 ,1, 劳昕2
,1, 劳昕2Evolution and enlightenment of foreign spatial planning: Exploration from the perspective of geography
YANG Qingyuan1, LUO Kui ,1, LAO Xin2
,1, LAO Xin2通讯作者:
收稿日期:2019-01-1修回日期:2020-03-12网络出版日期:2020-06-25
| 基金资助: |
Received:2019-01-1Revised:2020-03-12Online:2020-06-25
| Fund supported: |
作者简介 About authors
杨庆媛(1966-),女,云南腾冲人,教授,博士生导师,主要从事土地经济与政策、国土资源与区域发展研究E-mail:yizyang@swu.edu.cn。

摘要
关键词:
Abstract
Keywords:
PDF (3149KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
本文引用格式
杨庆媛, 罗奎, 劳昕. 基于地理学视角的国际空间规划嬗变与启示. 地理学报[J], 2020, 75(6): 1223-1236 doi:10.11821/dlxb202006010
YANG Qingyuan.
1 引言
人类文明的发展史,某种程度上也是一部人类对空间的开发利用史[1]。在农业文明时代,生产力长期维持在较低水平,人类对空间的开发利用主要表现为平面的扩张,“毁林开荒”等不可持续模式与“桑基鱼塘”等协调发展模式并存,人地冲突程度较轻,主要表现为局部地区的水土流失等;随着工业文明的开启,生产力迅速提升,空间开发利用演变为城市地域的快速扩张与高强度开发,城市同时也成为人地冲突最为剧烈的地区,爆发了诸如伦敦烟雾事件、日本水俣病事件等诸多环境公害事件;随着第三次科技革命与全球化的迅速推进,人类对空间的开发利用呈现出全方位、大尺度、从太空到海底全覆盖的态势,人地冲突极为激烈,呈现出面状蔓延乃至拓展到全球的趋势,例如2013年1月覆盖中国143.00万km2国土面积的严重雾霾、全球温室效应等[2]。整体而言,随着人类生产力水平的快速提升,人地冲突强度逐渐加剧,冲突空间尺度由点及面并逐步扩展至全球,甚至威胁到人类发展本身。人地剧烈冲突倒逼人类不断调整自身活动与地域系统之间的关系,其中空间规划作为调和人地矛盾的一种有效工具,正发挥着越来越重要的作用[3]。然而,由于人地关系地域系统的区域性、综合性、复杂性及多尺度特征[4],当前空间规划尚未能窥破其内在机理,所制定的规划方案往往滞后于人地关系演变,极端情况下甚至成为人地关系协调发展的掣肘,因此空间规划改革受到广泛关注,成为学界的热点议题。空间规划的本质在于遵循人地关系地域系统演进规律的基础上,统筹空间资源的科学利用与合理布局。但当前,大部分研究仍局囿于规划本身,较少有****从人地关系的角度对空间规划改革进行探讨。深入解析人地关系演变规律与驱动机制,进而对区域发展前景进行合理展望是提升空间规划科学性的基石,而厘清空间规划实施对人地关系的综合影响并探寻改进路径则是强化空间规划可操作性的保障。因而基于地理学视角对空间规划嬗变进行探讨并凝炼其经验就极为必要,这也是本研究的目的所在。空间规划是经济、社会、文化、生态等政策的地理表达,是实现区域发展战略、兼顾发展效率与公平,同时推动可持续发展的极重要手段[5]。空间规划(Spatial Planning)作为特定含义的专用概念由欧盟委员会于20世纪80年代提出,其初衷是与其成员国各自的空间发展制度相区分,其与城市规划、区域规划等均是协调人地关系的重要工具,但在空间尺度与协调内容方面有所区别。空间规划改革涉及多学科、多部门的统筹与协调,其中地理学作为一门专注于“空间”的科学,在空间规划改革中具有不可替代的重要作用。纵览历史,从古代以“左青龙,右白虎,前朱雀,后玄武”指导城市选址中所蕴含的古人对地理现象的归纳总结[6],再到近代中心地理论、工业区位论等地理学理论对城市规划的指导,直至当下在生态环境承载力与可持续发展理论等指引下编制的区域发展规划,地理学无一不为其提供了坚实的理论指引与方法支撑。事实上,中国从早期关注区域均衡发展(西部大开发、东北振兴、中部崛起)到当下侧重于重点地区优化提升(包括京津冀协同发展规划、粤港澳大湾区发展规划、城市群发展规划、都市圈培育),这一演变即暗含了全球产业链在规模经济驱动下不断肢解并围绕核心城市及其周边地区进行空间重组的客观规律[7],而这正是地理学的研究范畴。可见,地理学对于空间规划改革至关重要,尤其对中国而言,高速发展的工业化与城镇化压缩了传统的区域集聚-扩散过程,日趋严峻的资源压力与生态环境胁迫激化了人地冲突,空间规划所面临的问题与压力史无前例。在此背景下,更应深入发掘人地关系地域系统的演化特征、内在机理与主控要素,以便更好地为空间规划改革提供坚实支撑,而在这一过程中地理学责无旁贷。
本文尝试以“他山之石”为中国空间规划改革提供指引:以国外对空间规划的研究和实践为对象,采用文献计量与典型案例分析,力求呈现出其所蕴含的地理学原理,以期对中国空间规划改革提供相应经验与借鉴,为建设绿水青山美丽中国做出应有的贡献。
2 基于文献计量的空间规划与地理学关系剖析
为深入探讨空间规划与地理学之间的关系,本文采用Citespace软件进行文献计量与可视化分析[8]。分析采用数据来源于科学引文索引(ISI Web of Knowledge)“Web of Science”核心合集数据库,其能够反映出某一学科当前国际研究的最高水平。以“spatial planning”“regional planning”“territorial management”作为主题进行搜索,数据截至时间为2019年4月10日,共获取文献6860篇,涵盖时间范围为1924—2019年,以这一数据进行分析。2.1 研究领域演变
基于“Web of Science”研究领域分类而言(图1),目前对空间规划研究集中在环境科学与生态(Environment Sciences & Ecology)、环境研究(Environment Studies)、地理学(Geography)、公共管理(Public Administration)、区域与城市规划(Regional & Urban Planning)以及环境科学(Environment Sciences)等领域。由图1中的时间线(Timeline View)可见,地理学为空间规划研究的开端,对其后的研究产生了持续影响。但整体而言,当前对空间规划研究的热点集中在生态环境领域,如何提升地理学在空间规划研究中的影响力,尚需要进一步的探讨。图1
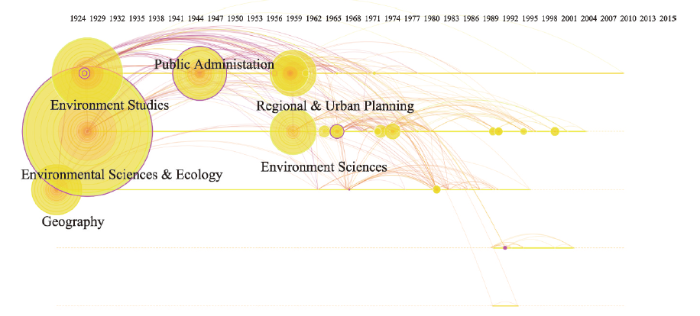 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图1空间规划主题论文研究领域分布
Fig. 1Distribution of literatures published in the fields related with spatial planning
