徐富贤1,,,
张林1,
周兴兵1,
朱永川1,
郭晓艺1,
刘茂1,
陈琳1,
张容2,
熊洪1
1.四川省农业科学院水稻高粱研究所/农业部西南水稻生物学与遗传育种重点实验室/四川省作物生理生态及栽培重点实验室 德阳 618000
2.遂宁市安居区玉丰镇农业服务中心 遂宁 629023
基金项目:国家自然科学基金项目(31971844)、四川省农业科学院青年基金项目(2019QNJJ-020)和现代农业产业技术体系建设专项资金(CARS-01-25)资助
详细信息
作者简介:蒋鹏, 主要研究方向为水稻栽培生理生态。E-mail: jiangyipeng137@163.com
通讯作者:徐富贤, 主要研究方向为水稻高产高效栽培理论与技术。E-mail: xu6501@163.com
中图分类号:S311; S314计量
文章访问数:95
HTML全文浏览量:51
PDF下载量:35
被引次数:0
出版历程
收稿日期:2021-05-18
录用日期:2021-06-30
网络出版日期:2021-07-14
刊出日期:2021-10-01
Effect of increased plant density with reduced nitrogen on yield formation and nitrogen use efficiency of hybrid rice under high temperature and high humidity conditions
JIANG Peng1,,XU Fuxian1,,,
ZHANG Lin1,
ZHOU Xingbing1,
ZHU Yongchuan1,
GUO Xiaoyi1,
LIU Mao1,
CHEN Lin1,
ZHANG Rong2,
XIONG Hong1
1. Rice and Sorghum Research Institute, Sichuan Academy of Agricultural Sciences / Key Laboratory of Southwest Rice Biology and Genetic Breeding, Ministry of Agriculture / Crop Ecophysiology and Cultivation Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province, Deyang 618000, China
2. Yufeng Town Agricultural Service Center of Anju District, Suining City, Suining 629023, China
Funds:This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31971844), the Foundation of Youth Science Program of Sichuan Academy of Agricultural Sciences (2019QNJJ-020) and the Special Fund for the Industrial Technology System Construction of Modern Agriculture of China (CARS-01-25)
More Information
Corresponding author:E-mail: xu6501@163.com
摘要
HTML全文
图
参考文献
相关文章
施引文献
资源附件
访问统计
摘要
摘要:探明高温高湿稻区增密减氮对杂交稻产量形成和氮肥利用率的影响, 可为高温高湿稻区氮肥优化管理和合理密植提供依据。本研究以杂交稻‘内6优107’为材料, 于2018—2019年在典型的高温高湿稻区四川省泸州市进行大田试验。试验设6个密度与施氮量组合, 分别为低密高氮(习惯移栽密度16.5 万穴?hm?2, 施氮量为180 kg?hm?2, LDNck)、低密减氮15% (LDN?15%)、低密减氮30% (LDN?30%)、增密减氮15% (增密27%, HDN?15%)、增密减氮30% (HDN?30%)和低密不施氮(LDN0)。结果表明: 不同密肥组合对杂交稻产量影响显著(P<0.01)。与LDNck相比, HDN?15%和HDN?30%杂交稻产量分别增加4.3%~4.9%和2.3%~3.6%, 其优势主要表现在每穗粒数、结实率、花前干物质转运量、花前干物质转运效率、花前干物质转运对产量的贡献率和收获指数上。LDN?15%和LDN?30%杂交稻产量较LDNck分别降低2.3%~2.5%和4.8%~5.0%, 较低的有效穗、干物质、花后干物质积累及花后干物质积累对产量的贡献率是其减产的主要原因。HDN?15%和HDN?30%杂交稻花后氮素积累量、成熟期氮素吸收量低于LDNck处理, 但其花前氮素转运量、花前氮素转运效率、花前氮素转运贡献率、氮素干物质生产效率、氮素籽粒生产效率和氮素收获指数均高于LDNck处理, 因而HDN?15%和HDN?30%处理每生产100 kg稻谷需氮量分别减少6.8%~8.4%和9.0%~9.9%。与LDNck处理相比, HDN?15%和HDN?30%杂交稻氮肥农学利用率分别增加36.7%~37.4%和55.5%~60.4%、氮肥偏生产力增加22.8%~23.5%和46.3%~48.2%、氮肥吸收利用率增加5.6%~12.0%和17.0%~20.0%。可见, 在高温高湿稻区杂交稻生产上宜采用栽插密度为21.0万穴?hm?2和施氮量为126~153 kg?hm?2的组合。
关键词:杂交稻/
增密减氮/
产量/
氮肥利用率/
高温高湿
Abstract:The effects of increased plant density with reduced nitrogen (N) application rate on yield formation and nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) of hybrid rice were studied to provide a theoretical basis for optimum nitrogen fertilizer management and plant density under high temperature with high humidity conditions. Field experiments were conducted in Luzhou City from 2018 to 2019. The high yield and high quality hybrid rice variety ‘Nei6you107’ was grown under six combinations of plant density and N application rate: 1) locally recommended combination with a plant density of 16.5×104 hills?hm?2 and a N rate of 180 kg?hm?2 (LDNck); 2) combination of a plant density of 16.5×104 hills?hm?2 and a reduced N rate by 15% (153 kg?hm?2, LDN?15%); 3) combination of a plant density of 16.5×104 hills?hm?2 and a reduced N rate by 30% (126 kg?hm?2, LDN?30%); 4) combination of a increased plant density by about 27% (21.0×104 hills hm?2) and a reduced N rate by 15% (153 kg?hm?2, HDN?15%); 5) combination of a increased plant density by about 27% (21.0×104 hills?hm?2) and a reduced N rate by 30% (126 kg?hm?2 HDN?30%); and 6) combination of a plant density of 16.5×104 hills?hm?2 and zero N rate (LDN0). The grain yield, yield components, dry matter, N uptake and NUE were measured. The results showed that the grain yield of hybrid rice was significantly affected by different combinations of plant density and N rate (P<0.01). HDN?15% and HDN?30% produced higher grain yields than LDNck by 4.3%?4.9% and 2.3%?3.6%, respectively. The higher grain yields