李善伟,
徐璞,
上海海洋大学经济管理学院 上海 201306
基金项目:上海市哲学社会科学规划项目(2018BGL015)资助
详细信息
作者简介:李玉峰, 主要研究方向为食品安全与消费、都市农业、生鲜农产品品牌与渠道。E-mail: liyf@shou.edu.cn
通讯作者:徐璞, 主要研究方向为休闲农业、食品安全。E-mail: pxu@shou.edu.cn
中图分类号:F301计量
文章访问数:97
HTML全文浏览量:35
PDF下载量:35
被引次数:0
出版历程
收稿日期:2021-06-02
录用日期:2021-07-16
网络出版日期:2021-07-29
刊出日期:2021-10-01
Realization path of moderate expansion of management scale of urban leisure agriculture
LI Yufeng,LI Shanwei,
XU Pu,
School of Economics and Management, Shanghai Ocean University, Shanghai 201306, China
Funds:This study was supported by the Philosophy and Social Science Planning Project of Shanghai City (2018BGL015)
More Information
Corresponding author:E-mail: pxu@shou.edu.cn
摘要
HTML全文
图
参考文献
相关文章
施引文献
资源附件
访问统计
摘要
摘要:限于大都市的资源与政策限制, 为实现都市休闲农业主体规模经营意愿, 寻求休闲农业主体如何在现有资源约束下适度扩大规模, 有效促进都市休闲农业可持续发展, 本文基于上海市87家休闲农业主体问卷数据, 构建Logistic-ISM模型, 以休闲农业主体农地规模意愿为测度目标, 研究影响意愿的显著性因素及各因素间的逻辑层次关系。结果表明: 适度扩大规模取决于3个层次因素的影响。1)深层根源因素中, 受到政府建设用地支持的休闲农业主体扩大农地规模意愿更强烈。2)中层间接因素中, 农业资源特色性、园区规划科学性、创新经营能力、经营产业结构对休闲农业主体扩大农地规模意愿具有显著的正向影响; 而农业生产生态性强, 则会减弱其扩大农地规模的意愿。3)表层直接因素中, 文化功能型的休闲农业主体愿意扩大农地规模, 而休闲功能型的经营主体倾向降低农地规模。为促进都市休闲农业适度规模经营, 政府应引入国企发挥示范效应, 盘活乡村存量的土地资源, 释放资源价值。同时, 休闲农业应为都市核心功能提供战略空间, 充分考虑休闲农业主体异质性, 深挖乡村文化底蕴, 促进从承担农产品保障供应功能向承担多元复合功能转变, 凸显农业农村的经济价值、生态价值、美学价值。
关键词:适度规模经营/
Logistic-ISM模型/
休闲农业主体/
农地规模意愿/
都市休闲农业
Abstract:It is necessary to determine how to appropriately expand the scale of leisure agriculture entities under constraints of existing resources and effectively promote sustainable development of urban leisure agriculture for realization of large-scale operational willingness of urban leisure agriculture entities limited to resources and policy restrictions of metropolises. Based on questionnaire data of 87 leisure agriculture entities in Shanghai, this study constructed a Logistic-ISM (interpretation structure model) model and took the willingness of leisure agriculture entities as measurement targets to study significant factors that affected the willingness, and logical hierarchical relationships between factors. Results showed that moderate expansion depended on the influence of the three levels of factors: 1) Among deep-seated factors, the leisure agriculture entities supported by government construction land were more willing to expand the scale of farmland. 2) Among middle-level indirect factors, the characteristics of agricultural resources, scientific park planning, innovative management capabilities, and business industrial structure positively affected the willingness of leisure agriculture entities to expand the scale of farmland, while the ecological nature of agricultural production was strong, the expansion of operators’ willingness to farmland size was weak. 3) Among the direct factors at the surface level, culturally functional leisure agriculture entities were willing to expand the scale of farmland, while leisure functional management entities tended to reduce the scale of farmland. To promote moderate scale operation of urban leisure agriculture, the government should introduce state-owned enterprises to play a demonstration effect to revitalize stock of rural land resources, and release value of resources. At the same time, leisure agriculture should provide strategic space for urban core functions, fully consider the heterogeneity of leisure agriculture entities, dig deep into rural cultural heritage, and promote transformation from undertaking the function of guaranteeing the supply of agricultural products for multiple functions to highlighting the economic, ecological, and esthetic values of agriculture and rural areas.