2.2 共引网络中的核心文献
基于引文共引网络分析(图2),本文探讨空间规划领域研究的核心论文。其中位于核心的论文为Douvere[9]于2008年所发表的“空间规划对于提升海洋管理水平重要性”,其与Ehler[10]合作以比利时、荷兰与德国为案例探讨生态系统管理及区划对海洋空间规划重要性的论文也同样为核心文献之一。Halpern等[11]于2008年发表的关于人类活动对全球海洋生态系统影响的论文成为海洋空间规划的科学依据。Foley等[12]提出的海洋空间规划的生态指导原则也成为指导海洋空间规划的基础。Crowder等[13]同样基于海洋生态系统视角观点提出了海洋空间规划及管理的要点。从论文组团的关键词可知,排名前三的分别为海洋空间规划(Marine Spatial Planning)、战略监控(Strategy Monitoring)、战略空间规划(Strategic Spatial Planning)。总体而言,海洋空间规划在共引网络中居于核心地位,是空间规划研究的领头羊。究其原因,可能是由于海洋空间性质相对均一,开发利用方式相对固定,对其的研究更为深入与透彻,这有力支撑了海洋空间规划的科学推进。但对陆地空间而言,其区域异质性突出,涉及要素众多,作用机制纷繁复杂,既有研究尚未能对其进行全面综合的解析,直接表现即为缺乏陆地空间规划的标志性文献,尚需要进一步的研究。图2
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图2空间规划主题论文共引网络
Fig. 2Co-citation network of research papers on spatial planning
2.3 共引网络中的地理学核心文献
为进一步探讨地理学在空间规划中的作用,本文识别出地理学在共引网络中的核心文献,分别为:de Vries[14]开展了绿色空间与健康关系的探究,证实绿色空间对人体健康具有显著的正面影响;Healey[15]探讨了地理学理论在欧洲战略规划中的变迁,在新的战略规划中,空间被处理为动态、不连续且更为概念化;Barredo[16]采用元胞自动机(CA)模型对城市空间动态变化进行了模拟,这一方法在现代空间规划中也得到了广泛应用;Davoudi[17]探讨了多中心理论在欧洲空间规划中的应用,其已经从一种分析工具转变为规范性议程;Allmendinger[18]以泰晤士河河口地区为案例,探讨了柔性空间与模糊边界在这一地区空间规划中的应用。综上可见,传统地理学理论如多中心理论等在空间规划中正发挥着越来越重要的作用,而关系地理学(Relational Geography)等后结构主义地理学思想等也在空间规划中得到了认可及逐步应用。此外,地理学还为空间规划提供了技术支撑(如CA模型等)。总之,基于文献计量的分析表明,地理学在理论与方法上均对空间规划影响深远。需要特别指出的是,上文所提到的Patsy Healey,其同时也是****共引网络中的第一核心作者,其成果在空间规划研究中具有举足轻重的地位。Healey[15]认为一个区域的品性并非“天然”,而是由其所处于的各种关系网络中的“位置”所赋予,而这恰好契合了关系地理学的观点。在传统地理学观点中,区域间的相互作用遵循距离衰减原则,北京郊区的小镇与北京的距离明显小于北京与上海的距离;但在关系地理学看来,若这一小镇与北京并未构成联系,则其距离北京的距离比上海距离北京更为“遥远”。Healey的研究很好地解释了空间战略规划在欧洲的“回归”。20世纪80年代,欧洲一度抛弃了空间战略规划,转而关注城市更新与景观再造,这种转向却一度让这些城市迷失了发展方向。在经历了长时间的迷茫之后,规划者终于认识到,唯有以关系网络的视角从更大的空间尺度探讨城市方可辨明其地位与发展目标,在关系地理学理论的指引下,欧洲在世纪之交迎来了空间战略规划的复兴。事实上,随着航空与信息技术的快速发展,人才、技术与资本的流动逐步由传统的空间距离衰减转变为关系层次衰减,在全球化程度较高的欧美地区这一现象更为明显,因此,关系地理学理论在这些地区得到了更为广泛的应用,但在中国,这一理论目前尚未能引起足够重视。
2.4 空间规划嬗变与地理学演化
空间规划作为推动空间资源优化配置的工具出现并逐步发展,其嬗变受到人类圈与地理圈的交互关系演变——也即人地关系地域系统演变的制约与影响,而同时人地关系地域系统也是地理学研究的核心命题。追溯历史,工业革命的出现带动了人类生产力的第一次飞跃,促成了人地关系的加速演化,进而催生了现代空间规划的产生与嬗变,也推动了地理学的发展与成熟(图3)。在空间规划方面,工业化与城市化的发展使得城市成为人类聚居新的空间模式,同时也引发了疫病爆发、环境污染等人地冲突升级形式,催生了城市规划这一调和工具的诞生与演化[19];全球化与产业演进使得区域成为参与全球竞争新的单元,推动区域经济增长、社会进步与空间重构成为人地协调所面临的新问题,区域规划应运而生[20];信息化与技术革命带来生产力的飞跃提升,与之相伴随,人地冲突的广度、深度与烈度也达到了前所未有的地步,国家间的经济、社会、文化冲突持续加剧,环境污染与生态破坏成为全球性问题,空间规划理念提出并得到广泛关注与应用[5]。地理学则一直在建构与解构之间波折前行,自18世纪末地理学即开始尝试建构事物分布的一般规律,但区域异质性与人地交互的复杂性则常常使得这种建构脱离抽象,转变为对具体事物的解构。具体而言,Alexander Humboldt、Carl Ritter等****推动了地理学的第一次建构,成功将地理学发展成为一门建立在自然科学模式上的解释性学科,但其尝试建构人类空间分布与演化通则的努力并未成功,****基于人与环境的关系、景观分析、区域类型与结构3个方向展开了新的解构,并发展出3个国家学派:以景观为核心的德国学派、以文化为重点的伯克利学派以及以区域为特色的法国学派。20世纪50年代,计量革命以及经济、社会因素的引入掀起了地理学建构的第二次热潮,基于数学与统计的模型构建及实证研究成为主导,构建具有广泛意义的空间理论成为地理****新的追求。然而,过于依赖计量模型与理性构建难以反映人对空间认知及交互的复杂性,人本主义地理学因而兴起。同时,全球化的持续推进带来了经济、社会、文化乃至生态环境的重构,多种思潮的兴起推动了地理学的制度、文化及关系转向。地理学关注内容与研究视角更为多元化,基于抽象空间、理性主导的研究受到批判,关注人类与空间交互、注重从人文与文化视角进行探讨成为当前西方地理学研究的主流[21]。图3
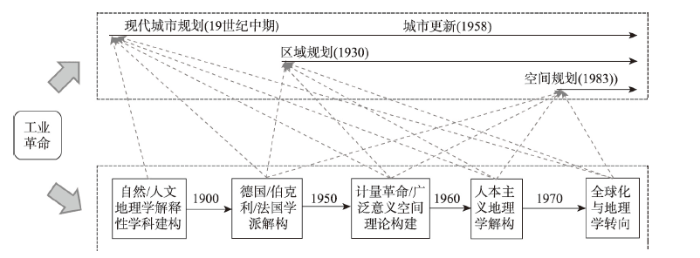 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图3空间规划嬗变与地理学演化
Fig. 3The relationship between spatial planning transmutation and the evolution of geographical research