under HDN?15% and HDN?30% were attributed to improvement in spikelets per panicle, grain filling rate, translocation of dry matter accumulated at heading stage (TDMHD), translocation percentage of dry matter accumulated at heading stage (TPDMHD), contribution percentage of pre-anthesis dry matter translocation to grain yield (CPDMTGHD) and harvest index. The LDN?15% and LDN?30% had 2.3%?2.5% and 4.8%?5.0% lower grain yield than LDNck, respectively. The yield gap between LDN?15%, LDN?30% and LDNck was attributed to the difference in effective panicles, total dry matter, dry matter accumulation from heading to maturity, and contribution percentage of dry matter accumulation from heading to maturity stage to grain yield (CPDMGHD-MA). The HDN?15% and HDN?30% had lower nitrogen accumulation from heading to maturity and total N uptake than LDNck, whereas the translocation of N accumulated at heading stage (NTGNHD), translocation percentage of N accumulated at heading stage (TPNHD), contribution percentage of pre-anthesis N accumulation translocation to grain N accumulation (CPNTGNHD), N use efficiency for biomass production (NUEBP), N use efficiency for grain production (NUEGP) and N harvest index under HDN?15% and HDN?30% were higher than those under LDNck. Consequently, HDN?15% and HDN?30% had lower N requirements to produce 100 kg of grain (NRPG) than LDNck by 6.8%?8.4% and 9.0%?9.9%, respectively. HDN?15% enhanced the agronomic efficiency of applied N (AEN) by 36.7%?37.4%, partial factor productivity of applied N (PFPN) by 22.8%?23.5% and recovery efficiency of applied N (REN) by 5.6%?12.0% over LDNck. The HDN?30% produced higher AEN, PFPN and REN than LDNck by 55.5%?60.4%, 46.3%?48.2% and 17.0%?20.0%, respectively. The rational combination of plant density and N rate can improve panicle number per unit area, grain filling, TDMHD, TPDMHD, NTGNHD, TPNHD and harvest index, which further increasing the grain yield and NUE. The optimum combination is plant density of 21.0×104 hills?hm?2 plus N rate of 126?153 kg?hm?2 in high temperature with high humidity condition.
Key words:Hybrid rice/
Increased plant density with reduced nitrogen/
Grain yield/
Nitrogen use efficiency/
High temperature with high humidity
HTML全文
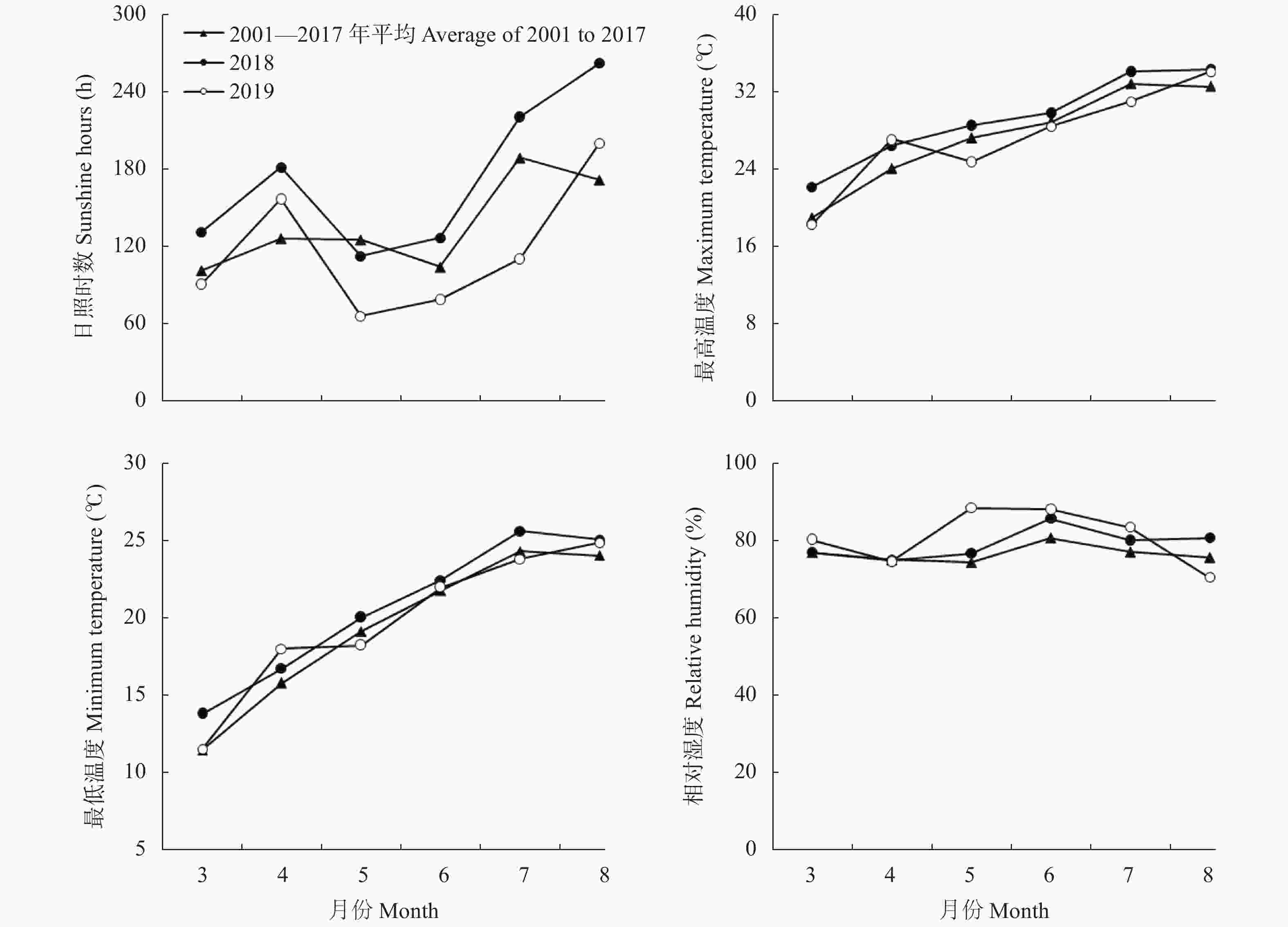
图12001—2019年研究区水稻生育期月日照时数、平均湿度、平均最高温度和平均最低
Figure1.Monthly sunshine hours, average humidity, mean maximum temperature and minimum temperature during rice-growing season from 2001 to 2019 in the study area
 下载: 全尺寸图片幻灯片
下载: 全尺寸图片幻灯片表1高温高湿区不同密肥处理对杂交稻产量及其构成的影响
Table1.Effect of combination of plant density and N rate on grain yield and yield components of hybrid rice under high temperature and high humidity conditions
| 年份 Year | 处理 Treatment | 有效穗数 Effective panicles (panicles?m?2) | 每穗粒数 Grains number per panicle | 结实率 Grain filling (%) | 粒重 Grain weight (mg) | 产量 Grain yield (t?hm?2) | ||
| 代码 Code | 密度 Plant density (×104 holes?hm?2) | 施氮量 N application rate (kg?hm?2) | ||||||
| 2018 | LDN0 | 16.5 | 0 | 155.3±13.7c | 138.0±4.2c | 89.5±1.9a | 28.1±0.2b | 6.22±0.42d |
| LDN?15% | 16.5 | 153 | 181.4±9.8b | 158.8±4.8a | 86.5±1.7a | 29.7±0.5a | 8.31±0.21bc | |
| LDN?30% | 16.5 | 126 | 179.2±10.4bc | 154.0±3.9ab | 88.4±3.0a | 29.3±0.3a | 8.11±0.14c | |
| HDN?15% | 21.0 | 153 | 199.7±9.1ab | 148.5±2.4b | 90.1±1.0a | 29.3±0.5a | 8.89±0.11a | |
| HDN?30% | 21.0 | 126 | 179.3±4.4bc | 160.4±5.1a | 90.6±0.9a | 29.3±0.6a | 8.72±0.37ab | |
| LDNCK | 16.5 | 180 | 206.4±22.6a | 145.5±6.5bc | 86.1±5.9a | 29.4±0.9a | 8.52±0.70abc | |
| 2019 | LDN0 | 16.5 | 0 | 179.2±12.9c | 159.3±7.1a | 80.9±2.4b | 28.1±0.3ab | 6.33±0.05c |
| LDN?15% | 16.5 | 153 | 205.4±5.2b | 149.3±10.9ab | 84.5±1.6ab | 27.7±0.6b | 8.62±0.25b | |
| LDN?30% | 16.5 | 126 | 204.1±21.2bc | 147.2±11.2ab | 85.4±2.0a | 28.8±0.2a | 8.38±0.15b | |
| HDN?15% | 21.0 | 153 | 237.6±9.1a | 138.2±1.8b | 84.3±3.1ab | 28.5±0.5ab | 9.25±0.13a | |
| HDN?30% | 21.0 | 126 | 234.7±16.6a | 141.1±3.9b | 84.9±1.4ab | 28.4±0.9ab | 9.14±0.23a | |