Key words:Moderate scale management/
Logistic-ISM model/
Leisure agriculture entities/
Farmland scale willingness/
Urban leisure agriculture
HTML全文
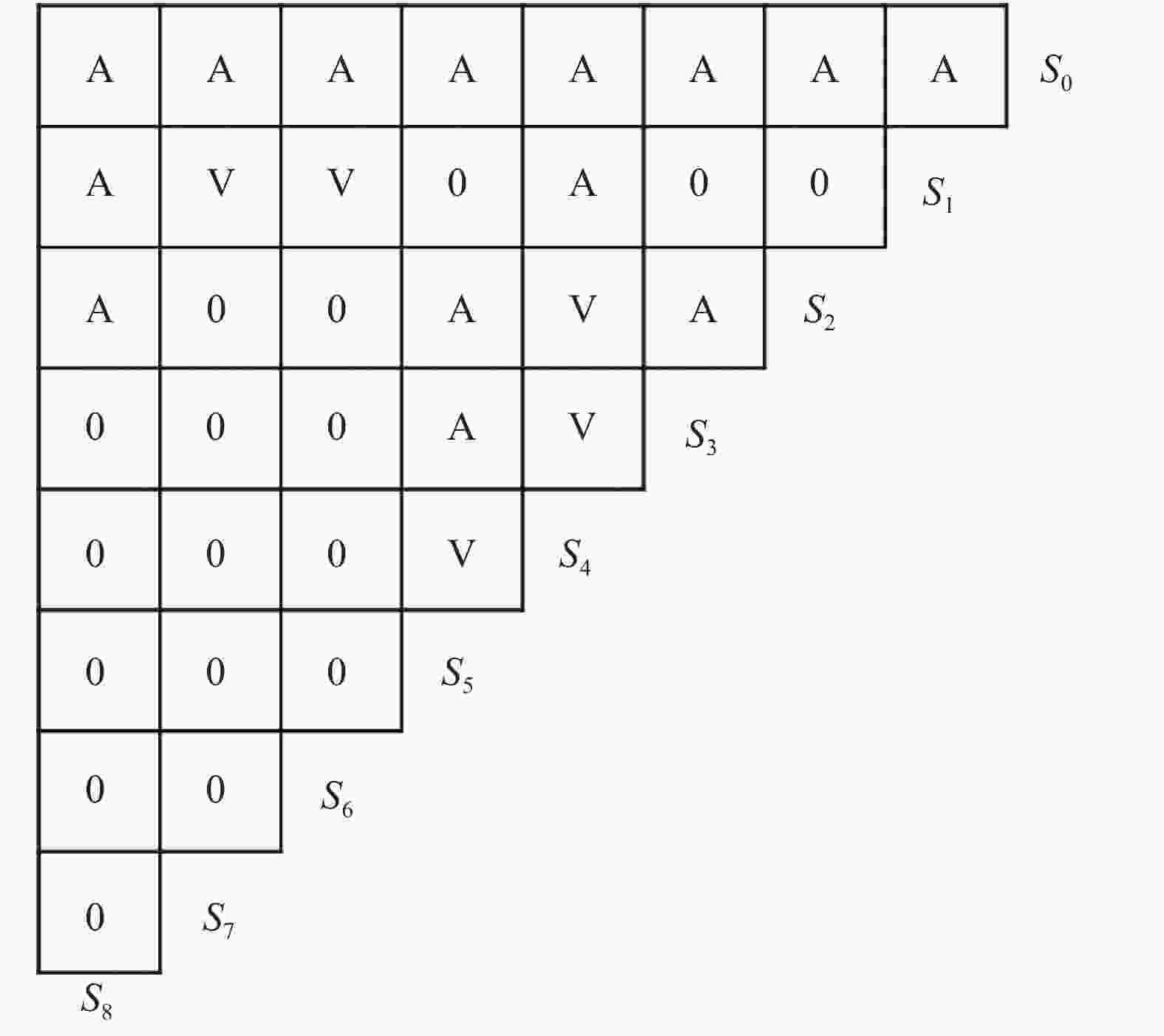
图1休闲农业主体农地规模意愿影响因素间的逻辑关系
S0、S1、S2、S3、S4、S5、S6、S7和S8分别表示休闲农业主体农地规模意愿、经营产业结构、农业资源特色性、农业生产生态性、园区规划科学性、创新经营能力、休闲功能型、文化功能型和建设用地支持; 例: 若行因素S0对列因素S1有直接或间接的影响, 则为“V”; 若列因素S1对行因素S0有直接或间接的影响, 则为“A”; 若S0与S1之间不存在影响关系, 则为“0”。S0, S1, S2, S3, S4, S5, S6, S7, and S8 respectively represent willingness of farmland scale of leisure agriculture entities, structure of business industry, characteristics of agricultural resources, ecological nature of agricultural production, scientific nature of park planning, ability of innovative management, leisure function, cultural function and construction land support. If row factor S0 has a direct or indirect influence on column factor S1, it is “V”; if column factor S1 has a direct or indirect influence on row factor S0, it is “ A”; if there is no influencing relationship between S0 and S1, it is “0”.