协调人地关系、推动人地关系地域系统的良性发展是横亘在人类发展历史上的永恒命题,而这也是空间规划与地理学所关注与致力于实现的目标。其中,空间规划侧重于实践,地理学则更为注重理论,二者在发展历程中相互促进,共同发展。具体而言,地理学中的农业区位论、工业区位论与中心地理论等至今仍是空间规划布局的重要理论支撑,而20世纪初区域规划的实践也推动了地理****对于经济社会系统的关注,进而通过计量革命迎来了地理学的快速发展。城市更新实践深化了地理学对全球化的思考,全球化背景下地区经济社会转型滞后是导致其衰退的重要原因,而摆脱衰退困境同样离不开地理学对于制度、文化及关系转向的研究。当前,应对全球气候/环境变化、提升区域可持续发展能力已经成为空间规划关注的要点,局囿于特定城市/区域的规划实践已经难以应对这一问题[22,23,24],唯有从全局尺度、综合视角出发,厘清人类活动与全球变化规律与机理,方可制订出科学的政策建议并推动空间规划的合理化,而这也正是地理学当前研究的核心。可见,地理学为空间规划提供了理论指引与方法支撑,而空间规划则为地理学发展提供了研究方向与实践平台,在当前人地交互要素日趋复杂、空间尺度持续扩张、冲突矛盾日趋激烈的背景下,以人地关系协调为主线推动空间规划与地理学的深度交融、互为促进不仅是构建高质量空间规划体系所不可或缺,同时也对地理学的深化提升意义深远。
3 国外空间规划的地理学基础剖析
区域异质性与路径依赖影响着不同地区地理学的演化,而这种差异也推动了空间规划的特色化发展。为尽可能全面地剖析国外空间规划嬗变及其背后所蕴含的地理学基础,本文分别选取欧洲、德国与日本作为案例。其中,欧洲是空间规划研究与实践的热点地区,作为现代空间规划的起源,地理学思想与理论在欧洲的空间规划中得到了充分体现。德国是近代地理学的发源地,同时也是较早推行空间规划实践的国家之一,其不仅是中心地理论、工业区位论等在空间规划实践中不可或缺基础理论的诞生地,同时也是公认空间规划较为成功的国家之一,探讨其地理学与空间规划的交互历程有助于深入理解地理学在空间规划中的作用。日本是国外地理学理论引进与本土创新结合的典范,地理学对于其空间规划实践以及经济社会发展均发挥了极为重要的推动作用,同时日本与中国社会文化相近,发展历程对中国具有较强的借鉴意义。通过深入剖析3个案例空间规划嬗变与地理学演化交互影响,尝试较为全面地厘清国外空间规划中的地理学基础,以期从地理学视角为中国空间规划改革提供现实参考。3.1 欧盟空间规划及其地理学基础
3.1.1 欧盟空间规划嬗变 在全球化及欧盟东扩的背景下,欧盟内部发展差异增大,社会与文化冲突逐步加剧,局限于区域或国家尺度的空间发展政策无法处理跨国界的各种问题,欧洲空间发展规划(European Space Development Planning, ESDP)正是在这样的背景下产生的[25]。从诞生之日起,推动区域均衡发展即成为ESDP的使命。自20世纪80年代开始,欧盟即已经开始推动欧洲标准区域划分(European Standard Area Division)的工作,这种基于地域功能、人口、兼顾行政区划的标准区域划分为欧洲空间规划的制定提供了扎实的基础资料与数据支撑。在经历了多次协商与讨论之后,欧洲空间发展战略于1999年5月正式发布,成为世界上最早的跨国空间规划,对欧盟的一体化进程及之后的空间规划编制均产生了巨大影响[26]。在ESDP的基础上,欧盟于2007年发布了《欧盟国土议程》,进一步凝练优先发展领域以促进区域均衡发展及竞争力的提升[27],其确定的6个优先领域为:① 建立区域与城市间的网络以促进多中心发展与创新;② 构建新型城乡合作伙伴关系与国土治理制度;③ 强化集群竞争力与创新性;④ 延伸与深化跨欧洲网络;⑤ 深化包括气候变化影响在内的跨欧洲风险管理;⑥ 提升生态与文化资源价值。3.1.2 欧盟空间规划中的地理学基础及作用 欧洲空间发展规划(ESDP)作为一个非法定的指导性章程,其通过制定发展原则指导各成员国的空间规划发挥作用。ESDP制定的发展原则有三:① 发展多中心与均衡的城市体系,建立新型城乡关系;② 平等地获得基础设施和知识,提高交通、通讯基础设施可达性及知识可获得性机会;③ 以明智管理手段开发和保护自然与文化遗产。显然,这些原则的提出及实践离不开地理学理论与方法的支撑。其中,发展多中心与均衡的城市体系离不开中心地理论与地域分工理论的指引;基于空间与基于网络的可达性解析理论及方法则有助于推动提升交通通讯基础设施可达性及知识获得性机会;而自然与文化遗产的合理开发与保护则更离不开生态环境承载力及文化地理学等相关理论。整体而言,支撑欧洲空间发展规划的主要为传统地理学理论,但“大城市走廊”等概念的提出以及对航空网络、货物贸易流的重视也可反映出对于关系网络的逐步关注。在《欧盟国土议程》所确定的6个优先领域中,关系网络的构建与延伸被提到了极为重要的地位,表明关系地理学得到了更多的认可,文献计量的结果也印证了这一点。可见,欧洲在空间规划实践中已经意识到发展在空间上并不连续,在全球化持续深入的今天,某一区域/城市在关系网络中的位置可能比其地理位置更为重要。根据关系地理学观点,空间相互作用可能发生在近处或“一定距离下”,某一地域的品性会随着其所处关系网络的变迁而不断变化,因而其“发展”通常并不是单一时间维度下的单向轨迹,而是在不同时间维度下不同网络“曲折重叠”“循环往复”“螺旋上升”或“线性延伸”轨迹复合叠加的结果[28]。因而,基于线性增长而制定的空间规划就容易出现偏误,进而难以科学指引地区发展。在2017年欧盟委员会发布的凝聚政策报告中,其发现在全球化背景下只有一部分地区能够引领区域发展,其他地区则并未享受到全球化红利,反而承受了全球化成本,经济未能成功转型,陷入“中等收入陷阱”,这再度印证了关系地理学的观点,即不能在全球价值链网络中占据一席之地的地区将被剥离在全球化之外,更容易陷入停滞或衰退。显然,对这一问题的解决离不开关系地理学等后结构主义地理学的支撑,其理论有助于规划者更好地理解科技革命与全球化下区域发展的时空格局演化,也有助于丰富个体与企业等体验与使用空间的层次,进而提升空间规划的科学性与前瞻性。在此后的空间规划中后结构主义地理学也得到了更多的运用[29]。
3.2 德国空间规划及其地理学基础