| LDNCK | 16.5 | 180 | 230.2±25.1ab | 137.5±2.6b | 84.0±3.0ab | 27.9±0.5ab | 8.82±0.50ab | |
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance | ||||||||
| 年份 Year (Y) | ** | ** | * | ** | ** | |||
| 处理 Treatment (T) | ** | ** | ns | ns | ** | |||
| 年份×处理 Y×T | ns | ** | ns | ns | ns | |||
| 同年同列数据后不同字母表示处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。*表示差异达P<0.05显著水平, **表示差异达P<0.01显著水平, ns 表示差异不显著。Values followed by different letters in a year within a column are significantly different at P<0.05 level. * and ** mean significance at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectively. ns denotes non-significance. | ||||||||
 下载: 导出CSV
下载: 导出CSV表2高温高湿区不同密肥处理对杂交稻干物质生产及收获指数的影响
Table2.Effect of combination of plant density and N rate on biomass production of hybrid rice under high temperature and high humidity condition
| 年份 Year | 处理 Treatment | 干物质 Dry matter (g?m?2) | 总干物质 Total dry matter (g?m?2) | 收获指数 Harvest index (%) | ||||
| 代码 Code | 密度 Plant density (×104 holes?hm?2) | 施氮量 N application rate (kg?hm?2) | 开花前 Before heading | 开花后 After heading | ||||
| 2018 | LDN0 | 16.5 | 0 | 612.3±30.2c | 280.6±44.4b | 892.8±60.9c | 60.3±0.9a | |
| LDN?15% | 16.5 | 153 | 981.7±13.1ab | 379.2±24.9a | 1360.9±37.3a | 54.3±0.8b | ||
| LDN?30% | 16.5 | 126 | 931.8±35.0b | 304.1±53.7ab | 1235.9±72.7b | 57.8±1.3ab | ||
| HDN?15% | 21.0 | 153 | 1013.1±44.7a | 307.4±28.9ab | 1320.5±56.6ab | 59.3±1.5a | ||
| HDN?30% | 21.0 | 126 | 968.2±72.5ab | 359.5±105.4ab | 1327.8±40.6ab | 57.5±2.5ab | ||
| LDNCK | 16.5 | 180 | 978.5±8.7ab | 381.6±29.0a | 1360.1±37.2a | 55.5±3.6b | ||
| 2019 | LDN0 | 16.5 | 0 | 846.3±43.8b | 299.6±77.9ab | 1145.9±38.9d | 56.6±0.4a | |
| LDN?15% | 16.5 | 153 | 1130.1±10.9a | 278.4±34.5ab | 1408.5±44.0ab | 52.5±2.2b | ||
| LDN?30% | 16.5 | 126 | 1106.5±26.9a | 207.4±74.2b | 1313.9±50.7c | 56.0±1.8a | ||
| HDN?15% | 21.0 | 153 | 1137.9±32.0a | 337.8±35.6a | 1475.7±19.6a | 53.3±0.7b | ||
| HDN?30% | 21.0 | 126 | 1102.8±23.6a | 285.7±44.4ab | 1388.5±21.2b | 55.9±0.4a | ||
| LDNCK | 16.5 | 180 | 1136.3±14.6a | 316.9±46.9ab | 1453.2±34.5ab | 51.7±0.8b | ||
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance | ||||||||
| 年份 Year (Y) | ** | * | ** | ** | ||||
| 处理 Treatment (T) | ** | * | ** | ** | ||||
| 年份×处理 Y×T | ns | ns | ** | ns | ||||
| 同年同列数据后不同字母表示处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。*表示差异达P<0.05显著水平, **表示差异达P<0.01显著水平, ns 表示差异不显著。Values followed by different letters in a year within a column are significantly different at P<0.05 level. * and ** mean significance at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectively. ns denotes non-significance. | ||||||||
 下载: 导出CSV
下载: 导出CSV表3高温高湿区不同密肥处理对杂交稻花前干物质转运的影响
Table3.Effect of combination of plant density and N rate on translocation of dry matter of hybrid rice at heading stage under high temperature and high humidity condition
| 年份 Year | 处理 Treatment | 花前干物质 转运量 TDMHD (g?m?2) | 花前干物质转 运效率 TPDMHD (g?m?2) | 花前干物质转运 对产量的贡献率 CPDMTGHD (g?m?2) | 花后干物质积累 对产量的贡献率 CPDMGHD-MA (g?m?2) | ||
| 代码 Code | 密度 Plant density (×104 holes?hm?2) | 施氮量 N application rate (kg?hm?2) | |||||
| 2018 | LDN0 | 16.5 | 0 | 341.4±73.2c | 55.7±11.7ab | 54.6±8.8a | 45.4±8.8a |
| LDN?15% | 16.5 | 153 | 452.1±15.0b | 46.1±2.1b | 54.4±2.2a | 45.6±2.2a | |
| LDN?30% | 16.5 | 126 | 507.3±67.2ab | 54.5±8.0ab | 62.4±7.3a | 37.6±7.3a | |
| HDN?15% | 21.0 | 153 | 581.7±30.9a | 57.4±3.4a | 65.4±3.3a | 34.6±3.3a | |
| HDN?30% | 21.0 | 126 | 512.7±75.7ab | 52.7±3.8ab | 59.0±10.5a | 41.0±10.5a | |
| LDNCK | 16.5 | 180 | 470.6±9.7b | 48.1±1.1ab | 55.3±2.2a | 44.7±2.2a | |
| 2019 | LDN0 | 16.5 | 0 | 333.3±74.4b | 39.2±6.8b | 52.7±12.0b | 47.3±12.0a |
| LDN?15% | 16.5 | 153 | 583.2±30.8a | 51.6±3.2a | 67.7±3.6a | 32.3±3.6b | |
| LDN?30% | 16.5 | 126 | 630.6±89.3a | 56.9±6.8a | 75.1±9.3a | 24.9±9.3b | |
| HDN?15% | 21.0 | 153 | 587.5±25.8a | 51.6±1.7a | 63.5±3.4ab | 36.5±3.4ab | |
| HDN?30% | 21.0 | 126 | 628.6±65.4a | 56.9±4.8a | 68.7±5.6a | 31.3±5.6b | |
| LDNCK | 16.5 | 180 | 565.3±91.9a | 49.7±4.8a | 63.9±5.6ab | 36.1±5.6ab | |