Figure1.Logical relationship among factors affecting willingness of agricultural farmland scale of leisure agriculture entities
 下载: 全尺寸图片幻灯片
下载: 全尺寸图片幻灯片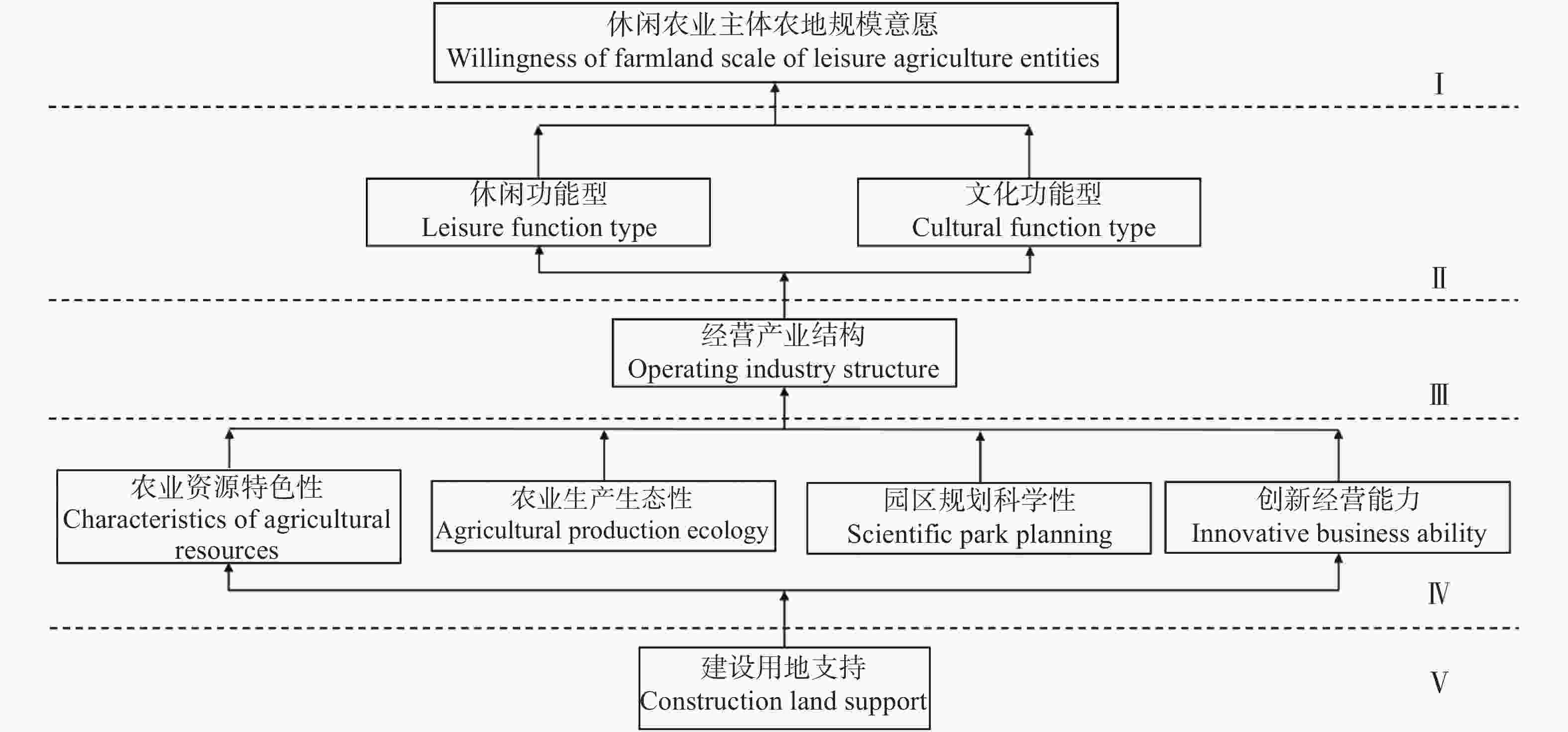
图2休闲农业主体农地规模意愿影响因素的关联关系与层级结构
Figure2.Correlation and hierarchical structure of factors affecting willingness of agricultural farmland scale of leisure agriculture entities
 下载: 全尺寸图片幻灯片
下载: 全尺寸图片幻灯片表1模型变量的解释及样本特征
Table1.Interpretation of model variables and sample characteristics
| 变量类型 Variable type | 变量名称 Variable | 含义及赋值 Connotation and assignment | 均值 Mean | 标准差 Standard deviation | 预期方向 Expected direction |
| 被解释变量 Explained variable | 农地规模意愿 Willingness to scale farmland | 降低农地规模=1; 保持农地规模不变=2; 扩大农地规模=3 Reduce scale of farmland=1; keep scale of farmland unchanged=2; expand scale of farmland=3 | 2.460 | 0.606 | |
| 解释变量 Explanatory variables | |||||
| 主体特征 Entities characteristics | 农园经营规模 Farm management scale | <5 hm2=1; 5~100 hm2=2; 100~200 hm2=3; >200 hm2=4 | 1.954 | 0.608 | ? |
| 经营产业结构 Operating industry structure | 仅涉及第一产业=1; 涉及第一、第二产业=2; 涉及第一、第三产业=3; 涉及第一、第二、第三产业=4 Only involving primary industry=1; involving primary and secondary industries=2; involving primary and tertiary industries=3; all=4 | 2.609 | 1.145 | + | |
| 经营者年龄 Operator’s age | ≤40=1; 41~50 =2; 51~60 =3; ≥61=4 | 1.897 | 0.683 | ? | |
| 经营者文化程度 Educational level of operator | 初中及以下=1; 中专或高中=2; 大专=3; 本科及以上=4 Junior high school and below=1; technical secondary school or high school=2; junior college=3; undergraduate and above=4 | 2.713 | 0.820 | ? | |
| 环境特征 Environmental characteristics | 农业资源特色性 Characteristics of agricultural resources | 没有特色=1; 特色不明显=2; 特色一般=3; 比较有特色=4; 很有特色=5 No features=1; not obvious features=2; general features=3; more distinctive=4; very distinctive=5 | 3.920 | 1.059 | + |
| 农业生产生态性 Agricultural production ecology | 很差=1; 较差=2; 一般=3; 较好=4; 很好=5 Very poor=1; poor=2; general=3; good=4; very good=5 | 4.046 | 0.939 | ? | |
| 园区规划科学性 Scientific park planning | 很差=1; 较差=2; 一般=3; 较好=4; 很好=5 Very poor=1; poor=2; general=3; good=4; very good=5 | 3.724 | 1.008 | + | |
| 硬件设施完备性 Completeness of hardware facilities | 很差=1; 较差=2; 一般=3; 较好=4; 很好=5 Very poor=1; poor=2; general=3; good=4; very good=5 | 3.644 | 0.927 | + | |
| 经营能力 Management capacity | 内部管理能力 Internal management capabilities | 很低=1; 较低=2; 一般=3; 较高=4; 很高=5 Very low=1; low=2; general=3; high=4; very high=5 | 3.828 | 0.810 | + |
| 营销推广能力 Marketing ability | 很低=1; 较低=2; 一般=3; 较高=4; 很高=5 Very low=1; low=2; general=3; high=4; very high=5 | 3.563 | 0.924 | + | |
| 创新经营能力 Innovative business ability | 很低=1; 较低=2; 一般=3; 较高=4; 很高=5 Very low=1; low=2; general=3; high=4; very high=5 | 3.609 | 0.957 | + | |