3.2.1 德国空间规划嬗变 德国为现代空间规划起源地之一,是欧洲乃至全球范围内空间发展最为均衡的国家。德国空间规划最早起源于居民点规划,在大规模工业化与城镇化的推动下,为满足城市建设与区域协调发展需求,空间规划在规划范围、统筹要素与管制政策方面不断拓展完善,在二战后逐步建立了覆盖全国的多层次的空间规划体系。目前,德国的空间规划体系分为5个层级,自上而下依次为欧盟→联邦→州→地区→城镇。其中,欧盟层面主要为ESDP所确定的发展原则;在联邦层面则主要依托《联邦空间秩序规划法》提出方向性、总结性的发展愿景;州层面在全国空间规划总体框架及相关法律规定下,因地制宜对全国空间发展规划进行细化与具体化,形成州级空间规划,这一规划除对财政支出、公共设施、基础设施等作出决定性安排外,其余多为指导性内容;地区为州级空间规划的进一步明确化和具体化,更注重协调各城镇发展目标与空间边界;城镇规划则是在上级规划指导下编制土地利用规划与建造规划,其作用类似于中国的城市总体规划与控制性详细规划[30]。这一空间规划体系中,前三层次侧重于宏观层面的发展目标与调控政策,后两层次则直接指导地区具体建设,自上而下不断深化与细化,同时保证底层规划所划定的空间开发利用方案能够贯彻上层规划的原则与发展理念。3.2.2 德国空间规划中的地理学基础及作用 从全国尺度而言,自两德统一以来,德国政府发布了3个联邦级空间规划文件,分别为1993年的《空间规划政策指导框架》、2006年的《德国空间战略规划》及2016年的《德国空间战略规划》,其确定了德国空间规划的原则与纲领,指引了国土空间协调发展的方向,重点以其进行探讨。大体上,德国空间规划的指导思想经历了从追求代内公平到代际公平再到强调提升核心竞争力的过程。这一转变过程中,地理学不仅是剖析国际国内形势演变的得力工具,更是制订优化调控政策方针的坚实支撑。在2006年德国空间战略中,其提出了3项原则:① 增长与创新,分别关注大都市区、大都市之外地区、潜在衰退地区的经济增长与创新;② 确保公共利益最大化,包括保障公共服务质量、公共服务设施配置应符合中心地理论;③ 强化资源保护及重塑文化景观,包括推动土地集约利用、保护开放空间与自然资源、重塑文化景观。可见,这一时期主要是对传统地理学理论的应用,尤其是对于中心地理论这一德国原创理论的重视。而在2016年德国空间战略规划中[31],其提出了5项原则(图4):① 提升竞争力,包括推动大都市圈建设、强化区域联系、推动衰退地区复兴、确保基础设施的联系和流动性;② 公共服务均等化,包括持续采用中心地理论进行公共服务配置、建立合作体系、强化乡村地区公共服务供给、确保可达性;③ 推动土地可持续利用,包括减少空间利用冲突、建立大尺度开放空间网络、重塑文化景观、减少占用新的土地、确保矿产等地下资源的可持续利用、海岸与海洋的可持续利用;④ 应对气候变化及调整能源体系,包括调整空间结构以应对洪水、热浪,建设节约能源与减少交通的居民点等;⑤ 开发可再生能源并构建能源网络。可见,在重视中心地理论、工业区位论等传统地理学理论的同时,关系地理学也得到了一定体现,如强化区域联系、确保基础设施的联系和流动性等。此外,最早由德国地理****C.Troll提出的景观生态学理论对于土地可持续利用及应对气候变化也具有重要的指导意义。可见,随着空间规划的嬗变,支撑其的地理学理论也在不断发展。
图4
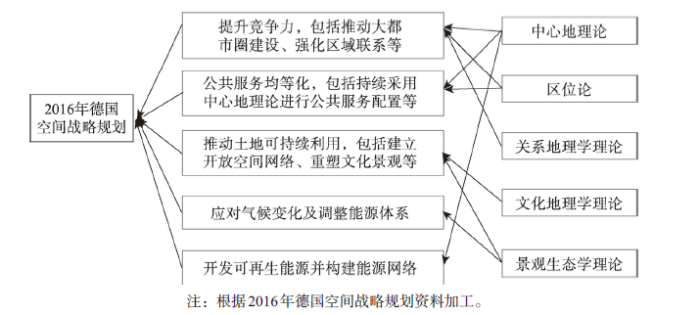 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图42016年德国空间战略规划发展原则及其地理学基础
注:根据2016年德国空间战略规划资料加工。
Fig. 4Development principles and geographical basis of German spatial strategic planning in 2016
综上可见,中心地理论、工业区位论、农业区位论及景观生态学等理论在德国空间规划中起到了举足轻重的作用,这些理论的贡献者分别为Christaller W/L?sch A、Weber A、Von Thünen J H、Troll C,均为德国****。就发展结果而言,在各种理论尤其是中心地理论的指引下,德国通过推动公共服务设施合理布局并强化基础设施建设,同时解决要素与市场分割来推动人口合理布局,最终成为空间发展最为均衡的国家之一。可见,提升本国地理学研究水平是推动本国空间规划高质量发展的基石。然而,在全球化这一浪潮中,德国地理****的研究并未有太多亮眼的成果,因而其对空间规划的支撑水平也没有显著提升。在地理学迈向制度、文化及关系转向过程中,德国****似乎并未跟上这一步伐,对于全球价值链与关系地理学的研究不足,在空间规划中仍以传统理论为主导,过于追求均衡发展。这在一定程度上导致了德国缺失与其经济体量相对应的全球城市(Global City),在新一轮全球产业变革中缺乏相应话语权,尤其在智能产业方面远远落后于中美两国,经济社会的可持续发展面临挑战。在2016年空间战略规划中,这一问题已经得到一定程度的修正,关系地理学的初步应用即是证明。但在全球化导致地区分化愈演愈烈的背景下,仍需紧随全球趋势提升地理学研究水平并以此指引空间规划实践,方可有效保障空间规划目标的实现。
3.3 日本空间规划及其地理学基础
3.3.1 日本空间规划嬗变 日本的空间规划包括国土空间规划、土地利用规划与城市规划,其中全国范围的空间规划即为国土空间规划。截止目前,日本共发布了七版国土空间规划,其空间规划以服务国家战略需求为目的,随着国际国内形势的变化而不断调整,指导思想从早期的效率优先过渡到注重公平再到坚持可持续发展,规划目标与策略也不断变化(图5)。早期的国土空间规划以服务经济社会发展为目标,后期则更为注重居民生活水平的提升以及生态环境的可持续发展[32]。具体而言,第一、第二次国土空间规划以发展为主导,服务经济发展是其主要目标。随着经济发展水平的提升以及生态环境问题的日益凸显,第三、第四次国土空间规划的重心回归至以人为本,提升国民生活水平成为关注的核心。随着大规模国土开发的基本结束,国土规划的重点由开发转向管理,为顺应这一趋势,日本将国土开发规划更名为国土形成规划,第五、第六及第七次国土形成规划围绕提升国土空间利用质量及可持续发展能力展开,重点关注创新转型、扩大开放及文化自立。在空间策略方面,早期空间规划以一极(东京)一轴(环太平洋发展轴)为重点地区,随着人口、经济等向东京一极集中现象愈演愈烈,第四次空间规划明确提出形成“多极分散型国土结构”,第五次空间规划进一步细化为“一极四轴”空间结构,希望以此推动空间均衡发展;随着全球化加速与老龄化形势越发严峻,第六次空间规划提出“自立的多样性广域地方圈”,第七次空间规划进一步提出构建“对流促进型”国土空间结构[33],更为注重区域文化特色培育与生活氛围营造,藉此缓解中小城市人口外流,推动区域可持续发展。图5
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图5日本国土空间规划嬗变与地理学演变
Fig. 5The relationship between Japanese territorial spatial planning transmutation and the evolution of geographical research