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance | |||||||
| 年份 Year (Y) | ** | ns | ** | ** | |||
| 处理 Treatment (T) | ** | ns | * | * | |||
| 年份×处理 Y′T | ns | * | ns | ns | |||
| 同年同列数据后不同字母表示处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。*表示差异达P<0.05显著水平, **表示差异达P<0.01显著水平, ns 表示差异不显著。Values followed by different letters in a year within a column are significantly different at P<0.05 level. * and ** mean significance at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectively. ns denotes non-significance. TDMHD, TPDMHD, CPDMTGHD, CPDMGHD-MA represent translocation of dry matter accumulated at heading stage, translocation percentage of dry matter accumulated at heading stage, contribution percentage of pre-anthesis dry matter translocation to grain yield, contribution percentage of dry matter accumulation from heading to maturity stage to grain yield, respectively. | |||||||
 下载: 导出CSV
下载: 导出CSV表4高温高湿区不同密肥处理对杂交稻植株氮素吸收积累的影响
Table4.Effect of combination of plant density and N rate on N uptake of hybrid rice under high temperature and high humidity condition
| 年份 Year | 处理 Treatment | 氮素吸收量 N uptake (g?m?2) | 氮素总吸收量 Total N uptake (g?m?2) | 氮素收获指数 N harvest index (%) | ||||
| 代码 Code | 密度 Plant density (×104 holes?hm?2) | 施氮量 N application rate (kg?hm?2) | 开花前 Before heading | 开花后 After heading | ||||
| 2018 | LDN0 | 16.5 | 0 | 6.2±0.5d | 2.5±1.0abc | 8.7±0.5d | 75.3±4.4a | |
| LDN?15% | 16.5 | 153 | 12.6±0.2a | 1.4±0.4c | 14.0±0.2bc | 68.6±0.7cd | ||
| LDN?30% | 16.5 | 126 | 9.8±0.8c | 3.4±0.9ab | 13.2±0.8c | 70.0±1.7bcd | ||
| HDN?15% | 21.0 | 153 | 12.4±0.4a | 2.1±0.6bc | 14.5±0.9ab | 71.9±2.2abc | ||
| HDN?30% | 21.0 | 126 | 11.5±0.5b | 2.6±1.6abc | 14.1±1.4bc | 72.6±1.0ab | ||
| LDNCK | 16.5 | 180 | 11.6±0.5b | 3.5±0.5a | 15.1±0.9a | 67.6±2.3d | ||
| 2019 | LDN0 | 16.5 | 0 | 6.4±0.4d | 2.8±0.7a | 9.1±0.4c | 73.3±1.5a | |
| LDN?15% | 16.5 | 153 | 11.4±0.2a | 2.4±0.6a | 13.8±0.5a | 69.0±1.0b | ||
| LDN?30% | 16.5 | 126 | 10.6±0.7bc | 2.3±1.2a | 13.0±0.7b | 69.7±1.4b | ||
| HDN?15% | 21.0 | 153 | 11.1±0.4ab | 2.9±0.2a | 14.0±1.0a | 68.5±1.9b | ||
| HDN?30% | 21.0 | 126 | 10.2±0.4c | 3.1±0.3a | 13.3±0.4ab | 71.2±2.1b | ||
| LDNCK | 16.5 | 180 | 10.9±0.2abc | 3.4±0.5a | 14.3±0.4ab | 64.9±0.9c | ||
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance | ||||||||
| 年份 Year (Y) | ** | ns | ns | * | ||||
| 处理 Treatment (T) | ** | * | * | ** | ||||
| 年份×处理 Y×T | ** | ns | ns | ns | ||||
| 同年同列数据后不同字母表示处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。*表示差异达P<0.05显著水平, **表示差异达P<0.01显著水平, ns 表示差异不显著。Values followed by different letters in a year within a column are significantly different at P<0.05 level. * and ** mean significance at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectively. ns denotes non-significance. | ||||||||
 下载: 导出CSV
下载: 导出CSV表5高温高湿区不同密肥处理对杂交稻齐穗期茎叶氮素运转的影响
Table5.Effect of combination of plant density and N rate on nitrogen translocation of stem and leaf of hybrid rice under high temperature and high humidity condition
| 年份 Year | 处理 Treatment | 氮素转运量 N translocation (g?m?2) | 氮素表观转运率 Apparent N translocation rate (%) | 氮素转运贡献率 N translocate contribution rate (%) | ||
| 代码 Code | 密度 Plant density (×104 holes?hm?2) | 施氮量 N application rate (kg?hm?2) | ||||
| 2018 | LDN0 | 16.5 | 0 | 2.8±0.8c | 56.2±10.5abc | 43.1±12.2d |
| LDN?15% | 16.5 | 153 | 6.6±0.2a | 60.0±1.4ab | 68.8±2.4a | |
| LDN?30% | 16.5 | 126 | 4.3±0.8b | 51.9±3.4bc | 46.7±9.6cd | |
| HDN?15% | 21.0 | 153 | 6.4±0.8a | 61.4±2.3a | 62.0±1.3ab | |
| HDN?30% | 21.0 | 126 | 5.8±0.3a | 60.1±1.4ab | 57.0±1.6bc | |
| LDNCK | 16.5 | 180 | 4.8±0.6b | 49.2±4.9c | 46.5±4.6cd | |
| 2019 | LDN0 | 16.5 | 0 | 2.8±0.5c | 52.8±4.0a | 41.5±9.7b |
| LDN?15% | 16.5 | 153 | 4.9±0.3ab | 53.1±2.7a | 51.0±3.2ab | |
| LDN?30% | 16.5 | 126 | 5.0±0.6a | 55.9±2.9a | 55.7±9.9a | |
| HDN?15% | 21.0 | 153 | 4.8±0.5ab | 52.3±3.8a | 50.4±3.2ab | |
| HDN?30% | 21.0 | 126 | 4.6±0.5ab | 54.6±1.4ab | 48.2±2.6ab | |
| LDNCK | 16.5 | 180 | 4.0±0.4b | 44.6±3.2b | 43.7±5.1ab | |