| 功能类型 Function type | 休闲功能型 Leisure function type | 是=1; 否=0 Yes=1; no=0 | 0.529 | 0.502 | +/? |
| 游乐功能型 Amusement function type | 是=1; 否=0 Yes=1; no=0 | 0.379 | 0.488 | +/? | |
| 文化功能型 Cultural function type | 是=1; 否=0 Yes=1; no=0 | 0.241 | 0.430 | +/? | |
| 政府支持 Governmental support | 土地流转扶持与优惠 Land transfer support and concessions | 是=1; 否=0 Yes=1; no=0 | 0.299 | 0.460 | + |
| 建设用地支持 Construction land support | 是=1; 否=0 Yes=1; no=0 | 0.264 | 0.444 | + | |
| 人员培训支持 Personnel training support | 是=1; 否=0 Yes=1; no=0 | 0.287 | 0.455 | + | |
 下载: 导出CSV
下载: 导出CSV表2休闲农业主体农地规模意愿影响因素的Logistic回归结果
Table2.Logistic regression results of factors influencing willingness of farmland scale of leisure agriculture entities
| 变量类型 Variable type | 变量 Variable | 方程(1) Equation (1) | 方程(2) Equation (2) | |||||
| 系数 Coefficient | Z统计量 Z-statistics | 概率比 Odds | 系数 Coefficient | Z统计量 Z-statistics | 概率比 Odds | |||
| 主体特征 Entities characteristics | 农园经营规模 Farm management scale | ?0.20 | ?0.43 | 0.82 | — | — | — | |
| 经营产业结构 Operating industry structure | 0.65 | 1.64 | 1.91 | 0.74** | 2.13 | 2.09 | ||
| 经营者年龄 Operator’s age | ?0.60 | ?1.21 | 0.55 | — | — | — | ||
| 经营者文化程度 Educational level of operator | ?0.42 | ?1.09 | 0.66 | — | — | — | ||
| 环境特征 Environmental characteristics | 农业资源特色性 Characteristics of agricultural resources | 0.93* | 1.94 | 2.53 | 0.88** | 2.01 | 2.41 | |
| 农业生产生态性 Agricultural production ecology | ?0.93** | ?2.18 | 0.39 | ?0.89** | ?2.50 | 0.41 | ||
| 园区规划科学性 Scientific park planning | ?0.77 | ?1.62 | 0.46 | ?0.67* | ?1.75 | 0.51 | ||
| 硬件设施完备性 Completeness of hardware facilities | 0.65 | 1.51 | 1.91 | — | — | — | ||
| 经营能力 Management capacity | 内部管理能力 Internal management capabilities | ?0.17 | ?0.24 | 0.85 | — | — | — | |
| 营销推广能力 Marketing ability | ?0.59 | ?1.03 | 0.56 | — | — | — | ||
| 创新经营能力 Innovative business ability | 1.81*** | 3.09 | 6.08 | 1.48*** | 3.43 | 4.38 | ||
| 功能类型 Function type | 休闲功能型 Leisure function type | ?2.02** | ?2.13 | 0.13 | ?2.04*** | ?2.62 | 0.13 | |
| 游乐功能型 Amusement function type | 0.65 | 0.86 | 1.91 | — | — | — | ||
| 文化功能型 Cultural function type | 1.17 | 1.56 | 3.22 | 1.22* | 1.92 | 3.38 | ||
| 政府支持 Governmental support | 土地流转扶持与优惠 Land transfer support and concessions | 0.89 | 1.39 | 2.42 | — | — | — | |
| 建设用地支持 Construction land support | ?1.41* | ?1.78 | 0.24 | ?1.29* | ?1.83 | 0.28 | ||
| 人员培训支持 Personnel training support | ?0.26 | ?0.39 | 0.77 | — | — | — | ||
| Pseudo R2 | 0.31 | 0.25 | ||||||
| Prob>chi2 | 0.000 | 0.000 | ||||||
