivanoff J., Blagdon R., Feener S., McNeil M., & Muir P. H., ., (2014). On the temporal dynamics of spatial stimulus- response transfer between spatial incompatibility and Simon tasks. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 8, 243. |
| [17] | Kornblum S., Hasbroucq T., & Osman A . (1990). Dimensional overlap: Cognitive basis for stimulus- response compatibility-A model and taxonomy. Psychological Review, 97(2), 253-270. doi: 10.1037/0033-295X.97.2.253URL |
| [18] | Lugli L., Iani C., Milanese N., Sebanz N., & Rubichi S . (2015). Spatial parameters at the basis of social transfer of learning. Journal of Experimental Psychology Human Perception & Performance, 41(3), 840-849. |
| [19] | Lugli L., Iani C., Nicoletti R., & Rubichi S . (2013). Emergence of the go/no-go Simon effect by means of practice and mixing paradigms. Acta Psychologica, 144(1), 19-24. doi: 10.1016/j.actpsy.2013.04.021URL |
| [20] | Luo C., & Proctor R. W . (2016). Transfer of an implied incompatible spatial mapping to a Simon task. Acta Psychologica, 164, 81-89. doi: 10.1016/j.actpsy.2015.11.011URL |
| [21] | Marini M., Iani C., Nicoletti R., & Rubichi S . (2011). Between-task transfer of learning from spatial compatibility to a color Stroop task. Experimental Psychology, 58(6), 473-479. doi: 10.1027/1618-3169/a000115URL |
| [22] | Milanese N., Iani C., & Rubichi S . (2010). Shared learning shapes human performance: Transfer effects in task sharing. Cognition, 116(1), 15-22. doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2010.03.010URL |
| [23] | Milanese N., Iani C., Sebanz N., & Rubichi S . (2011). Contextual determinants of the social-transfer-of-learning effect. Experimental Brain Research, 211(3-4), 415-422. doi: 10.1007/s00221-011-2679-yURL |
| [24] | Miles J. D., & Proctor R. W . (2012). Correlations between spatial compatibility effects: Are arrows more like locations or words? Psychological Research, 76(6), 777-791. doi: 10.1007/s00426-011-0378-8URL |
| [25] | Proctor R. W., & Lu C. H . (1999). Processing irrelevant location information: Practice and transfer effects in choice-reaction tasks. Memory & Cognition, 27(1), 63-77. |
| [26] | Proctor R. W., Yamaguchi M., & Vu K. P. L ., (2007). Transfer of noncorresponding spatial associations to the auditory Simon task. Journal of Experimental Psychology Learning Memory & Cognition, 33(1), 245-253. |
| [27] | Proctor R. W., Yamaguchi M., Zhang Y & Vu K. P. L ., (2009). Influence of visual stimulus mode on transfer of acquired spatial associations. Journal of Experimental Psychology Learning Memory & Cognition, 35(2), 434-445. |
| [28] | Rottermann A., & Vu K. P. L . (2009). Reversing the Simon effect with prior practice of noncorresponding location words. Human Interface and the Management of Information. Designing Information Environments, 5617, 287-295. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-02556-3URL |
| [29] | Sebanz N., Knoblich G., & Prinz W . (2003). Representing others' actions: Just like one's own? Cognition, 88(3), B11-B21. doi: 10.1016/S0010-0277(03)00043-XURL |
| [30] | Simon J. R., & Rudell A. P . (1967). Auditory S-R compatibility: The effect of an irrelevant cue on information processing. Journal of Applied Psychology, 51(3), 300-304. doi: 10.1037/h0020586URL |
| [31] | Soetens E., Maetens K., & Zeischka P . (2010). Practice- induced and sequential modulations of the Simon effect. Attention Perception & Psychophysics, 72(4), 895-911. |