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance | ||||||
| 年份 Year (Y) | ** | ** | * | |||
| 处理 Treatment (T) | ** | ** | ** | |||
| 年份×处理 Y×T | ** | ns | * | |||
| 同年同列数据后不同字母表示处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。*表示差异达P<0.05显著水平, **表示差异达P<0.01显著水平, ns 表示差异不显著。Values followed by different letters in a year within a column are significantly different at P<0.05 level. * and ** mean significance at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectively. ns denotes non-significance. | ||||||
 下载: 导出CSV
下载: 导出CSV表6高温高湿区不同密肥处理对杂交稻氮肥利用率的影响
Table6.Effect of combination of plant density and N rate on nitrogen use efficiency of hybrid rice under high temperature and high humidity condition
| 年份 Year | 处理 Treatment | 氮肥农学利用率 Agronomic efficiency of applied N (kg?kg?1) | 氮肥偏生产力 Partial factor productivity of applied N (kg?kg?1) | 氮肥吸收利用率 Recovery efficiency of applied N (%) | ||
| 代码 Code | 密度 Plant density (×104 holes?hm?2) | 施氮量 N application rate (kg?hm?2) | ||||
| 2018 | LDN?15% | 16.5 | 153 | 13.7±2.1c | 54.3±1.4d | 34.5±3.7b |
| LDN?30% | 16.5 | 126 | 15.0±3.6bc | 64.4±1.1b | 36.0±3.2ab | |
| HDN?15% | 21.0 | 153 | 17.5±2.1ab | 58.1±0.7c | 38.2±4.5ab | |
| HDN?30% | 21.0 | 126 | 19.9±3.2a | 69.2±2.9a | 43.4±9.5a | |
| LDNCK | 16.5 | 180 | 12.8±3.1c | 47.3±1.5e | 36.2±1.8ab | |
| 2019 | LDN?15% | 16.5 | 153 | 14.9±2.0c | 56.3±1.6d | 30.7±3.1a |
| LDN?30% | 16.5 | 126 | 16.3±1.2bc | 66.5±1.2b | 30.5±7.8a | |
| HDN?15% | 21.0 | 153 | 19.1±0.9b | 60.5±0.8c | 31.7±3.4a | |
| HDN?30% | 21.0 | 126 | 22.3±1.9a | 72.6±1.8a | 33.1±5.5a | |
| LDNCK | 16.5 | 180 | 13.9±3.0c | 49.0±2.8e | 28.3±4.1b | |
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance | ||||||
| 年份 Year (Y) | ns | ** | ** | |||
| 处理 Treatment (T) | * | ** | ns | |||
| 年份×处理 Y×T | ns | ns | ns | |||
| 同年同列数据后不同字母表示处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。*表示差异达P<0.05显著水平, **表示差异达P<0.01显著水平, ns 表示差异不显著。Values followed by different letters in a year within a column are significantly different at P<0.05 level. * and ** mean significance at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectively. ns denotes non-significance. | ||||||
 下载: 导出CSV
下载: 导出CSV表7高温高湿区不同密肥处理对杂交稻每生产100 kg稻谷需氮量、氮素干物质生产效率、氮素籽粒生产效率的影响
Table7.Effect of combination of plant density and N rate on N use efficiency for biomass and grain yield production and N requirement for produced 100 kg grain of hybrid rice under high temperature and high humidity condition
| 年份 Year | 处理 Treatment | 100 kg稻谷需氮量 N requirement of 100 kg grains (kg) | 氮素干物质生产效率 N use efficiency for biomass production (kg?kg?1) | 氮素籽粒生产效率 N use efficiency for grain production (kg?kg?1) | ||
| 代码 Code | 密度 Plant density (×104 holes?hm?2) | 施氮量 N application rate (kg?hm?2) | ||||
| 2018 | LDN0 | 16.5 | 0 | 1.39±0.19 b | 103.8±9.0 a | 72.5±9.1 a |
| LDN?15% | 16.5 | 153 | 1.67±0.04 a | 97.8±1.1 ab | 59.8±1.3 b | |
| LDN?30% | 16.5 | 126 | 1.62±0.03 a | 93.9±6.3 b | 61.6±1.1 b | |
| HDN?15% | 21.0 | 153 | 1.63±0.05 a | 91.3±2.7 b | 61.5±1.8 b | |
| HDN?30% | 21.0 | 126 | 1.62±0.22 a | 95.1±12.7 ab | 62.5±9.2 b | |
| LDNCK | 16.5 | 180 | 1.78±0.04 a | 89.9±1.5 b | 56.3±1.4 b | |
| 2019 | LDN0 | 16.5 | 0 | 1.45±0.06 b | 125.4±2.1 a | 69.3±2.9 a |
| LDN?15% | 16.5 | 153 | 1.61±0.02 a | 101.8±3.4 b | 62.2±0.6 c | |
| LDN?30% | 16.5 | 126 | 1.55±0.11 ab | 101.3±5.5 b | 64.7±4.5 bc | |
| HDN?15% | 21.0 | 153 | 1.51±0.02 abc | 105.4±0.8 b | 66.1±1.0 abc | |
| HDN?30% | 21.0 | 126 | 1.46±0.04 bc | 104.4±4.2 b | 68.7±1.7 ab | |
| LDNCK | 16.5 | 180 | 1.62±0.04 a | 102.2±5.3 b | 61.9±1.7 c | |
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance | ||||||
| 年份 Year (Y) | ** | * | ** | |||
| 处理 Treatment (T) | ** | ** | ** | |||
| 年份×处理 Y×T | ns | ns | ns | |||
| 同年同列数据后不同字母表示处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。*表示差异达P<0.05显著水平, **表示差异达P<0.01显著水平, ns 表示差异不显著。Values followed by different letters in a year within a column are significantly different at P<0.05 level. * and ** mean significance at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectively. ns denotes non-significance | ||||||
