王慎强1,
孙朋飞1,
陈小琴1,
沈健林2,
王华3,
肖智华3,
李晓明1,
杨广1,
颜晓元1
1.江苏常熟农田生态系统国家野外观测研究站/中国科学院南京土壤研究所 南京 210008
2.中国科学院亚热带农业生态研究所 长沙 410125
3.湖南农业大学资源环境学院 长沙 410128
基金项目:国家重点基础研究发展计划项目(2018YFC0213302)资助
详细信息
通讯作者:夏永秋, 研究方向为农田氮素循环与环境效应。E-mail: yqxia@issas.ac.cn
中图分类号:S158.5计量
文章访问数:108
HTML全文浏览量:24
PDF下载量:44
被引次数:0
出版历程
收稿日期:2021-04-22
录用日期:2021-07-10
网络出版日期:2021-07-14
刊出日期:2021-12-09
Ammonia emission patterns of typical planting systems in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River and key technologies for ammonia emission reduction
XIA Yongqiu1,,,WANG Shenqiang1,
SUN Pengfei1,
CHEN Xiaoqin1,
SHEN Jianlin2,
WANG Hua3,
XIAO Zhihua3,
LI Xiaoming1,
YANG Guang1,
YAN Xiaoyuan1
1. Changshu Agro-Ecological National Field Scientific Observation and Research Station / Institute of Soil Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Nanjing 210008, China
2. Institute of Subtropical Agriculture, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changsha 410125, China
3. College of Resources & Environment, Hunan Agricultural University, Changsha 410128, China
Funds:This study was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (2018YFC0213302)
More Information
Corresponding author:XIA Yongqiu, E-mail: yqxia@issas.ac.cn
摘要
HTML全文
图
参考文献
相关文章
施引文献
资源附件
访问统计
摘要
摘要:长江中下游稻、菜、果种植业发达, 是氨挥发的主要场所, 迫切需要掌握其氨排放特征与减排关键技术。本文系统梳理了“十三五”国家重点研发计划项目课题“长江中下游种植业高效控氨减排关键技术研发”取得的主要进展, 并展望了“十四五”期间的研究重点。取得的主要研究结果包括: 1)明确了典型稻菜果氨排放系数与特征, 稻田氨排放系数和变异最大, 平均为14.2%, 露天蔬菜次之(平均为11.2%), 果树最低(平均为4.76%)。2)以“减、抑、控、固”全链条氨减排思路, 提出稻田优化减氮技术、稻田深施控氨技术、稻田周丛生物成膜抑氨技术、果树大颗粒肥料深施与蔬菜新型缓释肥等减排技术, 实现了高效控氨减排的目标。“十四五”期间, 建议加强氨挥发损失的长期原位监测与模拟, 氨减排环境和经济效益核算, 以及操作简易、成本低廉的氨挥发减排技术研发。
关键词:减排潜力/
氨减排全链条/
排放系数/
机具/
综合效益/
长江中下游
Abstract:Rice, vegetables, and fruit fields in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River are the main sites of ammonia volatilization in the planting system of China. Therefore, there is an urgent need to understand the characteristics and key control technologies of ammonia emissions in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River. This paper systematically reviewed the major progresses of the National Key Research and Development Project of the National 13th Five-Year Plan: “Research and Development of Key Technologies for Efficient Ammonia Control and Emission Reduction in Planting System in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River,” and foreseen the research focus during the 14th Five-Year period. The main research results included the followings: 1) The ammonia emission coefficient and characteristics of typical rice, and vegetables and fruit trees fields were identified, indicating that the paddy field had the largest ammonia emission coefficient and variation, averaging 14.2%, followed by open-air vegetables (averaging 11.2%), and fruit fields (averaging 4.76%). 2) After verifying the whole process of ammonia emission reduction, “reduction, retrain, control, and immobilization”, we put forward technologies such as optimized nitrogen reduction technology in paddy fields, deep fertilizer applications for ammonia emission control technology in paddy fields, ammonia emission immobilization by periphyton technology in paddy fields, deep application of large-size granular fertilizer for fruit trees, and slow-release fertilizer for open-air vegetables. With these technologies, we achieved the goals of reducing ammonia volatilization. During the 14th Five-Year Plan period, the long-term in-situ monitoring and simulation of ammonia volatilization should be strengthened, ammonia emission reduction technologies should be evaluated environmentally and economically, and simple and low-cost ammonia volatilization emission reduction technology should be developed.