3.3.2 日本空间规划中的地理学基础及作用 与欧洲、德国相比,日本地理学界与规划界之间的联系更为紧密,许多地理****直接参与了日本空间规划的研究与编制,这在很大程度上推动了二者的融合共进[34]。从日本地理学的发展历程而言(图5),在二战后至20世纪70年代,地理学主要是对于西方地理学理论的引进、吸收与应用,重点关注区域政策制定、产业区位选择等问题,包括工业区位论、中心地理论等的引入,结合日本地域特色的实践对于第一、第二次国土空间规划的施行起到了重要的指导与支撑作用。20世纪70—80年代为日本地理学的快速发展期,日本****在消化国际理论的基础上结合地区实际进行了卓有成效的创新工作,其中又以藤田昌久与克鲁格曼合作开创的新经济地理学最为知名,其不仅提升了经济地理学理论深度,对于空间规划也起到了积极的指导作用。进入90年代,日本****更为关注全球化下的区域应对与可持续发展问题,形成美丽的国土面貌成为地理学研究与空间规划的共同目标。21世纪以来,日本****的研究紧跟地理学的制度、文化与关系转向,并成为“对流促进型”国土空间结构的理论基础。总体而言,地理学在日本空间规划嬗变中发挥了无可取代的作用,立足开放的理论创新与因地制宜的规划实践是日本经济成功转型的关键支撑,也是形成以东京、大阪与名古屋三大城市群为主导的国土开发格局的坚实基础。第七次国土空间规划提出的“对流促进型”国土空间结构是日本地理学研究成果的集中体现(图6),将国土空间划分为城市地区、农村地区与科教地区,3个地区之间通过产业联动、产学联动与农业信息化进行对流,同时高度重视每个地区与国际的对流,形成“对流促进型”国土空间结构,以此实现地理空间与知识、信息空间的深度协作与融合。其中对科教地区的划分是首次将创新落实到地理空间上,这与日本****对新经济地理学、全球生产网络与产业空间组织的研究密不可分,对日本而言,创新是驱动经济增长的核心要素,科教地区的提出是保障创新的极重要举措。同时,“对流促进型”国土空间结构的提出则反映出日本对于关系地理学的理解与把握,即对某一地区而言,在全球关系网络中的“位置”是决定其未来发展的核心因素,这一关系网络不仅包括物质空间的流动,也包括非物质空间的联动,因而通过关系网络的构建与完善实现区域与全球的“对流”成为决定区域未来的核心因素。总体而言,与国际地理学前沿接轨并结合空间规划实践进行创新是日本地理学研究的特色,而这一特色也很好地支撑了空间规划的实践与发展。
图6
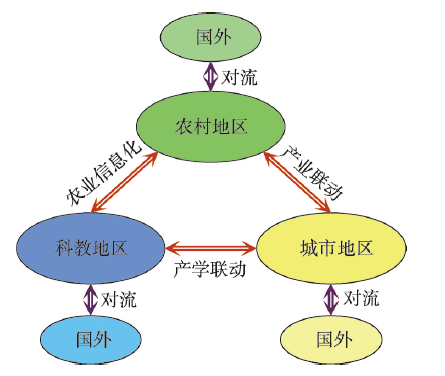 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图6日本对流促进型国土空间结构
注:根据日本第七次国土规划(2015)资料转绘。
Fig. 6Convective territorial and spatial structure of Japan
4 结论与展望
本文从地理学视角出发,采用文献计量与典型案例分析方法,在对国外空间规划研究与实践进行深入剖析和系统总结的基础上,明确对中国空间规划改革的启示,主要结论如下:(1)地理学作为一门专注于“空间”的科学,其理论与方法在空间规划改革中不可或缺。传统的地理学理论在空间规划中仍起着中流砥柱的作用,而关系地理学等后结构主义地理学理论在空间规划中的应用也日渐广泛,同时,地理学还为空间规划提供了方法与技术支撑。如文中所揭示,欧洲曾经一度仅仅关注城市更新与景观再造,迷失了城市发展的目标与方向,最终在关系地理学等理论指引下迎来了空间规划复兴。欧盟、德国的实践更是证明了地理学在空间规划中的无可取代。对关系地理学等理论的忽视是导致欧盟区域均衡发展受挫的重要因素,其同样导致了德国在产业变革上的相对滞后。随着全球化的持续深入,区域不再是一个孤立个体,其意义由被其所位于的各种关系网络中的“位置”所赋。因此,基于孤立视角与线性增长的传统空间规划往往难以满足当下经济社会发展需求,拓展地理学研究内容广度与空间尺度成为编制高质量空间规划的保障。区域发展已经不仅仅是一种经济现象,而逐步演变为经济、社会、文化、生态、环境等多要素的多尺度地理集成,探寻地方全球化、全球地方化大趋势下区域不同要素的演变趋势与规划策略不仅是推动区域发展的必然,也是保障区域可持续发展所必需。
(2)因地制宜提升本土地理学研究水平是推动中国空间规划科学化、合理化的基石。结合案例可知,本土地理学研究水平在很大程度上决定了空间规划的效果,德国的地理学研究成果推动其成为空间发展最为均衡的国家之一,日本的地理学研究成果则支撑其形成了以三大城市群为主导国土开发格局并推动了经济的成功转型升级。对中国而言,吸收国外地理学理论并结合实际情况进行本土理论、方法及实践创新是推动空间规划科学发展的必然途径。同时,国外空间规划的实践对中国也具有很强的借鉴意义。譬如,采用中心地理论对公共服务与重大基础设施布局,以推动空间均衡发展,基于景观生态学理论等推动构建开放空间网络,以及依托文化特质推动区域自立发展等。值得注意的是,对于部分长期困扰中国空间规划的难题,国外同样未能很好地解决。最典型的即为人地冲突,国外在很大程度上通过污染产业的国际转移“回避”了这一难题,但对中国而言,高强度、高密度、时间高度压缩的工业化与城镇化进程导致了空前激烈的人地冲突,而地域发展的不均衡使得中国难以通过产业转移回避这一问题。因而,这就要求地理****进一步深入挖掘人地关系地域系统的内在机理、演化特征及主控要素,以此为中国空前激烈人地冲突的解决提供科学指引,走出一条中国特色的空间规划改革和空间治理现代化之路。
(3)构建层次分明、功能互补的空间规划体系是推动空间规划目标性与操作性相统一的保障。综合德国与日本的空间规划体系可见,其顶层规划主要为发展原则与目标制定,为柔性规划;底层则为刚性的土地利用规划与建造规划等,直接指导规划建设;中间层则为不同地区发展目标的协调。与中国空间规划改革对接,本文建议构建全国—省域级—市县—乡镇四级规划体系,其中全国层次空间规划以可持续发展为导向,以实现空间资源永续利用为目标,在综合国家战略及基本原则基础上,进一步结合生态环境承载力、景观生态学等理论对国土资源进行统筹,尤其关注国家重点生态功能区识别与生态红线划定;省级层次空间规划以协调为导向,以落实全国国土空间规划为目标,主要依托全球价值链与区域发展理论等协调不同城市的发展目标与方向,同时统筹重大基础设施与公共服务设施的布局,以此推动区域协同发展并提升国际竞争力;市县与乡镇层次空间规划均以落实上层国土空间规划为导向,其中市县层次空间规划侧重在区位论、中心地理论及产业集群等理论指引下,科学确定开发边界与空间布局,为发展目标的实现提供空间依托,乡镇层次空间规划则在沿袭既有控制性详细规划、修建性详细规划的基础上,强化对空间绩效的研究,以此进一步增强规划的科学性。各层次规划相互协作,确保空间规划有效服务于国家战略的顺利实现。
结合研究启示与中国空间规划实践,本文认为当前空间规划改革中应对如下3个方面给予足够关注。① 应重视关系地理学在空间规划中的应用,正如人是一切社会关系的总和,城市的“品性”也是由其所处的各种关系网络中的“位置”所赋予的。伴随着全球/区域价值链的重构与分化,核心城市的持续扩张与边缘城市的相对收缩成为现实图景,对于不同城市尤其是边缘城市而言,若不能在全球/区域价值链中找准自身定位,发挥自身无可替代的特殊作用,则其衰落就难以避免。② 应更为注重以人为本,尤其在当前生育率持续走低、人口老龄化不断加剧的现实下,适度的人口规模与合理的人口结构已经成为地区可持续发展的基础,这也可由当前愈演愈烈的“抢人大战”所印证。因而,空间规划一方面应着重为城市居民提供多样化的工作岗位与高质量的生活水准,以此吸引人口流入;另一方面空间规划在编制中应强化当地居民参与,注重融入地区文化特质,以此破解“千城一面”,着力打造地域特色品牌,以形成长久的人口吸力。③ 应更为注重从系统、综合的视角进行空间治理。正如前文所述,区域发展已经演变为经济、社会、文化、生态、环境等多要素的多尺度地理集成,割裂或片面的空间治理政策其效果可能难如人意。譬如,希望通过人口疏解以解决城市问题,事实上,根据柯布—道格拉斯生产函数