| ***、**和*分别表示在P<1%、P<5%和P<10%的水平显著; 方程1为初始样本回归结果, 方程2为采用向后消元法后的样本回归结果。***, ** and * indicate significant at level of P<1%, P<5% and P<10% respectively. Equation 1 is initial sample regression result, and Equation 2 is sample regression result after adopting backward elimination method. | ||||||||
 下载: 导出CSV
下载: 导出CSV参考文献
| [1] | 冯建国, 陈奕捷. 以休闲农业为核心, 带动都市农业产业融合[J]. 中国农业资源与区划, 2011, 32(4): 61?65 FENG J G, CHEN Y J. Take the leisure agriculture as the core, driving the urban agriculture convergence[J]. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, 2011, 32(4): 61?65 |
| [2] | 李新仓. 农地规模经营法律规制的理论阐释与制度重构[J/OL]. 中国矿业大学学报(社会科学版). [2021-07-25]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/32.1593.C.20201203.0917.002.html LI X C. Legal regulations on scale management of agricultural land of legal interpretation and system reconstruction[J/OL]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology (Social Sciences). [2021-07-25]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/32.1593.C.20201203.0917.002.html |
| [3] | 陈磊, 刘志青, 赵邦宏. 中国休闲农业发展研究[J]. 湖北农业科学, 2012, 51(12): 2644?2647, 2656 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0439-8114.2012.12.067 CHEN L, LIU Z Q, ZHAO B H. Study on the development of leisure agriculture in China[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2012, 51(12): 2644?2647, 2656 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0439-8114.2012.12.067 |
| [4] | 任开荣, 董继刚, 吴元芳, 等. 农户对休闲农业的认知及参与意愿研究?基于山东省615份农户调研问卷的实证[J]. 中国农业资源与区划, 2020, 41(11): 218?225 REN K R, DONG J G, WU Y F, et al. Farmers’ cognition and willingness to participate in leisure agriculture—based on the survey of 615 farmers in Shandong[J]. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, 2020, 41(11): 218?225 |
| [5] | SZNAJDER M, PRZEZBóRSKA L, SCRIMGEOUR F. Agritourism[M]. Wallingford: CABI, 2009 |
| [6] | 王馨, 陈颖. 新时期我国家庭农场发展的困境与对策[J]. 学术交流, 2019, (7): 114?119 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8284.2019.07.013 WANG X, CHEN Y. Study on the difficulties and countermeasures of family farm development in China in the new period[J]. Academic Exchange, 2019, (7): 114?119 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8284.2019.07.013 |
| [7] | 刘婧, 王征兵, 张洁. 家庭农场的个体差异、要素投入与规模经济研究?基于山西省109家果蔬类家庭农场的实证分析[J]. 西部论坛, 2017, 27(3): 14?24 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8131.2017.03.003 LIU J, WANG Z B, ZHANG J. Research on individual differences, factor input and scale economy of family farmland—empirical analysis based on 109 vegetable and fruit type of farmlands in Shanxi Province[J]. West Forum, 2017, 27(3): 14?24 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8131.2017.03.003 |
| [8] | ATWOOD J A, HELMERS G A, SHAIK S. Farm and nonfarm factors influencing farm size[R/OL]. Long Beach: American Agricultural Economics Association, 2002. https://ideas.repec.org/p/ags/aaea02/19725.html |