Key words:Potential of emission reduction/
Whole chain of ammonia emission reduction/
Ammonia emission coefficient/
Machines and tools/
Comprehensive benefits/
Middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River
HTML全文
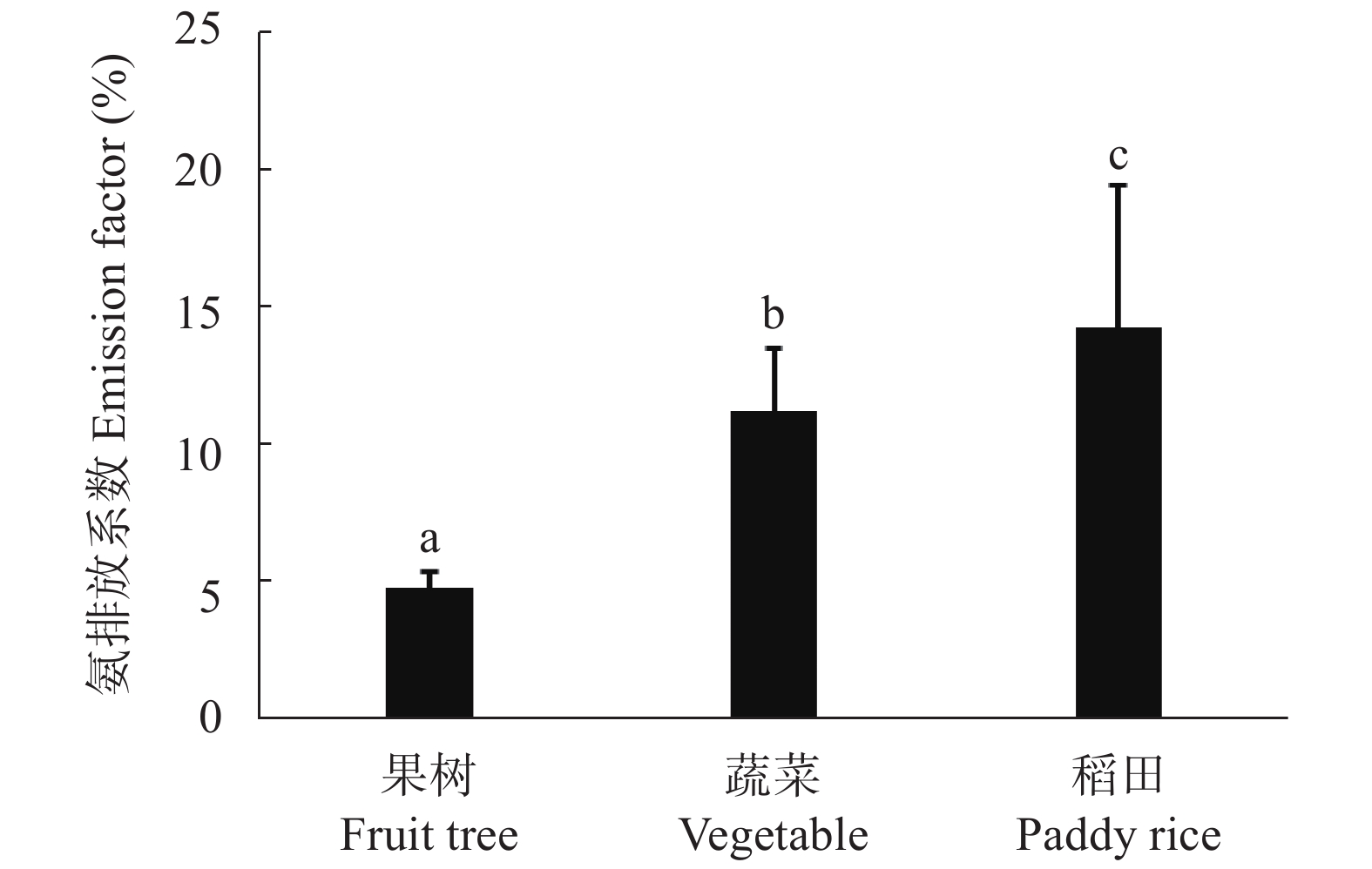
图1长江中下游典型稻菜果田氨排放系数及变异(不同字母表示在 P<0.05水平差异显著, 方差分析软件为SPSS V19.0)
Figure1.Ammonia emission coefficients and variations of paddy rice, open-air vegetables, and peach tree in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River (different letters indicate significant differences at P<0.05 level, variance analysis is conducted by SPSS V19.0)
 下载: 全尺寸图片幻灯片
下载: 全尺寸图片幻灯片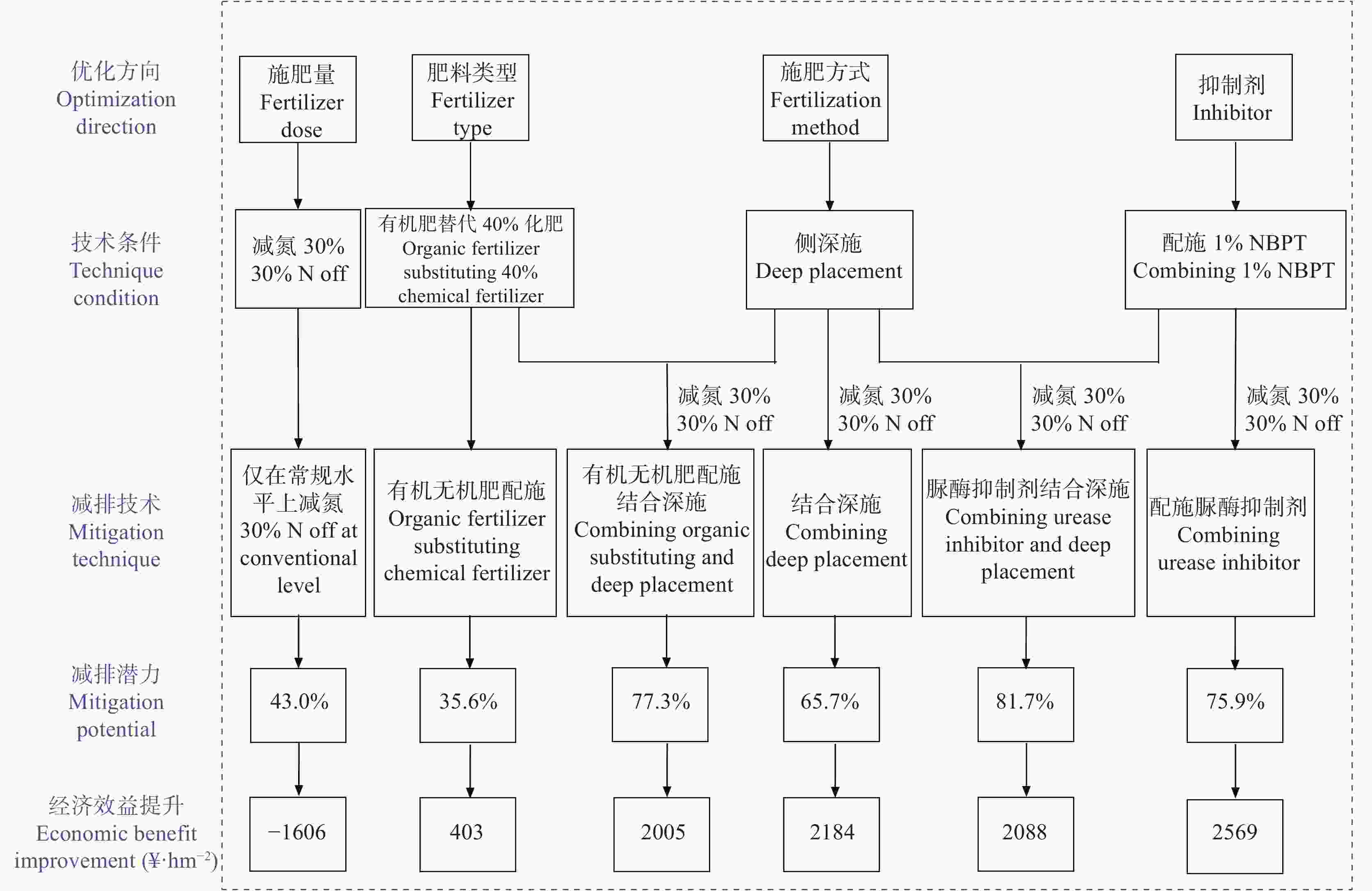
图2双季稻稻田优化减氮技术及其减排潜力和经济效益
Figure2.Optimized nitrogen reduction technology of double-cropping rice field and its mitigation potential of ammonia emission and economic benefit
 下载: 全尺寸图片幻灯片
下载: 全尺寸图片幻灯片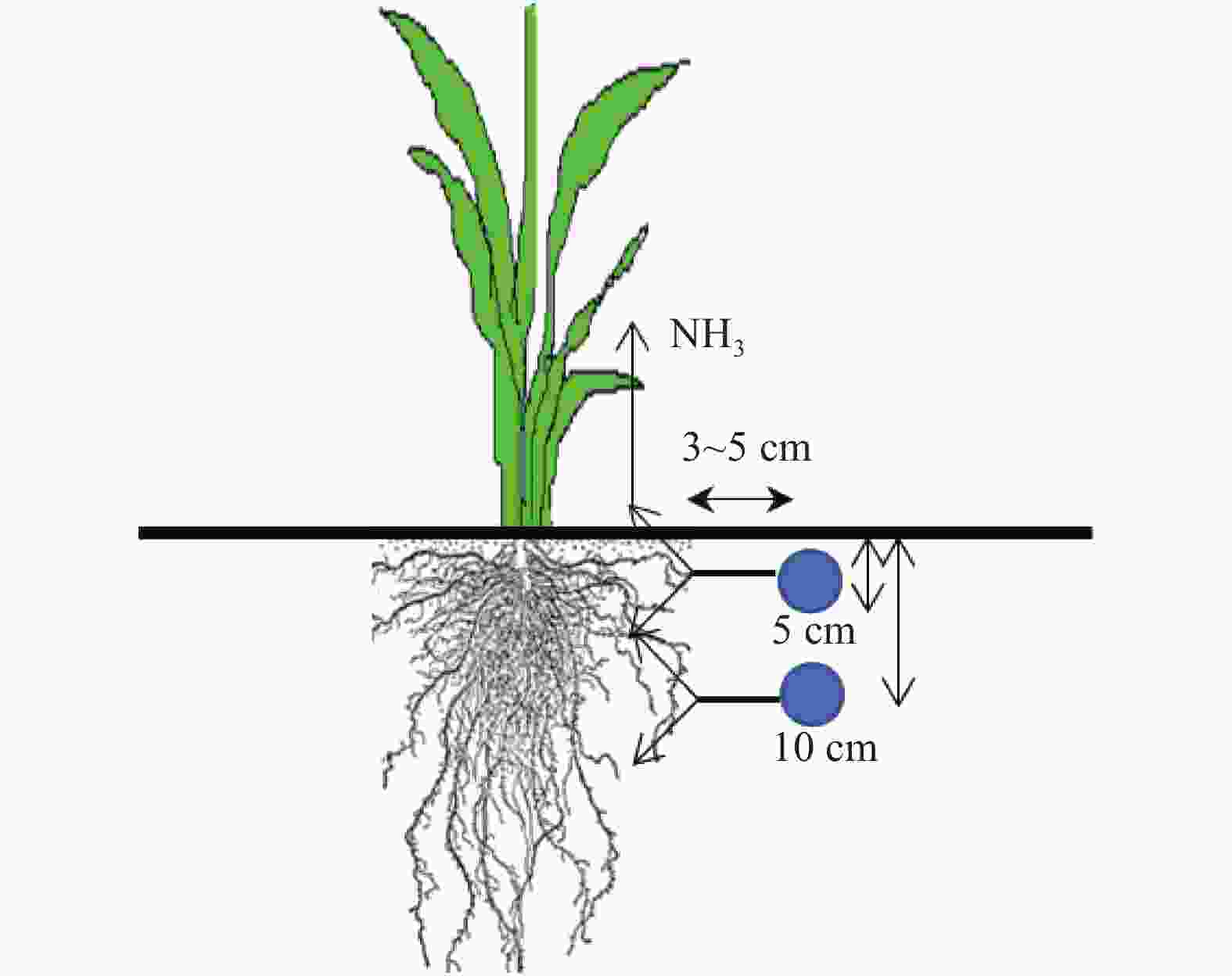
图3稻田肥球点位(圆点)优化
Figure3.Location optimization for ball fertilizer (dots) in paddy field
 下载: 全尺寸图片幻灯片
下载: 全尺寸图片幻灯片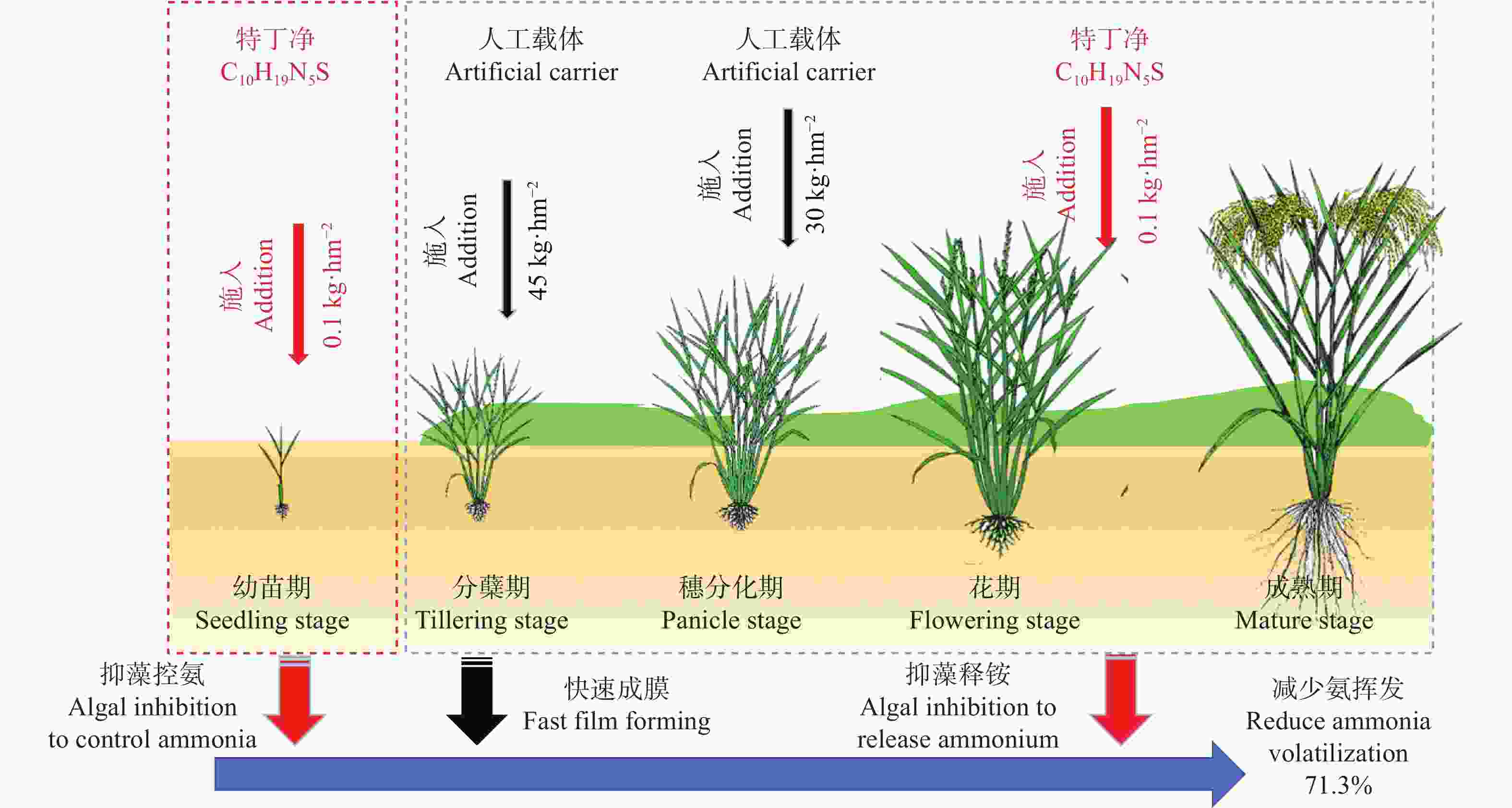
图4稻田周丛生物“控-固-释”技术
Figure4.Periphyton “retrain-immobilization-release” technology in paddy field