总而言之,地理学作为一门经世致用的科学,其综合性、复杂性及多尺度特征对于空间规划改革不可或缺。地理学应面向这一国家重大需求,不断创新理论、方法与技术途径,为空间规划改革和空间治理现代化提供理论指引与实践支撑,以此为国家经济社会与生态环境的协调可持续发展做出应有的贡献。
参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201711001URL [本文引用: 1]

Geography is a subject to explore spatial distribution, time evolution and regional characteristics of geographical elements or geographical complexes. Geography is unique in bridging social sciences and natural sciences, and has characteristics of comprehensiveness, interdisciplinary research and regionalism. With the development of geographical science technology and research methods, geography is in the gorgeous historical process towards geographical science. Research themes of geography are focusing on the comprehensive research on the earth surface. The research paradigms of geography are shifting from geography knowledge description, coupling pattern and process, to the simulation and prediction of complex human and earth system. The development of Chinese geography needs to be rooted in the major needs of national strategy, and plays important roles in the studies of urbanization development, coupling ecological processes and services, water resources management and geopolitics. Under the country's major needs, China's geography tends to achieve the geography theory innovation, new method and technology application and developed disciplinary system with Chinese characteristics, and make more contribution to national and global sustainable development.
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201711001URL [本文引用: 1]

Geography is a subject to explore spatial distribution, time evolution and regional characteristics of geographical elements or geographical complexes. Geography is unique in bridging social sciences and natural sciences, and has characteristics of comprehensiveness, interdisciplinary research and regionalism. With the development of geographical science technology and research methods, geography is in the gorgeous historical process towards geographical science. Research themes of geography are focusing on the comprehensive research on the earth surface. The research paradigms of geography are shifting from geography knowledge description, coupling pattern and process, to the simulation and prediction of complex human and earth system. The development of Chinese geography needs to be rooted in the major needs of national strategy, and plays important roles in the studies of urbanization development, coupling ecological processes and services, water resources management and geopolitics. Under the country's major needs, China's geography tends to achieve the geography theory innovation, new method and technology application and developed disciplinary system with Chinese characteristics, and make more contribution to national and global sustainable development.
DOI:10.11820/dlkxjz.1999.04.001URL [本文引用: 1]

