 ,1
,1Comparison of different single cell whole genome amplification methods and MALBAC applications in assisted reproduction
Yaxin Yao1, Yongfu La2, Ran Di1, Qiuyue Liu1, Wenping Hu1, Xiangyu Wang1, Mingxing Chu ,1
,1通讯作者:
编委: 方向东
收稿日期:2018-04-7修回日期:2018-06-9网络出版日期:2018-08-16
| 基金资助: |
Received:2018-04-7Revised:2018-06-9Online:2018-08-16
| Fund supported: |
作者简介 About authors
姚雅馨,博士,助理研究员,研究方向:动物遗传育种E-mail:
喇永富,博士研究生,专业方向:动物遗传育种E-mail:

摘要
关键词:
Abstract
Keywords:
PDF (482KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
本文引用格式
姚雅馨, 喇永富, 狄冉, 刘秋月, 胡文萍, 王翔宇, 储明星. 不同单细胞全基因组扩增方法的比较及MALBAC在辅助生殖中的应用[J]. 遗传, 2018, 40(8): 620-631 doi:10.16288/j.yczz.18-091
Yaxin Yao, Yongfu La, Ran Di, Qiuyue Liu, Wenping Hu, Xiangyu Wang, Mingxing Chu.
单细胞研究是当前生命科学研究的重要方向之一。许多关键的生命活动都和细胞间的个体差异密切相关,许多重要的生命科学和医学问题所能依赖的样品往往也是极少数细胞。在单细胞的基因组学研究中,由于细胞内DNA的含量极少,因此首先需要通过全基因组扩增技术将DNA进行扩增。全基因组扩增(whole genome amplification, WGA)是一种对极低起始量的基因组进行非选择性扩增的技术,其目的是在没有序列倾向性的前提下大幅度增加DNA总量,以满足后续分析需求[1]。近年来,随着二代测序的发展和全基因组分析的不同需求,不同的WGA技术得到了相应的开发。本文综述了全基因组扩增技术的研究应用,并且比较了各种WGA技术的扩增效果,旨在为相关领域的科研工作提供借鉴参考。
1 不同单细胞全基因组扩增方法的介绍
全基因组扩增技术从1992年出现至今已产生了多种方法,主要可以分为3类:一类为基于聚合酶链式反应(polymerase chain reaction, PCR)技术的WGA方法,如引物延伸预扩增(primer extension preamplification PCR, PEP-PCR)和简并寡核苷酸引物PCR (degenerate oligonucleotide primed PCR, DOP- PCR);一类为恒温全基因组扩增反应,如多重置换扩增(multiple displacement amplification, MDA);另一类为多次退火环状循环扩增(multiple annealing and looping-based amplification cycles, MALBAC)。随着高通量测序技术的发展,科研人员在细胞分选技术、核酸扩增技术、信噪比提高等方面进行不断优化和改进,进一步开创了乳液全基因组扩增(emulsion whole-genome amplification,eWGA)、通过转座子插入的线性放大(linear amplification via transposon insertion, LIANTI)、微流体反应器法单链测序(single- stranded sequencing using microfluidic reactors, SISSOR)等技术。1.1 PEP-PCR
在单细胞WGA方法中,PEP-PCR是使用较早的一种方法。Zhang等[2]最早应用PEP-PCR方法实现了单个单倍体细胞基因组的全扩增。其基本原理是使用15个碱基长的随机引物在37℃进行较长时间的退火,然后缓慢升温至55℃进行长时间的引物延伸,如此反复多个循环。Anchordoquy等[3]对其进行了改良优化,包括对模板DNA的提取方法、反应循环条件的优化以及高保真聚合酶的使用等。但是由于PEP-PCR方法使用随机引物以及较为不严格的 PCR循环参数,因此可能导致不均衡的扩增[4, 5]以及较大程度上限制了该方法的应用。目前,该方法的研究报道较少。María等[6]利用PEP-PCR方法检测人类亮氨酰氨肽酶(leucyl aminopeptidase, LNPEP)基因编码的胰岛素氨基肽酶rs4869317多态性,同时利用限制性内切酶消化检测验证该方法,发现以上两种方法结果一致。1.2 DOP-PCR
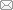
与PEP-PCR类似,DOP-PCR也是一种基于PCR技术的全基因组扩增方法,最早由Telenius等[7]提出。其基本原理是使用部分简并的引物进行PCR反应(引物中间部分含有6个随机碱基),在最初的几个循环过程中使用较低的温度(25℃)进行退火以确保引物与模板结合,并缓慢升温至引物延伸温度进行引物延伸,完成最初几个循环后使用相对较高的退火温度(55℃)进行多循环常规PCR反应[8](图1)。美国Sigma-Aldrich公司的GenomePlex Single Cell Whole Genome Amplification Kit就是基于DOP-PCR技术研发出来的。尽管DOP-PCR技术具有简单、快速和廉价的优势,但是该技术具有灵敏度低和错误率高等不足[8]。因此,Konstantin等[9]在DOP-PCR技术的基础上通过调整引物设计以及热稳定DNA聚合酶对该技术进行改进,从而发明了一种改进的DOP- PCR (improved degenerate oligonucleotide-primed PCR, iDOP-PCR)技术,该技术与传统的DOP-PCR技术相比具有更高的扩增质量和效率。图1
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图1简并寡核苷酸引物PCR原理示意图
含有6个随机碱基(N)的引物首先与模板结合,然后在适当的温度下从5°端向3°端延伸形成单链DNA,之后引物从单链3°端结合进行延伸最终形成双链DNA。参考文献[8]修改绘制。
Fig. 1Schematic of the degenerate oligonucleotide-primed polymerase chain reaction
1.3 MDA
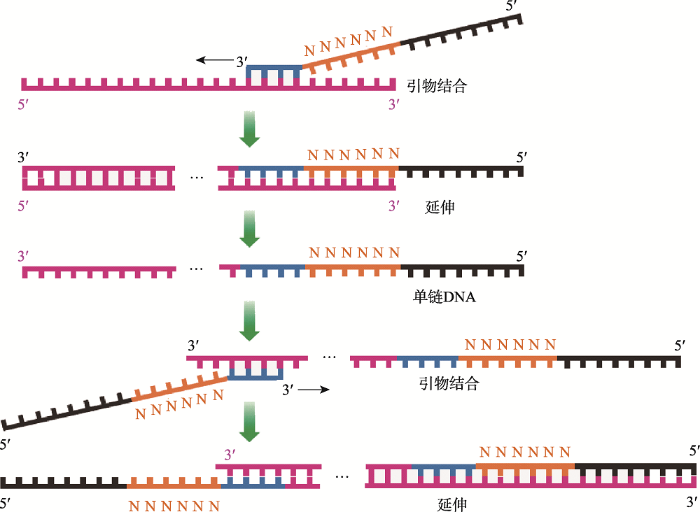
MDA出现较晚,最早由Dean等[10]以传统的WGA技术为基础改进而成。该方法首先由随机6碱基引物在多个位点与模板DNA退火,然后phi29 DNA聚合酶在DNA的多个位点同时开始复制;复制合成的DNA取代模板的互补链,同时被置换的互补链又成为新的模板来进行扩增(图2)。因此,利用该技术可以获得大量高分子量的DNA。由于MDA是恒温扩增,所以存在一定的非特异性扩增问题。此外,该方法对模板质量的要求相对较高,在非最佳实验条件下亦可导致非均衡扩增[11]。Gilbert等[12]基于MDA技术发明了一种用于进行多重置换扩增反应的方法试剂盒和系统,该试剂盒中包括几种聚合酶、引物和纯化试剂,在进行扩增时将核酸与反应液(寡核苷酸引物与几种聚合酶以及纯化试剂按比例混合)混合之后按照扩增产物所需条件进行扩增,从而使得该方法更为简单快捷。图2