 下载: 全尺寸图片幻灯片
下载: 全尺寸图片幻灯片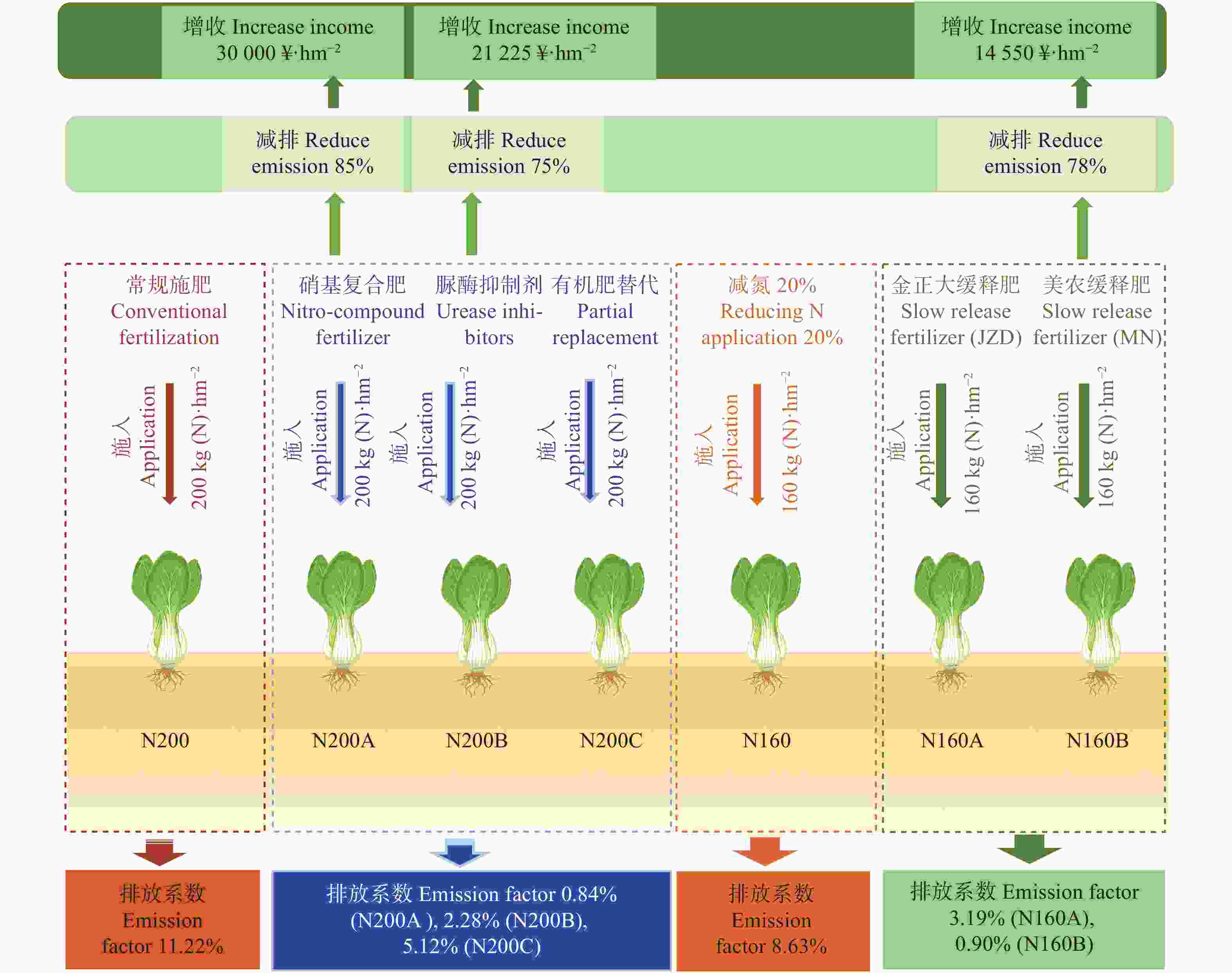
图5露天蔬菜新型缓释抑氨技术
Figure5.Slow-release fertilizers in reducing ammonia emission for open-air vegetables
 下载: 全尺寸图片幻灯片
下载: 全尺寸图片幻灯片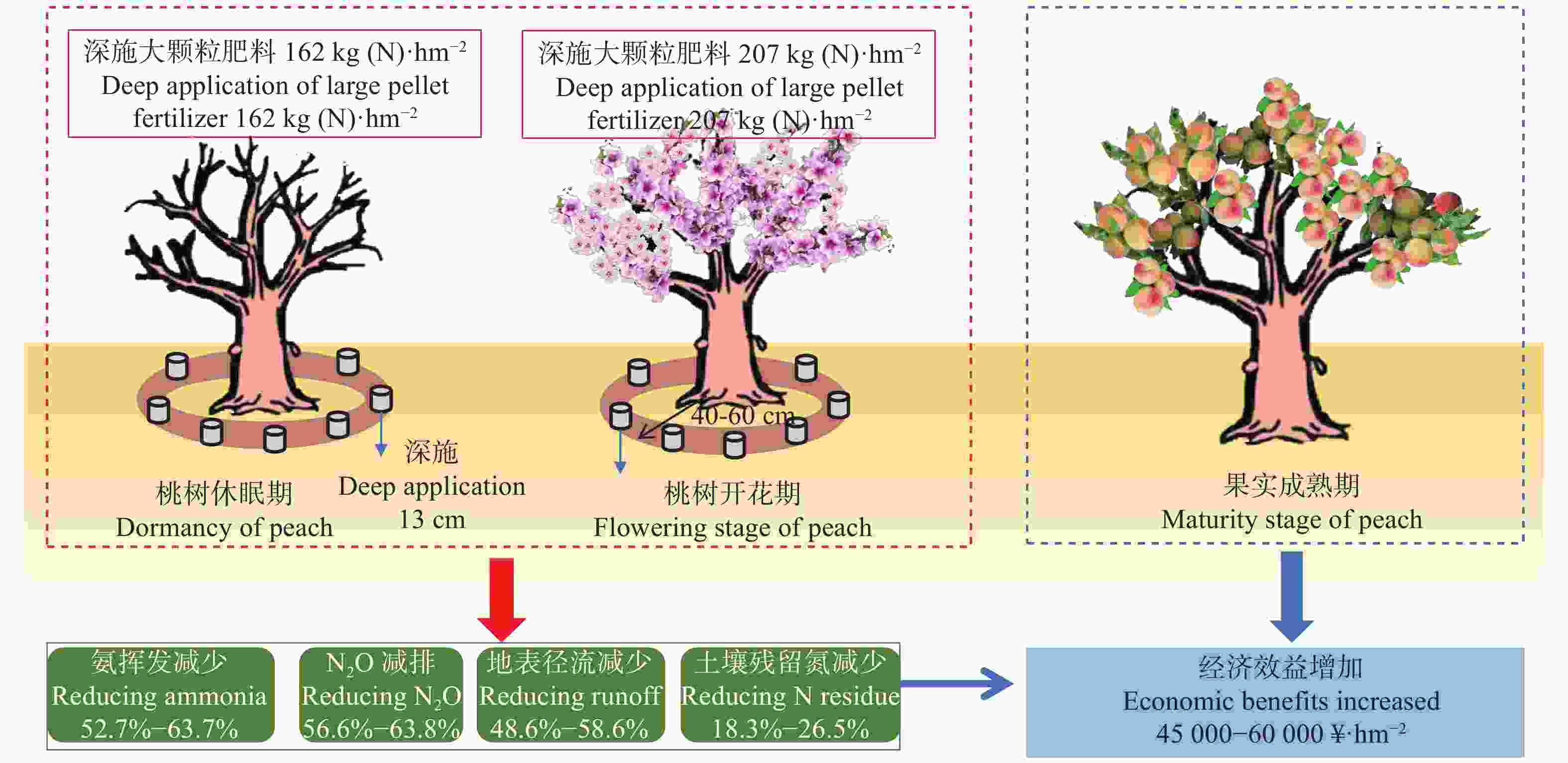
图6果树大颗粒肥深施控氨技术
Figure6.Deep application of large-size granular fertilizer in reducing ammonia emission for fruit trees
 下载: 全尺寸图片幻灯片
下载: 全尺寸图片幻灯片表1不同施肥期稻田人工诱导的周丛生物氮储量
Table1.Nitrogen storage in artificial induced and naturally growth periphyton in different fertilization periods of paddy field
| 处理 Treatment | 基肥 Basal fertilizer | 分蘖肥 Tillering fertilizer | 穗肥 Panicle fertilizer |
| 自然生长 Natural growth | 1.11 | 4.46 | 2.37 |
| 载体诱导 Carrier induced | 1.55 | 10.92 | 4.60 |
 下载: 导出CSV
下载: 导出CSV表2抑氨技术对稻田氨挥发累积量及损失率的影响
Table2.Effects of ammonia inhibition technology on ammonia volatilization accumulation and ammonia volatilization loss rate in periphyton in paddy field
| 处理 Treatment | 氨挥发排放量 NH3 emission [kg(N)?hm?2] | 氨挥发损失率 NH3 emission rate (%) | |||
| 基肥 Basal fertilizer | 分蘖肥 Tillering fertilizer | 穗肥 Panicle fertilizer | 累计排放量 Total NH3 flux | ||