The theoretical basis of this paper is the PRED interaction in regional or inter regional time space scales. The factors that restrict regional social and economic development are very different in different regions because the PRED relationships have their own natures in the social and economic activities of various regions. The nature of regional sustainable development lies in the way to harmonize their internal relations and to approach the goal of rational allocation among population, material, energy and information flow in PRED process. This is the essential to Human Nature relationship. This paper take the Human Nature system as the theoretical basis. At first, the author studies the work beginning with the perception process, structure, function, dynamic evolution of Human Nature relationships. Secondly, the mechanism of regional PRED coordination and theoretical models and methods of regional sustainable development are discussed. Thirdly, the author inquire into the theoretical study of system regulation.
DOI:10.11820/dlkxjz.1999.04.001URL [本文引用: 1]

The theoretical basis of this paper is the PRED interaction in regional or inter regional time space scales. The factors that restrict regional social and economic development are very different in different regions because the PRED relationships have their own natures in the social and economic activities of various regions. The nature of regional sustainable development lies in the way to harmonize their internal relations and to approach the goal of rational allocation among population, material, energy and information flow in PRED process. This is the essential to Human Nature relationship. This paper take the Human Nature system as the theoretical basis. At first, the author studies the work beginning with the perception process, structure, function, dynamic evolution of Human Nature relationships. Secondly, the mechanism of regional PRED coordination and theoretical models and methods of regional sustainable development are discussed. Thirdly, the author inquire into the theoretical study of system regulation.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201807002URL [本文引用: 1]

Since the 20th century, geography came into being with distinctive disciplinary characteristics by sustained effort of geographers. This paper puts forward predicament from cognitive and thought in the new era, and depicts new geographic characteristics from five aspects: new technology, new orders, new data, new approaches and new driving factors. According to new content of geo-regionality and new approaches of geo-comprehensiveness, the paper proposes that complexity research would be a successful new path in geography, and the complexity would be the third characteristic of geography. Then, the paper details some complex spatial patterns, complex time processes and complex spatio-temporal mechanisms in geography research. Based on the concept of a geographic complex system, this paper presents core issues and corresponding complex research tools. Finally, the paper puts forward new challenges and new requirements for geography in the new era.