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图2多重置换扩增原理示意图
首先含有6个随机碱基(N)的引物在恒温条件下与基因组随机退火,并在具有强链置换活性的phi29 DNA 聚合酶的作用下发生链置换扩增反应,置换产生的单链序列又可与随机引物任意退火延伸,形成超分支扩增结构。参考文献[8]修改绘制。
Fig. 2Schematic of multiple displacement amplification
1.4 MALBAC
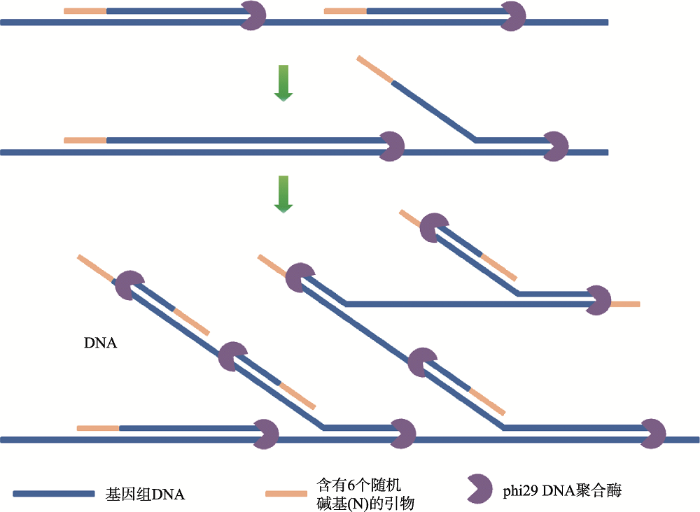
2012年底,谢晓亮等在Science杂志上连续发表两篇应用其新发明的WGA 方法进行单细胞测序研究的文章,引出“多次退火环状循环扩增技术” (MALBAC)这一全新的WGA方法[11]。MALBAC结合了MDA与PCR方法的特点,使用35 nt长的引物由一段固定的27 nt通用引物序列和8 nt随机碱基序列(N8)组成。在0℃时,8 nt随机碱基序列与模板随机结合,梯度升温至65℃后在具有链置换活性的DNA聚合酶作用下发生链置换聚合反应,得到一系列长度不一的(0.2~2.0 kb)半扩增子(semi amplicons);在94℃变性、0℃退火以及65℃延伸循环后,以上一循环中的半扩增子为模板形成了两端具有互补结构(27 nt)的全扩增子(amplicons);随后降低温度至58℃使得到的扩增子两端互补形成环状结构,从而可以避免引物与其进行结合导致指数扩增,因此可以很大程度上保证该循环发生的是线性扩增。在经过线性扩增循环后可得到大量全扩增子并作为指数扩增反应的模板,并使用该27 nt通用引物进行指数PCR反应,因此只有全扩增子才能得到有效扩增,从而实现对整个基因组的高效而又均衡的全扩增(图3)。应用该方法成功实现了单细胞水平的单核苷酸变异(single nucleotide variations, SNVs)以及拷贝数变异(copy number variations, CNVs)的研究[13]。由于MALBAC克服了对微量初始模板进行PCR放大过程中产生的偏倚,对单细胞全基因组扩增具有很高的覆盖率(93%)和均衡性,所以一经问世便在业内引起巨大轰动。图3
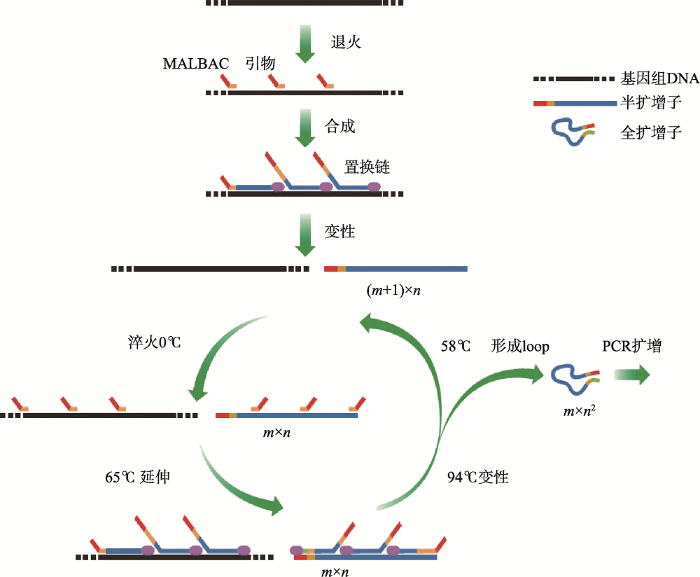 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图3多次退火环状循环扩增技术原理示意图
首先35 nt长的引物与模板随机结合,梯度升温至65℃后在具有链置换活性的DNA聚合酶作用下发生链置换聚合反应,得到一系列长度不一的(0.2~2.0 kb)半扩增子;在94℃变性、0℃退火以及65℃延伸循环后,以上一循环中的半扩增子为模板形成了两端具有互补结构的全扩增子。m是温度循环的次数;n是结合的引物数量;(m+1)×n是第m个循环中存在的半扩增子的数量;m×n2是第m个循环中生成的所有扩增子的数量。参考文献[8]修改绘制。
Fig. 3Schematic of multiple annealing and looping-based amplification cycles
1.5 eWGA
eWGA利用微流控技术,将一个细胞的基因组片段分散在包含有几十万个皮升量级微型反应液滴的乳液中,其中每个液滴中含有约一个待扩增的DNA片段和用于等温MDA的其他原料。对整个乳液体系进行等温扩增时,每个分隔的液滴内都在进行独立的扩增反应。这些独立的反应之间虽然在动力学上存在显著差异,但是在这一受限体系内可以相继达到饱和。这样,每个片段的扩增比起传统的MDA反应,在均匀性上得到了显著改善,同时由于使用了高保真的聚合酶还可以保证扩增结果的高度准确性。实验结果表明,eWGA方法超越了以往的单细胞扩增方法,提供了更好的扩增均匀性、更完整的基因组覆盖率和最好水平的复制准确率,无需矫正即可准确检测单个细胞中尺寸更小的CNV并同时实现高精度的SNV检测。将该方法应用于单个癌症细胞中的CNV检测,最高尺寸分辨率可以达到250 kb。此外,该方法兼容常见的序列富集方法如外显子富集,具备广阔的医学诊断应用前景。综合考虑,eWGA使得从一个单细胞出发的精确CNV和SNV检测成为可能,是目前最好的单细胞全基因组扩增技术[14]。
1.6 LIANTI
LIANTI是一项经过改良的单细胞全基因组扩增方法。LIANTI法首先利用Tn5转座子结合LIANTI序列,形成Tn5转座复合体(含T7启动子),之后该复合体随机插入单细胞基因组DNA,经转座后,将DNA随机片段化并连接T7启动子。随后T7启动子行使体外转录功能,用转录获得大量线性扩增的转录本,转录本再经过逆转录之后得到大量的扩增产物,随后进行正常的建库测序操作。整个过程仅进行线性扩增,没有进行指数扩增,大大增强了扩增稳定性,降低PCR干扰。此外,该技术将测量拷贝数的空间分辨率提高了3个数量级(能在千碱基分辨率进行微CNV检测,基因组覆盖率可达到97%),助力更有效、更精准地检测出更多遗传疾病[15]。1.7 SISSOR
SISSOR利用微流体处理器将单个细胞染色体DNA的正负双链进行分离,并将百万碱基大小的DNA片段随机分割成大量的纳升级的组分,用于扩增和构建测序文库,从而实现对同源染色体的互补双链分别进行独立的测序。这样就能够进行Long- range单倍体的组装,并且还能利用冗余和单倍体型信息纠正测序错误。结果显示,该方法的纠错能力可以将单细胞测序错误率降低至10-8,并且单倍体片段平均可组装长度为500 kb,contig达到N50大于7 Mb。该方法能够获得精准的单细胞基因组序列以及单倍体信息以满足临床对基因组测序的不同需求。SISSOR是对单细胞测序技术的一次突破,将测序准确性提高了两个数量级。这项技术潜在的应用包括对患者血液中循环肿瘤细胞进行准确的检测,以及对体外受精的健康胚胎进行筛选和检测经过基因编辑的人体细胞[16]。综上所述,PCR 类全基因组扩增方法对样品质量要求相对较低且扩增效率高,但全基因组扩增产物片段较短,指数反应易导致所有片段的非均衡扩增;而 MDA法成功应用的前提是高质量基因组模板的获得,其扩增产物较为均衡且更有利于全基因组测序;但无论 PCR 类方法或是恒温全扩增方法,目前都存在一定的非特异性扩增现象,即使在较为严格的PCR反应条件下这一问题仍无法完全避免。MALBAC的扩增效率好于其他商业方法,因此适合用于单个细胞的分析,特别是生殖细胞的全基因组分析。
2 不同单细胞全基因组扩增方法的比较
WGA能对整个基因组进行扩增,从而满足后续分析的要求。然而,如何将基因组DNA进行均匀和精确的全基因组扩增具有极大的挑战性。扩增均匀性不够,将降低覆盖率和分辨率,并增加等位基因脱扣的几率;扩增精确性不够,则将导致大量假阳性结果。因此,全基因组扩增技术的优劣严重影响极少量DNA分析的精确度及准确性。De Bourcy等[17]对不同单细胞全基因组扩增方法进行了定量比较,通过比较均一性、错误率以及模板污染水平等评价了MDA、MALBAC和PEP 3种单细胞扩增方法的优劣,并且对3种方法的CNV分析、单核苷酸多态性(single nucleotide polymorphisms, SNPs)检测以及de novo全基因组拼接的效果进行了比较。研究发现,MDA的扩增产率越高,其扩增均匀性越低,MALBAC和PEP的扩增均匀性与扩增产率的关系相对于MDA没有那么敏感。另外,当扩增产率高于106时,MALBAC和PEP的覆盖度都高于MDA;而当扩增产率高于2.5×103时,MALBAC和PEP检测CNV的效果优于MDA。但是,当扩增产率小于5×106时,3种方法均不能很好地用于de novo拼接,拼接效果无差异。Nie等[18]在进行常规短串联重复序列(short tandem repeat, STR)分型之前加入全基因组扩增步骤,并从等位基因不平衡、等位基因丢失、伪等位基因、基因座丢失等4个方面比较了MDA和PEP两种全基因组扩增方法对微量DNA分型的效果。发现MDA扩增效率较高,但是等位基因丢失和伪等位基因严重;PEP技术分型正确率高于MDA技术,但小片段DNA优势扩增现象较严重;最后得出结论MDA技术不适用于STR分型。