 下载: 导出CSV
下载: 导出CSV参考文献
| [1] | 邹应斌, 周上游, 唐起源. 中国超级杂交水稻超高产栽培研究的现状与展望[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2003, 5(1): 31?35 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0864.2003.01.007 ZOU Y B, ZHOU S Y, TANG Q Y. Status and outlook of high yielding cultivation researches on China super hybrid rice[J]. Review of China Agricultural Science and Technology, 2003, 5(1): 31?35 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0864.2003.01.007 |
| [2] | 朱德峰, 林贤青, 曹卫星. 超高产水稻品种的根系分布特点[J]. 南京农业大学学报, 2000, 23(4): 5?8 ZHU D F, LIN X Q, CAO W X. Characteristics of root distribution of super high yielding rice varieties[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 2000, 23(4): 5?8 |
| [3] | 袁小乐, 潘晓华, 石庆华, 等. 超级早、晚稻的养分吸收和根系分布特性研究[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2010, 16(1): 27?32 doi: 10.11674/zwyf.2010.0105 YUAN X Y, PAN X H, SHI Q H, et al. Characteristics of nutrient uptake and root system distribution in super early and super late rice[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2010, 16(1): 27?32 doi: 10.11674/zwyf.2010.0105 |
| [4] | 朱铁忠, 柯健, 姚波, 等. 沿江双季北缘区机插早稻的超高产群体特征[J]. 中国农业科学, 2021, 54(7): 1553?1564 doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2021.07.018 ZHU T Z, KE J, YAO B, et al. Super-high yield characteristics of mechanically transplanting double-cropping early rice in the northern margin area of Yangtze River[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2021, 54(7): 1553?1564 doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2021.07.018 |
| [5] | JIANG P, XIE X B, HUANG M, et al. Potential yield increase of hybrid rice at five locations in Southern China[J]. Rice, 2016, 9(1): 1?14 doi: 10.1186/s12284-015-0073-2 |
| [6] | 邹应斌. 长江流域双季稻栽培技术发展[J]. 中国农业科学, 2011, 44(2): 254?262 doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2011.02.004 ZOU Y B. Development of cultivation technology for double cropping rice along the Changjiang River valley[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2011, 44(2): 254?262 doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2011.02.004 |
| [7] | PENG S B, TANG Q Y, ZOU Y B. Current status and challenges of rice production in China[J]. Plant Production Science, 2009, 12(1): 3?8 doi: 10.1626/pps.12.3 |
| [8] | 朱兆良. 我国土壤供氮和化肥氮去向研究的进展[J]. 土壤, 1985, 17(1): 2?9 ZHU Z L. Research in soil supply nitrogen and fate of fertilizer nitrogen Chinese[J]. Soils, 1985, 17(1): 2?9 |
| [9] | WANG G H, DOBERMANN A, WITT C, et al. Performance of site-specific nutrient management for irrigated rice in southeast China[J]. Agronomy Journal, 2001, 93(4): 869?878 doi: 10.2134/agronj2001.934869x |
| [10] | HUANG M, YANG C L, JI Q M, et al. Tillering responses of rice to plant density and nitrogen rate in a subtropical environment of Southern China[J]. Field Crops Research, 2013, 149: 187?192 doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2013.04.029 |
| [11] | AO H J, XIE X B, HUANG M, et al. Decreasing hill density combined with increasing nitrogen rate led to yield decline in hybrid rice under low-light conditions[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9: 15786 doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-52376-2 |
| [12] | 朱兆良, 金继运. 保障我国粮食安全的肥料问题[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2013, 19(2): 259?273 doi: 10.11674/zwyf.2013.0201 ZHU Z L, JIN J Y. Fertilizer use and food security in China[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2013, 19(2): 259?273 doi: 10.11674/zwyf.2013.0201 |
| [13] | PENG S B, BURESH R J, HUANG J L, et al. Improving nitrogen fertilization in rice by sitespecific N management. A review[J]. Agronomy for Sustainable Development, 2010, 30(3): 649?656 doi: 10.1051/agro/2010002 |
| [14] | WU W, NIE L X, LIAO Y C, et al. Toward yield improvement of early-season rice: Other options under double rice-cropping system in central China[J]. European Journal of Agronomy, 2013, 45: 75?86 doi: 10.1016/j.eja.2012.10.009 |