| 对照田 Control field | 24.75±1.05 | 10.92±0.07 | 0.21±0.03 | 35.88 | 14.9 |
| 试验田 Treatment field | 7.11±0.53 | 6.63±0.07 | 0.10±0.25 | 13.84 | 5.8 |
 下载: 导出CSV
下载: 导出CSV参考文献
| [1] | 朱兆良. 中国土壤氮素[M]. 南京: 江苏科技出版社, 1992 ZHU Z L. Nitrogen in Soils of China[M]. Nanjing: Jiangsu Science and Technology Press, 1992 |
| [2] | ZHANG Y S, LUAN S J, CHEN L L, et al. Estimating the volatilization of ammonia from synthetic nitrogenous fertilizers used in China[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2011, 92(3): 480?493 doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2010.09.018 |
| [3] | PAN B B, LAM S K, MOSIER A, et al. Ammonia volatilization from synthetic fertilizers and its mitigation strategies: A global synthesis[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 2016, 232: 283?289 |
| [4] | 肖其亮, 朱坚, 彭华, 等. 稻田氨挥发损失及减排技术研究进展[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2021, 40(1): 16?25 doi: 10.11654/jaes.2020-0767 XIAO Q L, ZHU J, PENG H, et al. Ammonia volatilization loss and emission reduction measures in paddy fields[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2021, 40(1): 16?25 doi: 10.11654/jaes.2020-0767 |