eWGA相对于其他技术具有更好的扩增均匀性、基因组覆盖率和高精度的SNV检测[14]。LIANTI法消除了其他单细胞全基因组扩增方法中的非特异性启动和指数扩增,极大地降低了扩增偏差和误差。Chen等[15]分别利用LIANTI、MDA、MALBAC和DOP-PCR方法扩增人类皮肤成纤维细胞并进行系统比较,发现LIANTI扩增效率以及均匀性高于其他WGA方法,其中基因组覆盖率为97%,ADO为17%。在检测时LIANTI达到最低的CV值,从而达到最准确的CNV检测。常见的方法如DOP-PCR、MDA、MALBAC等需要用DNA聚合酶对细胞基因组进行大量的体外扩增,然后构建文库进行相对读长较短的高通量测序。这些方法有两个明显的缺点:(1)聚合酶的错误扩增产生假阳性;(2)短的序列读长几乎不包含任何单倍体类型信息。面对以上问题,张鹍教授团队研发了SISSOR技术,该技术能够准确进行单细胞基因组测序和单倍型分析[16]。以上3种方法虽然效率高、准确性好,但是由于出现较晚,目前应用较少。
目前,最经典的单细胞扩增方法主要包括MDA和MALBAC,MALBAC的扩增均一性优于MDA。以人类1号染色体为例,MALBAC的扩增均一,约93%的覆盖度,适合进行染色体分析,而MDA的扩增不均一,只有约70%的覆盖度,不适合进行染色体的CNV分析。另外,MALBAC检测到的杂合SNP明显多于MDA。Chen等[19]从 NCBI Short Read Archive 数据库中获得MDA和 MALBAC 扩增单精子的测序数据,同时获得 MALBAC 扩增的同一个人的血样测序数据,通过比较覆盖度、均一性、特异性和SNPs检出率可以客观比较二者的扩增效率。结果显示,MALBAC的覆盖度约为75%,而MDA的覆盖度仅为30%,MALBAC的覆盖度明显优于MDA,MALBAC的扩增产物浓度低于MDA。 He等[20]利用MDA和MALBAC技术对β地中海贫血基因分型、单核苷酸多态性以及拷贝数变异分析,并统计分析两种方法的扩增效率、敏感性以及等位基因脱扣率,发现MDA技术的扩增效率比MALBAC高,能更好地检测出SNPs。然而在单细胞水平进行CNV检测时发现MALBAC比MDA具有更好的稳定性,从而得出结论MALBAC更适合CNV检测而MDA更适合于SNV检测。
研究发现MDA的扩增产率与扩增偏倚性存在相关性,产率越高偏倚性越高。所以可通过控制MDA的扩增产率来降低偏倚性,而MALBAC和PEP的扩增偏倚性与产率的关系不明显;另外MALBAC和PEP更适合进行CNV分析;在序列拼接方面,3种方法并没有表现出明显的差异。综上所述,3种WGA技术各有优缺点,研究者应当根据需要选择合适的方法(表1)。
Table 1
表1
表1 不同单细胞全基因组扩增方法的优缺点比较
Table 1
| WGA技术 | 原理 | 优点 | 缺点 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MALBAC | 多重退火环状循环扩增技术结合恒温扩增与PCR法 | 操作简单,产量高,最低起始模板几个pg,结果可靠可重复,且灵敏度高,扩增均衡度高 | 起始模板量极低时扩增难度加大;模板拷贝数极低时易扩增偏差,可能出现非特异性扩增 | [12,16] |
| DOP-PCR | 部分随机引物法基于PCR法 | 操作简单,最低起始模板量达 50 pg,产物片段大小0.5~10 kb | 起始模板量低时扩增偏差大 | [6~8] |
| PEP-PCR | 完全随机引物法基于PCR法 | 对模板DNA质量要求低,操作简单,易改进,50 ng 起始模板可产0.2~0.5μ g产物,最低起始模板量可达5 pg | 产量低,保真性差;使用随机引物易产生扩增偏差及片段丢失 | [21,22] |
| MDA | 多重置换扩增恒温扩增法 | 产量高,50 ng起始模板量可产生10~20 μ g产物,最低起始模板量可达10 pg,忠实性好 | 起始模板量低时扩增偏差大,对模板质量要求高,可能产生非特异性产物 | [10,11] |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
等位基因脱扣(allele dropout, ADO)是单细胞全基因组扩增的特性之一,也是导致单碱基突变漏报的关键诱因。MALBAC与其他单细胞全基因组扩增方法比较,其ADO率较低。MALBAC的扩增均一性最高、等位基因脱扣率最低,所以对于CNV分析和SNV检测,MALBAC的效果最好。Liu等[23]利用MALBAC和MDA方法在单细胞水平上检测成肌纤维细胞样本的CNV和ADO,并用高通量测序结果进行评估比较。发现MALBAC和MDA对样本CNV检测成功率分别为100%和91.67%,总ADO分别为4.55%和22.5%。然而当提高起始模板浓度时,ADO率显著降低,并且这两种方法之间没有显著差异。基于二代测序技术的CNV分析结果,通常以变异系数(coefficient of variation, CV)作为评估其扩增均一性的关键参数,CV值越低,CNV分析的准确性越高。在同等条件下,利用MALBAC技术进行CNV分析的效果好于其他WGA方法,说明MALBAC比其他方法更适合于CNV分析。
3 MALBAC技术在辅助生殖中的应用
3.1 MALBAC技术在精子与卵细胞中的应用
从卵母细胞的减数分裂开始到与精子融合形成受精卵的过程中,每一个生殖细胞的健康对新生儿的健康都至关重要。在这个过程中,要经历父系和母系染色体交叉以及基因组重组,从而导致人类的进化以及遗传多样性。正常男子的精细胞非整倍体的概率为3%~4%,这是由于染色体异常导致的,该概率不会随着年龄的增长而改变。精子细胞的这种非整倍体会导致流产或家族遗传病的产生[24,25,26]。然而,卵母细胞发生非整倍性的概率显著高于精子细胞,并且会随着女性年龄的增长显著增高。卵母细胞非整倍性是导致婴儿出生率下降的一个主要因 素[27]。每个人的生殖细胞都具有独特的基因组,因此第一例单精子细胞测序技术应运而生[28, 29]。Lu等[28]使用MALBAC技术对一个亚洲男性的体细胞和99个精子进行全基因组扩增,并深度测序检测了个人全基因组,绘制了重组图谱。该研究发现随着常染色体非整倍体增加,重组频率降低;个体水平上基因区附近的重组率有降低的现象,证明了这一现象由分子机制决定而非自然选择的结果。该研究成功使用MALBAC在每次核减数分裂的基础上直接进行减数重组和染色体分裂错误检测,构建了迄今为止覆盖度最高的单精子基因图谱,证明了MALBAC技术可以用于基因组不稳定性和男性不育等研究。 Sha等[30]利用MALBAC和新一代测序技术对罗伯逊易位携带者单精细胞进行全基因组分析,全面描绘出来自两个罗伯逊易位携带者的88个单精子的染色体拷贝数,从而在全基因组鉴定染色体畸变,为研究染色体疾病提供了工具。研究表明基于MALBAC的测序技术可以用于人单个卵细胞基因组分析[8]。通过对来自同一个卵母细胞的第一极体、第二极体以及卵细胞进行测序,绘制了卵母细胞的重组图谱。通过第一极体和第二极体的基因组检测成功推测了卵细胞的基因组,包括非整倍体信息以及与疾病相关等位基因的SNPs,说明了基于MALBAC的胚胎植入前遗传学筛查可以准确、低成本筛选正常的卵细胞进行胚胎移植。