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201807002URL [本文引用: 1]

Since the 20th century, geography came into being with distinctive disciplinary characteristics by sustained effort of geographers. This paper puts forward predicament from cognitive and thought in the new era, and depicts new geographic characteristics from five aspects: new technology, new orders, new data, new approaches and new driving factors. According to new content of geo-regionality and new approaches of geo-comprehensiveness, the paper proposes that complexity research would be a successful new path in geography, and the complexity would be the third characteristic of geography. Then, the paper details some complex spatial patterns, complex time processes and complex spatio-temporal mechanisms in geography research. Based on the concept of a geographic complex system, this paper presents core issues and corresponding complex research tools. Finally, the paper puts forward new challenges and new requirements for geography in the new era.
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/S0022-1996(98)00075-0URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.marpol.2008.03.021URL [本文引用: 1]

Abstract
During the past 10 years, the evolution of marine spatial planning (MSP) and ocean zoning has become a crucial step in making ecosystem-based, sea use management a reality. The idea was initially stimulated by international and national interest in developing marine protected areas, e.g., the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park. More recent attention has been placed on managing the multiple use of marine space, especially in areas where conflicts among users and the environment are already clear, e.g., in the North Sea. Even more recent concern has focused on the need to conserve nature, especially ecologically and biologically sensitive areas, in the context of multi-use planning of ocean space. Despite academic discussions and the fact that some countries already have started implementation, the scope of MSP has not been clearly defined. Terms such as integrated management, marine spatial management, and ocean zoning are all used inconsistently. This is one of the reasons why its importance is not more seriously reflected at the levels of policy and decision-making in most countries. This article attempts to deal with this problem. It describes why MSP is an essential step to achieve ecosystem-based sea use management, how it can be defined and what its core objectives are. The article concludes with an analysis of the use and achievements of MSP worldwide, with particular focus on new approaches in Europe.DOI:10.1016/j.jenvman.2008.07.004URL [本文引用: 1]

Abstract
Increased development pressures on the marine environment and the potential for multiple use conflicts, arising as a result of the current expansion of offshore wind energy, fishing and aquaculture, dredging, mineral extraction, shipping, and the need to meet international and national commitments to biodiversity conservation, have led to increased interest in sea use planning with particular emphasis on marine spatial planning. Several European countries, on their own initiative or driven by the European Union's Marine Strategy and Maritime Policy, the Bergen Declaration of the North Sea Conference, and the EU Recommendation on Integrated Coastal Zone Management, have taken global leadership in implementing marine spatial planning. Belgium, The Netherlands, and Germany in the North Sea, and the United Kingdom in the Irish Sea, have already completed preliminary sea use plans and zoning proposals for marine areas within their national jurisdictions. This paper discusses the nature and context of marine spatial planning, the international legal and policy framework, and the increasing need for marine spatial planning in Europe. In addition, the authors review briefly three marine spatial planning initiatives in the North Sea and conclude with some initial lessons learned from these experiences.DOI:10.1126/science.1149345URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.marpol.2010.02.001URL [本文引用: 1]

Abstract
The declining health of marine ecosystems around the world is evidence that current piecemeal governance is inadequate to successfully support healthy coastal and ocean ecosystems and sustain human uses of the ocean. One proposed solution to this problem is ecosystem-based marine spatial planning (MSP), which is a process that informs the spatial distribution of activities in the ocean so that existing and emerging uses can be maintained, use conflicts reduced, and ecosystem health and services protected and sustained for future generations. Because a key goal of ecosystem-based MSP is to maintain the delivery of ecosystem services that humans want and need, it must be based on ecological principles that articulate the scientifically recognized attributes of healthy, functioning ecosystems. These principles should be incorporated into a decision-making framework with clearly defined targets for these ecological attributes. This paper identifies ecological principles for MSP based on a synthesis of previously suggested and/or operationalized principles, along with recommendations generated by a group of twenty ecologists and marine scientists with diverse backgrounds and perspectives on MSP. The proposed four main ecological principles to guide MSP—maintaining or restoring: native species diversity, habitat diversity and heterogeneity, key species, and connectivity—and two additional guidelines, the need to account for context and uncertainty, must be explicitly taken into account in the planning process. When applied in concert with social, economic, and governance principles, these ecological principles can inform the designation and siting of ocean uses and the management of activities in the ocean to maintain or restore healthy ecosystems, allow delivery of marine ecosystem services, and ensure sustainable economic and social benefits.DOI:10.1016/j.marpol.2008.03.012URL [本文引用: 1]

Abstract
The abrupt decline in the sea's capacity to provide crucial ecosystem services requires a new ecosystem-based approach for maintaining and recovering biodiversity and integrity. Ecosystems are places, so marine spatial planners and managers must understand the heterogeneity of biological communities and their key components (especially apex predators and structure-forming species), and of key processes (e.g., population connectivity, interaction webs, biogeochemistry) that maintain them, as well as heterogeneity of human uses. Maintaining resistance and resilience to stressors is crucial. Because marine populations and ecosystems exhibit complex system behaviors, managers cannot safely assume they will recover when stressors are reduced, so prevention is a far more robust management strategy than seeking a cure for degraded systems.DOI:10.1068/a35111URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 2]
DOI:10.1016/S0169-2046(02)00218-9URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1080/0965431032000146169URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1068/a40208URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1080/0964401042000310178URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1068/c0416jURL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/S0962-6298(99)00085-2URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