| [9] | SNIDER L, LANGEMEIER M. A long-term analysis of changes in farm size and financial performance[R/OL]. Atlanta: Agricultural Economics Association, 2009. https://ideas.repec.org/p/ags/saeana/45915.html |
| [10] | DOLEV Y, KIMHI A. Does farm size really converge? the role of unobserved farm efficiency[R/OL]. Jerusalem: Hebrew University of Jerusalem, 2008. https://ideas.repec.org/p/ags/huaedp/45778.html |
| [11] | VIAGGI D, BARTOLINI F, PUDDU M, et al. Farm/household-level simulation: results of testing policy and other scenarios[J] Factor Markets Working Document, 2013, 54: 1−14 |
| [12] | Wl A, Pl A, Sm B. The proposed algorithm for identifying agricultural problem areas for the needs of their reasonable management under land consolidation works[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2018, 152: 333?339 doi: 10.1016/j.compag.2018.07.028 |
| [13] | 李冬艳, 余晓洋. 新型农业经营主体发展水平评价体系构建及测度[J]. 经济纵横, 2020, (2): 113?120 LI D Y, YU X Y. Construction and measurement of the evaluation system for the development of new agricultural management entities[J]. Economic Review Journal, 2020, (2): 113?120 |
| [14] | 赵宏伟, 黄秀娟. 休闲农业供应链的理论思考[J]. 福建论坛: 人文社会科学版, 2020, (2): 45?54 ZHAO H W, HUANG X J. Theoretical thinking on supply chain of leisure agriculture[J]. Fujian Tribune, 2020, (2): 45?54 |
| [15] | 李彬彬, 米增渝, 张正河. 休闲农业对农村经济发展贡献及影响机制?以全国休闲农业与乡村旅游示范县为例[J]. 经济地理, 2020, 40(2): 154?162 LI B B, MI Z Y, ZHANG Z H. The contribution and influence mechanism of leisure agriculture to rural economic development: taking the national demonstration county of leisure agriculture and rural tourism as an example[J]. Economic Geography, 2020, 40(2): 154?162 |
| [16] | 赵晓峰, 赵祥云. 农地规模经营与农村社会阶层结构重塑?兼论新型农业经营主体培育的社会学命题[J]. 中国农村观察, 2016, (6): 55?66 ZHAO X F, ZHAO X Y. Farmlands’ large-scale management and the re-stratification in rural society: the sociological proposition about cultivating new agricultural business entities[J]. China Rural Survey, 2016, (6): 55?66 |
| [17] | 赵鲲, 刘磊. 关于完善农村土地承包经营制度发展农业适度规模经营的认识与思考[J]. 中国农村经济, 2016, (4): 12?16 ZHAO K, LIU L. On perfecting the rural land contract management system development agriculture moderate scale management understanding and thinking[J]. Chinese Rural Economy, 2016, (4): 12?16 |
| [18] | 汪发元, 吴学兵, 孙文学. 新型农业经营者特征对其经营规模的影响研究[J]. 华东经济管理, 2016, 30(5): 61?64 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5097.2016.05.010 WANG F Y, WU X B, SUN W X. A study on the impact of new agricultural business entities’ characteristics on their business scale[J]. East China Economic Management, 2016, 30(5): 61?64 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5097.2016.05.010 |