3.2 MALBAC用于胚胎植入前遗传学筛查/诊断
体外受精(in vitro fertilization, IVF)、胚胎植入前遗传学诊断(preimplantation genetic diagnosis, PGD)、胚胎植入前遗传学筛查(preimplantation genetic screening, PGS)可避免以往产前诊断方式可能的治疗性引产给母体带来精神和身体上的创伤,因而受到了生殖和遗传领域专家们的关注。常染色体显性遗传性多囊肾(autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease, ADPKD)是常染色体显性遗传病,具有家族聚集性,男女均可发病。利用MALBAC技术可在胚胎植入前进行基因诊断并筛选胚胎细胞,从而获得染色体正常的健康后代[31]。也有研究者利用3对年龄小于35岁的患病夫妇体外受精得到的23个处于卵裂期的胚胎,分别使用MALBAC、比较基因组杂交(comparative genomic hybridization, CGH)和 SNP 3种方法比较检测染色体非整倍性的效果。结果在23个胚胎中,18个胚胎的 MALBAC 检测结果与CGH或SNP一致,其中8个胚胎的3种方法检测结果完全一致。就整倍体而言,这23个胚胎中只有6个是二倍体。说明了MALBAC检测结果的可靠性及一致性优于其他两种方法,MALBAC的可靠性与一致性最好[32]。
PGS和PGD技术可以帮助患者选择无单基因病和染色体异常的胚胎。第二代测序技术(next generation sequencing, NGS)大大提高了PGD/PGS准确度,其成本也在快速降低。但是PGD的准确度受到了SNV假阳性和假阴性的限制,这些假阳性和假阴性的结果对 IVF 的影响是不可接受的。
研究利用MALBAC技术对胚胎活检样本进行全基因组扩增后,为避免ADO的产生,使用连锁分析的方法,比如短串联重复(STR)或者核型定位[33],来避免假阳性和假阴性的产生。现有的技术对同一个胚胎进行SNV、CNV检测以及连锁分析需要分开进行。研究者报道了一种新的以NGS为基础的PGD/PGS的检测方法,它能同时检测到单基因病和非整倍体,还能以较低的成本进行连锁分析,这种检测方法叫测序揭示突变等位基因同时进行染色体异常和连锁分析(mutated allele revealed by sequencing with aneuploidy and linkage analyses, MARSALA),它融合了MALBAC单细胞全基因组扩增技术。通过对MALBAC扩增产物进行PCR扩增检测单基因疾病相关的SNV、CNV来检测非整倍体。SNV检测中的假阳性和假阴性可以用基于NGS的连锁分析规避。使用这种胚胎选择方法,已有两个不携带父母单基因病的健康孩子出生,这两种单基因疾病分别是来自父亲的常染色体单碱基突变和来自母亲的X染色体单碱基突变引起的。
3.3 MALBAC技术用于染色体平衡重排携带者的囊胚染色体分析
染色体平衡重排(chromosomal rearrangements, CRs)是人类中最为常见的遗传异常。虽然荧光原位杂交技术(fluorescence in situ hybridisation, FISH)被广泛应用于染色体重排携带者[34],但极少证据证明它能够有效地预测胚胎在之后的发育过程中的染色体组成。嵌合现象可能更常见于染色体重排携带者的囊胚中,尤其是携带重排相关的染色体。已有的调查研究表明未知染色体异常的患者,其囊胚内细胞团(inner cell mass, ICM)和滋养外胚层(trophectoderm, TE)染色体的组成高度一致,染色体平衡重排,TE检测可能会因为胚胎嵌合而被混淆[35]。所以基于卵裂期FISH的PGD不能精确检测重排相关染色体的不平衡,也不能有效反映相关囊胚的染色体组成。芯片技术的胚胎植入前遗传学诊断(PGD)被广泛应用于染色体重排携带者[36],以选择正常或染色体平衡的胚胎进行移植。此外,非整倍体常见于染色体平衡重排携带者的胚胎甚至常见于正常/平衡的胚胎的重组相关的染色体[37]。Gui等[38]以染色体平衡重排携带者的早期囊胚内细胞团和滋养外胚层为研究对象,首次对其染色体组成的一致性进行了研究。通过MALBAC单细胞全基因组扩增结合低覆盖度的下一代测序技术(NGS)的全基因组拷贝数变异分析,筛查了ICM和TE的染色体非整倍体和重组相关染色体的非平衡异常,结果显示,染色体平衡重排携带者ICM和TE的染色体组成高度一致,而且基于卵裂期FISH进行PGD并不够准确。所以,检测染色体平衡重排携带者的胚胎染色体非平衡,建议以TE作为活检细胞进行基于NGS的PGD检测。
3.4 基于MALBAC-NGS的无创胚胎染色体筛查(NICS)技术
单细胞全基因组测序有助于破译基因组异质性,并有助于分析微量遗传物质,如人类胚胎细胞中的遗传物质。线粒体虽然是真核细胞遗传物质的重要组成部分,但是在单细胞基因组分析中经常被忽略。近年来,基于MALBAC开发的单细胞全基因组扩增方法MALBAC-NGS,用于在单细胞水平同时分析染色体和线粒体基因组。该技术通过一系列技术和生物学复制得到验证,并用于来自81对夫妇的399个体外受精胚胎的染色体和线粒体拷贝数分析。发现母亲的年龄与线粒体数量成正相关。在成功植入的胚胎中检测到线粒体数量较低但差异不显著,表明该方法可能用于胚胎植入前基因筛选,同时评估染色体组成和线粒体拷贝数[39]。也有研究通过MALBAC技术结合第二代高通量测序的方法,检测培养至囊胚期的培养液,获得24条染色体的非整倍体情况,通过对比培养液与对应整个胚胎(供体胚胎)的染色体非整倍体情况,对NICS技术用于胚胎植入前染色体筛查做出评价,评价结果显示NICS样本与胚胎样本存在高度的相关性,敏感度和特异性达88.2%和84%。鉴于这样的评价结果,经患者同意后,研究使用NICS的方法完成了对平衡易位家庭胚胎的染色体检测,挑选染色体正常的胚胎移植后,患者成功怀孕并活产一健康男婴[40]。由此可见,NICS是一项操作简便、无创安全的胚胎植入前检测方法,可有效提高胚胎移植成功率。4 展 望
“精准医疗”的提出使得基因检测技术快速发展,而基于全基因组扩增技术的单细胞测序技术作为精准医疗最生动的案例也被大力应用于临床。而单细胞测序在辅助生殖领域的应用需朝着以下方向发展:首先,实现无创,由于WGA技术对微量DNA的高度敏感性,利用胚胎培养液中的游离DNA这种无创的获取样本的方式代替有创的胚胎活检,将降低胚胎的安全性风险,未来对于胚胎的染色体水平甚至单基因水平检测,势必将朝着无创的方向发展;其次,对于胚胎质量的评价除了基因组水平还应朝向转录组水平甚至表观遗传方向发展,以全面分析胚胎的质量和发育潜能;再次,WGA技术如何同时满足扩增准确性和操作便捷性,将是科研工作者未来努力的方向。随着全基因组扩增技术的不断发展以及检测技术的不断更新,相信全基因组扩增技术将被应用于越来越多的领域,为更多的科学研究提供坚实的基础。参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
URLMagsci [本文引用: 1]