| [15] | 谢小兵, 王玉梅, 黄敏, 等. 单本密植机插对杂交稻生长和产量的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2016, 42(6): 924?931 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2016.00924 XIE X B, WANG Y M, HUANG M, et al. Effect of mechanized transplanting with high hill density and single seedling per hill on growth and grain yield in hybrid rice[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2016, 42(6): 924?931 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2016.00924 |
| [16] | HUANG M, CHEN J N, CAO F B, et al. Increased hill density can compensate for yield loss from reduced nitrogen input in machine-transplanted double-cropped rice[J]. Field Crops Research, 2018, 221: 333?338 doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2017.06.028 |
| [17] | 马金玉, 梁宏, 罗勇, 等. 中国近50年太阳直接辐射和散射辐射变化趋势特征[J]. 物理学报, 2011, 60(6): 069601 doi: 10.7498/aps.60.069601 MA J Y, LIANG H, LUO Y, et al. Variation trend of direct and diffuse radiation in China over recent 50 years[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2011, 60(6): 069601 doi: 10.7498/aps.60.069601 |
| [18] | 周开达. 四川水稻超高产育种的发展趋势[J]. 西南农业学报, 1998, 11(S2): 1 ZHOU K D. Trends of super high yield breeding in rice (Oryza sativa L.) in Sichuan Province[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 1998, 11(S2): 1 |
| [19] | 周开达, 马玉清, 刘太清, 等. 杂交水稻亚种间重穗型组合选育?杂交水稻超高产育种的理论与实践[J]. 四川农业大学学报, 1995, 13(4): 403?407 ZHOU K D, MA Y Q, LIU T Q, et al. The breeding of subspecific heavy ear hybrid rice—exploration about super-high yield breeding of hybrid rice[J]. Journal of Sichuan Agricultural University, 1995, 13(4): 403?407 |
| [20] | 徐富贤, 熊洪, 朱永川, 等. 川东南冬水田杂交中稻进一步高产的栽培策略[J]. 作物学报, 2007, 33(6): 1004?1009 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0496-3490.2007.06.023 XU F X, XIONG H, ZHU Y C, et al. Cultivation strategy of hybrid mid-season rice for further high yield in winter water-logged field in the southeast of Sichuan Province[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2007, 33(6): 1004?1009 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0496-3490.2007.06.023 |
| [21] | 陈佳娜, 曹放波, 谢小兵, 等. 机插条件下低氮密植栽培对“早晚兼用”双季稻产量和氮素吸收利用的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2016, 42(8): 1176?1187 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2016.01176 CHEN J N, CAO F B, XIE X B, et al. Effect of low nitrogen rate combined with high plant density on yield and nitrogen use efficiency of machine-transplanted early-late season double cropping rice[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2016, 42(8): 1176?1187 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2016.01176 |
| [22] | 周建霞, 张玉屏, 朱德峰, 等. 空气湿度和土壤水分对高温诱导水稻颖花不育的影响[J]. 江西农业学报, 2017, 29(2): 24?27 ZHOU J X, ZHANG Y P, ZHU D F, et al. Effects of air humidity and soil moisture on rice spikelet sterility induced by high temperature[J]. Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi, 2017, 29(2): 24?27 |
| [23] | 蒋鹏, 熊洪, 张林, 等. 不同生态条件下施氮量和移栽密度对杂交稻旌优127产量及稻米品质的影响[J]. 核农学报, 2017, 31(10): 2007?2015 doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2017.10.2007 JIANG P, XIONG H, ZHANG L, et al. Effects of nitrogen fertilization and planting density on grain yield and quality of Jingyou127 and rice quality under different ecological conditions[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 31(10): 2007?2015 doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2017.10.2007 |
| [24] | 马均, 朱庆森, 马文波, 等. 重穗型水稻光合作用、物质积累与运转的研究[J]. 中国农业科学, 2003, 36(4): 375?381 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0578-1752.2003.04.004 MA J, ZHU Q S, MA W B, et al. Studies on the photosynthetic characteristics and accumulation and transformation of assimilation product in heavy panicle type of rice[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2003, 36(4): 375?381 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0578-1752.2003.04.004 |
| [25] | YANG J C, PENG S B, ZHANG Z J, et al. Grain and dry matter yields and partitioning of assimilates in Japonica/indica hybrid rice[J]. Crop Science, 2002, 42(3): 766 doi: 10.2135/cropsci2002.0766 |