| [19] | 孔令成. 基于综合效益视角的家庭农场土地适度规模研究——以松江粮食家庭农场为例[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2016 KONG L C. Research on the moderate land scale of family farms based on comprehensive benefit perspective—taking grain family farms in Songjiang as a case[D]. Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2016 |
| [20] | 李文明, 罗丹, 陈洁, 等. 农业适度规模经营: 规模效益、产出水平与生产成本?基于1552个水稻种植户的调查数据[J]. 中国农村经济, 2015, (3): 4?17 LI W M, LUO D, CHEN J, et al. Moderate scale management of agriculture: scale benefit, output level and production cost[J]. Chinese Rural Economy, 2015, (3): 4?17 |
| [21] | 毕雪昊, 周佳宁, 邹伟. 家庭劳动力约束下经营规模对农户种植结构选择的影响[J]. 中国土地科学, 2020, 34(12): 68?77 BI X H, ZHOU J N, ZOU W. The effect of operation scale on farmers’ planting structure selection under the constraints of family labor[J]. China Land Science, 2020, 34(12): 68?77 |
| [22] | 许庆, 尹荣梁, 章辉. 规模经济、规模报酬与农业适度规模经营?基于我国粮食生产的实证研究[J]. 经济研究, 2011, 46(3): 59?71 XU Q, YIN R L, ZHANG H. Economies of scale, returns to scale and the problem of optimum-scale farm management: an empirical study based on grain production in China[J]. Economic Research Journal, 2011, 46(3): 59?71 |
| [23] | 郑阳阳, 罗建利. 农户究竟想要多大的经营规模??12省2340个农户的现实需求及其影响因素分析[J]. 中国土地科学, 2019, 33(9): 74?83 ZHENG Y Y, LUO J L. How large is the operational scale preferred by farmers?: analysis of the actual demand and influencing factors of 2340 farmers in 12 provinces[J]. China Land Science, 2019, 33(9): 74?83 |
| [24] | 郑阳阳, 罗建利. 小农户愿意扩大经营规模吗??14省2074个小农户的现实需求及其影响因素分析[J]. 农村经济, 2020, (6): 9?15 ZHENG Y Y, LUO J L. Are small farmers willing to expand the scale of their operations?— analysis of the actual demand and influencing factors of 2047 small farmers in 14 provinces[J]. Rural Economy, 2020, (6): 9?15 |
| [25] | 王清军. 规模经营背景下农村环境行政管理的挑战和对策[J]. 环境保护, 2014, 42(21): 51?54 WANG Q J. Challenges and countermeasures of rural environmental administration under the background of the scale management[J]. Environmental Protection, 2014, 42(21): 51?54 |
| [26] | 杨芳, 郑淋议, 张应良. 农业经营范式的共生样态和演进逻辑[J]. 农村经济, 2019, (1): 22?28 YANG F, ZHENG L Y, ZHANG Y L. Symbiosis pattern and evolution logic of agricultural management paradigm[J]. Rural Economy, 2019, (1): 22?28 |
| [27] | 畅倩, 李晓平, 谢先雄, 等. 非农就业对农户生态生产行为的影响?基于农业生产经营特征的中介效应和家庭生命周期的调节效应[J]. 中国农村观察, 2020, (1): 76?93 CHANG Q, LI X P, XIE X X, et al. The impact of non-agricultural employment on farmers’ ecological production behavior: based on the mediating effect of agricultural production and operation characteristics and the regulating effect of the family life cycle[J]. China Rural Survey, 2020, (1): 76?93 |