全基因组扩增(Whole genome amplification, WGA)技术是一种对全部基因组序列进行非选择性扩增的技术。近几年来, 对 WGA技术扩增痕量DNA检材的研究日渐深入, 这些研究可望用于刑案现场采集到的痕量DNA样品的扩增, 为法医个体识别提供足量的DNA模板。然而, 对实际案件中复杂检材的扩增偏差问题一直困扰着法医工作者, 寻求一个低扩增偏差、高扩增产率的WGA技术是法医工作者的主要目标。文章综述了WGA技术在法医个体识别中的研究进展及应用前景, 为法医解决扩增偏差问题提供参考。
URLMagsci [本文引用: 1]

全基因组扩增(Whole genome amplification, WGA)技术是一种对全部基因组序列进行非选择性扩增的技术。近几年来, 对 WGA技术扩增痕量DNA检材的研究日渐深入, 这些研究可望用于刑案现场采集到的痕量DNA样品的扩增, 为法医个体识别提供足量的DNA模板。然而, 对实际案件中复杂检材的扩增偏差问题一直困扰着法医工作者, 寻求一个低扩增偏差、高扩增产率的WGA技术是法医工作者的主要目标。文章综述了WGA技术在法医个体识别中的研究进展及应用前景, 为法医解决扩增偏差问题提供参考。
URL [本文引用: 1]