| [32] | Tagliabue M., Zorzi M., & Umiltà C . (2002). Cross-modal re-mapping influences the Simon effect. Memory & Cognition, 30(1), 18-23. |
| [33] | Tagliabue M., Zorzi M., Umiltà C., & Bassignani F . (2000). The role of long-term-memory and short-term- memory links in the Simon effect. Journal of Experimental Psychology Human Perception & Performance, 26(2), 648-670. |
| [34] | Verghese A., Mattingley J. B., Palmer P. E., & Dux P. E . (2018). From eyes to hands: Transfer of learning in the Simon task across motor effectors. Attention Perception & Psychophysics, 80(1), 193-210. |
| [35] | Vu K. P. L . (2007). Influences on the Simon effect of prior practice with spatially incompatible mappings: Transfer within and between horizontal and vertical dimensions. Memory & Cognition, 35(6), 1463-1471. |
| [36] | Vu K. P. L . (2011). Unintentional and intentional learning of noncorresponding stimulus-response associations in the Simon task. Acta Psychologica, 136(2), 217-224. doi: 10.1016/j.actpsy.2010.05.005URL |
| [37] | Vu K. P. L., Proctor R. W., & Urcuioli P . (2003). Transfer effects of incompatible location-relevant mappings on a subsequent visual or auditory Simon task. Memory & Cognition, 31(7), 1146-1152. |
| [38] | Wang J. X., Rogers L. M., Gross E. Z., Ryals A. J., Dokucu M. E., Brandstatt K. L., … Voss J. L . (2014). Targeted enhancement of cortical-hippocampal brain networks and associative memory. Science, 345(6200), 1054-1547. doi: 10.1126/science.1252900URL |
| [39] | Wang L., & Weekes B. , (2014). Neural correlates of the Simon effect modulated by practice with spatial mapping. Neuropsychologia, 63(1), 72-84. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2014.08.019URL |
| [40] | Wascher E., Schatz U., Kuder T., & Verleger R . (2001). Validity and boundary conditions of automatic response activation in the Simon task. Journal of Experimental Psychology Human Perception & Performance, 27(3), 731-751. |
| [41] | Yamaguchi M., Chen J., & Proctor R. W . (2015). Transfer of learning in choice reactions: The roles of stimulus type, response mode, and set-level compatibility. Memory & Cognition, 43(6), 825-836. |
| [42] | Yamaguchi M., & Proctor R. W . (2009). Transfer of learning in choice reactions: Contributions of specific and general components of manual responses. Acta Psychologica, 130(1), 1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.actpsy.2008.09.008URL |
| [43] | Zhong Q., Xiong A., Vu K. P. L., & Proctor R. W . (2017). Vertically arrayed stimuli and responses: Transfer of incompatible spatial mapping to Simon task occurs regardless of response-device orientation. Experimental Brain Research, 236(1), 1-11. doi: 10.1016/bs.pbr.2017.07.003URL |
| [44] | Zorzi M., & Umiltá C. , (1995). A computational model of the Simon effect. Psychological Research, 58(3), 193-205. doi: 10.1007/BF00419634URL |
相关文章 6
| [1] | 陈丝璐, 张光磊, 刘文兴. 伦理导向人力资源管理实践的跨层次作用机制:基于社会情境与社会认知理论[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(11): 1800-1813. |
| [2] | 郭秀艳, 郑 丽, 程雪梅, 刘映杰, 李 林. 不公平感及相关决策的认知神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2017, 25(6): 903-911. |
| [3] | 徐胜;宋晓蕾. 联合Simon效应:现状、影响因素与理论解释[J]. 心理科学进展, 2016, 24(3): 367-378. |
| [4] | 王力;张栎文;张明亮;陈安涛. 视觉运动Simon效应和认知Simon效应的影响因素及机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2012, 20(5): 662-671. |
| [5] | 郭昫澄;郭永玉. 社会情境中的控制感[J]. 心理科学进展, 2012, 20(11): 1860-1868. |
| [6] | 钱兰英. 留澳海外学生的社会生活和学业困难[J]. 心理科学进展, 1996, 4(4): 49-531. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlkxjz/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=4725