| [28] | 高强, 孔祥智, 邵峰. 现代农业园区建设中的土地问题与对策分析[J]. 农村经济, 2012, (11): 9?13 GAO Q, KONG X Z, SHAO F. Land issues and countermeasures in construction of modern agricultural parks[J]. Rural Economy, 2012, (11): 9?13 |
| [29] | 张红宇. 现代农业与适度规模经营[J]. 农村经济, 2012, (5): 3?6 ZHANG H Y. Modern agriculture and appropriate scale management[J]. Rural Economy, 2012, (5): 3?6 |
| [30] | 曹铁毅, 王雪琪, 邹伟. 经营规模、农业技术培训与家庭农场收入?基于江苏省的调查[J]. 农业现代化研究, 2020, 41(2): 237?244 CAO T Y, WANG X Q, ZOU W. Farm operation scale, agricultural technical training, and farm income in Jiangsu[J]. Research of Agricultural Modernization, 2020, 41(2): 237?244 |
| [31] | 余翔, 郑晓云, 唐卫宁, 等. 基于关系嵌入视角的农户生产经营能力提升研究?以浙江省203家农户调研数据为例[J]. 华东经济管理, 2019, 33(7): 21?26 YU X, ZHENG X Y, TANG W N, et al. Research on the improvement of farmer’s production and management capability based on perspective of relation embedding—A case study of 203 farmers in Zhejiang Province[J]. East China Economic Management, 2019, 33(7): 21?26 |
| [32] | 杨宗耀, 仇焕广, 纪月清. 土地流转背景下农户经营规模与土地生产率关系再审视?来自固定粮农和地块的证据[J]. 农业经济问题, 2020, 41(4): 37?48 YANG Z Y, CHOU H G, JI Y Q. Re-exploration of the inverse productivity-size relationship using the fixed farmers’ fixed plots data in the context of land transfer[J]. Issues in Agricultural Economy, 2020, 41(4): 37?48 |
| [33] | 上海市农业农村委员会. 上海市休闲农业和乡村旅游布局规划(2018—2022年)[EB/OL]. (2019-11-13)[2021-5-21]. http://nyncw.sh.gov.cn/cyrhfz/20191225/d9e197153c4e4f7499cd3d6373d8ef2d.html Shanghai Agriculture and Rural Committee. Shanghai leisure agriculture and rural tourism layout plan (2018—2022)[EB/OL]. (2019-11-13)[2021-5-21]. http://nyncw.sh.gov.cn/cyrhfz/20191225/d9e197153c4e4f7499cd3d6373d8ef2d.html |
| [34] | 邵瑶春. 长三角地区传统农业规模化经营的现实困境及优化路径[J]. 南通大学学报: 社会科学版, 2020, 36(5): 41?47 SHAO Y C. Practical difficulties and optimized path of traditional agricultural scale operation in the Yangtze River Delta[J]. Journal of Nantong University: Social Sciences Edition, 2020, 36(5): 41?47 |
| [35] | 常玉, 刘显东, 杨莉. 应用解释结构模型(ISM)分析高新技术企业技术创新能力[J]. 科研管理, 2003, (2): 41?48 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2995.2003.02.008 CHANG Y, LIU X D, YANG L. Application of interpretative structural modeling in the analysis of high-tech enterprises’ technologic innovation capability[J]. Science Research Management, 2003, (2): 41?48 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2995.2003.02.008 |
| [36] | 上海市农业旅游经济协会. 上海休闲农业点信息[EB/OL]. (2018-01-09)[2021-5-21]. http://nyncw.sh.gov.cn/sc/20180719/0009-76124.html Shanghai Agricultural Tourism Economic Association. Shanghai leisure agriculture spot information[EB/OL]. (2018-01-09)[2021-05-21]. http://nyncw.sh.gov.cn/sc/20180719/0009-76124.html |