We have developed an in vitro method for amplifying a large fraction of the DNA sequences present in a single haploid cell by repeated primer extensions using a mixture of 15-base random oligonucleotides. We studied 12 genetic loci and estimate that the probability of amplifying any sequence in the genome to a minimum of 30 copies is not less than 0.78 (95% confidence). Whole genome amplification beginning with a single cell, or other samples with very small amounts of DNA, has significant implications for multipoint mapping by sperm or oocyte typing and possibly for genetic disease diagnosis, forensics, and the analysis of ancient DNA samples.
URL [本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
URLPMID:24360273 [本文引用: 6]

MALBAC genome amplification and high-throughput sequencing of the two polar bodies allowed inference of the health status of the oocyte, both in terms of aneuploidy and single-nucleotide variants associated with Mendelian diseases, demonstrating proof of principle for MALBAC-based preimplantation genomic screening in IVF.
[本文引用: 1]
URLPMID:11959976 [本文引用: 1]

Fundamental to most genetic analysis is availability of genomic DNA of adequate quality and quantity. Because DNA yield from human samples is frequently limiting, much effort has been invested in developing methods for whole genome amplification (WGA) by random or degenerate oligonucleotide-primed PCR. However, existing WGA methods like degenerate oligonucleotide-primed PCR suffer from incomplete coverage and inadequate average DNA size. We describe a method, termed multiple displacement amplification (MDA), which provides a highly uniform representation across the genome. Amplification bias among eight chromosomal loci was less than 3-fold in contrast to 4-6 orders of magnitude for PCR-based WGA methods. Average product length was > 10 kb. MDA is an isothermal, strand-displacing amplification yielding about 20-30 g product from as few as 1-10 copies of human genomic DNA. Amplification can be carried out directly from biological samples including crude whole blood and tissue culture cells. MDA-amplified human DNA is useful for several common methods of genetic analysis, including genotyping of single nucleotide polymorphisms, chromosome painting, Southern blotting and restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis, subcloning, and DNA sequencing. MDA-based WGA is a simple and reliable method that could have significant implications for genetic studies, forensics, diagnostics, and long-term sample storage.
URLPMID:23258894 [本文引用: 2]