| [5] | 侯萌瑶, 张丽, 王知文, 等. 中国主要农作物化肥用量估算[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2017, 34(4): 360?367 HOU M Y, ZHANG L, WANG Z W, et al. Estimation of fertilizer usage from main crops in China[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2017, 34(4): 360?367 |
| [6] | MENCARONI M, DAL FERRO N, FURLANETTO J, et al. Identifying N fertilizer management strategies to reduce ammonia volatilization: Towards a site-specific approach[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2021, 277: 111445 doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111445 |
| [7] | SOARES J R, CANTARELLA H, MENEGALE M L D C. Ammonia volatilization losses from surface-applied urea with urease and nitrification inhibitors[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2012, 52: 82?89 doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2012.04.019 |
| [8] | LIN D X, FAN X H, HU F, et al. Ammonia volatilization and nitrogen utilization efficiency in response to urea application in rice fields of the Taihu Lake region, China[J]. Pedosphere, 2007, 17(5): 639?645 doi: 10.1016/S1002-0160(07)60076-9 |
| [9] | JU X T, XING G X, CHEN X P, et al. Reducing environmental risk by improving N management in intensive Chinese agricultural systems[J]. PNAS, 2009, 106(19): 8077 doi: 10.1073/pnas.0902655106 |
| [10] | 田昌, 周旋, 谢桂先, 等. 控释尿素减施对双季稻田氨挥发损失和氮肥利用率的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(4): 387?397 TIAN C, ZHOU X, XIE G X, et al. Ammonia volatilization loss and nitrogen use efficiency in double-cropping rice field as affected by decreasing controlled-release urea application level[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2018, 32(4): 387?397 |
| [11] | SHAN L N, HE Y F, CHEN J, et al. Ammonia volatilization from a Chinese cabbage field under different nitrogen treatments in the Taihu Lake Basin, China[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2015, 38: 14?23 doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2015.04.028 |
| [12] | ZHANG Y F, LUO J J, PENG F T, et al. Application of bag-controlled release fertilizer facilitated new root formation, delayed leaf, and root senescence in peach trees and improved nitrogen utilization efficiency[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2021, 12: 627313 doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.627313 |