| [26] | 谢小兵, 蒋鹏, 黄敏, 等. 基于黄金分割法的双季稻合理密植研究[J]. 核农学报, 2016, 30(12): 2467?2476 doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2016.12.2467 XIE X B, JIANG P, HUANG M, et al. Study on rational close planting based on golden section method for double cropping rice[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 30(12): 2467?2476 doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2016.12.2467 |
| [27] | 徐新朋, 周卫, 梁国庆, 等. 氮肥用量和密度对双季稻产量及氮肥利用率的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2015, 21(3): 763?772 doi: 10.11674/zwyf.2015.0324 XU X P, ZHOU W, LIANG G Q, et al. Effects of nitrogen and density interactions on grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency of double-rice systems[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2015, 21(3): 763?772 doi: 10.11674/zwyf.2015.0324 |
| [28] | 黄巧义, 唐拴虎, 张发宝, 等. 减氮配施控释尿素对水稻产量和氮肥利用的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2017, 25(6): 829?838 HUANG Q Y, TANG S H, ZHANG F B, et al. Effect of combined application of controlled-release urea and conventional urea under reduced N rate on yield and N utilization efficiency of rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2017, 25(6): 829?838 |
| [29] | 肖小平, 李超, 唐海明, 等. 秸秆还田下减氮增密对双季稻田土壤氮素库容及氮素利用率的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文), 2019, 27(3): 422?430 XIAO X P, LI C, TANG H M, et al. Soil nitrogen storage and recovery efficiency in double paddy fields under reduced nitrogen dose and increased crop density[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2019, 27(3): 422?430 |
| [30] | CHEN Y T, PENG J, WANG J, et al. Crop management based on multi-split topdressing enhances grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency in irrigated rice in China[J]. Field Crops Research, 2015, 184: 50?57 doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2015.09.006 |
| [31] | PENG S B, BURESH R J, HUANG J L, et al. Strategies for overcoming low agronomic nitrogen use efficiency in irrigated rice systems in China[J]. Field Crops Research, 2006, 96(1): 37?47 doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2005.05.004 |
| [32] | JIANG L G, DAI T B, JIANG D, et al. Characterizing physiological N-use efficiency as influenced by nitrogen management in three rice cultivars[J]. Field Crops Research, 2004, 88(2/3): 239?250 |
| [33] | QIAO J, YANG L Z, YAN T M, et al. Nitrogen fertilizer reduction in rice production for two consecutive years in the Taihu Lake area[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 2012, 146(1): 103?112 |
| [34] | 敖和军, 王淑红, 邹应斌, 等. 不同施肥水平下超级杂交稻对氮、磷、钾的吸收累积[J]. 中国农业科学, 2008, 41(10): 3123?3132 doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2008.10.028 AO H J, WANG S H, ZOU Y B, et al. Characteristics of nutrient uptake and utilization of super hybrid rice under different fertilizer application rates[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2008, 41(10): 3123?3132 doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2008.10.028 |
| [35] | 徐富贤, 熊洪, 张林, 等. 西南稻区不同地域和施氮水平对杂交中稻氮、磷、钾吸收累积的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2011, 37(5): 882?894 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2011.00882 XU F X, XIONG H, ZHANG L, et al. Characteristics of nutrient uptake and utilization of mid-season hybrid rice under different nitrogen application rates in different locations of southwest China[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2011, 37(5): 882?894 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2011.00882 |
| [36] | 蒋鹏, 熊洪, 张林, 等. 不同生态条件下施氮量和移栽密度对杂交稻氮、磷、钾吸收积累的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2017, 23(2): 342?350 doi: 10.11674/zwyf.16280 JIANG P, XIONG H, ZHANG L, et al. Effects of N rate and planting density on nutrient uptake and utilization of hybrid rice under different ecological conditions[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2017, 23(2): 342?350 doi: 10.11674/zwyf.16280 |