Kindred cells can have different genomes because of dynamic changes in DNA. Single cell sequencing is needed to characterize these genomic differences but has been hindered by whole-genome amplification bias, resulting in low genome coverage. Here we report a new amplification method: Multiple Annealing and Looping Based Amplification Cycles (MALBAC) that offer high uniformity across the genome. Sequencing MALBAC amplified DNA achieves 93% genome coverage 1x for a single human cell at 25x mean sequencing depth. We detected digitized copy number variations (CNVs) of a single cancer cell. By sequencing three kindred cells, we were able to call individual single nucleotide variations (SNVs) with no false positives observed. We directly measured the genome-wide mutation rate of a cancer cell line and found that purine-pyrimidine exchanges occurred unusually frequently among the newly acquired SNVs.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
URLPMID:26340991 [本文引用: 2]

Whole-genome amplification (WGA) for next-generation sequencing has seen wide applications in biology and medicine when characterization of the genome of a single cell is required. High uniformity and fidelity of WGA is needed to accurately determine genomic variations, such as copy number variations (CNVs) and single-nucleotide variations (SNVs). Prevailing WGA methods have been limited by fluctuation of the amplification yield along the genome, as well as false-positive and -negative errors for SNV identification. Here, we report emulsion WGA (eWGA) to overcome these problems. We divide single-cell genomic DNA into a large number (10(5)) of picoliter aqueous droplets in oil. Containing only a few DNA fragments, each droplet is led to reach saturation of DNA amplification before demulsification such that the differences in amplification gain among the fragments are minimized. We demonstrate the proof-of-principle of eWGA with multiple displacement amplification (MDA), a popular WGA method. This easy-to-operate approach enables simultaneous detection of CNVs and SNVs in an individual human cell, exhibiting significantly improved amplification evenness and accuracy.
URLPMID:28408603 [本文引用: 2]

Single-cell genomics is important for biology and medicine. However, current whole-genome amplification (WGA) methods are limited by low accuracy of copy-number variation (CNV) detection and low amplification fidelity. Here we report an improved single-cell WGA method, Linear Amplification via Transposon Insertion (LIANTI), which outperforms existing methods, enabling micro-CNV detection with kilobase resolution. This allowed direct observation of stochastic firing of DNA replication origins, which differs from cell to cell. We also show that the predominant cytosine-to-thymine mutations observed in single-cell genomics often arise from the artifact of cytosine deamination upon cell lysis. However, identifying single-nucleotide variations (SNVs) can be accomplished by sequencing kindred cells. We determined the spectrum of SNVs in a single human cell after ultraviolet radiation, revealing their nonrandom genome-wide distribution.
URL [本文引用: 2]

Accurate sequencing and haplotyping of diploid genomes of single cells are intrinsically difficult due to the small amount of starting materials and limited read lengths of current DNA sequencing methods. In SISSOR (single-stranded sequencing using microfluidic reactors), we aim to improve sequencing accuracy and haplotype assembly by taking advantage of the redundant complementary sequence information in the double-stranded DNA and by partitioning megabase-size single-stranded DNA fragments from the homologous chromosome pairs into multiple compartments for amplification by MDA (multiple displacement amplification) and subsequent sequencing using short-read DNA sequencing platforms. We report the demonstration of the most accurate single-cell genome sequencing to date with data from three single human cells. Our approach can simultaneously provide higher accuracy and longer haplotypes than existing approaches. Accurate detection of variants and long-range haplotypes in genomes of single human cells remains very challenging. Common approaches require extensive in vitro amplification of genomes of individual cells using DNA polymerases and high-throughput short-read DNA sequencing. These approaches have two notable drawbacks. First, polymerase replication errors could generate tens of thousands of false-positive calls per genome. Second, relatively short sequence reads contain little to no haplotype information. Here we report a method, which is dubbed SISSOR (single-stranded sequencing using microfluidic reactors), for accurate single-cell genome sequencing and haplotyping. A microfluidic processor is used to separate the Watson and Crick strands of the double-stranded chromosomal DNA in a single cell and to randomly partition megabase-size DNA strands into multiple nanoliter compartments for amplification and construction of barcoded libraries for sequencing. The separation and partitioning of large single-stranded DNA fragments of the homologous chromosome pairs allows for the independent sequencing of each of the complementary and homologous strands. This enables the assembly of long haplotypes and reduction of sequence errors by using the redundant sequence information and haplotype-based error removal. We demonstrated the ability to sequence single-cell genomes with error rates as low as 10 8and average 500-kb-long DNA fragments that can be assembled into haplotype contigs with N50 greater than 7 Mb. The performance could be further improved with more uniform amplification and more accurate sequence alignment. The ability to obtain accurate genome sequences and haplotype information from single cells will enable applications of genome sequencing for diverse clinical needs.
URLPMID:25136831 [本文引用: 1]

Single-cell sequencing is emerging as an important tool for studies of genomic heterogeneity. Whole genome amplification (WGA) is a key step in single-cell sequencing workflows and a multitude of methods have been introduced. Here, we compare three state-of-the-art methods on both bulk and single-cell samples of E. coli DNA: Multiple Displacement Amplification (MDA), Multiple Annealing and Looping Based Amplification Cycles (MALBAC), and the PicoPLEX single-cell WGA kit (NEB-WGA). We considered the effects of reaction gain on coverage uniformity, error rates and the level of background contamination. We compared the suitability of the different WGA methods for the detection of copy-number variations, for the detection of single-nucleotide polymorphisms and for de-novo genome assembly. No single method performed best across all criteria and significant differences in characteristics were observed; the choice of which amplifier to use will depend strongly on the details of the type of question being asked in any given experiment.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
URL