| [13] | YAO Y L, ZHANG M, TIAN Y H, et al. Urea deep placement for minimizing NH3 loss in an intensive rice cropping system[J]. Field Crops Research, 2018, 218: 254?266 doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2017.03.013 |
| [14] | 刘学军, 沙志鹏, 宋宇, 等. 我国大气氨的排放特征、减排技术与政策建议[J]. 环境科学研究, 2021, 34(1): 149?157 LIU X J, SHA Z P, SONG Y, et al. China’ s atmospheric ammonia emission characteristics, mitigation options and policy recommendations[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2021, 34(1): 149?157 |
| [15] | SHA Z P, MA X, LOICK N, et al. Nitrogen stabilizers mitigate reactive N and greenhouse gas emissions from an arable soil in North China Plain: Field and laboratory investigation[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 258: 121025 doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121025 |
| [16] | 葛顺峰, 彭玲, 任饴华, 等. 秸秆和生物质炭对苹果园土壤容重、阳离子交换量和氮素利用的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2014, 47(2): 366?373 doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2014.02.016 GE S F, PENG L, REN Y H, et al. Effect of straw and biochar on soil bulk density, cation exchange capacity and nitrogen absorption in apple orchard soil[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2014, 47(2): 366?373 doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2014.02.016 |
| [17] | LARNED S T, KILROY C. Effects of Didymosphenia geminata removal on river macroinvertebrate communities[J]. Journal of Freshwater Ecology, 2014, 29(3): 345?362 doi: 10.1080/02705060.2014.898595 |
| [18] | 王梦凡, 俞映倞, 杨梖, 等. 不同表面分子膜材料抑制稻田氨挥发的效果及其作用途径[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2019, 38(8): 1685?1695 doi: 10.11654/jaes.2019-0657 WANG M F, YU Y L, YANG B, et al. Effect of different surface molecular membrane materials on inhibition of ammonia volatilization and the action pathways in paddy fields[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2019, 38(8): 1685?1695 doi: 10.11654/jaes.2019-0657 |
| [19] | HUANG J, LIU X M, LIU Y Q, et al. Non-linear response of ammonia volatilization to periphyton in paddy soils[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences, 2021, DOI: 10.1029/2020jg005870 |