DNA芯片及下一代测序等高通量技术的发展极大促进了分子生物学技术在各领域的广泛应用,但此时样品数量与质量往往是制约研究进行的重要因素,全基因组扩增技术(Whole genome amplification,WGA)则可有效解决这一问题,其可使极微量目标基因组DNA同时得到扩增从而提供满足高通量分析研究所需的起始材料。高效可靠的全基因组扩增技术使基于单细胞水平的大规模全基因组分析成为现实,且随着研究的不断深入,对全基因组扩增技术提出了更高的要求。对过去常用的以及近期发展的全基因组扩增技术进行了概述,阐明了各种方法的原理,并对各种方法的特点从原理上进行了分析总结,以期为全基因组扩增技术的应用提供一定的参考。
URL

DNA芯片及下一代测序等高通量技术的发展极大促进了分子生物学技术在各领域的广泛应用,但此时样品数量与质量往往是制约研究进行的重要因素,全基因组扩增技术(Whole genome amplification,WGA)则可有效解决这一问题,其可使极微量目标基因组DNA同时得到扩增从而提供满足高通量分析研究所需的起始材料。高效可靠的全基因组扩增技术使基于单细胞水平的大规模全基因组分析成为现实,且随着研究的不断深入,对全基因组扩增技术提出了更高的要求。对过去常用的以及近期发展的全基因组扩增技术进行了概述,阐明了各种方法的原理,并对各种方法的特点从原理上进行了分析总结,以期为全基因组扩增技术的应用提供一定的参考。
URL
[本文引用: 1]
URLPMID:17728321 [本文引用: 1]

Defects in early meiotic events are thought to play a critical role in ; however, little is known regarding the relationship between early meiotic events and the chromosomal constitution of sperm. Thus, we analyzed testicular tissue from 26 men (9 fertile and 17 infertile men), using immunofluorescent techniques to examine meiotic , and fluorescent in situ hybridization to assess sperm aneuploidy. Based on a relatively small sample size, we observed that 42% (5/12) of men with impaired displayed reduced genome-wide recombination when compared to the fertile men. Analysis of individual showed -specific defects in recombination: 13 and 18 bivalents with only a single crossover and 21 bivalents lacking a crossover were more frequent among the infertile men. We identified two infertile men who displayed a novel meiotic defect in which the failed to recombine: one had an absence of sperm in the testes, while the other displayed increased aneuploidy in the sperm, resulting in a 45,X abortus after intracytoplasmic sperm injection. When all men were pooled, we observed an inverse correlation between the frequency of recombination and XY disomy in the sperm. Recombination between the may be a useful indicator for identifying men at risk of producing chromosomally abnormal sperm. An understanding of the molecular mechanisms that contribute to sperm aneuploidy in infertile men could aid in risk assessment for couples undergoing assisted .
URLPMID:21212646 [本文引用: 1]

Finding a positive association between paternal age and the incidence of aneuploidy is not difficult. A cursory analysis however reveals that any association is indirect, brought about by a close correlation between paternal age and maternal age. Approaches for dissecting out the confounding age effects of the mother has led to a lively exchange among epidemiologists, with perhaps a consensus for the absence of a paternal age effect, at least for trisomy 21. Molecular studies revealed the relatively minor contribution of paternal errors to trisomy, but even research on the paternally derived trisomies alone has been inconclusive; thus studies focussed directly on the sperm heads. Human-hamster fusion assays were superseded by FISH for establishing any possible link between age and the proportion of disomic sperm in an ejaculate. Despite innumerable microscope hours however, although convincing studies suggesting an age effect for disomies 1, 9, 18 and 21 and the sex chromosomes are in the literature, others failed to notice any association for these or other chromosomes. It is biologically plausible that chromosomal non-disjunction errors should increase with age. Male reproductive hormone production, testicular morphology and semen parameters all decline slowly with age and paternal age is implicated in congenital birth defects, such as achondroplasia and Apert syndromes and also linked to compromised DNA repair mechanisms. Despite several decades of epidemiological and molecular cytogenetic studies, however, we are still not close to a definitive answer of whether or not there is a paternal age effect for aneuploidy. In this review we conclude by questioning the efficacy of FISH because of difficulties in detecting nullisomy and because of evidence that the centromeres (from which most sperm-FISH probes are derived) cluster at the nuclear centre. Array-based approaches may well supersede FISH in addressing the question of a paternal age effect; for now, however, the jury is still out.
URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
URLPMID:23258895 [本文引用: 2]

Abstract Meiotic recombination creates genetic diversity and ensures segregation of homologous chromosomes. Previous population analyses yielded results averaged among individuals and affected by evolutionary pressures. We sequenced 99 sperm from an Asian male by using the newly developed amplification method-multiple annealing and looping-based amplification cycles-to phase the personal genome and map recombination events at high resolution, which are nonuniformly distributed across the genome in the absence of selection pressure. The paucity of recombination near transcription start sites observed in individual sperm indicates that such a phenomenon is intrinsic to the molecular mechanism of meiosis. Interestingly, a decreased crossover frequency combined with an increase of autosomal aneuploidy is observable on a global per-sperm basis.
URL [本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
URLPMID:29203383 [本文引用: 1]

AbstractSingle cell whole genome sequencing helps to decipher the genome heterogeneity within a cell population and facilitates the analysis of trace amounts of genetic material, such as is found in human embryos. The mitochondrial genome, although an important part of the genetic composition of eukaryotic cells, is often neglected in single cell genome analysis. A recently developed single cell whole genome amplification method was used, known as multiple annealing and looping based amplification cycles (MALBAC-NGS), for simultaneous analysis of chromosomal and mitochondrial genomes at the single cell level. The platform was validated by a series of technical and biological replicates and used for chromosomal and mitochondrial copy number analysis in 399 in-vitro fertilized embryos from 81 couples. A positive correlation of maternal age with increased mitochondria quantity ( = 0.176, P = 0.001) was observed after adjusting for the impact of cell type. Lower numbers of mitochondria were detected in successfully implanted embryos, although the difference was not significant. It is proposed that MALBAC-NGS could potentially be used for an advanced pre-implantation genetic screening procedure with both chromosomal constitution and mitochondrial copy number being evaluated.
URL [本文引用: 1]
